
Exploration and Validation of Specialized Loss Functions for Generative
Visual-Thermal Image Domain Transfer
Simon Fischer, Benedikt Kottler
a
, Eva Strauß and Dimitri Bulatov
b
Fraunhofer IOSB Ettlingen, Gutleuthausstrasse 1, 76275 Ettlingen, Germany
Keywords:
Thermal Infrared, Domain Transfer, Style Transfer, GAN, Loss Function, Image Generation.
Abstract:
This paper presents an enhanced approach to visual-to-thermal image translation using an improved InfraGAN
model, incorporating additional loss functions to increase realism and fidelity in generated thermal images.
Building on the existing InfraGAN architecture, we introduce perceptual, style, and discrete Fourier trans-
form (DFT) losses, aiming to capture intricate image details and enhance texture and frequency consistency.
Our model is trained and evaluated on the FLIR Adas dataset, providing paired visual and thermal images
across diverse contexts, from urban traffic scenes. To optimize the interplay of loss functions, we employ
hyperparameter tuning with the Optuna library, achieving an optimal balance among the components of the
loss function. First, experimental results show that these modifications lead to significant improvements in the
quality of generated thermal images, underscoring the potential of advanced loss functions for domain transfer
tasks. This work contributes a refined framework for generating high-quality thermal imagery, with implica-
tions for fields such as surveillance, autonomous driving, and facial recognition in challenging environmental
conditions.
1 INTRODUCTION
Image transfer from the visual to the thermal or in-
frared domains has multiple military and civil ap-
plications. For the former, target detection, preci-
sion guidance, and training autonomous vehicles in
challenging illumination and weather conditions are
among the first use cases that come to mind (Xiong
et al., 2016; Su
´
arez and Sappa, 2024). One may
imagine an additional screen showing the driver the
infrared view of the night scene with possible obsta-
cles. Gaming applications are related to this field; in
order to achieve immersive simulations, realistic night
views are desired. As for the latter, RGB-to-thermal
and RGB-to-infrared transfer also support artistic ap-
plications, enabling creative photography and design
by showcasing scenes in a different spectrum. In
forensic science, these techniques assist in recon-
structing crime scenes by uncovering hidden details
like heat signatures that may help in investigations.
Last but not least, from the point of view of environ-
mental monitoring, surface temperature retrieval from
remote sensing data is an elegant way to infer poten-
tially risky areas of the scene. One may think about
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0498-0646
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0560-2591
Urban Heat Islands, where trapping and multiple ra-
diations contribute to the increase of temperatures in
metropolitan centers in comparison to their surround-
ings (Bulatov et al., 2020). These physical processes
are difficult to measure and to simulate due to the
precise knowledge of material properties estimation
and the need to incorporate atmospheric effects and
to validate synthetic images against real-world data
(Su
´
arez and Sappa, 2024). Furthermore, for direct
measurements, multiple temperature boxes (Kottler
et al., 2023) or thermal scanning robots (L
´
opez-Rey
et al., 2023) must be employed, which, on the one
hand, produce large amounts of data, and, on the other
hand, may be stolen and not provide any data at all.
Satellite data allow for relatively broad coverage of
areas and time; however, they have, in turn, a too
coarse resolution so that 3D effects remain unconsid-
ered.
This article is supposed to make use of two im-
portant latest trends: the omnipresence of optical data
and tremendous progress in generative style trans-
fer. Billions of images are taken worldwide by smart-
phone cameras every day, land to a large share on so-
cial networks, and not seldomly are used for training
by large corporations. For thermal and infrared im-
ages, such wide training data are unavailable or have
Fischer, S., Kottler, B., Strauß, E. and Bulatov, D.
Exploration and Validation of Specialized Loss Functions for Generative Visual-Thermal Image Domain Transfer.
DOI: 10.5220/0013274400003912
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 20th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2025) - Volume 2: VISAPP, pages
527-534
ISBN: 978-989-758-728-3; ISSN: 2184-4321
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
527

been created only recently. Thus, we make use of the
recently published Generative Adversarial Network
called InfraGAN (
¨
Ozkano
˘
glu and Ozer, 2022). The
main contribution of this article is the idea to add new
loss functions to improve the performance on the im-
age transfer task from the visual into the thermal do-
main.
The paper is structured as follows: Section 2 will
summarize the main findings in the aforementioned
research field. All the reader is supposed to know
about InfraGAN and its loss functions is reported in
Section 3. The methodology is presented in Section 4.
The results and conclusions are reported in Sections 5
and 6, respectively.
2 RELATED WORK
Ever since the high success of works like (Isola et al.,
2016) and (Zhu et al., 2017), generative adversarial
networks (GANs), introduced by (Goodfellow et al.,
2014) form the standard approach for image-to-image
translation. In particular, this is true for subsets of
the problem like visual-thermal image domain trans-
fer (see for example (Ma et al., 2024), (Ordun et al.,
2023) and (
¨
Ozkano
˘
glu and Ozer, 2022)). Neverthe-
less, there are exceptions like (Sun et al., 2023) which
rely on the use of transformers in the generation pro-
cess. (Ordun et al., 2023) further introduce a diffusion
model and compares its result to those of the GAN.
