
A Leaf Disease Detection Using Machine Learning and Deep
Learning: Comparative Study
Mooad Al-shalout
1a
, Mohamed Elleuch
2b
and Ali Douik
3c
1
Computer Science Department ISITCom, University of Sousse, Sousse, Tunisia
2
National School of Computer Science (ENSI), University of Manouba, Tunisia
3
National Engineering School of Sousse NOCCS-ENISO Lab, University of Sousse, Sousse, Tunisia
Keywords: Detecting Diseases, Corn, Potato, Tomato, VGG19, SVM, SIFT, Gabor.
Abstract: This study aims to provide innovative methods and additional suggestions for detecting plant diseases using
deep learning techniques. The study focused on identifying diseases affecting major daily consumed plants,
such as tomatoes, corn, and potatoes. The detected diseases included rust, early and late spots, mildew, and
bacterial spots. The study relied on machine learning and deep learning algorithms, such as Support Vector
Machine and VGG19 algorithm, to detect plant diseases. SIFT and Gabor filters were also incorporated into
the work and tested using SVM algorithm. The study reached highly accurate results, as the accuracy rate
reached 98% using SVM, and 97% using VGG19 algorithm, which are satisfactory results compared to
previous studies, confirming the effectiveness of the methods used in detecting plant diseases.
1 INTRODUCTION
Agricultural crops are among the most important
basic pillars of human life, which they depend on
completely in their lives. For thousands of years,
humans have paid attention to agricultural crops,
especially in some developing countries that depend
for their economic components on agriculture
because it is the basic resource in human life, and it
also provides a large portion of Work for some
people.
Sometimes, agricultural crops are afflicted by
diseases, which can be a significant cause of their
complete or partial destruction. Any disease affecting
these plants negatively impacts their quality, either in
terms of health or economic aspects, leading to a
decrease in their value. Farmers often incur
substantial losses, resorting at times to agricultural
experts and pesticides to combat diseases. This is
where artificial intelligence comes into play in
diagnosing diseases affecting medicinal plants. It has
achieved remarkable success in diagnosing and
distinguishing certain diseases, attempting to limit the
spread of diseases among other agricultural crops,
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0000-1913-658X
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4702-7692
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0178-501X
and improving the agricultural and economic sectors
simultaneously by reducing the cost of diagnosing
plant diseases. A large number of machine learning
algorithms have been employed to produce better
crops, training on a wide range of data related to the
agricultural sector to mitigate diseases (Goralski &
Tan, 2020).There are many studies that have proven
its efficiency in detecting plant diseases and working
on them seriously and extensively (Shruthi,
Nagaveni, & Raghavendra, 2019). In this study, we
tried to discover diseases that affect corn, tomatoes,
and potatoes using CNN deep learning algorithms.
These particular plants were selected due to their
status as fundamental crops essential for people's
daily sustenance, ones they frequently find
indispensable (Mohanty, Hughes, & Salathé, 2016).
Research was conducted on the identification of plant
diseases employing both the SVM algorithm and the
VGG19 algorithm.
Each of these attempts led to a high score in some
type of plant, with accuracy reaching approximately
98% in some algorithms.
In this paper, we looked at three main types of
plants that affects human life, as we mentioned
940
Al-shalout, M., Elleuch, M. and Douik, A.
A Leaf Disease Detection Using Machine Learning and Deep Learning: Comparative Study.
DOI: 10.5220/0013240400003890
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2025) - Volume 3, pages 940-947
ISBN: 978-989-758-737-5; ISSN: 2184-433X
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

previously, which are corn, potatoes, and tomatoes.
There were a number of nematode diseases that affect
these plants, including common rust, leaf spot, and
northern leaf blight in corn plants, and then early
blight and late blight in potatoes, in addition to the
bacterial spot that affects tomatoes and Spectura
leaves, which are among the targeted diseases in
tomato plants.
Work was done on deep learning algorithm,
compared with traditional machine learning methods
such as SVM. These algorithms were chosen because
they achieved good results in detecting and
classifying diseases in many studies (Arora &
Agrawal, 2020). Furthermore, it can be used in many
areas including image classification, and object
detection (Song et al., 2019).
The structure of the paper was as follows: In the
second section, we provided an overview of prior
studies, discussing various research endeavors and
advancements in the scientific field. Following that,
the third section detailed the methodology employed
in conducting our study, transitioning to the
subsequent stage. Here, we presented and analyzed
the results we obtained. The research work concluded
by summarizing our findings and outlining the
intended objectives for future work.
