
The Influence of Pro-Environmental Behavior Stages on e-Learning
Platform Acceptance in Public Works
Lisa Michanol and Jean-Christophe Sakdavong
CLLE Lab, UMR5263 CNRS, University of Toulouse, Allée A. Machado, 31058 Toulouse cedex 9, France
Keywords: UTAUT2, SSBC, Public Works, e-Learning, Ecological Transition.
Abstract: This study investigates the correlation between awareness of the importance of ecological transition and the
acceptance of a digital platform providing educational resources for Public Works professionals. Using data
from 42 users of the platform "tpdemain", the research examines the influence of an individual's stage in pro-
environmental behavior change (as defined by the SSBC model) on their acceptance of the platform's
resources. The study also explores the relationship between perceived organizational responsibility for
ecological transition and social influence on platform adoption. While the level of individual awareness did
not significantly influence platform acceptance, the individual's stage in pro-environmental behavior change
did. The organizational dimension significantly impacted social influence, which in turn influenced the
perceived acceptability of the platform's resources. These findings provide insights for further research on the
intersection of pro-environmental behavior and technology acceptance in the context of Public Works.
1 INTRODUCTION
Climate change is a growing concern for citizens
worldwide, impacting all regions from glaciers to the
Pacific Islands and posing a significant threat to
biodiversity, agriculture, citizens, and infrastructures.
In France, the public sector is playing a major role in
addressing the consequences of climate change. The
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC)
estimates a temperature increase of 4°C by 2100. The
National Federation of Public Works (NFPW) has
implemented measures to mitigate these effects, such
as exposing schools to extreme heat, 50% of the
railway network, and 75% of the road network to
extreme heat risks.
Digital technologies are increasingly being used
in the public sector, particularly for facilitating
technical learning through virtual and augmented
reality. E-learning platforms are also available for
public sector professionals, offering courses on
various topics. However, the use of digital
technologies by trainers is not automatic. To ensure
the best use of these technologies, they must be well-
accepted and mentored.
1
https://travail-emploi.gouv.fr/deffinum
This study focuses on two aspects: the acceptance
of information and communication technology (ICT)
for professional enrichment and the recognition of the
need to be aware of the environmental damage that
can lead to public sector jobs being forced to adapt to
the ecological transition. The study will explore
different models of technology acceptance,
distinguishing between acceptability and acceptance.
It will also explore the relationship between a more
environmentally friendly behavior and technology
acceptance.
The research methodology used will be discussed,
with the aim of concluding with the results obtained
and proposing complementary research perspectives.
The study will also explore the role of e-learning in
public sector jobs, highlighting the importance of
promoting sustainable practices and fostering a
positive attitude towards climate change.
The question of the ecological transition is
increasingly present in public work, as the
consequences of climate change become more visible
each year. Public works sector is one of the largest
energy consumers, producers of waste, and a
contributor to artificial soil use. As part of a
DEFFINUM
1
project, an analysis on the cognitive
ergonomics of the platform is being conducted. In
Michanol, L. and Sakdavong, J.-C.
The Influence of Pro-Environmental Behavior Stages on e-Learning Platform Acceptance in Public Works.
DOI: 10.5220/0013275900003932
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2025) - Volume 1, pages 349-355
ISBN: 978-989-758-746-7; ISSN: 2184-5026
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
349
parallel, researchers are focusing on the acceptance of
educational resources dedicated to the ecological
transition.
The study aims to explore the influence of the
perception of the importance of the ecological
transition on the acceptance of a public work-oriented
course platform.
The following part will provide an overview of the
literature on the two important subjects of this paper:
Pro-Environmental behavior and Technology
Acceptance.
1.1 Pro-Environmental Behavior
Pro-environmental behavior refers to conscious
actions taken by individuals to reduce negative
impacts on the environment and/or increase
environmental quality. There are several theories to
explain this behavior, including the Theory of
Planned Behavior (TPB) (Ajzen, 1991), the Norm
Activation Model (NAM) (Schwartz, 1977), and the
Value-Belief-Norm Theory (VBN) (Stern, 20002).
