
A Survey of Evaluating AutoML and Automated Feature Engineering
Tools in Modern Data Science
Dinesha Dissanayake
∗ a
, Rajitha Navarathna, Praveen Ekanayake and Sumanaruban Rajadurai
OCTAVE – Data and Advanced Analytics Division, John Keells Holdings PLC, Colombo, Sri Lanka
Keywords:
Automated Machine Learning (AutoML), Automated Feature Engineering, Benchmarking, Machine
Learning, Classification, Regression.
Abstract:
This survey provides a comprehensive comparison of several AutoML tools, along with an evaluation of
three feature engineering tools: Featuretools, Autofeat, and PyCaret. We conducted a benchmarking analysis
of four AutoML tools (TPOT, H2O-AutoML, PyCaret, and AutoGluon) using seven datasets sourced from
OpenML and the UCI Machine Learning Repository, covering binary classification, multiclass classification,
and regression tasks. Key metrics such as F1-score for classification and RMSE for regression were used to
assess performance. The tools are also compared in terms of execution time, memory usage, and optimization
success. AutoGluon consistently demonstrated strong predictive performance, while H2O-AutoML showed
reliable results but was limited by long optimization times. PyCaret was the most efficient, showing notably
shorter execution times and lower memory usage across all datasets compared to other tools, though it had
slightly lower accuracy. TPOT frequently struggled to complete optimization within the set time limit, achiev-
ing successful completion in only 42.86% of total cases. Overall, this survey provides insights into which
AutoML tools are best suited for different task requirements.
1 INTRODUCTION
The rapid advancements in Machine Learning (ML)
have developed powerful models capable of handling
complex tasks across domains such as healthcare, fi-
nance, and marketing. However, building effective
ML models is often a complex process that involves
several steps, such as data preprocessing, feature en-
gineering, model selection, and hyperparameter tun-
ing. This usually requires deep expertise and signifi-
cant time investment, which can be a barrier for many
potential users.
To address these challenges, Automated Machine
Learning (AutoML) has been introduced to sim-
plify the ML pipeline. AutoML tools automate key
steps in model development and make it easier for
users without extensive knowledge in ML. Tools like
Auto-sklearn, TPOT, H2O AutoML, and Auto-Keras
handle tasks like model selection and hyperparam-
eter optimization with minimal human intervention
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0004-9361-4390
∗
This work was undertaken while the first author was
interning at OCTAVE – Data and Advanced Analytics Di-
vision of John Keells Group PLC, Colombo, Sri Lanka
(Zhong et al., 2024; Blohm et al., 2020). Despite these
advancements, challenges remain, particularly in han-
dling different types of data and tasks such as binary
classification, multiclass classification, and regression
(Truong et al., 2019; Arag
˜
ao et al., 2023).
Another critical aspect of ML is feature engi-
neering, which involves creating and transforming
raw data into features that improve model perfor-
mance. To simplify this process, Automated Feature
Engineering tools like FeatureTools, Autofeat and
TSFresh have been developed. These tools can save
a lot of time and improve model accuracy, particu-
larly in scenarios involving structured data (Z
¨
oller and
Huber, 2019; Mumuni and Mumuni, 2024). How-
ever, prior studies primarily focus on AutoML tools or
feature engineering frameworks separately and often
lack empirical benchmarking on large-scale, industry-
related datasets that reflect real-world challenges.
This creates a gap in understanding how these tools
perform under diverse conditions, and which are most
suitable for specific applications.
This paper aims to address this gap by provid-
ing a comprehensive review of these tools, examin-
ing their strengths and limitations, and performing
218
Dissanayake, D., Navarathna, R., Ekanayake, P. and Rajadurai, S.
A Survey of Evaluating AutoML and Automated Feature Engineer ing Tools in Modern Data Science.
DOI: 10.5220/0013266700003929
In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2025) - Volume 1, pages 218-225
ISBN: 978-989-758-749-8; ISSN: 2184-4992
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

a benchmarking analysis using seven datasets from
the OpenML and UCI Machine Learning reposito-
ries. The study evaluates the performance of AutoML
tools based on key metrics such as model performance
(e.g., accuracy, F1-score, and Area Under the ROC
Curve (AUC) for classification; Root Mean Squared
Error (RMSE) and Mean Absolute Error (MAE) for
regression), execution time, memory usage, and ef-
ficiency. This study aims to provide practical in-
sights for both researchers and practitioners seeking
AutoML solutions for real-world applications.
The primary contributions of this survey are:
• This survey compares various AutoML and feature
engineering tools, examining their capabilities, ad-
vantages, limitations, and typical applications.
• We perform a comprehensive benchmarking of four
widely-used AutoML tools: TPOT, H2O-AutoML,
PyCaret, and AutoGluon, across seven datasets,
covering binary classification, multiclass classifica-
tion, and regression tasks.
When selecting AutoML tools, we focused on acces-
sibility, documentation, community support, and the
diversity of features offered by these tools. The selec-
tion of TPOT, H2O-AutoML, PyCaret, and AutoGluon
over others such as Auto-sklearn and MLBox was
due to practical considerations. Auto-sklearn was
not chosen because of its incompatibility with Win-
dows operating systems, which limits accessibility
and reproducibility. MLBox was excluded due to its
lack of established community support and documen-
tation, which are essential for practical use.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows: Sec-
tion 2 summarizes related work on AutoML and Au-
tomated Feature Engineering tools. Section 3 com-
pares the capabilities, strengths, and limitations of
various AutoML frameworks. Section 4 outlines Au-
tomated Feature Engineering frameworks and their
contributions. Section 5 covers the benchmark de-
sign, including datasets, metrics, and experimental
setup. Section 6 presents the benchmark results, and
Section 7 concludes with key findings.
