
CGLearn: Consistent Gradient-Based Learning for Out-of-Distribution
Generalization
Jawad Chowdhury
a
and Gabriel Terejanu
b
Department of Computer Science, University of North Carolina at Charlotte, North Carolina, U.S.A.
Keywords:
Invariant Learning, Causal Invariance, Robust Machine Learning, Domain Generalization, Supervised Deep
Learning, Optimization for Neural Networks.
Abstract:
Improving generalization and achieving highly predictive, robust machine learning models necessitates learn-
ing the underlying causal structure of the variables of interest. A prominent and effective method for this is
learning invariant predictors across multiple environments. In this work, we introduce a simple yet powerful
approach, CGLearn, which relies on the agreement of gradients across various environments. This agreement
serves as a powerful indication of reliable features, while disagreement suggests less reliability due to poten-
tial differences in underlying causal mechanisms. Our proposed method demonstrates superior performance
compared to state-of-the-art methods in both linear and nonlinear settings across various regression and classi-
fication tasks. CGLearn shows robust applicability even in the absence of separate environments by exploiting
invariance across different subsamples of observational data. Comprehensive experiments on both synthetic
and real-world datasets highlight its effectiveness in diverse scenarios. Our findings underscore the impor-
tance of leveraging gradient agreement for learning causal invariance, providing a significant step forward in
the field of robust machine learning. The source code of the linear and nonlinear implementation of CGLearn
is open-source and available at: https://github.com/hasanjawad001/CGLearn.
1 INTRODUCTION
Machine learning models have achieved remarkable
success in various domains driven by the recent avail-
ability of large datasets, sophisticated algorithms, and
highly advanced complex models. However, these
models perform well only when the test data fol-
lows the same distribution as the training data (i.i.d.),
but they often suffer from overfitting due to over-
parametrization, learning spurious correlations from
training data (Sagawa et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2021;
Ming et al., 2022). This issue arises because tradi-
tional models focus on predictive power without con-
sidering the causal relationships underlying the data.
As a result, when the training and test distributions
differ, models that rely on spurious correlations can
perform very poorly, compromising their robustness,
leading to poor generalization on out-of-distribution
(OOD) test data (Arjovsky et al., 2019; He et al.,
2021).
Learning causal relationships is the key to model
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0004-6986-3063
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8934-9836
explainability and enhancing generalization and ro-
bustness (Shin, 2021; Wang et al., 2022; Santil-
lan, 2023). Although the ideal method for learn-
ing causal structures is through Randomized Control
Trials (RCTs), these are often expensive, unethical,
or impractical. Various methods have been devel-
oped for causal discovery. Constraint-based meth-
ods use conditional independence tests to identify
causal directions (Spirtes et al., 2001; Pearl, 2009;
Colombo et al., 2012). This however often results in
the Markov Equivalence Class (MEC) of causal struc-
tures. Score-based methods optimize causal graphs
over Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs) (Chickering,
2002; Ramsey et al., 2017; Huang et al., 2018),
but the combinatorial nature of the search space can
make it computationally expensive. Advances like
NOTEARS (Zheng et al., 2018) transform this combi-
natorial challenge into continuous optimization, lead-
ing to various effective variants (Zheng et al., 2020;
Yu et al., 2019; Lachapelle et al., 2019; Wei et al.,
2020; Ng et al., 2020; Ng et al., 2022). How-
ever, learning causal structures purely from observa-
tional data can be challenging due to issues like se-
lection bias, measurement errors, and confounding
Chowdhury, J. and Terejanu, G.
CGLearn: Consistent Gradient-Based Learning for Out-of-Distribution Generalization.
DOI: 10.5220/0013260400003905
In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods (ICPRAM 2025), pages 103-112
ISBN: 978-989-758-730-6; ISSN: 2184-4313
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
103
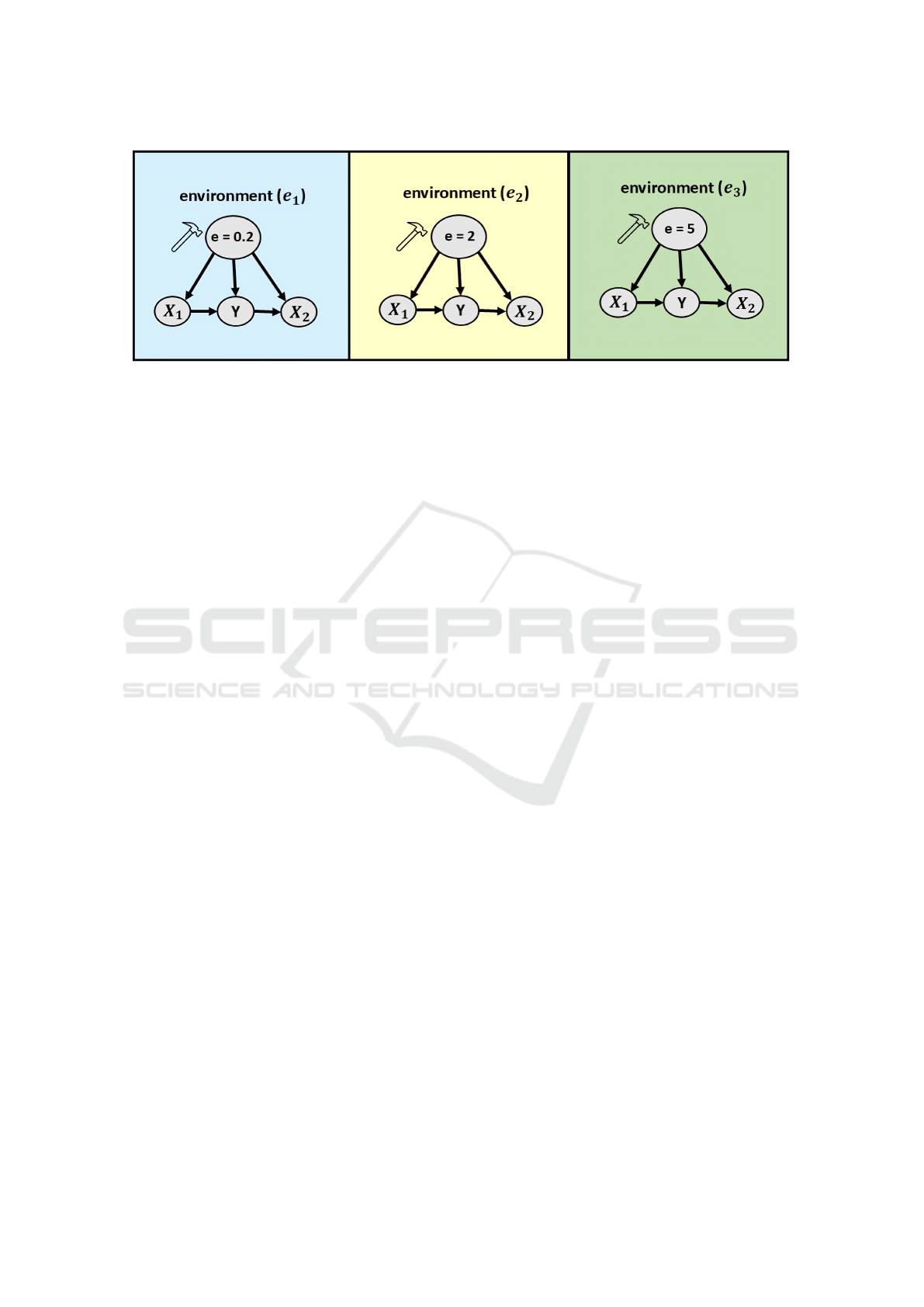
Figure 1: Illustration of three environments generated by intervening on the variable e, which takes distinct values e = 0.2,
e = 2, and e = 5 in environments e
1
, e
2
, and e
3
, respectively. In each environment, X
1
acts as a causal factor for the target
variable Y , while X
2
is a spurious (non-causal) factor with respect to Y . This figure exemplifies how different interventions on
e create distinct environments.
factors (Zadrozny, 2004; Torralba and Efros, 2011).