The social cognitive perspective, with its model of
reciprocal causality (Bandura, 1986) (Triadic
Reciprocal Causation Model), suggests that three
factors have a bi-directional effect on each other
(cognitive or personal factors affecting the
environment and behavior). Personal agency is also
considered, as individuals can choose, execute, and
manage their own actions to achieve desired
outcomes.
The concept of ‘goal’ (the intention of an
individual to engage in an activity) is another
important notion in the social cognitive perspective.
These theories focus on processes of behavioral
change, particularly in the field of ecology. However,
in our research, we will focus on a particular model:
the Self-Regulated Behavioral Change (SSBC) model
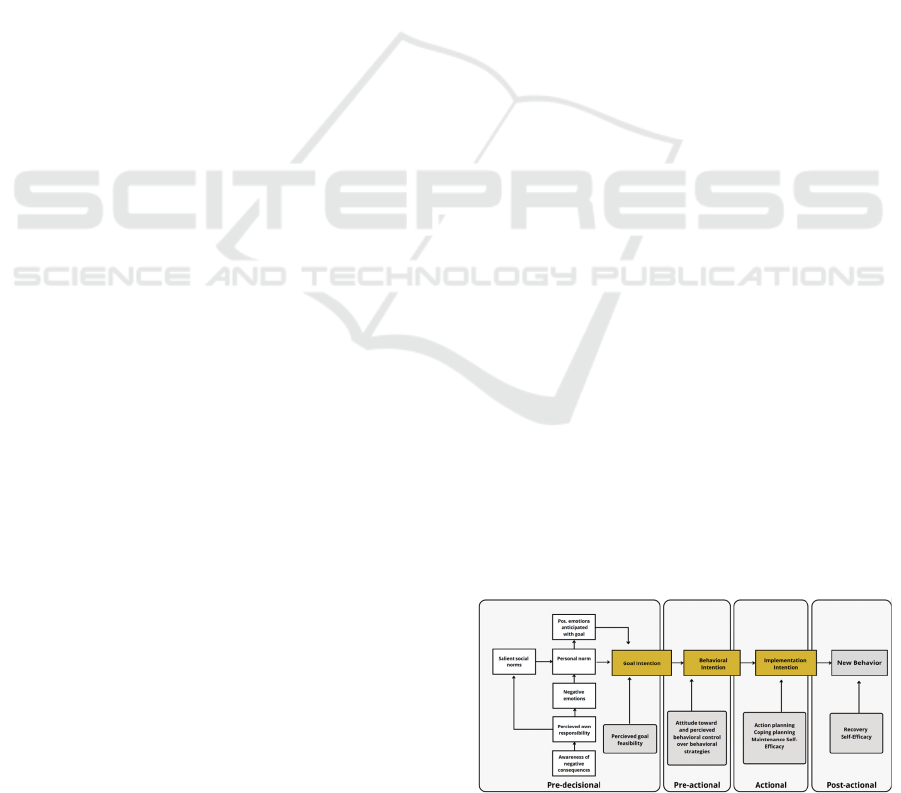
(Bamberg, 2013) (see figure 1).
1.2 From MAP to SSBC
The MAP (Heckhausen and Gollwitzer, 1987) is used
as a theoretical base to conceptualize behavioral
changes as a transition through four stages: pre-
decisional, pre-actional, and post-actional. The first
stage corresponds to the moment when an individual
formulates voluntary wishes that they transform into
actions. This form of self-engagement is called the
intention of goal and is formed by the individual
reflecting on the feasibility and desirability of
achieving these goals. The second stage, pre-actional,
occurs when an individual selects the best strategies
for achieving fixed goals, followed by a phase of
reflection on the pros and cons of adopting an
alternative behavior.
