
DeepGen: A Deep Reinforcement Learning and Genetic
Algorithm-Based Approach for Coverage in Unknown Environment
Nirali Sanghvi
a
, Rajdeep Niyogi
b
and Ribhu Mondal
c
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee, Roorkee 247667, India
Keywords:
Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning, Genetic Algorithm, Coverage in Unknown Environment.
Abstract:
In this paper, a novel approach to optimize waypoint placement and coverage in multi-agent systems in un-
known environments using a combined Genetic Algorithm and Deep Reinforcement Learning has been pro-
posed. Effective exploration and coverage are essential in various fields, such as surveillance, environmental
monitoring, and precision agriculture, where agents must cover large and often unknown environments ef-
ficiently. The proposed method uses a Genetic Algorithm to identify optimal waypoint configurations that
maximize coverage while minimizing overlap among waypoints, after which a deep reinforcement learning
policy refines the agents’ coverage policy to adaptively navigate and explore new areas. Simulation results
demonstrate that this GA-DDQN approach significantly improves both the effectiveness of coverage and com-
putational efficiency compared to traditional single-strategy methods. This combined framework offers a ro-
bust solution for real-world applications requiring optimized, adaptive multi-agent exploration and coverage.
1 INTRODUCTION
The coverage problem, which aims to ensure an agent
visits all feasible points in an environment, is funda-
mental across diverse, real-world applications. These
applications span critical domains such as search and
rescue, space exploration, military operations, and
inspection robotics as well as more routine appli-
cations like autonomous cleaning, agricultural field
management, and industrial automation. The objec-
tive in these varied settings is to maximize coverage
efficiently, capturing a comprehensive representation
of the environment through an optimal sequence of
movements, or “coverage path,” to fulfill the task at
hand. Coverage tasks may occur in environments that
are either fully known or unknown prior to deploy-
ment, depending on the specific requirements.
In known environments, predefined factors like
obstacle placement and boundaries enable offline-
optimized, pre-planned coverage strategies. For in-
stance, (Mannadiar and Rekleitis, 2010) uses Bous-
trophedon cellular decomposition, while (Karapetyan
et al., 2017) proposes heuristic methods: one ex-
tends single-agent exact cellular decomposition, and
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0003-4245-0587
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1664-4882
c
https://orcid.org/0009-0008-6779-2694
the other divides the environment among agents us-
ing a greedy approach. However, in partially known
or unpredictable environments, such as post-disaster
scenarios, agents must devise online coverage paths,
dynamically adjusting movements to maximize cov-
erage without prior information.
The use of multiple agents, rather than a single
agent, has proven advantageous for improving effi-
ciency in time-sensitive or large-scale coverage tasks.
Single-agent approaches, including cellular decom-
position, grid-based coverage, and graph-based cov-
erage (Galceran and Carreras, 2013), can effectively
cover small areas but lack scalability for expansive
terrains or urgent situations such as search and rescue
operations. Multi-agent systems, on the other hand,
can enhance efficiency by reducing task completion
times and improving system robustness. However,
multi-agent coverage introduces additional complex-
ity, including the risk of overlap (agents covering the
same areas redundantly) and dynamic obstacles cre-
ated by other moving agents. The multi-agent cover-
age problem can be mapped to a set of multiple Trav-
eling Salesperson Problems, making it an NP-hard
challenge (Rekleitis et al., 2008).
More recently, Reinforcement Learning (RL) has
emerged as a powerful framework for solving cover-
age problems, offering a model in which agents can
autonomously learn optimal actions through interac-
564
Sanghvi, N., Niyogi, R. and Mondal, R.
DeepGen: A Deep Reinforcement Learning and Genetic Algorithm-Based Approach for Coverage in Unknown Environment.
DOI: 10.5220/0013259400003890
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2025) - Volume 1, pages 564-571
ISBN: 978-989-758-737-5; ISSN: 2184-433X
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

tions with their environment. In RL, agents receive
rewards or penalties based on their actions, iteratively
refining their strategies to maximize cumulative re-
wards (Ladosz et al., 2022). The advent of Deep Rein-
forcement Learning (DRL), which incorporates deep
learning to handle high-dimensional state spaces, has
broadened RL’s applicability, enabling agents to op-
erate in complex environments such as agricultural
fields, where they must navigate large, intricate ter-
rains (Li, 2017). DRL can support tasks such as au-
tonomous field exploration, pest control, crop moni-
toring, and resource allocation, fostering optimal cov-
erage and adaptive, efficient resource management.
Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning
(MADRL) extends DRL principles to systems of
multiple agents, enabling collaborative and com-
petitive interactions that optimize coverage tasks in
distributed, decentralized environments like agricul-
tural fields (Gronauer and Diepold, 2022). In this
paper, we propose a MADRL-based approach to
coverage in agricultural fields, aiming to minimize
redundancy through reduced overlap and improve
efficiency via an innovative reward function. This
reward function encourages cooperative coverage
among agents, maximizing coverage efficiency and
significantly enhancing task performance. Genetic
Algorithm is an optimization approach which follows
the process of natural evolution. The strongest one
survives same is done by genetic algorithm. Out of
all the possible prospective solutions, it selects the
best solution as the final output.
In this paper, we propose an approach for cov-
erage in unknown environments using genetic algo-
rithm and deep reinforcement learning. Extensive
simulations considering various environment sizes
and varying other parameters to test the efficiency of
the proposed approach. The rest of this article is struc-
tured as follows. Related work is discussed in Section
2. Formalization of the proposed approach in Sec-
tion 3. The proposed approach is given in Section 4.
