
Attached Shadow Constrained Shape from Polarization
Momoka Yoshida
1
, Ryo Kawahara
2 a
and Takahiro Okabe
3 b
1
Department of Artificial Intelligence, Kyushu Institute of Technology, 680-4 Kawazu, Iizuka, Fukuoka 820-8502, Japan
2
Graduate School of Informatics, Kyoto University, Yoshida-honmachi, Sakyo-ku, Kyoto, 606-8501, Japan
3
Information Technology Track, Faculty of Engineering, Okayama University,
3-1-1 Tsushima-naka, Kita-ku, Okayama 700-8530, Japan
Keywords:
3D Shape Reconstruction, Polarization, Shape-from-X.
Abstract:
This paper tackles a long-standing challenge in computer vision: single-shot, per-pixel surface normal recov-
ery. Although polarization provides a crucial clue to solving this problem, it leaves ambiguity in the normal
estimation even when the refractive index is known. Therefore, previous studies require additional clues or
assumptions. In this paper, we propose a novel approach to resolve this ambiguity and the unknown refrac-
tive index simultaneously. Our key idea is to leverage attached shadows to resolve normal ambiguity while
measuring the refractive index based on wavelength characteristics in a single-shot scenario. We achieve this
by separating the contributions of three appropriately placed narrow-band light sources in the RGB channel.
We further introduce disambiguation uncertainty to address cast shadows and achieve more accurate normal
recovery. Our experimental evaluations with synthetic and real images confirm the effectiveness of our method
both qualitatively and quantitatively.
1 INTRODUCTION
Reconstructing dense 3D surfaces has been a central
research topic in computer vision. Single-shot re-
covery of the surface normals, in particular, has vari-
ous applications, including industrial product inspec-
tion, robotics, digital archiving, and medicine. On
the other hand, as an independent problem of depth
sensing, solving per-pixel surface normals from a sin-
gle 2D image is a long-standing, challenging task for
fine-detailed geometry.
Polarization is one of the crucial cues for surface
shape recovery. When a surface reflects unpolarized
light, the reflected light becomes partially polarized
depending on the surface normal and refractive in-
dex. The shape recovery method utilizing this cue
is called Shape from Polarization (SfP). However, the
core issue is the ambiguity that exists in its normal es-
timation, even with a known refraction index. There-
fore, previous SfP methods require additional cues or
assumptions for per-pixel estimation, such as known
albedo for shading cues and surface integrability.
Are any additional pixel-independent cues avail-
able for a per-pixel solution in a single-shot scenario
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9819-3634
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2183-7112
for objects with various shapes and textures? The dis-
ambiguation of the normal solution by fusion with a
depth or low-frequency geometry cannot be entirely
separated from the issue of shape discontinuities. We
tackle obtaining a unique solution for the normals in
this single-shot problem while relaxing the need for
assumptions about the object.
In this paper, we show that we can identify the
correct answer of SfP solution candidates by the at-
tached shadows. Our focus for achieving this concept
in a single-shot scenario is to leverage three differ-
ent narrow bandwidth light sources that are separa-
ble by RGB channels in a direction layout that dis-
ambiguates the SfP. We further show that the refrac-
tive index, which is often uniform across the object
surface, can be estimated from the consistency of the
zenith angle at each of the three wavelengths and ap-
plied to unknown dielectric materials.
In addition, to distinguish cast shadows and elim-
inate ambiguous estimations, we introduce certainty
based on a fusion of attached shadow clarity metrics
and strategies for detecting cast shadows. We apply
the belief propagation method for regions of low cer-
tainty to select a normal candidate and recover the en-
tire shape.
We experimentally validate our method on ob-
jects with various shapes, materials, and textures. We
640
Yoshida, M., Kawahara, R. and Okabe, T.
Attached Shadow Constrained Shape from Polarization.