The network introduced by (
¨
Ozkano
˘
glu and Ozer,
2022) stands out by its encoder-decoder structure that
is used not only for the generator but also the discrim-
inator, applying a discriminator loss function to the
whole image. Further, the authors expand the genera-
tor loss by an additional term based on the Structural
Similarity Index Measure (SSIM (Wang et al., 2004))
which improves the overall results.
The authors of (Ordun et al., 2023) compare their
introduced GAN to a conditional Denoising Diffusion
Model. They are able to show that in the case of
facial images, the visual-to-thermal transfer of their
GAN outperforms the diffusion-based state-of-the-art
approach. This confirms GANs forming a state-of-
the-art model in image domain transfer.
Further, in their GAN, the authors introduced the use
of a new loss function called Fourier Transform Loss.
This approach was earlier used in the task of image
super-resolution (Fuoli et al., 2021). Their idea is to
transfer both the generated and the real thermal image
into the frequency domain and to compare their am-
plitude and phase. “The motivation is to not only map
the visible-to-thermal pixel space, but also achieve
similarity between high and low frequencies such as
hair, teeth, and glasses.” We use this idea and adapt it
for our purposes.
Recent studies have expanded these methodolo-
gies. For example, (Su
´
arez and Sappa, 2024) in-
troduce a depth-conditioned approach to generating
thermal-like images, further advancing the contex-
tual adaptation of thermal image synthesis techniques.
Additionally, (Liu et al., 2021) explore diverse condi-
tional image synthesis through a contrastive GAN ap-
proach, showcasing a method to encourage variation
in generated outputs. Another recent study by (Yu
et al., 2023) addresses the complexities in unpaired
infrared-to-visible video translation, focusing on fine-
grained, content-rich patch transfers.
While approaches like diffusion models and trans-
formers offer alternatives, GANs remain widely used
in visual-to-thermal image translation. In our work
we try to further enhance them with the focus on loss
functions.
3 PRELIMINARIES
This section provides the InfraGAN architecture and
its core loss functions, preparing the groundwork for
further modifications and optimizations detailed in
the methodology section.
3.1 InfraGAN Model Architecture
The generator in InfraGAN is based on a U-Net,
which consists of an encoder-decoder structure. The
encoder progressively down-samples the input image
through a series of convolutional layers, each fol-
lowed by batch normalization and LeakyReLU acti-
vation functions. The decoder mirrors the encoder’s
structure, progressively up-sampling the compressed
features to the original resolution using transposed
convolutions. Skip connections are introduced be-
tween corresponding encoder and decoder layers, al-
lowing information from the encoder to flow directly
to the decoder, preserving fine-grained image fea-
tures. The final layer produces the generated infrared
image.
The discriminator of InfraGAN uses a U-Net-
based architecture designed for classification at both
the image (global) and pixels (local). Similar to the
generator, the discriminator’s encoder (D
enc
) down-
samples the input image to extract essential features.
However, here the encoder is trained to detect pat-
terns and textures specific to real infrared images, as-
sisting in distinguishing real from generated images.
The discriminator’s decoder (D
dec
) up-samples fea-
tures extracted by the encoder to classify individual
VISAPP 2025 - 20th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
528

pixels. This pixel-level classification provides fine-
grained authenticity checks across the image, helping
the discriminator to enforce more detailed supervision
on the generator. This dual-output structure enhances
the discriminator’s ability to guide the generator to
produce highly realistic infrared images.
The generator and discriminator are trained to-
gether in an adversarial setup. The generator aims to
create increasingly realistic infrared images to “fool”
the discriminator, while the discriminator continually
improves at distinguishing real from generated im-
ages. Over time, this adversarial process pushes the
generator to produce lifelike infrared images with de-
tailed, realistic features.
3.2 Losses Used in InfraGAN
In InfraGAN, the generator and discriminator are
optimized by minimizing a respective loss function
composed of multiple terms. Loss functions play a
vital role in training neural networks offering a mea-
sure of how “similar” the generated output is to the
ground truth. While the discriminator loss remains
unchanged, we later expand the generator loss by ad-
ditional terms in Section 4.1. To ensure that the reader
can understand the components without having to re-
fer to the original paper (
¨
Ozkano
˘
glu and Ozer, 2022),
we briefly introduce each term here. Let X be the in-
put image in visible domain, and Y be the ground truth
thermal image. Then the generated thermal image is
denoted by
ˆ
Y = G(X), D(X , Y ) and D(X,
ˆ
Y ) refers to
the binary outputs of the discriminator and E(·) to the
expected value.
InfraGAN’s generator loss is composed of the var-
ious losses weighted with hyperparameters λ
1
, λ
2
∈ R
and is defined as:
l
G
= l
cGAN
+ λ
1
l
L1
+ λ
2
l
SSIM
, (1)
where the Conditional GAN Loss (l
cGAN
) encourages
the generated images to appear realistic according to
the discriminator. It is given by:
l
cGAN
=E
X
"
∑
i, j
log
D
dec
(X,
ˆ
Y )
i, j
#
+ E
X
log
D
enc
X,
ˆ
Y
.
