
DigiVillage Chronicles: A Serious Game Designed to Improve Digital
Skills for Accessing Public Services
Ilenia Fronza, Shiva Saket Parida
a
and Aziya Mehboob
b
Free University of Bozen/Bolzano, Italy
{ilenia.fronza, shivasaket.parida, aziya.mehboob}@unibz.it
Keywords:
Serious Game, Digital Skills, e-Government, Smart Village, Computing Education.
Abstract:
Smart villages have transformed rural areas by using innovative solutions to provide improved public services.
However, citizens often struggle to access these services due to a lack of digital skills. To address this issue,
we present DigiVillage Chronicles, a serious game designed for young adults aged 18 to 35 to enhance their
digital skills to access public services in smart villages. The game is set in a fictional smart village where the
player participates in digital activities related to public services and gains insight into navigating the platforms
offering these services in real life. The activities include browsing and applying for jobs, transferring money
online, and booking a doctor’s appointment. In this paper, we present a proof of concept for the game and
evaluate its quality using criteria related to both the serious and game components, as well as the balance
between these elements.
1 INTRODUCTION
Digitalization has greatly changed our society by en-
abling access to various commercial and public ser-
vices via online platforms, particularly on mobile
devices (Olsson et al., 2019). The transition to-
wards digital services has expanded beyond urban
areas, with rural communities implementing smart
village initiatives that utilize technology and inno-
vation to improve access to essential services, pro-
mote sustainable development, and strengthen local
economies (Adamowicz and Zwoli
´
nska-Ligaj, 2020;
Zavratnik et al., 2018). Smart villages are rural com-
munities that use innovative solutions to enhance re-
silience, quality of life, and development opportuni-
ties in economic, social, health, and communication
sectors (European Commission, 2017; Komorowski
and Stanny, 2020). These villages aim to bridge the
gap between rural and urban communities by integrat-
ing smart technologies, infrastructure, and services
to support agricultural and non-agricultural sectors
(Bokun and Nazarko, 2023). Smart villages focus
on the specific challenges and opportunities faced in
rural areas, leading to distinct implementation strate-
gies that differ from those used in urban settings (Ko-
morowski and Stanny, 2020).
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0000-0367-8907
b
https://orcid.org/0009-0005-4377-9362
A considerable challenge for smart villages is
achieving the digital transformation of local govern-
ment operations, which involves using innovative and
smart solutions to deliver public services (Satoła and
Milewska, 2022). In this context, the digital divide
becomes a major obstacle, particularly in rural areas
(Esteban-Navarro et al., 2020): e-government initia-
tives may fail to engage citizens if they do not possess
the necessary skills (Yu et al., 2017; Sundberg, 2019).
The Digital Competence Framework for Citizens,
commonly called DigComp, helps policymakers de-
velop policies and plan educational and training ini-
tiatives to enhance the digital skills of various target
groups (Vuorikari et al., 2016). While existing stud-
ies primarily focus on education (Fern
´
andez-Batanero
et al., 2022; Spante et al., 2018), information literacy
(Grabowsky and Weisbrod, 2020), and communica-
tion (Van Laar et al., 2017), there has been less em-
phasis on e-government.
To address this issue, in this paper, we propose Di-
giVillage Chronicles, a serious game designed to en-
hance the acquisition of digital skills to access digital
public services.
The paper is organized as follows: Section 2 pro-
vides background information and related work. Sec-
tion 3 describes the serious game. Section 4 describes
the evaluation of the game, and Section 5 concludes
the paper and outlines ideas for future work.
Fronza, I., Parida, S. S. and Mehboob, A.
DigiVillage Chronicles: A Serious Game Designed to Improve Digital Skills for Accessing Public Ser vices.
DOI: 10.5220/0013290600003932
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2025) - Volume 2, pages 745-751
ISBN: 978-989-758-746-7; ISSN: 2184-5026
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
745

2 RELATED WORK
Clark C. Abt (Abt, 1987) popularized the term “se-
rious games”, which are defined as games “in which
education, in its various forms, is the primary goal
rather than entertainment” (Michael and Chen, 2005).
