
Integrating Traditional Technical Analysis with AI: A Multi-Agent
LLM-Based Approach to Stock Market Forecasting
Michał Wawer
a
and Jarosław A. Chudziak
b
Institute of Computer Science, Warsaw University of Technology, Warsaw, Poland
Keywords:
Multi-Agent Systems, Elliott Wave Principle, Large Language Models (LLMs), Investment Strategies, Deep
Reinforcement Learning (DRL).
Abstract:
Traditional technical analysis methods face limitations in accurately predicting trends in today’s complex
financial markets. This paper introduces ElliottAgents, an multi-agent system that integrates the Elliott Wave
Principle with AI for stock market forecasting. The inherent complexity of financial markets, characterized by
non-linear dynamics, noise, and susceptibility to unpredictable external factors, poses significant challenges
for accurate prediction. To address these challenges, the system employs LLMs to enhance natural language
understanding and decision-making capabilities within a multi-agent framework. By leveraging technologies
such as Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL), ElliottAgents
performs continuous, multi-faceted analysis of market data to identify wave patterns and predict future price
movements. The research explores the system’s ability to process historical stock data, recognize Elliott wave
patterns, and generate actionable insights for traders. Experimental results, conducted on historical data from
major U.S. companies, validate the system’s effectiveness in pattern recognition and trend forecasting across
various time frames. This paper contributes to the field of AI-driven financial analysis by demonstrating how
traditional technical analysis methods can be effectively combined with modern AI approaches to create more
reliable and interpretable market prediction systems.
1 INTRODUCTION
The development of AI, including LLMs, has signifi-
cantly increased interest in multi-agent systems (Zhao
et al., 2023; Weng, 2023). These advancements en-
able each agent to specialize in a specific area, en-
hancing the overall capability and performance of
multi-agent systems beyond what was previously pos-
sible.
Traditional methods of predicting future stock
prices using AI have often yielded unsatisfactory re-
sults due to limitations in processing vast amounts of
data (Gamil et al., 2007; Luo et al., 2002) and adapt-
ing to rapidly changing market conditions.
How can a multi-agent system enhanced by LLMs
improve the interpretability and efficiency of finan-
cial market trend analyses using the technical anal-
ysis method - Elliott Wave Principle (EWP)? Uti-
lizing framework for orchestrating AI agents, com-
bined with advanced technologies like Retrieval-
Augmented Generation (RAG) (Lewis et al., 2021),
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0004-2717-1616
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4534-8652
Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) and dynamic
context management (Wittkampf, 2024), we have cre-
ated ElliottAgents, a system designed to analyze stock
market using LLM-based agents and EWP.
The EWP is a form of technical analysis that in-
vestors use to forecast markets trends, which are pre-
sented on basic stock market chart on Fig. 1. This the-
ory identifies extremes in investor psychology, highs
and lows in prices, and other collective factors by
recognizing patterns described by Elliott Ralph Nel-
son (Frost et al., 2001). By applying EWP through
agents, it is possible to analyze these patterns more
efficiently than traditional agent systems or manual
analysis (Tirea et al., 2012). Additionally, agents can
learn from previous interactions and, over time, re-
fine their strategies to determine what works best for
a given company. This enables more accurate stock
market forecasts, creating new opportunities for in-
vestors and analysts. By combining classical and con-
temporary approaches, we aim to create a platform for
traders that can support them with multi-aspect anal-
ysis in the investment-making process.
The experiments demonstrate that agents are capa-
100
Wawer, M. and Chudziak, J. A.
Integrating Traditional Technical Analysis with AI: A Multi-Agent LLM-Based Approach to Stock Market Forecasting.
DOI: 10.5220/0013191200003890
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2025) - Volume 1, pages 100-111
ISBN: 978-989-758-737-5; ISSN: 2184-433X
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
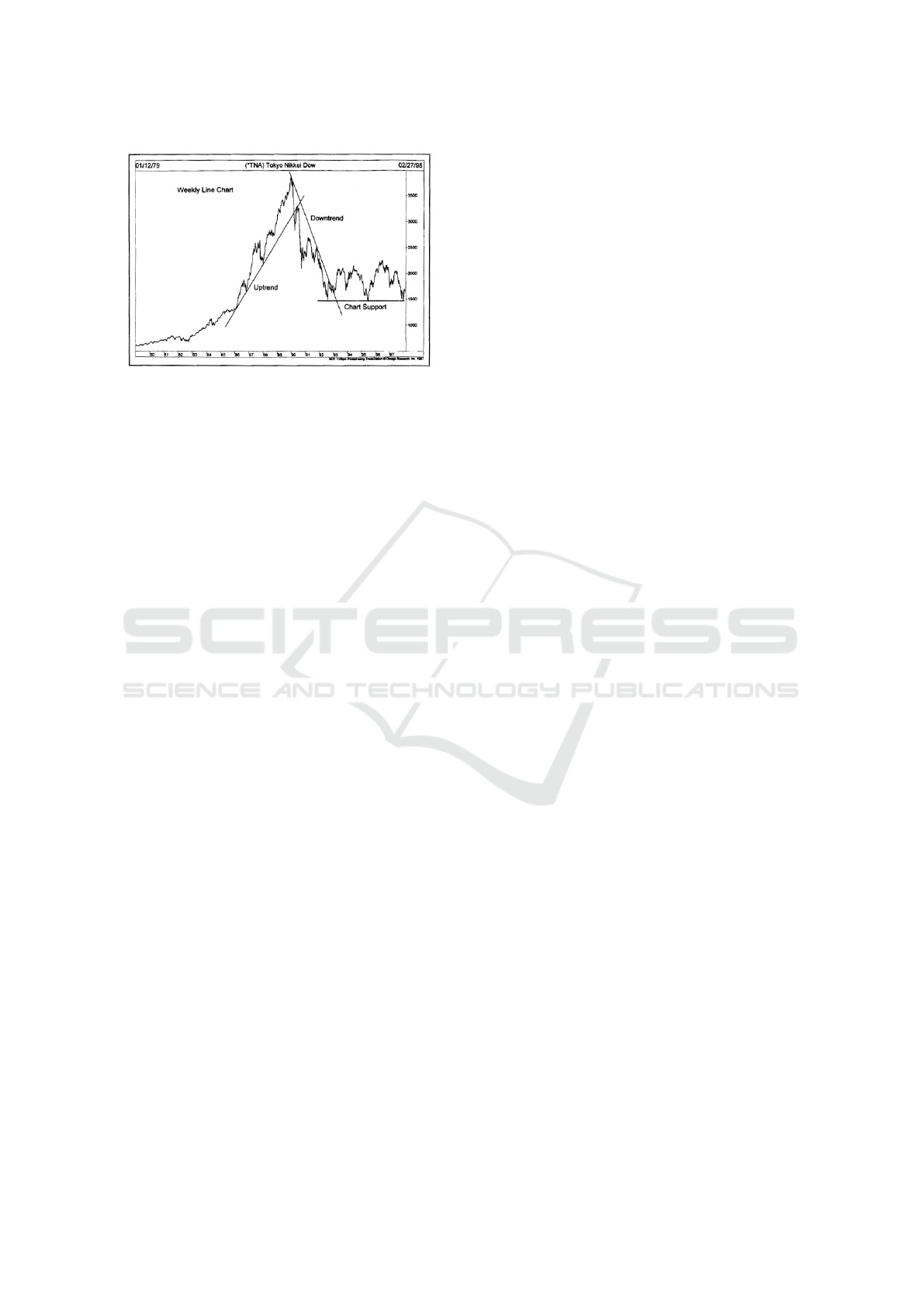
Figure 1: Basic trends in stock market, presented in (Mur-
phy, 1999).
ble of recognizing wave patterns and analyzing them
based on their knowledge, creating forecasts of future
stock prices that can be utilized by traders and ana-
lysts. The results indicate that these agents can adapt
to changing financial markets, achieving profits in the
medium and long term. Furthermore use of DRL
(Kabbani and Duman, 2022; Lussange et al., 2020)
can improve these results by implementing continu-
ous learning mechanism to constantly adapt to chang-
ing market conditions. However, their effectiveness
in short-term is limited due to large minute-to-minute
fluctuations and the presence of other high-frequency
trading algorithms in the market.
