
Learning Game Co-Design by Second-Year Nursing Students
and Its Effects on Knowledge
Sebastian Gajewski
1
, Nour El Mawas
2a
and Jean Heutte
1b
1
Univ. Lille, ULR 4354 - CIREL - F-59000 Lille, France
2
Université de Lorraine, Crem, F-57000 Metz, France
Keywords: Co-Design, Learning Games, Nursing Students, Knowledge.
Abstract: Previous research works show the role of game-based learning to improve student’s learning. Furthermore,
there are more and more game design tools. They are easy-to-use even by people without any technical skills.
This paper presents the experimentation of learning game co-design by the 110 second-year nursing students
of the Catholic Institute of Lille conducted from April to June 2022, and its effects on learning. To measure
the effects of the learning game co-design on learning, the students answered a knowledge questionnaire
before (pre-test) and after (post-test) the learning game co-design. The results highlight that the knowledge
score increased after the learning game co-design. However, no significant difference was found between the
students who co-developed successfully a playable game and those who didn’t.
1 INTRODUCTION
Previous research works show the role of game-based
learning to increase the students’ learning and
motivation (Tan et al., 2017). Game-based learning
includes gameplay-based learning and game design-
based learning (Kafai, 2006). In the gameplay-based
learning, students play a game to learn while in the
game design-based learning, they learn by designing
their own games. So, this paper is about game-based
learning and more specifically about game design-
based learning because (1) game design engines are
increasingly easier to use even by people without any
technical skills and (2) students learn better when
they are actively engaged in the construction of
concrete artefacts, as video games, they can share
with others (Papert & Harel, 1991).
This paper is a part of a thesis work where we
experimented a method of learning game co-deign
with second-year nursing students and assessed the
effects of this learning game co-design on students’
learning and motivation. However, in this paper, we
especially focus on its effects on learning.
This paper is structured as follows. Section 2
oversees the theoretical works which conduct us to
propose our method of learning game co-design and
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0214-9840
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2646-3658
to choose the game design tools the more suitable for
our needs. Section 3 details how we have
experimented the method of learning game co-design.
Section 4 presents the results which are discussed in
section 5. Section 6 concludes this paper and presents
further perspectives.
2 RELATED WORK
In this section, we first present the method of learning
game co-design we have developed (Gajewski et al.,
2020). Then, we present a guide to help teachers,
game designers, pedagogical engineers, and
researchers to identify the game design tool the more
suitable for their needs (Gajewski et al., 2022, 2023).
2.1 Our Method of Learning Game Co-
Design
Since nursing students are learning, they are novices
in the topic, and since they have not any programming
experience, we needed a method of learning game co-
design with pedagogical objectives, clear steps and
not requiring pedagogical and technical skills.
654
Gajewski, S., El Mawas, N. and Heutte, J.
Learning Game Co-Design by Second-Year Nursing Students and Its Effects on Knowledge.
DOI: 10.5220/0013212200003932
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2025) - Volume 2, pages 654-661
ISBN: 978-989-758-746-7; ISSN: 2184-5026
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

Table 1: Comparison of game design methods.
Pedagogical
objectives
Clear steps Pedagogical skills
not require
d
Technical skills
not require
d
The six facets of
serious game
d
esign
X
X
LEGADEE
X
X
ARGILE
X
DODDEL
X
X
EMERGO
X
X
KTM Advance
X
X
The content-centric
development process
model
X
La méthode du jeu
cadre
X
X
Adventure Author
X
X
X
We have conducted a literature review on
methods of game design. Nine methods of game
design have been identified: the six facets of serious
game design (Marne et al., 2011), LEGADEE
(Marfisi-Schottman, 2012), ARGILE (El Mawas,
2013), DODDEL (McMahon, 2009), EMERGO
(Nadolski et al., 2008), KTM Advance (Ibanez et al.,
2009 ; Yusoff, 2010), the content-centric
development process model (Moreno-Ger et al.,
2008), la méthode du jeu-cadre (Sauvé, 2010), and
Adventure Author (Robertson & Nicholson, 2007).
As shown in Table 1, none were suitable for our
needs: Almost all require pedagogical or technical
skills. One of them has no pedagogical objectives.
So, we needed to develop our method of learning
game co-design.
From a literature review based on 20 papers on
game design-based learning, we developed a method
of learning game co-design (Gajewski et al., 2020).