Moreover, relying solely on empirical risk optimiza-
tion can result in models highly dependent on spuri-
ous relationships. To tackle this problem, researchers
often use prior domain knowledge to improve causal
discovery (O’Donnell et al., 2006; Gencoglu and Gru-
ber, 2020; Andrews et al., 2020; Liu et al., 2021;
Chowdhury. et al., 2023; Chowdhury and Terejanu,
2023). Unfortunately, many causal discovery meth-
ods depend on specific assumptions (e.g., linearity,
non-Gaussian noise) that do not always hold in real-
world data. In addition to that some of these methods
exploit variance scales e.g. var-sortability to identify
causal orderings, performing well on unstandardized
data but poorly after standardization (Reisach et al.,
2021; Kaiser and Sipos, 2022; Reisach et al., 2024;
Ormaniec et al., 2024).
A recent line of study focuses on exploiting the
invariance property of causal relationships across dif-
ferent environments. Methods like Invariant Causal
Prediction (ICP) (Peters et al., 2016) aim to identify
causal predictors by ensuring the conditional distri-
bution of the target given these predictors remains
stable across environments. This method leverages
the invariance of causal relationships under differ-
ent interventions, iterating over feature subsets to
find those invariant across environments, considering
them as potential causal parents of the target vari-
able. Another study, IRM (Arjovsky et al., 2019)
optimizes a penalty function to achieve OOD gener-
alization for predictive models, ensuring robust per-
formance across environments. These methods sig-
nificantly reduce the absorption of spurious correla-
tions by focusing on stable and invariant relation-
ships. The invariant learning framework provides a
promising approach to improve model robustness and
generalization in the presence of distribution shifts,
with various domains exploiting invariance to learn
better predictors and robust models (Montavon et al.,
2012; Wang et al., 2017; Chowdhury et al., 2024;
Bose and Roy, 2024). Some relevant works such as
AND-mask (Parascandolo et al., 2020), Fishr (Rame
et al., 2022), Fish (Shi et al., 2021), IGA (Koyama
and Yamaguchi, 2020) use environment-specific gra-
dients to improve generalization in diverse settings.
Moreover, approaches examining the signal-to-noise
ratio (GSNR) in gradients, such as the work in Ref.
study (Liu et al., 2020), measure the alignment of gra-
dient directions across samples, while a similar strat-
egy has been employed in large-batch training scenar-
ios to improve model stability (Jiang et al., 2023).
Motivated by this line of work and the current
drawbacks of existing methods in structure learning
and OOD generalization, we introduce CGLearn, a
general framework designed to improve the gener-
alization of machine learning models by leveraging
gradient consistency across different environments.
CGLearn does not require extensive domain knowl-
edge or assumptions over data linearity or noise, mak-
ing it a versatile and practical approach for learning
robust predictive models. By focusing on feature in-
variance, emphasizing on reliable features, and reduc-
ing dependence on spurious correlations, CGLearn
enhances the reliability and robustness of the mod-
els. The main contributions of this study are stated as
follows:
• We propose a novel general framework, CGLearn,
which improves consistency in learning robust
predictors by focusing on features that show con-
sistent behavior across environments.
• We provide both linear and nonlinear implemen-
tations of CGLearn, demonstrating its versatility
and applicability across different model architec-
tures.
• We demonstrate that CGLearn achieves superior
ICPRAM 2025 - 14th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
104
predictive power and generalization, even without
multiple environments, unlike most state-of-the-
art methods in this arena that require diverse envi-
ronments for effective generalization.
• Our empirical evaluations on synthetic and real-
world datasets, covering both linear and nonlinear
settings, as well as regression and classification
tasks, validate the effectiveness and robustness of
the proposed method.
The remainder of this paper is organized as fol-
lows: First, we delve into the methodology of
CGLearn, detailing its linear and nonlinear imple-
mentations. Next, we present our experimental set-
tings and evaluations. Finally, we encapsulate our
conclusions, highlight the significant takeaways, and
discuss future directions.
2 METHODOLOGY
In this section, we present the methodology of
CGLearn, detailing both its linear and nonlinear im-
plementations. We start by explaining the regular Em-
pirical Risk Minimization (ERM) approach and then
introduce the concept of gradient consistency used in
CGLearn. The primary concept of CGLearn is to en-
force gradient consistency for each factor of our vari-
able of interest across multiple environments to iden-
tify and utilize invariant features, thereby enhancing
generalization and reducing dependence on spurious
correlations.
2.1 Empirical Risk Minimization
(ERM)
Let’s consider a simple linear problem where the goal
is to predict the target variable Y using two features
X
1
(causal) and X
2
(spurious) across multiple envi-
ronments. Let e
1
, e
2
, . . . , e
m
represent different envi-
ronments. Environments can be considered as distinct
distributions generated by different interventions, all
of which share similar underlying causal mechanisms
(see Figure. 1).
In the ERM framework, the weights for the fea-
tures are updated by minimizing the empirical risk
or the cost function (L), which is typically the mean
squared error (MSE) between the predicted and actual
values for a regression problem and cross-entropy loss
for a classification task. Suppose the weights for the
features at step t are w
t
1
for X
1
and w
t
2
for X
2
. The
gradient of the loss (L) with respect to the weight as-
sociated with the j-th feature X
j
in environment e
i
is
given by ∇L
e
i
j
, where j ∈ {1, 2} and i ∈ {1, . . . , m}.