2 BACKGROUND
2.1 Prior Work
The integration of AI and multi-agent systems in
stock market analysis has been a subject of ongo-
ing research over the past two decades. An early at-
tempt to combine traditional technical analysis with
AI-driven approaches resulted in a multi-agent rec-
ommendation system (Tirea et al., 2012). This system
utilized a Java Agent Development (JADE) frame-
work to implement a multi-agent architecture, demon-
strating the potential of distributed analysis in finan-
cial forecasting. However, this early implementation
was limited by the computational capabilities of its
time and lacked the advanced natural language pro-
cessing (NLP) capabilities now available.
The use of fuzzy logic within a multi-agent frame-
work for technical analysis was explored in previous
research (Gamil et al., 2007). This approach intro-
duced a flexibility in decision-making processes, al-
lowing for better handling of market uncertainties.
While innovative, the system’s reliance on static rules
and fuzzy logic constrained its adaptability to rapidly
changing market conditions, a limitation that more re-
cent AI technologies have sought to overcome.
Earlier work on multi-agent decision support sys-
tems for stock trading highlighted the potential of col-
laborative agent-based approaches in financial anal-
ysis (Luo et al., 2002). This research emphasized
the importance of integrating diverse data sources
and decision-making strategies within a multi-agent
framework. However, the system’s effectiveness was
limited by the absence of advanced machine learn-
ing techniques that have since become integral to AI-
driven financial analysis.
More recent advancements have seen the inte-
gration of neural networks and deep learning in
stock market prediction systems (Szydlowski and
Chudziak, 2024). The potential of deep neural net-
works in enhancing profit through stock price predic-
tion has been demonstrated in recent studies (Abr-
ishami et al., 2019). This work showcased the abil-
ity of neural networks to capture complex patterns
in financial data, yet it did not fully address the in-
terpretability challenges often associated with deep
learning models in financial decision-making con-
texts.
2.2 Research Gap
Despite advancements in the integration of AI and
multi-agent systems, existing stock market analysis
tools exhibit several limitations.
Firstly, many AI-driven financial forecasting
tools, such as those leveraging neural networks, ex-
cel in recognizing complex patterns but fail to pro-
vide interpretable results. This lack of interpretability
undermines trader trust and limits actionable insights.
Secondly, early implementations, such as fuzzy logic-
based systems (Gamil et al., 2007), introduced flexi-
bility in decision-making but were hindered by static
rule sets that could not adapt to rapidly changing mar-
ket conditions. Thirdly, while some studies (Tirea
et al., 2012) attempted to incorporate the EWP into
multi-agent frameworks, these efforts were limited
by outdated computational capabilities and lacked ad-
vanced tools for automated wave pattern recognition.
Furthermore, existing tools often focus exclusively on
either technical analysis or purely data-driven meth-
ods.
To address these gaps, we introduce ElliottA-
gents system (Chudziak and Wawer, 2024). By in-
tegrating the EWP into its core framework, Elliot-
tAgents ensures that market analyses are grounded
in well-established financial theories, making predic-
tions more transparent and interpretable for traders.
Integrating Traditional Technical Analysis with AI: A Multi-Agent LLM-Based Approach to Stock Market Forecasting
101

The system employs LLMs for improved natural lan-
guage understanding and decision-making, and RAG
to access external knowledge bases, ensuring up-to-
date and contextually relevant analyses.
In addition, ElliottAgents leverages DRL to incor-
porate a continuous learning mechanism that refines
strategies based on historical data, allowing it to adapt
to evolving market conditions. The system’s architec-
ture also enables specialized agents to collaborate dy-
namically, each focusing on distinct tasks such as data
processing, pattern recognition, and strategy formula-
tion. This collaborative approach ensures efficiency
and scalability.
3 THEORETICAL
FOUNDATIONS
3.1 Elliott Wave Principle (EWP)
The EWP, introduced by Ralph Nelson Elliott, is a
technical analysis framework that suggests market
prices follow identifiable patterns influenced by col-
lective investor behavior and psychology (Frost et al.,
2001; Murphy, 1999). According to this principle,
market trends alternate between periods of optimism
and pessimism, producing consistent wave-like price
movements. Elliott categorized these patterns into
thirteen recurring structures, referred to as ”waves”
which are broadly divided into two primary types: im-
pulsive waves and corrective waves.
Motive (impulsive) waves, presented on Fig. 2,
are the driving force behind market trends and con-
sist of five sub-waves. These five sub-waves move in
the direction of the overall trend. Within an impul-
sive wave, waves 1, 3, and 5 are the main movement
waves, while waves 2 and 4 are corrective and move
against the trend. The structure of an impulsive wave
Figure 2: Impulse and corrective waves patterns, adapted
from Prechter and Frost, 1978 (Frost et al., 2001).
ensures progress in the direction of the primary trend,
with Wave 3 typically being the strongest and longest
of the three impulsive waves. Corrective waves, move
against the main trend and consist of three sub-waves
labeled A, B, and C. These corrective waves provide
a counterbalance to the impulsive waves, retracing a
portion of the preceding trend.
Market movements can be broken down into
larger and smaller waves, creating a fractal-like struc-
ture named wave degrees. Smaller waves combine
to form larger waves, which in turn combine to form
even larger waves, creating a nested pattern. This
fractal nature allows the EWP to be applied to differ-
ent time frames, from short-term market movements
to long-term trends.
The EWP does not offer certainty but provides a
framework for assessing the probabilities of different
market scenarios. It helps traders understand the cur-
rent market context and predict potential future paths,
making it a valuable tool for technical analysis.
3.2 Fibonacci Approach in EWP
The Fibonacci sequence is integral to the EWP, pro-
viding a mathematical framework that enhances the
predictability and structure of market movements.
The Fibonacci sequence is a series of numbers where
each number is the sum of the two preceding ones.
This sequence is known for its prevalence in nature,
art, and architecture, and it similarly manifests in the
financial markets.
In the context of the EWP, the Fibonacci sequence
helps to quantify the relationships between different
waves in the market (Boroden, 2008). Elliott ob-
served that market waves often unfold in a pattern that
aligns with Fibonacci ratios (Frost et al., 2001). Based
on Fig. 3, the length of one wave might be 1.618
times the length of another, reflecting the Golden Ra-
tio, which is approximately 1.618. This ratio, also
known as Phi (ϕ), is fundamental to the proportional-
ity observed in wave patterns.
The fractal nature of Elliott waves means that Fi-
bonacci relationships apply across different degrees
of trend, from minute charts to long-term market cy-
cles (Boroden, 2008). This fractal characteristic en-
Figure 3: Fibonacci retracements in corrective waves (Frost
et al., 2001).
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
102

sures that patterns observed on smaller scales can be
seen on larger scales, maintaining the same Fibonacci
proportionality. For instance, a complete market cy-
cle might consist of a series of waves that adhere to
Fibonacci ratios, creating a cohesive and predictable
structure throughout the market’s evolution.
3.3 LLMs in Time Series Prediction
Time series prediction using LLMs has emerged as
a powerful approach in financial forecasting, integrat-
ing the latest advancements in AI to improve the accu-
racy and reliability of predictions. At its core, time se-
ries analysis aims to understand the underlying struc-
ture and function that produce the observed data. This
understanding is then used for forecasting future val-
ues of the series.Traditional time series analysis meth-
ods, such as ARIMA and exponential smoothing, fo-
cus on decomposing a series into trend, seasonal, and
residual components to identify patterns and predict
future values (Tsay, 2010). These models rely on his-
torical data and linear assumptions, often struggling
with non-linear and complex temporal dependencies
inherent in financial markets.
LLMs, on the other hand, leverage deep learning
techniques and extensive datasets to understand and
predict time series data. These models leverage their
capability to understand and generate sequential data,
which is crucial for accurate forecasting of time series
characterized by trends and seasonal patterns.