DOI: 10.5220/0013248700003912
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 20th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2025) - Volume 3: VISAPP, pages
640-647
ISBN: 978-989-758-728-3; ISSN: 2184-4321
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
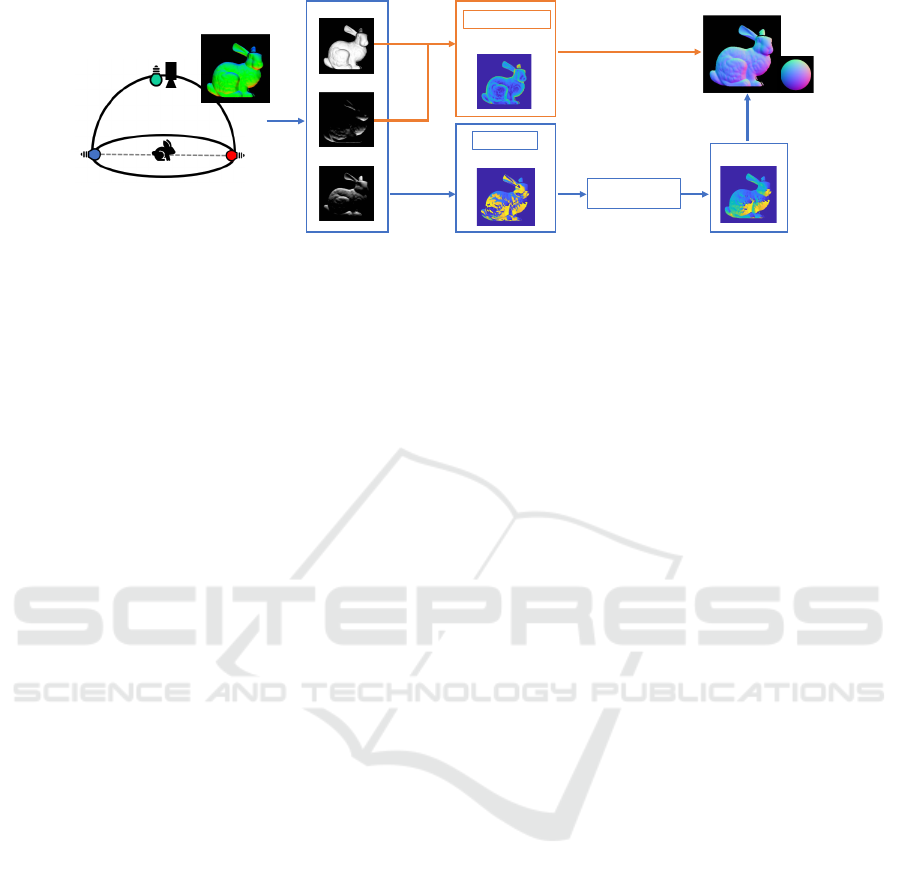
Input
Output
R
G
B
Refractive index
Zenith angle
Azimuth angle
Uncertainty-aware
disambiguation
Certainty
Azimuth angle
(a)
(b)
(c)
Figure 1: Attached Shadow Constrained Shape from Polarization. (a) We utilize single-shot images taken under three appro-
priately placed narrow-band light sources. (b) By separating and utilizing their wavelength contributions in the RGB channel,
we achieve normal disambiguation through attached shadows while estimating the object’s refractive index. This stage also
provides certainty for pixels where ambiguity becomes unstable due to cast shadows or shadow boundaries. (c) We apply
belief propagation to this low-certainty region and achieve per-pixel normal recovery in a single shot.
conducted a thorough quantitative evaluation of the
proposed method’s impact on ”shadow-based disam-
biguation,” ”cast shadow handling with the introduc-
tion of disambiguation certainty,” and ”refractive in-
dex estimation” using synthetic images. Additionally,
we demonstrated these effects qualitatively through
real image experiments.
Our main contributions are as follows,
• Demonstrating attached shadows can be used to
identify the correct normals among SfP solution
candidates.
• Achieving disambiguation in a single shot by sep-
arating and utilizing the contributions of three
different narrow-band light sources in the RGB
channel.
• Introducing a novel method for estimating the re-
fractive index of an object’s surface from the con-
sistency of the zenith angle at three wavelengths.
• Defining the certainty of disambiguation and ap-
plying the belief propagation method to uncertain
regions to improve the accuracy of shape recon-
struction.
2 RELATED WORK
Methods for normal estimation have advanced with
many challenges and solutions. Physics-based deduc-
tive methods such as photometric stereo (Woodham,
1980; Ackermann et al., 2015), shape from shading
(Ikeuchi and Horn, 1981; Zhang et al., 1999), and SfP
(Atkinson and Hancock, 2006; Miyazaki et al., 2003;
Rahmann and Canterakis, 2001) have been proposed
for decades. However, single-shot normal estimation
has always been a challenging task as an inverse prob-
lem from 2D to 3D.
Multi-spectral photometric stereo (MPS) (Ander-
son et al., 2011; Chakrabarti and Sunkavalli, 2016;
Ozawa et al., 2018; Guo et al., 2021) is one approach
to this challenge. MPS utilizes light sources of differ-
ent wavelengths to estimate normals from single-shot
images. However, since the intensity observed by the
camera depends on the object’s reflectance, additional
constraints are required, such as albedo, chromaticity
clustering, and integrability of the surface geometry.
Thus, a barrier to per-pixel single-shot estimation ex-
ists.
On the other hand, the single-shot SfP method
has the problem that the zenith angle depends on the
refractive index, so the wrong refractive index dis-
torts the normal (Kadambi et al., 2015). Addition-
ally, it is known that there are two candidate solu-
tions for the azimuth angle (Atkinson and Hancock,
2006; Miyazaki et al., 2003). Therefore, single-shot
SfP also requires additional constraints or prior, such
as shading cues and surface integrability (Mahmoud
et al., 2012; Smith et al., 2016; Smith et al., 2018).
There are methods for polarization and multi-spectral
fusion. Huynh et al. (Thanh et al., 2015) proposed a
method for simultaneously estimating the normal and
refractive index using a polarization multi-spectral
image. However, this method assumes that the scene
geometry is smooth and convex.
In contrast, we leverage the binary information of
whether each pixel is an attached shadow or not to
resolve the ambiguity of SfP. Utilizing the fact that
the normal solution space is limited by the bound-
ary of the attached shadow(Kriegman and Belhumeur,
2001), our method eliminates assumptions about the
chromaticity of the object and the integrability of
its shape, allowing independent estimation for each
pixel. Therefore, our method realizes a more flexible
single-shot normal estimation, even for textured ob-
jects.
Attached Shadow Constrained Shape from Polarization
641

Zenith angle
Azimuth angle
Surface
normal
Surface
normal
n
n
^
Figure 2: Ambiguity of surface normals in Shape from Po-
larization. Since π-ambiguity exists in the azimuth angle
estimated from the diffuse polarization, there are two can-
didates for the normal.