2 RELATED WORK
Several studies have focused on evaluating and com-
paring AutoML frameworks. For instance, a novel
study introduced a comprehensive AutoML bench-
mark tool that evaluates nine frameworks across 71
classification and 33 regression datasets (Gijsbers
et al., 2024). This study provides insights into per-
formance trade-offs between model accuracy, infer-
ence time, and the choice of framework. Similarly, El-
deeb et al. (2024) provide a detailed evaluation of six
AutoML frameworks, focusing on performance vari-
ability under different time budgets and search spaces.
Both studies, however, primarily addressed AutoML
tools and did not consider the integration of feature
engineering frameworks or the practical challenges of
large-scale, industry-related datasets.
Other studies focus on state-of-the-art AutoML
tools across a variety of datasets and tasks (Truong
et al., 2019; Elshawi et al., 2019; Karmaker et al.,
2022; Zhong et al., 2024; Majidi et al., 2022; Doke
and Gaikwad, 2021). A notable study by Truong
et al. (2019) evaluated several AutoML tools, includ-
ing H2O-AutoML, TPOT, and Auto-sklearn, across
nearly 300 datasets. The study assessed metrics such
as accuracy and execution time, while also addressing
challenges related to dataset characteristics and task
complexity.
In addition to these broad surveys, some stud-
ies combine benchmarking and survey approaches to
offer both theoretical insights and empirical evalu-
ations (Z
¨
oller and Huber, 2019; Urbanowicz et al.,
2023; Ferreira et al., 2021; Gijsbers et al., 2019;
Hanussek et al., 2021). Z
¨
oller and Huber (2019)
assessed 14 AutoML and hyperparameter optimiza-
tion (HPO) frameworks using a standardized set of
datasets. Their study emphasizes the importance of
flexible pipeline structures and highlights the limita-
tions of fixed pipelines used by some frameworks and
potential overfitting on benchmark datasets.
Furthermore, other studies have examined Au-
toML tools in domain-specific contexts. Paladino
et al. (2023) and Narayanan et al. (2023) explored
AutoML applications in heart disease diagnosis and
computational drug discovery, respectively. Both
studies highlighted that AutoGluon outperformed
other tools in terms of accuracy but did not con-
sider the broader applicability of these frameworks
across diverse data types and tasks. Similarly,
Mumuni and Mumuni (2024) provided a detailed
overview of automated feature engineering tools
such as Featuretools and Tsfresh and their role
in improving machine learning model performance.
The paper emphasizes the advantages of integrating
these tools with AutoML frameworks, particularly for
structured and time-series data, which results in bet-
ter model accuracy. However, it lacks a benchmark
evaluation alongside AutoML frameworks.
Compared to these prior studies, this paper makes
major unique contributions. First, it focuses on
benchmarking AutoML frameworks across a diverse
set of large-scale, industry-related datasets, address-
ing a critical gap in existing literature. Additionally,
this survey discusses the role of some feature engi-
neering frameworks in improving machine learning
A Survey of Evaluating AutoML and Automated Feature Engineering Tools in Modern Data Science
219

workflows. Finally, it compares tools based on model
performance, execution time, memory usage, and op-
timization success, thereby offering a comprehensive
perspective on their strengths, limitations, and suit-
ability for various tasks.
3 AutoML FRAMEWORKS
This section presents the key features of popular
open-source AutoML tools, followed by a detailed
comparison of their strengths and weaknesses.
3.1 Capabilities of AutoML Tools
In this section, we focus on the key capabilities of
some widely used open-source AutoML frameworks.
Each tool offers different levels of automation and
support for various machine learning tasks, which
makes them suited to specific use cases. Table 1 pro-
vides a comprehensive summary of the capabilities of
each tool. It covers aspects such as data type support,
supervised and unsupervised learning tasks, data pre-
processing functionalities, feature engineering capa-
bilities, and model evaluation.
Data Type Detection. Many AutoML tools are
equipped with the ability to automatically detect and
process different data types, such as structured/ tab-
ular data, image data, text data, and time-series
data. For instance, AutoGluon, Auto-keras, and
H2O-AutoML are highly flexible in handling struc-
tured, image, text and time-series data, whereas
tools like Auto-WEKA, Auto-skearn, TPOT, PyCaret,
Recipe, and MLBox are more specialized in tabular
data.
Supervised Learning. Almost all the tools discussed
in this section support supervised learning tasks, in-
cluding binary classification, multiclass classification,
and regression.
Unsupervised Learning. Not all tools provide
comprehensive support for unsupervised learning, as
many are more focused on optimizing supervised
models, only PyCaret supports unsupervised learn-
ing tasks like clustering and anomaly detection.
Data Preprocessing. Most tools provide capabil-
ities for encoding categorical variables and han-
dling imbalanced data. Tools like AutoGluon,
Auto-sklearn, PyCaret, and H2O AutoML excel in
handling missing values and imbalanced datasets,
while others like Auto-WEKA and Recipe offer only
limited preprocessing tasks. Moreover, not all tools
include exploratory data analysis (EDA) or data
cleaning, with some requiring more manual interven-
tion for these tasks.
