
Human Pose Estimation from an Extremely Low-Resolution Image
Sequence by Pose Transition Embedding Network
Yasutomo Kawanishi
1 a
, Hitoshi Nishimura
2 b
and Hiroshi Murase
3 c
1
Guardian Robot Project, RIKEN, Kyoto, Japan
2
KDDI Research, Saitama, Japan
3
Graduate School of Informatics, Nagoya University, Aichi, Japan
Keywords:
Low Resolution, Human Pose Estimation, Temporal Information.
Abstract:
This paper addresses the problem of human pose estimation from an extremely low-resolution (ex-low) image
sequence. In an ex-low image (e.g., 16 × 16 pixels), it is challenging, even for human beings, to estimate
the human pose smoothly and accurately only from a frame because of resolution and noise. This paper
proposes a human pose estimation method, named Pose Transition Embedding Network, that considers the
temporal continuity of human pose transition by using a pose-embedded manifold. This method first builds
a pose transition manifold from the ground truth of human pose sequences to learn feasible pose transitions
using an encoder-decoder model named Pose Transition Encoder-Decoder. Then, an image encoder, named
Ex-Low Image Encoder Transformer, encodes an ex-low image sequence into an embedded vector using a
transformer-based network. Finally, the estimated human pose is reconstructed using a pose decoder named
Pose Transition Decoder. The performance of the method is confirmed by evaluating an ex-low human pose
dataset generated from a publicly available action recognition dataset.
1 INTRODUCTION
Human pose estimation is an essential task in various
computer vision applications such as action recog-
nition (Song et al., 2021), motion prediction (Fujita
and Kawanishi, 2024), anomaly detection (Temuroglu
et al., 2020), and internal state recognition (Mizuno
et al., 2023). It has been applied to various kinds
of video, such as in-vehicle cameras, drone cameras,
smartphone cameras, and surveillance cameras. Be-
cause of their importance, this topic has been ac-
tively developed, and state-of-the-art methods have
achieved very high accuracy, even in complicated
scenes. One of the most important applications of
human pose estimation is skeleton-based human ac-
tion recognition and prediction. The estimated results
should be accurate enough when using the human
pose estimation results in pose-based action recogni-
tion tasks; the estimated results should be accurate
enough. In addition, they should be temporally as
smooth as the actual human poses to express their hu-
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3799-4550
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9552-3837
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8103-9294
man motion.
Most existing human pose estimation methods re-
quire the persons in an image to be somewhat large,
for example, more than 100 pixels in height. How-
ever, in videos for practical applications, such as in-
vehicle cameras or surveillance cameras, the size of
the person is often small in the frame of the videos,
that is, person images are often of low resolution.
Even with recent advances in camera sensors, the size
of persons captured by cameras from afar remains
small. If given an extremely low-resolution cropped
image (ex-low; e.g., a person is 16 × 16 pixels), is it
possible to estimate the human pose from the ex-low
input? In this study, we focus on a situation in which
the size of a person in a cropped image is very small.
If a person image is extremely low-resolution (ex-
low), human pose estimation becomes difficult for the
following reasons. First, an ex-low image contains lit-
tle information for estimating human pose. It is also
difficult to distinguish the body region of the target
person in an image from the background of the im-
age because of the poor features in the ex-low im-
age and blurry boundaries. Because the number of
pixels for a person in an ex-low image is small, the
signal-to-noise ratio is low and the effect of salt-and-
478
Kawanishi, Y., Nishimura, H. and Murase, H.
Human Pose Estimation from an Extremely Low-Resolution Image Sequence by Pose Transition Embedding Network.
DOI: 10.5220/0013239600003912
In Proceedings of the 20th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2025) - Volume 2: VISAPP, pages
478-485
ISBN: 978-989-758-728-3; ISSN: 2184-4321
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

Figure 1: Human pose estimation from an ex-low image is
difficult, even for humans, because the input contains less
information. The small image in the middle represents the
input. The image on the left shows a magnified view of the
input. A high-resolution version of the input is shown on
the right side (for reference). (These photos are originally
from the NTU RGB+D dataset (Shahroudy et al., 2016).)
t
Figure 2: Temporal information helps us estimate human
pose. We think you can guess how the person is moving.
pepper noise is relatively more significant. These is-
sues make pose estimation from an ex-low image dif-
ficult. As shown in Fig. 1, it is extremely difficult
even for humans to use only a single ex-low image.
Meanwhile, once we see a video (i.e., an ex-low
image sequence), we can guess how the human pose
changes (Fig. 2). This implies that temporal infor-
mation is powerful for pose estimation. This is be-
cause human pose transitions have temporal continu-
ity. In this study, we focus on the temporal continuity
of human pose transition and propose a pose estima-
tion method named Pose Transition Embedding Net-
work from an extremely low-resolution (ex-low) im-
age sequence. Human detection and tracking should
be applied beforehand to handle the image sequence
of the target person. Thus, a top-down human pose
estimation approach that estimates the human pose af-
ter human detection is suitable for this scenario. This
study assumes that each human region is detected and
tracked during preprocessing.