Simulation results are given in Section 5 and conclu-
sions in Section 6.
2 RELATED WORK
Coverage problems, known to be NP-hard, have at-
tracted significant research interest. These problems
are often simplified to the Travelling Salesman Prob-
lem (TSP) or the lawn mowing problem, highlight-
ing their computational complexity as NP-hard. Tra-
ditionally, many area coverage approaches assume
that a complete map of the environment is available,
enabling efficient navigation and coverage planning.
Several traditional strategies have been explored to
address the coverage problem. The greedy approach,
for instance, prioritizes the nearest unvisited points,
offering quick coverage but often yielding subopti-
mal results. A pairing method divides the environ-
ment into distinct regions, assigning each to a pair of
agents; while effective, this method is feasible only
when the agent-to-region ratio is balanced and may be
impractical for large or unknown environments. Al-
ternatively, exhaustive coverage methods (brute-force
approaches) can ensure complete coverage but are
computationally intensive and impractical for large-
scale deployments (Sharma and Tiwari, 2016).
Researchers have proposed various multi-robot
strategies for coverage in unknown environments.
Common methods include decomposition techniques,
such as Voronoi partitions for dividing areas among
robots (Guruprasad et al., 2012), and sweep-based
coverage using systematic sweeping paths (Sanghvi
et al., 2024). A distributed approach assigns robots
start and goal positions, enabling autonomous navi-
gation based on their location (Sanghvi and Niyogi,
2024). However, suboptimal direction choices can
hinder complete coverage. The spanning tree ap-
proach for multi-robot coverage was introduced
in (Agmon et al., 2006). A bio-inspired method
with ant-like robots marking paths for others was pro-
posed for unknown environments in (Senthilkumar
and Bharadwaj, 2012). Multi-spanning tree coverage
methods, including simultaneous and extended varia-
tions, are discussed in (Chibin et al., 2008), while (Li
et al., 2022) details a credit-based approach for robots
with varying speeds. In (Nair and Guruprasad, 2020),
a cooperative method combines Voronoi partitions
with frontier-based exploration for simultaneous ex-
ploration and coverage.
Reinforcement learning provides an effective so-
lution to address the limitations of traditional cover-
age methods. When combined with deep learning,
reinforcement learning becomes a powerful tool for
coverage tasks in large, complex environments. In
(Wang et al., 2023), the authors propose a cover-
age path planning approach using DQN, specifically
adapted for a targeted task. In (Piardi et al., 2019) em-
ploys Q-learning to determine optimal coverage paths
while aiming to avoid overlapping areas, though it
assumes known obstacle positions. In contrast, our
proposed approach operates without prior knowledge
of the environment, barriers, or the positions of other
agents, allowing for more autonomous exploration. In
(Din et al., 2022) presents a DDQN-based method for
multi-agent coverage, allowing certain areas to be re-
visited. However, in many coverage tasks, revisiting
the same location may be inefficient and resource-
DeepGen: A Deep Reinforcement Learning and Genetic Algorithm-Based Approach for Coverage in Unknown Environment
565
intensive. Our approach utilizes deep reinforcement
learning within a discrete action space, providing a
practical and efficient solution for complex scenarios.
In (Such et al., 2017), the authors have proposed
an approach for using genetic algorithm for training
of neural networks. There the authors present that us-
ing genetic algorithm helps in better and faster train-
ing the neural network and this approach can work
well with various deep reinforcement learning ap-
proaches. In (Sehgal et al., 2019), the authors have
used genetic algorithm for parameter optimization of
deep reinforcement learning. In this paper, we com-
bine the genetic algorithm approach with deep rein-
forcement learning for the coverage problem of an un-
known environment.
3 FORMALIZATION
Definition 1. Waypoints Waypoints are the interme-
diate targets that guide the movement of the agents to
increase the overall coverage.
Definition 2. Coverage (C
g
) Let C
i
be the area cov-
ered by agent i. Coverage C
g
is the union of the areas
covered by each agent, i.e., C
g
=
S
n
i=1
C
i
Definition 3. Coverage Percentage (C
%
)
Coverage Percentage (C
%
) is the ratio of Coverage
(C
g
) to the total area (A) that needs to be covered.
C
%
=
C
g
A
× 100
3.1 Problem Definition
Let I denote the set of agents I = {1, . . . , n}, where n
denotes the total number of agents in the given en-
vironment. Let W be the set of waypoints W =
{w
1
, . . . , w
k
}, where k denotes the total number of
waypoints placed. Let O denote the set of obstacles
that are placed randomly in the environment. The
agents have no knowledge about the placement of the
obstacles in the environment. Also, the agents do
not have any information about the position of other
agents or the placement of the waypoints. The main
goal is to attain better coverage of the environment.
3.2 Problem Formalization
We propose an approach using a genetic algorithm
and Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) to address
the coverage problem. In this proposed approach, the
waypoints are placed in the environment using the ge-
netic algorithm (GA). The main goal is to maximize
the coverage and get better coverage with reduced
overlap for which DRL is used. In this, the agent
I interacts with the environment using its individual
policy based on its local observations. The goal is
to maximize the rewards and thus attain better cover-
age and reduced overlap. At a given time, the agents
collectively take a joint action a
t
= (a
1
t
, . . . , a
n
t
) ∈ A,
where A is the action space composed of individual
action spaces A
i
for agent i. Then, the agents transi-
tion to a new state s
′
∈ S with a probability distribu-
tion of P(s
′
|s, a). Upon transitioning to the new state,
the agent receives a reward r
t
.