Behavioral intention marks the transition to the
third stage, the action stage, where the individual is
tasked with putting the chosen behavioral strategies
into action by initiating and implementing the
necessary actions. This implementation is facilitated
according to (Gollwitzer, 1999, as cited in Bamberg,
2013) by the implementation intention, which creates
a strong mental link between the desired new
behavior and a future situation. This situation is
critical, as it is what allows reaching the final stage,
the post-actional stage, which is the stage of
evaluating what has been done by the individual and
reflecting on what requires further actions or not. It is
also the stage where the individual must prove that
they can maintain their new behavior and not regress.
The MAP does not describe in detail the
psychological factors that contribute to progressions
through the stages. The SSBC will also incorporate
parts of the TPB (Ajzen, 1991) and the NAM
(Schwartz, 1977). The TPB views Pro-Environmental
behaviors as a consequence of a ‘rational choice.’
According to the TPB, the closest behavioral factors
are behavioral intentions, influenced by the degree to
which the individual maintains a positive attitude
towards the behavior, the perceptions the individual
has of the norms and conventions regarding the
behavior (for example, the subjective norm), and the
degree to which the individual perceives the behavior
as being within their control.
The SSBC as a theoretical basis is also applicable
to research on behavior change. Unlike static models
like the TPB, the SSBC argues that behavior change
is a decision made in multiple stages. The SSBC will
also remove the social norm present in the TPB, as
Bamberg rather assumes that in the pre-decisional
phase, perceived social disapproval can motivate the
individual to reflect on personal goals.
The four stages of behavior change, the three
types of intentions, and the affective and socio-
cognitive factors outlined by the SSBC (see figure 1)
provide a solid theoretical foundation in behavior
change research.
Figure 1: SSBC Model (Bamberg, 2013).
CSEDU 2025 - 17th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
350
1.3 The Acceptance of Technology
The concept of technology acceptance is an important
element for their proper use and appropriation by
users. Research on technology acceptance has been
inspired by social psychology research, particularly
the Theory of Reasoned Action (TRA) (Sheppard,
1988, as cited in Venkatesh and al., 2003) and the
Technology Acceptance Model (TAM).
Davis (1989) developed the TAM, which aimed to
explain and predict an individual's acceptance of
technologies. It encompasses two main concepts: the
perception of usefulness and ease of use. If the
technology is easy to use and useful, it increases the
chances of actually using it. Davis and Venkatesh
(2000) developed a second version of the TAM called
TAM-2, which is an extension offering more
variables.
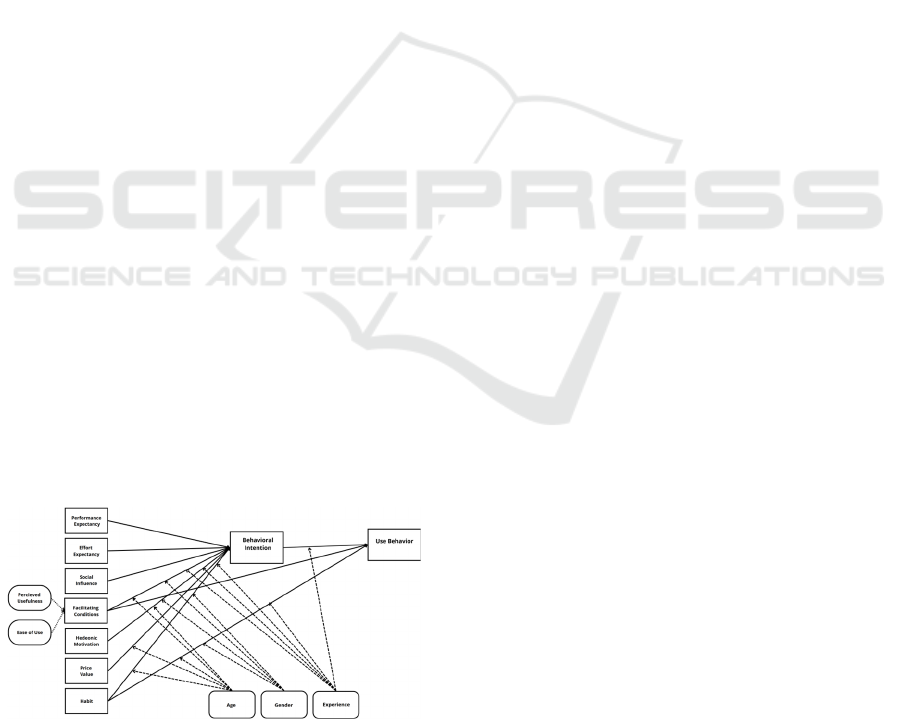
The Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of
Technology (UTAUT) (Venkatesh and al., 2003) is
the result of a theoretical study of major acceptance
models and a longitudinal study on the other hand
(see figure 2). The TAM models and their variants,
TAM2 and 3 and UTAUT1 and 2, are based on the
psychosocial theories of TRA and TPB.