Methods such as natural language paraphrasing
and incorporating external knowledge into prompts
have been demonstrated to enhance their performance
further (Jin et al., 2024). However, challenges re-
main, particularly with multi-period datasets where
LLMs struggle to recognize distinct periods (Tan
et al., 2024), similar problems apply to all other meth-
ods (Chudziak, 2023). Despite their computational
demands, LLMs often perform on par with simpler
models, suggesting that they hold potential but more
research is needed to prove their effectiveness. The
use of agents may be a factor that will greatly im-
prove the results of time series prediction by distribut-
ing tasks among agents, enabling a more robust anal-
ysis of complex big sets of data.
3.4 Deep Reinforcement Learning
(DRL)
As a subset of machine learning, called DRL inte-
grates principles of deep learning and reinforcement
learning (RL). In RL, an agent learns to make sequen-
tial decisions by interacting with an environment to
maximize cumulative rewards. This process involves
observing the current state, selecting actions, and re-
ceiving feedback in the form of rewards, iterating this
cycle to improve the agent’s policy, which is the strat-
egy for choosing actions (Lapan, 2020).
Deep learning, which uses neural networks with
multiple layers, enhances RL by enabling the han-
dling of high-dimensional state and action spaces.
Key DRL algorithms include Deep Q-Networks
(DQN), which use neural networks to estimate Q-
values (expected rewards for actions), and Policy Gra-
dient methods, which directly optimize the policy
(Kabbani and Duman, 2022). DRL leverages tech-
niques like experience replay, where past experiences
are stored and reused during training, and target net-
works, which help stabilize training by providing con-
sistent target values.
In the backtesting process, we use DRL to ana-
lyze historical market data (Lussange et al., 2020).
A DRL agent can learn which patterns are effective
for a given company and understand how each pattern
can affect future price movements. This enables the
agent to make informed buy, sell, or hold decisions,
optimizing long-term returns. By continuously learn-
ing and adapting, DRL agent will increase accuracy
in dynamic and uncertain environments.
3.5 Multi-Agent Architecture
Multi-agent systems (MAS) have a longstanding role
in modeling complex systems, where autonomous
agents interact with each other and their environment
(Minsky, 1988). These systems were traditionally
built using rule-based systems, symbolic equations,
stochastic modeling, and early machine learning tech-
niques (Russell and Norvig, 1995).
The integration of LLMs, such as ChatGPT, has
significantly enhanced MAS by equipping agents
with advanced NLP capabilities (Guo et al., 2024).
NLP enables agents to comprehend complex instruc-
tions, collaborate effectively, and explain their ac-
tions, thereby increasing transparency and trust within
the MAS. LLMs allow agents to operate more au-
tonomously, dynamically perceiving and responding
to changes in their environment while learning from
experiences to adapt to new situations without explicit
instructions (Zhao et al., 2023). This learning process
mirrors human behavior, allowing for more realistic
simulations.
LangChain is a framework that facilitates the
chaining of different components within an LLM ap-
plication, including agents (Auffarth, 2023). Our
system utilizes LangGraph, a LangChain compo-
nent, to visualize and manage relationships between
agents, enhancing clarity and interpretability in com-
Integrating Traditional Technical Analysis with AI: A Multi-Agent LLM-Based Approach to Stock Market Forecasting
103

plex multi-agent interactions. Agents in an LLM-
powered MAS collaborate, performing sequential and
hierarchical tasks that culminate in a comprehensive
analysis. Some agents utilize advanced tools that en-
hance their analytical capabilities, allowing for the
generation of more precise and accurate results.
3.6 ReAct Agent
The ReAct paradigm (Yao et al., 2023) represents a
significant advancement in leveraging LLMs for com-
plex problem-solving tasks. ReAct, which stands
for ”Reasoning + Acting,” combines the strengths
of chain-of-thought reasoning (series of intermediate
steps to arrive at a solution) with the ability to interact
with external environments, creating a more robust
and adaptable system for tackling diverse challenges.
At its core, ReAct prompts LLMs to generate both
verbal reasoning traces and task-specific actions in an
interleaved manner (Yao et al., 2023). This approach
allows the model to perform dynamic reasoning to
create, maintain, and adjust high-level plans for act-
ing (reason to act), while also interacting with exter-
nal environments to incorporate additional informa-
tion into its reasoning process (act to reason).
4 ElliottAgents SYSTEM
ARCHITECTURE
The development of ElliottAgents aims to integrate
traditional financial analysis with modern AI capabil-
ities. This section outlines the basic assumptions and
design principles underlying the platform’s architec-
ture and implementation.
4.1 ElliottAgents Design Approaches
The increasing complexity of financial markets, cou-
pled with recent advances in AI, presents both op-
portunities and challenges for developing new market
analysis tools. ElliottAgents system’s architecture is
designed to support these functions:
1. Configurable Analysis Parameters. The plat-
form implements a flexible parametrization that
allow user to specify the asset, timeframe, and
data granularity.
2. Dynamic Data Integration. ElliottAgents incor-
porates real-time market data through an external
yfinance API, enabling analysis of large collec-
tions, the most recent data.
3. Pattern Recognition and Analysis. The plat-
form implements algorithms for identifying El-
liott Wave patterns across multiple timeframes as
a tool for agents. Then results of this tool are in-
terpreted by LLM-based agents. The integration
of AI enables more nuanced pattern recognition
than traditional technical analysis methods.
4. Multi-Agent Collaboration. A crew of spe-
cialized agents works in concert to analyze mar-
ket data. Each agent maintains specific exper-
tise, from data processing to pattern recogni-
tion and strategy formulation. The collaborative
framework enables comprehensive market anal-
ysis through the synthesis of multiple analytical
perspectives.
5. Continuous Learning and Optimization. The
platform incorporates continuous learning mech-
anisms that enable it to refine its analytical ca-
pabilities over time. This includes real-time data
processing, strategy backtesting, and performance
optimization through DRL implementation.
4.2 Agents Definition
At the core of ElliottAgents is a multi-agent archi-
tecture that orchestrates specialized agents, each re-
sponsible for distinct aspects of the analysis process.
These agents can dynamically perceive and respond
to changes in their environment, learning from their
experiences to improve future responses. The ar-
chitecture of ElliottAgents consists of 7 agents who
communicate with each other in a structured way, as
shown in the Fig. 4.
The Coordinator agent orchestrates the entire pro-
cess. It begins by receiving user input, including the
desired stock symbol and analysis timeframe. This in-
formation is then passed to the Data Engineer, which
gathers the necessary historical stock data. Next,
the Coordinator triggers the Elliott Waves Analyst,
equipped with a specialized tool to identify and clas-
sify Elliott Wave patterns within the historical data.