To address this pose estimation problem, we pro-
pose Pose Transition Embedding Network to estimate
an accurate and smooth human pose sequence from an
ex-low image sequence. This method consists of two
parts: the Pose Transition Encoder-Decoder, which
captures how the human pose changes, and Ex-Low
Image Encoder Transformer, which extracts a feature
from an ex-low image sequence.
First, the Pose Transition Encoder-Decoder model
is trained to capture the continuity of the human pose
transition. Because there is a strong correlation be-
tween human poses in adjacent frames, pose transi-
tion can be described as a feature vector in a low-
dimensional embedding space. The encoder-decoder
model is trained using ground-truth pose annotation
sequences to encode human pose transitions into vec-
tors in a low-dimensional embedding space. After
training, each vector in the space is associated with
a feasible human-pose transition.
Then, the Ex-Low Image Encoder Transformer,
followed by the Pose Transition Decoder, learns the
mapping from an input image sequence to the human
pose sequence. The Ex-Low Image Encoder Trans-
former captures the spatial and temporal variations
of the input ex-low image sequence using CNN and
Transformer structures. The reconstructed human-
pose sequence is expected to be smooth and feasible.
The contributions of this paper are summarized as
follows;
• We addressed a new computer vision problem of
human pose estimation from an extremely low-
resolution (ex-low; 16 × 16 pixels) image se-
quence.
• We propose the Pose Transition Embedding Net-
work, which consists of the Pose Transition
Encoder-Decoder model and the Ex-Low Image
Encoding Transformer. This method can handle
the feasible temporal transitions of human poses
in an embedded space.
• We also propose a pseudo dataset generation
method based on the existing datasets.
The remainder of this paper is organized as fol-
lows. In Section 2, recent studies on human pose es-
timation are summarized. In Section 3, the details of
the proposed Pose Transition Embedding Network are
described. In Section 4, experimental results are pre-
sented. Finally, we conclude the paper in Section 5.
2 RELATED WORK
In this section, we first summarize single-frame hu-
man pose estimation methods that have been actively
developed in computer vision. Then, because we fo-
cus on low-resolution images, we summarize the hu-
man pose estimation methods for low-resolution im-
ages.
2.1 Human Pose Estimation
Human pose estimation has been widely developed
and applied to various applications. Generally, hu-
man pose estimation methods can be divided into two
categories: top-down (e.g., (Xiao et al., 2018)) and
bottom-up approaches (e.g., (Kreiss et al., 2019)).
The top-down approach first detects human bounding
boxes, and then estimates the human pose for each
Human Pose Estimation from an Extremely Low-Resolution Image Sequence by Pose Transition Embedding Network
479

bounding box. Generally, the detected human bound-
ing boxes are resized to fit the input for the pose esti-
mator. This approach is robust to the size of the target
person, because the input to the pose estimator is re-
sized. DeepPose (Toshev and Szegedy, 2014) is the
most earliest deep learning-based human pose esti-
mation. This method directly estimates the joint lo-
cations of the human body using a regression model.
Recently, heatmap-based approaches have been
mainly used for human pose estimation. This ap-
proach first estimates the heat maps of the body joints,
and then selects the actual locations from the heat
maps. PoseNet (Papandreou et al., 2017a) estimates
the heatmaps of the body joints and their offset maps.
While state-of-the-art methods have become compli-
cated, a Simple Baseline (Xiao et al., 2018) achieves
good performance even with a very simple network.
This method is widely used as a baseline for top-down
human pose estimation.
These methods assume that only one person is
present in an input image. To handle temporal con-
tinuity, the target person must be tracked. In this case,
a sequence of bounding boxes of the target person is
provided as an input to the pose estimation process.
Therefore, this top-down approach makes it easier to
extend the multi-frame human pose estimation.
Meanwhile, recent studies focus on bottom-up
human pose estimation. This approach first esti-
mates the heatmap of each body joint and then finds
an optimal combination of their locations. Several
well-known methods are available, including Open-
Pose (Cao et al., 2021), and PifPaf (Kreiss et al.,
2019). This approach is weak for low-resolution hu-
man pose estimation because each body joint of the
people small in the image becomes too small.
2.2 Multi-Frame Human Pose
Estimation
Several studies have been proposed to handle tem-
poral information for human pose estimation. A
straightforward approach is to use convolutional
LSTMs, such as LSTM Pose Machine (Luo et al.,
2018), UniPose (Artacho and Savakis, 2020), Mo-
tion Adaptive Pose Esitmation (Fan et al., 2021), and
FAMI Pose (Liu et al., 2022). (Liu et al., 2022).