Serious games provide an interactive and effective
method for transferring knowledge and promoting
learning or behavior change outcomes (Connolly
et al., 2012). Unlike traditional video games, they
focus on problem-solving and learning while utiliz-
ing similar media and interactive elements as recre-
ational games, making them engaging and enjoyable.
They are designed to facilitate learning, skill devel-
opment, and behavior change by following a game
design process that prioritizes achieving educational
goals through gameplay (Bergeron, 2005).
Based on the constructive learning theory, serious
games create learning environments where partici-
pants can address real problems, explore various solu-
tions, learn from their mistakes, and gain new insights
without the fear of real-world consequences (Deterd-
ing et al., 2011). For this reason, they are used across
diverse fields, such as healthcare (Maheu-Cadotte
et al., 2018), education (Deshpande and Huang, 2011;
Rajaravivarma, 2005; Sch
¨
afer et al., 2013), military
(Johnson et al., 2000), and language teaching (Zou
et al., 2021; Hung et al., 2018). Hanna Wirman
(Wirman et al., 2018) explored and categorized se-
rious games into fourteen domains based on themes
and learning goals and discussed games related to
Hong Kong public services, including building main-
tenance, postal services, and tunnel systems.
The use of serious games to engage citizens in
public service processes has been explored in various
studies. For instance, Pflanzl et al. proposed a serious
game aimed at helping citizens understand the retire-
ment process in Brazil (Pflanzl et al., 2017). While
they outlined potential stages of game design, their
proposal remained theoretical. Moreira de Classe et
al. investigated how serious games could improve
citizens’ understanding of service delivery through
a game called Play Your Process (PYP). This game
was designed for three different public service sce-
narios in Brazil and demonstrated positive outcomes
(De Classe et al., 2021). Hassan L. provided a the-
oretical framework and guidelines for implementing
gamification on platforms designed for civic engage-
ment (Hassan, 2017).
Serious games have also been used to engage citi-
zens in wider civic initiatives. For example, Poplin A.
proposed a game to encourage citizens to share their
opinions about a marketplace and gain insights into
the city’s existing conditions and challenges (Poplin,
2011). Aguilar et al. presented a city simulator game
to facilitate collective decision-making and to pro-
mote citizens’ electronic participation (Aguilar et al.,
2019).
The aforementioned research uses serious games
to promote citizens’ understanding of public pro-
cesses and encourage participation. They do not pri-
marily focus on designing serious games to access
digital public services and enhance citizens’ digital
skills.
3 THE SERIOUS GAME
In this paper, we present DigiVillage Chronicles, a se-
rious game aimed at helping citizens of smart villages
designed to assist citizens of smart villages in devel-
oping essential skills for accessing digital public ser-
vices. The splash screen of the serious game is shown
in Figure 1).
Figure 1: DigiVillage splash screen.
DigiVillage Chronicles targets young adults aged
18 to 35, particularly those in rural areas having lim-
ited familiarity with digital public services. However,
regardless of background, it can benefit anyone look-
ing to improve their understanding. The game is set in
a fictional smart village named DigiVillage, where the
local government’s operations have undergone digi-
tal transformation. This transformation involves the
implementation of innovative and smart solutions to
enhance the delivery of public services.
As shown in Table 1, to demonstrate the seri-
ous game as a proof of concept, we included three
services identified as essential or important in the
European Union Access Factsheet (European Union,
2022). In each service, we selected one activity,
such as browsing and applying for jobs from youth
services, transferring money online from bank ser-
vices, and booking a doctor’s appointment online
from health services. The player controls the protago-
CSEDU 2025 - 17th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
746

nist, who will engage in activities that reflect real-life
interactions with digital public services.
Table 1: Services and activities included in the proof of con-
cept of the serious game.
Service Activity
Youth services Browsing and applying for jobs
Bank services Money transfer
Health services Booking a doctor’s appointment
3.1 The Story Telling
Once known for its vineyards and rolling hills, Di-
giVillage has evolved into a smart village that offers
digital access to all public services, along with a Dig-
ital Competence Center that assists residents in learn-
ing about digital services. Figure 2 shows the map of
DigiVillage and its services, highlighting the services
and activities listed in Table in Table 1.