This method involves four different actors (the
game designer, the teacher, the researcher, and the
students), and is composed of 11 steps. In step 1, the
teacher specifies the pedagogical objectives. In step
2, the game designer identifies the game design
software the more suitable for his needs. In step 3 the
game designer identifies games with similar field. In
step 4, the students play games with similar field for
inspiration for their own games. In step 5, the teacher
delivers learning content to students. In step 6, the
students read, watch and listen the learning content.
In step 7, the game designer teaches students about
how to design a game. In step 8, the game designer
teaches students about how to use the game design
software. In step 9, the students co-design the game.
In step 10, the students co-develop the game. In step
11, the four actors (the game designer, the researcher,
the students, and the teacher) evaluate the game
(Gajewski et al., 2020). Table 2 illustrates our method
of learning game co-design.
2.2 Choice of the Game Design Tool
Since in step 2, the game designer identifies the game
design software the more suitable for his needs, we
have conducted a systematic literature review
following the PRISMA methodology between 2010
(2010-01-01) and 2020 (2020-12-18) from five
databases (IEEE Xplore, ScienceDirect, Scopus,
Springer, and Web of Science), with the search words
“game design tools” and its synonyms (Gajewski et
al., 2022, 2023).
From 302 identified research works, 18 have been
used for the discussion. And from eight game design
tools advised by a pedagogical engineer, three have
been used for the discussion. Figure 1 illustrates the
flow diagram of that systematic literature review.
Learning Game Co-Design by Second-Year Nursing Students and Its Effects on Knowledge
655
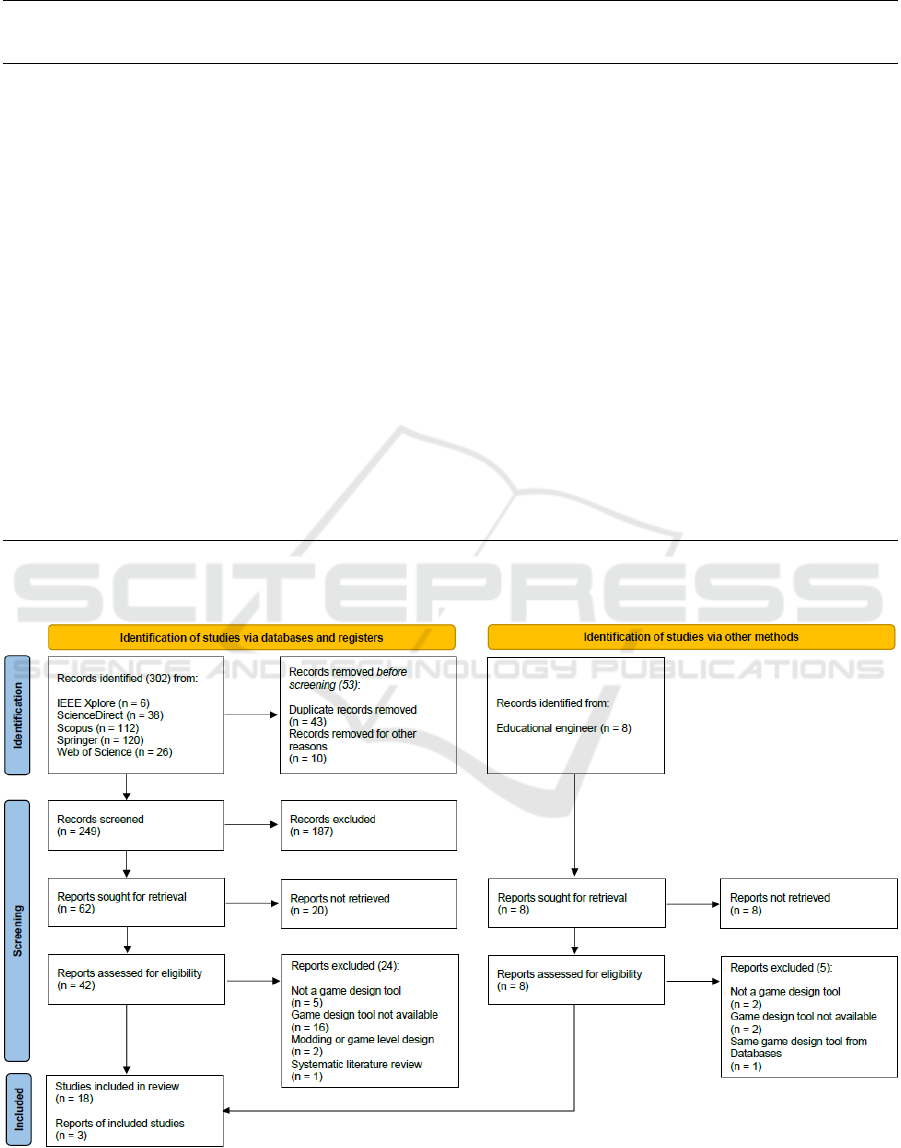
Table 2: Our method of learning game co-design (Gajewski et al., 2020).