4 PROPOSED APPROACH
4.1 Genetic Algorithm
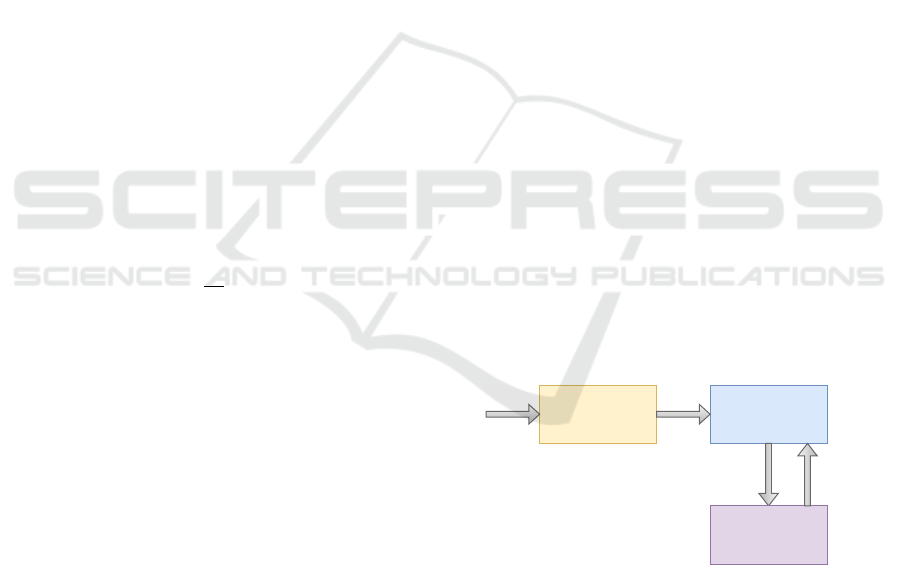
Figure 1 gives the overview the proposed approach
When multiple agents need to explore and cover an
unknown environment, a Genetic Algorithm (GA) can
optimize the placement of waypoints to maximize
coverage while minimizing overlap. Because the en-
vironment layout is initially unknown, the GA itera-
tively refines waypoint configurations, aiming for so-
lutions that allow agents to efficiently cover the area.
Each configuration (or individual) in the GA popula-
tion represents a potential waypoint arrangement that
directs agents’ paths to achieve effective coverage.
The algorithm includes five key stages: generating an
initial population, evaluating fitness, selecting high-
performing configurations, applying crossover to cre-
ate new configurations, and using mutation to main-
tain diversity and explore the solution space. Below
are the important functions used.
Genetic
Algorithm
Waypoint
Placement in the
environment
n-Agents
{a
1,
a
2, ...
a
n,
}
reward,
state
action
Figure 1: Proposed Approach.
4.1.1 Initial Population
The initial population represents a varied set of candi-
date waypoint configurations, where each configura-
tion is a different arrangement of waypoints for agent
deployment. Given that the environment’s layout and
potential obstacles are not known beforehand, these
configurations are generated randomly to provide a
wide range of possible solutions. Each configuration
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
566

suggests different points where agents might begin or
move toward, encouraging broad exploration. This
diversity is essential in unknown environments as it
offers a range of strategies that the algorithm can eval-
uate and refine.
4.1.2 Fitness Function
The fitness function is a measure that evaluates each
individual’s quality or effectiveness in solving the
problem. It assigns a fitness score to each individ-
ual based on how well they fulfill the objectives. The
fitness function is crucial because it guides the selec-
tion process, helping the GA focus on individuals that
show the most promise for improvement over gener-
ations. The fitness function evaluates each waypoint
configuration based on its effectiveness in maximiz-
ing coverage and minimizing overlap among agents.
In this coverage scenario, fitness scores are calcu-
lated by balancing two primary metrics: Waypoint
Coverage (W
c
) and Waypoint overlap (W
o
). Waypoint
Coverage (W
c
) measures how well the waypoints are
placed in the environment. It checks on the efficiency
of the waypoint placement. Waypoint overlap (W
o
)
measures if the waypoints are placed in a very close
proximity or if they are placed at the same locations.
The fitness function for each configuration is cal-
culated as:
f (W ) = α·W
c
− β ·W
o
(1)
where α and β are constants that weigh the impor-
tance of coverage and overlap respectively. A high
fitness score indicates that the waypoint configura-
tion effectively maximizes coverage while minimiz-
ing overlap.
4.1.3 Selection
Selection is a process by which individuals with
higher fitness scores are chosen as parents for the
next generation, as they are more likely to produce
offspring with advantageous traits. Selection aims to
prioritize individuals that are closer to the optimal so-
lution, increasing the probability that beneficial traits
will be passed down.
4.1.4 Crossover
Crossover is a genetic operation applied to the
selected parents to produce the next generation.
Crossover combines segments of genetic information
from two parents to generate offspring, which inherit
characteristics from both. This operation enables ex-
ploration of the solution space by creating new indi-
viduals with potentially improved traits.
4.1.5 Mutation
Mutation introduces random alterations to the genetic
makeup of offspring, typically with a small probabil-
ity. Mutation prevents premature convergence to local
optima by introducing genetic diversity, which helps
the population explore a broader solution space. This
random change might involve modifying a waypoint
position or altering a path sequence. By maintain-
ing a low mutation rate, the algorithm balances diver-
sity with stability, ensuring that beneficial traits from
previous generations are retained while still exploring
new solutions.