Recently, polarization-based methods using deep
prior (Ba et al., 2020; Deschaintre et al., 2021; Hwang
et al., 2022; Lei et al., 2022) have shown effective re-
sults, but they rely on supervised learning and require
large data sets. In contrast, our method achieves nor-
mal recovery from a single input image and estimates
objects’ refractive indices.
3 BASICS: SHAPE FROM
POLARIZATION
We will first briefly introduce the fundamental theory
of SfP and its ambiguity, which needs to be resolved.
3.1 Polarization
Unpolarized light consists of electromagnetic waves
oscillating in a random direction and having uniform
intensity around the direction of light travel. Sunlight
and common light sources correspond to this type of
light. When an object reflects unpolarized light, the
oscillation direction of the electromagnetic wave is
biased, resulting in partially polarized light. Polar-
ization cameras can extract angular components by
observing light through a linear polarizer at a certain
angle. When rotating the linear polarizer with angle
ψ, the intensity of light can be described as following
sinusoidal:
I(ψ) = I
max
cos
2
(ψ −ϕ) + I
min
sin
2
(ψ −ϕ)
=
I
max
+ I
min
2
+
I
max
−I
min
2
cos2(ψ −ϕ),
(1)
where I
max
and I
min
are the maximum and minimum
intensity for angle ψ. The angle ϕ is called the an-
gle of linear polarization (AoLP), where observed in-
tensity reaches I
max
. Thanks to recent advances in
technology, quad-bayer polarization cameras can pro-
vide polarization images for four filter angles ψ =
(0,π/4,π/2,3π/4) from a single image. Hence, we
can recover the sinusoidal in single-shot (Huynh et al.,
2010).
3.2 Normal Estimation from
Polarization and Its Ambiguity
The basic concept of SfP is to utilize the fact that the
polarization changes during reflection depending on
the surface normal, and to calculate the surface nor-
mal as an inverse problem. Fresnel equations can de-
scribe these relationships, which differ for diffuse and
specular reflection. In this study, we mainly focus on
the polarization of diffuse reflections, as we utilize a
distant point source. The treatment of specular reflec-
tions will be discussed in Sec. 4.
As shown in Fig. 2, let us denote the surface nor-
mal n by the zenith angle θ and azimuth angle φ fol-
lows,
1
n =
sinθ cos φ
sinθ sin φ
cosθ
. (2)
Since the diffuse polarization component has a max-
imum intensity in the direction along the plane
spanned by the viewing direction (z-axis in the Fig. 2)
and the normal, the following holds;
φ = ψ or ψ + π. (3)
On the other hand, independent of this, the zenith
angle θ depends on the Fresnel transmission ratio r
2
=
q
I
min
I
max
, and the following holds (Huynh et al., 2010);
θ ≃ arcsin
η
√
1 −r
2
p
η
2
−2rη + 1
. (4)
Thus, even when the refractive index is known, there
are two candidate normals (n, ˆn) due to the ambigu-
ity of the azimuth angle in Eq. 3.
4 METHOD
We propose a physics-based, per-pixel solution for
single-shot SfP without assuming geometry integra-
bility or uniform albedo. We employ a quad-Bayer
color polarization camera and capture objects simul-
taneously illuminated by three light sources of differ-
ent directions and colors as shown in Fig. 1(a).
1
For a perspective projection camera, it can be defined
similarly as a local coordinate system such that the viewing
direction becomes the z-axis (Pistellato and Bergamasco,
2024).
VISAPP 2025 - 20th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
642

Assumptions. Our method relies on several as-
sumptions throughout the paper:
1. Orthographic camera or known focal length
2. Dielectric objects
3. Diffuse-dominant materials
4. Known narrow-band distant point sources
5. Spatially uniform refraction index
Note that assumption 3 requires that the amplitude
of the diffuse polarization component be larger than
the amplitude of the specular polarization component,
which does not significantly limit the material (Smith
et al., 2018). Additionally, We typically observe spec-
ular reflections as saturated sharp highlights with our
three distant point sources setup. We exclude these
highlight regions from our estimation to maintain the
dynamic range. Consequently, the observations in the
target region can be approximated by diffuse polar-
ization components (Kadambi et al., 2015), and Eq. 4
holds.
4.1 Estimation of Candidate Normals
with Unknown Refraction Index
This section shows that we can estimate candidate
normals with unknown refractive indices under our
narrow-band wavelength source. Since the refractive
index depends on wavelength, we can use the fact that
different Fresnel transmittances in each RGB band
refer to the same zenith angle. When using a wide-
bandwidth light source, even if the spectral intensity
is known, note that the contribution of wavelengths
will not be uniform for objects with spatially varying
spectral reflectance. We can practically avoid this is-
sue with narrow bandwidth light sources.
Let η
R
, η
G
, and η
B
be the refractive indices, and
r
R
, r
G
, and r
B
be the observed Fresnel transmittance
ratio for each RGB wavelength, respectively, and the
following holds from Eq. 4,
η
R
q
1 −r
2
R
q
η
2
R
−2r
R
η
R
+ 1
=
η
B
q
1 −r
2
B
q
η
2
B
−2r
B
η
B
+ 1
,
η
B
q
1 −r
2
B
q
η
2
B
−2r
B
η
B
+ 1
=
η
G
q
1 −r
2
G
q
η
2
G
−2r
G
η
G
+ 1
.
