
Investigating Reinforcement Learning for Histopathological Image
Analysis
Mohamad Mohamad
1
, Francesco Ponzio
2
, Maxime Gassier
3
, Nicolas Pote
3
, Damien Ambrosetti
4
and Xavier Descombes
1
1
Universit
´
e C
ˆ
ote d’Azur, INRIA, CNRS, I3S, INSERM, IBV, Sophia Antipolis, France
2
Department of Control and Computer Engineering, Politecnico di Torino, Turin, Italy
3
Department of Pathology, Bichat Hospital, Assistance Publique-H
ˆ
opitaux de Paris, Paris, France
4
Department of Pathology, CHU Nice, Universit
´
e C
ˆ
ote d’Azur, Nice, France
Keywords:
Deep Reinforcement Learning, Computational Pathology, Whole Slide Images, Medical Image Analysis,
Goal-Conditioned Reinforcement Learning.
Abstract:
In computational pathology, whole slide images represent the primary data source for AI-driven diagnostic
algorithms. However, due to their high resolution and large size, these images undergo a patching phase. In
this paper, we approach the diagnostic process from a pathologist’s perspective, modeling it as a Sequential
decision-making problem using reinforcement learning. We build a foundational environment designed to
support a range of whole slide applications. We showcase its capability by using it to construct a toy goal-
conditioned Navigation environment. Finally, we present an agent trained within this environment and provide
results that emphasize both the promise of reinforcement learning in histopathology and the distinct challenges
it faces.
1 INTRODUCTION
In modern histopathology, precise and efficient analy-
sis of tissue samples is crucial for accurate diagnostics
that determine appropriate treatment. Pathologists ex-
amine slides under a light microscope, identifying
histopathological lesions with various diseases (can-
cers, inflammatory disorders, infectious diseases...).
However, recent technological advances, especially
in digital imaging and computational pathology (Pan-
tanowitz et al., 2011; Cornish et al., 2012), have revo-
lutionized this process. Whole slide imaging (WSI)
has played an essential role in this transformation.
WSI allows entire glass slides to be scanned at high
resolution and stored digitally. With WSI, pathol-
ogists can visually analyze the digitalized slides in
a pyramidal, multi-magnification format ( see Fig-
ure 1), accessing both structural and granular infor-
mation that enhances diagnostic capabilities.
WSI has not only improved the diagnostic pro-
cesses for pathologists but also facilitated the cre-
ation and development of computer-aided systems us-
∗
The code is available at the following repository:
https://github.com/mohamad-m2/HistoRL
ing digital slides. In particular, the integration of ad-
vances in machine learning (ML) and deep learning
(DL) has facilitated the creation of a variety of mod-
els and algorithms (Cui and Zhang, 2021). These
encompass traditional ML approaches (Naik et al.,
2007), supervised and weakly supervised DL meth-
ods (Mukherjee et al., 2019; Shao et al., 2021; Wang
et al., 2018; Ponzio et al., 2023), and the latest ad-
vancements in self-supervised DL (Chen et al., 2024a;
Xu et al., 2024). However, due to their substantial
size, WSIs cannot be processed entirely by these mod-
els. Instead, they are segmented into smaller patches
from a specified magnification level, which are then
input into the algorithms for prediction. This results
in predictions made at the patch level, necessitating
an additional aggregation step. This process often re-
quires considerable manual tuning and the intuitive
design of various pre-processing and post-processing
steps, frequently relying on the expertise of patholo-
gists. As a result, these approaches tend to produce
less flexible pipelines. Moreover, they require signif-
icant computational resources and time during the in-
ference stage.
Pathologists follow a different diagnostic process;
Mohamad, M., Ponzio, F., Gassier, M., Pote, N., Ambrosetti, D. and Descombes, X.
Investigating Reinforcement Learning for Histopathological Image Analysis.