Feature Engineering. Most tools provide automated
feature extraction, transformation, and selection. All
tools, except Auto-WEKA and Auto-sklearn, support
all three aspects of feature engineering. Auto-WEKA
offers limited support for feature transformation,
while Auto-sklearn does not support feature extrac-
tion.
Hyperparameter Optimization. All the tools dis-
cussed in this survey are capable of automating hyper-
parameter optimization. This automation ensures that
models are finely tuned without requiring manual in-
tervention. As a result, model accuracy and efficiency
are significantly improved.
Model Evaluation, Ensemble Learning, and Pre-
dictions. AutoML frameworks offer different lev-
els of support for model evaluation, ensemble learn-
ing, and predictions. Most tools, such as AutoGluon,
Auto-sklearn, TPOT, PyCaret, H2O AutoML, and
MLBox, can handle all three aspects. They in-
clude robust model evaluation metrics such as accu-
racy, RMSE, and F1-score. These tools also sup-
port ensemble learning and allow multiple models
to be combined for improved predictive accuracy.
However, some tools, like Auto-WEKA, Recipe, and
Auto-Keras, offer limited or no support for ensem-
ble learning. All tools, except Recipe, provide func-
tionalities to generate predictions once the model is
trained.
3.2 Comparison of AutoML
Frameworks
When comparing various AutoML frameworks, it
is clear that each has distinct strengths and weak-
nesses tailored to different needs. They differ based
on usability, functionality, performance, and task
complexity. AutoML tools such as Auto-WEKA,
PyCaret, and Auto-Keras are designed with user-
friendly interfaces, making them suitable for begin-
ners. Auto-WEKA is particularly suited for smaller
datasets due to its memory constraints. PyCaret ex-
cels in offering a low-code environment for quick ex-
perimentation and deployment of machine learning
models. Auto-Keras focuses exclusively on neu-
ral networks and lacks support for broader machine
learning algorithms.
On the other hand, AutoGluon and H2O-AutoML
are effective for processing large and complex
datasets; AutoGluon requires substantial computa-
tional resources, and H2O-AutoML often has lengthy
training times due to their thorough search and tun-
ing processes. Additionally, AutoGluon has limited
support for non-tabular data such as time-series and
text.
ICEIS 2025 - 27th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
220
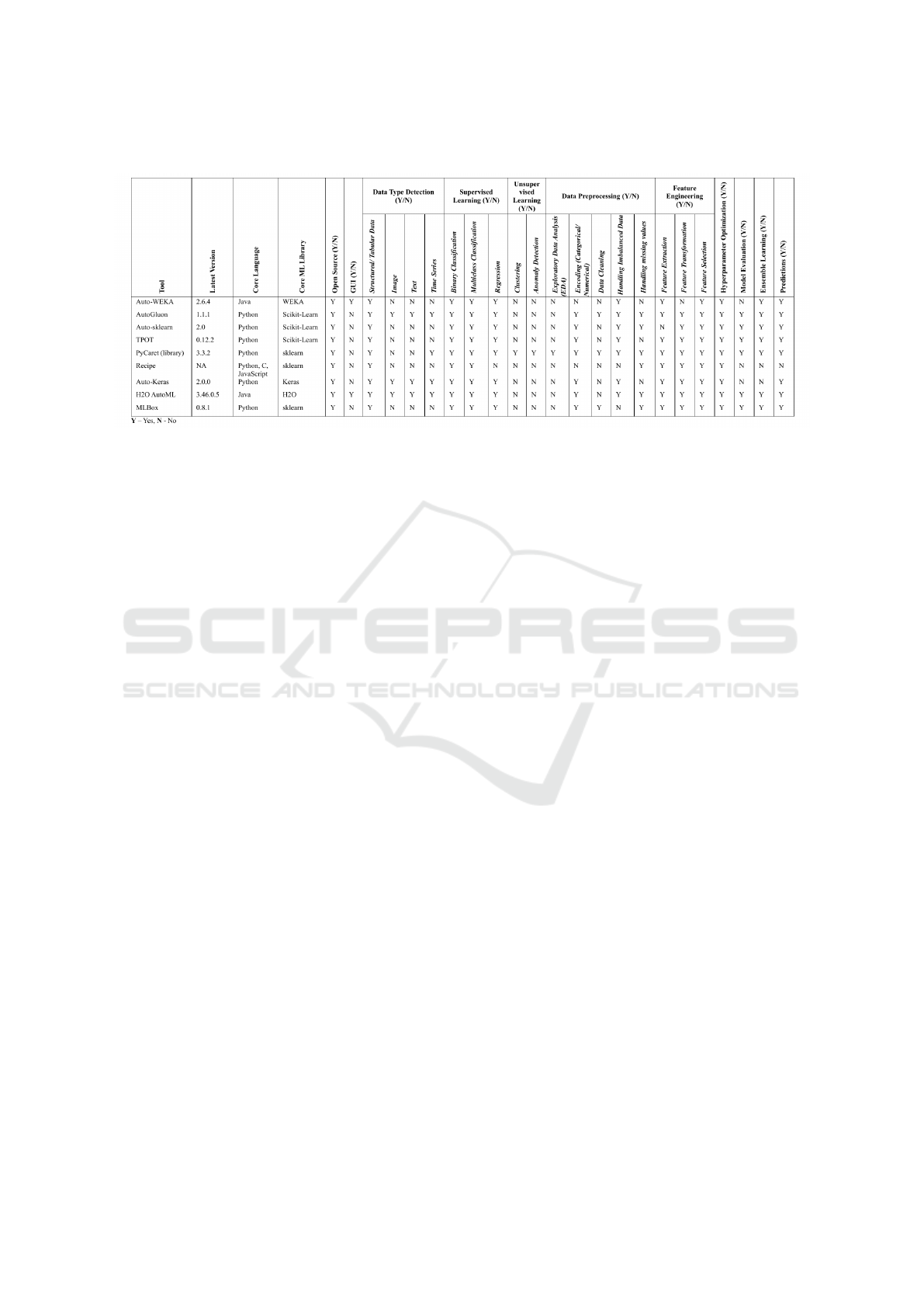
Table 1: Capabilities of AutoML Tools.