(5)
Using two or more pixels with different zenith angles
can estimate the refractive indices of one band pair
(e.g. R and B). We further estimated the refractive in-
dices η
R
, η
G
, η
B
using RANSAC for robust estima-
tion. The zenith angle is then estimated using the re-
fractive indices and Fresnel transmission coefficients.
(a) Acute angle or obtuse angle
(b) Both acute angle
Figure 3: Overview of disambiguation. The condition un-
der which the normal (orange arrow) can be disambiguated
by whether it is an attached shadow or not is whether its
status changes depending on the candidate normals. i.e.,
when the angle between the normal and the light source is
divided into (a) an acute angle and an obtuse angle, it can
be resolved, while it cannot in the case of (b).
The azimuth angle is estimated from Eq. 3. Up
to this point, we obtain two potential normals for the
object with an unknown refractive index.
4.2 Azimuthal Disambiguation from
Attached Shadow
4.2.1 Overview of Disambiguition
We resolve that azimuth angle ambiguity based on
the attached shadow. The clue, whether the attached
shadow or not, suggests the angle between the direc-
tion of the light source and the true normal. That is,
the observed intensity depends on the inner product
of the source direction and the true normal, which
is positive when the pixel is illuminated. Also, the
inner product at the attached shadow pixels is neg-
ative. Therefore, by taking the inner product of the
source direction and the candidate normals and select-
ing the candidate normals that are consistent with the
observed radiance, the π-ambiguity regarding the nor-
mal azimuth angle can be resolved.
Let us consider the example shown in Fig. 3 for
a better understanding of the conditions required for
disambiguation. In Fig. 3(a), the angle between the
light source direction and the candidate normal is
acute on one side and obtuse on the other, allowing
us to resolve the ambiguity. However, both angles are
acute in Fig. 3(b), so the ambiguity cannot be resolved
for that pixel.
4.2.2 Design of Light Source Direction
All pixels need to be illuminated to obtain candidate
normals by polarization analysis. Considering ob-
jects with various shapes, our reasonable approach is
to illuminate one of the light sources coaxially with
the viewing direction (we call it base light hereafter).
Therefore, this section discusses the design of the re-
Attached Shadow Constrained Shape from Polarization
643
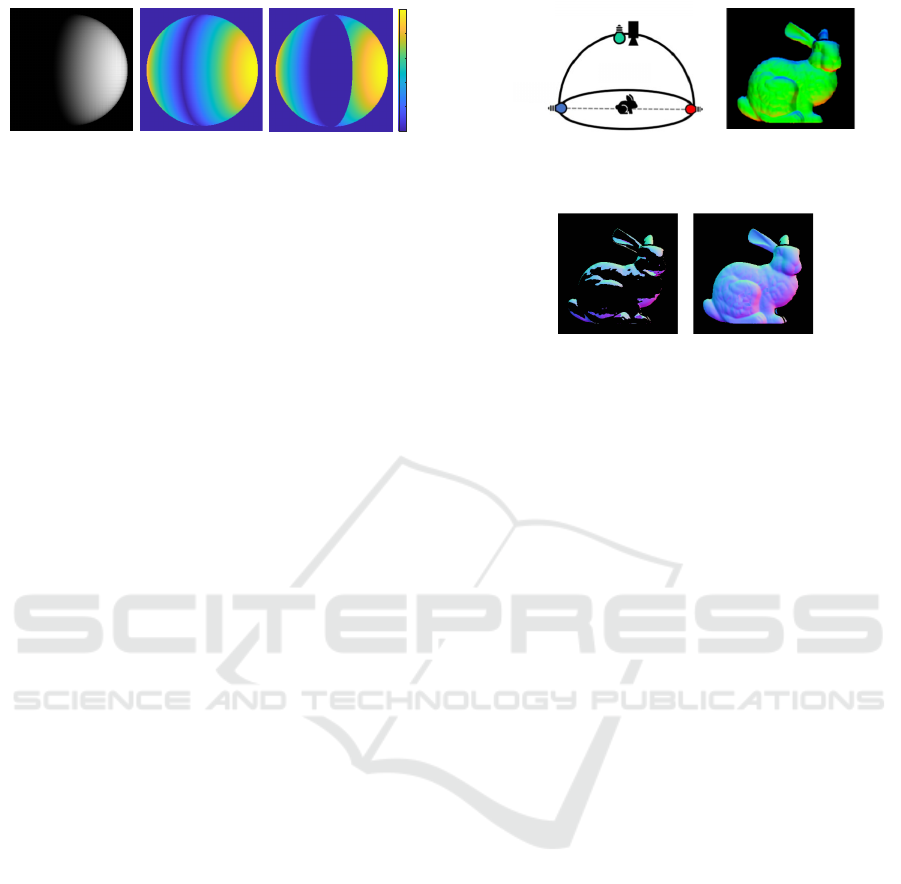
(a) Input (b) | cosα | (c) Certainty
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
Figure 4: Certainty of disambiguation. (a) (b) Near the
boundary of the attached shadow, it is ambiguous whether it
is a shadow or not. (c) Furthermore, disambiguation is not
feasible in the case corresponding to Fig. 3(b), so we define
certainty as a combination of these two.
maining two source directions to disambiguate the
normals.
The discussion in Sec. 4.2.1 indicates that when
there is only a single side light source, it should be
illuminated from a direction orthogonal to the base
light source, but when there are two side light sources,
the optimal arrangement is non-trivial. Therefore,
we consider a practical layout by introducing the cer-
tainty of disambiguation.