Steps
Actions
Actors
1
Specify the pedagogical objectives
Teache
r
2
Identify the game design software
Game designe
r
3
Identify games with similar fiel
d
Game designe
r
4
Play games with similar field for inspiration
Students
5
Deliver learning content to students
Teache
r
6
Read, watch, listen the learning content
Students
7
Teach students about how to design a game
Game designe
r
8
Teach students about how to use the game design software
Game designe
r
9
Co-design the game
Students
10
Co-develo
p
the
g
ame
Students
11
Evaluate the game
GD / R / S / T
GD
(
Game Desi
g
ner
)
/ R
(
Researcher
)
/ S
(
Students
)
/ T
(
Teacher
)
Figure 1: PRISMA flow diagram for a systematic literature review about game design tools from 2010-01-01 to 2020-12-18
(Gajewski et al., 2022, 2023).
CSEDU 2025 - 17th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
656

Overall, 12 game design tools have been
identified: Agentsheets, Alice, Celestory,
GameMaker, Gamestar Mechanic, Microsoft Kodu,
RPG Maker VX Ace, Scratch, Stagecast Creator,
Unity, Unreal Engine, and VTS Editor.
Those game design tools have been described and
compared according to nine criteria: programming
language, tool language, tutorials, scenes and
characters, game type, target audience-designer, 2D
or 3D modelling, prize, and export.
Regarding the programming language,
“programming a video game traditionally required
extensive typing in which the smallest syntax error
could offset game play” (Burke & Kafai, 2014, p. 8)
whereas other game design tools use a visual and
simple programming languages as “drag-and-drop”.
Regarding the tool language, some game design tools
are only in English. Others are in different languages
as in French. Regarding the tutorials, some game
design tools provide tutorials (manuals, videos, etc.);
others don’t. Regarding the scenes and characters,
some game design tools provide resources as
backgrounds for the scene and sprites for the
characters. If the game design tool doesn’t provide
resources, users have to draw them by themselves
(requiring skills and time) or ask a game design
character to do it for them. Regarding the game type,
some game design tools offer the possibility to
develop different game type (e.g., adventure, arcade,
racing); others are limited to just one. Regarding the
target audience-designer, some game design tools are
intended for adults or experts; others are suitable for
children or novices. Regarding the 2D or 3D
modelling, some game design tools allow users to
develop 3D games. “Compared to 2D environments,
the ability to create 3D games […] makes it visually
more appealing for young students” (Akcaoglu, 2016,
p. 115). Regarding the prize, some game design tools
are freeware; for others, users have to pay a fee to use
it. Regarding the export, the games developed by
some game design tools can be played offline; others
require an internet connexion. Table 3, which is a
guide to help teachers, game designers, pedagogical
engineers, and researchers to identify the game design
tool the more suitable for their needs, describes and
compares the 12 game design tools according the nine
criteria.
3 EXPERIMENTATION
Our method of learning game co-design has been
experimented with the 110 second year nursing
students of the Catholic Institute of Lille from April
to June 2022 which were divided into 21 groups.
3.1 Method
In step 1, the teacher specified the pedagogical
objectives. In our experimentation, the pedagogical
objective was to allow students to co-design a
learning game about liver cirrhosis for them to learn
about this topic.
In step 2, the game designer identified the game
design software the more suitable for his needs. To
identify the game design software, we used the
summary table (Table 2) of the different game design
tools. We decided to use VTS Editor because it
doesn’t require any technical skills. Indeed, VTS
Editor uses a drag-and-drop interface. VTS Editor
interface is in French making the game design tool
easier to use. VTS Editor provides tutorials. VTS
Editor provides backgrounds for scenes and
characters. VTS Editor allow users to develop
simulation games which are suitable because
“nursing students are generally well acquainted with
visually realistic game environments” (Koivisto et
al., 2016)
In step 3, the game designer identified games with
similar field. In our experimentation, the learning
field is about nursing and clinical reasoning. Different
games were identified, as The blood typing game or
eMergenSIM.