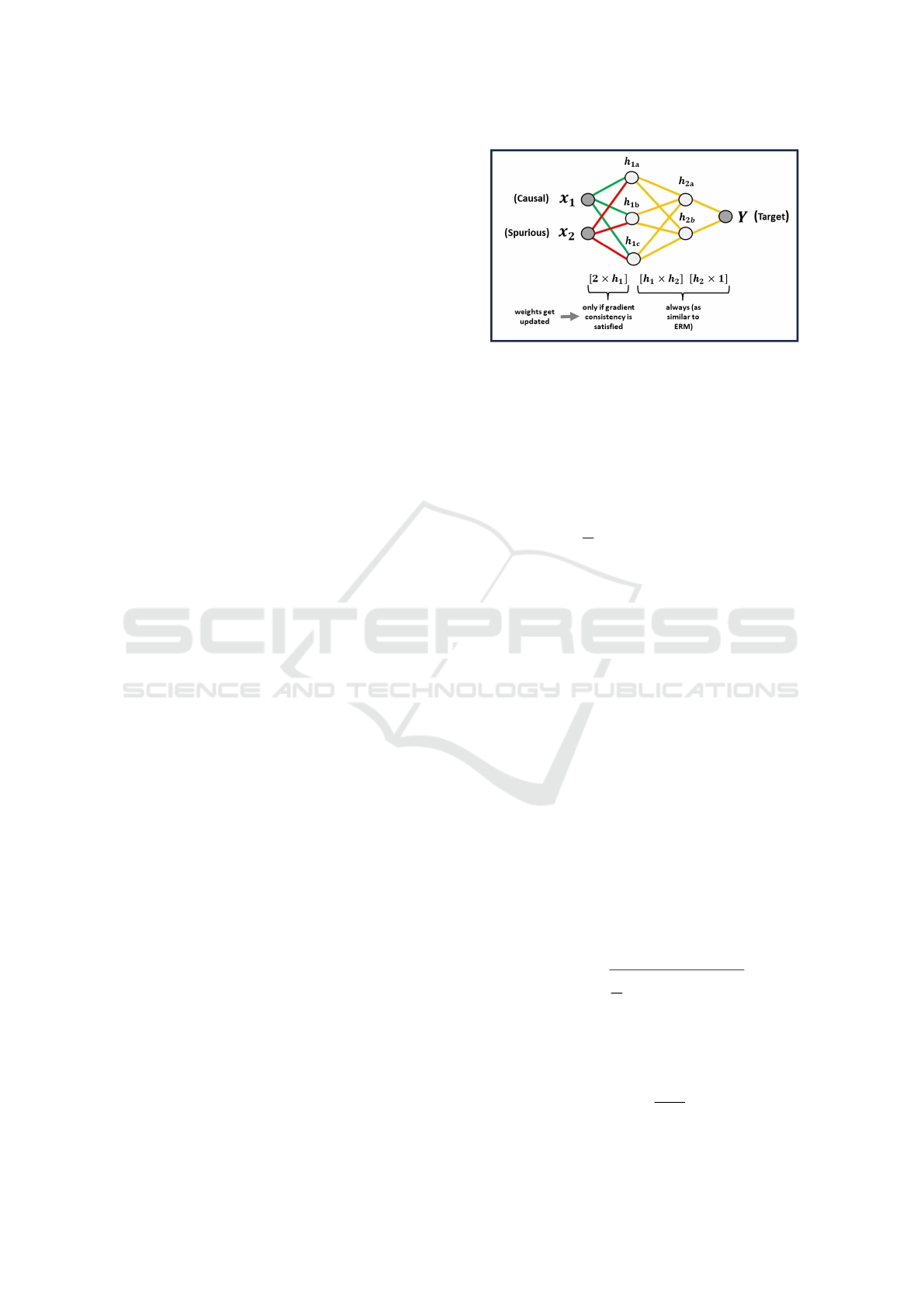
Figure 2: Nonlinear MLP implementation of CGLearn. X
1
(causal) and X
2
(spurious) feed into the first hidden layer h
1
.
Weight updates in h
1
are performed based on gradient con-
sistency (using L
2
-norm) for each feature across all training
environments. The rest of the weights such as weights in h
2
,
are updated similarly to ERM (without imposing any con-
sistency constraints).
The aggregated gradient across all environments
can be calculated as the mean of the gradients:
µ
grad
j
=
1
m
m
∑
i=1
∇L
e
i
j
for j ∈ {1, 2} (1)
Using this aggregated gradient, the weights are
updated as follows:
w
t+1
j
= w
t
j
− ηµ
grad
j
for j ∈ {1, 2} (2)
where η is the learning rate. In this setup of a standard
Empirical Risk Minimization, the weights for both X
1
and X
2
get updated in each step regardless of their
consistency across environments.
2.2 Linear Implementation of CGLearn
CGLearn modifies this approach by introducing a
consistency check for the gradients. The idea is to
update the weights only if the gradients are consistent
across the available environments. This strategy fo-
cuses on invariant features and ignores spurious ones,
expecting better generalization.
First, we calculate the gradient of each feature in
every environment, as described in the previous sec-
tion. The mean of the gradients can be calculated as
described in Eq. 1. Next, we compute the standard
deviation of the gradients for each feature across all
environments as follows:
σ
grad
j
=
s
1
m
m
∑
i=1
∇L
e
i
j
− µ
grad
j
2
(3)
We then calculate the consistency ratio, which is
the absolute value of the ratio of the mean gradient to
the standard deviation of the gradients:
C
ratio
j
=
µ
grad
j
σ
grad
j
(4)
CGLearn: Consistent Gradient-Based Learning for Out-of-Distribution Generalization
105

The consistency ratio, C
ratio
j
defined in Eq. 4, is
considered to be an indicator of the invariance of the
gradient of variable X
j
across all the training environ-
ments. A relatively larger mean compared to the stan-
dard deviation would indicate more similar or invari-
ant gradients across the environments for the feature
X
j
, resulting in a higher value of C
ratio
j
. On the other
hand, a larger standard deviation indicates more di-
versity across the environments for X
j
. Finally, we
formulate a consistency mask based on a predefined
threshold C
thresh
:
C
mask
j
=
(
1 if C
ratio
j
≥ C
thresh
0 otherwise
(5)
The weights are updated only for the feature that
has a nonzero mask and remains unchanged otherwise
as per the following equation:
w
t+1
j
= w
t
j
− η
µ
grad
j
·C
mask
j
for j ∈ {1, 2} (6)
Considering our motivating example, where X
1
is
causal and expected to show more consistency across
environments, C
mask
1
is expected to be 1. Conversely,
X
2
is spurious with respect to the target, expected to
show inconsistency across environments, and C
mask
2
is expected to be 0. Therefore, the weight for X
1
is
mostly updated throughout the training steps while
the weight for X
2
is not. The model thus focuses
on the features that show consistency for learning the
predictors of the target. This implementation strat-
egy ensures to emphasis on reliable, invariant features
while minimizing the impact of unreliable features
by keeping their weights unchanged (or keeping the
changes to a minimum). As a result, the contributions
of the spurious features remain constant in the context
of the model updates. In the next section, we extend
the CGLearn method to a nonlinear setting using mul-
tilayer perceptron (MLP) as an instance.
2.3 Nonlinear Implementation
For the nonlinear implementation of CGLearn using a
multilayer perceptron (MLP), we focus on the gradi-
ents in the first hidden layer (h
1
), where feature con-
tributions can be distinctly identified. By controlling
the contribution of spurious features at the first hidden
layer, we ensure they do not influence the final output.
The process involves calculating the L
2
-norm of the
gradients for each feature in each environment, fol-
lowed by determining the consistency ratio and mask
to impose the consistency constraint.
