
Enhancing Railway Obstacle Detection System Based on Incremental
Learning
Qiushi Guo, Bin Cao, Dehao Hao, Cheng Wang, Lijun Chen and Peng Yan
China SWJTU Railway Development Co., Ltd (CSRD), China
Keywords:
Obstacle Detection, Railway Security, Deep Learning.
Abstract:
Obstacle detection systems face challenges related to the Catastrophic forgetting problem, where old obstacles
may be misclassified when training new unseen obstacles. Re-training a model from scratch for every new
obstacle is often impractical. In this work, we propose a continual learning-based approach to efficiently
update the model without repeatedly retraining on previous data, while simultaneously mitigating catastrophic
forgetting. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method.
1 INTRODUCTION
With the advancement of high-speed rail systems,
their safety and reliability have garnered significant
public attention in recent years. Obstacles within rail-
way zones represent a major threat to railway safety.
Potential obstacles encompass a wide variety of cate-
gories, including rocks, animals, pedestrians, and tree
branches. A core challenge in railway obstacle detec-
tion is the inherent difficulty of predefining all possi-
ble obstacles. Furthermore, the dynamic environmen-
tal conditions(Guo, 2024) surrounding railway areas
add additional complexity to this task.
Deep learning-based approaches have achieved
significant success in domains such as mobile pay-
ment(Guo et al., 2023), disaster detection(Sazara
et al., 2019), and remote sensing(Bischke et al.,
2019). Obstacle detection in railway areas can be
framed as an Out-of-Distribution (OOD) problem
(Yang et al., 2024). In real-world scenarios, obsta-
cles may not be encountered during training, present-
ing a significant challenge. Traditional deep learning-
based approaches struggle with this issue, as models
trained on specific datasets can only detect objects
represented within the training data. One potential so-
lution is to update existing models when new obstacle
categories emerge. For example, consider an obsta-
cle detection model at stage T that is trained to detect
pedestrians. At stage T+1, the model must be updated
to detect new obstacles, such as rocks. Consequently,
the training dataset must also be expanded to include
both categories—pedestrians and rocks.
However, this approach presents several chal-
stage 1
stage2
stageT
train
predict
fine-tune
Figure 1: Demonstration of the Catastrophic Forgetting
Problem: In the early stages, both previous and current ob-
stacle categories are accurately predicted (denoted by the
green box). However, as time progresses, the likelihood
of misprediction for objects from previous stages increases,
leading to a higher probability of incorrect classifications
(denoted by the red box).
lenges. First, model updating is time-consuming
and costly, as it requires retraining the model. Sec-
ond, training a model necessitates a large volume
of data, and storing previous object images becomes
increasingly burdensome over time. Finally, when
a model is fine-tuned on new data, it often experi-
ences a loss of performance on previously learned
tasks, a phenomenon known as catastrophic forget-
ting, which can be detrimental in our scenario. As
illustrated in fig. 1, obstacles such as pedestrians and
rocks may be misclassified during later stages, under-
scoring the critical nature of mitigating catastrophic
forgetting(Kirkpatrick et al., 2017) in obstacle detec-
tion tasks.
In this work, we propose a incremental learning-
Guo, Q., Cao, B., Hao, D., Wang, C., Chen, L. and Yan, P.
Enhancing Railway Obstacle Detection System Based on Incremental Learning.
DOI: 10.5220/0013268300003941
In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Vehicle Technology and Intelligent Transport Systems (VEHITS 2025), pages 413-420
ISBN: 978-989-758-745-0; ISSN: 2184-495X
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
413

based approach to address the aforementioned chal-
lenges. To alleviate storage pressure, we introduce
an object-level memory bank that retains information
about obstacles and their corresponding priority in-
dices. The obstacle information represents previously
encountered objects, which can be fused with current
images, while the priority index determines the like-
lihood of an object being selected for inclusion in the
model. The selected objects are then overlaid onto the
current image, which incorporates both previous and
new obstacles into a single frame.