2 RELATED WORKS
Tomato an individual consumes approximately 42
kilograms, especially in North America, and in order
to preserve that plant efforts are made to preserve it
(Albawi, Mohammed, & Al-Zawi). Artificial
intelligence has been used to discover potential
diseases on tomatoes and use some artificial
intelligence applications and algorithms for to an
early detection of those diseases that affect those
plants and classify the condition if the disease is
found or not (Laranjeira et al., 2022).
In (Natarajan, Babitha, & Kumar, 2020),
researchers worked on developing techniques used in
deep learning to detect diseases in a number of plants,
including tomatoes. The most common diseases in
that plant were bacterial spot, leaf curl, bacterial
spots, and early and late end blights of that plant. A
number of techniques were adopted in deep detection
of the plant. Including: Single Shot Detectors (SSD),
VGG, and AlexNet. In addition to the ResNet
algorithm for detecting diseases that affect plants. In
that study, a small number of real images containing
a number of diseases were worked on, and they were
detected in a number of early, intermediate, and final
stages of the disease. The results in that case showed
that the accuracy rate reached 95.71%.
In (Shijie, Peiyi, & Siping, 2017), the researcher
worked on developing a CNN model with transfer
learning algorithms in the VGG16 algorithm to detect
a number of diseases related to plants, such as spider
mite, gray spot, mosaic viruses, targeted bacterial
spots, and leaf spot. A healthy leaf is considered
healthy disease, but there is no injury. A number of
real photographs (7040) were used in this study. The
researcher extracted features from the original images
using VGG16 and compiled them into the Support
Vector Machine algorithm to classify them to
determine the disease and its type. The average
accuracy obtained was 89%, and the deep learning
framework Keras/TensorFlow was used in that study.
Furthermore, in (Arora & Agrawal, 2020)
researchers worked on proposing a new approach to
classify corn leaf diseases through the application of
a number of algorithms, such as Deep Forest. They
used something new to discover three diseases, which
are: leaf spot and rust disease common in plants. In
addition to leaf spot disease, work has been done on
a small dataset consisting of only 400 images, and
these studies have shown good results. The accuracy
in that study in describing and identifying the disease
in corn plants reached 96.25%, while in the algorithm
LeNet5 reached 83.46% accuracy, and finally the
CNN algorithm reached 91.25% accuracy. From
there, the researcher arrived at the approach he
proposed that is capable of competing with traditional
deep learning methods and is a good alternative to
image-based applications.
In (Al-Shalout, Elleuch, & Douik, 2023), the
study employed several algorithms, including
VGG16, VGG19, and CNN utilizing around 25000
images. Among these algorithms, VGG19
demonstrated superior performance, achieving a
remarkable accuracy rate of 95%. The CNN
algorithm also yielded promising results, with an
accuracy rate of 90%, while the accuracy rate for the
VGG16 algorithm reached 86%.
In (Reis & Turk, 2024), a novel approach to plant
disease classification is introduced, utilizing the
Integrated Deep Learning (IDLF) and Ensemble
Learning (EL) framework. This methodology
integrates pre-trained deep neural networks,
including the ImageNet-based model, with 13 distinct
deep learning architectures (DLA), comprising
models trained from scratch and hybrid variations.
Various image quality enhancement techniques, such
as hypercolumn, contrast stretching, and Contrast
Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization (CLAHE),
were applied. The primary objective is to attain robust
A Leaf Disease Detection Using Machine Learning and Deep Learning: Comparative Study
941

classification performance. In experimental trials, the
RegNetY080 model trained from scratch achieved an
accuracy of 97.64% on the original dataset, which
increased to 98.33% with CLAHE optimization.
In (Alzahrani & Alsaade, 2023), the pressing issue
of early detection of tomato leaf diseases, vital for
sustaining crop quality and yield, was tackled.
Utilizing computer vision and advanced artificial
intelligence, the study utilizes three deep learning
models - DenseNet169, ResNet50V2, and Vision
Transformer (ViT) - to classify tomato diseases.
3 METHODOLOGY
In this section, we present the proposed processes and
methodologies that we worked on (See Figure 1).
Figure 1: Proposed Methodology.
3.1 Phase One: Data Collection and
Data Pre-Processing
3.1.1 Data Collection
The data utilized in our research was sourced from the
Kaggle dataset, comprising 25272 images. These
images encompass various plant diseases, with a
specific focus on three types: tomatoes, corn, and
potatoes, as mentioned earlier. The targeted images
represent authentic plant leaves, featuring both
healthy and diseased specimens within each category.