Another approach involves estimating the motion of
a target human body as an intermediate representa-
tion (Liu et al., 2021). This approach includes Flow-
ing ConvNets (Pfister et al., 2015) and Thin-Slicing
Network (Song et al., 2017). These methods estimate
motion flows to incorporate information from adja-
cent frames for pose estimation. DCPose (Liu et al.,
2021) estimates motion offsets using Pose Residual
Fusion. The above approach is also adopted as a
heatmap-based approach.
2.3 Estimation from Low-Resolution
Images
The accuracy of human pose estimation using a
heatmap-based approach is limited by the resolution
of the output heatmap (the same as that of the in-
put image). To tackle the difficulty of the heatmap-
based approach, several researchers have proposed
the offset-map-based human pose estimation meth-
ods (Papandreou et al., 2017b; Zhang et al., 2019).
These methods output an offset map for each body
joint. Each pixel value in the offset map indicates
the offset of the target keypoint from the pixel. They
also output a binary heatmap for each body joint and
calculate each keypoint location by averaging the off-
set map values within the selected pixels in the corre-
sponding binary heatmap.
These methods increase the pose-estimation ac-
curacy even if the input image is low resolution.
Wang et al. (Wang et al., 2022) extended this method
by replacing a binary heatmap with a Gaussian dis-
tribution. The method was evaluated using a low-
resolution version of the MSCOCO (Lin et al., 2014)
dataset with a resolution of 128 × 96 pixels.
Srivastav et al. (Srivastav et al., 2019) have pro-
posed a human pose estimation from a low-resolution
depth image. They use low-resolution images for pri-
vacy protection since their target situation is medical
surgery where there are several medical doctors and
a patient. They used a low-resolution version of the
MVOR dataset (Srivastav et al., 2018). In the pa-
per, the resolution of the input images is 64 × 48 pix-
els. The method learns super-resolution and bottom-
up pose estimation simultaneously.
Xu et al. (Xu et al., 2020) have proposed the RSC-
Net, which can estimate 3D human pose and shape
from a low-resolution image. In the paper, the res-
olution of the input image is 32 × 32 pixels. They
parametrize the 3D model of a person by using SMPL
model (Loper et al., 2015). The model is trained using
multi-scale images, not only low-resolution images.
Iwata et al. (Iwata et al., 2021) introduced
LFIR2Pose to estimate the human pose from 16 ×16
Far-infrared (LFIR) image sequence, which makes it
easier to distinguish the traget person from the back-
ground. By assuming that only one person is in an
LFIR image, they estimate the human pose based on
the top-down approach. The model is a 3D Con-
volutional Neural Network followed by a regression
network. This method is very simple, but effectively
uses temporal information for human pose estimation
VISAPP 2025 - 20th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
480
𝑡 − 𝑘
𝑡 + 𝑘
𝒴
!
∈ ℝ
"#$"%&'(
𝐲
!)%
∈ ℝ
"#
𝒴
%
!
∈ ℝ
"#$"%&'(
𝐲&
!)%
∈ ℝ
"#
𝐯
!
∈ ℝ
*
𝐲
(
!)%
∈ ℝ
"#
𝐯
(
!
∈ ℝ
*
𝐠
!)%
∈ ℝ
+
𝐟
!)%
∈ ℝ
,
16×16×3
𝑡 − 𝑘
𝑡 + 𝑘
𝑡 − 𝑘
𝑡 + 𝑘
𝑡 − 𝑘
𝑡 + 𝑘
𝒴
+
!
∈ ℝ
"#$"%&'(
𝐠
-
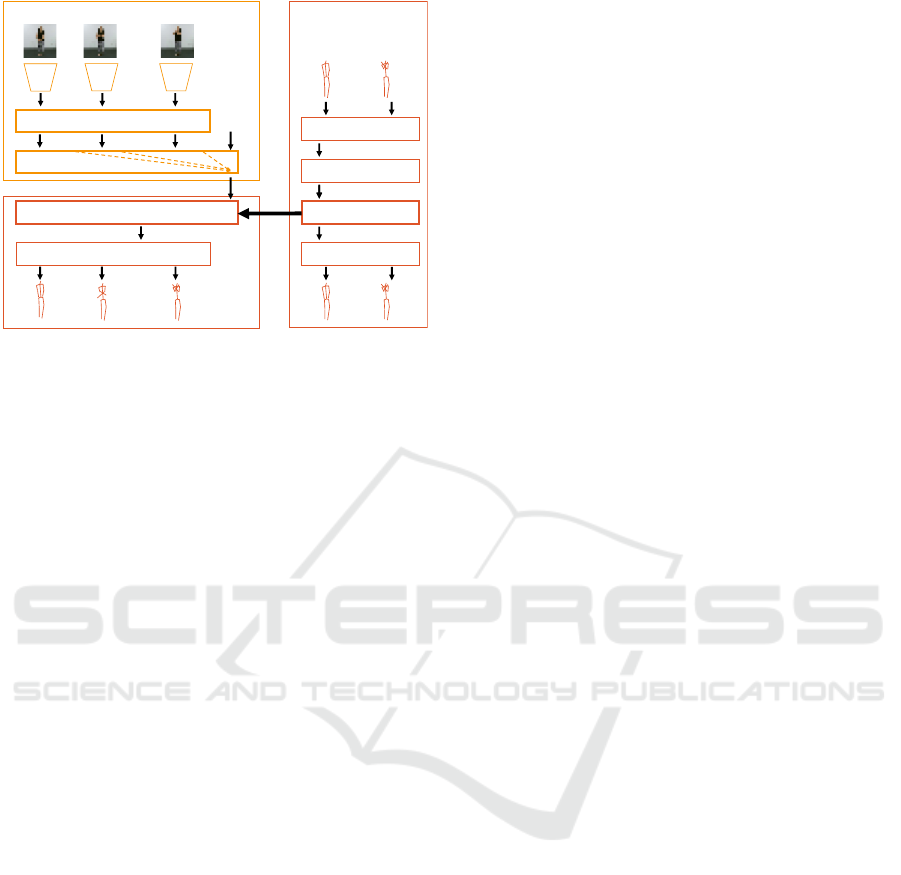
Figure 3: (a) The proposed Temporal Embedding Network
consists of the Ex-Low Image Encoding Transformer fol-
lowed by the Pose Transition Decoder. The texts beside the
arrows in the figure indicate the dimension of the data. (b)
Pose Transition Encoder-Decoder model. The texts beside
the arrows in the figure denote the dimension of the data.