4.2 Deep Reinforcement Learning
Based Coverage
State Space: The state space for the coverage prob-
lem is the set of all states in the environment. State
space in the grid of size M × N is all the cells present
in the grid, which may be either covered, uncovered,
or have obstacles.
Action Space: For every agent, there are four dis-
crete actions up, down, right, left.
Reward: The reward in DDQN represents the en-
vironment’s response to an agent’s action and sig-
nificantly influences learning efficiency and behav-
ior. A well-designed reward function promotes ef-
ficient coverage, exploration, and collaboration, par-
ticularly in multi-agent systems. Dense rewards pro-
vide immediate feedback, accelerating learning and
convergence. Adjusting the reward structure balances
trade-offs such as coverage efficiency, energy use, or
collision avoidance, encouraging faster convergence
and mitigating overfitting or unintended behaviors. In
multi-agent settings, rewards emphasizing team per-
formance enhance coordination, while penalizing re-
dundancy ensures effective collaboration.
The reward function depends on the number of
waypoints and the total area covered by the agents.
They get more reward on exploring unknown area
which indeed improvises the coverage. We model the
reward function. The reward function R
t
at each time
step t is defined as:
R
t
= α ·W
c
+ β ·C
g
where α and β are weighing factors that balance the
importance of total coverage and exploration.
In this function, the term α · W
c
rewards agents
based on overall coverage, motivating them to maxi-
mize the total area covered. The term β·C
g
adds an in-
centive for exploring previously unexplored regions,
thus encouraging agents to seek new areas rather than
revisiting known ones. By tuning α and β, the reward
DeepGen: A Deep Reinforcement Learning and Genetic Algorithm-Based Approach for Coverage in Unknown Environment
567
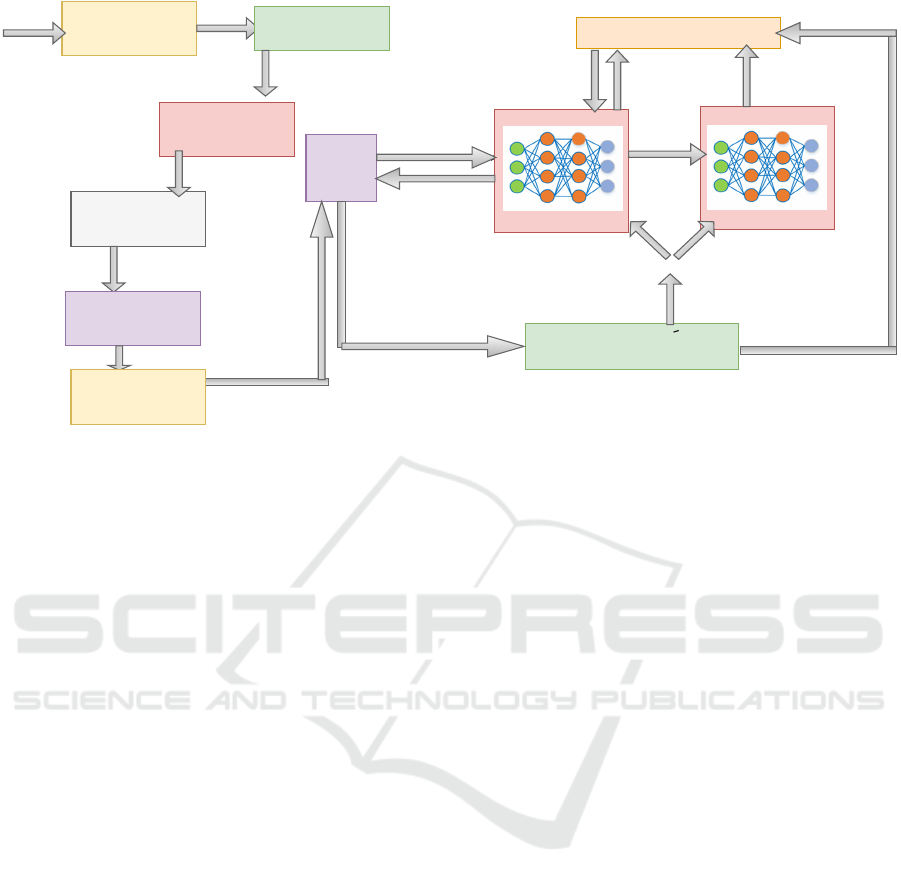
n-Agents
DDQN Loss Function
States
Target Network
reward r
W*
Soft Update
Action
Loss(θ)
Main network
Experience replay buffer
Genetic Algorithm Initializing Population
Computing fitness and
evaluating fitness
Computing fitness and
evaluating fitness
Cross Over of the
parents and Mutation
Mini-Batch
Waypoints placed in the
Environment
Waypoints placed
in the environment
Experience being
stored
Figure 2: Working of the proposed approach.
function can prioritize between broad coverage and
the exploration of unknown areas, enhancing efficient
exploration. This cycle of selection, crossover, and
mutation repeats until the specified maximum num-
ber of generations, G
max
, is reached. At this point, the
best-performing waypoint configuration W
∗
based on
the highest fitness score, is selected as the final output.