The main character, John, lives in DigiVillage
and appreciates the convenience of living in a digi-
tal world, but he is still acquiring the necessary skills.
In the game, the player controls John as he faces var-
ious digital challenges in his daily life. The proof of
concept includes the following three scenarios, each
centered around a digital activity.
Scenario 1. Searching for Job Openings Online.
John is on his way to meet his friend Anna (Figure 3),
who recently started a new job and invited John to cel-
ebrate together. John congratulates Anna and shares
that he is currently job hunting. He mentions that he
has visited several companies to submit his CV but
has not yet found the right fit. Anna tells him about
the Digital Competence Center in town, where she re-
ceived valuable guidance on browsing and applying
for jobs online. Grateful for the tip, John heads to the
Digital Competence Center. A staff member intro-
duces him to the platform and shows how it can help
him learn essential digital skills, including a step-by-
step guide to online job searching. Eager to start, John
learns about online job search. After completing the
search and application process for a job, John gets a
digital badge.
Scenario 2. Making an Online Money Transfer.
One day, John receives a call from his friend Mark,
who asks him to transfer some money urgently. John
heads to the bank but finds it closed. When John calls
Mark to explain the situation, Mark advises him to
send the money online (Figure 4). John figured out
he could learn to send money online from the Digi-
tal Competence Center. After completing the online
bank transfer activity, Mark calls John to inform him
that he received the money. John gets a digital badge
for successfully learning about online banking.
Scenario 3. Booking a Doctor Appointment On-
line. John’s mother texts him, saying she made his
favorite dish and invited him to visit. During lunch,
she asks him to go to the clinic and book an appoint-
ment with the doctor for her (Figure 5). John says that
it could be done online. She is curious to learn how,
and John shows her the Digital Competence Center.
After completing the activity of booking a doctor’s
appointment, his mother thanks him. John gets a digi-
tal badge for successfully learning about online health
services.
3.2 Game Mechanics
Each of the three scenarios in the game focuses on a
challenge that requires understanding and accessing a
specific digital public service. As the player navigates
the village, they interact with various characters, set-
ting the stage for a digital challenge.
The Digital Competence Center provides support
by offering an informative quiz and a step-by-step
guide to complete the challenge. The quiz consists of
four multiple-choice questions. The player earns one
point for each correct response and receives feedback
for incorrect responses. To pass the quiz, the player
must score at least 3 out of 4 points and can retake
the quiz as many times as necessary to achieve this
score. When the player passes the quiz, the activity
is unlocked, and the player must follow certain steps
correctly to complete the activity.
For example, in Scenario 3, for booking a doctor
appointment online, the main character completes a
quiz (shown in Figure 6) to gain essential knowledge
about the service and the required information for ac-
cessing it. After completing the quiz, he performs the
activity (shown in Figure 7) where he follows specific
steps, such as logging into the website using his health
card number, selecting the date and time, and finally
confirming the appointment.
4 EVALUATION
We used criteria for high-quality serious games based
on the framework proposed in (Caserman et al., 2020)
to evaluate the proposed game.
These evaluation criteria consider the aspects as-
sociated with serious and game parts along with the
balance between these elements. The core elements
of the serious part include the presence of a char-
acterizing goal, the creation of suitable methods for
accomplishing these goals, and the assessment of the
game’s quality. he core elements of the game part
include suitable game design and appropriate media
DigiVillage Chronicles: A Serious Game Designed to Improve Digital Skills for Accessing Public Services
747

Figure 2: Map of DigiVillage. The legend categorizes services as essential, important, and good-to-have according to the
European Union Access Factsheet (European Union, 2022).
Figure 3: In Scenario 1, the main character, John, interacts
with his friend, Anna, who tells him about the Digital Com-
petence Center in town.
Figure 4: In Scenario 2, the main character, John, interacts
with his friend Mark, who advises him to make an online
money transfer.
presentation. The criteria for balance between the
serious and game part evaluate how well these two
components are integrated and interconnected.