These patterns are visually represented through auto-
matically generated charts. The Backtester agent then
receives the identified patterns and employs DRL to
validate them against historical trends, assessing their
effectiveness. The Technical Analysis Expert then
steps in, combining the Elliott Wave patterns with the
backtesting results. This agent determines the most
probable pattern for the current market conditions,
providing a refined prediction. This refined predic-
tion, along with the original data and wave patterns,
is then forwarded to the Investment Advisor. This
agent synthesizes all the information, incorporating
insights from a RAG tool, to formulate a comprehen-
sive investment strategy. This strategy includes spe-
cific buy/sell signals, price targets, and contingency
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
104
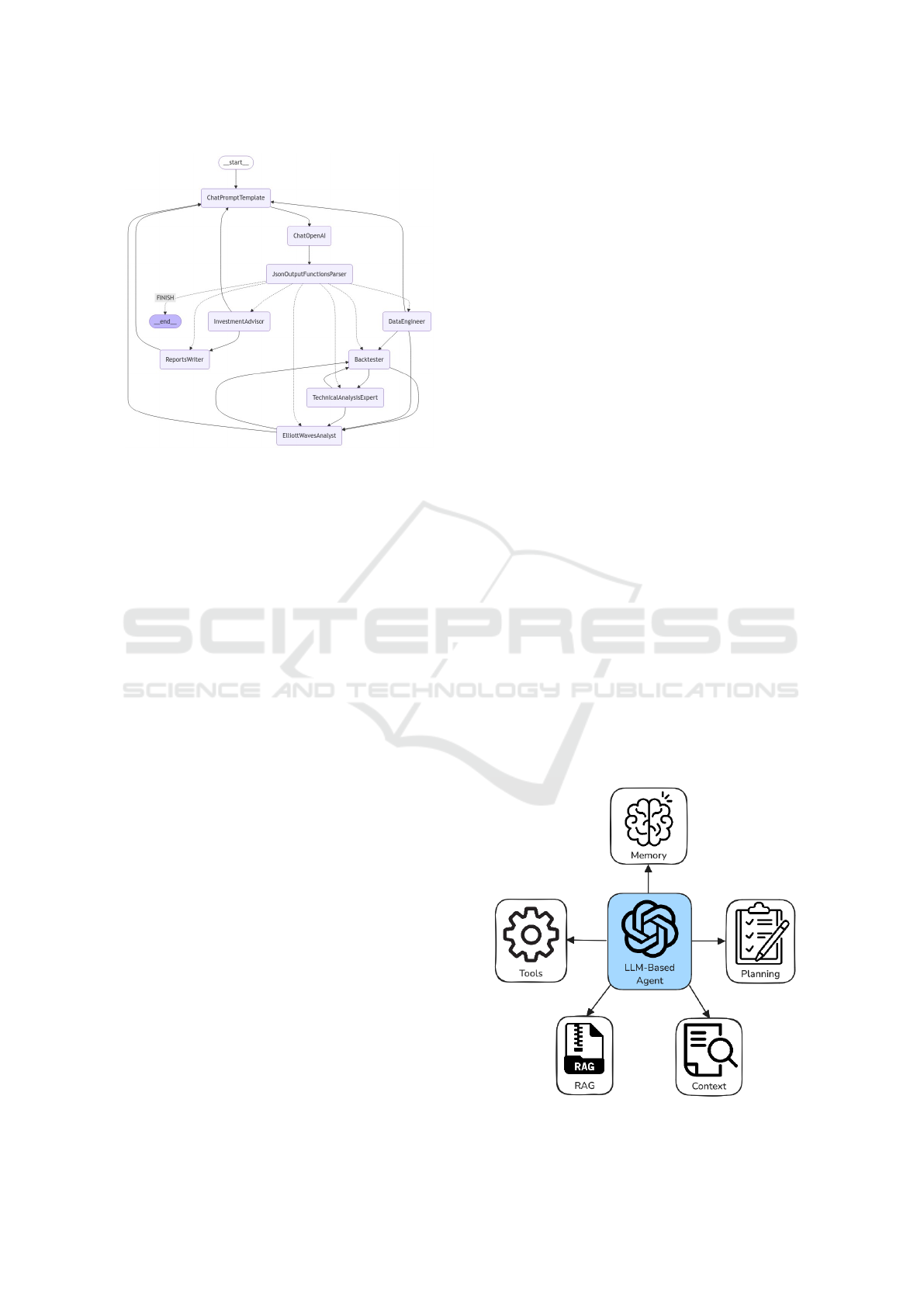
Figure 4: Graph presenting data flow between agents, gen-
erated in LangGraph framework.
plans. Finally, the Reports Writer receives all the
compiled information and generates a clear, concise
report for the end-user. This report presents the in-
vestment strategy in an easily understandable format,
ensuring the user has actionable insights based on the
latest data and analysis.
Each agent in the system is provided with a spe-
cific context through a natural language prompt, en-
abling it to perform its designated role effectively.
The following prompt defines the context and respon-
sibilities of the Investment Advisor agent, focusing
on synthesizing analyses into actionable investment
strategies.
You are the Investment Advisor. Your role is
crucial in synthesizing the analyses provided
by other agents and formulating actionable
investment advice. Your tasks include:
1. Interpret the Elliott Wave patterns
identified by the Elliott Waves Analyst.
2. Consider the backtesting results provided
by the Backtester agent.
3. Integrate information from the rag tool
to provide context to your recommendations.
4. Formulate a comprehensive investment strategy
that includes:
- Buy, sell, or hold recommendations
- Price targets for entry and exit points
- Stop-loss levels
- Time frames for the transactions
5. Highlight any potential risks or limitations
in the analysis, ensuring a balanced view of
the investment opportunity.
6. Provide any additional insights that could
be valuable for decision-making, such as
correlations with broader market trends.
Remember, your advice should be based on the
collective intelligence of the multi-agent
system. Aim to present your investment advice
in a structured format that can be easily
understood the end users.
4.3 Agents Customization
As presented on Fig. 5 agent is build using different
components, technologies used by our agents are de-
scribed below:
• Memory: preserve and regulate knowledge, ex-
periential data, and historical information (Li
et al., 2024). It typically consists of short-term
memory (for immediate context and task-related
information) and long-term memory (for storing
substantial volumes of knowledge and past expe-
riences). Memory mechanism helps agents gener-
ate responses based on past interactions, improv-
ing decision-making and context-awareness over
time (Weng, 2023).
• Planning: is a ability to devise action sequences
based on set objectives and environmental con-
straints (et al., 2024). For LLM-based agents,
planning often utilizes in-context learning meth-
ods like Chain of Thought (CoT), Tree of Thought
(ToT), or external capabilities. It involves task
analysis, action anticipation, and optimal action
selection to address complex problems.
• Context: refers to the ability of AI agents
to adaptively adjust their contextual understand-
ing based on real-time information (Wittkampf,
2024). Agents can utilize various types of con-
text, including tools, documents accessed through
RAG, the history of conversations, and the ability
to reflect and plan future actions. This approach
Figure 5: Overview of a LLM autonomous agent.
Integrating Traditional Technical Analysis with AI: A Multi-Agent LLM-Based Approach to Stock Market Forecasting
105

leverages ongoing interactions and updates the
context dynamically, enabling the agent to main-
tain relevance and accuracy throughout a session.
By incorporating new data as it becomes avail-
able, dynamic context helps agents refine their re-
sponses and improve decision-making processes.
• Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG): im-
proves the factual reliability of generative AI by
integrating external information retrieval into its
workflow (Lewis et al., 2021). Instead of relying
solely on pre-trained parameters, RAG dynami-
cally fetches relevant data from external knowl-
edge bases, which enhances both the accuracy and
relevance of generated responses. This process
involves encoding user queries as embeddings,
comparing them against a vectorized database,
and incorporating the retrieved information into
the model’s output (Larson and Truitt, 2024). By
reducing hallucinations and providing traceable
sources, RAG addresses common challenges in
AI-driven content generation.
In our system, a knowledge graph-based RAG
framework is employed. This structure organizes
data into interconnected graphs, allowing for pre-
cise query disambiguation and improved contex-
tual relevance. Leveraging these structured rela-
tionships, our approach supports advanced tasks
like interpreting the mathematical underpinnings
of the EWP while ensuring accuracy and consis-
tency in the generated responses.
• Tools: LLM-based agents often integrate various
tools to enhance their problem-solving abilities
and interact with external environments or data
sources. The tools component presents specific
instruments that were created for our system to
adjust it for analysis of finncial markets:
– Stock Market Data: provides access to real-
time and historical market information, essen-
tial for informed decision-making.
– Elliot Waves Reader: tool for technical analy-
sis, helping the agent identify and interpret El-
liot wave patterns in price movements.
– Chart Generator: allows the agent to vi-
sualize market data, especially Elliott waves,
creating graphical representations of detected
waves. This tool is directly connected to Elliott
waves reader tool.
– Database connector: enables the agent to ac-
cess and manage structured data of backtesting
results.
4.4 Continous Learning Agent
The ElliottAgents platform implements a continuous
learning process (Wang et al., 2024) that enables
agents to adapt and refine their knowledge over time
(Hu et al., 2024). This process is designed to enhance
the system’s predictive capabilities without relying
on traditional fine-tuning methods. Instead, agents
learn organically through their interactions and obser-
vations of the stock market environment.