4.3 Algorithm
The GA-DDQN algorithm optimizes waypoint place-
ment and coverage in a grid environment by combin-
ing Genetic Algorithm (GA) for global optimization
and Double Deep Q-Network (DDQN) for policy re-
finement. In Stage 1, GA determines the optimal
waypoint configuration W
∗
by iteratively generating
and evaluating random populations of configurations.
Fittest individuals undergo selection, crossover, and
mutation, and the process continues for G
max
genera-
tions to yield W
∗
. In Stage 2, DDQN refines the cov-
erage policy using W
∗
. Initialized with parameters
(E, S
max
, α, γ, ε), an agent interacts with the envi-
ronment, learning from experiences stored in a replay
buffer. Training continues until the coverage target
or step limit is reached, leveraging DDQN’s ability to
handle large state spaces efficiently. The result is an
optimized waypoint configuration W
∗
and a refined
coverage policy maximizing grid efficiency.
Figure 2 illustrates the workflow of the proposed
GA-DDQN (Genetic Algorithm-Double Deep Q-
Network) framework for optimizing waypoint place-
ment and coverage. The process begins with the
Genetic Algorithm (GA) component, where an ini-
tial population of waypoint configurations is gener-
ated. Each configuration undergoes fitness evaluation,
where coverage effectiveness is assessed. Using se-
lection, crossover, and mutation, the GA evolves the
waypoint configurations, producing an optimized set,
denoted as W
∗
, which is then placed in the environ-
ment.
Once waypoints are set, multiple agents interact
with the environment, gathering experiences by nav-
igating through the waypoints and avoiding obsta-
cles. Each agent’s interaction yields states and ac-
tions, which are processed by the DDQN module.
The DDQN consists of a Main Network and a Tar-
get Network. The agents’ actions and resulting states,
along with the obtained rewards r, are stored in an
experience replay buffer. Periodically, mini-batches
from this buffer are used to train the DDQN, mini-
mizing the loss function Loss(θ), which updates the
network parameters and refines the policy for optimal
navigation and coverage. This proposed approach us-
ing GA for waypoint optimization and the DDQN for
adaptive policy learning allows for effective naviga-
tion, maximizing coverage efficiency while reducing
redundant overlaps.
5 EXPERIMENTS AND RESULTS
In this section, we present the simulation results of
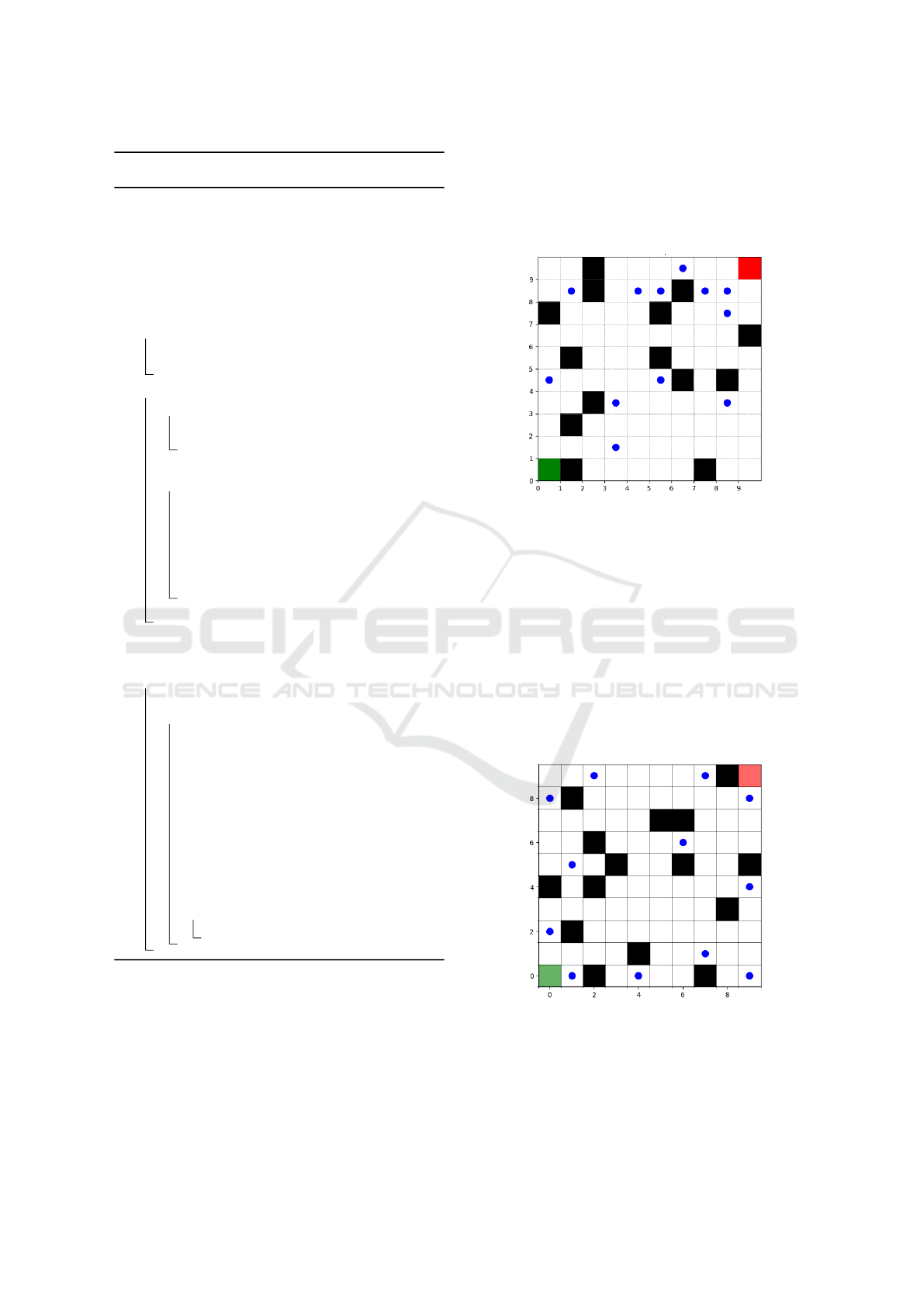
our proposed approach. Figure 3 shows a 10x10
grid environment used for simulation, featuring var-
ious elements relevant to a coverage task. Black cells
represent obstacles that add complexity by restricting
movement, simulating real-world barriers. Blue dots
denote waypoints, which are key locations that agents
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
568
Algorithm 1: GA-DDQN for Optimizing Waypoint
Placement and Coverage.