∥∇L
e
i
jh
1
∥
2
denotes the L
2
-norm of the gradients of
the j-th feature X
j
in the i-th environment e
i
at the first
hidden layer h
1
. We compute the mean and standard
deviation of the L
2
-norm of the gradients across all
environments as follows:
µ
grad
j
=
1
m
m
∑
i=1
∥∇L
e
i
jh
1
∥
2
(7)
σ
grad
j
=
s
1
m
m
∑
i=1
∥∇L
e
i
jh
1
∥
2
− µ
grad
j
2
(8)
We then calculate the consistency ratio, C
ratio
j
and
the consistency mask, C
mask
j
for feature X
j
by follow-
ing Eq. 4 and 5 respectively. All the weights that
belong to a particular feature, X
j
in the first hidden
layer h
1
, are updated by following a similar strategy
to Eq. 6. This updating strategy that depends on the
consistency ratio, ensures that only the features that
show consistency across the environments are consid-
ered to be updated. Otherwise, the weights remain un-
changed, effectively treating them as constants similar
to the linear implementation. For weights correspond-
ing to the rest of the model other than the first hidden
layer are updated as similar to ERM.
Figure. 2 illustrates a simple demonstration of the
nonlinear MLP implementation of CGLearn. In this
figure, X
1
and X
2
represent causal and spurious fea-
tures, respectively, in accordance with our earlier mo-
tivating example. The gradient consistency is checked
in the first hidden layer (h
1
), and weights are updated
only if the consistency ratio exceeds the threshold, en-
suring that features that show invariance across envi-
ronments are utilized.
In both implementations, the goal is to ensure
that the model relies on features that show invariance
across different environments. This leads to more
robust and generalizable models by reducing depen-
dency on spurious correlations.
3 EXPERIMENTS AND RESULTS
We have considered three different major scenarios
to assess the predictivity, robustness, and generaliza-
tion capabilities of CGLearn. The first two scenarios
are the ones where we considered linearly generated
dataset-based experiments and in the last experimen-
tal case we have used the nonlinear implementation
of CGLearn using multilayer perceptron (MLP) and
applied it to different real world regression and clas-
sification tasks.
For all evaluations, we reported the mean and
standard deviation of the performance metrics consid-
ered. For statistical significance tests, we used a t-test
with α = 0.05 as the significance level.
ICPRAM 2025 - 14th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
106
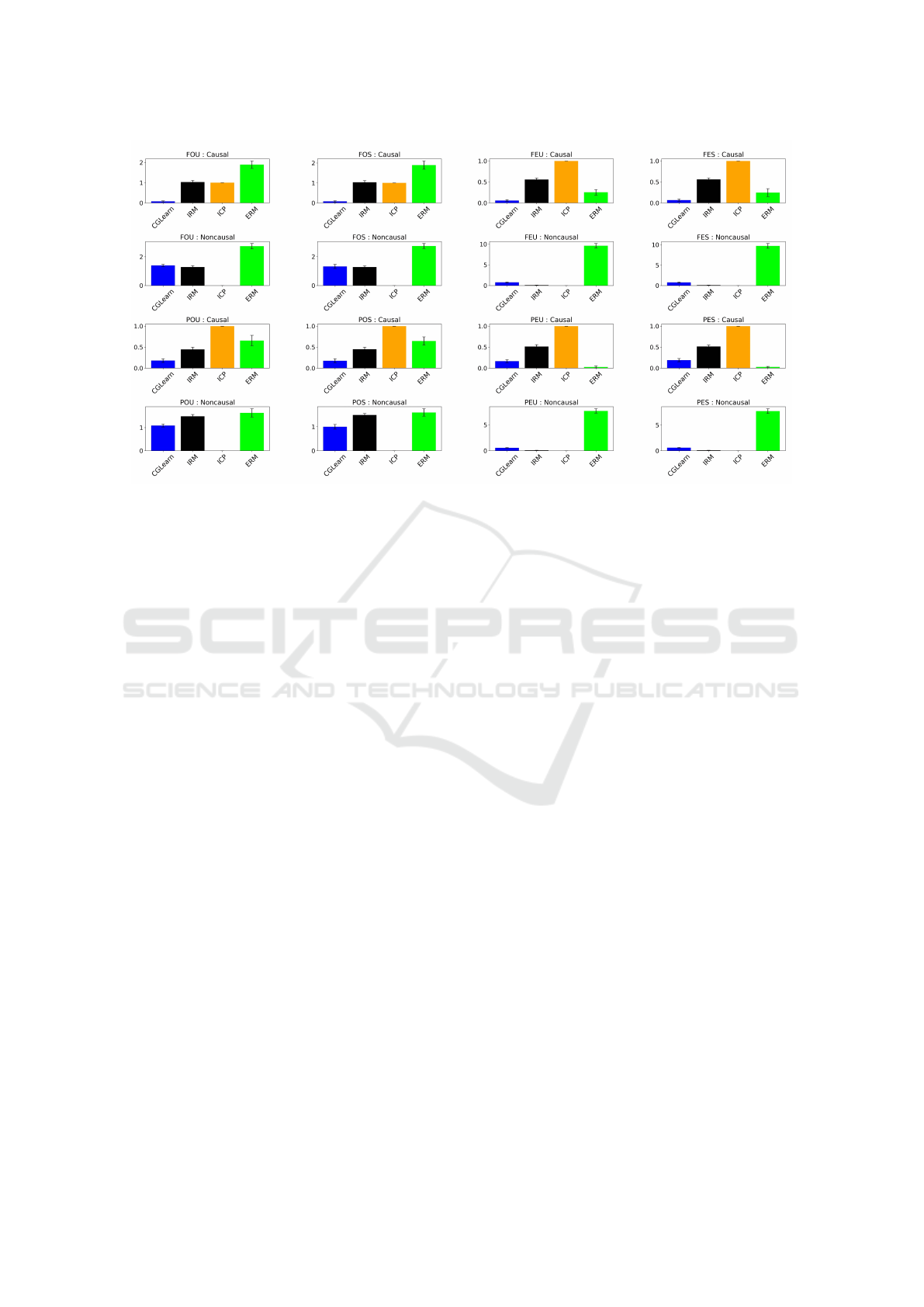
Figure 3: Performance comparison of CGLearn, IRM, ICP, and ERM across various linear multiple environment setups.
Each subplot represents different configurations of the data, showing the mean squared error (MSE) for causal and noncausal
variables over 50 trials.
3.1 Linear Multiple Environments
To evaluate the performance of our proposed
CGLearn method, we generated synthetic linear
datasets inspired by the approach used in the Invariant
Risk Minimization (IRM) framework (Arjovsky et al.,
2019). Our goal was to create diverse environments to
test the robustness of our model under varying condi-
tions.
We generated eight different experimental setups
based on three key factors. Each setup included
datasets with one target variable Y and ten feature
variables X
1
to X
10
. Features X
1
to X
5
acted as causal
parents of Y , while X
6
to X
10
were influenced by Y
(non-causal). First, we distinguished between scram-
bled (S) and unscrambled (U) observations by apply-
ing an orthogonal transformation matrix S for scram-
bled data and using the identity matrix I for unscram-
bled data. This scrambling ensures that the features
are not directly aligned with their original scales,
making the learning task more challenging. Second,
we designed fully-observed (F) scenarios where hid-
den confounders did not directly affect the features
(i.e., no hidden confounder effects on features), and
partially-observed (P) scenarios where hidden con-
founders influenced the features with Gaussian noise.