Figure 5: In Scenario 3, the main character, John, interacts
with his mother, who needs to book a doctor’s appointment.
Figure 6: The informative quiz regarding doctor appoint-
ments can be found in Scenario 3.
Table 2 details how the proposed game, DigiVil-
lage Chronicles, has been designed to fulfill each
of these criteria, ensuring that it qualifies as a high-
quality serious game.
CSEDU 2025 - 17th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
748
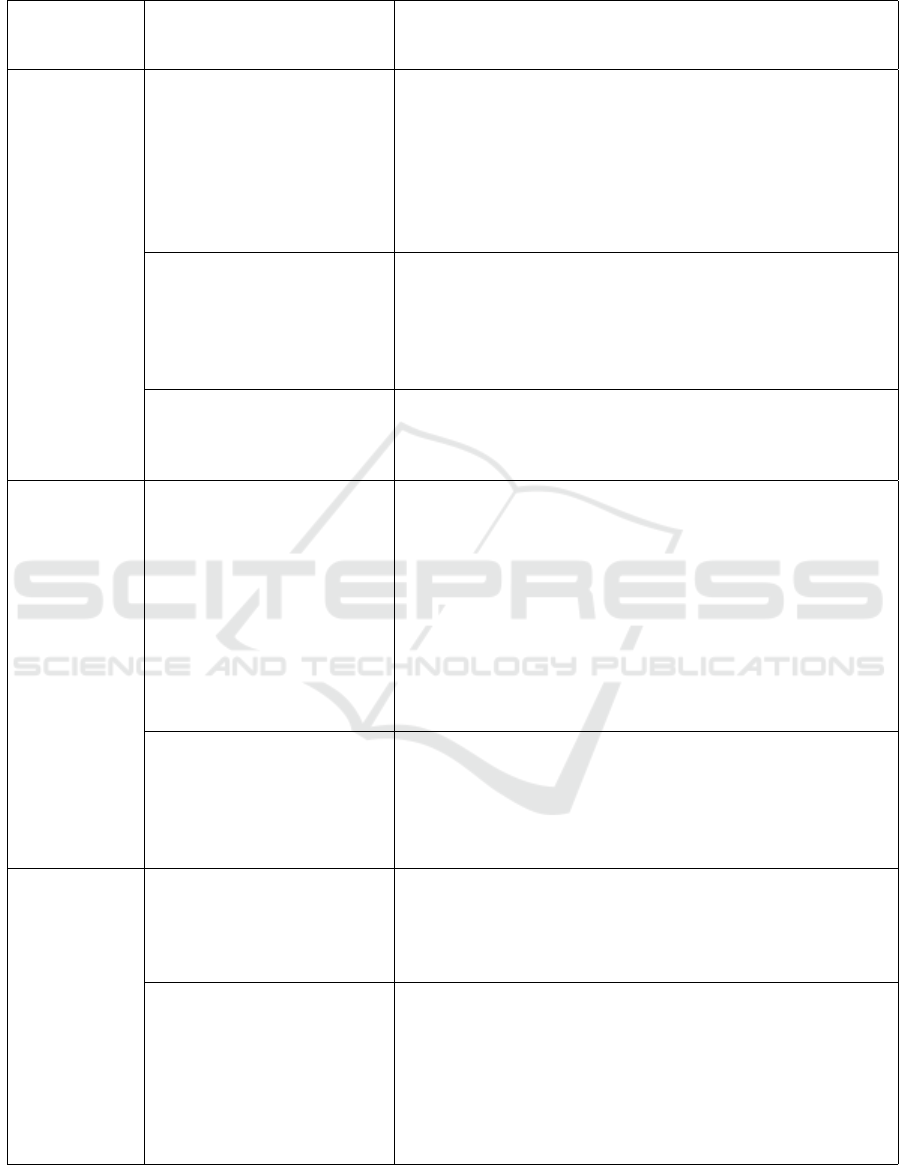
Table 2: Evaluation of the game with the quality criteria for serious games proposed by (Caserman et al., 2020).