The observable symptoms on these leaves encompass
leaf spot diseases, bacterial spots, and target spots on
tomato plants, as depicted in Figure 2(a). On corn
plants, the symptoms include leaf blight, common
rust, and leaf spot, as shown in the respective figure
2(b). The figure also illustrates advanced and late
blight, along with bacterial spots on potato plants in
Figure 2(c). The images given in figure 2 illustrate
real pictures of both diseased and healthy plant
leaves.
(a) (b) (c)
Figure 2: (a) Tomato Disease, (b) Potato Disease and (c)
Corn Disease.
3.1.2 Data Pre-Processing
Central processing is one of the key procedures
necessary for extracting data from images. The data
extraction process is defined as a data extraction
method that works to convert raw data into a format
for the purpose of determining the data you are
working with. Before initiating the data extraction
process in images, it is crucial to perform a significant
pre-processing step, primarily involving the central
processing unit. This step is essential because the data
often tends to be perplexing or ambiguous, lacking
accurate and meaningful values necessary for
training, extraction, and obtaining reliable results. To
enhance the quality of the data and achieve optimal
outcomes, thorough cleaning and processing of the
images are carried out prior to the commencement of
the work, as emphasized in (Lazzeri, Bruno, Nijhof,
Giorgetti, & Castoldi, 2015).
Our research involves a three-stage data
processing approach: Labels and image unification in
addition to data normalization.
Labels: This process involves transforming labels
and images into digital representations, enabling easy
comprehension and interpretation by the program. It
facilitates instructing the machine in reading, defining
the utilized control, and managing digital
components.
Table 1: Label encoding.
Tree Label Disease
Corn
(4 Classes)
0 Vercos
p
ora leaf s
p
ot
1 Common_rust
2 Northern Leaf Blight
3 Corn health
y
Potato
(3 Classes)
0Earl
y
Bli
g
ht
1 Late Bli
g
ht
2 Health
y
Tomato
(4 Classes)
0 Bacterial Spot
1 Health
y
2Se
p
toria Leaf S
p
ot
3Tar
g
et S
p
ot
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
942
This constitutes a fundamental step in handling
structured data, serving a supervisory role (Singh &
Singh, 2020). Table 1 displays the encoding present
in the specified dataset.
Data Normalization: It is the process of
converting image pixel values into a more common
or familiar meaning. In this process, image data pixels
(intensity) are projected onto a specific scale or the
data is rescaled (usually (0,1) or (-1,1)). This process
is used when the dataset contains many image formats
and only one algorithm will be applied to it (Reis &
Turk, 2024).
Image Standardization: defined as the process
of controlling the image and its remainder (height
with width), that is, controlling the pixels of the
image, whose goal is to improve quality, standardize
measurements, and maintain consistency for all
images.
Image Data Generation from the Kera's Library
provides a sample for each image and data set, which
is obtained from the average and standard deviation
statistics necessary to standardize the values in the
images, and is done through the individual pixel
values in each image or the groups as a whole
(Weinberger, Seroussi, & Sapiro, 2000).
3.2 Phase Two: Training and Testing
Dataset, Applied ML and DL
Algorithms and Evaluation Process
3.2.1 Training and Testing Dataset
To train the data according to our study, we used the
Python TensorFlow package and divided the data into
two groups, a training group and a test group, in ratios
of 8:2, according to the table 2 explanation for the
training and testing processes for the data sets.
Table 2: Traning and Testing Dataset.
Tree Diseases Trainin
g
Testin
g
Corn
Common Rust 1907 477
Vercospora Leaf
S
p
ot
1642 410
Northern Leaf Blight 1908 477
Health
y
1859 465
Potato
Earl
y
Bli
g
ht 1939 485
Late Bli
g
ht 1939 485
Health
y
1824 456
Tomato
Bacterial Spot 1702 425
Septoria Leaf Spot 1745 436
Target Spot 1827 457
Health
y
1926 481
3.2.2 Applied ML and DL Algorithms
In this section, artificial intelligence algorithms,
specifically the VGG19 algorithm and the Support
Vector Machine (SVM) algorithm, were presented.
They are used for the detection and classification of
plant diseases. Additionally, we incorporated SIFT
and the Gabor filter in our work to enhance the results
obtained with the Support Vector Machine algorithm.
The outcomes demonstrated significant
improvements compared to our previous studies (Al-
Shalout et al., 2023).