(2)
The L1 Loss (l
L1
) measures the pixel-wise differences
between the generated and ground truth images:
l
L1
=
1
N
∑
i, j
ˆ
Y
i, j
−Y
i, j
, and (3)
the SSIM Loss (l
SSIM
) is based on the Structural Sim-
ilarity Index (SSIM) and encourages structural simi-
larity between generated and ground truth images:
l
SSIM
=
1
m
m−1
∑
i=0
1 − SSIM(
ˆ
Y
i
, Y
i
))
. (4)
where the SSIM between two images
ˆ
Y and Y is cal-
culated as:
SSIM(
ˆ
Y , Y ) =
2µ
ˆ
Y
µ
Y
+C
1
µ
2
ˆ
Y
+ µ
2
Y
+C
1
·
σ
ˆ
Y ,Y
+C
3
σ
2
ˆ
Y
+ σ
2
Y
+C
2
, (5)
where the constants C
1
and C
2
are calculated based on
the range of pixel values L, where C
1
= 0, 0001 · L
2
,
C
2
= 0, 0009 · L
2
.
The discriminator loss combines global and pixel-
wise discrimination capabilities, defined as:
l
D
= l
D
enc
+ l
D
dec
, (6)
where the global and pixelwise losses are defined as
follows:
l
D
enc
= − E
X,Y
[logD
enc
(X, Y )]
− E
X
log
1 − D
enc
(X,
ˆ
Y )
.
(7)
l
D
dec
= − E
X,Y
"
∑
i, j
log(D
dec
(X, Y )
i, j
)
#
− E
X
"
∑
i, j
log(1 − [D
dec
(X,
ˆ
Y )]
i, j
)
#
.
(8)
4 METHODOLOGY
In this section, we outline our approach for refining
InfraGAN’s performance. We introduce additional
loss functions, perceptual, style, and DFT loss, to
capture nuanced image features that enhance realism
in thermal image generation. Finally, we then con-
duct a hyperparameter search, using the Optuna li-
brary for Bayesian optimization, to fine-tune the bal-
ance among these losses for optimal model outcomes.
4.1 Additional Losses
The additional loss functions, perceptual loss, style
loss, and DFT loss, are chosen to address differ-
ent aspects of image realism and quality. Each of
these losses provides unique benefits that collectively
guide the network towards generating images that
align more closely with human perception and retain
realistic textural and frequency characteristics.
Exploration and Validation of Specialized Loss Functions for Generative Visual-Thermal Image Domain Transfer
529

Perceptual Loss for Human-Centric Evaluation
First, we introduce a perceptual loss l
perc
. This
method was introduced by (Johnson et al., 2016).
As the name suggests, the loss is supposed to rep-
resent the human perception. Therefore, the ground
truth and the generated image are evaluated on a layer
of a classification network. More precisely, we use
the V GG19 network by (Simonyan and Zisserman,
2015).
We set ϕ as the VGG19 network trained on Ima-
geNet (Russakovsky et al., 2015). Further, let ϕ
j
(y)
be the activation of the j-th layer of ϕ. That layer is a
convolution layer, and it has the shape C
j
× H
j
×W
j
.
Then the perceptual loss is defined by
l
perc
=
J
∑
j
1
C
j
H
j
W
j
ϕ
j
(
ˆ
Y ) − ϕ
j
(Y )
2
2
. (9)
Style Loss for Textural Consistency
The second loss we want to expand our network with
comes from the same paper as the perceptual loss. For
the style loss l
style
we again make use of VGG19 and
its layers ϕ
j
. As before, we define the activation to
have shape C
j
× H
j
×W
j
. We calculate the Gram ma-
trix G
ϕ
j
(y) for image y. Its elements are defined by the
following formula:
G
ϕ
j
(Y ) =
1
C
j
H
j
W
j
· ψψ
⊺
, (10)
where ψ is ϕ
j
(Y ) reshaped as a matrix. The style loss
then is defined by
l
style
=
J
∑
j=1
G
ϕ
j
(
ˆ
Y ) − G
ϕ
j
(Y )
2
F
, (11)
where ∥ · ∥
F
is the Frobenius norm.
Following the approach in (Kottler et al., 2022),
we set J = 5 in both the perceptual loss and the style
loss.
DFT Loss for Frequency-Based Comparison
Lastly, we introduce the discrete Fourier transform
(DFT) loss l
DFT
. The idea to use the DFT as a loss
function was first introduced by (Fuoli et al., 2021)
for image super-resolution, and applied to the task of
domain transfer by (Ordun et al., 2023). The idea is
to transfer the ground truth and the generated image
into the frequency domain via DFT and then calcu-
late a difference in this domain. Given the real R and
imaginary I part of the Fourier version of an image,
we calculate:
l
DFT
=
R (
ˆ
Y ) − R (Y )
2
2
+
I (
ˆ
Y ) − I (Y )
2
2
. (12)
Unlike (Fuoli et al., 2021) and (Ordun et al.,
2023), we do not compare amplitude and phase in the
frequency domain but the real and imaginary parts of
the image’s frequency counterpart. We decided to ad-
just the approach, because of two observations that
lead to some doubts concerning the use of amplitude
and phase. Our first observation was that there could
be problems when comparing the periodic phase val-
ues: Imagine two images with values close to 0 and
2π. Ideally, their distance should create a small loss
while, in reality, the L1 distance is nearly at maxi-
mum. Secondly, we realized that the ranges of ampli-
tude and phase are very different. While the phase is
limited to [0, 2π], the amplitude can have up to five-
digit values. Therefore, simply adding the phase and
amplitude differences could create a huge imbalance.