from a low-resolution image sequence. In LFIR im-
ages, the human body and background can be distin-
guished easily because the temperature of the human
body is relatively higher than that of the background
in a room. This is an advantage against using RGB
images; however, the method would not work outside,
especially under the sun.
3 POSE TRANSITION
EMBEDDING NETWORK
3.1 Overview
Human pose estimation from an ex-low image se-
quence is difficult because of the lack of informa-
tion in the image, the ambiguity of the border be-
tween a target person, cluttered background, and the
effect of noise. The proposed method overcomes
these difficulties by focusing on the temporal conti-
nuity and feasible transitions of human poses. The
input of the method is an ex-low image sequence I
t
=
(I
t−k
, . . . , I
t
, . . . , I
t+k
), that is, 2k + 1 frames around
frame t, and the output is the human pose y
t
in the
middle image I
t
. This section describes the proposed
method for extremely low-resolution (ex-low) human
pose estimation, named Temporal Embedding Net-
work, which consists of the Pose Transition Encoder-
Decoder and the Ex-Low Image Encoding Trans-
former.
3.2 Ex-Low Image Encoding
Transformer
This model captures the temporal information of the
human pose sequence from an ex-low image se-
quence using a convolutional neural network and
transformer. The CNN captures spatial information
from each frame, and then the transformer captures
temporal information. Finally, the Ex-Low Image
Encoding Transformer outputs an embedded vector
ˇ
v
t
∈ R
M
. The architecture of the model is visualized
in Fig. 3 (a).
First, each color image I
t
∈ R
16×16×3
in the input
sequence I
t
= (I
t−k
, . . . , I
t
, . . . , I
t+k
) is fed into a CNN
model specialized for an ex-low image, and each fea-
ture vector f
t
∈ R
D
corresponds to the input image I
t
is
obtained. Then, each of the features is embedded into
E dimensional space using a Multi-Layer Perceptron
(MLP) layer, and each feature vector g
t
∈ R
E
is ob-
tained. This sequence of features together with an fea-
ture aggregation token g
a
is fed into the transformer
block, which consists of multiple transformer layers.
Each transformer layer consists of a multi-head atten-
tion layer and an MLP layer. In this paper, the number
of layers was determined empirically and set to four.
Among the outputs of the transformer layers, the ag-
gregated output
ˇ
v
t
∈ R
M
is selected as the final output
of this module. This procedure is denoted as
ˇ
v
t
= f
i
(I
t
). (1)
The embedded vector
ˇ
v
t
is fed to the Pose Transition
Decoder f
d
explained in Section 3.3, and a pose se-
quence
ˇ
Y
t
= (
ˇ
y
t−k
, . . . ,
ˇ
y
t
, . . . ,
ˇ
y
t+k
) is obtained as
ˇ
Y
t
= f
d
(
ˇ
v
t
) = f
d
( f
i
(I
t
)). (2)
We empirically define the function f
i
by four 3×3
CNN layers whose channels are 16, 32, 64, and 128,
followed by a 1 × 1 convolution to obtain channel 64.
3.3 Pose Transition Encoder-Decoder
This model aims to capture temporally smooth and
feasible human pose transitions based on an encoder-
decoder architecture. The decoder part is used for
pose estimation by combining it with the Ex-Low Im-
age Encoding Transformer.
Here, we assume that human pose transition can
be described in a low-dimensional space. The en-
coder encodes a human pose sequence into a low-
dimensional vector, and then the decoder decodes the
feasible human pose sequence. The architecture of
the model is visualized in Fig. 3 (b).