Input : Grid environment G, number of
agents N, obstacles O, waypoints W ,
GA parameters (P, µ, G
max
), DDQN
parameters (E, S
max
, α, γ, ε, ε
decay
,
ε
min
)
Output: Optimal waypoint configuration and
DDQN-based coverage policy
1 for i = 1 to P do
2 Generate a random set of waypoints W
i
;
3 Add W
i
to initial population;
4 for j = 1 to G
max
do
5 for each individual W
i
in population do
6 Compute fitness for W
i
using
Equation( 1)
7 Select fittest individuals;
8 for each individual in new population do
9 Select two parents P
1
and P
2
based on
fitness;
10 Generate child by
CROSSOVER(P
1
, P
2
);
11 Mutate child with probability µ;
12 Add child to new population;
13 Update population with new population;
14 Select best waypoint configuration W
∗
from
population;
15 for e = 1 to E do
16 Reset environment with waypoints W
∗
;
17 for t ← 1 to S
max
do
18 Observe state s
t
;
19 Select action a
t
based on DDQN
policy;
20 Execute a
t
, observe next state s
t+1
and reward r
t
;
21 Store transition (s
t
, a
t
, r
t
, s
t+1
) in
replay buffer;
22 Perform DDQN update using
mini-batch from replay buffer;
23 if coverage target reached or done
then
24 Break;
aim to cover. The green cell in the bottom-left corner
likely marks the starting position, while the red cell in
the top-right corner serves as the target or endpoint.
This setup challenges agents to navigate around ob-
stacles and maximize waypoint coverage, providing a
basis for assessing the effectiveness of different cov-
erage strategies. During the simulation, other agents
may also serve as dynamic obstacles, further compli-
cating navigation and coverage. The coverage task
was executed with varying numbers of agents using
the proposed approach. All simulations were con-
ducted on a core-i7 processor with 32 GB RAM.
Figure 3: Waypoint Placement using Random Approach.
In figure 3 waypoints (blue dots) are placed ran-
domly across the grid without any optimization. The
grid contains black cells representing obstacles that
agents must avoid. The green cell in the bottom-left
corner likely indicates the starting point for agents,
while the red cell in the top-right corner serves as
the target or endpoint. This random placement may
lead to suboptimal coverage and inefficient movement
paths, as waypoints may be clustered or unevenly dis-
tributed, potentially requiring agents to revisit certain
areas or navigate inefficiently around obstacles. The
coverage obtained in this is 57.8%.
Figure 4: Waypoint Placement using GA.
In figure 4, Genetic Algorithm (GA) is used to
optimize the placement of waypoints, resulting in a
more structured distribution across the grid followed
by deep reinforcement learning for coverage. By op-
DeepGen: A Deep Reinforcement Learning and Genetic Algorithm-Based Approach for Coverage in Unknown Environment
569
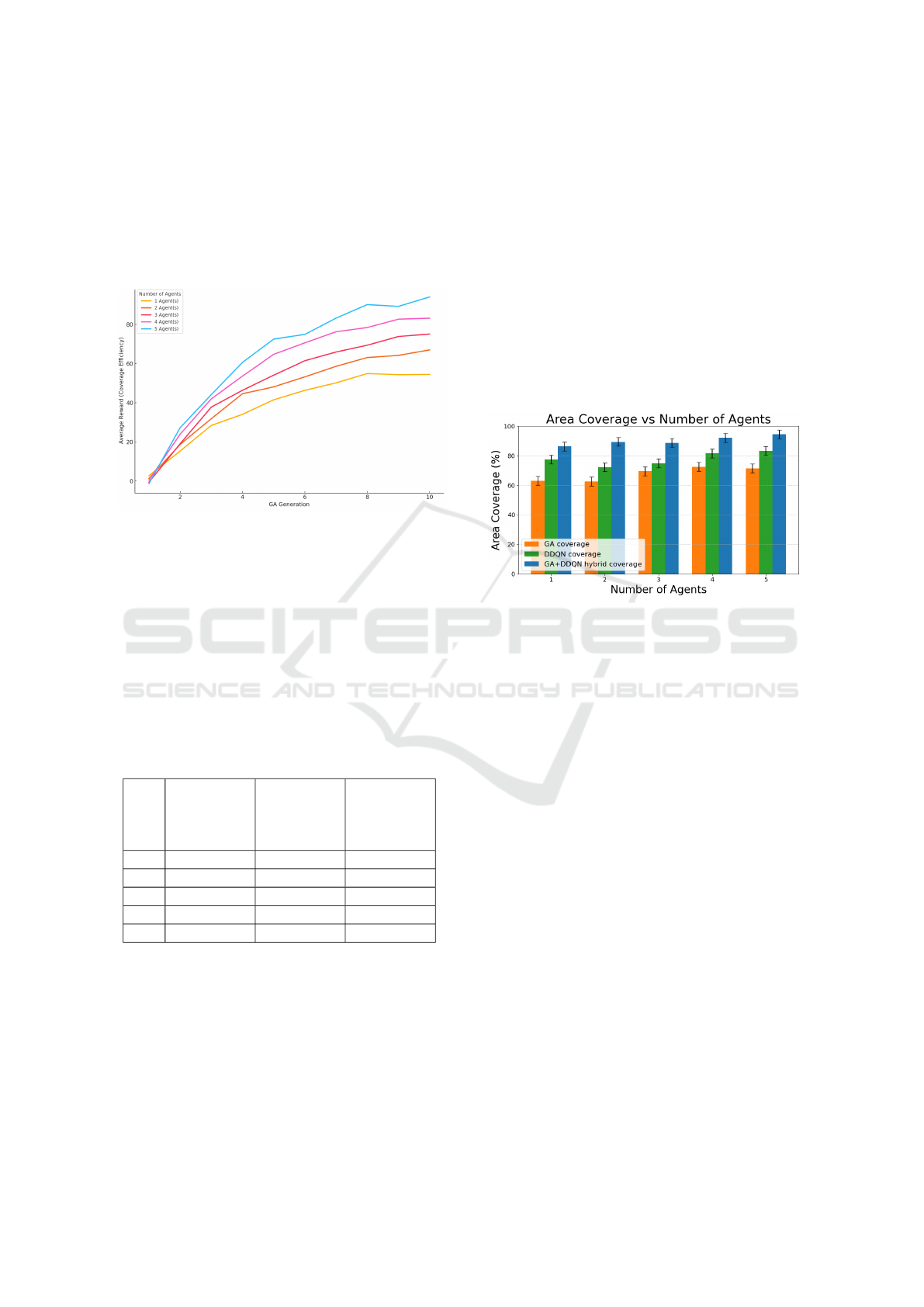
timizing waypoint positions, the GA approach aims
to improve coverage and minimize overlap, allowing
agents to navigate more efficiently and avoid unneces-
