
Automatic Ocular Artifact Correction in Electroencephalography for
Neurofeedback
Cassandra Dumas
1a
, Marie Constance Corsi
1b
, Claire Dussard
1c
, Fanny Grosselin
1,2 d
and Nathalie George
1,2 e
1
Sorbonne Université, Institut du Cerveau, Paris Brain Institute, ICM, Inserm, CNRS, APHP,
Hôpital de la Pitié Salpêtrière, Paris, France
2
Institut du Cerveau, ICM, Inserm, U1127, CNRS, UMR 7225, Sorbonne Université, CENIR,
Centre MEG-EEG, Paris, France
Keywords: Electroencephalography, Artifact Removal Methods, Blind Source Separation, Brain-Computer Interfaces.
Abstract: Ocular artifacts can significantly impact electroencephalography (EEG) signals, potentially compromising
the performance of neurofeedback (NF) and brain-computer interfaces (BCI) based on EEG. This study
investigates if the Approximate Joint Diagonalization of Fourier Cospectra (AJDC) method can effectively
correct blink-related artifacts and preserve relevant neurophysiological signatures in a pseudo-online context.
AJDC is a frequency-domain Blind Source Separation (BSS) technique, which uses cospectral analysis to
isolate and attenuate blink artifacts. Using EEG data from 21 participants recorded during a NF motor imagery
(MI) task, we compared AJDC with Independent Component Analysis (ICA), a widely used method for EEG
denoising. We assessed the quality of blink artifact correction, the preservation of MI-related EEG signatures,
and the influence of AJDC correction on the NF performance indicator. We show that AJDC effectively
attenuates blink artifacts without distorting MI-related beta band signatures and with preservation of NF
performance. AJDC was calibrated once on initial EEG data. We therefore assessed AJDC correction quality
over time, showing some decrease. This suggests that periodic recalibration may benefit long EEG recording.
This study highlights AJDC as a promising real-time solution for artifact management in NF, with the
potential to provide consistent EEG quality and to enhance NF reliability.
1 INTRODUCTION
Electroencephalography (EEG) enables the tracking
of electrical activity in large neuronal populations at
the scalp surface with millisecond-level precision.
Due to its non-invasive nature and exceptional
temporal resolution, EEG has become a cornerstone
in medical diagnostics (Thomas et al., 2021),
continuous health monitoring (Friedman et al., 2009),
and brain-controlled device operation (Al-Quraishi et
al., 2018). However, it faces significant challenges
due to its sensitivity to various artifacts – originating
from physiological, instrumental, and environmental
sources – which can severely degrade signal quality
(Tatum et al., 2011). This sensitivity necessitates
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5795-5700
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6262-5036
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7146-2486
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5512-8584
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1556-973X
continuous artifact management, as real-time
applications – such as Brain Computer Interface
(BCI) and neurofeedback (NF) systems, which
translate brain signals into commands – rely on
reliable data for effective interaction and feedback
(Lotte et al., 2015).
Eye blinks, particularly problematic during open-
eye sessions, are among the most disruptive artifacts,
because they produce high-amplitude fluctuations
across scalp channels (Iwasaki et al., 2005). Although
primarily concentrated in the delta (0.5 Hz – 4 Hz) and
theta (4 Hz – 8 Hz) bands, these artifacts can also
extend into the alpha (8 Hz – 13Hz) and beta (13 Hz –
30 Hz) bands (Hagemann & Naumann, 2001), thus
compromising signal integrity across many
Dumas, C., Corsi, M. C., Dussard, C., Grosselin, F. and George, N.
Automatic Ocular Artifact Correction in Electroencephalography for Neurofeedback.
DOI: 10.5220/0013260900003911
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 18th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2025) - Volume 1, pages 773-783
ISBN: 978-989-758-731-3; ISSN: 2184-4305
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
773

frequencies of interest in human electrophysiology.
Eye blinks have a distinctive spatial signature,
affecting signals primarily in the frontal and prefrontal
regions (Joyce et al., 2004). Thus, they can markedly
interfere with and hinder the decoding of brain activity
related to cognitive or motor tasks. Effective NF relies
on the precise, real-time extraction of EEG indicators,
often based on power within specific frequency bands.
This extraction is essential for training individuals to
modulate brain activity within these bands, supporting
processes of self-regulation and learning (Omejc et al.,
2019). While band-pass or notch filters are commonly
used in signal processing, they cannot be applied in this
context, as the blink-related artifactual activity
overlaps with the frequency bands of interest. Accurate
artifact filtering is therefore crucial, especially in NF
protocols where EEG signals serve as the basis for
feedback indicators. Inadequate handling of blink
artifacts can disrupt feedback quality, negatively
impacting NF training and real-time BCI performance
by distorting signals during training and interfering
with user control during live NF sessions (Jiang et al.,
2019).
Several artifact correction methods are widely
used in EEG signal processing, whether in real-time
or offline mode. Among them, one can cite blind
source separation (BSS) techniques, such as
independent component analysis (ICA) (Makeig et
al., 1996) frequency and time-frequency
decomposition methods, such as wavelet
decomposition (Zikov et al., 2002), regression-based
approaches (Croft & Barry, 2000), and artifact
subspace reconstruction (ASR) (Mullen et al., 2015).
Each method has strengths and limitations. On
one hand, effective methods such as ICA, regression,
and wavelet analysis require the manual intervention
of experts for optimal denoising, limiting their
suitability for real-time applications. ASR, on the
other hand, is advantageous for real-time settings due
to its ability to detect artifact components
automatically. However, it demands a calibration
phase of at least one minute with a clean signal, which
can pose practical difficulties when expert oversight
is unavailable, or calibration constraints are strict.
Additionally, mere artifact rejection is not desirable
in NF and BCI contexts, as these real-time
applications cannot afford the loss of data, which
would disrupt the continuity of feedback.
As Mumtaz et al., 2021 highlight, significant
challenges remain in achieving effective real-time
artifact correction. One key issue for BCI and NF
applications is the development of online correction
methods that are not only accurate but also quickly
and easily applicable in diverse environments.
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the
performance of a BSS technique, the Approximate
Joint Diagonalization of Fourier Cospectra (AJDC)
method (Congedo et al., 2008) for blink artifact
correction and assess its suitability for use in real-
time applications. AJDC is particularly promising
because it offers the advantage of calibration on short
data segments. We hypothesized that AJDC can
effectively reduce ocular artifacts while preserving
relevant neurophysiological signatures and that this
performance can be maintained even under online
constraints. To test these hypotheses, we compared
AJDC with ICA, which is widely adopted and
considered as a gold standard EEG denoising method.
This comparison was performed on a database of
motor-imagery (MI) based NF recordings from 21
subjects (Dussard et al., 2024). We analyzed, first,
blink artifact reduction and, second, EEG signal
preservation focusing on MI-related EEG signatures
in the beta band. Third, we examined the consistency
of NF performance with AJDC correction and the
robustness of AJDC over time.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Dataset and Preprocessing
2.1.1 Participants and EEG Acquisition
The data used in this study were the EEG data of 21
healthy participants (12 females, age: 28.5 ± 6.7 years
[mean ± SD]), which had been recorded in a single-
session NF study based on MI of the right hand (see
Dussard et al., 2024 for details of the original study).