Sections of
Quality Crite-
ria
Core Elements How DigiVillage Chronicles fulfills the criterion
Serious Part
Goal The game aims to improve digital literacy by teaching es-
sential skills for accessing public services, focusing on real-
world applications to ensure that the skills learned during the
game are transferable. The game provides the player with
clear step-by-step instructions and visual hints to achieve the
goal during the activity. The quiz delivers essential foun-
dational knowledge on accessing public services and is an
unavoidable step to unlock the corresponding activity.
Method The game provides appropriate feedback for responses in the
quiz and unlocks the activity after the player scores specific
points. The game offers positive reinforcement through digi-
tal badges upon completing each activity. The game includes
activities that mimic real-life scenarios the target group faces
in accessing public services.
Quality The player performs certain steps to complete specific activ-
ities. Upon completing an activity successfully, they receive
a badge, demonstrating their learning progress and ability to
navigate digital platforms.
Game Part
Enjoyment The game provides the player with new challenges and re-
wards with points and badges, which keeps the player en-
gaged. The game provides variety in gameplay through dif-
ferent user interface (UI) elements in each activity, such as
filters, search bars, text inputs, and radio buttons. The game
invokes a sense of accomplishment and satisfaction when
other characters are grateful to the protagonist for helping
them. While exploring Digivillage, the player can enter spe-
cific buildings and notice small environmental details like
falling leaves and cars passing by, all of which add a feel-
ing of immersion in the game world.
Media Presentation Vibrant images, approachable characters, and friendly dia-
logues create a welcoming experience. Visual hints and step-
by-step guidance during activities improve interactivity and
player support. The game also features engaging background
music and sound effects for events, such as correct or incor-
rect quiz responses and badge achievement.
Balance
Integrated serious part with
gameplay
The activities are directly related to the digital challenges oc-
curring during the interaction with non-playable characters
(NPCs) from the game environment. An interdisciplinary
team of game designers and domain experts worked together
to build the scientific foundation of the game.
Interaction technology Activities in the game are created from examples of several
public service websites. Activities mimic real-world digi-
tal portals with forms, input fields, clickable buttons, and
checkboxes, ensuring a seamless transition from the game to
actual applications. The game involves intuitive game con-
trols, such as a left mouse click to move the player and a
right mouse click to interact with objects and characters in
the game.
DigiVillage Chronicles: A Serious Game Designed to Improve Digital Skills for Accessing Public Services
749

Figure 7: The activity to book a doctor’s appointment in-
cluded in Scenario 3.
5 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
This paper presents the proof of concept of a seri-
ous game that aims to educate citizens about access-
ing digital public services using story scenarios cen-
tered around a digital challenge. The evaluation of
this game, based on the quality criteria for serious
games (Caserman et al., 2020) shows that the strong
point of the game lies in its integration of serious part
with the gameplay by incorporating activities around
a digital challenge arising from the story scenario and
character interactions. Also, the interactive game-
play provides an engaging and satisfying experience
with elements like points and badges that can enhance
the player’s motivation. However, to ensure a better
flow in the game, the difficulty of the game could dy-
namically adapt to the player’s performance. More-
over, the social interaction aspect could be improved
by introducing a multiplayer mode in which players
would work together and collaborate to accomplish
the game’s challenges.
The game combines educational goals with inter-
active gameplay, meeting the quality standards for se-
rious games while balancing educational content and
gaming elements. However, user evaluation is nec-
essary to assess the game’s effectiveness regarding
learning outcomes and to improve the gameplay expe-
rience based on user feedback. Therefore, our future
work will focus on testing and evaluating the game’s
effectiveness through pre and post-surveys.
To show the potential of the game concept, the
proof of concept presented in this paper includes three
digital activities, each selected from a distinct digital
public service. Future efforts will focus on evaluat-
ing the game’s effectiveness and incorporating more
activities on a broader variety of public services. Fur-
thermore, the game could introduce new mechanics,
such as allowing players to assist other characters who
encounter similar challenges related to digital skills.