The models primarily seem to allow for
understanding users' intentions "a priori"; however, in
our context, the participants are individuals who
already have access to the technology in question.
The TAM models and their variants seen earlier such
as UTAUT1 and 2, are based on the psychosocial
theories of TRA and TPB.
The interest of these approaches lies in the
predictions that can be made regarding the use of a
product. They seek to model probable future
behaviors based on a number of social cognitive
indicators. If the tool is not used effectively, these
approaches allow for anticipating the subjective
reasons for the rejection or adoption of the
technology.
Figure 2: UTAUT2 Model (Venkatesh et al., 2012).
However, these models seem to rely primarily on
a quantitative system, with a large number of
participants, thus risking overlooking the contextual
nature of the professional situation and the
heterogeneity of individuals. These predictive models
highlight the crucial and determining role those social
cognitions play, considering that the majority of
actions are under the user's control, that their
behavioral choices are deliberate, and that the
intention to use is a commitment regarding their
future behaviors.
1.4 Acceptability Models and Situated
Acceptance
This notion of "acceptability" is addressed by
technology acceptance models, which are described
as ergonomic devices to make them more practical,
usable, and digitally accessible. Models such as TAM
and UTAUT are part of acceptance models, but they
are also considered predictive models, allowing us to
determine if an individual is likely to accept, but not
whether they actually accept and concretely adopt a
technology, and even less whether they continue to
accept or reject a technology over time.
Practical acceptability (PA) is when we seek to
create ergonomic devices to make them more
practical, more usable, and digitally accessible, thus
more compatible with the specific needs that
individuals may have. PA is interesting when
concrete solutions are needed to evaluate and design
a system. It is a factor limited to functional and
instrumental dimensions. Nielsen proposed a model
in 1994 with Practical Usability (PU) and Social
Acceptability (SA), which introduces the idea of
taking into account users' perceptions regarding
technologies.
Social Acceptability is an initial step in the
process of adopting a technology, expressing the
potential degree of acceptance by the user. Attention
is thus focused on the subjective representation of
technology by its potential users. Models such as
TAM and UTAUT are part of the Social
Acceptability.
Social acceptability would predict less the
intentions of use for upcoming tools than it would
gather the feelings of past uses. It indeed considers
that social acceptability models would perceive
technology as an independent and autonomous object
in relation to the user and the environment in which it
operates. Social acceptability could therefore be a
first step in a broader process of individual
appropriation of a technology.
Situated Acceptance (SA) is described by
Bobillier-Chaumont (2016) as the implementation of
technology in its context of use, allowing for a
The Influence of Pro-Environmental Behavior Stages on e-Learning Platform Acceptance in Public Works
351
concrete evaluation of its contributions and
limitations, and thus defining its relevance in relation
to the individual's activities and projects. Technology
only makes sense within a framework and an
organization.
Bobillier-Chaumon (2016) proposes four
dimensions in SA: the individual or intra-personal
dimension, related to the individual's own activity;
the impersonal or organizational and technical
dimension, related to the organization in which the
individual works and the technology's ability to meet
needs and inspire trust from the individual; the
relational or interpersonal dimension, related to
collective and collaborative activities in the
workplace; and the transpersonal or professional and
identity dimension, related to the individual's sense of
self-efficacy.