EEG was recorded with a 32-channel active
electrode cap (ActiCAP Snap, Brain Products GmbH)
and an actiCHamp Plus amplification system (Brain
Products GmbH). The electrodes were positioned
according to the extended international 10-20 system
at the following sites: Fp1, Fp2, F7, F3, Fz, F4, F8,
FT9, FC5, FC1, FC2, FC6, FT10, T7, C3, Cz, C4, T8,
TP9, CP5, CP1, CP2, CP6, TP10, P7, P3, Pz, P4, P8,
O1, O2, and Oz. The reference electrode was placed
at Fz and the ground electrode at Fpz.
Electrode impedances were kept below 10 kΩ
wherever possible (median across electrode and
subjects = 11 ± 10 kΩ). During EEG recording,
participants were seated 80 cm from a computer
screen in a dimly lit Faraday room and were asked to
avoid moving to minimize artifacts. EEG data were
recorded with a sampling rate of 1 kHz and a DC-
280 Hz bandpass filter, using the BrainVision
recorder.
BIOSIGNALS 2025 - 18th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
774

2.1.2 Experimental Protocol
The experiment included six NF runs under three
different feedback modalities. Each run consisted of
five trials of 30 seconds each, with a one-minute
break between runs. During the trials, the participant
performed MI of the right hand for 25 s (from t = 0 s
to t = 25 s) while visual feedback reflecting the
associated desynchronization in the EEG beta band
(8-30 Hz) on the left central electrode C3 (located
over the right-hand motor cortex) was displayed. This
desynchronization, often observed in motor imagery
tasks, reflects a decrease in beta power associated
with the suppression of synchronized neural
oscillations, particularly within the motor cortex
(Pfurtscheller & Lopes da Silva, 1999). Intermittent
vibratory tactile feedback was also delivered in two
runs. The total duration of the NF session was
approximately 20 minutes.
The NF task was preceded by a brief training
phase consisting of three familiarization tasks, each
lasting 30 seconds. These tasks included (1)
observing a hand movement displayed on the screen,
(2) performing an actual hand movement, and (3)
imagining the hand movement while viewing it on the
screen. This 1.5-min training phase was followed by
5 minutes of control tasks before starting the NF runs.
2.1.3 EEG Preprocessing
We re-referenced the EEG data with respect to an
average reference across all electrodes, at each time
point. We applied a 50 Hz-centered notch filter to
attenuate mains frequency interference and a 0.5 Hz
high-pass filter to remove slow drifts, using 4th-order,
zero-phase, Butterworth filters as implemented in the
MNE 1.8.0 package (Gramfort et al., 2014; Larson et
al., 2024). Due to the presence of persistent muscle
artifacts, two electrodes (FT9 and TP9) were
excluded from the analyses.
2.2 Denoising Methods
We focused on BSS methods, since AJDC pertains to
this family of methods.
2.2.1 Blind Source Separation Principle
BSS is a signal analysis technique commonly used in
EEG signal processing to isolate neuronal sources of
interest or to remove artifact sources, such as eye
blinks or heartbeats, from cerebral activities
(Delorme et al., 2007). It relies on the principle of
statistical independence of the sources, which enables
the identification and reconstruction of the signals of
interest. The relationship between the multichannel
EEG signal X and the underlying source signals, S, is
modeled as follows:
𝑋=
𝐴
⋅ 𝑆
(1)
Where A is the mixing matrix, representing the
contributions of each source in each electrode.
The principle of BSS is to estimate the unmixing
matrix B, using method-specific optimization criteria
to reconstruct sources while minimizing
dependencies between them:
𝑆=𝐵⋅ 𝑋
(2)
𝑤𝑖𝑡ℎ 𝐵 = 𝐴
2.2.2 AJDC-Based Denoising
AJDC operates on the principle of minimizing inter-
source dependencies by diagonalizing cospectrum
matrices across frequencies. This joint
diagonalization isolates independent signal
components by making the matrices as diagonal as
possible, following several steps:
(a) Frequency transformation: The multi-channel
EEG signal X is first transformed into the frequency
domain. For each frequency f, the cospectrum matrix
𝐶
is the matrix of covariance between EEG channels
at this frequency:
𝐶
=𝐶𝑜𝑣𝑋
(3)
(b) Joint diagonalization: AJDC uses a cost
function 𝐽(𝐵) that measures the sum of the off-
diagonal elements of the transformed cospectrum
matrices, denoted 𝐷
, as:
𝐽
(
𝐵
)
=𝐷
,
(4)
Where 𝐷
,
represents the off-diagonal elements of
each transformed matrix 𝐷
=𝐵𝐶
𝐵
, and B is the
unmixing matrix. Minimizing 𝐽(𝐵) forces the
matrices 𝐷
to become quasi-diagonal, ensuring that
the sources are independent of each other.
(c) Application and source separation: The
estimated unmixing matrix B is then applied to
separate sources. The source of blinks is then
identified based on its spatial and temporal
signatures, and it is set to 0 to reconstruct an artifact-
free signal by applying A matrix (where 𝐴= 𝐵
) to
the remaining source signals S.
One of the main advantages of AJDC is the rapid
estimation of B. The method exploits the fact that
EEG artifacts, such as eye blinks, exhibit stable
spectral and spatial signatures over short time
Automatic Ocular Artifact Correction in Electroencephalography for Neurofeedback
775

periods. Thus, the rapid convergence of cospectrum
matrices 𝐶
provides a reliable estimate of B with a
limited amount of data.
We implemented AJDC using the pyriemann 0.6
package (Barachant et al., 2024). To simulate real-
time calibration and application, we used 20 seconds
of the EEG signal recorded during hand observation
in the training phase, to calibrate our B matrix, for
each subject. We performed AJDC between 1 and 80
Hz, and the source of eye blink artifact (N=1 for each
subject) was identified by an expert. The B matrix
was then applied in non-overlapping sliding 500-ms
time windows to the EEG data recorded during the
calibration and the six NF runs.
2.2.3 ICA-Based Denoising
Unlike AJDC, which operates in the frequency
domain, ICA separates sources by maximizing their
statistical independence in the time domain. In this
study, the FastICA algorithm was chosen due to its
computational efficiency and robust performance for
isolating artifacts in EEG data (Langlois et al., 2010).
It is based on a fixed-point algorithm that iteratively
maximizes non-Gaussianity, which serves as an
indicator of statistical independence. The process
comprises the following steps:
(a) Preprocessing: The EEG data matrix 𝑋
requires an initial whitening step in ICA to
decorrelate channels, simplifying the estimation of
independent components. Whitening, or sphering,
transforms the data to remove correlations between
channels by performing an eigenvalue
decomposition, where 𝑉 is the matrix of eigenvectors
and Λis the diagonal matrix of eigenvalues. The
whitened signal is then computed as:
𝑋
=Λ
𝑉
𝑋
(5)
This contrasts with AJDC that leverages
cospectrum matrices in the frequency domain, which
inherently contain reduced dependencies between
channels. By jointly diagonalizing these matrices,
AJDC further minimizes dependencies, bypassing the
need for whitening and directly isolating sources
based on their spectral characteristics.