Based on these concerns, we decided to calculate the
real and imaginary parts of the ground truth and the
generated thermal image and then compare these val-
ues. This gives us information about the distribution
of the image’s frequencies without any range-related
problems.
4.2 Evaluation Metrics
The evaluation of our model mainly follows the exam-
ple of (
¨
Ozkano
˘
glu and Ozer, 2022). Along with SSIM
and L1 metrics that were similarly used as loss func-
tions, it is crucial to use new metrics that were not
involved in the training process. Therefore, we add
the MSSIM (Mean SSIM), LPIPS (Learned Percep-
tual Image Patch Similarity) and PSNR (Peak Signal-
to-Noise Ratio) metrics. In the following, we ex-
plain their structure and why their usage is beneficial.
The Mean SSIM builds on SSIM and adds a global
perspective by forming the mean over several down-
scaled versions ˆy
k
, y
k
of the generated image
ˆ
Y and
ground truth Y . This also strengthens the noise im-
munity.
MSSIM(Y,
ˆ
Y ) =
1
K
K
∑
k=1
SSIM(Y
k
,
ˆ
Y
k
). (13)
The downscaling takes place according to (Wang
et al., 2004).
The LPIPS metric resembles in its idea the per-
ceptual loss above, as it measures the Euclidean dis-
tance between the feature vectors of Y and
ˆ
Y . How-
ever, for LPIPS, the smaller AlexNet is used instead
of VGG19 to obtain the features. Due to the fewer
number of weights, LPIPS focus more on low- and
mid-level features compared to VGG19.
LPIPS(Y,
ˆ
Y )=
L
∑
l=1
ω
l
H
l
W
l
∑
h,w
h
f
h,w
l
(Y )−f
h,w
l
(
ˆ
Y )
i
2
, (14)
VISAPP 2025 - 20th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
530

where we sum over the last L = 5 layers of AlexNet,
which are denoted by f . Hereby H
l
, W
l
is the height
and width of the l-th layer, h
l
, w
l
show the pixel coor-
dinates, f
l
(Y ) represents the normalized feature from
l-th layer, and vector ω
l
refers to the trained weights
of LPIPS.
Lastly, the PSNR aims to represent the quality of
reconstruction of the thermal image from a visual im-
age:
PSNR(Y,
ˆ
Y ) = −10log MSE(Y ,
ˆ
Y ), (15)
where we use the mean squared error
MSE(Y,
ˆ
Y ) =
1
HW
H
∑
i=0
W
∑
i=0
Y (i, j) −
ˆ
Y (i, j)
2
(16)
Again, H, W denote height and width of the image.
4.3 Hyperparameter Optimization
The different loss functions that combine to form the
generator loss are all weighted by prefactors similar
to equation (1). In our case, the additional losses are
weighted by the hyperparameters λ
3
, λ
4
, and λ
5
as
shown below:
l
G
=l
cGAN
+ λ
1
· l
L1
+ λ
2
· l
SSIM
+ λ
3
· l
perc
+ λ
4
· l
style
+ λ
5
· l
DFT
To enhance the interaction of the losses we aim to
optimize the hyperparameters λ
1
to λ
5
, which we
will summarize in vector Λ. The open-source library
Optuna provides a framework based on the Bayesian
optimization to iteratively find optimal hyperparam-
eters. It is specialized in the optimization of neural
network applications. Optuna enhances the process’s
efficiency by pruning trials that are unlikely to yield
promising results, thereby saving computational re-
sources. Optuna allows for customization of pruner
settings. We want it to utilize median performance
metrics in order to make better pruning decisions. Ad-
ditionally, we prohibit pruning before the tenth trial
to build up a comprehensive decision pool. We set a
minimum threshold of six epochs before pruning can
commence, as this has been shown to achieve a good
balance between accuracy and efficiency.
Since the framework must test multiple value con-
figurations for Λ, we want the optimization to have
a high number of trials. Specifically, we opted for
1000 trials based on extensive research. To main-
tain consistency with the initial values used in Infra-
GAN’s code, we define the suggested hyperparame-
ters to be integers. We enhance the likelihood of dis-
covering effective hyperparameter combinations by
allowing them to range between 1 and 1000. We
set them to follow a logarithmic distribution, mean-
ing the values will have logarithmic spacing, thereby
preferring smaller values. This approach allows for
nuanced hyperparameters adjustments across a wide
integer range, enhancing stability and control during
optimization.
To increase the efficiency of the optimization, we
use a reduced dataset of 60 varying image pairs from
the FLIR dataset. Furthermore, we reduce the number
of epochs in the network’s training from 200 to 100,
facilitating a more time-efficient optimization. Since
our goal is not to get a perfectly trained network but to
identify an optimal Λ, we prioritize fast optimization
iterations. The reduced network parameters are not
expected to impair our results.