1.5 SSBC, UTAUT2 and Situated
Acceptance
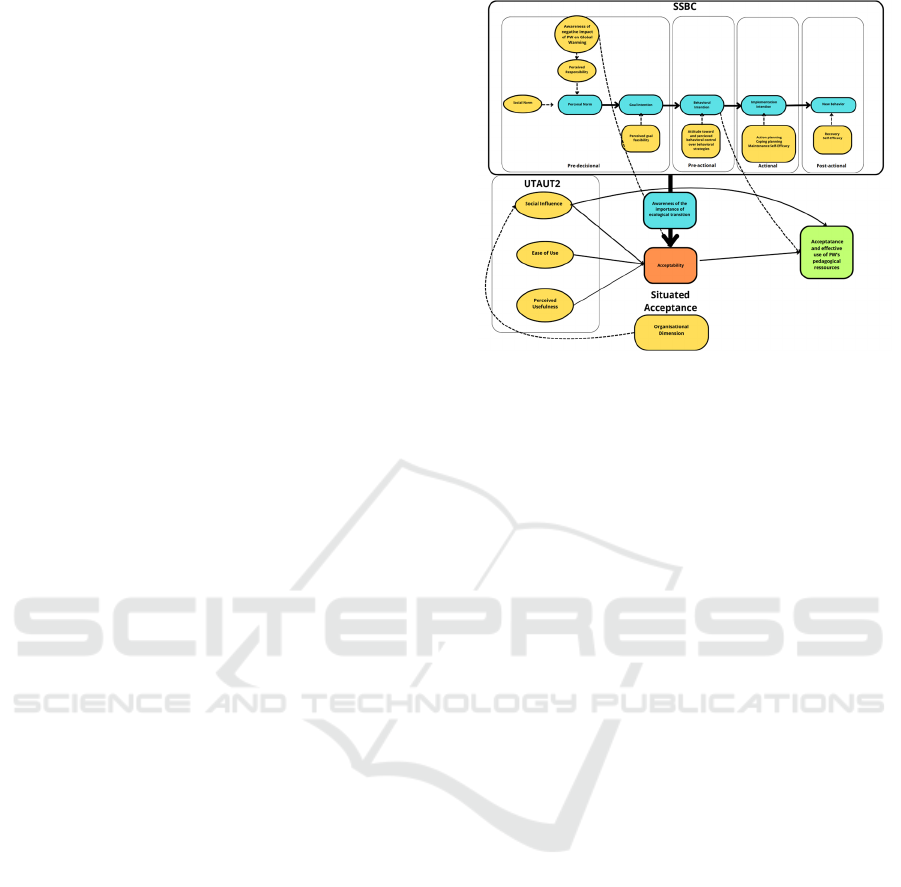
The choice in this research is to draw inspiration from
these studies on technology acceptance using the
UTAUT2 model and the concept of SA, and the
effective use of a device.
The SSBC and UTAUT2 are two behavioral
models designed to predict and understand behaviors
related to ecology and the use of new technologies.
While there are numerous articles referencing
these models for assessing the acceptance of
technologies and the adoption of Pro-Environmental
behavior, no studies have been conducted combining
them. In a study by Keller et al. (2021), it was found
that in addition to the four stages of transition,
individuals may be in a denial or inhibition phase of
transitioning from disposable to recyclable goblets.
This idea is interesting because it opens up the
possibility of seeing whether an individual in a pre-
decisional denial or inhibition phase would also be in
a less acceptable and effective form of accepting
resources from a Public Work (PW) platform.
The research on the acceptance of technologies
and Pro-Environmental behavior has allowed for a
global view of the state of the research. Many studies
have been conducted in various contexts, and it is
important to consider the elements of social
acceptability, with some factors of UTAUT2
(perceived usefulness, ease of use, and social
influence) and the elements of situated acceptance
(organizational dimension and effective utilization).