Certainty of Disambiguation. Near the boundary
of the attached shadow, where the inner product of
the normal and light source direction is zero, shadow
or not is ambiguous and difficult to determine. There-
fore, we introduce a certainty of disambiguation s
p
to
minimize the number of ambiguous pixels.
Basically, the certainty of either attached shadow
or not can be measured by the absolute value of the
inner product of the light source direction and the nor-
mal. Thus, we define the certainty of disambiguation
for a side light source as follows,
s
p
=
(
|cos α| (cosα
ˆ
cosα < 0),
0 otherwise,
(6)
where cos α and
ˆ
cosα denote the inner products of a
light source and two candidate normals, respectively.
Fig. 4 shows an example of this certainty. A pixel that
satisfies cosα
ˆ
cosα < 0 (the case of Fig. 3(b)) has zero
certainty because the ambiguity cannot be resolved.
For extensions on multiple side light sources, we
can focus on the fact that disambiguation is to be
achieved by one of them. Therefore, suppose that the
base light source corresponds to the G channel; the
certainty with the two side light sources can be de-
scribed using the individual certainties s
p,R
and s
p,B
as follows,
s
p
= max{s
p,R
,s
p,B
}. (7)
As a simulation experiment, we conducted a grid
search with 1-degree intervals to find the optimal
direction of the two-side light sources that maxi-
mizes the certainty calculated by Eq. 7 for a refer-
ence sphere. Our findings suggest that the position
Lights
Color polarization camera
Object
(a)
(b)
Figure 5: Our light source configuration. (a) Overview. (b)
An example of the captured image.
(a) (b)
Figure 6: Uncertainty-aware Azimuthal Disambiguation.
(a) We detect cast shadows and ambiguous attached shad-
ows by our proposed certainty and (b) disambiguate nor-
mals by belief propagation.
where the three light sources are orthogonal to each
other is suitable. Furthermore, as discussed in the next
section, we extend this model to consider cast shad-
ows and determine the practical arrangement of light
sources.
Cast Shadow Handling. Cast shadows are another
factor that must be considered when designing the di-
rection of the light source. It is essential to find the
cast shadow since the method in Sec. 4.2.1 cannot be
applied to resolve the ambiguity. However, since both
attached and cast shadows are not illuminated, it is
impossible to identify which shadow is which by the
observed luminance.
Based on these results and insights, as shown in
Fig. 5, we place the two side light sources (R and B)
so that they are orthogonal to the base light source
(G) and opposite each other. When either light source
does not illuminate the pixels, they are in a cast
shadow from at least one of the light sources. The
disambiguation based on the attached shadow cannot
be applied to such pixels. Thus, we extend the cer-
tainty for these pixels as the region where s
p
= 0, and
we utilize the method described in the next section to
resolve the ambiguity.
4.3 Uncertainty-Aware Azimuthal
Disambiguation
In this section, we propose a method for selecting can-
didate normals by propagating adjacent high-certainty
azimuths for pixels with cast shadows or small cer-
tainty. We solve this as a graph optimization problem
with each pixel as a node.
VISAPP 2025 - 20th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
644
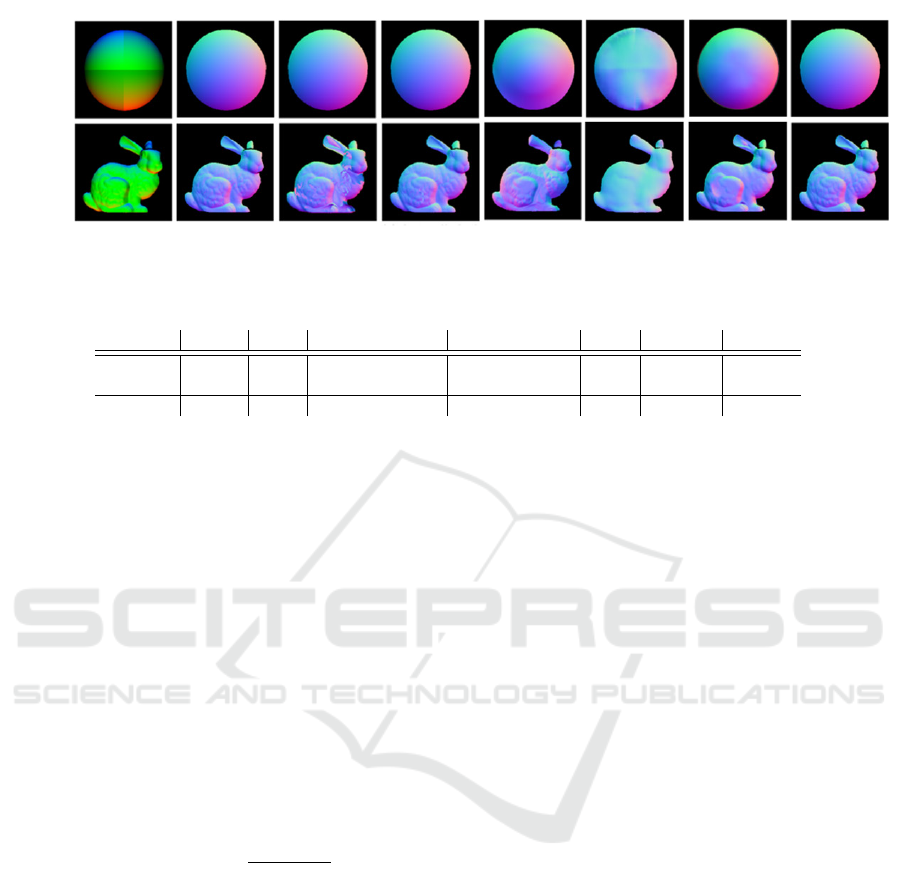
Sphere
(Textured)
Bunny
Input
Ours
DfP
DeepSfP
DeepPol
GT
w/o certainty
w/o η estimation
Figure 7: The reconstruction results with synthetic data. The leftmost is input single-shot images. The color of the results is
shown based on the normal XYZ component.