Our experiments showed that the quality of the
network oscillated strongly between subsequent train-
ing epochs. Therefore, any metric L on our network
must be smoothed. We first average the value of L
over data batches within the current epoch and, ulti-
mately, return the median over the last five epochs.
Arguably, the most important decision in optimiz-
ing with Optuna is how to define its objective function
L. This function outputs a value representing the net-
work’s quality considering the new hyperparameters.
Therefore, we need a good measure of how similar
the generated thermal image and the ground truth are.
We propose employing the LPIPS metric, as seen in
equation (14). This metric is not used in the training
and therefore does not interfere with the hyperparam-
eters during optimization. Thus, we assign L(Λ) to
be the walking average of the LPIPS metric for con-
figuration Λ = (λ
1
, · ·· , λ
5
).
5 RESULTS
In this section, we present the outcomes of our ap-
proach, including the dataset used, hyperparameter
optimization, and model evaluation. We first describe
the dataset that provided paired visual and thermal im-
ages, crucial for training and testing InfraGAN. We
then detail our hyperparameter optimization process
to find the optimal balance for the newly integrated
loss functions. Finally, we evaluate the model’s per-
formance, analyzing the effectiveness of our modifi-
cations in producing realistic thermal images.
5.1 Dataset
For our training, we used the Flir
1
Adas dataset con-
sisting of image pairs of the same motive, one in vi-
sual (RGB) and one in thermal (IR) domain. The
1
FLIR dataset, https://www.flir.com/oem/adas/
adas-dataset-form/.
Exploration and Validation of Specialized Loss Functions for Generative Visual-Thermal Image Domain Transfer
531
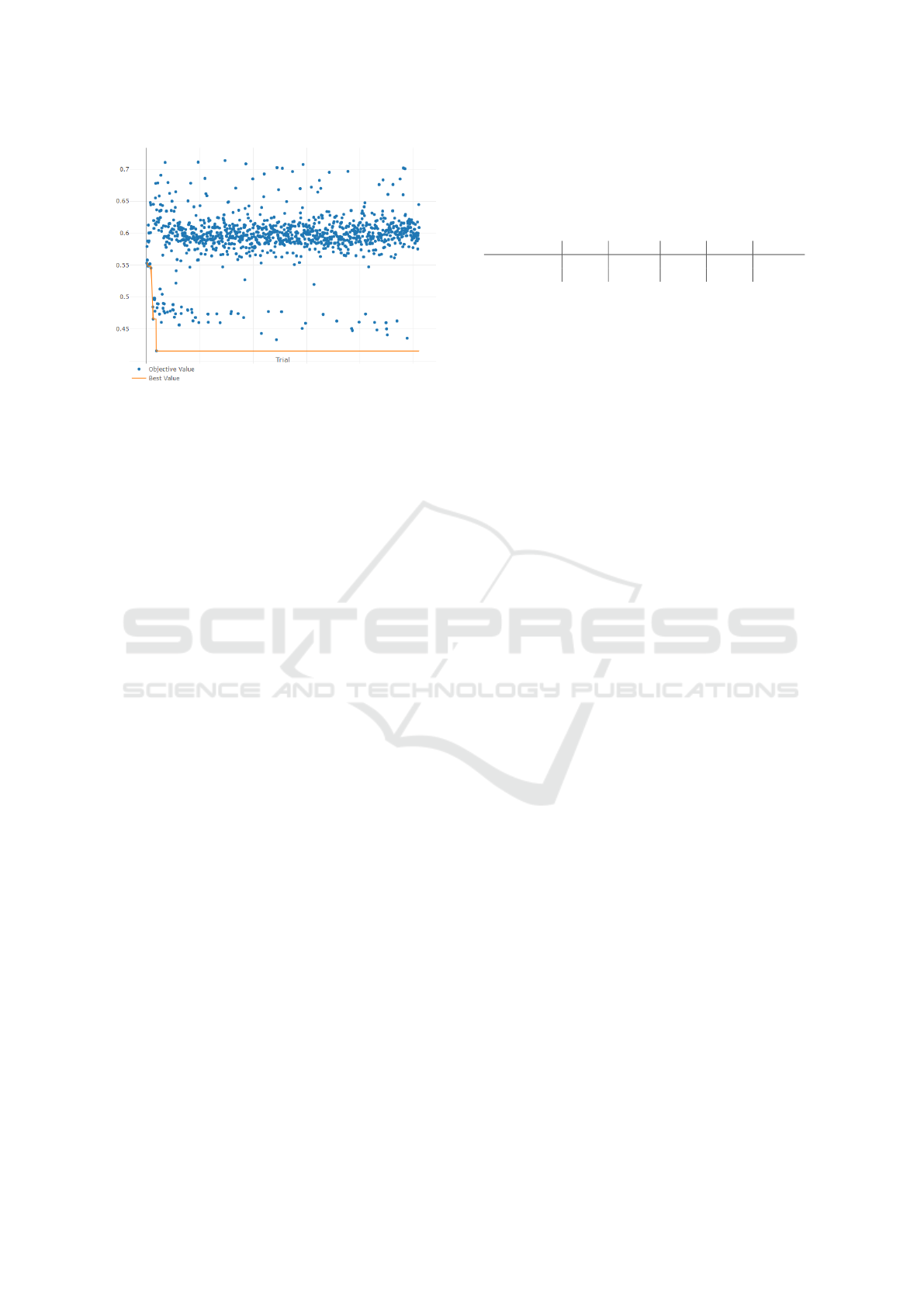
Figure 1: Optimization process of the hyperparameters on
the FLIR dataset. Each blue dot represents the activation
value L(Λ
n
) of the n-th configuration Λ
n
. The orange line
depicts the best value at time ˜n min
1≤n≤ ˜n
L(Λ
n
).