(b) Optimization: Unlike AJDC, which uses a cost
function to minimize the off-diagonal elements of
transformed cospectrum matrices, FastICA
maximizes source independence in the time domain
by iteratively updating the unmixing matrix 𝐵 based
on non-Gaussianity. This measure of non-Gaussianity
serves as an indicator of statistical independence,
guiding FastICA to refine 𝐵 until source
independence is maximized.
(c) Application and source separation: As for
AJDC, once the B matrix is estimated, artifactual
components can be identified and removed, and the
cleaned signal is reconstructed by applying A matrix
to the remaining source signals S.
We implemented FastICA using the MNE 1.8.0
package (Gramfort et al., 2014; Larson et al., 2024).
One major drawback of FastICA (and ICA in general)
is the need for sufficiently long data segments to
ensure reliable convergence and source estimation.
Thus, we performed ICA decomposition on each of
the six NF runs, as is standard in offline EEG data
processing. The components corresponding to the eye
blinks (N=1 or 2 for each subject) in each run were
identified by an expert.
2.3 Evaluation of AJDC
2.3.1 Artifact Reduction
To assess the effectiveness of blink artifact
correction, we compared the blink Evoked Potentials
(EPs) recorded on each electrode in the raw data and
after correction with AJDC or ICA. Blink events were
automatically detected on the raw data using the
find_eog_events function (with default parameters
and Fp1 and Fp2 as EOG references) from the MNE
package, centering the analysis on epochs of ±500ms
around the blink peaks. The same events were then
aligned with the data processed by AJDC and ICA.
Blink EPs were obtained by averaging all blink
epochs in each subject. Power Spectral Densities
(PSDs) were estimated between 1 and 80 Hz using the
multitaper method with Discrete Prolate Spheroidal
Sequence (DPSS) across all blink epochs and then
averaged. For illustration purposes, the PSDs were
averaged over three regions – frontal (Fp1, Fp2, F7,
F3, Fz, F4, F8), central (FC5, FC1, FC2, FC6, FT10,
T7, C3, Cz, C4, T8, CP5, CP1, CP2, CP6, TP10), and
posterior (P7, P3, Pz, P4, P8, O1, Oz, O2) – and the
EP and PSD data were averaged across subjects.
2.3.2 Preservation of MI Signatures
At the electrophysiological level, we assessed event-
related desynchronization / synchronization
(ERD/ERS) across frequencies throughout the NF
runs, for the RAW, AJDC-, and ICA-corrected data.
For each participant, EEG signals were segmented
into NF trials (from t = -5 s to t = 30 s, where 0 was
the start of the NF period). Trials with muscle
artifacts were visually inspected and excluded. We
used Morlet wavelets (with a 500 ms width) to
transform the data in the time-frequency domain
BIOSIGNALS 2025 - 18th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
776
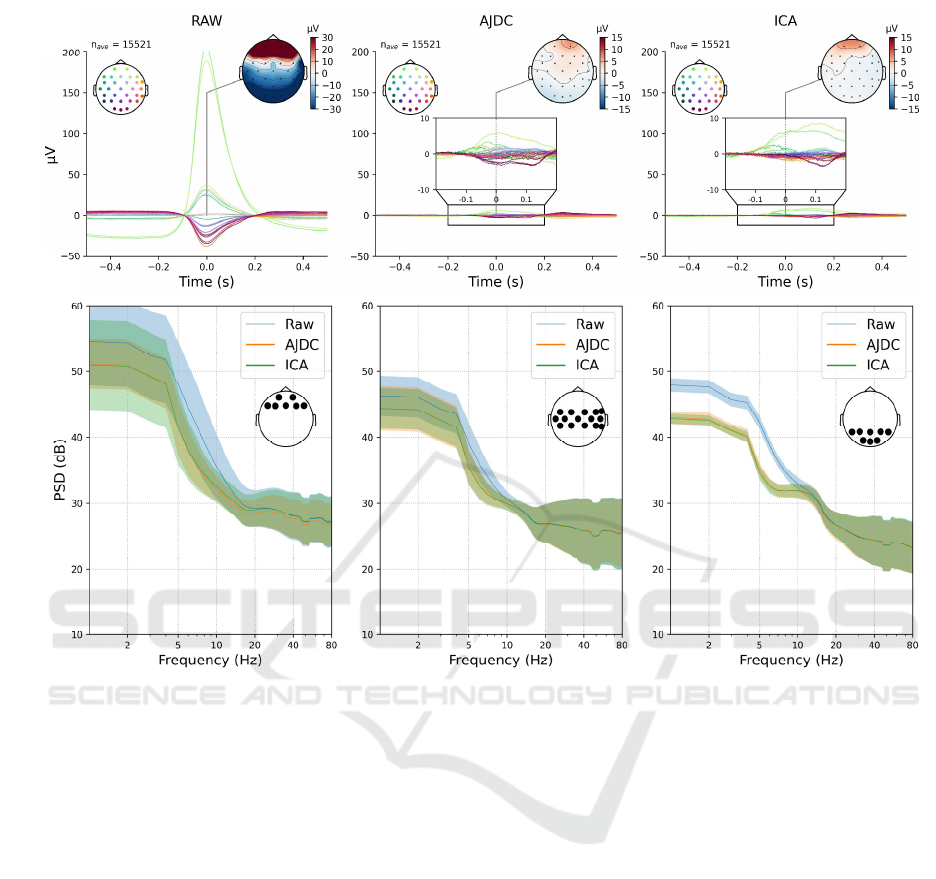
Figure 1: Artefact Reduction. (a) Blink EPs for the conditions: RAW (left), AJDC-corrected (centre), ICA-corrected (right)
signals. The grand average of the EPs across subjects is presented. At the top of each plot, topographies represent the spatial
distribution of the blink EPs at t = 0 s corresponding to the blink peak. The inset boxes zoom in on the corrected EPs for better
visualization of the differences between methods. Vertical axis: amplitude (µV); horizontal axis: time (s). (b) Power spectra
averaged on three scalp regions (from left to right: frontal, central, posterior) and averaged across subjects. Spectra derived
from raw signals are represented in blue, those from AJDC-corrected blink epochs in orange, and those from ICA-corrected
blink epochs in green. The lighter shaded area around each PSD represents the standard deviation across subjectts. Vertical
axis: spectral amplitudes (dB) ; horizontal axis: frequencies (Hz). An inset on each plot shows the electrodes that were
included in each scalp region.
between 1 Hz and 80 Hz, with 0.5 Hz frequency bins.