DOI: 10.5220/0013300900003911
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 18th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2025) - Volume 1, pages 369-375
ISBN: 978-989-758-731-3; ISSN: 2184-4305
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
369

Figure 1: WSI. An illustration of a WSI showcasing its
multi-magnification levels. Here, level 0 represents the
highest magnification and level N is the lowest.
they handle diagnoses by zooming in and out and nav-
igating different slide regions, which is more akin
to a sequential decision process, rather than brute-
force patch analysis. A Markov decision process (Sut-
ton and Barto, 2018) (MDP) is a standard framework
for modeling sequential decision-making. The com-
plex nature of the histopathological environment, and
the absence of any modelization for WSIs, demand
interactive, experience-dependent learning, naturally
guiding us toward the reinforcement learning (RL)
paradigm (Sutton and Barto, 2018), which builds
upon the MDP formulation. In an RL problem, at
each time step, an agent, such as a pathologist, ob-
serves the environment—in this case, the WSI im-
age state—and takes action accordingly. This action
alters the state of the environment and produces a
new observation along with a reward for the agent.
The agent should learn optimal actions through the
reward feedback. Figure 2 provides a breakdown
of the above-mentioned RL scenario, embodying the
decision-making procedure of pathologists.
In this work, we model the pathologist’s diag-
nostic procedure following an RL paradigm, exploit-
ing its capability of learning skills and optimal be-
havior through direct interaction with the environ-
ment. This approach minimizes human interven-
tion in defining and fine-tuning pipelines that are
application-dependent or based on prior knowledge.
Besides, we expect RL to reduce the computation
time at inference by focusing on the most relevant
patches. In this primary work, our objective is to
frame WSI diagnosis as a general RL problem, rather
than applying RL agents to address a specific WSI
case study. Specifically, due to the scarcity of RL
works in the histopathological community, we first
develop a modular, general RL environment built on
the TorchRL framework (Bou et al., 2023), suitable
to manage WSI, which we termed HistoRL. Our en-
vironment should be ideally capable of supporting
a wide variety of WSI diagnostic applications, thus
serving as a framework for all specific functionalities.
As a first step towards a fully working RL framework
for WSI analysis, we showcase an example on a toy
problem and demonstrate how its environment can be
created on top of HistoRL. Lastly, we train an RL
agent on some instances of this problem, highlighting
the potential and challenges of RL in the histopatho-
logical imaging field. To summarize, our main contri-
butions are:
• HistoRL: A modular and versatile environment
framework designed specifically for WSI diag-
nostic applications, capable of supporting a vari-
ety of histopathological use cases and serving as a
foundation for application-specific environments.
• Practical Environment Example: A demonstra-
tion of HistoRL in practice through the develop-
ment of a toy problem environment, illustrating
how new WSI-related tasks can be built and man-
aged within this framework.
• RL Agent Training: Implementation and train-
ing of an RL agent on instances of the toy
problem, showcasing the feasibility, potential,
and challenges of applying RL approaches in
histopathological imaging.
2 BACKGROUND
Over the past decade, RL algorithms have achieved
significant success across a range of fields, includ-
ing video games (Mnih, 2013; Mnih et al., 2015),
robotics (Han et al., 2023), self-driving cars (Ki-
ran et al., 2021), and large language models (LLMs)
(Ziegler et al., 2019). Despite its considerable ad-
vancements, RL exploration in histopathology re-
mains limited. Qaiser (Qaiser and Rajpoot, 2019) and
Dong (Dong et al., 2018) were pioneers in exploring
RL for histopathological images. Qaiser’s approach
involves using a policy to select diagnostically rel-
evant regions from an image tile for calculating the
Her2 score (Vance et al., 2009), coupled with a recur-
rent convolutional neural network. Dong, on the other
hand, proposed Auto-Zoom Net, which segments tu-
mors in breast cancer at different magnification levels
using RL to determine the optimal level for segmen-
tation tile by tile. Chen et al. (Chen et al., 2024b) was
the first to deploy a hierarchical reinforcement learn-
ing scheme with a worker and manager for super-
resolution. Unfortunately, none of these works es-
tablished a general environment for histopathological
BIOIMAGING 2025 - 12th International Conference on Bioimaging
370

Figure 2: The reinforcement learning scheme applied to histopathology. On the right side, the neural network represents
the agent, which can take actions such as moving up, down, left, or right, as well as zooming in and out, along with other
decision-making actions. On the left side, the environment is represented by a WSI image, which dynamically responds to
the agent’s actions. The environment provides basic observations, including the current patch image at the agent’s position,
the x and y coordinates, the zoom level, and the ability to create sub-environments within defined bounds of the WSI.