FLIR dataset is a publicly available collection of high-
resolution images. It includes various traffic scenarios
with different light and weather conditions. Multiple
scenarios include pedestrians and other road users.
5.2 Hyperparameter Optimization
This section details the optimization process and ad-
justments made to find the best weight values for each
of the generator’s loss functions.
The optimization made on the FLIR dataset in-
cluded 1000 trials, testing different configurations of
vector Λ, and evaluating them using the objective
function LPIPS, denoted by L. A total of 76 out of
1000 trials, approximately 8 percent, were completed,
while the rest was pruned.
Figure 1 shows the results of each trial. The or-
ange line represents the best value at the correspond-
ing time ˜n: min
1≤n≤ ˜n
L(Λ
n
). The overall best result was
achieved in trial n = 36:
min
n
L(Λ
n
) = L(Λ
36
) ≈ 0.41534, (17)
where Λ
36
= [250, 9, 69, 1, 273]. The L(Λ
n
) values in
Figure 1 are divided into two main areas. Except for
the first 10 trials, which were not allowed to prune, the
upper part of the point cloud, approximately between
0.55 and 0.65, consists entirely of pruned trials. Most
of the completed trials yield objective values of 0.5
and lower. A noticeable gap exists between L(Λ
36
)
and the next best result, L(Λ
487
). Their ratio of these
values is approximately 0.95.
5.3 Evaluation
Here, we assess InfraGAN’s performance with the
enhanced loss functions and optimized parameters,
measuring improvements in thermal image generation
quality compared to InfraGAN.
Table 1: Quantitative Results: Original InfraGAN vs Our
enhanced approach.
FLIR dataset SSIM MSSIM LPIPS L1 PSNR
InfraGAN 0.2401 0.3429 0.2275 0.3039 16.3238
Our approach 0.2683 0.3534 0.2558 0.2979 16.4590
The quantitative evaluation of our enhanced ap-
proach compared to the original InfraGAN model is
presented in Table 1. The table compares the metrics
SSIM, MSSIM, LPIPS, L1, and PSNR. Our approach
demonstrates improvements across several metrics,
indicating enhanced image quality. For SSIM, our
method surpasses the original model, reflecting bet-
ter preservation of spatial details. Similarly, MSSIM
shows an improvement of approximately 0.01, sug-
gesting enhanced structural consistency. While the
LPIPS metric shows a slight increase and therefore
a minor decrease in perceptual quality, our approach
shows a modest improvement in L1 loss, indicat-
ing more precise image reconstruction in terms of
pixel-level accuracy. Additionally, the PSNR met-
ric improves from 16.3238 to 16.4590, reflecting bet-
ter overall image fidelity. Despite the slight increase
in LPIPS, overall, our enhanced model demonstrates
significant improvements in most metrics.
Figure 2 provides a comparison of qualitative re-
sults between the original InfraGAN algorithm and
our enhanced approach. The rows of the Figure show-
case various scenes from the FLIR dataset, differing
in scenario and exposure. The Figure shows that In-
fraGAN often suffers from artifacts in its generated
images. These artifacts can obscure important de-
tails and diminish the images’ utility. In contrast, our
model successfully mitigates these artifacts, resulting
in cleaner and more coherent images. However, it
is noteworthy that the images exhibit a ”smooth” ap-
pearance, similar to the effect of a blurring filter. This
characteristic may limit the texture and detail of the
images. Nevertheless, the qualitative and quantitative
results highlight the potential of the new loss func-
tions in improving the perceptual quality of generated
images.