The wavelet cycles were linearly scaled with
frequency to ensure consistent time-frequency
resolution. Morlet wavelets were chosen for their
optimal trade-off between temporal and spectral
resolution (Bertrand et al., 2000). This approach
ensures precise characterization of both low- and
high-frequency bands while preserving consistent
temporal accuracy across the entire frequency range.
The trials were averaged, and the signal power was
then baseline-corrected using a log-ratio, with each
time point corrected relative to the mean power
during a 2-s fixation period (from t = -3 s to t = -1 s).
Furthermore, to check the preservation of MI
signatures after AJDC relative to ICA correction, we
employed Representational Similarity Analysis
(RSA) (Kriegeskorte et al., 2008) of the topographical
patterns. For each participant, we constructed
dissimilarity matrices from the MI-related
topographical maps after AJDC and after ICA,
respectively, by computing pairwise Euclidean
distances between electrode pairs. The similarity
between these matrices was then assessed using
Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient. By
leveraging RSA – which combines the computation
of dissimilarity matrices and their subsequent
correlation – we quantitatively assessed whether the
topographical structure of MI patterns was
maintained across different correction methods.
a)
b)
Automatic Ocular Artifact Correction in Electroencephalography for Neurofeedback
777
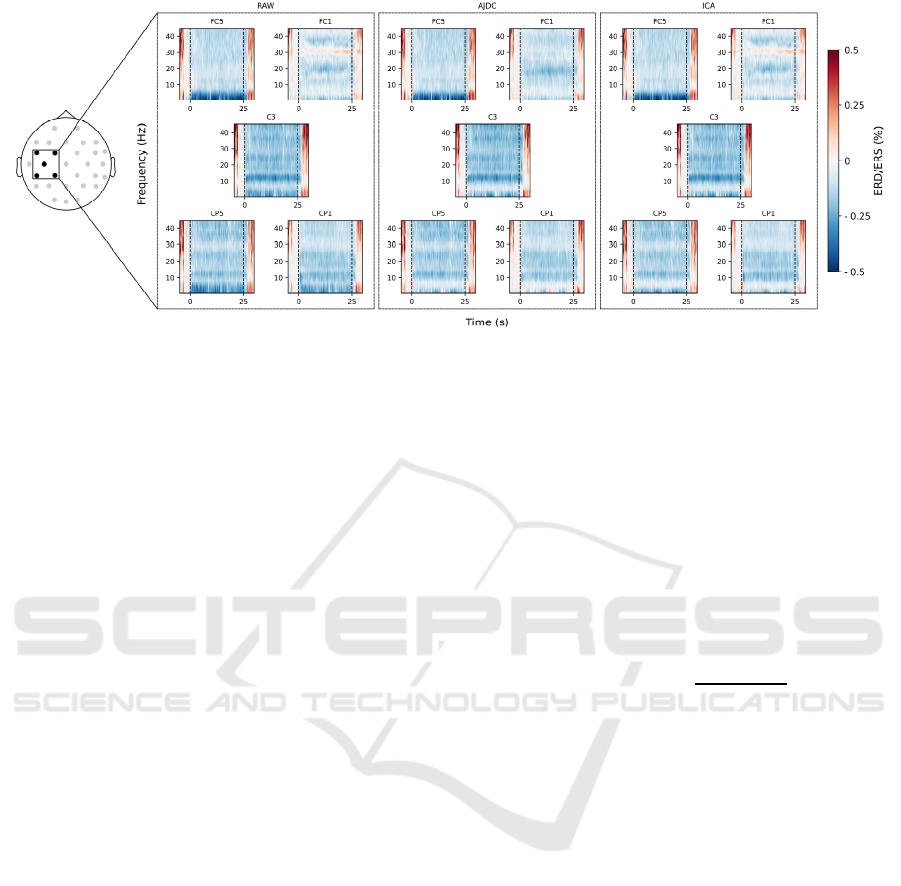
Figure 2: Preservation of MI signatures. Time-frequency representation of EEG power on each electrode of the Laplacian
filter in RAW, AJDC and ICA conditions, during the NF trials. The grand average of the data across subjects is represented.
The thin black dashed lines at 0 and 25 s represent the start and end of NF during the trials. ERD/ERS values are color coded,
with the blue colors representing ERD and the red colors representing ERS. Vertical axis: frequencies (Hz) ; horizontal axis:
time (s).
2.3.3 Simulation of Online Application
To quantify the beta-band (β) activity that participants
aimed to regulate through NF in a pseudo-online
fashion (aka. NF performance), we used the
OpenViBE 2.2.0 (Renard et al., 2010) processing
pipeline applied during the experiment. This pipeline
calculated online β power (online β), during NF trials
and compared it to a reference β power (reference β).
A Laplacian spatial filter was applied to electrode C3
by subtracting signals from adjacent electrodes (CP5,
CP1, FC1, and FC5). The resulting signal was band-
pass filtered between 8 and 30 Hz using an 8
th
-order
Butterworth filter, then segmented into 1 s epochs
with a 0.75 s overlap. For each epoch, β power was
calculated by squaring and averaging the signal.
Online β was derived by averaging β power values
over the 4 epochs preceding each feedback cycle
during the NF runs (see Dussard et al., 2024 for
details). It was compared to a common reference β
power value derived from a 60 s baseline period
recorded before the NF task. This reference β was
calculated by averaging the median β power of the
AJDC-corrected baseline period and the median β
power of the RAW baseline period.
NF performance was then computed as follows.
Each trial included 16 feedback cycles based on 16
online β values, which were compared to the
participant’s reference β. We divided each online β
value by the reference β and computed the median of
these 80 ratios (16 values per trial × 5 trials per run)
for every NF run. The result was log-transformed,
with the sign inverted, so that positive values
indicated a reduction in online β relative to reference
β, thus reflecting successful NF performance.
Finally, since AJDC was calibrated at the
beginning of the experiment and applied throughout
the NF runs, we also examined the quality of the
correction over time. To do this, we extracted a
signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of the blink EPs,
calculated across the NF runs as follows:
𝑆𝑁𝑅 = −10log
𝑠𝑖𝑔𝑛𝑎𝑙
𝑠𝑖𝑔𝑛𝑎𝑙
(6)
2.3.4 Statistical Analyses
(1) For artifact reduction analysis, PSD values of
blink epochs on each electrode and at each frequency
(1 to 80 Hz) were compared between ICA and AJDC
corrections.
(2) For MI-related signature preservation analysis,
power in the frequency band and electrodes of interest
(that is, 8-30 Hz band on FC1, FC5, C3, CP1, and
CP5) was averaged and compared 2-by-2 between the
RAW, AJDC, and ICA conditions.
(3) For SNR analysis, SNR values on each electrode
were compared between the first and last NF runs,
which were separated by an interval of 15-20 minutes.
When relevant, normality was assessed with the
Shapiro-Wilk test. When normality was met, paired t-
tests across subjects were used; otherwise, we used
Wilcoxon signed-rank tests. For each analysis, the p-
values were corrected for multiple comparisons using
the False Discovery Rate (FDR) correction from
Benjamini-Hochberg (Benjamini & Hochberg, 1995),
with FDR-corrected significance level (pFDR) set at
0.05.