sary detours. This structured placement supports bet-
ter exploration and coverage, as agents can follow an
optimized path that maximizes area coverage while
avoiding obstacles, attaining a coverage of 87.8%.
Figure 5: Reward obtained using different number of
agents.
Figure 5 shows the increase in average reward
(coverage efficiency) across GA generations for dif-
ferent agent counts (1 to 5). Each line represents a
specific number of agents, with more agents achieving
higher rewards. The trend indicates that, as GA gen-
erations progress, coverage efficiency improves con-
sistently, with the 5-agent configuration reaching the
highest rewards. This demonstrates the effectiveness
of the GA-DDQN hybrid approach in optimizing cov-
erage through more agents and iterative learning.
Table 1: Area Coverage (%) vs. Number of Agents.
(n) GA Cover-
age (%)
DDQN
Coverage
(%)
GA+DDQN
Hybrid
Coverage
(%)
1 63.1 77.5 86.3
2 62.7 72.2 89.4
3 69.6 74.8 88.6
4 72.5 81.5 92.1
5 71.3 83.3 94.5
Table 1 compares the area coverage percentages
achieved by Genetic Algorithm (GA), Double Deep
Q-Network (DDQN), and the hybrid GA+DDQN
method across varying agent counts (n). With one
agent, GA achieves 63.1% coverage, DDQN performs
better at 77.5%, and the hybrid method outperforms
both with 86.3%. With two agents, GA coverage de-
creases slightly to 62.7%, DDQN remains stable at
72.2%, while the hybrid approach achieves a signif-
icant increase to 89.4%. For three agents, GA im-
proves to 69.6%, DDQN rises to 74.8%, and the hy-
brid method continues to lead with 88.6% coverage.
With four agents, GA and DDQN achieve 72.5%
and 81.5% coverage, respectively, while the hybrid
approach reaches 92.1%. At five agents, GA achieves
71.3%, DDQN improves to 83.3%, and the hybrid ap-
proach achieves its highest coverage of 94.5%, fully
utilizing the increased agent count for optimized cov-
erage. Table 1 demonstrates the hybrid method’s su-
perior performance by combining GA’s global way-
point optimization with DDQN’s adaptive learning,
significantly enhancing coverage in multi-agent envi-
ronments.
Figure 6: Coverage obtained by DQN and our proposed
DDQN in the same environment.
Figure 6 shows the relationship between the num-
ber of agents and the area coverage percentage
achieved by Genetic Algorithm (GA), Double Deep
Q-Network (DDQN), and the hybrid GA+DDQN ap-
proach. The x-axis represents the number of agents
(1 to 5), and the y-axis shows the percentage of area
covered. As depicted, coverage increases with the
number of agents across all methods. GA consis-
tently achieves the lowest coverage, highlighting its
limitations in independently covering the area effec-
tively. DDQN performs better than GA, achieving
higher coverage as the number of agents increases,
but it still lags behind the hybrid method. The
hybrid GA+DDQN approach combines GA’s global
waypoint optimization with DDQN’s adaptive explo-
ration, achieving the highest coverage percentages for
all agent counts.