In step 4, the students played those games for
inspiration for their own learning games.
In step 5, the teacher delivered learning content to
students. The learning content was uploaded on our
Learning Management System (LMS) Moodle. The
learning content was an eBook with the anatomy and
the physiology of the liver, the definition, the
pathophysiology, the clinical signs and the treatments
of the liver cirrhosis, etc. (Figure 2), videos, and
exercises (case studies).
Figure 2: Screenshot of the eBook created in Moodle.
Learning Game Co-Design by Second-Year Nursing Students and Its Effects on Knowledge
657

Table 3: Comparison of game design tools according to 9 criteria (Gajewski et al., 2022, 2023).
Programm
ing
lan
g
ua
g
e
Language Tutorials
Scenes
and
characters
Game
Type
target
audience-
desi
g
ne
r
2D or 3D
modelling
Prize
Export
Agentsheet
s
Drag and
drop
English
French
English
- For kids 3D Free Online
Alice
Drag and
drop
English
English
-
For
anyone
3D Free Locally
Celestory
Drag and
drop
English
French
English
French
≠ types of
games
-
2D
Free or
Fees
Various
GameMak
er
Code or
Drag and
drop
English
French
English
French
≠ types of
games
beginners
and
profession
als
2D
Free or
fees
Various
Gamestar
Mechanic
Drag and
drop
English English
≠ types of
games
7 to 14-
year old
children
2D Free Online
Microsoft
Kodu
Visual by
tiles
English
French
English
≠ types of
games
9 to 10-
year old
children
3D Free Online
RPG
Maker VX
A
ce
Point and
click
English
French
English
RPG
For
anyone
2D
Free (30
days)
64,99 €
Windows
Scratch
Drag and
snap
English
French
English
French
≠ types of
games
8 to 16
years old
2D Free
Locally or
online
Stagecast
Creator
Point and
click
English
French
English
≠ types of
games
8-year old
children
2D
Demo
(120 days)
Locally or
Online
Unity Code English English
asset store
Not for
free
≠ types of
games
For
profession
als
2D or 3D
Free
conditiona
ll
y
Various
Unreal
Engine
Code or
visual
English English Templates
≠ game
templates
For
profession
als
3D
Free
conditiona
ll
y
Various
VTS
Editor
Drag and
drop
English
French
English
French
Simulation
games
-
2D and 3D
Trial or
fees
Various
In step 6, the students read, watched, and listen to
the learning content for them to understand them. In
this step, the students could help each other. They
could compare their understanding of the learning
content.
In step 7, the game designer taught students about
how to design a game (What is a learning game? What
are the benefits of using games at school? What are
game mechanics? Etc.).
In step 8, the game designer taught students about
how to use the game design software. Firstly, in half
group, while the teacher created a project on VTS
Editor, students reproduced it by mimicry. Secondly,
students had to watch the tutorials uploaded on our
LMS. Thirdly, students had to realize exercises on the
use of VTS Editor. Finally, students explored in depth
VTS Editor for them to discover all its functionalities.
Figure 3 is an overview of the VTS Editor’s interface.
Figure 3: Screenshot of the VTS Editor’s interface.
CSEDU 2025 - 17th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
658

In step 9, the students co-designed the game. The
students were asked to create a paper prototype of
their game. To do that, they had to describe the game
storyline, the characters, the rules of the game, the
sound effects and the music, the gameplay, the game
mechanics, the aim of the game, the pedagogical
objectives, etc.
Figure 4: Screenshot of the learning game of one of the
groups.
In step 10, once the paper prototype was over,
students could co-develop their games by using VTS
Editor. Figure 4 is an example of one learning game
developed by one of the groups.
In step 11, the game was evaluated. The students
were encouraged to look at and to test the games of
the others groups, so that they could get inspiration
for their own games, and give feedbacks to the other
groups to help them to improve their games. The
game designer evaluated the playful aspects
introduced into the games. Is the game playable?
What are the game mechanics introduced into the
games? Etc. The teacher evaluated the serious aspects
introduced into the games. Did the game meet the
pedagogical objectives? Did the students discuss all
the aspects of the liver cirrhosis? Is the knowledge
introduced into the games true? The researcher
evaluated the method of learning game co-design. Is
it suitable? What are the effects of the learning game
co-design on learning?