images. Recently, Liu et al. (Liu et al., 2024) pro-
posed an environment built on OpenAI Gym frame-
work (Brockman, 2016), specifically for tumor re-
gion identification. While this environment offers
some degree of configurability in terms of actions and
observations, it is inherently tailored for tumor area
identification, making it less suitable and challenging
to extend for other types of histopathological applica-
tions. Thus, there remains a need for a generic envi-
ronment capable of supporting a wide range of appli-
cations in histopathological research and adaptable to
enable broader RL research in histopathology.
3 METHODOLOGY
Seeking the modeling of histopathological image di-
agnosis as a sequential decision-making problem,
we aim to develop a versatile environment that sup-
ports a wide range of downstream applications on
WSIs, including tumor detection, tumor segmenta-
tion, and tissue classification tasks. In this section,
we present a general problem formulation using RL.
In the following, we detail our HistoRL, highlighting
the RL elements it defines and solidifies, as well as
those it leaves to be specified by downstream applica-
tions. We then illustrate how the complete framework
comes together using a simple goal-conditioned envi-
ronment designed to solve a localization task. Lastly,
we detail the fully defined elements of its RL formu-
lation.
3.1 RL Formulation
We follow the definition of an MDP, where M =
(S, A, G, R, γ), with the following components (Schaul
et al., 2015):
• S is the set of possible states s ∈ S.
• A is the set of possible actions a ∈ A.
• G is the set of goals g ∈ G.
• R(s, a | g) is the reward function that provides a re-
ward for being in state s and taking action a given
the goal g.
• γ is the discount factor, γ ∈ [0,1).
The objective is to find a goal-dependent policy π
g
:
S × G → A. The policy π
g
(a | s, g) defines the proba-
bility of taking action a when in state s and under goal
g, aiming to maximize the expected discounted future
reward. The optimal policy π
∗
g
is defined as:
π
∗
g
= argmax
π
g
E
π
g
[G
t
| s, g] (1)
where the return G
t
over a specific timestep t in an
episode is given by:
G
t
=
T
∑
n=t
γ
n−t
r
n+1
(2)
r
n+1
represents R(s
n
, a
n
|g). An episode consists of a
sequence {(s
0
, a
0
, r
1
), (s
1
, a
1
, r
2
), . . . , (s
T
, a
T
, r
T +1
)}
following policy π
g
. The episode terminates when the
termination condition is met or when another stopping
condition is enforced.
V
π
g
(s, g) = E
π
g
[G
t
| s, g] (3)
Investigating Reinforcement Learning for Histopathological Image Analysis
371
Finally, the value function is the expectation of the
returns G
t
. It defines the ”goodness” of being in a
specific state s under the policy π
g
, while considering
the goal g.
3.2 HistoRL
As aforementioned, the purpose of our base environ-
ment is to serve as a framework for WSI downstream
applications. Hence, it implements all the shared and
general functionalities across these various applica-
tions. Observing how pathologists perform diagnoses
by navigating WSI, we find that they primarily engage
in two actions: moving along the X and Y axes and
zooming in and out. Thus, HistoRL defines and han-
dles these two actions, while not hindering the defini-
tion of others, thus rendering A to {A
move
, A
zoom
, . . .}.