To identify previous objects that are more likely
to be misclassified, we employ two strategies. First,
we design a policy to update the memory bank. At
the end of each training stage, the priority index is
updated based on the sum of the absolute gradient
values of the pasted images. Second, we update the
shallow layers of our model at the beginning of each
stage. This targeted modification is based on the
premise that shallow layers capture shape-related fea-
tures(Geirhos et al., 2018), which are critical to the
accuracy of our task. The details of our methods are
provided in Section 3.
In this work, our contributions can be summarized
as follow:
• We propose a data-efficiency approach to fuse
previous obstacles with current new emerging ob-
stacles without increasing the number of total
training images.
• We propose a memory bank and corresponding
update policy. The memory bank is updated based
on the sum of absolute gradient of fused images.
• We update the shallow layer of current network
with previous one to retain previous learned fea-
tures.
2 RELATED WORKS
2.1 Railway Obstacles Detection
In recent years, several approaches have been ap-
plied in obstacle detection in railway areas. Rahman
et.al. (Rahman et al., 2022) propose a classification
based method which leverage MobileNetV2 to clas-
sify the obstacled images. They claim that proposed
model outperforms other approaches; Brucker et.al.
(Brucker et al., 2023) propose utilizing a shallow net-
work to learn railway segmentation from normal rail-
way images, besides they explore the controlled in-
clusion of global information by learning to hallu-
cinate obstacle-free images; Zhang et. al. (Zhang
et al., 2023)propose an intelligent obstacle detection
system based on deep learning to improve the safety
of train operation. To further improve the robust-
ness and reliability of the system, signals of other
modal signals are introduced, LiDAR, for instance.
Bai et al .(Bai et al., 2024) fuse visual and Lidar data
in real time railway obstacle detection task. How-
ever, LiDAR is expensive compared to camera and
is easily affected by temperature, which is impracti-
cal to be widely deployed in practical scenarios. Wen
et. al.(Wen et al., 2024) propose a multi-contrastive
learning strategy to improve point cloud segmentation
in complex weather for rail-obstacle detection.
2.2 Incremental Learning
Incremental learning, also known as lifelong learning
or continual learning, has been applied across various
computer vision tasks (Douillard et al., 2021; Si et al.,
2025). The primary objective of incremental learning
is to address catastrophic forgetting (Robins, 1995),
wherein a model gradually loses its ability to recog-
nize objects from earlier stages. Some approaches
retain a limited number of previous data samples or
features for integration with current data (Zhu et al.,
2023). Other methods focus on modifying network
structures to accommodate new tasks (Frankle and
Carbin, 2018), designing effective sample selection
policies for task adaptation (Prabhu et al., 2020), or
generating pseudo-labels and synthetic images to mit-
igate class imbalance (Douillard et al., 2021). To the
best of our knowledge, incremental learning has not
yet been applied to railway obstacle detection. We
believe that a well-designed incremental learning sys-
tem could improve efficiency while simultaneously
addressing catastrophic forgetting.