3.2 Instrument
One of the aims of this study was to measure the
effects of the learning game co-design on the
students’ knowledge.
A 20-item questionnaire was developed by the
researcher to assess the students’ knowledge on liver
cirrhosis. Each question was marked on one point.
The questionnaire was therefore marked on 20 points.
4 RESULTS
As shown in Figure 5, there was a significant
difference between the pre-test (M = 6.77) and the
post-test (M = 9.78) mean score on knowledge (p <
.001) with an increase of 3.01 points (out of 20) in the
post-test in comparison with the pre-test.
However, as shown in Table 4, no significant
difference was found in the post-test between the
students who co-developed successfully a playable
game and those who didn’t. Indeed, there was a
significant difference between the pre-test (M = 6.72)
and the post-test (M = 9.62) mean score on
knowledge within the students who co-developed
successfully a playable game (p < .001) with an
increase of 2.90 points (out of 20) in the post-test in
comparison with the pre-test. In the same way, there
was a significant difference between the pre-test (M
= 7.13) and the post-test (M = 10.85) mean score on
knowledge within the students who didn’t succeed in
co-developing a learning game (p < .05) with an
increase of 3.72 points (out of 20) in the post-test in
comparison with the pre-test.
Figure 5: Pre-test and post-test mean scores on knowledge.
5 DISCUSSION
As shown in Table 4, no significant difference was
found in the post-test between the students who co-
developed successfully a playable game and those
who didn’t. Indeed, the students who co-developed
successfully a playable game and those who didn’t
have increased their mean score on knowledge in the
post-test in comparison with the pre-test. We can
conclude that co-development a learning game didn’t
improve students’ knowledge. The mere participation
in the learning game co-design activity even if
students didn’t succeed in co-developing a learning
game increased mean score on knowledge.
6,77
9,78
0
5
10
15
20
pre-test post-test
Learning Game Co-Design by Second-Year Nursing Students and Its Effects on Knowledge
659

Table 4: Mean scores on knowledge within the students who co-developed successfully a playable game and those who didn’t.
Total
Yes
No
Difference
n
48
42
6
Pre-test
M = 6.77
SD = 2.14
M = 6.72
SD = 2.06
M = 7.13
SD = 2.82
ns
Post-test
M = 9.78
SD = 3.13
M = 9.62
SD = 3.07
M = 10.85
SD = 3.70
ns
Difference
3.01 (+ 44 %)
p < .001
2.90 (+ 43 %)
p < .001
3.72 (+ 52%)
p < .05
Furthermore, even if no significant difference was
found in the post-test between the students who co-
developed successfully a playable game and those
who didn’t, the post-test mean score on knowledge
within the students who didn’t succeed in co-
developing a learning game is higher than those who
co-developed successfully a playable game. In the
same way, the post-test mean score on knowledge
further increased within the students who didn’t
succeed in co-developing a learning game than within
the students who co-developed successfully a
playable game. We can suppose that students who
didn’t succeed in co-developing a learning game
focused more on serious aspects to introduce into the
game than playful aspects.
6 CONCLUSION AND
PERSPECTIVES
This paper is about game-based learning and more
specifically about game design-based learning.
We first have presented the method of learning
game co-design we have developed (Gajewski et al.,
2020). Then, we have presented a guide to help
teachers, game designers, pedagogical engineers, and
researchers to identify the game design tool the more
suitable for their needs (Gajewski et al., 2022, 2023).
We finally have presented the experimentation of a
learning game co-design activity by using our
method.
The results highlight that the knowledge score
increased after the learning game co-design.
However, no significant difference was found
between the students who co-developed successfully
a playable game and those who didn’t. We could
conclude that the mere participation in the learning
game co-design activity even if students didn’t
succeed in co-developing a learning game increased
mean score on knowledge.
In terms of perspectives, it could be interesting to
let the students explain their games during a showcase
to evaluate if they are able to articulate the knowledge
introduced into their games, as other authors have
already done (Khalili et al., 2011).
Furthermore, it could be interesting to conduct a
second experimentation with control groups (playing
a game or taking a lecture) to evaluate the relevance
of game design-based learning in comparison with
other pedagogical methods.
REFERENCES
Akcaoglu, M. (2016). Design and Implementation of the
Game-Design and Learning Program. TechTrends, 60,
114–123. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11528-016-0022-y
El Mawas, N. (2013) Architecture pour la co-conception
des jeux sérieux participatifs et intensifs en
connaissances.