TPOT optimizes machine learning pipelines using
genetic programming, which explores and evolves
pipeline structures automatically; however, it can be
resource-intensive and time-consuming or stop early
with higher generations or large datasets. MLBox
offers robust feature selection and precise hyperpa-
rameter optimization in high-dimensional settings but
faces challenges due to limited community support
and less flexibility than more established frameworks.
The selection of an AutoML tool should balance
specific project needs, considering data complexity,
urgency of task completion, and computational de-
mands.
4 FEATURE ENGINEERING
FRAMEWORKS
In this survey, we conducted a comparative sur-
vey on automated feature creation tools. We evalu-
ated Featuretools, AutoFeat, and PyCaret based
on several key aspects: feature creation time, con-
trol over generated features, integration with ML
pipelines, and their ability to handle relational data.
The study found that Featuretools demonstrate ex-
ceptional efficiency in generating complex features
from relational datasets. This makes it ideal for fi-
nance or transactional data applications. It provides
users with significant control through trans-primitives
but requires external methods for feature selection.
AutoFeat, while also integrating with ML
pipelines, showed slower feature creation and lim-
ited flexibility in controlling transformations and re-
lational data handling. This makes it less adaptable
for complex, multi-table datasets. AutoFeat may also
face challenges in handling large datasets effectively.
Conversely, PyCaret excelled in providing both
automated and customizable feature engineering
along with seamless integration into ML pipelines.
It offers advanced feature selection methods, such as
Lasso and recursive feature elimination. However,
similar to AutoFeat, it is not optimized for relational
data. PyCaret stands out for single-dataset use cases
where both feature engineering and model building
can be achieved in one environment.
5 BENCHMARK DESIGN
The benchmark design includes a detailed description
of the selected datasets, the performance metrics ap-
plied, the data preprocessing steps, the experimental
setup, and the baseline model used for AutoML tools
comparison.
5.1 Datasets
In this project, we selected seven diverse datasets
from the OpenML and UCI ML Repositories, cov-
ering regression, binary classification, and multiclass
classification tasks (Table 2). The datasets vary in
sample size from moderate to large and in the num-
ber of features from low to moderate. This variety
ensures our study addresses the complexity and vol-
ume of data that AutoML tools typically handle in
real-world applications. We also include datasets with
missing values, such as the Flight Delay Data, and
datasets with imbalanced classes, which are common
in scenarios like fraud detection.
5.2 Performance Metrics
AutoML frameworks are evaluated using common
metrics: accuracy, F1-score (weighted for multiclass),
A Survey of Evaluating AutoML and Automated Feature Engineering Tools in Modern Data Science
221

Table 2: Dataset Details.
Dataset Name OpenML
ID
Task
No. of
Instances
No. of
Features
No. of
Missing
Values
No. of
Classes
Sample
Size
Dimension
Bank Marketing Data 1461 Binary Class. 45,211 16 0 2 Moderate Low
Credit Card Fraud Detection 42175 Binary Class. 284,807 30 0 2 Large Moderate
Connect-4 - Multiclass Class. 67,557 42 0 3 Moderate Moderate
Flight Delay Data - Regression 171,666 21 3803 - Large Moderate
Rossmann Store Sales 45647 Regression 804,056 18 0 - Large Low
Online News Popularity 4545 Regression 39,644 60 0 - Moderate Moderate
Workers Compensation 42876 Regression 100,000 14 0 - Large Low
Note: Sample Size: Small (<10,000), Moderate (10,000<=), Large (100,000<=). Dimension: Low (<20), Moderate (20<=), High (100<=).
Empty OpenML ID indicates the dataset is from the UCI ML repository.
and AUC for classification, and RMSE and MAE for
regression. Additionally, training time, peak memory
usage, and whether the framework completed its run
within the set time limit are tracked to evaluate com-
putational efficiency and reliability.
5.3 Data Preprocessing
Several preprocessing techniques were applied before
feeding the datasets into the AutoML frameworks.
Cleaning. Minor data cleaning was performed, such
as removing duplicates and irrelevant columns.
Handling Missing Values. Some AutoML tools (e.g.
TPOT) do not directly support handling missing val-
ues. To maintain consistency across all tools, missing
numerical features were imputed using the “mean”,
while the “most frequent category” was used for miss-
ing categorical features.
Class Imbalance. For highly imbalanced datasets,
SMOTE (Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Tech-
nique) was applied.
Encoding and Scaling. Numerical features were
standardized using scaling techniques. For categori-
cal features, one-hot encoding was used for variables
with few categories, while target encoding was ap-
plied to those with many categories.