3 METHODS
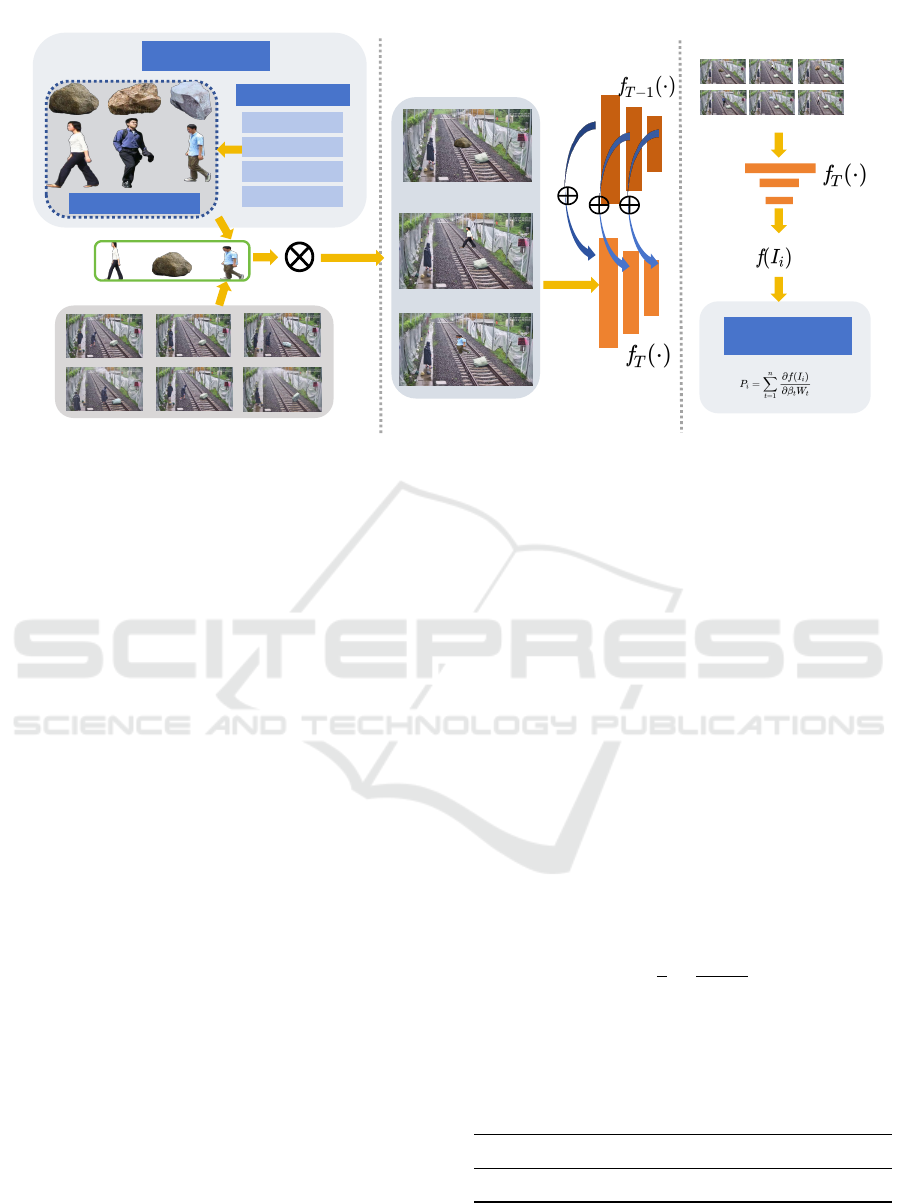
In this section, we describe the components of our
system in detail. As illustrated in fig. 2, our system
comprises the following key components: an Object-
based Memory Bank, an Absolute Gradient Value Up-
date Policy, and Shallow Layer Replacement. These
components work together to integrate past informa-
tion with current images, effectively addressing the
catastrophic forgetting problem.
3.1 Reformulation
Railway Obstacle Detection
Given an Image I ∈ R
C×H×W
, a sub-area M ⊂
I, which indicates that there exists a railway area
VEHITS 2025 - 11th International Conference on Vehicle Technology and Intelligent Transport Systems
414
Memory Bank
Update Module
Priority index
obj-1
obj-2
...
obj-n
(a)Object-Level fusion
(b)Model Training stage
(c)Memory Bank update
Obstacle Gallery
Memory Bank
Figure 2: (a) Data Fusion Module: In this step, objects are retrieved from the Object Memory Bank based on their priority
index. These objects are then overlaid onto the images in the current stage to integrate both past and present obstacle infor-
mation. (b) Training Process: During the training phase, the shallow layers of the convolutional neural network (CNN) are
replaced with the corresponding layers from the previous stage at the start of each new training cycle. (c) Memory Bank
Update: The memory bank is updated at the end of each training stage, with updates determined by the absolute gradient
change of each fused image.
in the image; an obstacle set with n classes
O =
{
o
1
,o
2
,...,o
n
}
, The Railway obstacles detec-
tion system aims to obtain a CNN model ϕ : I 7−→
{
B
i
, p
i
,c
i
}
n
i
, where B
i
=
{
x
i
,y
i
,h,w
}
. p
i
∈ [0, 1].
y =
(
0, if p
i
> H and ∃i,s.t.,B
i
T
M ̸=
/
0
1, else
(1)
where y is the prediction of the system, 1 is obstacles
detected and 0 is no obstacles; H is the threshold of
confidence of detected candidates, which can be ad-
justed based on different scenarios.