The SSBC model's transition stages (pre-decisional,
pre-actional, actional, and post-actional) and the
intention to implement are considered.
Figure 3: Combination of SSBC and UTAUT2 Models with
Situated Acceptance.
The research aims to determine the impact of
awareness of the impact of climate change on the
level of advancement in ecological transition in the
PW instructor's work with a PW e-learning platform.
The proposed hypotheses are the following:
H1. The level of awareness positively influences the
acceptance of a PW e-learning platform.
H2a. The stages of SSBC positively influence the
acceptability of a PW e-learning platform.
H2b. The stages of SSBC positively influence the
acceptance of a PW e-learning platform.
H3. The organizational dimension of situated
acceptance has a positive influence on the social
influence (from UTAUT2).
H4. The “social influence” has a positive influence on
the acceptance of the resources from a PW e-learning
platform.
2 METHOD
This research was conducted with participants from
the tpdemain platform, an e-learning PW platform
created by the Fédération Nationale des Travaux
Publics (NFPW) in France. tpdemain is a platform
that gives access to educational resources such as
texts playlists, videos, and educational pathways
accessible without the need for account creation. It
responds to the DEFINUM project, a plan of
transformation and digitalization of training piloted
by the Ministry of Labour, and the ‘Ecological
Transition in Public Works’ project within France
2030.
CSEDU 2025 - 17th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
352

tpdemain proposes a wide range of themes related
to various public sector jobs, ecological transition,
and a training program for PW instructors, aiming to
sensibilize them to pedagogy in an autonomous
training path. The platform offers various types of
content, including educational videos, images, and
courses produced with the French Learning Content
Management System (LCMS) Storiz.
The majority of the educational resources on
tpdemain are creative e-learning content for different
clients, their employees, and their instructors, and can
be used without a teacher.
The study involved 59 participants who were
instructors and had previously used resources from
the PW platform. The selection criteria included the
knowledge of the platform, age limit, and potential
affinities with technologies or climate change. Only
42 participants completed at least 18% of the
questionnaire, while 17 others were excluded due to
lack of data to handle.
The questionnaire was sent via social networks to
a community of PW instructors who had already used
the platform. It was available for about two months.
The research was conducted on various axes, with
several hypotheses proposed. The questionnaire was
divided into four blocks: one on UTAUT2 (thirty-four
items), one on SSBC (with questions for the four
stages of transition), and one block on the
organization's responsibility (one question divided
into five parts). For each item, a five-point Likert
scale was used.
We created the questionnaire and collected the
data on Qualtrics. The data has then been statistically
treated on Jamovi.
3 RESULTS
Among the 42 participants, most were men (n=30),
with a smaller number of women (n=4). One
participant did not specify their gender, and 7 did not
answer the question. The average age of the
participants was 49.1 years for men, 45.5 years for
women, and 53 years for the participant who did not
specify their gender.
The majority of the participants (91.2%) indicated
that they had used the digital platform at least once.
In terms of the level of awareness of the importance
of ecological transition, the participants showed an
average level of awareness. Regarding the stages of
the SSBC model (Bamberg, 2013), most of the
participants were in stage 4 (post-actional).
To test the hypothesis H1 (the level of awareness
positively influences the acceptance of a PW e-
learning platform), we conducted an ANOVA test
that showed the level of awareness did not have a
significant influence on acceptance (measured by
Effective Use) (F (1.33), p = .268, η2 =.541). This
suggests that the level of awareness of the training
organization does not influence the acceptance of the
resources by the trainers.
For Hypothesis H2a (the stages of SSBC
positively influence the acceptability of a PW e-
learning platform) and H2b (the stages of SSBC
positively influence the acceptance of a PW e-
learning platform), we tested the influence of SSBC
stages on both Acceptability and Acceptance with
two ANOVA tests.
The ANOVA test for the influence of SSBC
stages on UTAUT2 was close to significance (F
(2.83), p =.054, η2=.209), indicating a potential
positive effect.