Note that the exact implementation of A
move
and A
zoom
is left to the downstream environment. This means
that HistoRL does not directly impose a specific im-
plementation for these actions (for example move one
or half a patch to the right); instead, it expects to
receive and handle them within its dynamics (move
horizontally by factor X). In addition, it can simul-
taneously execute multiple actions, such as zooming
and moving within a single timestep. Managing these
movements lays the foundation for WSIs’ navigation
and, consequently, for any RL-defined task based on
WSIs.
Being in a state s, at a specific position p in the
WSI, and receiving the navigator actions a
move
and
a
zoom
, forces the current position to evolve to the state
s
′
at the position p
′
. While HistoRL does not de-
fine what exactly is the state space, it forces one of
its components to be the image view (patch) at the
current position p (where p includes the x, y, and
zoom level coordinates). It also allows for the po-
sition coordinates to be included in the state if the
downstream task requests them (see Figure 2, Observ-
able section), resulting in a state space structured as
{S
current patch
, ...}. Any extra components of the state
must be defined by the downstream environment. The
other components, including goals, reward functions,
and termination conditions, are entirely left for the
downstream environment to implement, as they are
fully application-dependent. However, HistoRL pro-
vides the functionality to handle these elements once
they are provided. When the goal is omitted, the task
shifts to a standard, non-goal-conditioned RL prob-
lem.
Finally, due to the complexity of WSI images,
HistoRL can create a sub-environment that focuses on
a bounded region within the WSI instead of using the
entire WSI as the environment (see Figure 2 on the
left, Sub-Env).
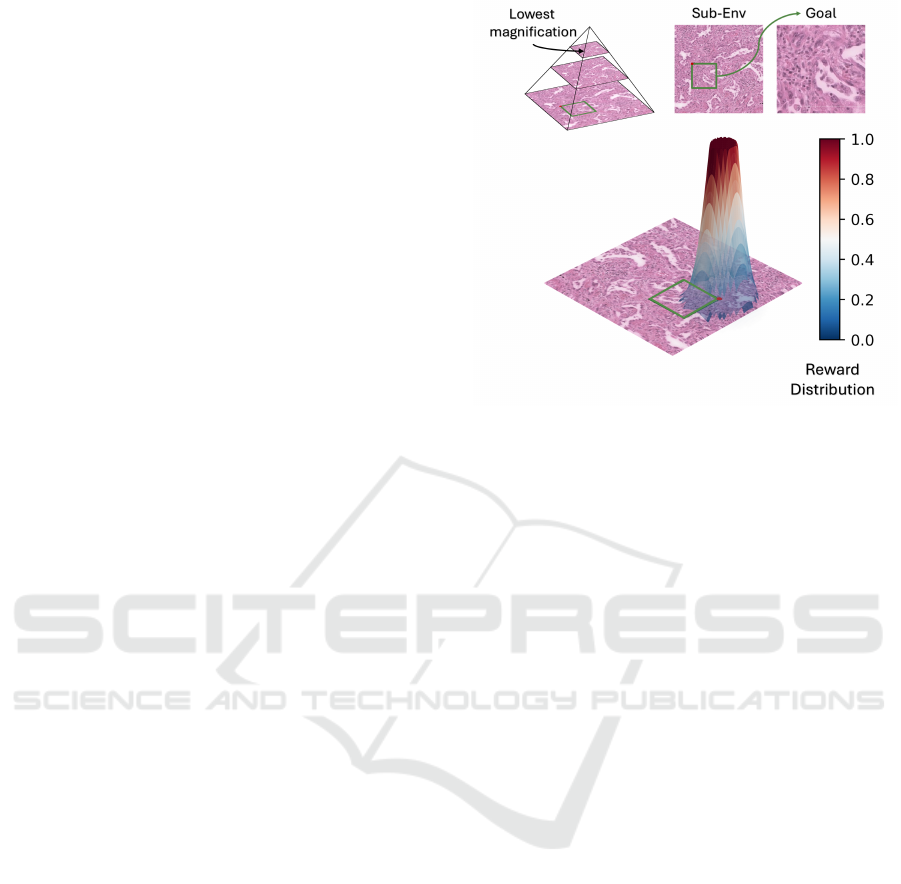
Figure 3: The localization task and its reward distribution.