Gajewski, S., El Mawas, N. & Heutte, J. (2020). Towards a
Methodology to Co-design a Learning Game by
Nursing Students. In I., Marfisi-Schottman, F., Bellotti,
L., Hamon & R., Klemke R. (eds). Games and Learning
CSEDU 2025 - 17th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
660

Alliance. GALA 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer
Science, 12517, Springer, pp.273-282, 978-3-030-
63463-6. ⟨halshs-03092035⟩
Gajewski, S., El Mawas, N., & Heutte, J. (2022). A
Systematic Literature Review of Game Design Tools.
Dans M. Cukurova, N. Rummel, D. Gillet, B. McLaren,
& J. Uhomoibhi (eds), Proceedings of the 14th
International Conference on Computer Supported
Education - (Volume 2), SciTePress, 404-414.
https://doi.org/10.5220/0011137800003182
Gajewski, S., El Mawas, N., & Heutte, J. (2023). Game
Design Tools: A Systematic Literature Review: Choice
of a Game Design Tool for an Experimentation in the
Nursing Field. In: Uhomoibhi, J. (eds) Computer
Supported Education. CSEDU 2022. Communications
in Computer and Information Science, vol 1817.
Springer, Cham.
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-40501-3_4
Ibanez, B.C., Boudier, V., & Labat J.-M. (2009).
Knowledge Management Approach to Support a
Serious Game Development. Advanced Learning
Technologies, ICALT, p. 420-422.
Kafai, Y. B. (2006). Playing and making games for
learning: Instructionist and constructionist:
Perspectives for games studies. Games and Culture
Volume 1 Number 1, 36-40.
Khalili, N., Sheridan, K., Williams, A., Clark, K., &
Stegman, M. (2011). Students designing video games
about immunology: Insights for science learning.
Computers in the Schools, 28, 228-240.
https://doi.org/10.1080/07380569.2011.594988
Koivisto, J.-M., Multisilta, J., Niemi, H., Katajisto, J., &
Eriksson, E. (2016). Learning by playing: A cross-
sectional descriptive study of nursing students’
experiences of learning clinical reasoning. Nurse
Education Today, 45, 22‑28. https://doi.org/10.1016/
j.nedt.2016.06.009
Marfisi-Schottman, I. (2012) Méthodologie, modèles et
outils pour la conception de Learning Games.
Marne, B., Huynh-Kim-Bang, B., & Labat, J.-M. (2011).
Articuler motivation et apprentissage grâce aux facettes
du jeu sérieux. EIAH 2011 - Conférence sur les
Environnements Informatiques pour l’Apprentissage
Humain, May 2011, Mons, Belgique. pp.69-80.
McMahon, M. (2009). Using the DODDEL model to teach
serious game design to novice designers. Ascilite.
Moreno-Ger, P., Burgos, D., Martinez-Ortiz, I., Sierra, J.L.,
& Fernandez-Manjou, B. (2008). Educational game
design for online education. Computers in Human
Behaviour, vol. 24, n°6, p. 2530-2540.
Nadolski, R. J., Hummel, H. G. K., Van Den Brink, H. J.,
Hoefakker, R. E., Slootmaker A., Kurvers, H. J., &
Storm, J. (2008). EMERGO: A methodology and
toolkit for developing serious games in higher
education. Simulation & Gaming, 39(3), 338-352.
https://doi.org/10.1177/1046878108319278
Papert, S., & Harel, I. (1991). Situating constructionism.
Dans S. Papert & I. Harel, Constructionism (36, 1-11).
Ablex Publishing.
Robertson, J., & Nicholson, K. (2007). Adventure Author:
a learning environment to support creative design. 6th
International Conference on Interaction Design and
Children, 37-44. https://doi.org/10.1145/1297277.1297
285
Sauvé, L., & Kaufman, D. (2010). Jeux et simulations en
éducation. Presse Université du Québec.
Tan, A.J.Q., Lee, C.C.S., Lin, P.Y., Cooper, S., Lau, L.S.T.,
Chua, W.L., & Liaw, S.Y. (2017). Designing and
evaluating the effectiveness of a serious game for safe
administration of blood transfusion: A randomized
controlled trial. Nurse Education Today, 55, 38-44.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2017.04.027
Yusoff, A. (2010). A Conceptual Framework for Serious
Games and its Validation.
Learning Game Co-Design by Second-Year Nursing Students and Its Effects on Knowledge
661