5.4 Experimental Setup
Each AutoML framework was evaluated using its de-
fault settings, except for the cross-validation folds and
runtime limits. A 5-fold cross-validation was applied,
and the training runtime for each tool was limited to
one hour.
For a clearer understanding of the experimental
process, Figure 1 provides an overview of the bench-
marking design.
All experiments were performed on a laptop
equipped with an Intel Core i7-1195G7 processor
(11th Gen, 2.90 GHz), 16 GB of RAM, and running
Windows 11 (64-bit).
5.5 Baseline Model
An XGBoost model was chosen as a baseline due to its
efficiency in handling structured data and its common
use in benchmarking. The model was trained with
default hyperparameters and evaluated using the same
5-fold cross-validation setup and performance metrics
applied to the AutoML tools.
6 RESULTS
This section compares the performance of AutoML
tools across multiple datasets using multiple metrics
(Table 3).
For classification tasks, AutoGluon and
H2O-AutoML consistently achieved the highest
F1-scores across datasets. AutoGluon had the
highest F1-score on the Credit Card Fraud Detection
dataset (0.8462), surpassing PyCaret (0.8244) and
H2O-AutoML (0.8193). H2O-AutoML also performed
well on the Bank Marketing dataset (F1-score:
0.6359) and multiclass Connect-4 dataset (F1-score:
0.8657), where AutoGluon closely followed with
scores of 0.5986 and 0.8613, respectively.
The ROC curves (Figure 2) further confirm that
AutoGluon and H2O-AutoML consistently performed
well across the classification tasks, while PyCaret,
TPOT, and XGBoost showed more varied results,
which might reflect differences in how these tools
handle specific types of data complexities or class
distributions. AutoGluon achieved the highest AUC
(0.985) for Credit Card Fraud Detection, illustrating
its ability to differentiate between classes effectively.
PyCaret (0.974) also performed well, while TPOT fell
behind with 0.943, indicating a need for extensive pa-
rameter tuning. In the Connect-4 multiclass classifi-
cation task, H2O-AutoML performed best with an AUC
ICEIS 2025 - 27th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
222
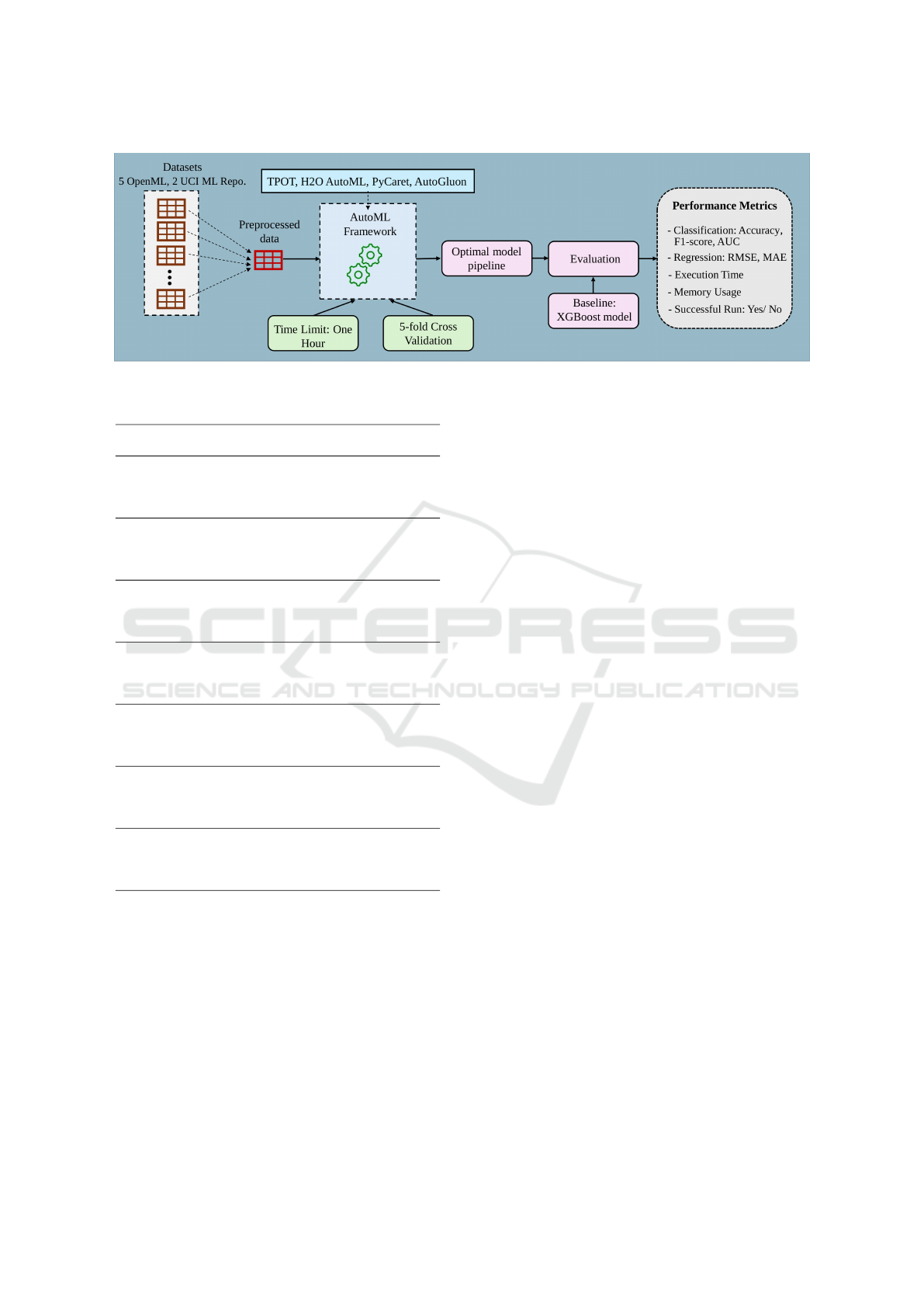
Figure 1: Benchmarking Design of the AutoML Frameworks.