BIOSIGNALS 2025 - 18th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
778
3 RESULTS
3.1 Artifact Reduction
We first investigated the artifact reduction resulting
from AJDC and ICA. For this purpose, we compared
the blink EPs averaged from RAW signals and from
signals corrected by AJDC and ICA. (see Figure 1.a).
Both correction methods visibly reduced blink
artifacts, as shown in the topographies at t = 0 s
corresponding to the peak of the blink artifact, though
some
f
rontal activity remained present in the
corrected signals. Focusing on frontal electrodes
(Fp1, Fp2, F7, F3, Fz, F4, F8), the average artifact
amplitude reduction was of 75.88 µV (± 24.28 µV;
[mean ± SD]) for AJDC and 75.56 µV (± 23.49 µV;
[mean ± SD]) for ICA. The differences between
AJDC and ICA seemed minimal, with only slight
variations in the spatial distribution and intensity of
residual activity.
To further investigate the effects of AJDC and ICA
on artifact reduction, we analyzed the PSD averaged
from blink epochs across frontal, central, and
posterior regions for both raw and corrected signals
(see Figure 1.b). A slight divergence between AJDC-
and ICA-corrected PSDs emerged only in the frontal
region, particularly at frequencies above 10 Hz.
However, AJDC- and ICA- corrected PSDs did not
show any significant difference on either electrode or
frequency (all pFDR > 0.05).
3.2 Preservation of MI Signatures
We investigated the extent to which the AJDC
preserved neurophysiological information of interest
despite the ocular artifact removal. Figure 2 shows the
time-frequency representation of the targeted beta
ERD during the NF trials, across the electrodes
involved in the Laplacian filter (that was used during
the NF protocol, see Methods). Both correction
methods appeared to preserve a similar MI-related
signature, except for electrode FC1 were a high-
frequency activity (around 30 Hz) was present in
RAW and ICA-corrected data but absent in AJDC-
corrected data. Some weak differences between
AJDC- and ICA-corrected time-frequency
representations were also visible in the low-frequency
range (<5 Hz) on CP1. Yet, the comparison of the
mean ERD in the beta band (8-30 Hz) between 0 and
25 s on the five-electrode involved in the Laplacian
computation did not show any statistically significant
2-by-2 difference between RAW, AJDC-corrected
and ICA-corrected data (pFDR > 0.05).
Furthermore, RSA analysis revealed a mean
similarity score of 0.87 ± 0.07 ([mean ± SD]),
indicating a preservation of the topographical
structure of MI patterns across the AJDC and ICA
correction methods.
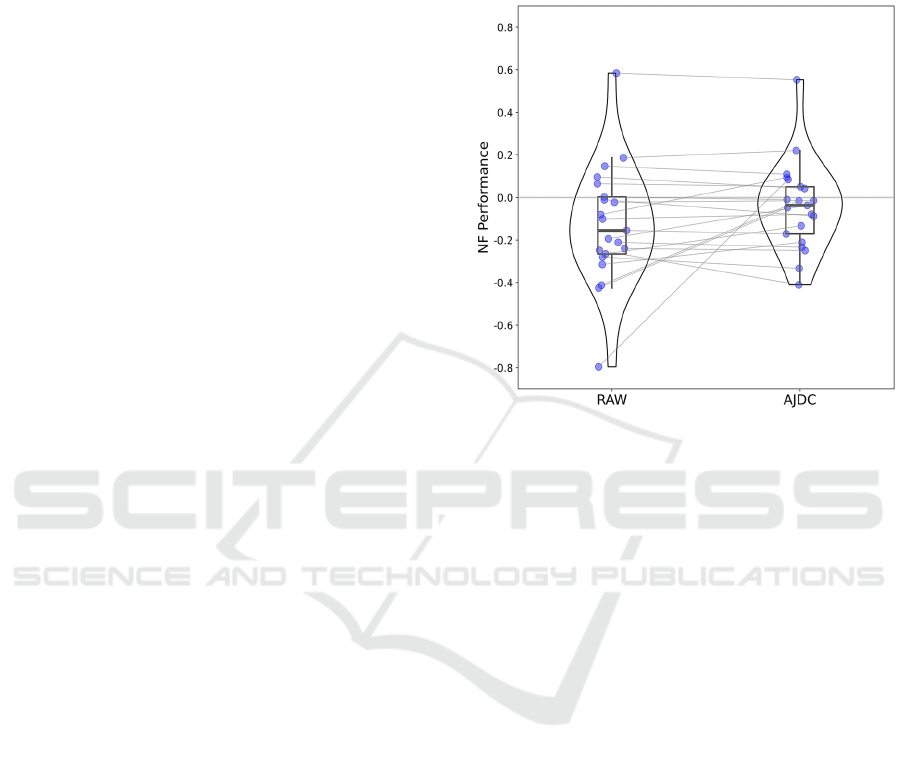
Figure 3: Comparison of NF performance between RAW
and AJDC conditions. Blue dots represent individual data.
For each condition, the thick horizontal black line is the
median value across subjects, the box plot corresponds to
the second and third quartiles, and the vertical these black
lines correspond to the lower and upper quartiles (excluding
outlier values). Violin plots of the individual data are also
included. Vertical axis: NF performance; horizontal axis:
conditions.
3.3 Simulation of Online Application
We evaluated the potential impact of AJDC on NF
performance in a pseudo-online framework,
replaying the data in real-time in OpenVibe to
simulate live recording conditions. Analysis of RAW
versus AJDC-corrected neurofeedback performance
showed no significant effect, with pFDR > 0.05.
0
Moreover, to evaluate the consistency of
the AJDC correction over time, we compared
SNR values between the first and last NF runs (see
Figure 4). A general decrease in SNR was observed
across electrodes, with lower SNR values in the last
run compared to the first one. Statistical analysis
revealed significant SNR differences on three
electrodes (F3, F8 and FC5; pFDR < 0.05). However,
this did not seem to impact NF performance insofar
as there was no significant difference between the
delta of NF performance between AJDC and RAW in
the first run and the delta of NF performance between
AJDC and RAW in the last run (pFDR > 0.05).