6 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, a hybrid GA-DDQN approach for op-
timizing waypoint placement and coverage in a grid-
based environment has been developed. Using Ge-
netic Algorithm for waypoint optimization with Dou-
ble Deep Q-Network for adaptive policy learning,
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
570

the approach achieves efficient navigation and en-
hanced coverage, outperforming traditional single-
method approaches. Our results show that coverage
ranges from approximately 86.3% with one agent to
94.5% with five agents, demonstrating significant im-
provements with increasing the number of agents.
As a part of future work, we aim to extend the
proposed algorithm to handle environments where the
obstacles are moving.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The second author was in part supported by a research
grant from Google.
REFERENCES
Agmon, N., Hazon, N., and Kaminka, G. A. (2006). Con-
structing spanning trees for efficient multi-robot cov-
erage. In Proceedings 2006 IEEE International Con-
ference on Robotics and Automation, 2006. ICRA
2006., pages 1698–1703. IEEE.
Chibin, Z., Xingsong, W., and Yong, D. (2008). Complete
coverage path planning based on ant colony algorithm.
In 2008 15th International Conference on Mechatron-
ics and Machine Vision in Practice, pages 357–361.
IEEE.
Din, A., Ismail, M. Y., Shah, B., Babar, M., Ali, F., and
Baig, S. U. (2022). A deep reinforcement learning-
based multi-agent area coverage control for smart
agriculture. Computers and Electrical Engineering,
101:108089.
Galceran, E. and Carreras, M. (2013). A survey on coverage
path planning for robotics. Robotics and Autonomous
systems, 61(12):1258–1276.
Gronauer, S. and Diepold, K. (2022). Multi-agent deep re-
inforcement learning: a survey. Artificial Intelligence
Review, 55(2):895–943.
Guruprasad, K., Wilson, Z., and Dasgupta, P. (2012). Com-
plete coverage of an initially unknown environment
by multiple robots using voronoi partition. In Interna-
tional Conference on Advances in Control and Opti-
mization in Dynamical Systems.
Karapetyan, N., Benson, K., McKinney, C., Taslakian, P.,
and Rekleitis, I. (2017). Efficient multi-robot cover-
age of a known environment. In 2017 IEEE/RSJ In-
ternational Conference on Intelligent Robots and Sys-
tems (IROS), pages 1846–1852. IEEE.
Ladosz, P., Weng, L., Kim, M., and Oh, H. (2022). Ex-
ploration in deep reinforcement learning: A survey.
Information Fusion, 85:1–22.
Li, L., Shi, D., Jin, S., Kang, Y., Xue, C., Zhou, X.,
Liu, H., and Yu, X. (2022). Complete coverage
problem of multiple robots with different velocities.
International Journal of Advanced Robotic Systems,
19(2):17298806221091685.
Li, Y. (2017). Deep reinforcement learning: An overview.
arXiv preprint arXiv:1701.07274.
Mannadiar, R. and Rekleitis, I. (2010). Optimal coverage
of a known arbitrary environment. In 2010 IEEE In-
ternational conference on robotics and automation,
pages 5525–5530. IEEE.
Nair, V. G. and Guruprasad, K. (2020). Mr-simexcoverage:
Multi-robot simultaneous exploration and coverage.
Computers & Electrical Engineering, 85:106680.
Piardi, L., Lima, J., Pereira, A. I., and Costa, P. (2019). Cov-
erage path planning optimization based on q-learning
algorithm. In Aip conference proceedings, volume
2116. AIP Publishing.
Rekleitis, I., New, A. P., Rankin, E. S., and Choset, H.
(2008). Efficient boustrophedon multi-robot cover-
age: an algorithmic approach. Annals of Mathematics
and Artificial Intelligence, 52:109–142.
Sanghvi, N. and Niyogi, R. (2024). Distributed coverage
algorithm using multiple robots in an unknown envi-
ronment.
Sanghvi, N., Niyogi, R., and Milani, A. (2024). Sweeping-
based multi-robot exploration in an unknown environ-
ment using webots. In ICAART (1), pages 248–255.
Sehgal, A., La, H., Louis, S., and Nguyen, H. (2019). Deep
reinforcement learning using genetic algorithm for pa-
rameter optimization. In 2019 Third IEEE Interna-
tional Conference on Robotic Computing (IRC), pages
596–601. IEEE.
Senthilkumar, K. and Bharadwaj, K. K. (2012). Multi-
robot exploration and terrain coverage in an unknown
environment. Robotics and Autonomous Systems,
60(1):123–132.
Sharma, S. and Tiwari, R. (2016). A survey on multi
robots area exploration techniques and algorithms.
In 2016 International Conference on Computational
Techniques in Information and Communication Tech-
nologies (ICCTICT), pages 151–158. IEEE.
Such, F. P., Madhavan, V., Conti, E., Lehman, J., Stanley,
K. O., and Clune, J. (2017). Deep neuroevolution: Ge-
netic algorithms are a competitive alternative for train-
ing deep neural networks for reinforcement learning.
arXiv preprint arXiv:1712.06567.
Wang, Y., He, Z., Cao, D., Ma, L., Li, K., Jia, L., and Cui, Y.
(2023). Coverage path planning for kiwifruit picking
robots based on deep reinforcement learning. Com-
puters and Electronics in Agriculture, 205:107593.
DeepGen: A Deep Reinforcement Learning and Genetic Algorithm-Based Approach for Coverage in Unknown Environment
571