Incremental Learning
Assuming we are given a data stream D =
{
D
1
,D
2
,...
}
, D
i
∩ D
j
=
/
0. θ
i
is the parameters of
model f
i
(·), which is updated at stage i. The model is
initialized based on D
0
f
0
(·) = ψ
0
(D
0
) (2)
where ψ
0
is training strategy in stage 0. At stage T ,
the model is updated in following way:
f
T
= φ
T
(D
T
,D
bank
, f
T −1
). (3)
Where D
bank
is memory bank, which saves informa-
tion of previous D
i,...,T −1
. φ(·) is the update strategy,
which takes previous model, memory bank and cur-
rent data as input. The updated strategies may vary
along with the change of stages.
3.2 Memory-Bank Module
Object-Level Memory Bank
Previous continual learning based approach save
whole image in Memory-Bank(Qu et al., 2021). With
the accumulation of time, the memory bank will suf-
fer from storage burden. To alleviate this issue, we
propose a object-level memory bank. We extract tar-
get obstacle objects in each stage. The extract object
patches are no bigger than the original images. In this
way, one training image contain both previous obsta-
cles and current obstacles. To simulate the practical
scenarios, the objects need to be re-scaled according
to their pasted positions.
k =
1
n
n
∑
1
patch
i
s
i
(4)
where s
i
is the size of original image. We iterate our
dataset, calculate the average k in different categories.
as illustrated in 1, object-level can save 90% space
Table 1: Object-image ratios in our scenario.
Pedestrian rocks Branch board avg.
k 0.12 0.07 0.09 0.11 0.10
compared to image-level approach.
Extracted patches are then fed into Segment-
Anything-Model(SAM) to obtain corresponding
Enhancing Railway Obstacle Detection System Based on Incremental Learning
415

mask, which will be used in our copy paste step.
Copy-Paste Object Fusion
Traditional approaches also suffer from the burden of
data accumulating. Assuming we have N stages, in
each stages we have M images. Training time of an
batch of images(B) is P. The estimated time
˜
T is cal-
culated as follow:
˜
T =
M × N × P
B
(5)
The Training costs become prohibitively expen-
sive as N increases, Not to mention the impact caused
by class imbalance.
To alleviate this problem, we introduce a copy-
paste approach to fuse history object with current cat-
egories. The procedures are as follow: firstly, pre-
vious obstacle object are sampled based on priority
index in memory bank. As illustrated part a in 2, the
sampled objects are pasted on the current stage im-
ages according to Mask. In this approach, the training
image remain the same in each stage. This approach
simultaneously reduces training time and maintains
data class balance.
ˆ
I = M ⊗ P + (1 − M) ⊗ I (6)
Update Policy
The core component of the Object Memory Bank
module is the Update Policy, which serves two main
functions. First, it identifies objects or categories
that are more likely to be misclassified; second,
it refreshes the Memory Bank to prevent excessive
growth. In deep neural networks, changes in gra-
dient values can indicate the model’s sensitivity to
specific input data (Selvaraju et al., 2017). Given
a trained model and an input image, gradient val-
ues are obtained through an inference process, where
higher values indicate greater sensitivity to that ob-
ject class. Additionally, objects within the same cat-
egory contribute differently to model training. To as-
sess the priority of objects in the Memory Bank, we
introduce the Absolute Gradient Value Update Pol-
icy. Given a Model f (·) and fuse image samples
I
cp
=
{
I
1
,I
2
,...,I
n
}
. At the end of each stage, the pri-
ority index of each image can be calculated as follow:
p
i
=
n
∑
i=1
∂ f (I
i
)
∂βW
i
(7)
where n is the number of kernels in model, W
i
is the
corresponding weights in kernels. β
i
is a parameter
to adjust the importance of each channel, which is be-
tween 0.1 to 0.8, shallow layer is with a larger value
compared to deeper layer. At stage K, a priority queue
L
k
is formed based p
i
, 1/k items in L
k
will be replaced
randomly by current stage obstacles.