Human pose is described as a set of body joint
locations. Each body joint location in a 2D coordi-
nate system is described as a two-dimensional vector.
Human Pose Estimation from an Extremely Low-Resolution Image Sequence by Pose Transition Embedding Network
481

Therefore, the human pose at frame t can be described
as a 2J dimensional vector y
t
∈ R
2J
, where J denotes
the number of body joints. Thus, a pose transition
consisting of 2k + 1 frames around time t can be de-
scribed as a concatenated vector Y
t
∈ R
2J(2k+1)
.
Here, we assume that the pose transition is re-
stricted such that they form a low-dimensional mani-
fold in the M-dimensional pose-transition space. We
named this low-dimensional manifold Pose Transition
Manifold. The proposed model estimates an embed-
ded vector v
t
∈ R
M
from input Y
t
using an AutoEn-
coder whose intermediate dimension is M. The en-
coder and decoder of the AutoEncoder are denoted as
f
e
and f
d
, respectively.
v
t
= f
e
(Y
t
), (3)
b
Y
t
= f
d
(v
t
). (4)
The details of f
e
(·) and f
d
(·) are visualized in Fig. 3.
Both of them consist of two fully connected layers.
This encoder-decoder model is trained to reduce the
reconstruction loss, L
r
, which is defined as the sum of
the Euclidean distances of all body joints. Its equation
is as follows,
L
r
=
∑
(y
i
,
b
y
i
,m
i
)∈(Y
t
,
b
Y
t
,M
t
)
d(y
i
,
b
y
i
, m
i
), (5)
d(a, b, m) =
J
∑
j=1
m
j
q
(a
2 j−1
− b
2 j−1
)
2
+ (a
2 j
− b
2 j
)
2
,
(6)
where m
i
∈ {0, 1}
J
is a mask indicating visible body
joints in frame i, and M
t
is a sequence of m
i
around
a frame at t. Note that Y and
b
Y are considered as
sequences of y
i
and
b
y
i
in equation (5) around a frame
at t, respectively.
We empirically set M = 40, and the functions f
e
and f
d
using two fully-connected layers with a middle
layer dimension of 85.
3.4 Training the Whole Model
The proposed Pose Transition Embedding Network is
trained in an End-to-End manner with a pre-trained
Pose Transition Encoder-Decoder.
First, the Pose Transition Encoder-Decoder is
trained using the ground truth pose sequence to recon-
struct the input themselves using equation (5). Then,
the decoder part of the model is extracted and con-
nected to the Ex-Low Image Encoding Transformer to
build the Temporal Embedding Network as shown in
equation (2). Finally, the model is trained in a super-
vised learning manner, using input image sequences
and corresponding ground truth pose sequences by
𝑡 − 𝑘
𝑡 + 𝑘
Figure 4: Temporal sliding window approach with stride
one frame for long sequence. The estimated result of the
center frame in a sliding window is selected for the result of
the corresponding frame.
minimizing the pose estimation loss defined as,
L
e
=
∑
(y
i
,
ˇ
y
i
,m
i
)∈(Y
t
,
ˇ
Y
t
,M
t
)
d(y
i
,
ˇ
y
i
, m
i
). (7)
Note that the Pose Transition Decoder is fine-tuned in
the training.
3.5 Pose Estimation for a Long
Sequence
We use a temporal sliding window approach to es-
timate human poses in a long sequence. The pro-
posed model accept 2k + 1 frames of ex-low im-
ages I
t
around time t, and outputs 2k + 1 poses
(
ˇ
y
t−k
, . . . ,
ˇ
y
t
, . . . ,
ˇ
y
t+k
). For the final estimation re-
sult, we select the center of the output
ˇ
y
t
as shown
in Fig. 4. We apply this sliding window with a stride
of one frame.
4 EVALUATION
4.1 Dataset
To evaluate ex-low human pose estimation, we re-
quire a dataset consisting of low-resolution human
images. As the proposed method utilizes temporal in-
formation, the input should be a sequence of ex-low
images. In addition, the dataset should contain di-
verse poses. Therefore, we generated a dataset from a
large-scale video action recognition dataset.
In this evaluation, we selected the NTU
RGB+D (Shahroudy et al., 2016) dataset as the
source dataset. This dataset consists of videos
captured by Kinect v2 sensors. It contains 60 human
action classes acted on by 40 participants. The res-
olution of the images is 1, 920 × 1, 080 pixels. This
dataset also has 2D/3D skeletons data provided by
the Kinect sensors. Since the 2D/3D skeleton data is
not very accurate, we applied YOLOv8-pose (Jocher
et al., 2023) to estimate 2D human poses for each
high-resolution frame. Because the pose estimation
VISAPP 2025 - 20th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
482

Figure 5: Generation of the dataset. The human pose and
bounding box were estimated using YOLOv8-pose. Each
cropped image is resized to 16 × 16 pixels. Each human
pose is normalized to the [−1, 1] range in the cropped im-
age.
on high-resolution images by YOLOv8-pose is quite
accurate, we use them as the ground truth human
poses. Within the pose estimation results, we only
use reliable samples based on the confidence scores
of the pose estimator. Note that the “ground truth” in
this case is, in fact, a silver standard.