6 CONCLUSION
In this work, we explored enhancements of InfraGAN
for visual-to-thermal image translation by introduc-
ing additional loss functions—perceptual, style, and
DFT losses—that capture finer image details and im-
prove realism. We trained and tested our model with
the FLIR dataset consisting of traffic scenes. Through
VISAPP 2025 - 20th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
532
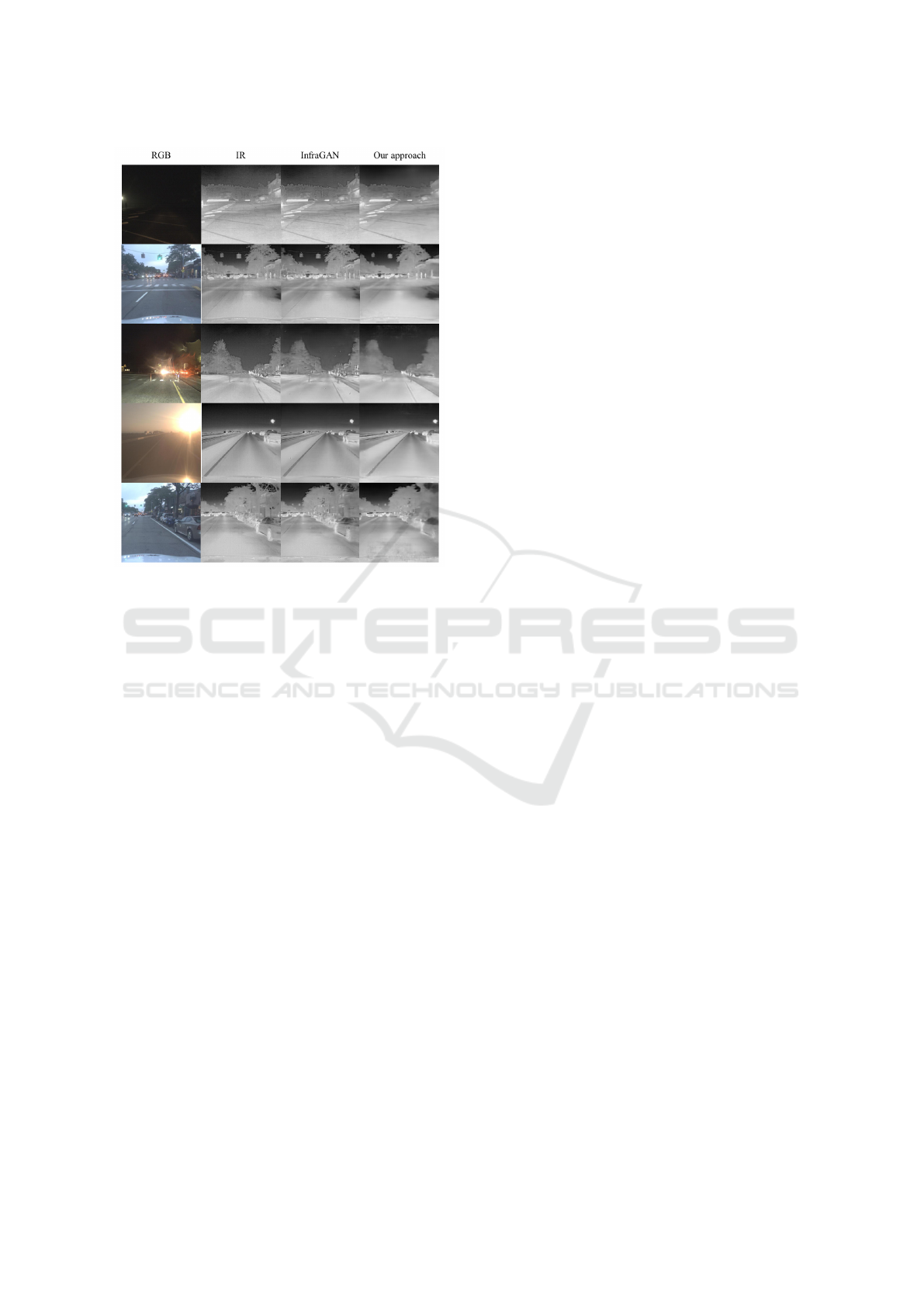
Figure 2: Comparison of Qualitative Results: Original In-
fraGAN algorithm vs. our enhanced approach. The rows of
the Figure showcase various scenes from the FLIR dataset,
differing in exposure and content.
hyperparameter optimization with the Optuna frame-
work, we refined the trade-off between the loss com-
ponents, significantly enhancing InfraGAN’s perfor-
mance and establishing a framework for further ex-
periments.
Our results indicate that these modifications im-
prove InfraGAN’s ability to generate high-fidelity
thermal images with more accurate detail and struc-
tural consistency. This approach demonstrates the ef-
fectiveness of advanced loss configurations in domain
transfer tasks, contributing valuable insights to the
field of image synthesis and domain translation. Fu-
ture work could extend this methodology to other do-
mains and explore additional optimization techniques
for further performance gains.
A primary direction for extending this work is to
test the methods on additional datasets, such as the
Vis-TH dataset for facial expressions (introduced in
(Mallat and Dugelay, 2018)). Evaluating the approach
on a broader range of data will enhance its generaliz-
ability and robustness. Another critical avenue is the
modification of the DFT loss. In its current state, the
DFT loss behaves similarly to the L
2
norm. Introduc-
ing a filter in the DFT loss into a more distinct and
potentially effective metric, warranting further explo-
ration. Hyperparameter optimization presents oppor-
tunities for deeper investigation. A key question is
whether the optimal hyperparameters differ signifi-
cantly between datasets or exhibit consistent patterns.