Third, we incorporated two types of noise for the tar-
get variable Y : homoskedastic (O) noise, where the
noise variance remained constant across different en-
vironments, and heteroskedastic (E) noise, where the
noise variance varied depending on the environment,
increasing with higher values of e. This distinction
captures different real-world scenarios where noise
may or may not depend on external factors. For each
of these eight configurations (combinations of S/U,
F/P, and O/E), we generated datasets corresponding
to three distinct environments defined by the values
e ∈ {0.2, 2, 5}. Each dataset consisted of 1000 sam-
ples. To ensure consistency with the IRM methodol-
ogy and experimental setup, we used e = 5 as the val-
idation environment and determined the optimal con-
sistency threshold (C
thresh
) for our CGLearn method
using the performance based on this validation data.
We selected the threshold C
thresh
from the candidate
values {0.25, 1, 4, 16, 64} based on validation perfor-
mance. This threshold, which varies based on the pro-
portion of causal and spurious features in the dataset,
is critical for identifying the invariant and most reli-
able features across different environments. For more
details on the data generation process, we refer read-
ers to the IRM paper (Arjovsky et al., 2019).
We compared the performance of CGLearn
with Empirical Risk Minimization (ERM), Invariant
Causal Prediction (ICP) (Peters et al., 2016), and IRM
(Arjovsky et al., 2019). We considered 50 random
trials and reported the results in Figure. 3. In most
cases, our proposed method CGLearn achieves the
lowest mean squared error (MSE), demonstrating su-
perior performance across various test cases to distin-
guish the causal and noncausal factors of the target
by exploiting invariance across environments. IRM
performs better than ERM but does not match the ac-
curacy of CGLearn. ERM shows the highest errors in
most cases, as it fails to differentiate between causal
CGLearn: Consistent Gradient-Based Learning for Out-of-Distribution Generalization
107

and noncausal features, relying on spurious correla-
tions. Interestingly, ICP performs well in noncausal
scenarios but poorly in causal ones. This observa-
tion aligns with the findings from the IRM study (Ar-
jovsky et al., 2019), which noted that ICP’s conserva-
tive nature leads it to reject most covariates as direct
causes, resulting in high causal errors.
3.2 Linear Single Environment
To evaluate the performance of our proposed
CGLearn method in scenarios with only one environ-
ment, we generated synthetic linear datasets without
relying on multiple environments as in previous ex-
periments. For each of the eight cases, we used a sin-
gle setting with e = 2. The data generation process
was similar to the previous section, with each dataset
consisting of 1000 samples and ten feature variables,
X
1
to X
10
. The first five features (X
1
to X
5
) acted as
causal parents of the target variable Y , while the re-
maining five features (X
6
to X
10
) were influenced by
Y . Given the single environment setup, we could not
apply IRM and ICP methods, as they require multiple
environments to distinguish between causal and non-
causal factors. Therefore, we compared our results
solely with Empirical Risk Minimization (ERM).
In the case of CGLearn, we created multiple
batches, with b = {3, 5} representing the number of
batches created from the dataset. The last batch was
used as the validation batch to determine the opti-
mal consistency threshold parameter (C
thresh
). We
selected the threshold C
thresh
from the candidate val-
ues {0.25, 1, 4, 16, 64} based on validation perfor-
mance. We imposed gradient consistency across dif-
ferent batches to learn consistent and reliable factors
of the target.
Table 1 shows the results of our experiments
in the single environment setup. Considering the
causal error across all eight cases, CGLearn consis-
tently achieves significantly lower mean squared er-
rors (MSE) compared to ERM. For the noncausal er-
ror, CGLearn also outperforms ERM in most cases,
suggesting the superiority of the proposed approach.
Even in the absence of multiple environments, the
optimization strategy based on gradient consistency
across different batches enables CGLearn to achieve
better predictive power than standard ERM.
3.3 Nonlinear Multiple Environments
For the nonlinear experimental setups, we considered
two types of supervised learning tasks: regression and
classification, both on real-world datasets. This ap-
proach allows us to evaluate the performance and ro-
bustness of our proposed CGLearn method in differ-
ent real-world contexts. Recent work has highlighted
limitations in the original Invariant Risk Minimiza-
tion (IRM) framework, particularly in nonlinear set-
tings where deep models tend to overfit (Rosenfeld
et al., 2021). To address this, we included Bayesian
Invariant Risk Minimization (BIRM) as a baseline,
which has been shown to alleviate overfitting issues
by incorporating Bayesian inference and thereby im-
proving generalization in nonlinear scenarios (Lin
et al., 2022).
Regression Tasks. In the nonlinear implemen-
tation of CGLearn, we used a multilayer perceptron
(MLP) to evaluate its performance on real-world re-
gression tasks, comparing it with other baselines. For
the regression tasks, we used the Boston Housing
dataset (Harrison and Rubinfeld, 1978) and the Yacht
Hydrodynamics dataset (Gerritsma et al., 2013). The
Boston Housing dataset consists of 506 instances and
13 continuous attributes. It concerns housing values
in suburbs of Boston, with the task being to predict
the median value of owner-occupied homes (MEDV)
based on attributes such as per capita crime rate
(CRIM), proportion of residential land zoned for large
lots (ZN), average number of rooms per dwelling, and
etc. The Yacht Hydrodynamics dataset consists of
308 instances and 6 attributes. The task is to predict
the residuary resistance per unit weight of displace-
ment of a yacht based on various hull geometry co-
efficients and the Froude number, such as the longi-
tudinal position of the center of buoyancy, prismatic
coefficient, and beam-draught ratio.
Since real-world datasets do not naturally come
with different environments, we followed a similar
approach to the study in Ref. (Ge et al., 2022). We
used the K-Means (Lloyd, 1982) clustering algorithm
to generate diverse environments and determined the
optimal number of environments (between 3 to 10)
using the Silhouette (Rousseeuw, 1987) method. For
each dataset, we created all possible test cases where
each environment was considered as the test environ-
ment once, and the rest were used as training envi-
ronments. We averaged the results over all possible
test cases and repeated the process for 10 random tri-
als. We evaluated the models based on RMSE, with
the results shown in Table 2. For the Boston Hous-
ing dataset, we found the optimal number of envi-
ronments was 7, while for the Yacht Hydrodynamics
dataset, it was 5. From Table 2, we observe that all
four methods perform better on the training environ-
ments than the test environments, as expected. How-
ever, CGLearn shows significantly lower error in the
testing or unseen environments compared to the other
methods, demonstrating that imposing gradient con-
ICPRAM 2025 - 14th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
108
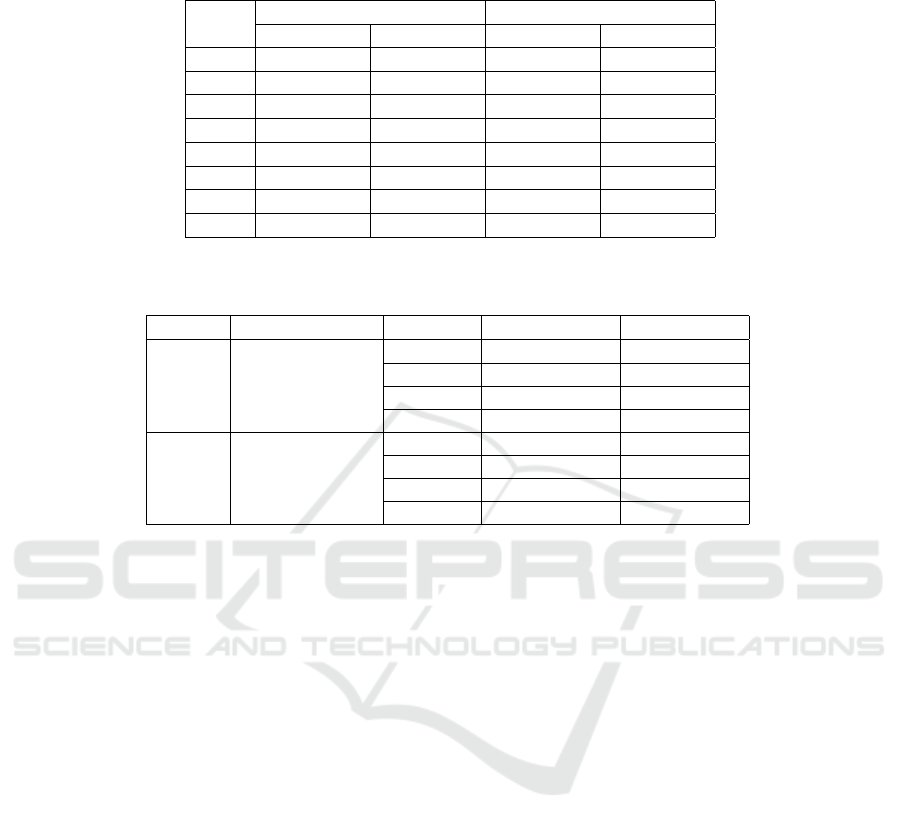
Table 1: Performance evaluation of CGLearn and ERM in linear single environmental setups. The table shows the Mean
Squared Errors (MSE) for causal and noncausal variables across 50 trials for each configuration.