Automatic Ocular Artifact Correction in Electroencephalography for Neurofeedback
779
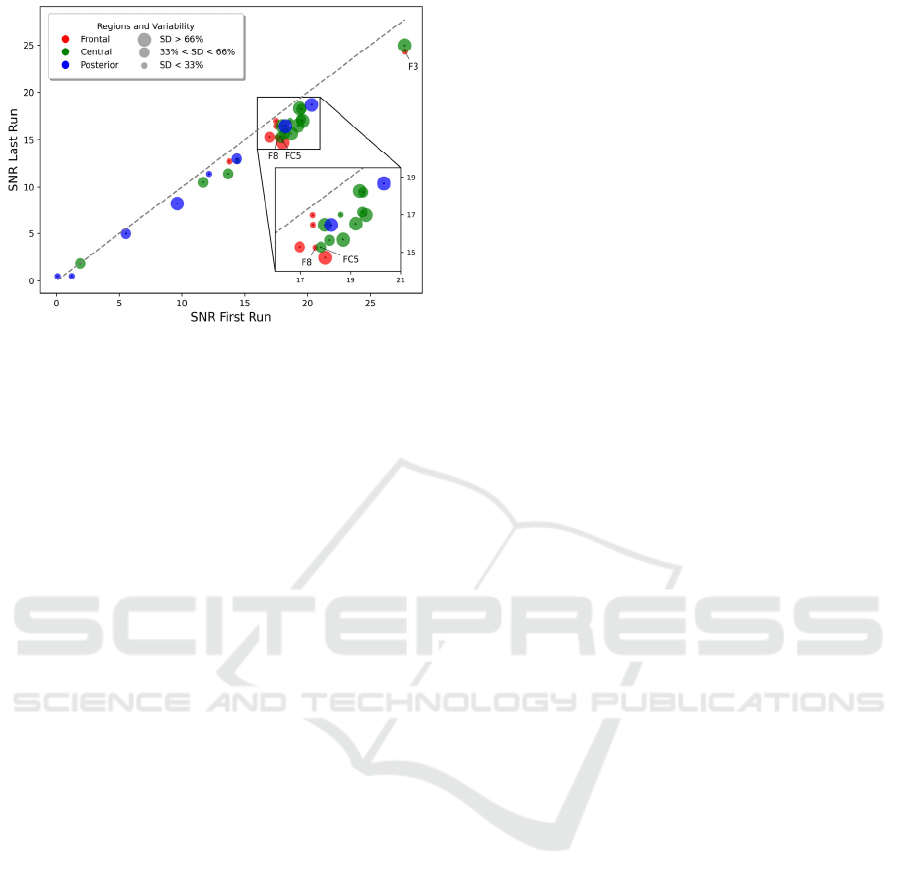
Figure 4: Difference in SNR between the first and last NF
runs for each electrode. The electrodes are colored
according to their scalp region: frontal (red), central
(green), and posterior (blue), corresponding to the same
regions as in Figure 2. The size of the colored circle reflects
the variability (standard deviation, SD) of the first vs. last
run SNR difference across subjects. For visualization
purpose, 3 circle size are represented: the larger circles
represent the electrodes with a SD of SNR difference
belonging to the 66% higher percentile of all SD values
across electrodes, the medium size circles represent the
electrodes with a SD value between 33% and 66% of all SD
values, and smaller circles represent electrodes with a SD
less than 33% of all SD values.
4 DISCUSSION
In NF and BCI, ocular artifacts – particularly those
from eye blinks – present a substantial challenge, as
they can severely distort EEG signatures. This study
evaluated the efficacy of the AJDC method for
automatic blink artifact correction in EEG data,
benchmarking it against the well-known ICA.
Our study showed that AJDC effectively reduces
blink artifacts in EEG signals, notably by attenuating
the frontal blink-related activity, which often disrupts
BCI and NF applications (Jiang et al., 2019). This
result aligns with expectations, as blink artifacts are
known to predominantly impact frontal channels due
to their proximity to the ocular sources (Joyce et al.,
2004). Although both AJDC and ICA methods
offered comparable performance, minor differences
appeared in high frequencies (>10 Hz) in the frontal
regions, where AJDC exhibited a correction profile
distinct from ICA. In the PSD analysis, the mean PSD
across scalp regions and subjects was lower for AJDC
compared to ICA; ICA PSD was closer to the RAW
PSD. This slight variation may reflect specific
characteristics of the AJDC decomposition process,
potentially influencing the spectral content (Congedo
et al., 2008). Although these differences did not reach
statistical significance, they may reflect unique
characteristics of AJDC correction. These
observations align with the conclusions of
Barthélemy et al., 2017, who demonstrated that
AJDC can effectively isolate and reduce ocular
artifacts. They also found minor differences between
manual denoising by ICA and automatic denoising by
AJDC in the PSD of frontal electrodes, suggesting
that AJDC may offer a distinct profile in terms of
power distribution in this region.
Beyond artifact reduction, we also considered the
AJDC method’s ability to preserve essential
neurophysiological information of interest, that is,
here, ERD in the beta band. In this regard, AJDC
seemed to preserve MI-related activity within the 8-
30 Hz band; there was no evidence of signal
deformation in this frequency range (see Figure 2).
This observation is in line with the findings from
Barthélemy et al., 2017, who demonstrated that
event-related potentials (ERPs) remained unaffected
by distortions from AJDC correction, supporting its
suitability for preserving key neural signals. That
said, some difference was observed around 30Hz on
electrode FC1. We went back to individual data and
noted that this difference was attributable to a single
subject who exhibited a high fluctuation in EEG
activity at this frequency. This fluctuation was absent
in the AJDC calibration data and therefore picked up
to some extent in the ocular component targeted for
removal during the NF runs. This outcome suggests
that while AJDC is robust in most cases, subject-
specific EEG variations or outliers may lead to
unanticipated inclusions in the correction process.
This is further supported by the RSA scores, which
indicated an average similarity above 85%. While this
represents a high degree of similarity, it is not perfect
(i.e., not 100%), suggesting the presence of residual
differences. Such variations can influence the motor
signature by introducing unintended corrections. This
observation resonates with findings from prior
studies, which emphasized the challenges posed by
intra-subject variability in EEG and artifact
correction methods (Ronca et al., 2024; Wei et al.,
2021).
In terms of NF performance, no significant
difference was found between the RAW and AJDC-
corrected conditions in a pseudo-online framework,
where data were replayed in real-time in OpenVibe to
simulate live recording conditions (see Figure 3). For
the purpose of this analysis, a common reference β
power was used for both methods, calculated as the
mean of the reference β power from each method.
BIOSIGNALS 2025 - 18th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
780

However, we checked that a method-specific
reference β did not alter our conclusions. This is
consistent with the findings of Dussard et al., 2024,
who demonstrated that Laplacian techniques are
resilient to ocular artifacts. It is however worth noting
that more complex spatial filtering methods that
integrate information from the entire scalp, such as
Common Spatial Patterns (CSP) (Blankertz et al.,
2008), are more sensitive to ocular artifacts,
potentially impacting their performance. CSPs are
commonly used in BCI protocols due to their
effectiveness in discriminating MI-related EEG
patterns, yet they are sensitive to ocular artifacts that
can degrade their accuracy if not adequately managed
(Jafarifarmand & Badamchizadeh, 2019). AJDC may
be particularly useful in the context of CSP and other
advanced feature extraction methods.