VGG19
The primary contribution of the VGG network lies in
its focus on augmenting the depth of the
convolutional neural network to improve accuracy
(Yin, Wortman Vaughan, & Wallach, 2019). This is
accomplished by replacing a single 5×5 convolution
layer with two layers of size 3×3, and substituting one
7×7 convolutional layer with three 3×3 convolutional
layers. This structural adjustment not only increases
the network's depth but also minimizes the number of
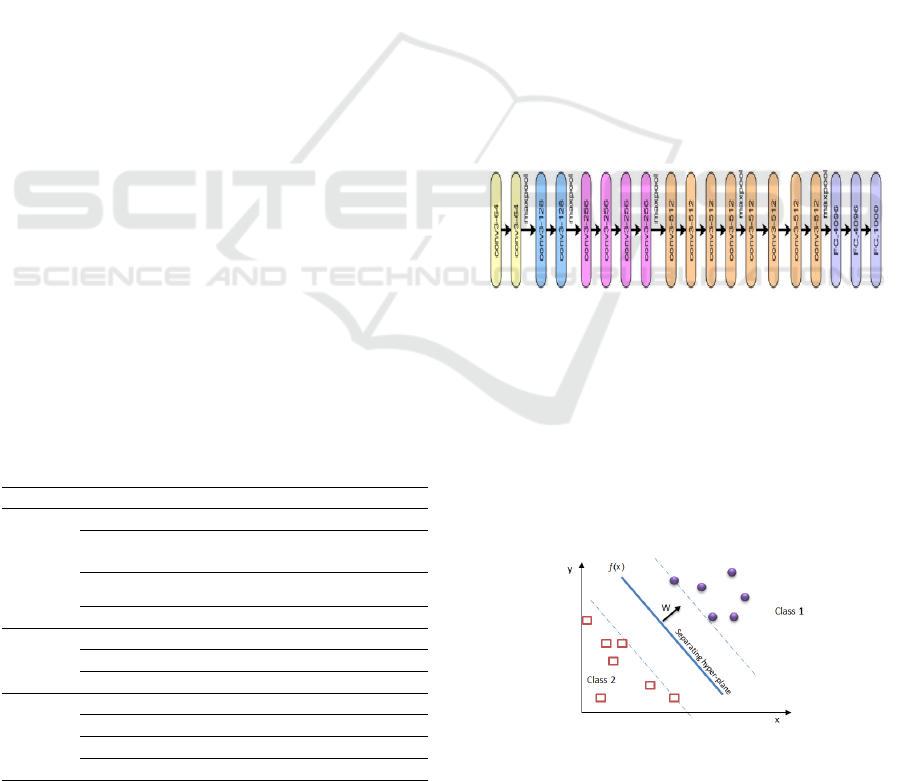
parameters needed for the model (Qi, 2024). The
architecture of the VGG19 network is depicted in
Figure 3.
Figure 3: VGG 19 Network Structure (Qi, 2024).
SVM Classifier
Support Vector Machine (SVM) (Vapnik, 1998) is a
supervised machine learning algorithm used for both
classification and regression tasks. It's particularly
effective in scenarios where the data is not easily
separable through linear boundaries. SVM works by
finding the optimal hyperplane that maximally
separates different classes in the feature space (see
Figure 4).
Figure 4: Principle of Support Vector Machine; two-class
hyper-plane example (Elleuch, Maalej, & Kherallah, 2016).
A Leaf Disease Detection Using Machine Learning and Deep Learning: Comparative Study
943
SIFT
Scale-Invariant Feature Transform (SIFT) is a
computer vision algorithm that was introduced by
David G. Lowe in 1999 (Lowe, 1999). It is widely
used for object recognition, image stitching, and other
applications in computer vision and image
processing. SIFT is particularly powerful because it
is invariant to changes in scale, rotation, and
illumination, making it robust in various real-world
scenarios.
Gabor Filters
Gabor filters have become prominent in the domain
of pattern recognition. The primary focus of Gabor
filters is their ability to remain invariant to translation,
rotation, scale, and illumination variations. We
directly derive features from gray-level images using
Gabor filters, allowing us to extract pertinent
information in both spatial and frequency domains
(Daugman, 1985; Jain & Farrokhnia, 1991).
3.2.3 Evaluation Process
In this paper, we used many metrics to evaluate the
effectiveness of the proposed approach, and we
adopted Accuracy, loss function, and Recall, in
addition to F1 score, Precision and finally Confusion
Matrix.
- Accuracy: ACC= (TP+TN)/(TP+FP+FN+TN)
- Precision: Precision = TP/(FP+TP)
- Recall: Recall =TP/(TP+FN)
- F1 score: F1 Score= 2*(Recall*Precision) / (Recall
+ Precision)
- Loss Function:
Mean Squared Error =(y
− y
)
n
4 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
AND DISCUSSION
In this study, we conducted many experiments to
verify the proposed algorithms for predicting diseases
of target plants, namely potato, tomato, and corn.