At the core of this process is the Backtester agent,
which plays a crucial role in accumulating and lever-
aging historical knowledge. The Backtester’s work-
flow begins with a query to determine if relevant re-
sults are already available in the backtesting knowl-
edge base. If not, the agent initiates a analysis by
fetching the necessary data, performing EWP anal-
ysis, and interpreting the results. These findings are
then stored in the Neo4j graph database for future ref-
erence. This iterative process allows the system to
build a repository of analyzed patterns and outcomes
over time. This approach ensures that the system’s
predictions are grounded in a historical data and pre-
viously observed market behaviors.
4.5 Agents Flow Engineering
The orchestration of the system is designed to facil-
itate seamless collaboration among agents, ensuring
an efficient workflow. The system employs a hierar-
chical structure wherein each agent is assigned a spe-
cialized role (Guo et al., 2024), contributing to scala-
bility. The coordinator is the agent who manages the
whole flow of information in the system, distributes
the tasks and ensures their execution, as presented on
Fig. 6.
Asynchronous task execution enables agents to
operate in parallel, mitigating bottlenecks and en-
hancing throughput (Li et al., 2024). Tasks such
as backtesting and wave analysis, which do not re-
quire immediate interdependence, are executed con-
currently. This asynchronous design is further sup-
ported by the system’s capacity for dynamic scaling,
instantiating additional agents when computational
demands increase.
Task decomposition and memory management
are fundamental to the system’s architecture (Chen,
2024). Complex tasks are divided into smaller,
manageable subtasks, allowing agents to focus on
well-defined objectives. Memory management en-
sures continuity through memory identifiers, enabling
agents to retain context across tasks. For example,
outputs from the Elliott Wave Analyst inform sub-
sequent validation by the Technical Analysis Expert,
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
106
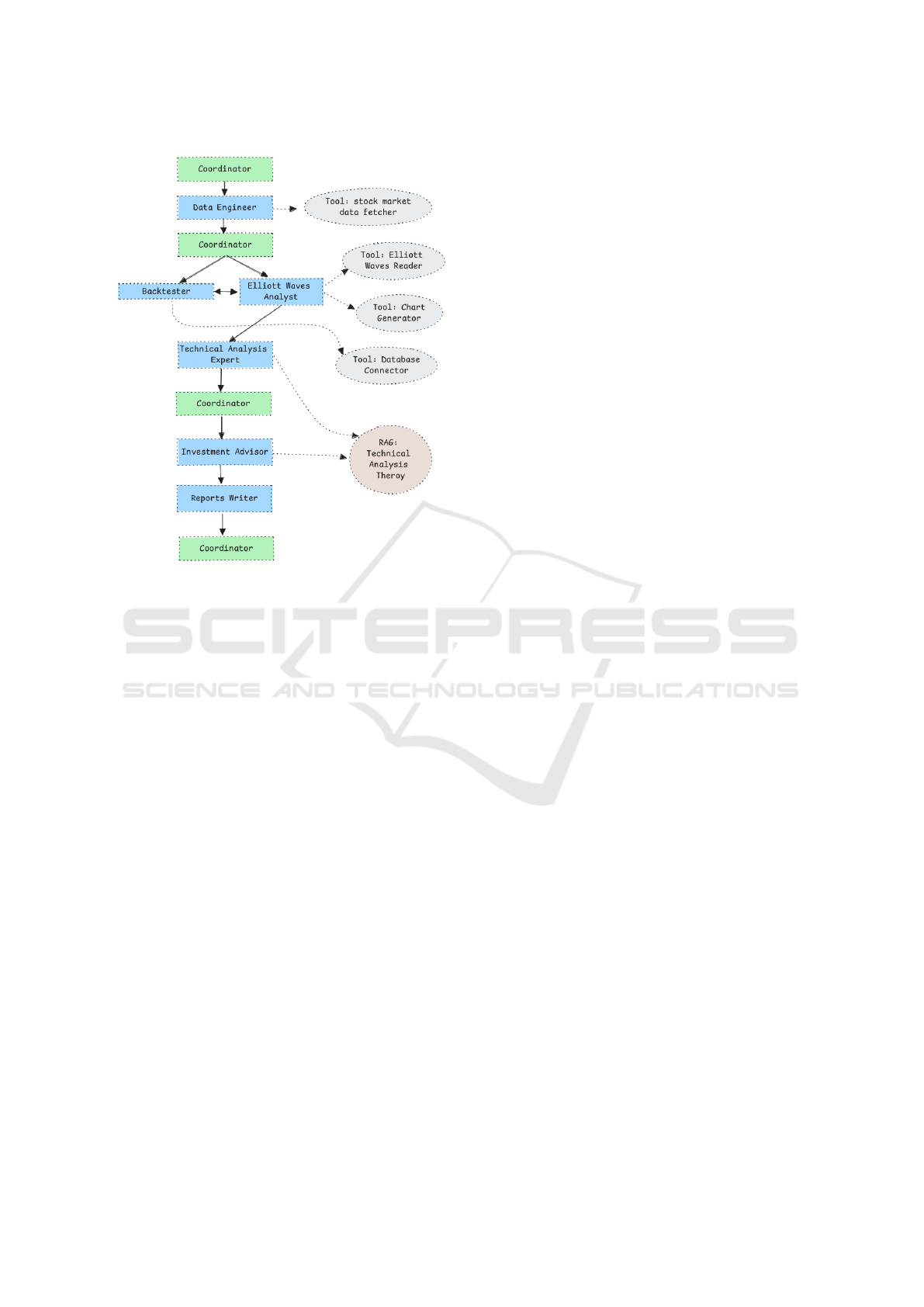
Figure 6: Interactions between agents and tools.
leading to actionable strategies devised by the Invest-
ment Advisor and finalized in reports by the Reports
Writer under the coordinator’s supervision.
The designed flow is integral to its efficiency, scal-
ability, and resilience. By delegating tasks to spe-
cialized agents and leveraging dynamic scaling, the
system adapts to varying demands without compro-
mising performance. The asynchronous execution re-
duces latency, while the collaborative interactions be-
tween agents ensure the production of accurate out-
puts (Chi-Min Chan, 2023). These design principles
collectively enable the system to perform complex an-
alytical tasks with precision, speed, and adaptability.
5 EXPERIMENTAL SETUP AND
METHODOLOGY
The experiments conducted on the created platform
were designed to test its use in the real market, ef-
fectiveness of pattern recognition and to study the
impact of the backtesting process on the final result.
Historical The data on which we conducted our tests
came from the yfinance library, we focused on 2 time
intervals: daily and hourly. In the performed tests,
our agents used the gpt-4o-mini model from OpenAI.
Currently, ElliottAgents allows the detection of only
a few wave patterns, there are more patterns discov-
ered and described in Elliott Wave Theory, and in our
study we focused on describing only a few selected
ones. Current state of our system is able to recognize
impulse and corrective patterns, with additional wave
extensions. By recognizing these patterns we are able
to determine support, resistance and target price lev-
els.
The experimental evaluation of the ElliottAgents
platform was conducted in two distinct phases, each
designed to assess different aspects of the system’s
performance and reliability in stock market predic-
tion.
The initial phase of our experimentation focused
on demonstrating the practical application of the El-
liottAgents system through a detailed case study. We
selected a specific company and time frame to show-
case a complete analysis cycle. This phase aimed
to illustrate the inter-agent communication process,
highlighting how different specialized agents collab-
orate to produce a comprehensive market analysis.
It also demonstrated the step-by-step reasoning and
decision-making process employed by the agents.
Furthermore, this analysis provided insights into the
potential real-world applicability of the system’s out-
puts, including the identification of Elliott Wave pat-
terns and the generation of trading signals.
The second phase of our experimentation was de-
signed to assess the system’s pattern recognition capa-
bilities and the accuracy of its predictions. This eval-
uation utilized a cross-validation method applied to
a substantial dataset of historical market price move-
ments. We utilized 1,000 samples each representing
a one candlestick from the price charts of selected
stocks in daily and hourly interval.