3.3 Shallow-Channels Fusion
Another contributor to catastrophic forgetting is the
shift in kernel weights.(Jin et al., 2021) During model
fine-tuning, the weights in kernels responsible for
recognizing previous objects are overwritten by new
weights, leading to an irreversible shift. This weight
shift can worsen over time, compounding the issue.
To address this, we propose a kernel-level informa-
tion fusion mechanism.
Previous studies have shown that shallow CNN
layers are more effective at capturing shape-based
features, while deeper layers tend to capture texture-
based features(Hermann et al., 2020). Since shape-
based features are robust and crucial for obstacle-
related tasks, we enhance our model’s resilience
against catastrophic forgetting by replacing the shal-
low CNN layers, enabling better retention of earlier
learned features. The target channel k is determined
as follow:
k
i
= arg max
k
∂ f (I
i
)
∂W
k
(8)
channels = [k
1
,k
2
,.., k
n
] (9)
Here, I
i
represents a randomly sampled fused im-
age with a high priority index. At the start of each
stage, channels from the fine-tuned model in the pre-
vious stage randomly replace the corresponding chan-
nels in the current model. Through experimenta-
tion, we observed that fusing channels from multiple
prior models can slightly improve robustness. How-
ever, this approach also increases storage require-
ments and inference time. As a trade-off, we choose
to replace channels using only the model from the
immediately preceding stage. yellow box), respec-
tively. On the right: after training, intra-class dis-
tances become smaller, while inter-class distances be-
come larger. (ViT) (Dosovitskiy, 2020) as its back-
bone, whereas the light-type employs a modified ver-
sion of MobileNetV2 (Sandler et al., 2018). To re-
duce the model size further, we compress the original
MobileNetV2 by reducing its width, i.e., decreasing
the number of channels. Both ViT and the modified
MobileNetV2 replace the final layer with a fully con-
nected layer of size n × 128.
3.4 Pseudo Code
The pseudo code of our update policy is illustrated as
algorithm 1.
VEHITS 2025 - 11th International Conference on Vehicle Technology and Intelligent Transport Systems
416

(a) ballasted track
(b) ballastless track
(c) Obstacles
Figure 3: Experiment sites and obstacles in our work. ballasted track(a) is around 70 meters ling and 8 meters wide; b)
ballastless track is around 100 meters long and 6 meters wide. Obstacles from left to right: rocks(20cm), rocks(30cm),
rocks(40cm), parcels, pedestrians, steel board and branches.
Algorithm 1: Update policy.
Input: Model f (·), Memory Bank M
T −1
,
image set in stage T
D
T
=
{
I
1
,I
2
,...,I
n
}
Result: Updated Memory Bank M
T
Data: Priority index P = [...]
foreach I
i
do
// copy-paste to generate fused
image
I
f use
= m ⊗ P + (1 − m) ⊗ I
i
;
// Calculate absolute gradient
across layers
P
i
=
∑
n
i=1
∂ f (I
f use
)
∂βW
i
;
P.append(p
i
);
end
sort(P);
for i = 0 to n do
// Replace Memory bank objects
according to priority index
M .Patch[i] = ranndom(ob j
t
,P[i])
end
4 EXPERIMENTS
4.1 Configuration
Our method is implemented using the PyTorch frame-
work and the model is trained on an RTX 3090Ti, with
24 GB memory. CPU processor is Intel i7-12700F
with 20 cores. We select Adam(Kingma, 2014) as the
optimizer. Starting learning rate is set to 0.001. The
batch size is set to 16 and the number of epochs to
25. Albumentation(Buslaev et al., 2020) is utilized
to perform data augmentation. Data transformations
include horizontal flip, coarse dropout, and random
brightness contrast adjustments.