Table 1: Quantitative evaluation of recovered normals. (Mean angular errors in degree).
Input Object Ours w/o C.S. handling w/o η estimation DfP DeepSfP DeepPol
Synthetic
Sphere 0.03 0.03 2.01 8.17 30.77 11.84
Bunny 0.20 12.25 2.13 15.75 33.56 14.74
Real Sphere 6.44 22.95 6.48 22.92 35.89 12.89
In particular, assuming the azimuth angle of each
pixel φ
p
takes two states, ψ or ψ+ π, consider the fol-
lowing energy cost function w.r.t. the set of azimuth
angles Φ of all pixels;
E(Φ) =
∑
p∈P
∑
q∈N
p
C
s
(p,φ
p
,φ
q
) +
∑
p∈P
C
d
(p,φ
p
), (8)
where P denotes the set of all pixels, and N
p
denotes
the set of pixels q in the four neighbors to pixel p.
C
d
represents the data cost term, which is set to a
uniform value regardless of the state when the cer-
tainty s
p
is s
p
< γ for some threshold γ. C
s
repre-
sents the smoothness cost term formulated by the dis-
similarity of azimuth angles between adjacent pixels.
The smoothness cost term C
s
can be described us-
ing the vector representation of azimuthal directions
v
p
= (cosφ
p
,sin φ
p
)
⊤
and v
q
= (cosφ
q
,sin φ
q
)
⊤
as
C
s
(p,φ
p
,φ
q
) = 1 −
v
p
·v
q
+ 1
2
. (9)
We minimize the energy function in Eq. 8 with be-
lief propagation. Specifically, we input the energy
E(Φ) into the potential function and compute Φ to
maximize it. The potentials for C
d
and C
s
, respec-
tively, become as follows,
B
d
(p,φ
p
) = e
−C
d
(p,φ
p
)
,B
s
(p, φ
p
,φ
q
) = e
−C
s
(p,φ
p
,φ
q
)
.
(10)
Therefore, using the following message function, Φ
can be obtained by iteratively propagating belief to
adjacent pixels until convergence,
m
p→q
(φ
q
) =
∑
φ
p
={η,η+π}
B
d
(p, φ
p
) ×B
s
(p, φ
p
,φ
q
)
∏
k∈N
p
\q
m
k→q
(φ
k
,φ
q
).
(11)
Since only the message m
p→q
is updated and B
d
, B
s
are fixed, it converges to a quasi-globally optimal so-
lution.
Fig. 6 show an example of our disambiguation.
In regions with cast shadows or low certainty s
p
(black area in “Bunny”), our BP effectively resolves
ambiguity, enabling us to select a candidate normal
uniquely.
5 EXPERIMENTAL RESULT
We experimentally evaluate the effectiveness of our
method using synthetic and real images. Based on the
discussion in Sec. 4.2.2, our setup consists of the base
light source illuminated from the viewing direction
for the candidate normals estimation and two light
sources illuminated from the side direction for the az-
imuth angle disambiguation.
As for disambiguation based on attached shadows,
to avoid uncertain detection of illuminated pixels, the
certainty threshold is empirically set to γ = 0.4 for
all the data, and for the cast shadow pixels and low-
certainty pixels, disambiguation is performed using
the method described in Sec. 4.3.
As a baseline for comparison, we used the
physics-based (Smith et al., 2016), learning-based
(Ba et al., 2020)(Deschaintre et al., 2021), our method
without cast shadow handling (”w/o certainty”) and
our method without refractive index estimation (”w/o
η estimation”). For the methods (Smith et al., 2016)
and (”w/o η estimation”), the normal is estimated by
assuming that the refractive index of the base light
source is 1.5, following previous works.
Attached Shadow Constrained Shape from Polarization
645

5.1 Quantitative Evaluation with
Synthetic Data
We quantitatively evaluate the reconstruction accu-
racy of our method using synthetic images. As shown
in Fig. 5, we correspond the base light source to the
G-channel for the proof of concept. We used ren-
dered objects with different shapes (“Sphere” and
“Bunny”) which have ideal diffuse reflective surfaces.
We added texture to the “Sphere” to represent the
spatially varying albedo. The refractive index was set
to (R:1.44, G:1.45, B:1.46) for all the objects.
Fig. 7 and Table 1 show the results of surface nor-
mal recovery. These results clearly demonstrate that
the proposed method can recover the shape of objects
with bumps, such as “Bunny,” with higher accuracy
than the baseline results. In addition, the shape is suc-
cessfully recovered without any assumptions regard-
ing texture or albedo, as in the results for the texture-
added “Sphere.”