Table 3: Performance comparison of AutoML tools.
Dataset Metric XGBoost TPOT
H2O
Au-
toML
PyCaret AutoGluon
Bank Accuracy 0.9061 0.9075 0.9005 0.9108 0.9084
Marketing F1-Score 0.5391 0.5479 0.6359 0.5528 0.5986
Data CV. F1-Score 0.5586 0.6316 0.6390 0.5578 0.6094
Exec. time (S) 0.2031 2278.9412 3606.7060 37.6750 763.2224
Memory (MiB) 558.27 681.16 338.20 393.04 884.43
Successful Run YES YES NO YES YES
Credit Accuracy 0.9993 0.9988 0.9995 0.9995 0.9995
Card F1-Score 0.7770 0.6645 0.8193 0.8244 0.8462
Fraud CV. F1-Score 0.9998 0.9999 0.9999 0.9999 0.9999
Detection Exec. time (S) 2.3940 3756.9307 3602.9343 966.7086 3476.6021
Memory (MiB) 892.17 2318.73 564.79 825.92 1483.21
Successful Run YES NO NO YES YES
Connect Accuracy 0.8390 0.8584 0.8731 0.8435 0.8714
-4 F1-Score 0.8184 0.8511 0.8657 0.8238 0.8613
CV. F1-Score 0.8116 0.8315 0.8630 0.8204 0.8545
Exec. time (S) 0.7790 1566.5880 3603.9905 72.2768 1553.2549
Memory (MiB) 460.86 670.68 539.32 439.61 2082.31
Successful Run YES YES NO YES YES
Flight RMSE 20.0900 0.5991 4.0976 0.5994 8.7222
Delay MAE 3.1584 0.05300 2.2078 0.0568 1.7110
Data CV. RMSE 18.3391 0.5801 4.0287 0.5966 7.8119
Exec. time (S) 6.7101 4134.5008 3656.4672 1629.2889 1957.3204
Memory (MiB) 2680.86 5929.63 1722.16 3620.68 6891.87
Successful Run YES NO NO YES YES
Ross. RMSE 909.0793 1196.7631 693.0951 830.5985 653.4289
Store MAE 640.6478 846.9798 471.5256 558.0058 450.4649
Sales CV. RMSE 922.0261 1201.5169 713.5470 853.5296 669.4508
Exec. time (S) 1.7982 3808.9894 3651.5380 1122.9731 3598.5135
Memory (MiB) 922.77 1317.59 415.17 3880.22 4438.67
Successful Run YES NO NO YES YES
Online RMSE 13653.64 12970.80 12967.58 12996.68 12987.69
News MAE 3513.79 3078.01 3101.40 3105.60 3029.47
Popularity CV. RMSE 11524.44 10802.16 10553.70 11984.99 10775.93
Exec- time (S) 0.41 3659.47 3531.61 146.29 747.0031
Memory (MiB) 496.01 578.59 469.76 526.71 1798.55
Successful Run YES NO YES YES YES
Workers RMSE 43737.61 40954.68 40988.46 41014.83 40945.97
Comp. MAE 12419.85 10987.48 10512.37 11745.04 10966.23
CV. RMSE 43405.48 40017.79 39467.60 46463.42 40265.9112
Exec. time (S) 0.17 1456.74 3546.72 58.1437 901.98
Memory (MiB) 585.22 699.18 661.57 443.02 1756.29
Successful Run YES YES YES YES YES
of 0.974, closely followed by AutoGluon at 0.972.
This suggests both tools are well-suited for complex
classification tasks involving multiple outcomes.
In regression tasks, AutoML tools generally out-
performed XGBoost, with lower RMSE and MAE val-
ues across datasets (Figure 3). This highlights the effi-
ciency of AutoML tools in optimizing model param-
eters and features compared to traditional methods.
Particularly, in the Rossmann Store Sales and Work-
ers Compensation datasets, which vary in sample
sizes and feature dimensions, AutoGluon achieved
the lowest RMSE. This demonstrates its strength in
handling large datasets with relatively low feature di-
mensions. For the Flight Delay Data, the RMSE
values of TPOT and AutoGluon differ considerably
(0.5991 and 8.7222, respectively). The complex-
ity of the Flight Delay Data, including factors like
time of day and seasonal variations, introduces non-
linear interactions among features. TPOT’s genetic
programming excels in such settings by developing
customized pipelines that better capture these com-
plex dynamics, outperforming AutoGluon in this in-
stance. AutoGluon, by contrast, has limited capabili-
ties for time-series and text data.
In terms of execution time and memory usage,
PyCaret was the most efficient tool. It consistently
provided the fastest runs. H2O-AutoML and TPOT, on
the other hand, often took the maximum allocated
time of one hour. This resulted in several unsuccess-
ful runs, particularly in large datasets such as Credit
Card Fraud Detection and Rossmann Store Sales.