Cases
Causal Error (MSE) Noncausal Error (MSE)
CGLearn ERM CGLearn ERM
FOU 1.28 ± 0.40 1.57 ± 0.13 0.61 ± 0.19 0.54 ± 0.05
FOS 1.40 ± 0.43 1.61 ± 0.10 0.53 ± 0.17 0.52 ± 0.06
FEU 0.13 ± 0.05 0.20 ± 0.04 7.22 ± 2.15 8.28 ± 0.28
FES 0.16 ± 0.06 0.20 ± 0.04 7.47 ± 2.23 8.36 ± 0.30
POU 0.28 ± 0.11 0.37 ± 0.08 0.51 ± 0.18 0.48 ± 0.11
POS 0.34 ± 0.13 0.39 ± 0.07 0.46 ± 0.17 0.48 ± 0.10
PEU 0.24 ± 0.10 0.32 ± 0.07 5.11 ± 1.57 5.83 ± 0.43
PES 0.26 ± 0.10 0.31 ± 0.06 5.21 ± 1.58 5.81 ± 0.36
Table 2: Performance comparison in nonlinear experimental setups for regression tasks. The table shows the RMSE for
training and test environments across 10 trials.
Dataset # Optimal Envs. Method RMSE (Train) RMSE (Test)
Boston 7
ERM 3.57 ± 0.11 6.43 ± 0.45
IRM 3.79 ± 0.33 6.99 ± 0.74
BIRM 3.77 ± 0.50 7.70 ± 0.52
CGLearn 1.91 ± 0.26 5.49 ± 0.28
Yacht 5
ERM 0.21 ± 0.04 3.47 ± 1.15
IRM 2.90 ± 0.03 4.36 ± 0.38
BIRM 0.71 ± 0.19 3.15 ± 0.75
CGLearn 0.48 ± 0.23 2.29 ± 0.42
sistency leads to less dependence on spurious features
and thus better generalization.
Classification Tasks. For the classification tasks,
we evaluated the performance on two real-world clas-
sification datasets: the Wine Quality dataset for red
and white wines from the UCI repository (Cortez
et al., 2009). The Wine Quality dataset for red wine
has 1599 instances and 11 attributes, while the dataset
for white wine has 4898 instances and 11 attributes.
The goal is to model wine quality based on physic-
ochemical tests, such as fixed acidity, volatile acid-
ity, citric acid, residual sugar, pH, and etc. Similar
to the regression tasks, we used K-means clustering
to generate diverse environments and determined the
optimal number of environments using the Silhouette
method, finding 4 as the optimal number of environ-
ments for both classification datasets. We then gener-
ated all possible test cases where each environment
was considered the test environment once, and the
rest were used as training environments (as we did
with the regression tasks). We averaged the perfor-
mance over all possible test cases and conducted the
process for 10 random trials. We used accuracy and
F1-score as evaluation metrics, with the results shown
in Table 3. As expected, all methods performed bet-
ter in training environments compared to test environ-
ments. However, we found that CGLearn achieved
higher accuracy and F1-scores, which are desirable,
and the superior performance was statistically signifi-
cant for the F1-score on the Wine Quality Red dataset.
It also had significantly better accuracy on the Wine
Quality White dataset. Similar to the regression tasks,
CGLearn demonstrated better predictive power and
generalization over ERM, IRM, and BIRM for the
classification tasks.
Limitations of CGLearn with Invariant Spuri-
ous Features. We evaluated CGLearn on the Col-
ored MNIST dataset, a synthetic binary classification
task derived from MNIST (LeCun et al., 1995) and
proposed in the IRM study (Arjovsky et al., 2019).
This dataset introduces color as a spurious feature that
strongly correlates with the label in the training envi-
ronments but has the correlation reversed in the test
environment. We applied the nonlinear implemen-
tation of CGLearn and compared it with the results
of ERM and IRM as reported in the IRM study (Ar-
jovsky et al., 2019). Over 10 trials, ERM achieved a
training accuracy of 87.4 ± 0.2 and a test accuracy of
17.1 ± 0.6, while IRM achieved a training accuracy
of 70.8 ± 0.9 and a test accuracy of 66.9 ± 2.5. In
our experimental study, CGLearn achieved a training
accuracy of 93.1 ± 0.8 and a test accuracy of 29.1 ±
0.8. While CGLearn slightly outperformed ERM in
the test environment, it still struggled to generalize.
This limitation arises because CGLearn imposes gra-
dient consistency on the training environments to dis-
CGLearn: Consistent Gradient-Based Learning for Out-of-Distribution Generalization
109
Table 3: Performance comparison in nonlinear setups for classification tasks. The table shows accuracy and F1-score for
training and test environments across 10 trials. WQ Red and WQ White represent the Wine Quality Red and Wine Quality
White datasets respectively.