Our tests focused on two key Elliott Wave forma-
tions: incomplete impulsive waves (1-2-3-4) consist-
ing of four sub-waves, and complete impulsive waves
(1-2-3-4-5) comprising all five sub-waves. In both
cases, we enforced the EWP rule that waves must not
overlap. To evaluate the effect of our DRL compo-
nent, we conducted parallel tests with and without
the DRL backtesting process. The DRL model was
trained on 10 years of historical data for each com-
pany under examination.
For each identified pattern, the system generated
a prediction for the subsequent price movement (up-
ward or downward). We evaluated these predictions
using specific criteria. For incomplete waves (1-2-
3-4), a prediction was deemed correct if the average
price over the next n candlesticks (where n is calcu-
lated to approximate 1.62 times the length of the first
wave) moved in the predicted direction. For complete
waves (1-2-3-4-5), a prediction was considered accu-
rate if the subsequent corrective wave A exhibited a
Integrating Traditional Technical Analysis with AI: A Multi-Agent LLM-Based Approach to Stock Market Forecasting
107
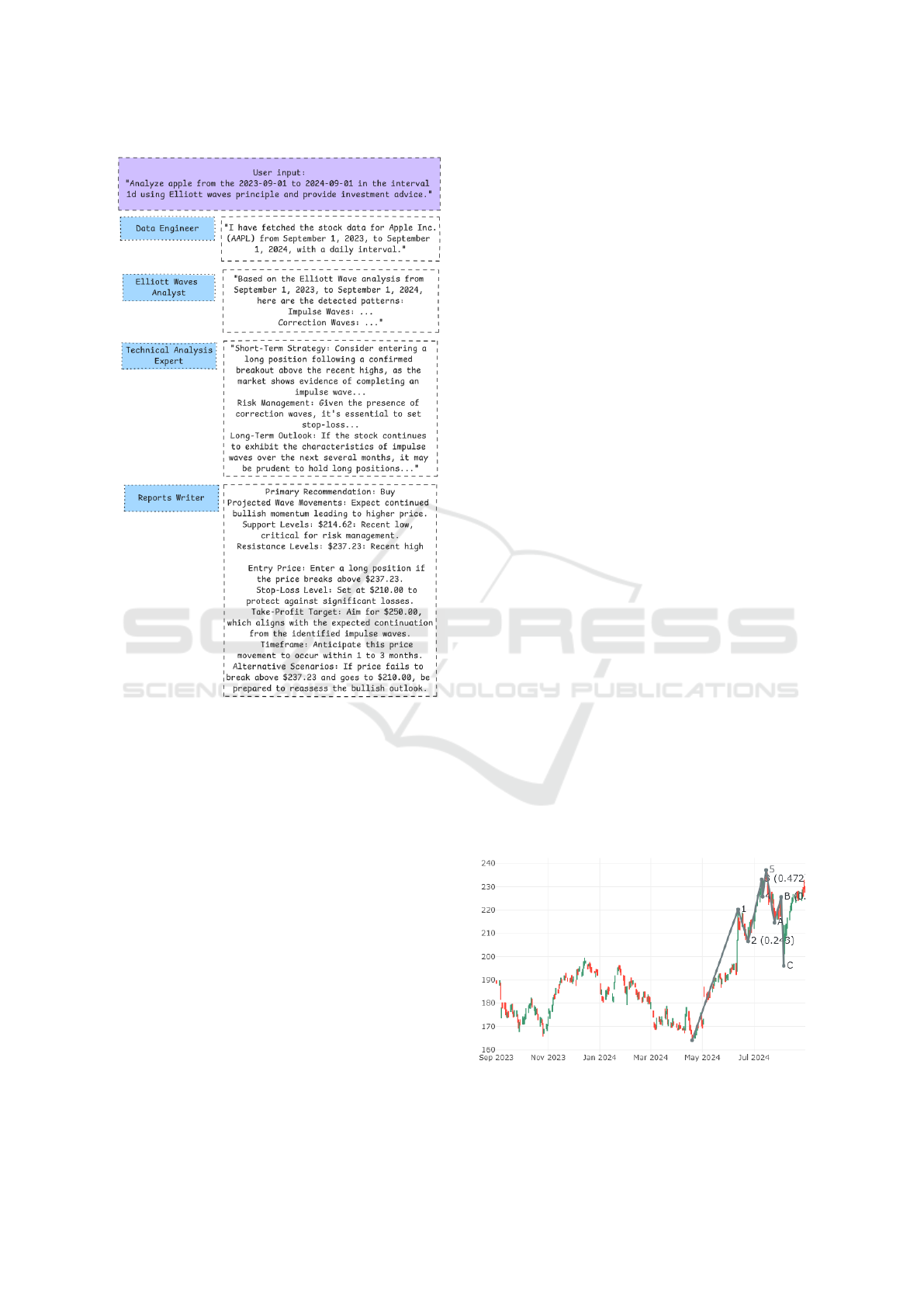
Figure 7: Example interactions between agents analyzing
Apple stock, with messages returned by each agent.
exact same length to that of wave 5, moving in the
opposite direction.
6 RESULTS AND ANALYSIS
The first phase of the experiments was performed on
Apple (AAPL) price data from September 2023, to
September 2024. The system was run on limited his-
torical data from to recognize all waves pattern and
identify possible buy or sell signals. Based on them,
we could simulate transactions and calculate theoret-
ical investment returns, proving the effectiveness of
predictions of future prices. Here we’ll describe just
one example of the analysis by presenting the mes-
sage exchange between agents and the final analysis
with the result of the simulated transaction.
The interaction between agents is depicted in
Fig. 7, while Fig. 8 illustrates a chart with analysis
of Apple stock over a one-year period, with data ag-
gregated at a daily interval. During this period, Elliot-
tAgents successfully identified an impulsive wave se-
quence labeled 1-2-3-4-5 and a subsequent corrective
wave pattern denoted as A-B-C. According to estab-
lished wave theory, the occurrence of this configura-
tion indicates a likely reversal surpassing the peak of
the fifth wave.
Upon identifying this wave structure and confirm-
ing the initiation of a reversal, ElliottAgents issued a
buy recommendation at a price of $232 per share. The
target price was set at $250 per share, correspond-
ing to the peak of the fifth wave. This price also
considered the resistance level observed at the peak
of wave B ($225), resulting in a dual-target strategy.
Such a strategy aims to ensure an optimal exit point
while providing a buffer for potential resistance at
critical levels. As illustrated in the chart, the predic-
tion proved accurate, with the stock price stabilizing
near the $250 mark—aligned with the peak of the fifth
wave—where it encountered notable resistance.
The second part of the experiment focus on quan-
tity tests for the correctness of the detected pattern and
the impact of DRL on results. Test was conducted us-
ing a cross-validation method on 1000 samples (can-
dlesticks) with a daily interval for the stocks. We
compared the results with and without a DRL back-
testing process.
Table 1 presents the results of the cross-validation
experiments for 1000 data samples in two time inter-
vals. As we can see, the identification of a complete
impulsive wave pattern contributes to better predic-
tions of subsequent price movements than incomplete
impulse wave pattern. In case of hourly intervals our
system detected smaller number of patterns, mainly
because price changes on the hourly interval were
smaller. The use of DRL resulted in a improvement
in prediction, showing that agents are able to use the
learning process on historical data in better interpre-
tation of patterns.
Figure 8: Impulsive and corrective waves found on Apple
stock on 1d interval.