We cropped a human body from each image with a
square bounding box, and they were resized to 16×16
pixels ex-low images. Each ground-truth human pose
was normalized to the [−1, 1] range within the corre-
sponding bounding box. In this coordinate, the height
of each bounding box was 2, thus the value of 1 in
the corrdinate can be considered to be approximately
0.8 m. The procedure is illustrated in Fig. 5. For the
dataset, we selected 2k + 1 consecutive frames with
one stride, where one human pose can be estimated
from an image. In this experiment, we used k = 2;
thus the length of the sequence was five frames.
We divided the 40 subjects into five groups for
five-fold cross-validation. In each split, we used 29
subjects for training, 3 subjects for validation, and 8
subjects for testing.
4.2 Evaluation Metrics
We evaluated the results from two viewpoints: the ac-
curacy of the estimation and the smoothness of the
estimation as the ground truth. For accuracy, we used
the average of the Euclidean distance between the cor-
responding body joints. We named this metric the In-
dependent Frame Error (IFE) in this paper, defined as
IFE(A, B, M ) =
1
2k + 1
∑
(a
i
,b
i
,m
i
)∈(A,B,M )
d
m
(a
i
, b
i
, m
i
),
(8)
d
m
(a, b, m) =
1
∑
J
j=1
m
j
d(a, b, m), (9)
where A, B, M are estimated, ground-truth, and
mask sequences, respectively.
On the other hand, we used the absolute differ-
ence of inter-frame differences of the corresponding
body joints between the estimated and ground-truth
sequences as a smoothness metric. This is based on
𝑡 𝑡 + 1 𝑡 + 2 𝑡 + 3 𝑡 + 4
Figure 6: Example of pose estimation results. We can see
both methods quite well estimate the human poses; but the
results of SimpleBaseline is unstable around the ground-
truth body-joint locations, which makes them non-smooth.
the idea that the estimated data should be as smooth
as the ground truth. We named this metric the Frame
Difference Absolute Error (FDAE). First, this metric
calculates the inter-frame difference in the Euclidean
distance between adjacent frames and then calculates
their absolute difference from that of the ground truth
for each frame. The FDAE is calculated as follows,
FDAE(A, B, M ) =
1
2k
2k
∑
i=1
d
e
(A, B, M , i), (10)
d
e
(A, B, M , i) = |d
f
(A, M , i) − d
f
(B, M , i)|,
(11)
d
f
(A, M , i) = d
m
(a
i
, a
i+1
, m
i+1
i
), (12)
m
i+1
i
= m
i
⊙ m
i+1
, (13)
where ⊙ is the Hadamard product of vectors. Equa-
tion (12) calculates the inter-frame difference be-
tween i-th and i + 1-th frames using Equation (6) with
a mask, which is an intersection of the masks of the
frames.
Additionally, We also use mean Average Precision
(mAP) of each joint based on the Object Keypoint
Similarity (OKS) defined in COCO Keypoint Detec-
tion Task (Lin et al., 2015).
4.3 Comparison with Existing Method
and Ablation Study
We compared the proposed method with top-down
and bottom-up methods. For the bottom-up methods,
we just applied well-known pre-trained methods to
the ex-low images (OpenPifPaf (Kreiss et al., 2019)).
Also, for the top-down method, we applied Pose
ResNet, as known as SimpleBaseline (Xiao et al.,
2018) trained on our dataset. The method is a sim-
ple, but known to be able to provide a strong baseline.
Since this method estimate human pose from an im-
age one by one, it does not use temporal information.
Human Pose Estimation from an Extremely Low-Resolution Image Sequence by Pose Transition Embedding Network
483

Table 1: Pose estimation results. We compared the proposed method with the existing bottom-up and top-down methods.
Most bottom-up methods cannot detect any pose from a low-resolution image. An ablation study was also conducted.
Method IFE ↓ FDAE ↓ mAP (%) ↑
Existing
Bottom-up method
(OpenPifPaf (Kreiss et al., 2019)) inappricable 0
Top-down method
(SimpleBaseline (Xiao et al., 2018)) 0.1076 0.0879 78.142
Proposed
IndependentCNN (= w/o temporal information) 0.0944 0.0573 82.802
ChannelCombinedCNN (= w/o Transformer) 0.0935 0.0494 83.158
CNNTransformer (= w/o Pre-training) 0.0789 0.0466 88.279
Full model 0.0789 0.0466 88.314
As described in Section 3, the proposed method
consists of a CNN, Transformer, and AutoEncoder.