First of all, we performed the operations via the VGG
19 algorithm. The study was carried out on the entire
number of images, i.e. 25272 real images. The results
are shown in Table 3.
The results showed that the algorithm works
excellently, as the accuracy rate in corn plants
reached 97%, while in potatoes it reached 96%, and
finally in tomatoes it reached 95%, which is
considered an excellent result in relation to the
number of data.
Table 3: Experimental results using VGG19 algorithm.
Tree Recall Recall F1 Accurac
y
Corn
Common
Rust
0.99 0.92
0.97
Vercospor
Leaf S
p
ot
0.79 1.00
Northern
Leaf
Blight
0.66 0.98
Health
y
0.89 0.29
Potato
Early
Bli
g
ht
0.78 0.96
0.96
Late
Bli
g
ht
0.99 0.62
Health
y
0.87 0.99
Tomato
Bacterial
S
p
ot
0.92 0.95
0.95
Septoria
Leaf Spot
1.00 0.88
Target
S
p
ot
0.98 0.79
Health
y
0.29 0.44
Non-trainable parameters refer to the number of
parameters in a neural network model that are not
updated or learned during the training process. In this
study, we mention that there are 20024384 non-
trainable parameters in our VGG19 model (see Table
4).
Table 4: Parameters of VGG19 Model.
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
vgg19 (Functional) (None,7,7,512) 20 024 384
flatten (Flatten) (None,25088) 0
dense
(
Dense
)
(
None , 4
)
100 356
Total params: 20 124 740
Trainable
p
arams: 100 356
Non-trainable params: 20 024 384
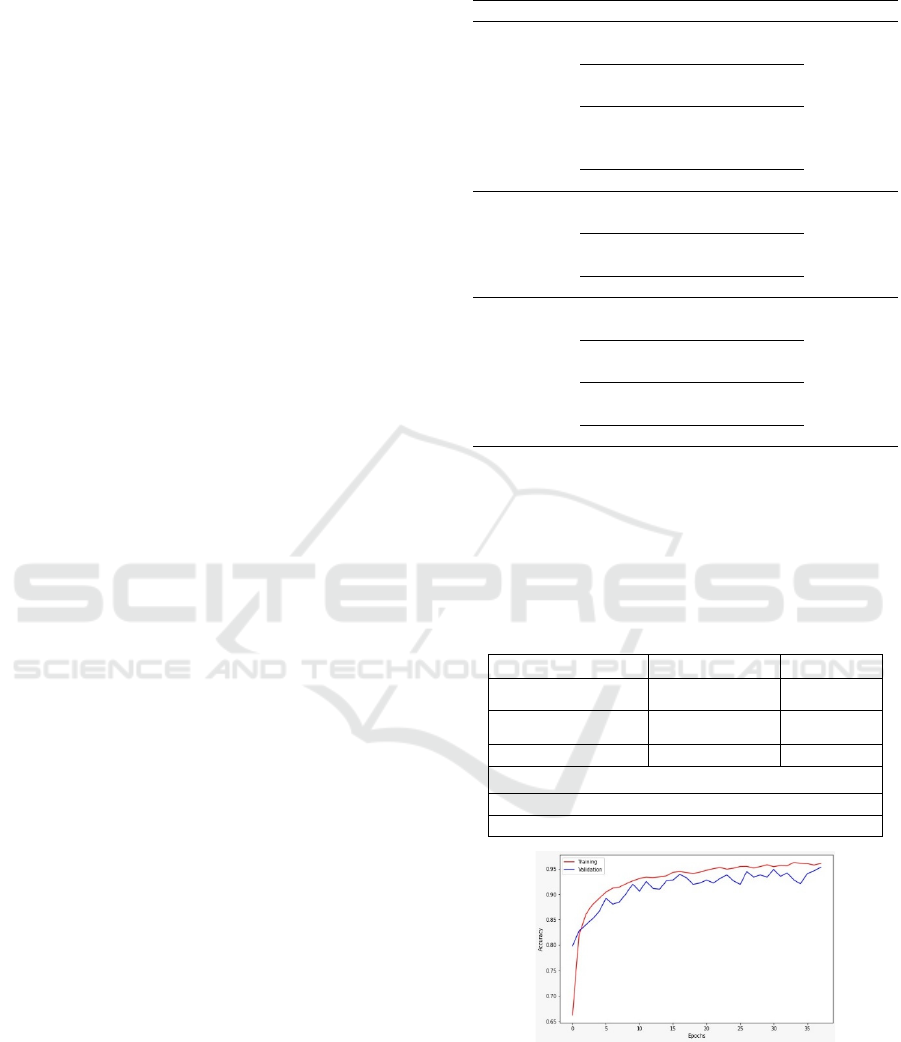
Figure 5: Performance of our proposed Model (VGG19).