4.2 Dataset & Policy
Dataset
The images used in this study were captured at our
experimental site in Chengdu, China. As shown in
fig. 3, the site includes two types of railway scenarios:
ballastless track and ballasted track. The obstacles
we prepared include rocks of varying sizes (20 cm,
30 cm, and 40 cm), branches, pedestrians, parcels,
and steel boards. For each stage, we collected 2,000
images—1,200 on ballastless track and 1,200 on bal-
lasted track. Obstacles were positioned at varying dis-
tances between 10 m and 50 m. The dataset was split
randomly into training and test sets, with an 80:20 ra-
tio.
Policy
The categories of obstacles—rocks (20 cm, 30 cm,
40 cm), parcels, pedestrians, steel boards, and
branches—are designated as A through G, respec-
tively. In each training stage, only data from one
Enhancing Railway Obstacle Detection System Based on Incremental Learning
417

Table 2: Results w/wo our approach across popular detection architectures.
D/A → A D/B → B D/C → C D/D → D D /E → E D/F → F D/G → G
Yolo v5(Jocher, 2020) 0.824 0.837 0.842 0.791 0.917 0.684 0.635
Yolov5+Ours 0.831 0.849 0.857 0.811 0.934 0.713 0.651
Yolo v10(Wang et al., 2024) 0.819 0.847 0.837 0.811 0.924 0.714 0.672
Yolov10+Ours 0.827 0.853 0.859 0.836 0.928 0.733 0.691
Faster Rcnn(Ren et al., 2016) 0.807 0.825 0.831 0.776 0.909 0.723 0.667
Faster Rcnn+Ours 0.813 0.834 0.844 0.791 0.924 0.737 0.681
nanodet(RangiLyu, 2021) 0.821 0.826 0.847 0.808 0.916 0.696 0.659
nanodet+Ours 0.833 0.829 0.857 0.831 0.931 0.717 0.683
Swin(Liu et al., 2021) 0.827 0.841 0.847 0.822 0.938 0.735 0.649
Swin+Ours 0.839 0.857 0.862 0.831 0.946 0.749 0.661
Table 3: Ablation study on sub-component.
copy-paste Layer-fusion GMBU mIoU
0.813
✓ 0.847
✓ 0.821
✓ 0.871
✓ ✓ ✓ 0.889
Table 4: Ablation results on pasted objects fused on images.
# objs 1 2 3 4 5 6
mIoU 0.864 0.875 0.894 0.889 0.896 0.890
category and the corresponding entries in the Object
Memory Bank are accessible. The notation D/A → A
indicates that the current task is to detect category A,
where D represents the union of all categories. We set
the training steps to 2, meaning that two categories are
trained in each step.
For example, in the stage D/A → A, the model
is fine-tuned using data from category A along with
fused data from other categories. The test set consists
of all images except those from category A, as our
objective is to assess the effectiveness of the method
in addressing catastrophic forgetting.
4.3 Results
Quantitative Evaluation
The results of quantitative evaluation is illustrated
as below. We deploy our approach on several pop-
ular detection architectures(YOLO-V5, YOLO-V10,
Faster-RCNN, Swin, nanodet) to verify the effec-
tiveness of it. The results indicates that our pro-
posed methods are effective across all architectures
we listed. The improvement of mIoU range from
0.006 to 0.024. Besides, it is noticeable that the ef-
fects of Catastrophic Forgetting is different across cat-
egories. It is severe in D/F −→ F setting, which in-
dicates that the learned features of steel board may
overlap the previous ones. The setting D/A −→
A,D/B −→ B and D/C −→ C show subtle improve-
ments indicates that cubes share similar features in
terms of contours and shapes.
Ablation Study
To verify the effectiveness of each module, we con-
duct an ablation study in terms of Copy-Paste, Layer
fusion and Gradient-Memory-Bank update module.