Dataset # Optimal Envs. Method Accuracy (Train) Accuracy (Test) F1-score (Train) F1-score (Test)
WQ Red 4
ERM 62.07 ± 0.34 58.08 ± 1.72 0.692 ± 0.004 0.535 ± 0.010
IRM 63.68 ± 0.19 58.70 ± 1.54 0.644 ± 0.003 0.542 ± 0.014
BIRM 64.94 ± 0.37 57.97 ± 0.93 0.626 ± 0.004 0.536 ± 0.011
CGLearn 61.59 ± 0.44 59.60 ± 0.46 0.638 ± 0.008 0.553 ± 0.007
WQ White 4
ERM 58.73 ± 0.22 51.15 ± 0.34 0.590 ± 0.002 0.447 ± 0.008
IRM 58.82 ± 0.26 51.60 ± 0.40 0.566 ± 0.003 0.450 ± 0.013
BIRM 58.04 ± 0.18 51.87 ± 0.32 0.530 ± 0.006 0.460 ± 0.026
CGLearn 58.23 ± 0.38 52.33 ± 0.32 0.555 ± 0.005 0.460 ± 0.007
tinguish invariant features from spurious ones. How-
ever, in the Colored MNIST setup, the spurious fea-
ture (color) is consistent across both training environ-
ments, leading CGLearn to erroneously treat it as an
invariant feature. Consequently, CGLearn relies on
color and performs poorly in the test environment.
This highlights a limitation of the proposed method,
as it may fail to meet expectations in scenarios where
spurious relationships remain invariant across envi-
ronments. To improve CGLearn’s generalization, fu-
ture work should focus on adapting the method to ac-
count for the varying nature of spurious features, even
when they appear consistent across training environ-
ments.
4 CONCLUSIONS
In this study, we presented CGLearn, a novel ap-
proach for developing robust and predictive machine
learning models by leveraging gradient consistency
across multiple environments. By focusing on the
agreement of gradients, CGLearn effectively identi-
fies and utilizes invariant features, leading to supe-
rior generalization and reduced reliance on spurious
correlations. Our extensive experiments on both syn-
thetic and real-world datasets, including regression
and classification tasks, demonstrated that CGLearn
outperforms traditional ERM and state-of-the-art in-
variant learners like ICP, IRM, and BIRM, achieving
lower errors and better generalization in diverse sce-
narios. Notably, even in the absence of predefined
environments, we demonstrated that CGLearn can be
effectively applied to different subsamples of data,
leading to better predictive models than regular ERM.
This flexibility enhances the applicability of CGLearn
in a wide range of real-world scenarios where many
state-of-the-art methods require diverse and defined
environments for OOD generalization.
Despite its strengths, CGLearn has limitations,
particularly in scenarios where spurious features are
invariant across environments, as observed in the Col-
ored MNIST experiments. Such cases violate our as-
sumption as generally we expect and observe causal
features to be stable and invariant in nature whereas
spurious features do not (Woodward, 2005; Wang
et al., 2022). CGLearn erroneously considers these
invariant but spurious features as reliable, impacting
its generalization performance. Addressing this lim-
itation and adapting CGLearn to better handle such
cases is a promising direction for future research.
Overall, CGLearn provides a significant step for-
ward in the field of robust machine learning by ef-
fectively harnessing causal invariance. Our work
opens new avenues for developing models that are not
only highly predictive but also resilient to distribution
shifts, paving the way for more reliable applications
in real-world settings.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Research was sponsored by the Army Research Of-
fice under Grant Number W911NF-22-1-0035 and by
the National Science Foundation under Award Num-
ber 2218841. The views and conclusions contained in
this document are those of the authors and should not
be interpreted as representing the official policies, ei-
ther expressed or implied, of the Army Research Of-
fice or the U.S. Government. The U.S. Government
is authorized to reproduce and distribute reprints for
Government purposes notwithstanding any copyright
notation herein.
REFERENCES
Andrews, B., Spirtes, P., and Cooper, G. F. (2020). On the
completeness of causal discovery in the presence of la-
tent confounding with tiered background knowledge.
In International Conference on Artificial Intelligence
and Statistics, pages 4002–4011. PMLR.
Arjovsky, M., Bottou, L., Gulrajani, I., and Lopez-Paz, D.
ICPRAM 2025 - 14th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
110

(2019). Invariant risk minimization. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1907.02893.
Bose, R. and Roy, A. M. (2024). Invariance embedded
physics-infused deep neural network-based sub-grid
scale models for turbulent flows. Engineering Appli-
cations of Artificial Intelligence, 128:107483.
Chickering, D. M. (2002). Optimal structure identification
with greedy search. Journal of Machine Learning Re-
search, 3(Nov):507–554.
Chowdhury, J., Fricke, C., Bamidele, O., Bello, M., Yang,
W., Heyden, A., and Terejanu, G. (2024). Invariant
molecular representations for heterogeneous cataly-
sis. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling,
64(2):327–339.
Chowdhury., J., Rashid., R., and Terejanu., G. (2023). Eval-
uation of induced expert knowledge in causal struc-
ture learning by notears. In Proceedings of the 12th
International Conference on Pattern Recognition Ap-
plications and Methods - ICPRAM, pages 136–146.
INSTICC, SciTePress.
Chowdhury, J. and Terejanu, G. (2023). Cd-notears: Con-
cept driven causal structure learning using notears. In
2023 International Conference on Machine Learning
and Applications (ICMLA), pages 808–813. IEEE.
Colombo, D., Maathuis, M. H., Kalisch, M., and Richard-
son, T. S. (2012). Learning high-dimensional directed
acyclic graphs with latent and selection variables. The
Annals of Statistics, pages 294–321.
Cortez, P., Cerdeira, A., Almeida, F., Matos, T., and Reis, J.
(2009). Wine Quality. UCI Machine Learning Repos-
itory. DOI: https://doi.org/10.24432/C56S3T.
Ge, Y., Arik, S.
¨
O., Yoon, J., Xu, A., Itti, L., and Pfister,
T. (2022). Invariant structure learning for better gen-
eralization and causal explainability. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2206.06469.
Gencoglu, O. and Gruber, M. (2020). Causal modeling
of twitter activity during covid-19. Computation,
8(4):85.
Gerritsma, J., Onnink, R., and Versluis, A. (2013). Yacht
Hydrodynamics. UCI Machine Learning Repository.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.24432/C5XG7R.
Harrison, D. and Rubinfeld, D. L. (1978). Hedonic prices
and the demand for clean air. J. Environ. Econ. and
Management. UCI Machine Learning Repository,
http://lib.stat.cmu.edu/datasets/boston.
He, Y., Shen, Z., and Cui, P. (2021). Towards non-iid im-
age classification: A dataset and baselines. Pattern
Recognition, 110:107383.
Huang, B., Zhang, K., Lin, Y., Sch
¨
olkopf, B., and Glymour,
C. (2018). Generalized score functions for causal dis-
covery. In Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGKDD
international conference on knowledge discovery &
data mining, pages 1551–1560.
Jiang, G.-q., Liu, J., Ding, Z., Guo, L., and Lin, W. (2023).
Accelerating large batch training via gradient signal to
noise ratio (gsnr). arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.13681.
Kaiser, M. and Sipos, M. (2022). Unsuitability of notears
for causal graph discovery when dealing with di-
mensional quantities. Neural Processing Letters,
54(3):1587–1595.
Koyama, M. and Yamaguchi, S. (2020). Out-of-distribution
generalization with maximal invariant predictor.
Lachapelle, S., Brouillard, P., Deleu, T., and Lacoste-Julien,
S. (2019). Gradient-based neural dag learning. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1906.02226.
LeCun, Y., Jackel, L. D., Bottou, L., Cortes, C., Denker,
J. S., Drucker, H., Guyon, I., Muller, U. A., Sackinger,
E., Simard, P., et al. (1995). Learning algorithms
for classification: A comparison on handwritten digit
recognition. Neural networks: the statistical mechan-
ics perspective, 261(276):2.