This would reward players with social points and en-
hance the protagonist’s social status within DigiVil-
lage, reinforcing their learning by applying the con-
cepts experienced during gameplay. Future develop-
ments may also include a multiplayer aspect, where
players join various digital villages as virtual citizens
and collaboratively work towards goals to increase the
digital literacy of their village.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This study was funded by the European Union -
NextGenerationEU, in the framework of the consor-
tium iNEST - Interconnected Nord-Est Innovation
Ecosystem (PNRR, Missione 4 Componente 2, Inves-
timento 1.5 D.D. 1058 23/06/2022, ECS 00000043 –
Spoke1, RT1A, CUP I43C22000250006). The views
and opinions expressed are solely those of the authors
and do not necessarily reflect those of the European
Union, nor can the European Union be held responsi-
ble for them.
REFERENCES
Abt, C. (1987). Serious Games. University press of Amer-
ica.
Adamowicz, M. and Zwoli
´
nska-Ligaj, M. (2020). The
“smart village” as a way to achieve sustainable de-
velopment in rural areas of poland. Sustainability,
12(16):6503.
Aguilar, J., D
´
ıaz, F., Altamiranda, J., Cordero, J., Chavez,
D., and Gutierrez, J. (2019). Metropolis: an emerging
serious game for the smart city. Dyna, 86(211):215–
224.
Bergeron, B. (2005). Developing serious games (game de-
velopment series). Charles River Media, Inc.
Bokun, K. and Nazarko, J. (2023). Smart villages con-
cept—a bibliometric analysis and state-of-the-art lit-
erature review. Progress in Planning, 175:100765.
Caserman, P., Hoffmann, K., M
¨
uller, P., Schaub, M.,
Straßburg, K., Wiemeyer, J., Bruder, R., G
¨
obel, S.,
et al. (2020). Quality criteria for serious games: seri-
ous part, game part, and balance. JMIR serious games,
8(3):e19037.
Connolly, T. M., Boyle, E. A., MacArthur, E., Hainey, T.,
and Boyle, J. M. (2012). A systematic literature re-
view of empirical evidence on computer games and
serious games. Computers & education, 59(2):661–
686.
De Classe, T. M., De Araujo, R. M., Xex
´
eo, G. B., and
Siqueira, S. W. M. (2021). Public processes are open
for play. Digital Government: Research and Practice,
2(4):1–18.
CSEDU 2025 - 17th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
750

Deshpande, A. A. and Huang, S. H. (2011). Simulation
games in engineering education: A state-of-the-art re-
view. Computer applications in engineering educa-
tion, 19(3):399–410.
Deterding, S., Dixon, D., Khaled, R., and Nacke, L. (2011).
From game design elements to gamefulness: defin-
ing” gamification”. In Proceedings of the 15th inter-
national academic MindTrek conference: Envisioning
future media environments, pages 9–15.
Esteban-Navarro, M.-
´
A., Garc
´
ıa-Madurga, M.-
´
A., Morte-
Nadal, T., and Nogales-Bocio, A.-I. (2020). The rural
digital divide in the face of the covid-19 pandemic in
europe—recommendations from a scoping review. In
Informatics, volume 7, page 54. MDPI.
European Commission (2017). Eu action for smart vil-
lages.2017. https://ec.europa.eu/enrd/news-events/
news/eu-action-smart-villages\ en.html/. Accessed:
2024-09-09.
European Union (2022). European union access fact-
sheet. https://ec.europa.eu/enrd/sites/default/files/
enrd-factsheet\textunderscoreaccess-to-services.pdf.
Fern
´
andez-Batanero, J. M., Montenegro-Rueda, M.,
Fern
´
andez-Cerero, J., and Garc
´
ıa-Mart
´
ınez, I. (2022).
Digital competences for teacher professional develop-
ment. systematic review. European Journal of Teacher
Education, 45(4):513–531.
Grabowsky, A. and Weisbrod, L. (2020). The effective-
ness of library instruction for graduate/professional
students: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Evidence Based Library and Information Practice,
15(2):100–137.
Hassan, L. (2017). Governments should play games:
Towards a framework for the gamification of civic
engagement platforms. Simulation & Gaming,
48(2):249–267.
Hung, H.-T., Yang, J. C., Hwang, G.-J., Chu, H.-C., and
Wang, C.-C. (2018). A scoping review of research on
digital game-based language learning. Computers &
Education, 126:89–104.