The ANOVA test for the influence of SSBC
stages on acceptability measured by effective use was
significant (F(4.92), p =.006, η2 =.316), indicating
that the SSBC stages have an influence on the
acceptance of the platform by individuals with a large
effect size.
To test Hypothesis H3 (The organizational
dimension of situated acceptance has a positive
influence on the social influence), we conducted an
ANOVA test which confirmed that the organizational
dimension of situated acceptance has a significant
impact on social influence (F (3.88), p =.002, η2
=.556) with a large effect size.
For hypothesis H4 (The “social influence” has a
positive influence on the acceptance of the resources
from a PW e-learning platform), we conducted a
linear regression analysis and an ANOVA test which
did not confirm the influence of social influence on
Effective Use (p = .491 and p = .349, respectively).
Based on the data, we cannot prove that social
influence has a direct impact on the effective use
(acceptance) of the platform.
4 DISCUSSION
4.1 Discussions of Findings
Due to our lack of participants, we can't reach
definitive conclusions. However, we can discuss the
results obtained with our sample.
The results of the study show that the level of
awareness of the impact of public works on the
climate at the organizational level has not been
The Influence of Pro-Environmental Behavior Stages on e-Learning Platform Acceptance in Public Works
353

significantly influenced by the acceptance of
technologies according to the hypothesis (H1). This
could be due to the fact that the questions were not
about individuals but about their organizations,
meaning that participants were not influenced by their
organization's acceptance and use of tpdemain
resources.
The study reveals that the progress in the
transition stages from SSBC is closely related to the
acceptability and acceptance of the resources form the
platform tpdemain.
The hypothesis H2a was near from significance,
but due to the small sample size and individual
variability, it is recommended to conduct a larger
study to confirm or refute this trend.
H2b has been confirmed with a large effect size,
showing a relationship between individuals'
awareness of climate-related issues and their desire to
change their behavior, as seen in Keller and al.’s
study ‘Why consumers shift from single-use to
reusable drink cups’ (2021), and the acceptance of the
tpdemain platform with effective and concrete use of
the other part.
Thus, we can determine that a possible link
between the adoption of a Pro-Environmental
behavior and Technology Acceptance can exist, at
least in Bobillier-Chaumon's Situated Acceptance
(2016).
Bobillier-Chaumon's organizational dimension
(2016) positively influences Venkatesh and al.’s
social dimension (2012) (H3), with higher scores
indicating a stronger influence on the social
dimension. The study has confirmed the relationship
between social acceptance and the situated
acceptance with a quite high effect size.
The hypothesis H4 aimed to highlight the
influence of the context in which individuals work,
highlighting the link between social acceptability
(UTAUT2) and effective acceptance (effective Use).
The organizational dimension of Situated Acceptance
has an impact on the social influence of UTAUT2, as
explained by Bobillier-Chaumon and Dubois (2013)
and Bobillier-Chaumon (2016).
This study shows no influence of SI on effective
use of tpdemain resources, suggesting that
participants may not use them effectively due to their
influence from colleagues or superiors.
The results did not confirm the hypothesis H4.
Further research is needed to determine if social
influence can be correlated to certain dimensions of
Situated Acceptance.
4.2 Limitations and Future Directions
In our research to write this study, we weren’t able to
identify studies about both Technological Acceptance
and Adoption of Pro-Environmentally behavior. This
is why we had several objectives such as trying to
determine if people in a pre-decisional denial of
inhibition (Keller and al., 2021) could also be in a
weaker acceptability and acceptance of an e-learning
platform’s resources. However, the study's sample
size seemed to be too small for this hypothesis to be
studied.
Furthermore, the analysis of the responses was
problematic due to the limited Likert scale, which
may have encouraged participants to make the choice
of not to actually choose their response. Future
research should propose a larger Likert scale with
four or six choices to better align participants'
expectations and needs. A larger sample is also
needed to study the hypothesis. Indeed, to be able to
generalize our findings, we need more participants. It
would be interesting to open this study to people who
are not used to the platform, as well as making a
longitudinal study to see if a change in the SSBC
stages of transition concretely influences the effective
use of the e-learning platform.