Lin, Y., Dong, H., Wang, H., and Zhang, T. (2022).
Bayesian invariant risk minimization. In Proceedings
of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and
Pattern Recognition, pages 16021–16030.
Liu, J., Chen, Y., and Zhao, J. (2021). Knowledge enhanced
event causality identification with mention masking
generalizations. In Proceedings of the twenty-ninth
international conference on international joint confer-
ences on artificial intelligence, pages 3608–3614.
Liu, J., Jiang, G., Bai, Y., Chen, T., and Wang, H.
(2020). Understanding why neural networks gener-
alize well through gsnr of parameters. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2001.07384.
Lloyd, S. (1982). Least squares quantization in pcm. IEEE
transactions on information theory, 28(2):129–137.
Ming, Y., Yin, H., and Li, Y. (2022). On the impact of
spurious correlation for out-of-distribution detection.
In Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial
intelligence, volume 36, pages 10051–10059.
Montavon, G., Hansen, K., Fazli, S., Rupp, M., Biegler,
F., Ziehe, A., Tkatchenko, A., Lilienfeld, A., and
M
¨
uller, K.-R. (2012). Learning invariant representa-
tions of molecules for atomization energy prediction.
Advances in neural information processing systems,
25.
Ng, I., Ghassami, A., and Zhang, K. (2020). On the role of
sparsity and dag constraints for learning linear dags.
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems,
33:17943–17954.
Ng, I., Zhu, S., Fang, Z., Li, H., Chen, Z., and Wang, J.
(2022). Masked gradient-based causal structure learn-
ing. In Proceedings of the 2022 SIAM International
Conference on Data Mining (SDM), pages 424–432.
SIAM.
Ormaniec, W., Sussex, S., Lorch, L., Sch
¨
olkopf, B., and
Krause, A. (2024). Standardizing structural causal
models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.11601.
O’Donnell, R. T., Nicholson, A. E., Han, B., Korb, K. B.,
Alam, M. J., and Hope, L. R. (2006). Causal discov-
ery with prior information. In AI 2006: Advances in
Artificial Intelligence: 19th Australian Joint Confer-
ence on Artificial Intelligence, Hobart, Australia, De-
cember 4-8, 2006. Proceedings 19, pages 1162–1167.
Springer.
Parascandolo, G., Neitz, A., Orvieto, A., Gresele, L., and
Sch
¨
olkopf, B. (2020). Learning explanations that are
hard to vary. arXiv preprint arXiv:2009.00329.
Pearl, J. (2009). Causality. Cambridge university press.
CGLearn: Consistent Gradient-Based Learning for Out-of-Distribution Generalization
111

Peters, J., B
¨
uhlmann, P., and Meinshausen, N. (2016).
Causal inference by using invariant prediction: identi-
fication and confidence intervals. Journal of the Royal
Statistical Society Series B: Statistical Methodology,
78(5):947–1012.
Rame, A., Dancette, C., and Cord, M. (2022). Fishr: In-
variant gradient variances for out-of-distribution gen-
eralization. In International Conference on Machine
Learning, pages 18347–18377. PMLR.
Ramsey, J., Glymour, M., Sanchez-Romero, R., and Gly-
mour, C. (2017). A million variables and more: the
fast greedy equivalence search algorithm for learn-
ing high-dimensional graphical causal models, with
an application to functional magnetic resonance im-
ages. International Journal of Data Science and Ana-
lytics, 3:121–129.
Reisach, A., Seiler, C., and Weichwald, S. (2021). Beware
of the simulated dag! causal discovery benchmarks
may be easy to game. Advances in Neural Information
Processing Systems, 34:27772–27784.
Reisach, A., Tami, M., Seiler, C., Chambaz, A., and Weich-
wald, S. (2024). A scale-invariant sorting criterion to
find a causal order in additive noise models. Advances
in Neural Information Processing Systems, 36.
Rosenfeld, E., Ravikumar, P. K., and Risteski, A. (2021).
The risks of invariant risk minimization. In Interna-
tional Conference on Learning Representations.
Rousseeuw, P. J. (1987). Silhouettes: a graphical aid to
the interpretation and validation of cluster analysis.
Journal of computational and applied mathematics,
20:53–65.
Sagawa, S., Raghunathan, A., Koh, P. W., and Liang, P.
(2020). An investigation of why overparameterization
exacerbates spurious correlations. In International
Conference on Machine Learning, pages 8346–8356.
PMLR.
Santillan, B. G. (2023). A step towards the applicability of
algorithms based on invariant causal learning on ob-
servational data. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.02286.
Shi, Y., Seely, J., Torr, P. H., Siddharth, N., Hannun, A.,
Usunier, N., and Synnaeve, G. (2021). Gradient
matching for domain generalization. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2104.09937.
Shin, D. (2021). The effects of explainability and causabil-
ity on perception, trust, and acceptance: Implications
for explainable ai. International journal of human-
computer studies, 146:102551.
Spirtes, P., Glymour, C., and Scheines, R. (2001). Causa-
tion, prediction, and search. MIT press.
Torralba, A. and Efros, A. A. (2011). Unbiased look at
dataset bias. In CVPR 2011, pages 1521–1528. IEEE.
Wang, J., Lan, C., Liu, C., Ouyang, Y., Qin, T., Lu, W.,
Chen, Y., Zeng, W., and Philip, S. Y. (2022). General-
izing to unseen domains: A survey on domain gener-
alization. IEEE transactions on knowledge and data
engineering, 35(8):8052–8072.
Wang, Q., Zheng, Y., Yang, G., Jin, W., Chen, X., and
Yin, Y. (2017). Multiscale rotation-invariant convolu-
tional neural networks for lung texture classification.
IEEE journal of biomedical and health informatics,
22(1):184–195.
Wang, T., Sridhar, R., Yang, D., and Wang, X. (2021).
Identifying and mitigating spurious correlations for
improving robustness in nlp models. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2110.07736.
Wei, D., Gao, T., and Yu, Y. (2020). Dags with no fears:
A closer look at continuous optimization for learning
bayesian networks. Advances in Neural Information
Processing Systems, 33:3895–3906.
Woodward, J. (2005). Making things happen: A theory of
causal explanation. Oxford university press.
Yu, Y., Chen, J., Gao, T., and Yu, M. (2019). Dag-gnn:
Dag structure learning with graph neural networks. In
International conference on machine learning, pages
7154–7163. PMLR.
Zadrozny, B. (2004). Learning and evaluating classi-
fiers under sample selection bias. In Proceedings of
the twenty-first international conference on Machine
learning, page 114.
Zheng, X., Aragam, B., Ravikumar, P. K., and Xing, E. P.
(2018). Dags with no tears: Continuous optimization
for structure learning. Advances in neural information
processing systems, 31.
Zheng, X., Dan, C., Aragam, B., Ravikumar, P., and Xing,
E. (2020). Learning sparse nonparametric dags. In In-
ternational Conference on Artificial Intelligence and
Statistics, pages 3414–3425. Pmlr.
ICPRAM 2025 - 14th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
112