In addition to the overall performance analysis, a
notable aspect of our results is the observed
progressive decline in the effectiveness of AJDC
correction over the course of the experiment (see
Figure 4). This trend suggests that periodic
adjustments or recalibrations may be necessary to
sustain the AJDC method efficacy. This temporal
degradation likely arises from dynamic changes in
artifact characteristics and neural signal properties
(Ambrogioni et al., 2017; Islam et al., 2021). This
observation is in agreement with broader findings in
the literature on BCI and NF systems, where
maintaining stable performance across time is often
challenging due to various sources of signal
variability, including changes in electrode
impedance, user fatigue, and cognitive state
fluctuations (Alkoby et al., 2018; Saha & Baumert,
2020; Vidaurre & Blankertz, 2010). Such fluctuations
can impact the consistency of the neural signals,
thereby complicating real-time processing and
artifact correction. An improvement to the AJDC
method could involve implementing a real-time,
offset calibration, where a new correction matrix is
recalculated in the background during real-time
artifact correction.
While the AJDC method shows promising results
in blink artifact correction, certain limitations remain.
First, AJDC requires manual identification of artifacts
components, a step conducted at the beginning of the
experiment in our protocol. While this initial
calibration minimizes variability, it relies on expert
input, which introduces inter-operator variability and
limits reproducibility across different experimental
setups (Barthélemy et al., 2017). Additionally,
although our study focused solely on blink artifacts, a
multitude of other artifact types – including
physiological (e.g. muscle activity) and
environmental noise – can significantly impact EEG
signals (Tatum et al., 2011). The efficacy of AJDC
for these types of artifacts has yet to be assessed
comprehensively, as various studies highlight the
importance of robust correction methods for diverse
EEG artifacts to ensure signal integrity in BCI
applications (McDermott et al., 2022).
Another limitation is the offline nature of our
comparison. While this approach was justified by the
shared BSS framework of both AJDC and ICA
methods, it would be interesting to also test AJDC
against a real-time method, such as ASR (Mullen et
al., 2015), for a fuller methodological benchmark.
This comparison is particularly relevant for BCI and
NF applications, where continuous adaptation and
real-time processing are critical (Saha & Baumert,
2020). Our comparison with ICA is valuable given
the well-documented strengths and limitations of ICA
in artifact correction. Another interesting suggestion
could be to test AJDC on clean EEG data artificially
contaminated with controlled artifacts (Chavez et al.,
2018). This approach would allow for a rigorous
evaluation of AJDC artifact correction efficacy and
its impact on neural signals. Furthermore, such a
setup would enable the exploration of additional
metrics, such as phase delay, relative root mean
square error, coherence or Riemannian distance.
These measures could provide complementary
insights into the quality of artifact correction.
Finally, this study serves as a proof of concept,
demonstrating the potential of the AJDC method in
comparison to ICA using data from healthy subjects.
However, to fully assess the robustness and clinical
applicability of AJDC, it would be essential to
evaluate its performance on patients’ data. Patients’
populations may exhibit more pronounced artifacts
due to various factors such as increased physiological
variability, medication effects, or underlying
neurological conditions (Karson, 1983; Kimura et al.,
2017). Evaluating AJDC on such data would provide
critical insights into its efficacy in real-world clinical
contexts.
In summary, our study offers a promising first
step toward robust real-time EEG artifact correction
with AJDC, highlighting areas for further
development in automating and validating the method
across diverse recording conditions and artifact types.
REFERENCES
Alkoby, O., Abu-Rmileh, A., Shriki, O., & Todder, D.
(2018). Can We Predict Who Will Respond to
Neurofeedback? A Review of the Inefficacy Problem
Automatic Ocular Artifact Correction in Electroencephalography for Neurofeedback
781

and Existing Predictors for Successful EEG
Neurofeedback Learning. Neuroscience, 378, 155–164.
Al-Quraishi, M. S., Elamvazuthi, I., Daud, S. A.,
Parasuraman, S., & Borboni, A. (2018). EEG-Based
Control for Upper and Lower Limb Exoskeletons and
Prostheses: A Systematic Review. Sensors (Basel,
Switzerland), 18, 3342.
Ambrogioni, L., Gerven, M. A. J. van, & Maris, E. (2017).
Dynamic decomposition of spatiotemporal neural
signals. PLOS Computational Biology, 13(5).
Barachant, A., Barthélemy, Q., Wagner vom Berg, G.,
Gramfort, A., King, J.-R., & Rodrigues, P. L. C. (2024).
pyRiemann/pyRiemann: V0.6 (Version v0.6)
[Computer software].
Barthélemy, Q., Mayaud, L., Renard, Y., Kim, D., Kang,
S.-W., Gunkelman, J., & Congedo, M. (2017). Online
denoising of eye-blinks in electroencephalography.
Clinical Neurophysiology, 47(5–6), 371–391.
Benjamini, Y., & Hochberg, Y. (1995). Controlling the
False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful
Approach to Multiple Testing. Journal of the Royal
Statistical Society: Series B (Methodological), 57(1),
289–300.
Bertrand, O., Tallon-Baudry, C., & Pernier, J. (2000). Time-
Frequency Analysis of Oscillatory Gamma-Band
Activity: Wavelet Approach and Phase-Locking
Estimation (Vol. 2, pp. 919–922).
Blankertz, B., Tomioka, R., Lemm, S., Kawanabe, M., &
Muller, K. (2008). Optimizing Spatial filters for Robust
EEG Single-Trial Analysis. IEEE Signal Processing
Magazine, 25(1), 41–56.
Chavez, M., Grosselin, F., Bussalb, A., De Vico Fallani, F.,
& Navarro-Sune, X. (2018). Surrogate-Based Artifact
Removal From Single-Channel EEG. IEEE
Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation
Engineering, 26(3), 540–550.
Congedo, M., Gouy-Pailler, C., & Jutten, C. (2008). On the
blind source separation of human electroencephalo-
gram by approximate joint diagonalization of second
order statistics. Clinical Neurophysiology, 119(12),
2677–2686.
Croft, R. J., & Barry, R. J. (2000). EOG correction of blinks
with saccade coefficients: A test and revision of the
aligned-artefact average solution. Clinical
Neurophysiology, 111(3), 444–451.
Delorme, A., Sejnowski, T., & Makeig, S. (2007).
Enhanced detection of artifacts in EEG data using
higher-order statistics and independent component
analysis. NeuroImage, 34(4), 1443–1449.
Dussard, C., Pillette, L., Dumas, C., Pierrieau, E.,
Hugueville, L., Lau, B., Jeunet-Kelway, C., & George,
N. (2024). Influence of feedback transparency on motor
imagery neurofeedback performance: The contribution
of agency. Journal of Neural Engineering, 21(5).
Friedman, D., Claassen, J., & Hirsch, L. J. (2009).
Continuous electroencephalogram monitoring in the
intensive care unit. Anesthesia and Analgesia, 109(2),
506–523.
Gramfort, A., Luessi, M., Larson, E., Engemann, D. A.,
Strohmeier, D., Brodbeck, C., Parkkonen, L., &
Hämäläinen, M. S. (2014). MNE software for
processing MEG and EEG data. NeuroImage, 86, 446–
460.
Hagemann, D., & Naumann, E. (2001). The effects of
ocular artifacts on (lateralized) broadband power in the
EEG. Clinical Neurophysiology, 112(2), 215–231.