5.2 Real World Objects
We also conduct evaluation experiments using real
images to demonstrate the effectiveness of our
method qualitatively. We use narrow-band LED light
sources of 450 nm, 525 nm, and 640 nm as unpo-
larized light sources. We capture the image using a
quad-Bayer color polarization camera (Blackfly BFS-
U3-51S5P-C). We built a single-shot system in our
indoor environment to demonstrate the proof of con-
cept. The position of the light source was adjusted in
advance using a reference sphere different from the
one used for the evaluation. The objects we use have
different shapes, textures, and materials (“Sphere,”
“Pear,” “Elephant”).
Fig. 8 shows the results of the surface normal es-
timation. Note that our method does not account for
specular reflection, so the areas of specular reflection
in the input image are masked out for evaluation. The
results clearly show that our method can successfully
recover the normals of these objects, regardless of the
textures and complex surface geometry. In order to
quantitatively evaluate the shape recovery results of
real objects, we obtain the ground truth of the normal
using a sphere with a known diameter (“Sphere”). Ta-
ble 1, the bottom row shows the result of our method
has the best performance for the surface recovery.
5.3 Ablation Study
The effectiveness of introducing certainty and ad-
dressing cast shadows by BP is demonstrated by the
method (”w/o certainty”). As Figs 7,8 show, quali-
Table 2: Results of refractive index estimation.
Input Object Ours GT
Synthetic
Sphere 1.45 1.45
Bunny 1.45 1.45
Real
Sphere 1.51 –
Pear 1.44 –
Elephant 1.41 –
tative differences are clearly evident in the concave
areas where cast shadows occur and in the boundary
areas and attached shadows become ambiguous. Ta-
ble 1 also demonstrates the effect quantitatively.
Additionally, the method (”w/o η estimation”)
demonstrates the impact of refractive index estima-
tion on the estimation results. This appears to be a
distortion of the normal’s zenith angle, and its im-
provement is shown especially in Table 1. Most im-
portantly, this result shows that the proposed method
is applicable to objects with unknown refractive in-
dices.
5.4 Refractive Index Estimation
Table 2 shows the results of refractive index estima-
tion. We show the refractive indices of the base light
sources (the G channel in the synthetic image exper-
iment and the B channel in the real image experi-
ment) used for zenith angle estimation. The results
with synthetic images quantitatively show that the
proposed method is capable of highly accurate esti-
mation. Also, while ground truth is not available in
the results with real images, we find they are within
the typical range of refractive indices for each mate-
rial.
6 CONCLUSION
This paper proposes a practical single-shot SfP that
estimates the per-pixel normal of objects with un-
known refractive indices. By effectively arranging
narrow-band R, G, and B light sources and a color po-
larization camera, we achieve effective disambigua-
tion by utilizing attached shadows and estimating the
unknown refractive indices, thus relaxing the conven-
tional single-shot SfP assumptions. Furthermore, we
introduce a novel BP-based uncertainty-aware disam-
biguation to address regions with cast shadows and
ambiguous presence or absence of attached shadows.
The major limitation of our method is that it assumes
diffuse-dominant surfaces. Even when leveraging a
distant point source, for some objects with high sur-
face roughness and specular reflectance, the specular
component will dominate in a wide area, limiting the
range of objects that can be recovered. Therefore, one
VISAPP 2025 - 20th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
646
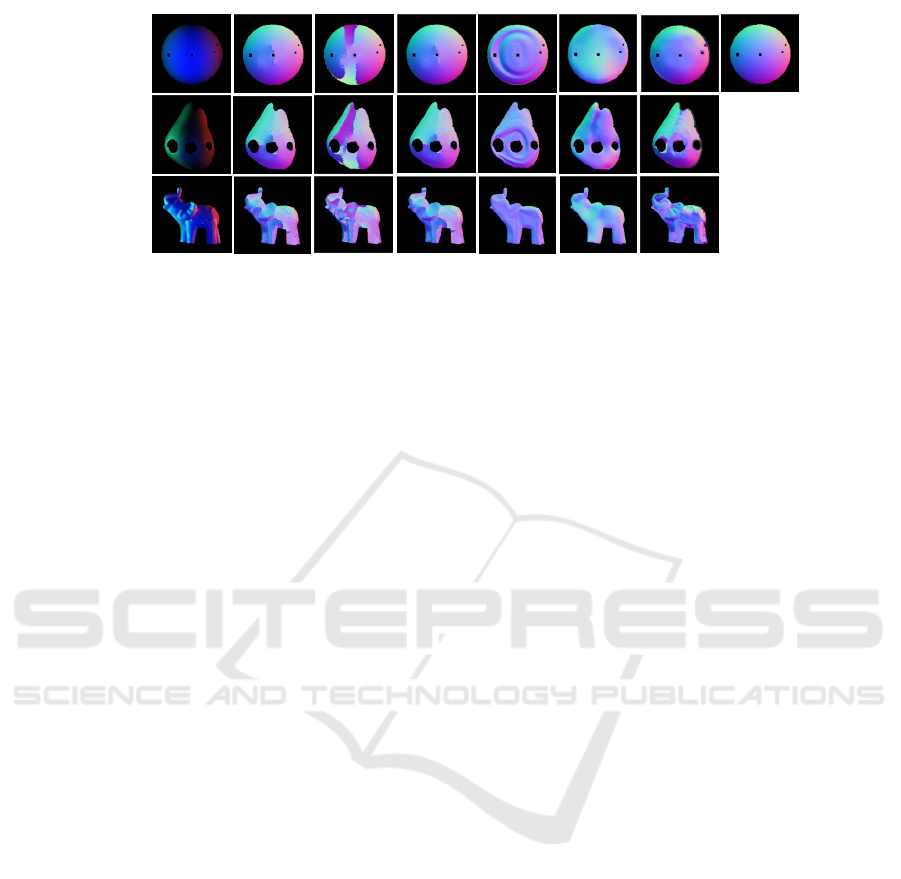
Sphere
Pear
Elephant
Input
Ours
DfP
DeepSfP
DeepPol
GT
w/o certainty
w/o η estimation
Figure 8: The reconstruction results of real-world objects. The leftmost is input single-shot images. The color of the results
is shown based on the normal XYZ component.