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
108
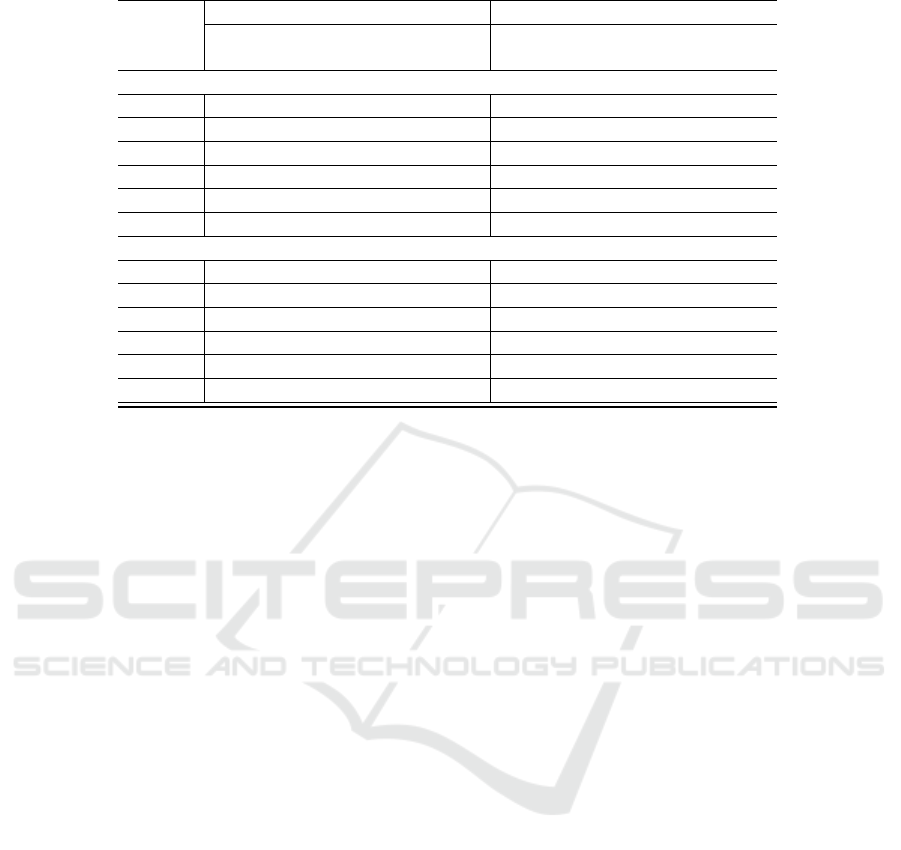
Table 1: Comparison of pattern recognition with and without backtesting.
Stock
1-2-3-4 Patterns 1-2-3-4-5 Patterns
N
Without
backtesting
With
backtesting
N
Without
backtesting
With
backtesting
Daily Interval
AMZN 24 58.34% 66.67% 18 66.67% 77.78%
GOOG 28 53.57% 67.86% 23 65.22% 82.61%
INTC 19 57.89% 73.68% 15 60.00% 73.34%
CSCO 12 58.34% 66.67% 9 66.67% 88.89%
ADBE 20 60.00% 65.00% 12 50.00% 66.67%
META 22 59.09% 63.64% 14 57.14% 64.29%
Hourly Interval
AMZN 10 50.00% 70.00% 8 62.50% 75.00%
GOOG 13 53.84% 61.54% 9 77.78% 77.78%
INTC 12 58.34% 66.67% 9 66.67% 88.89%
CSCO 9 44.45% 55.56% 8 50.00% 50.00%
ADBE 10 50.00% 70.00% 8 62.50% 75.00%
META 12 58.34% 58.34% 9 66.67% 88.89%
N: number of patterns found.
7 DISCUSSION
Multi-agent architectures have been utilized in stock
price prediction systems for many years (Akintola and
Oyetunji, 2021; Gamil et al., 2007; Luo et al., 2002).
However, advancements in AI over recent years have
significantly enhanced the capabilities of these sys-
tems. The introduction of fuzzy logic in earlier sys-
tems provided a foundation for integrating qualita-
tive judgments with quantitative analysis. Neverthe-
less, these systems required further optimization to
improve their decision-making processes. While it re-
mains challenging to directly compare the profitabil-
ity of our system with other stock price prediction sys-
tems currently available, experimental results indicate
that our approach effectively detects and interprets
wave patterns with greater accuracy than comparable
systems utilizing EWP (Tirea et al., 2012). Further-
more, the analyses generated by our agents present a
clear investment plan, including actionable price lev-
els, which can be directly applied by traders in real-
world scenarios.
The experiments conducted on ElliottAgents have
yielded several insights:
1. Pattern Recognition Accuracy: The system
demonstrated a high accuracy in identifying im-
pulsive and corrective waves patterns across vari-
ous time frames. Experiments conducted on his-
torical stock market data validate the system’s ca-
pability to recognize and interpret intricate market
structures effectively.
2. Impact of Backtesting: The implementation of
DRL for backtesting significantly enhanced the
system’s predictive accuracy. Across different
companies and time intervals, backtesting im-
proved pattern recognition validity by up to 16%,
demonstrating the importance of historical data
analysis in refining predictive models.
3. Multi-Agent Architecture Effectiveness: The
distributed approach of ElliottAgents, where spe-
cialized agents handle different aspects of anal-
ysis, proved highly effective. This architecture
allowed for more efficient processing of complex
data and improved the overall accuracy of predic-
tions.
The system’s ability to dynamically update con-
text and integrate EWP, significantly improves the ac-
curacy and reliability of the predictions. Backtesting
capabilities usind DRL further allow for the continu-
ous refinement of strategies.
The development and testing of ElliottAgents
have successfully addressed the primary research
question posed at the outset of this study. The plat-
form has demonstrated that it is indeed possible to
integrate the EWP into a multi-agent architecture to
more quickly and accurately predict future stock price
movements.
The development and testing of ElliottAgents
have successfully addressed the primary research
question posed at the outset of this study. The plat-
form has demonstrated that it is indeed possible to
integrate the EWP into a multi-agent architecture to
Integrating Traditional Technical Analysis with AI: A Multi-Agent LLM-Based Approach to Stock Market Forecasting
109

more quickly and accurately predict future stock price
movements. By leveraging AI technologies, the sys-
tem enhances both interpretability and efficiency, ad-
dressing the limitations of traditional methods. The
collaborative multi-agent design ensures scalability
and adaptability, making ElliottAgents a robust tool
for modern financial analysis. Furthermore, the re-
search has made substantial progress on several key
objectives:
1. Multi-Faceted Analysis: ElliottAgents have
shown the ability to perform comprehensive anal-
yses and present results in a user-friendly manner,
making complex financial data accessible to both
professional traders and individual investors.
2. LLMs in Time Series Prediction: The research
has provided valuable insights into the perfor-
mance of LLMs in time series prediction, particu-
larly in the context of stock market trends. While
challenges remain, the integration of LLMs with
traditional technical analysis methods has shown
promising results.
3. Real-Time Data Integration: The system has
demonstrated the ability to effectively utilize the
most recent stock market data, adapting to rapidly
changing market conditions in near real-time.
4. Agent Customization: The use of advanced tech-
nologies such as RAG, and memory management
techniques has allowed for better customization
of agents for specific tasks, enhancing the overall
performance of the system.
5. Multi-Agent Cooperation: The research has
shown that the multi-agent approach improves
performance compared to single-agent systems,
particularly in complex market scenarios.
8 FUTURE WORK AND
CONCLUSION
8.1 Future Work
Currently, our work has focused primarily on only
few patterns recognized by EWP. Expanding plat-
form to include additional wave formations such as
truncations, zigzags, flat corrections, triangles, and
other patterns could improve our predictive capabil-
ities (Frost et al., 2001). Following the successful in-
tegration of EWP, we could further improve our sys-
tem by incorporating other technical analysis methods
(Murphy, 1999), such as moving averages. This ex-
pansion could enhance our ability to determine more
accurate buy or sell signals, potentially improving sig-
nal reliability and profitability. Multi-agent architec-
ture allows us to easily expand our team of agents to
include new members with unique skills needed for
financial analysis.
The next big step could be to integrate Large Ac-
tion Models (LAMs) into the system. LAMs are de-
signed to understand and execute human intentions
by combining perception and action (Thomas, 2024).