As an ablation study, we also compared with the three
methods ablated from the proposed method; no tem-
poral information (Independent CNN), temporal in-
formation (ChannelCombinedCNN), and temporal in-
formation with the transformer module (CNNTrans-
former. This can be considered as the proposed
method without pretraining of the Pose Transition De-
coder.), while the proposed method utilize pretrained
autoencoder for decoding the pose sequence.
4.4 Experimental Results
The results are summarized in Table 1. Because it
is very difficult to detect small body parts from ex-
low images, most bottom-up methods cannot detect
any poses, while the top-down methods can some-
how detect poses. It is because top-down methods
assume that there is a person in an image. By com-
paring the top-down method, which is a heatmap-
based method, with IndependentCNN, we can see the
heatmap-based is not suitable for this ex-low task. By
comparing ChannelCombinedCNN and CNNTrans-
former, we can see spatio-temporal attention in the
transformer network contribute to smooth and accu-
rate estimation. The methods that use temporal infor-
mation achieved lower score in the FDAE. In addi-
tion, from the table, we can see that the transformer
can help improve accuracy. In this evaluation, the full
model slightly outperformed the CNNTransformer. It
is because CNNTransformer can also capture tempo-
ral transition quite well.
5 CONCLUSION
This study addressed the problem of human pose es-
timation from an extremely low-resolution (ex-low)
image sequence. From an application perspective, the
estimated human pose must be accurate and tempo-
rally smooth. This paper proposes a human pose es-
timation method, named the Pose Transition Embed-
ding Network, that considers the temporal continuity
of human pose transition by using a pose-embedded
manifold. The Ex-Low Image Encoding Transformer
captures spatial and temporal information and embeds
them into a feature vector. The Pose Transition De-
coder then reconstructs the feasible human pose from
the feature vector. The evaluation results demostrated
that the proposed method can estimate accurate and
smooth poses.
Analyzing and optimizing the architecture of the
network will be the subject of future work. In addi-
tion, the method was evaluated only on cropped im-
ages from the NTU RGB+D dataset. The dataset con-
tains several scenes and multiple people; however, it
would be better to evaluate various datasets. In ad-
dition, the top-down approach requires human body
detection before pose estimation. In future work, we
will develop a method for ex-low human body detec-
tion.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Parts of this research were supported by MEXT,
Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (24H00733).
REFERENCES
Artacho, B. and Savakis, A. (2020). UniPose: Unified hu-
man pose estimation in single images and videos. In
Proc. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conf. on Comput. Vision and
Pattern Recognit., pages 7033–7042.
Cao, Z., Hidalgo, G., Simon, T., Wei, S., and Sheikh, Y.
(2021). OpenPose: Realtime multi-person 2D pose es-
timation using part affinity fields. IEEE Trans. on Pat-
tern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 43(01):172–
186.
VISAPP 2025 - 20th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
484

Fan, Z., Liu, J., and Wang, Y. (2021). Motion adaptive pose
estimation from compressed videos. pages 11699–
11708.
Fujita, T. and Kawanishi, Y. (2024). Recurrent graph convo-
lutional network for sequential pose prediction from
3D human skeleton sequence. In Proc. 27th Interna-
tional Conf. on Pattern Recognit., pages 342–358.
Iwata, S., Kawanishi, Y., Deguchi, D., Ide, I., Murase, H.,
and Aizawa, T. (2021). LFIR2Pose: Pose estimation
from an extremely low-resolution fir image sequence.
In Proc. 25th International Conf. on Pattern Recog-
nit., pages 2597–2603.
Jocher, G., Chaurasia, A., and Qiu, J. (2023). Ultralytics
YOLO. (accessed on January 26, 2025).
Kreiss, S., Bertoni, L., and Alahi, A. (2019). PifPaf: Com-
posite fields for human pose estimation. In Proc.
2019 IEEE/CVF Conf. on Comput. Vision and Pattern
Recognit., pages 11969–11978.
Lin, T.-Y., Maire, M., Belongie, S., Bourdev, L., Girshick,
R., Hays, J., Perona, P., Ramanan, D., Zitnick, C. L.,
and Doll
´
ar, P. (2015). Microsoft COCO: Common ob-
jects in context. arXiv:1405.0312.
Lin, T.-Y., Maire, M., Belongie, S., Hays, J., Perona, P., Ra-
manan, D., Doll
´
ar, P., and Zitnick, C. L. (2014). Mi-
crosoft COCO: Common objects in context. In Fleet,
D., Pajdla, T., Schiele, B., and Tuytelaars, T., editors,
Computer Vision – ECCV2014, pages 740–755.
Liu, Z., Chen, H., Feng, R., Wu, S., Ji, S., Yang, B., and
Wang, X. (2021). Deep dual consecutive network
for human pose estimation. In Proc. 2021 IEEE/CVF
Conf. on Comput. Vision and Pattern Recognit., pages
525–534.
Liu, Z., Feng, R., Chen, H., Wu, S., Gao, Y., Gao, Y., and
Wang, X. (2022). Temporal feature alignment and mu-
tual information maximization for video-based human
pose estimation. In Proc. 2022 IEEE/CVF Conf. on
Comput. Vision and Pattern Recognit., pages 11006–
11016.