future work is to extend our method to the specular-
dominant surfaces. Another limitation arises from
overly complex surfaces, which disrupt the azimuthal
similarity of neighboring pixels and create extensive
cast shadows.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant
Numbers JP20H00612 and JP22K17914.
REFERENCES
Ackermann, J., Goesele, M., et al. (2015). A survey of pho-
tometric stereo techniques. Foundations and Trends®
in Computer Graphics and Vision, 9(3-4):149–254.
Anderson, R., Stenger, B., and Cipolla, R. (2011). Color
photometric stereo for multicolored surfaces. In
ICCV, pages 2182–2189. IEEE.
Atkinson, G. A. and Hancock, E. R. (2006). Recovery of
surface orientation from diffuse polarization. IEEE
TIP, 15(6):1653–1664.
Ba, Y., Gilbert, A., Wang, F., Yang, J., Chen, R., Wang, Y.,
Yan, L., Shi, B., and Kadambi, A. (2020). Deep shape
from polarization. In ECCV, pages 554–571.
Chakrabarti, A. and Sunkavalli, K. (2016). Single-image
rgb photometric stereo with spatially-varying albedo.
In 3DV, pages 258–266. IEEE.
Deschaintre, V., Lin, Y., and Ghosh, A. (2021). Deep polar-
ization imaging for 3d shape and svbrdf acquisition.
In CVPR, pages 15567–15576.
Guo, H., Okura, F., Shi, B., Funatomi, T., Mukaigawa, Y.,
and Matsushita, Y. (2021). Multispectral photomet-
ric stereo for spatially-varying spectral reflectances: A
well posed problem? In CVPR, pages 963–971.
Huynh, C. P., Robles-Kelly, A., and Hancock, E. (2010).
Shape and refractive index recovery from single-view
polarisation images. In CVPR, pages 1229–1236.
Hwang, I., Jeon, D. S., Munoz, A., Gutierrez, D., Tong, X.,
and Kim, M. H. (2022). Sparse ellipsometry: portable
acquisition of polarimetric svbrdf and shape with un-
structured flash photography. ACM TOG, 41(4):1–14.
Ikeuchi, K. and Horn, B. K. (1981). Numerical shape from
shading and occluding boundaries. Artificial intelli-
gence, 17(1-3):141–184.
Kadambi, A., Taamazyan, V., Shi, B., and Raskar, R.
(2015). Polarized 3d: High-quality depth sensing with
polarization cues. In ICCV, pages 3370–3378.
Kriegman, D. J. and Belhumeur, P. N. (2001). What shad-
ows reveal about object structure. JOSA, 18(8):1804–
1813.
Lei, C., Qi, C., Xie, J., Fan, N., Koltun, V., and Chen, Q.
(2022). Shape from polarization for complex scenes
in the wild. In CVPR, pages 12622–12631.
Mahmoud, A. H., El-Melegy, M. T., and Farag, A. A.
(2012). Direct method for shape recovery from polar-
ization and shading. In ICIP, pages 1769–1772. IEEE.
Miyazaki, D., Tan, R. T., Hara, K., and Ikeuchi, K. (2003).
Polarization-based inverse rendering from a single
view. In ICCV, pages 982–982.
Ozawa, K., Sato, I., and Yamaguchi, M. (2018). Single
color image photometric stereo for multi-colored sur-
faces. Computer Vision and Image Understanding,
171:140–149.
Pistellato, M. and Bergamasco, F. (2024). A geometric
model for polarization imaging on projective cameras.
IJCV, pages 1–15.
Rahmann, S. and Canterakis, N. (2001). Reconstruction
of specular surfaces using polarization imaging. In
CVPR, volume 1, pages I–I. IEEE.
Smith, W. A., Ramamoorthi, R., and Tozza, S. (2016). Lin-
ear depth estimation from an uncalibrated, monoc-
ular polarisation image. In ECCV, pages 109–125.
Springer.
Smith, W. A., Ramamoorthi, R., and Tozza, S. (2018).
Height-from-polarisation with unknown lighting or
albedo. IEEE TPAMI, 41(12):2875–2888.
Thanh, T. N., Nagahara, H., and ichiro Taniguchi, R.
(2015). Shape and light directions from shading and
polarization. In CVPR, pages 2310–2318.
Woodham, R. J. (1980). Photometric method for determin-
ing surface orientation from multiple images. Optical
engineering, 19(1):139–144.
Zhang, R., Tsai, P.-S., Cryer, J. E., and Shah, M.
(1999). Shape-from-shading: a survey. IEEE TPAMI,
21(8):690–706.
Attached Shadow Constrained Shape from Polarization
647