While AutoGluon excelled in predictive performance,
it consistently consumed more memory than the other
tools across nearly all datasets.
Overall, this comparison across datasets shows
that although XGBoost remains a powerful ML al-
gorithm, AutoML tools offer more adaptable and
often more accurate alternatives for complex, real-
world datasets requiring minimal user intervention.
AutoGluon provides strong predictive performance
for both classification and regression tasks, although
it requires higher resource consumption. PyCaret is
a strong alternative when fast execution is required,
though it tends to under-perform in terms of predic-
tive accuracy. Meanwhile, H2O-AutoML offers reli-
able model performance, but its lengthy execution
times make it less suitable for time-sensitive tasks.
Similarly, TPOT was also hindered by its inability to
complete optimization within the set time limit.
A Survey of Evaluating AutoML and Automated Feature Engineering Tools in Modern Data Science
223
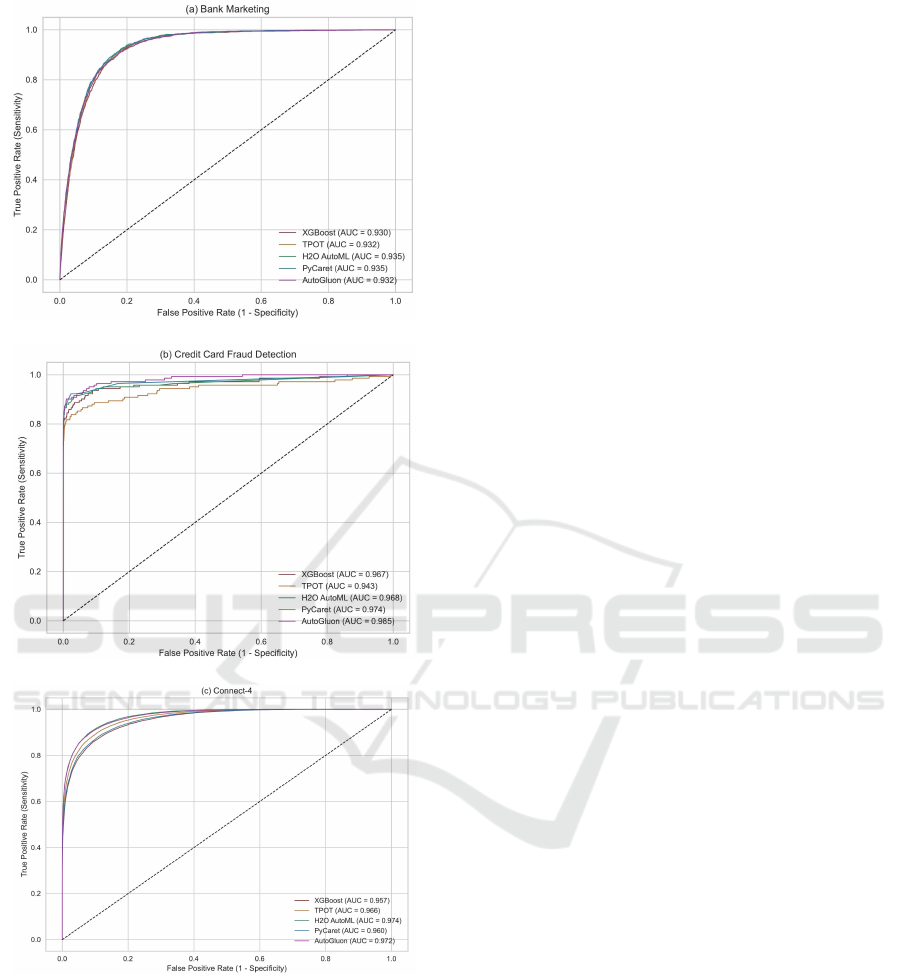
Figure 2: ROC curves for the classification datasets.
7 KEY FINDINGS AND
RECOMMENDATIONS
This survey provides an extensive comparison of Au-
toML tools and feature engineering tools.
Our findings show that AutoGluon stands out for
its strong predictive performance in both classifica-
tion and regression tasks. It is a reliable choice when
accuracy is the main priority. However, it requires
more computational power and has longer processing
times, which may be a drawback in situations where
quick results are essential. H2O-AutoML delivered ro-
bust model performance, but its lengthy optimization
times made it less suitable for time-sensitive applica-
tions. In contrast, PyCaret is the fastest tool, with
low memory usage. For scenarios where efficiency
and quick model deployment are prioritized, PyCaret
is a good option.
One challenge we experienced was that TPOT of-
ten struggled to complete its optimization within the
set time constraints. It only succeeded in some cases.
This suggests that TPOT may be less suitable when
working with tight time limits. To use TPOT effec-
tively, users may need to allocate more time for opti-
mization.
Moreover, in our evaluation of feature engineer-
ing tools, we found that Featuretools excels in han-
dling complex data relationships and is particularly
beneficial for datasets with rich features and relational
structures. Meanwhile, Autofeat and PyCaret are
easy to use and work well with simple datasets. They
are good choices for users seeking quick, automated
feature creation without much customization.
When working with large, real-world datasets and
industry-scale data, it’s important to select tools that
can efficiently manage large amounts of data and fea-
tures. Both AutoGluon and H2O-AutoML can handle
high-dimensional data, but they do require more re-
sources. For smaller datasets, PyCaret is an excellent
option because of its speed and lower computational
demands.