Johnson, W. L., Rickel, J. W., Lester, J. C., et al. (2000). An-
imated pedagogical agents: Face-to-face interaction in
interactive learning environments. International Jour-
nal of Artificial intelligence in education, 11(1):47–
78.
Komorowski, Ł. and Stanny, M. (2020). Smart villages:
Where can they happen? Land, 9(5):151.
Maheu-Cadotte, M.-A., Cossette, S., Dub
´
e, V., Fontaine,
G., Mailhot, T., Lavoie, P., Cournoyer, A., Balli, F.,
and Mathieu-Dupuis, G. (2018). Effectiveness of seri-
ous games and impact of design elements on engage-
ment and educational outcomes in healthcare profes-
sionals and students: a systematic review and meta-
analysis protocol. BMJ open, 8(3):e019871.
Michael, D. R. and Chen, S. L. (2005). Serious games:
Games that educate, train, and inform. Muska &
Lipman/Premier-Trade.
Olsson, T., Samuelsson, U., and Viscovi, D. (2019). At
risk of exclusion? degrees of ict access and literacy
among senior citizens. Information, Communication
& Society, 22(1):55–72.
Pflanzl, N., Classe, T., Araujo, R., and Vossen, G. (2017).
Designing serious games for citizen engagement in
public service processes. In Business Process Man-
agement Workshops: BPM 2016 International Work-
shops, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, September 19, 2016, Re-
vised Papers 14, pages 180–191. Springer.
Poplin, A. (2011). Games and serious games in urban plan-
ning: study cases. In Computational Science and
Its Applications-ICCSA 2011: International Confer-
ence, Santander, Spain, June 20-23, 2011. Proceed-
ings, Part II 11, pages 1–14. Springer.
Rajaravivarma, R. (2005). A games-based approach for
teaching the introductory programming course. ACM
SIGCSE Bulletin, 37(4):98–102.
Satoła, Ł. and Milewska, A. (2022). The concept of a smart
village as an innovative way of implementing pub-
lic tasks in the era of instability on the energy mar-
ket—examples from poland. Energies, 15(14):5175.
Sch
¨
afer, A., Holz, J., Leonhardt, T., Schroeder, U., Brauner,
P., and Ziefle, M. (2013). From boring to scoring–a
collaborative serious game for learning and practic-
ing mathematical logic for computer science educa-
tion. Computer Science Education, 23(2):87–111.
Spante, M., Hashemi, S. S., Lundin, M., and Algers, A.
(2018). Digital competence and digital literacy in
higher education research: Systematic review of con-
cept use. Cogent education, 5(1):1519143.
Sundberg, L. (2019). Electronic government: Towards e-
democracy or democracy at risk? Safety science,
118:22–32.
Van Laar, E., Van Deursen, A. J., Van Dijk, J. A., and
De Haan, J. (2017). The relation between 21st-century
skills and digital skills: A systematic literature review.
Computers in human behavior, 72:577–588.
Vuorikari, R., Punie, Y., Gomez, S., and Van den Brande,
G. D. (2016). 2.0: The digital competence framework
for citizens. update phase 1: The conceptual reference
model. Luxembourg: Publication Office of the Euro-
pean Union.
Wirman, H. et al. (2018). Serious games as social inno-
vation: case hong kong 2003-2017. Cubic journal,
1(1):186–195.
Yu, T.-K., Lin, M.-L., and Liao, Y.-K. (2017). Under-
standing factors influencing information communica-
tion technology adoption behavior: The moderators
of information literacy and digital skills. Computers
in human behavior, 71:196–208.
Zavratnik, V., Kos, A., and Stojmenova Duh, E. (2018).
Smart villages: Comprehensive review of initiatives
and practices. Sustainability, 10(7):2559.
Zou, D., Huang, Y., and Xie, H. (2021). Digital game-based
vocabulary learning: where are we and where are we
going? Computer Assisted Language Learning, 34(5-
6):751–777.
DigiVillage Chronicles: A Serious Game Designed to Improve Digital Skills for Accessing Public Services
751