The results are illustrated in table 3. One point that
needs to be clarified is, when GMBU is not activated,
we adapt a random update policy to update the mem-
ory bank. The results indicate that each part con-
tribute to improve the whole system, while GMBU
contributes the most.
We also conduct experiments to determine the best
number of pasted objects on current images, the re-
sults are illustrated as table 4. The results indicate
that the performance increase when number of objects
range from 1 to 4 and become saturate after that.
5 DISCUSSION
In this work, we have proposed a continual learning-
based approach to mitigate the catastrophic forget-
ting problem in obstacle detection for railway scenar-
ios. The proposed Object-Memory Bank reduces both
storage and training burdens simultaneously. The
memory bank update policy, along with modifications
to the CNN layers, facilitates the retention of previ-
ously learned features in later stages. Future work
could focus on optimizing the object fusion process,
such as incorporating light and shadow information
during the image generation stage, which would en-
hance the realism of the data. Additionally, further
VEHITS 2025 - 11th International Conference on Vehicle Technology and Intelligent Transport Systems
418

research on feature-based methods is needed to com-
press the memory bank more effectively.
REFERENCES
Bai, R., Wu, Z., and Xu, T. (2024). A lightweight camera
and lidar fusion framework for railway transit obsta-
cle detection. In Proceedings of the 2024 3rd Asia
Conference on Algorithms, Computing and Machine
Learning, pages 303–308.
Bischke, B., Helber, P., Folz, J., Borth, D., and Dengel, A.
(2019). Multi-task learning for segmentation of build-
ing footprints with deep neural networks. In 2019
IEEE International Conference on Image Processing
(ICIP), pages 1480–1484. IEEE.
Brucker, M., Cramariuc, A., Von Einem, C., Siegwart,
R., and Cadena, C. (2023). Local and global infor-
mation in obstacle detection on railway tracks. In
2023 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelli-
gent Robots and Systems (IROS), pages 9049–9056.
IEEE.
Buslaev, A., Iglovikov, V. I., Khvedchenya, E., Parinov, A.,
Druzhinin, M., and Kalinin, A. A. (2020). Albumen-
tations: Fast and flexible image augmentations. Infor-
mation, 11(2).
Dosovitskiy, A. (2020). An image is worth 16x16 words:
Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv
preprint arXiv:2010.11929.
Douillard, A., Chen, Y., Dapogny, A., and Cord, M.
(2021). Plop: Learning without forgetting for con-
tinual semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the
IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern
recognition, pages 4040–4050.
Frankle, J. and Carbin, M. (2018). The lottery ticket hypoth-
esis: Finding sparse, trainable neural networks. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1803.03635.
Geirhos, R., Rubisch, P., Michaelis, C., Bethge, M., Wich-
mann, F. A., and Brendel, W. (2018). Imagenet-
trained cnns are biased towards texture; increasing
shape bias improves accuracy and robustness. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1811.12231.
Guo, Q. (2024). A universal railway obstacle detection sys-
tem based on semi-supervised segmentation and opti-
cal flow. arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.18908.
Guo, Q., Chen, Y., Yao, Y., Zhang, T., and Ma, J. (2023).
A real-time chinese food auto billing system based on
instance segmentation. In 2023 IEEE Region 10 Sym-
posium (TENSYMP), pages 1–5. IEEE.
Hermann, K., Chen, T., and Kornblith, S. (2020). The ori-
gins and prevalence of texture bias in convolutional
neural networks. Advances in Neural Information
Processing Systems, 33:19000–19015.
Jin, X., Sadhu, A., Du, J., and Ren, X. (2021). Gradient-
based editing of memory examples for online task-free
continual learning. Advances in Neural Information
Processing Systems, 34:29193–29205.
Jocher, G. (2020). Ultralytics yolov5.
Kingma, D. P. (2014). Adam: A method for stochastic op-
timization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6980.