Figures 5 and 6 illustrate the effectiveness of the
VGG19 algorithm in detecting diseases in potato
plants. The figure visually represents the significant
enhancement in results, with 35 Epoch of successful
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
944
disease detection in the study, achieving a remarkable
accuracy rate of 96% for this plant.
Figure 6: Trainig and validation Loss function (VGG19).
The second experiment using the SVM, where the
feature was extracted through SIFT and Gabor Filter,
achieved excellent results, more than expected, and
with the same number of images, we obtained an
accuracy rate that reached 96% in the tomato plant,
98% in the corn plant, and finally 97% in potato
plants. The algorithm clearly excelled in detecting
diseases that affect plants, and the Table 5 shows the
results that appeared in the study and the experiments.
Table 5: Experimental results for SVM algorithm.
Tree Recall Recall F1 Accurac
y
Corn
Common Rust 0.94 0.95
0.98
Vercospora
S
p
ot
0.98 0.99
Northern Leaf
Blight
0.99 0.98
Health
y
0.91 0.93
Potato
Earl
y
Bli
g
ht 1.00 0.88
0.97
Late Bli
g
ht 0.91 0.92
Health
y
0.89 0.98
Tomato
Bacterial Spot 0.98 0.95
0.96
Septoria Leaf
Spot
0.96 0.98
Target Spot 0..87 0.93
Health
y
0.92 0.94
Table 6 describes the model summary for SVM
algorithm used in experiments.
Table 6: Summary details for SVM Model.
Train Data - Train Labels Test Data - Test
Labels
features shape (5702, 25088) (1426, 25088)
labels sha
p
e
(
5702
)
(
1426
)
S
p
latted train and test data
Train data (5702, 25088)
test data (1426, 25088)
Train labels (5702)
test labels (1426)
Figures 7 and 8 depict the model's performance in
detecting plant diseases using an SVM algorithm
specifically for potato plants. The figure 7 visually
demonstrates the improvement in results in terms of
the number of epochs, with the study yielding 18
epochs. The accuracy percentage for this plant
reached 97%, indicating a slight improvement
compared to the previous algorithm, where it was
96% for potato plants.
Figure 7: Performance of our proposed SVM Model.
Figure 8: Training and validation Loss function (SVM).
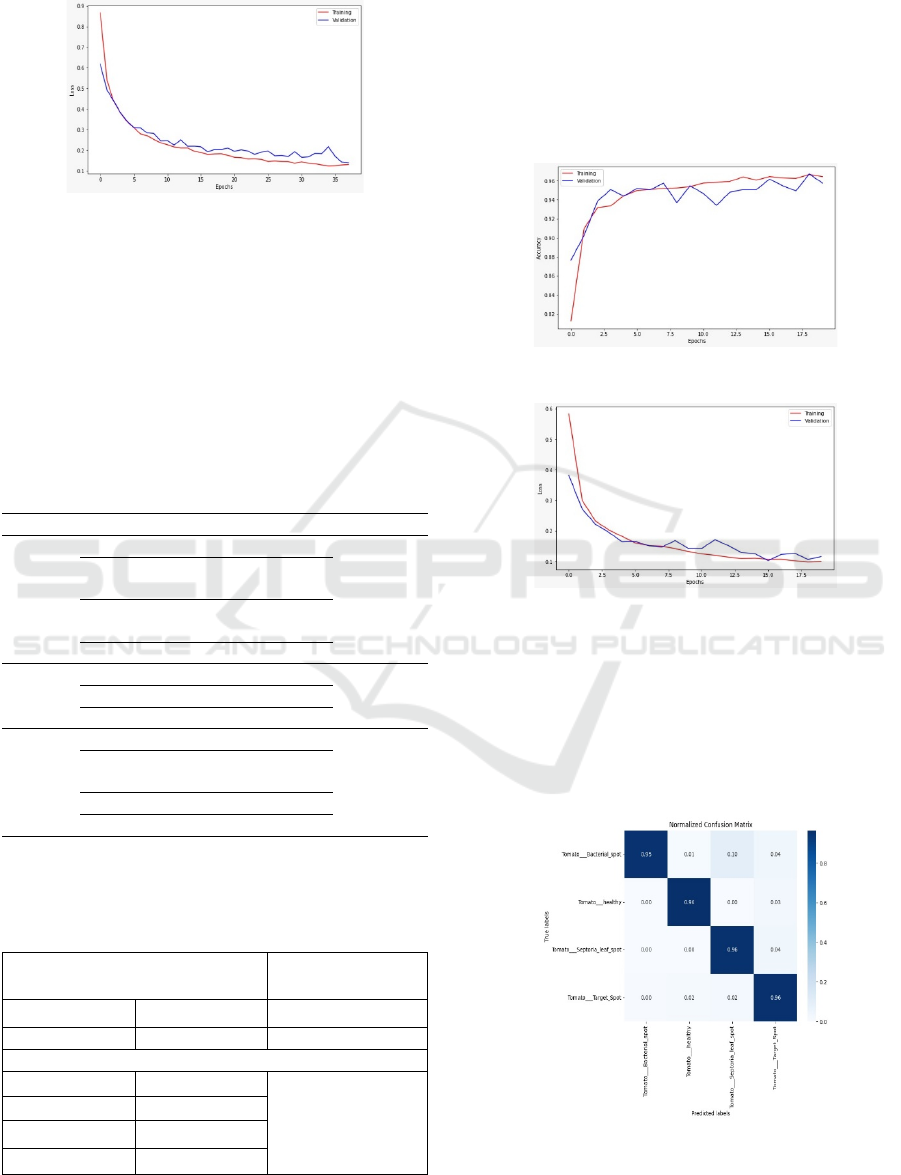
Figures 9 and 10 display the confusion matrix
regarding tomato plants, with an accuracy rate of
96%. Upon integrating the Gabor filter, the accuracy
improved, reaching 97%. This visualization
highlights the efficacy of the proposed system in
categorizing tomato plants across four distinct
classes.
Figure 9: Confusion matrix about VGG model.
A Leaf Disease Detection Using Machine Learning and Deep Learning: Comparative Study
945

Figure 10: Confusion matrix about SVM model.
The results were notably favorable, particularly with
the Support Vector Machine algorithm achieving an
impressive accuracy rate of 98% on our dataset across
multiple classes in a single stage. This high accuracy
rate is commendable. Meanwhile, the VGG19
algorithm achieved an accuracy rate of 97% on the
same dataset, representing a notable improvement