It is also important to have in mind that there are
potential biases in the data, due to the fact that it is
self-reported answers.
5 CONCLUSION
This study aimed to investigate the relationship
between the acceptance of technologies and the
adoption of a Pro-Environmental behavior.
The study also sought to determine if the
acceptability and acceptance of a technology,
specifically the resources of the tpdemain platform,
and the adoption of a Pro-Environmental behavior
could be significantly related. The hypothesis was
tested showed that the stages of the SSBC have a
positive influence on acceptance and possibly
acceptance. As a matter of fact, the results showed
that when the participants indicated to be in SSBC’s
stage 3 or 4, their results in questions about effective
use of the platform went in the same direction.
Furthermore, we have been able to determine that
a gateway can be made between Pro-Environmental
behavior and acceptability/ acceptance of
technologies. Further research is needed to better
understand how these factors can be combined to
improve the acceptability and acceptance of
technologies and support sustainable practices.
CSEDU 2025 - 17th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
354

ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
This research has been funded by TP D’AVENIR
without any conflict of interest.
REFERENCES
Ajzen, I. (1991). The Theory of Planned Behavior.
Organization Behavioral and Human Decision
Processes 50, 179-211.
Bamberg, S. (2013). Changing environmentally harmful
behaviors: A stage model of self-regulated behavioral
change. Journal of Environmental Psychology, Vol. 34,
151-159.
Bandura, A. (1986). Social foundations of thought and
action: A social cognitive theory. Englewood Cliffs,
NJ: Prentice Hall;1986.
Bobillier-Chaumon M-E. (2016). L’acceptation située des
technologies dans et par l’activité : premiers étayages
pour une clinique de l’usage. Psychologie du travail et
des organisations, 22 (1),
ff10.1016/j.pto.2016.01.001ff.
Bobillier-Chaumon M-E., Dubois M. (2009). L'adoption
des technologies en situation professionnelle : quelles
articulations possibles entre acceptabilité et acceptation
? Le travail humain, 2009/4 (Vol. 72), pp. 355-382. DOI
: 10.3917/th.724.0355.
Heckhausen, H., Gollwitzer, P.M. (1987) Thought contents
and cognitive functioning in motivational versus
volitional states of mind. Motiv Emot 11, 101–120
(1987). DOI:10.1007/BF00992338
Keller, E., Köhler, J. K., Eisen, c., Kleihauer, S., HANSS,
D. (2021). Why consumers shift from single-use to
reusable drink cups: An empirical application of the
stage model of self-regulated behavioural change.
Keller, E., Eisen, C., Hanss, D. (2019). Lessons Learned
From Applications of the Stage Model of Self-
Regulated Behavioral Change: A Review. Sec.
Environmental Psychology Vol. 10
Pinho, M., Gomes, S. (2023). What Role Does Sustainable
Behavior and Environmental Awareness from Civil
Society Play in the Planet’s Sustainable Transition.
Schwartz, S.H., 1977. Normative influences on altruism.
Adv. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 10, 221–279.
DOI:10.1016/S0065-2601(08)60358-5 .
Stern, P C. (2000). Toward a Coherent Theory of
Environmentally Significant Behavior. Journal of
Social Issues. Journal of Social Issues, Vol. 56, No. 3,
pp. 407–424.
Venkatesh, V., Morris, M. G., Davis, G. B., & DAVIS, F.
D. (2003). User acceptance of information technology:
Toward a unified view. MIS Quarterly, pp. 425-478.
Venkatesh, V., Thong, J. Y., & xu, X. (2012). Consumer
acceptance and use of information technology:
extending the unified theory of acceptance and use of
technology. MIS Quarterly, 36(1), 157-178.
The Influence of Pro-Environmental Behavior Stages on e-Learning Platform Acceptance in Public Works
355