Kirkpatrick, J., Pascanu, R., Rabinowitz, N., Veness, J.,
Desjardins, G., Rusu, A. A., Milan, K., Quan, J.,
Ramalho, T., Grabska-Barwinska, A., et al. (2017).
Overcoming catastrophic forgetting in neural net-
works. Proceedings of the national academy of sci-
ences, 114(13):3521–3526.
Liu, Z., Lin, Y., Cao, Y., Hu, H., Wei, Y., Zhang, Z., Lin,
S., and Guo, B. (2021). Swin transformer: Hierar-
chical vision transformer using shifted windows. In
Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international confer-
ence on computer vision, pages 10012–10022.
Prabhu, A., Torr, P. H., and Dokania, P. K. (2020). Gdumb:
A simple approach that questions our progress in con-
tinual learning. In Computer Vision–ECCV 2020:
16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, August 23–
28, 2020, Proceedings, Part II 16, pages 524–540.
Springer.
Qu, H., Rahmani, H., Xu, L., Williams, B., and Liu,
J. (2021). Recent advances of continual learning
in computer vision: An overview. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2109.11369.
Rahman, F. U., Ahmed, M. T., Hasan, M. M., and Jahan,
N. (2022). Real-time obstacle detection over railway
track using deep neural networks. Procedia Computer
Science, 215:289–298.
RangiLyu (2021). Nanodet-plus: Super fast and high accu-
racy lightweight anchor-free object detection model.
https://github.com/RangiLyu/nanodet.
Ren, S., He, K., Girshick, R., and Sun, J. (2016). Faster
r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with re-
gion proposal networks. IEEE transactions on pattern
analysis and machine intelligence, 39(6):1137–1149.
Robins, A. (1995). Catastrophic forgetting, rehearsal and
pseudorehearsal. Connection Science, 7(2):123–146.
Sandler, M., Howard, A., Zhu, M., Zhmoginov, A., and
Chen, L.-C. (2018). Mobilenetv2: Inverted residu-
als and linear bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the IEEE
conference on computer vision and pattern recogni-
tion, pages 4510–4520.
Sazara, C., Cetin, M., and Iftekharuddin, K. M. (2019). De-
tecting floodwater on roadways from image data with
handcrafted features and deep transfer learning. In
2019 IEEE intelligent transportation systems confer-
ence (ITSC), pages 804–809. IEEE.
Selvaraju, R. R., Cogswell, M., Das, A., Vedantam, R.,
Parikh, D., and Batra, D. (2017). Grad-cam: Visual
explanations from deep networks via gradient-based
localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE international
conference on computer vision, pages 618–626.
Si, C., Wang, X., Yang, X., and Shen, W. (2025). Tendency-
driven mutual exclusivity for weakly supervised incre-
mental semantic segmentation. In European Confer-
ence on Computer Vision, pages 37–54. Springer.
Wang, A., Chen, H., Liu, L., Chen, K., Lin, Z., Han, J.,
and Ding, G. (2024). Yolov10: Real-time end-to-end
object detection. arXiv preprint arXiv:2405.14458.
Wen, L., Peng, Y., Lin, M., Gan, N., and Tan, R. (2024).
Multi-modal contrastive learning for lidar point cloud
Enhancing Railway Obstacle Detection System Based on Incremental Learning
419

rail-obstacle detection in complex weather. Electron-
ics, 13(1):220.
Yang, J., Zhou, K., Li, Y., and Liu, Z. (2024). Generalized
out-of-distribution detection: A survey. International
Journal of Computer Vision, pages 1–28.
Zhang, Q., Yan, F., Song, W., Wang, R., and Li, G. (2023).
Automatic obstacle detection method for the train
based on deep learning. Sustainability, 15(2):1184.
Zhu, L., Chen, T., Yin, J., See, S., and Liu, J. (2023). Con-
tinual semantic segmentation with automatic memory
sample selection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF
Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recogni-
tion, pages 3082–3092.
VEHITS 2025 - 11th International Conference on Vehicle Technology and Intelligent Transport Systems
420