compared to earlier studies using the VGG16
algorithm, where the accuracy was 89% (Shijie et al.,
2017).
Several researchers have utilized diverse models,
incorporating CNN algorithms along with Transfer
Learning, AlexNet, and ResNet. Their results have
shown a range of accuracies, varying from 83.46% to
as high as 95.71%. These findings highlight the
significance of numerous studies focused on
identifying plant diseases, underscoring the crucial
role of plants in human life (see Table 7).
Table 7: Comparative results.
Id Dataset Al
g
orithms Accurac
y
(Natarajan
et al.,
2020)
1090 real
images
ResNet,
AlexNet, and
Squeeze Net
95.71%
(Shijie et
al., 2017)
7040
images
CNN model
with transfer
learning and
VGG16
89%
(Arora &
Agrawal,
2020
)
12332
images
LeNet5 83.46%
CNN 91.25%
(Mohanty
et al.,
2016)
54306
images
CNN 99.35%
Current
work
25272
ima
g
es
SVM (Gabor
filters & SIFT
)
98%
25272
ima
g
es
VGG19 97%
5 CONCLUSION
In this study, we targeted three types of plants in the
study and a number of diseases that affect them,
which were leaf spot, northern leaf blight, early and
late blight, in addition to rot and bacterial rust on the
plants.
The results showed that the proposed methods,
which were added manually to improve the images
using the Gabor filter in addition to Sift, achieved a
high accuracy rate in detecting diseases that affect
plants, reaching 98%, which is a good thing,
especially since the number of data used in the study
is large, Furthermore, an additional step in the future
involves employing data augmentation to augment
the number of images, thereby enhancing the results
further.
5.1 Future Work
Based on the findings, future work could focus on
enhancing disease detection algorithms to improve
their efficiency and accuracy in dealing with diverse
and large datasets. This could be achieved by
exploring advanced techniques such as transformers
or incorporating ensemble learning methods to
improve model performance. Furthermore, the study
could be expanded to include a wider range of plant
diseases and species, with a focus on early detection
at the initial stages before visible symptoms appear,
enabling faster and more effective interventions. The
integration of advanced technologies such as edge
computing and the Internet of Things could facilitate
real-time data collection and analysis, contributing to
the development of smart systems that leverage AI for
automated disease detection. These systems could be
designed for practical field use through mobile
applications or dedicated devices, making them
accessible to farmers. In addition, these systems could
support sustainable agriculture by reducing reliance
on chemical pesticides and achieving more
sustainable improvements in agricultural
productivity. Finally, it is recommended to enhance
collaboration with experts in plant science and
agriculture to develop comprehensive and integrated
solutions, leveraging modern technologies to create a
clear improvement in the agricultural sector.