The advanced understanding and action capabilities
of LAMs have the potential to fully automate the
trading process. Based on ElliottAgents analyses,
LAMs could automatically perform trades and adapt
to rapidly changing market conditions. However,
LAMs are currently in the early stages of adoption,
making their implementation in such systems chal-
lenging.
8.2 Conclusion
ElliottAgents represents a significant advancement in
the field of financial technology, bridging the gap be-
tween traditional technical analysis and AI method-
ologies. The platform’s success in combining the
EWP with multi-agent AI systems opens new area for
research in algorithmic trading. By demonstrating the
effectiveness of this integrated approach, this research
contributes to the ongoing evolution of intelligent fi-
nancial systems.
The proposed system, ElliottAgents, integrates
traditional financial analysis methods with AI tech-
nologies to enable a deeper and more precise analy-
sis of historical data for accurate future price predic-
tions. This research presents a system design capable
of thoroughly analyzing various American stock mar-
ket companies across different time frames and inter-
vals. While the system primarily focuses on medium
to long-term analysis, it can be customized for shorter
intervals like 5 minutes. However short team effec-
tiveness is limited due to price swings and the pres-
ence of other algorithms for high frequency trading.
It’s important to note that unforeseen market events,
such as rapid crashes or unexpected news, can signif-
icantly impact the accuracy of short-term predictions.
By demonstrating the effectiveness of this inte-
grated approach, this research contributes to the ongo-
ing evolution of intelligent financial systems. While
the current system demonstrates the feasibility of our
approach, future work will focus on incorporating ad-
ditional features and refining the system’s predictive
capabilities.
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
110

REFERENCES
Abrishami, S., Turek, M., Choudhury, A. R., and Kumar,
P. (2019). Enhancing profit by predicting stock prices
using deep neural networks. In 2019 IEEE 31st In-
ternational Conference on Tools with Artificial Intel-
ligence (ICTAI), Portland, OR, USA.
Akintola, K. and Oyetunji, O. (2021). Development of an
agent-based framework for stock market trading. IRE
Journals, 4(9).
Auffarth, B. (2023). Generative AI with LangChain, Build
large language model (LLM) apps with Python, Chat-
GPT, and other LLMs. Packt Publishing.
Boroden, C. (2008). Fibonacci Trading: How to Master the
Time and Price Advantage. McGraw Hill.
Chen, H. (2024). Understand the llm agent orchestration.
https://medium.com/scisharp/understand-the-llm-a
gent-orchestration-043ebfaead1f. Accessed: Jun. 1,
2024.
Chi-Min Chan, Weize Chen, Y. S. J. Y. W. X. S. Z. J. F. Z. L.
(2023). Chateval: Towards better llm-based evalua-
tors through multi-agent debate. arXiv:2308.07201v1
[cs.CL].
Chudziak, A. (2023). Predictability of stock returns using
neural networks: Elusive in the long term. Expert Sys-
tems with Applications, 213.
Chudziak, J. A. and Wawer, M. (2024). Elliottagents: A
natural language-driven multi-agent system for stock
market analysis and prediction. In Proceedings of the
38th Pacific Asia Conference on Language, Informa-
tion and Computation, Tokyo, Japan, (in press).
et al., Y. C. (2024). Exploring large language model
based intelligent agents: Definitions, methods, and
prospects. arXiv:2401.03428v1 [cs.AI].
Frost, A. J., Jr., R. R. P., and Collins, C. J. (2001). Elliott
Wave Principle: Key to Market Behavior. Wiley.
Gamil, A. A., El-fouly, R. S., and Darwish, N. M. (2007).
Stock technical analysis using multi agent and fuzzy
logic. In Proceedings of the World Congress on Engi-
neering, WCE 2007, London, UK.
Guo, T. et al. (2024). Large language model based
multi-agents: A survey of progress and challenges.
arXiv:2402.01680v2 [cs.CL].
Hu, B., Zhao, C., Zhang, P., Zhou, Z., Yang, Y., Xu, Z., and
Liu, B. (2024). Enabling intelligent interactions be-
tween an agent and an llm: A reinforcement learning
approach. arXiv:2306.03604v8 [cs.AI].
Jin, M., Tang, H., Zhang, C., Yu, Q., Liu, C., Zhu, S.,
Zhang, Y., and Du, M. (2024). Time series forecasting
with llms: Understanding and enhancing model capa-
bilities. arXiv:2402.10835v2 [cs.CL].
Kabbani, T. and Duman, E. (2022). Deep reinforcement
learning approach for trading automation in the stock
market. IEEE Access, 10.
Lapan, M. (2020). Deep Reinforcement Learning Hands-
On Second Edition. Packt.
Larson, J. and Truitt, S. (2024). Graphrag: Unlocking llm
discovery on narrative private data. https://www.micr
osoft.com/en-us/research/blog/graphrag-unlocking-l
lm-discovery-on-narrative-private-data. Accessed:
May. 10, 2024.
Lewis, P. et al. (2021). Retrieval-augmented generation for
knowledge-intensive nlp tasks. arXiv:2005.11401v4
[cs.CL].
Li, J., Zhang, Q., Yu, Y., Fu, Q., and Ye, D. (2024). More
agents is all you need. arXiv:2402.05120v1 [cs.CL].
Luo, Y., Liu, K., and Davis, D. N. (2002). A multi-agent
decision support system for stock trading. IEEE Net-
work, 16(1).
Lussange, J., Lazarevich, I., Bourgeois-Gironde, S.,
Palminteri, S., and Gutkin, B. (2020). Modelling stock
markets by multi-agent reinforcement learning. Com-
putational Economics. hal-03055070.
Minsky, M. (1988). The Society of Mind. Simon & Schuster.
Murphy, J. J. (1999). Technical Analysis of the Financial
Markets: A Comprehensive Guide to Trading Methods
and Applications. New York Institute of Finance.
Russell, S. and Norvig, P. (1995). Artificial Intelligence: A
Modern Approach. Prentice Hall.
Szydlowski, K. L. and Chudziak, J. A. (2024). Toward pre-
dictive stock trading with hidformer integrated into
reinforcement learning strategy. In Proceedings of
the 36th International Conference on Tools for Arti-
ficial Intelligence (ICTAI 2024), Herndon, VA, USA,
(in press).
Tan, M., Merrill, M. A., Gupta, V., Althoff, T.,
and Hartvigsen, T. (2024). Are language mod-
els actually useful for time series forecasting?
arXiv:2406.16964v1 [cs.LG].
Thomas, R. J. (2024). The rise of large action models, lams:
How ai can understand and execute human intentions?
https://medium.com/version-1/the-rise-of-large-act
ion-models-lams-how-ai-can-understand-and-execu
te-human-intentions-f59c8e78bc09. Accessed: Jun.
20, 2024.
Tirea, M., Tandau, I., and Negru, V. (2012). Stock market
multi-agent recommendation system based on the el-
liott wave principle. In International Conference on
Availability, Reliability, and Security, Prague, Czech
Republic.
Tsay, R. S. (2010). Analysis of Financial Time Series Third
Edition. Wiley.
Wang, L., Zhang, X., Su, H., and Zhu, J. (2024). A compre-
hensive survey of continual learning: Theory, method
and application. arXiv:2302.00487 [cs.LG].
Weng, L. (2023). Llm-powered autonomous agents. lilian-
weng.github.io.
Wittkampf, F. (2024). Next-level agents: Unlocking the
power of dynamic context. https://towardsdatascience
.com/next-level-agents-unlocking-the-power-of-dyn
amic-context-68b8647eef89. Accessed: Jun. 1, 2024.
Yao, S., Zhao, J., Yu, D., Du, N., Shafran, I., Narasimhan,
K., and Cao, Y. (2023). React: Synergizing reason-
ing and acting in language models. arXiv:2210.03629
[cs.CL].
Zhao, P., Jin, Z., and Cheng, N. (2023). An in-depth survey
of large language model-based artificial intelligence
agents. arXiv:2309.14365v1 [cs.CL].
Integrating Traditional Technical Analysis with AI: A Multi-Agent LLM-Based Approach to Stock Market Forecasting
111