Loper, M., Mahmood, N., Romero, J., Pons-Moll, G.,
and Black, M. J. (2015). SMPL: A skinned multi-
person linear model. ACM Transactions on Graphics,
34(6):1–16.
Luo, Y., Ren, J., Wang, Z., Sun, W., Pan, J., Liu, J., Pang,
J., and Lin, L. (2018). LSTM pose machines. In Proc.
2018 IEEE/CVF Conf. on Comput. Vision and Pattern
Recognit., pages 5207–5215.
Mizuno, M., Kawanishi, Y., Fujita, T., Deguchi, D., and
Murase, H. (2023). Subjective baggage-weight esti-
mation from gait: Can you estimate how heavy the
person feels? In Proc. 18th International Joint Con-
ference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer
Graphics Theory and Applications, volume 5, pages
567–574.
Papandreou, G., Zhu, T., Kanazawa, N., Toshev, A., Tomp-
son, J., Bregler, C., and Murphy, K. (2017a). Towards
accurate multi-person pose estimation in the wild. In
Proc. 2017 IEEE Conf. on Comput. Vision and Pattern
Recognit., pages 3711–3719.
Papandreou, G., Zhu, T., Kanazawa, N., Toshev, A., Tomp-
son, J., Bregler, C., and Murphy, K. (2017b). Towards
accurate multi-person pose estimation in the wild. In
Proc. 2017 IEEE Conf. on Comput. Vision and Pattern
Recognit., pages 3711–3719.
Pfister, T., Charles, J., and Zisserman, A. (2015). Flow-
ing ConvNets for human pose estimation in videos.
In Proc. 15th International Conf. on Comput. Vision,
pages 1913–1921.
Shahroudy, A., Liu, J., Ng, T.-T., and Wang, G. (2016).
NTU RGB+D: A large scale dataset for 3D human
activity analysis. In Proc. 2016 IEEE/CVF Conf. on
Comput. Vision and Pattern Recognit., pages 1010–
1019.
Song, J., Wang, L., Van Gool, L., and Hilliges, O. (2017).
Thin-Slicing Network: A deep structured model for
pose estimation in videos. In Proc. 2017 IEEE/CVF
Conf. on Comput. Vision and Pattern Recognit., pages
5563–5572. IEEE.
Song, L., Yu, G., Yuan, J., and Liu, Z. (2021). Human pose
estimation and its application to action recognition: A
survey. Journal of Visual Communication and Image
Representation, 76:103055.
Srivastav, V., Gangi, A., and Padoy, N. (2019). Human pose
estimation on privacy-preserving low-resolution depth
images. In Proc. 22nd Medical Image Computing and
Computer Assisted Intervention, pages 583–591.
Srivastav, V., Issenhuth, T., Kadkhodamohammadi, A.,
de Mathelin, M., Gangi, A., and Padoy, N. (2018).
MVOR: A multi-view rgb-d operating room dataset
for 2D and 3D human pose estimation. In Proc.
2018 MICCAI Workshop on Large-scale Annotation
of Biomedical data and Expert Label Synthesis.
Temuroglu, O., Kawanishi, Y., Deguchi, D., Hirayama, T.,
Ide, I., Murase, H., Iwasaki, M., and Tsukada, A.
(2020). Occlusion-aware skeleton trajectory repre-
sentation for abnormal behavior detection. In Proc.
26th International Workshop on Frontiers of Com-
puter Vision, volume 1212, pages 108–121, Singa-
pore. Springer Singapore.
Toshev, A. and Szegedy, C. (2014). DeepPose: Human
pose estimation via deep neural networks. In Proc.
2014 IEEE/CVF Conf. on Comput. Vision and Pattern
Recognit., pages 1653–1660.
Wang, C., Zhang, F., Zhu, X., and Ge, S. S. (2022). Low-
resolution human pose estimation. Pattern Recogni-
tion, 126:108579.
Xiao, B., Wu, H., and Wei, Y. (2018). Simple baselines
for human pose estimation and tracking. In Computer
Vision – ECCV2018, volume 11210, pages 472–487.
Xu, X., Chen, H., Moreno-Noguer, F., Jeni, L. A., and De la
Torre, F. (2020). 3D human shape and pose from a sin-
gle low-resolution image with self-supervised learn-
ing. In Computer Vision – ECCV2020, volume 12354,
pages 284–300.
Zhang, R., Zhu, Z., Li, P., Wu, R., Guo, C., Huang, G.,
and Xia, H. (2019). Exploiting offset-guided net-
work for pose estimation and tracking. In Proc.
2019 IEEE/CVF Conf. on Comput. Vision and Pattern
Recognit. Workshops, pages 1–9.
Human Pose Estimation from an Extremely Low-Resolution Image Sequence by Pose Transition Embedding Network
485