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
946

REFERENCES
Al-Shalout, M., Elleuch, M., & Douik, A. (2023). Detection
Plant Diseases Using Deep Learning Algorithms. Paper
presented at the 2023 International Conference on
Cyberworlds (CW).
Albawi, S., Mohammed, T., & Al-Zawi, S. Understanding
of a convolutional neural network. In2017 international
conference on engineering and technology (ICET) 2017
Aug 21 (pp. 1-6): IEEE.
Alzahrani, M. S., & Alsaade, F. W. (2023). Transform and
deep learning algorithms for the early detection and
recognition of tomato leaf disease. Agronomy, 13(5),
1184.
Arora, J., & Agrawal, U. (2020). Classification of Maize
leaf diseases from healthy leaves using Deep Forest.
Journal of Artificial Intelligence and Systems, 2(1), 14-
26.
Daugman, J. G. (1985). Uncertainty relation for resolution
in space, spatial frequency, and orientation optimized
by two-dimensional visual cortical filters. JOSA A,
2(7), 1160-1169.
Elleuch, M., Maalej, R., & Kherallah, M. (2016). A new
design based-SVM of the CNN classifier architecture
with dropout for offline Arabic handwritten
recognition. Procedia Computer Science, 80, 1712-
1723.
Goralski, M. A., & Tan, T. K. (2020). Artificial intelligence
and sustainable development. The International
Journal of Management Education, 18(1), 100330.
Jain, A. K., & Farrokhnia, F. (1991). Unsupervised texture
segmentation using Gabor filters. Pattern recognition,
24(12), 1167-1186.
Laranjeira, T., Costa, A., Faria-Silva, C., Ribeiro, D., de
Oliveira, J. M. P. F., Simões, S., & Ascenso, A. (2022).
Sustainable valorization of tomato by-products to
obtain bioactive compounds: Their potential in
inflammation and cancer management. Molecules,
27(5), 1701.
Lazzeri, F., Bruno, G., Nijhof, J., Giorgetti, A., & Castoldi,
P. (2015). Efficient label encoding in segment-routing
enabled optical networks. Paper presented at the 2015
International Conference on Optical Network Design
and Modeling (ONDM).
Lowe, D. G. (1999). Object recognition from local scale-
invariant features. Paper presented at the Proceedings
of the seventh IEEE international conference on
computer vision.
Mohanty, S. P., Hughes, D. P., & Salathé, M. (2016). Using
deep learning for image-based plant disease detection.
Frontiers in Plant Science, 7, 1419.
Natarajan, V. A., Babitha, M. M., & Kumar, M. S. (2020).
Detection of disease in tomato plant using Deep
Learning Techniques. International Journal of Modern
Agriculture, 9(4), 525-540.
Qi, J. (2024). Efficiency study of VGG networks in
autonomous driving tasks. Paper presented at the
Fourth International Conference on Computer Vision
and Data Mining (ICCVDM 2023).
Reis, H. C., & Turk, V. (2024). Integrated deep learning and
ensemble learning model for deep feature-based wheat
disease detection. Microchemical Journal, 197,
109790.
Shijie, J., Peiyi, J., & Siping, H. (2017). Automatic
detection of tomato diseases and pests based on leaf
images. Paper presented at the 2017 Chinese
automation congress (CAC).
Shruthi, U., Nagaveni, V., & Raghavendra, B. (2019).
A
review on machine learning classification techniques
for plant disease detection. Paper presented at the 2019
5th International conference on advanced computing &
communication systems (ICACCS).
Singh, D., & Singh, B. (2020). Investigating the impact of
data normalization on classification performance.
Applied Soft Computing, 97, 105524.
Song, Z., Fu, L., Wu, J., Liu, Z., Li, R., & Cui, Y. (2019).
Kiwifruit detection in field images using Faster R-CNN
with VGG16. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 52(30), 76-81.
Vapnik, V. (1998). Statistical learning theory. John Wiley
& Sons google schola, 2, 831-842.
Weinberger, M. J., Seroussi, G., & Sapiro, G. (2000). The
LOCO-I lossless image compression algorithm:
Principles and standardization into JPEG-LS. IEEE
Transactions on Image processing, 9(8), 1309-1324.
Yin, M., Wortman Vaughan, J., & Wallach, H. (2019).
Understanding the effect of accuracy on trust in
machine learning models. Paper presented at the
Proceedings of the 2019 chi conference on human
factors in computing systems.
A Leaf Disease Detection Using Machine Learning and Deep Learning: Comparative Study
947