In conclusion, while automated tools often out-
perform traditional machine learning algorithms like
XGBoost, each tool exhibits distinct strengths and
weaknesses that require careful consideration based
on the specific requirements, whether prioritizing pre-
dictive power, speed, or resource efficiency. Future
studies could expand on this work by testing newer
tools and using real-world datasets to assess perfor-
mance across diverse practical applications. Further,
it would be valuable to explore the integration of these
tools to address individual weaknesses, potentially
enhancing their overall effectiveness. Additionally,
investigating the combination of feature engineering
techniques with AutoML tools could provide deeper
insights into optimizing model performance across di-
verse applications.
ICEIS 2025 - 27th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
224

Figure 3: RMSE and MAE comparison for the regression datasets. The x-axis is displayed in log scale to better highlight
differences between the values.
REFERENCES
Arag
˜
ao, M. V. C., Afonso, A. G., and Ferraz, R. C. (2023).
A practical evaluation of automl tools for binary, mul-
ticlass, and multilabel classification. TechRxiv.
Blohm, M., Hanussek, M., and Kintz, M. (2020). Lever-
aging automated machine learning for text classifica-
tion: Evaluation of automl tools and comparison with
human performance. In Proc. Int. Conf. Agents Artif.
Intell.
Doke, A. and Gaikwad, M. (2021). Survey on automated
machine learning (automl) and meta learning. In Proc.
2021 12th Int. Conf. Comput. Commun. Netw. Tech-
nol. (ICCCNT), pages 1–5, Kharagpur, India.
Eldeeb, H., Maher, M., Elshawi, R., and Sakr, S. (2024).
Automlbench: A comprehensive experimental evalu-
ation of automated machine learning frameworks. Ex-
pert Syst. Appl., 243.
Elshawi, R., Maher, M., and Sakr, S. (2019). Automated
machine learning: State-of-the-art and open chal-
lenges. arXiv preprint arXiv:1906.02287.
Ferreira, L., Pilastri, A., Martins, C. M., Pires, P. M., and
Cortez, P. (2021). A comparison of automl tools for
machine learning, deep learning and xgboost. In Proc.
2021 Int. Joint Conf. Neural Netw. (IJCNN), pages 1–
8, Shenzhen, China.
Gijsbers, P., Bueno, M. L. P., Coors, S., LeDell, E., Poirier,
S., Thomas, J., Bischl, B., and Vanschoren, J. (2024).
Amlb: An automl benchmark. J. Mach. Learn. Res.,
25:1–65.
Gijsbers, P., LeDell, E., Thomas, J., Poirier, S., Bischl, B.,
and Vanschoren, J. (2019). An open source automl
benchmark. arXiv preprint arXiv:1907.00909.
Hanussek, M., Blohm, M., and Kintz, M. (2021). Can
automl outperform humans? an evaluation on pop-
ular openml datasets using automl benchmark. In
Proc. 2020 2nd Int. Conf. Artif. Intell. Robot. Control
(AIRC’20), pages 29–32, Cairo, Egypt.
Karmaker, S. K., Hassan, M. M., Smith, M. J., Xu, L.,
Zhai, C., and Veeramachaneni, K. (2022). Automl to
date and beyond: Challenges and opportunities. ACM
Comput. Surv., 54(8):Art. 175.
Majidi, F., Openja, M., Khomh, F., and Li, H. (2022). An
empirical study on the usage of automated machine
learning tools. In Proc. 2022 IEEE Int. Conf. Software
Maintenance and Evolution (ICSME), pages 59–70,
Limassol, Cyprus.
Mumuni, A. and Mumuni, F. (2024). Automated data pro-
cessing and feature engineering for deep learning and
big data applications: A survey. Journal of Informa-
tion and Intelligence.
Narayanan, A. N., Das, S. S., and Mirnalinee, T. T.
(2023). Evaluation of automl frameworks for compu-
tational admet screening in drug discovery & devel-
opment. In Proc. 2023 IEEE Int. Conf. Bioinformat-
ics Biomedicine (BIBM), pages 4929–4931, Istanbul,
Turkiye.
Paladino, L. M., Hughes, A., Perera, A., Topsakal, O., and
Akinci, T. C. (2023). Evaluating the performance of
automated machine learning (automl) tools for heart
disease diagnosis and prediction. AI, 4(4):1036–1058.
Truong, A. T., Walters, A., Goodsitt, J., Hines, K. E., Bruss,
B., and Farivar, R. (2019). Towards automated ma-
chine learning: Evaluation and comparison of automl
approaches and tools. In Proc. 2019 IEEE 31st Int.
Conf. Tools Artif. Intell. (ICTAI), pages 1471–1479.
Urbanowicz, R. J., Bandhey, H., and Keenan, B. T.
(2023). Streamline: An automated machine learning
pipeline for biomedicine applied to examine the util-
ity of photography-based phenotypes for osa predic-
tion across international sleep centers. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2312.05461.
Zhong, Y., Yang, C., Su, X., Li, B., Huang, X., and Shuai,
Y. (2024). Review on research of automated machine
learning. In Proc. 2023 7th Int. Conf. Comput. Sci.
Artif. Intell. (CSAI
´
23), pages 526–532. Association
for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA.
Z
¨
oller, M.-A. and Huber, M. F. (2019). Benchmark and
survey of automated machine learning frameworks. J.
Artif. Intell. Res., 70:409–472.
A Survey of Evaluating AutoML and Automated Feature Engineering Tools in Modern Data Science
225