Islam, Md. K., Rastegarnia, A., & Sanei, S. (2021). Signal
Artifacts and Techniques for Artifacts and Noise
Removal. In Signal Processing Techniques for
Computational Health Informatics (Vol. 192, pp. 23–
79). Springer.
Iwasaki, M., Kellinghaus, C., Alexopoulos, A. V., Burgess,
R. C., Kumar, A. N., Han, Y. H., Lüders, H. O., &
Leigh, R. J. (2005). Effects of eyelid closure, blinks,
and eye movements on the electroencephalogram.
Clinical Neurophysiology, 116(4), 878–885.
Jafarifarmand, A., & Badamchizadeh, M. A. (2019). EEG
Artifacts Handling in a Real Practical Brain–Computer
Interface Controlled Vehicle. IEEE Transactions on
Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 27(6),
1200–1208.
Jiang, X., Bian, G.-B., & Tian, Z. (2019). Removal of
Artifacts from EEG Signals: A Review. Sensors (Basel,
Switzerland), 19(5), 987.
Joyce, C. A., Gorodnitsky, I. F., & Kutas, M. (2004).
Automatic removal of eye movement and blink artifacts
from EEG data using blind component separation.
Psychophysiology, 41(2), 313–325.
Karson, C. N. (1983). Spontaneous Eye-Blinks Rates and
Dopaminergic Systems. Brain, 106(3), 643–653.
Kimura, N., Watanabe, A., Suzuki, K., Toyoda, H.,
Hakamata, N., Fukuoka, H., Washimi, Y., Arahata, Y.,
Takeda, A., Kondo, M., Mizuno, T., & Kinoshita, S.
(2017). Measurement of spontaneous blinks in patients
with Parkinson’s disease using a new high-speed blink
analysis system. Journal of the Neurological Sciences,
380, 200–204.
Kriegeskorte, N., Mur, M., & Bandettini, P. A. (2008).
Representational similarity analysis—Connecting the
branches of systems neuroscience. Frontiers in Systems
Neuroscience, 2
.
Langlois, D., Chartier, S., & Gosselin, D. (2010). An
Introduction to Independent Component Analysis:
InfoMax and FastICA algorithms. Tutorials in
Quantitative Methods for Psychology, 6(1), 31–38.
Larson, E., Gramfort, A., Engemann, D. A., Leppakangas,
J., Brodbeck, C., Jas, M., Brooks, T. L., Sassenhagen,
J., McCloy, D., Luessi, M., King, J.-R., Höchenberger,
R., Goj, R., Favelier, G., Brunner, C., van Vliet, M.,
Wronkiewicz, M., Rockhill, A., Holdgraf, C., …
luzpaz. (2024). MNE-Python (Version v1.8.0)
[Computer software].
Lotte, F., Bougrain, L., & Clerc, M. (2015).
Electroencephalography (EEG)‐Based Brain–
Computer Interfaces. In J. G. Webster (Ed.), Wiley
Encyclopedia of Electrical and Electronics
Engineering (1st ed., p. 44). Wiley.
Makeig, S., Bell, A., Jung, T.-P., & Sejnowski, T. (1996).
Independent Component Analysis of Electroencephalo-
BIOSIGNALS 2025 - 18th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
782

graphic Data. Advances in Neural Information
Processing Systems, 8.
McDermott, E. J., Raggam, P., Kirsch, S., Belardinelli, P.,
Ziemann, U., & Zrenner, C. (2022). Artifacts in EEG-
Based BCI Therapies: Friend or Foe? Sensors, 22(1),
96.
Mullen, T. R., Kothe, C. A. E., Chi, Y. M., Ojeda, A., Kerth,
T., Makeig, S., Jung, T.-P., & Cauwenberghs, G.
(2015). Real-Time Neuroimaging and Cognitive
Monitoring Using Wearable Dry EEG. IEEE
Transactions on Bio-Medical Engineering, 62(11),
2553–2567.
Mumtaz, W., Rasheed, S., & Irfan, A. (2021). Review of
challenges associated with the EEG artifact removal
methods. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control,
68, 102741.
Omejc, N., Rojc, B., Battaglini, P. P., & Marusic, U. (2019).
Review of the therapeutic neurofeedback method using
electroencephalography: EEG Neurofeedback. Bosnian
Journal of Basic Medical Sciences, 19(3), 213–220.
Pfurtscheller, G., & Lopes da Silva, F. H. (1999). Event-
related EEG/MEG synchronization and desynchroniza-
tion: Basic principles. Clinical Neurophysiology,
110(11), 1842–1857.
Renard, Y., Lotte, F., Gibert, G., Congedo, M., Maby, E.,
Delannoy, V., Bertrand, O., & Lécuyer, A. (2010).
OpenViBE: An Open-Source Software Platform to
Design, Test, and Use Brain–Computer Interfaces in
Real and Virtual Environments. Presence, 19(1), 35–
53.
Ronca, V., Capotorto, R., Di Flumeri, G., Giorgi, A., Vozzi,
A., Germano, D., Virgilio, V. D., Borghini, G.,
Cartocci, G., Rossi, D., Inguscio, B. M. S., Babiloni, F.,
& Aricò, P. (2024). Optimizing EEG Signal Integrity:
A Comprehensive Guide to Ocular Artifact Correction.
Bioengineering, 11(10), 1018.
Saha, S., & Baumert, M. (2020). Intra- and Inter-subject
Variability in EEG-Based Sensorimotor Brain
Computer Interface: A Review. Frontiers in
Computational Neuroscience, 13, 87.
Tatum, W. O., Dworetzky, B. A., & Schomer, D. L. (2011).
Artifact and Recording Concepts in EEG. Journal of
Clinical Neurophysiology, 28(3), 252–263.
Thomas, J., Thangavel, P., Peh, W. Y., Jing, J., Yuvaraj, R.,
Cash, S. S., Chaudhari, R., Karia, S., Rathakrishnan, R.,
Saini, V., Shah, N., Srivastava, R., Tan, Y.-L.,
Westover, B., & Dauwels, J. (2021). Automated Adult
Epilepsy Diagnostic Tool Based on Interictal Scalp
Electroencephalogram Characteristics: A Six-Center
Study. International Journal of Neural Systems, 31(5),
2050074.
Vidaurre, C., & Blankertz, B. (2010). Towards a Cure for
BCI Illiteracy. Brain Topography, 23(2), 194–198.
Wei, C.-S., Keller, C. J., Li, J., Lin, Y.-P., Nakanishi, M.,
Wagner, J., Wu, W., Zhang, Y., & Jung, T.-P. (2021).
Editorial: Inter- and Intra-subject Variability in Brain
Imaging and Decoding. Frontiers in Computational
Neuroscience, 15, 791129.
Zikov, T., Bibian, S., Dumont, G. A., Huzmezan, M., &
Ries, C. R. (2002). A wavelet based de-noising
technique for ocular artifact correction of the
electroencephalogram. 24th Annual Conference of the
Biomedical Engineering Society, 1, 98–105 vol.1.
Automatic Ocular Artifact Correction in Electroencephalography for Neurofeedback
783