Additionally, iterative refinement of hyperparameters
should be performed by re-optimizing for each hyper-
parameter. Furthermore, adopting an analytical ap-
proach could further constrain the search space by
leveraging inherent relationships, such as the connec-
tion between the style loss and perceptual loss. A
detailed analysis of the importance of each hyperpa-
rameter is also recommended. Understanding param-
eter importance will inform more targeted and effi-
cient optimization strategies in the future. Finally, al-
ternative accuracy functions beyond LPIPS should be
tested to evaluate the model comprehensively. This
could provide additional insights into its strengths
and areas for improvement. Addressing these recom-
mendations will further refine the methodology and
broaden its applicability, leading to more robust and
versatile outcomes.
REFERENCES
Bulatov, D., Burkard, E., Ilehag, R., Kottler, B., and
Helmholz, P. (2020). From multi-sensor aerial data to
thermal and infrared simulation of semantic 3d mod-
els: Towards identification of urban heat islands. In-
frared Physics & Technology, 105:103233.
Fuoli, D., Gool, L. V., and Timofte, R. (2021). Fourier space
losses for efficient perceptual image super-resolution.
Goodfellow, I. J., Pouget-Abadie, J., Mirza, M., Xu, B.,
Warde-Farley, D., Ozair, S., Courville, A., and Ben-
gio, Y. (2014). Generative adversarial networks.
Isola, P., Zhu, J., Zhou, T., and Efros, A. A. (2016). Image-
to-image translation with conditional adversarial net-
works. CoRR, abs/1611.07004.
Johnson, J., Alahi, A., and Fei-Fei, L. (2016). Perceptual
losses for real-time style transfer and super-resolution.
Kottler, B., Fischer, S., Strauss, E., Bulatov, D., and
Helmholz, P. (2023). Parameter optimization for a
thermal simulation of an urban area. ISPRS Annals
of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial
Information Sciences, 10:271–278.
Kottler, B., List, L., Bulatov, D., and Weinmann, M. (2022).
3gan: A three-gan-based approach for image inpaint-
ing applied to the reconstruction of occluded parts of
building walls. pages 427–435.
Liu, R., Ge, Y., Choi, C. L., Wang, X., and Li, H. (2021).
Divco: Diverse conditional image synthesis via con-
trastive generative adversarial network. In Proceed-
ings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision
and pattern recognition, pages 16377–16386.
L
´
opez-Rey, A., Ram
´
on, A., and Ad
´
an, A. (2023). Hard-
ware/software solutions for an efficient thermal scan-
ning mobile robot. In ISARC. Proceedings of the In-
ternational Symposium on Automation and Robotics
Exploration and Validation of Specialized Loss Functions for Generative Visual-Thermal Image Domain Transfer
533

in Construction, volume 40, pages 675–682. IAARC
Publications.
Ma, D., Xian, Y., and Li, B. e. a. (2024). Visible-to-infrared
image translation based on an improved cgan. Vis
Comput 40, pages 1289–1298.
Mallat, K. and Dugelay, J.-L. (2018). A benchmark
database of visible and thermal paired face images
across multiple variations. In BIOSIG 2018 - Proceed-
ings of the 17th International Conference of the Bio-
metrics Special Interest Group. K
¨
ollen Druck+Verlag
GmbH, Bonn.
Ordun, C., Raff, E., and Purushotham, S. (2023). When
visible-to-thermal facial gan beats conditional diffu-
sion. In 2023 IEEE International Conference on Im-
age Processing (ICIP), pages 181–185. IEEE.
Russakovsky, O., Deng, J., Su, H., Krause, J., Satheesh, S.,
Ma, S., Huang, Z., Karpathy, A., Khosla, A., Bern-
stein, M., Berg, A. C., and Fei-Fei, L. (2015). Ima-
genet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int. J.
Comput. Vision, 115(3):211–252.
Simonyan, K. and Zisserman, A. (2015). Very deep convo-
lutional networks for large-scale image recognition.
Su
´
arez, P. L. and Sappa, A. (2024). Depth-conditioned
thermal-like image generation. In 2024 14th Inter-
national Conference on Pattern Recognition Systems
(ICPRS), pages 1–8. IEEE.
Sun, Q., Wang, X., Yan, C., and Zhang, X. (2023). Vq-
infratrans: A unified framework for rgb-ir translation
with hybrid transformer. Remote Sensing, 15(24).
Wang, Z., Bovik, A., Sheikh, H., and Simoncelli, E. (2004).
Image quality assessment: from error visibility to
structural similarity. IEEE Transactions on Image
Processing, 13(4):600–612.
Xiong, X., Zhou, F., Bai, X., Xue, B., and Sun, C. (2016).
Semi-automated infrared simulation on real urban
scenes based on multi-view images. Optics express,
24(11):11345–11375.
Yu, Z., Li, S., Shen, Y., Liu, C. H., and Wang, S. (2023).
On the difficulty of unpaired infrared-to-visible video
translation: Fine-grained content-rich patches trans-
fer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference
on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages
1631–1640.
Zhu, J.-Y., Park, T., Isola, P., and Efros, A. A. (2017).
Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-
consistent adversarial networks. In 2017 IEEE In-
ternational Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV),
pages 2242–2251.
¨
Ozkano
˘
glu, M. A. and Ozer, S. (2022). Infragan: A gan
architecture to transfer visible images to infrared do-
main. Pattern Recognition Letters, 155:69–76.
VISAPP 2025 - 20th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
534