The top-left pyramid illustrates a bounded environment for
the task, with three magnification levels. Here, the goal be-
longs to the highest magnification level at the bottom of the
pyramid. The graph at the bottom of the figure displays the
reward distribution: when the agent approaches the goal’s
location, a reward is provided, starting within a specific area
around the goal and increasing as the agent gets closer, cap-
ping at a maximum value of one.
3.3 Localisation Pre-Text Enviroment
We developed a goal-conditioned toy task on top
of our HistoRL, showcasing a well-defined rein-
forcement learning problem in action. Our applica-
tion focuses on patch localization, leveraging a self-
supervised pretext task that we introduced in previous
work for whole slide images (Mohamad et al., 2024).
In this task, a low-magnification patch p
y
is extracted
from the image at level y, while a high-magnification
patch p
x
is extracted at level x, where 0 ≤ x < y ≤ n; 0
represents the highest magnification level, and n rep-
resents the lowest. Furthermore, p
x
is selected in a
way that ensures it lies within the area defined by
p
y
. The goal is to locate p
x
using p
y
as our sub-
environment (see Figure 3). Our primary motivation
for deploying this task as our initial application, lies
in its nature as a purely navigational task, requiring
the search for a specific patch using only visual input.
This task necessitates learning a goal-dependent nav-
igation behavior, a behavior we argue to be essential
in many WSI-based diagnostic procedures.
• Actions: The action space for the self-supervised
environment does not introduce any new actions.
It implements the existing actions of zooming and
moving as discrete actions defined as follows:
– Moving along the x and y axes by a factor of
−0.25, 0, or +0.25 relative to the current patch.
BIOIMAGING 2025 - 12th International Conference on Bioimaging
372

– Zooming in and out by a factor of 2 or staying
still.
• Goals: The goal is defined as the image represent-
ing p
x
in p
y
, and the coordinates are provided to
be used by the reward function.
• States: The state is composed of the current ob-
servation, represented by the patch image at the
current coordinates, the low-resolution image p
y
which serves as a view of the entire space, and the
goal image. Additionally, the coordinates are in-
cluded for the calculation of the reward function.
• Rewads: The reward function is defined such that
it increases as the current position gets closer to
the goal in terms of x and y coordinates (see Fig-
ure 3 bottom), if and only if the zoom level of the
observation is the same as the goal’s.
r =
(
min
25×2
g
l
∥g
c
−o
c
∥
2
+ε
, 1
if ∥g
c
− o
c
∥
2
< t
0 elsewhere
(4)
Where:
g
l
is the zoom level for the goal state, scaling the
reward accordingly.
g
c
denotes the (x, y) coordinates of the goal.
o
c
denotes the (x, y) coordinates of the observed
patch.
ε is a small positive constant added for numerical
stability.
t is the threshold distance value below which a
reward is granted.
• Termination: The episode ends when the agent
reaches the goal, as identified by the reward sig-
nal. Specifically, the termination condition is met
when r > 0.5 which represents an intersection
> 70% with the goal patch.
4 EXPERIMENTS
4.1 Experimental Setup
The agent architecture is based on a convolutional
neural network designed for feature extraction,
specifically utilizing a ResNet18 model that has been
pre-trained on ImageNet. This architecture features
two multi-layer perceptrons (MLPs), each comprising
two hidden layers with each layer containing 1536
neurons: one MLP is dedicated to the critic network,
while the other is dedicated to the actor network.
We employ Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO)
(Schulman et al., 2017) for training the agent. The
actor’s output is a discrete probability distribution
over seven possible actions: moving up, down, left,
right, zooming in, zooming out, and staying still.
Both the critic and actor share the weights of the
ResNet18 backbone, we perform the training while
keeping the batch-norm layers (Ioffe and Szegedy,
2015) in eval mode. The training process spanned 7
hours on a single NVIDIA A100 GPU.
In this study, we implement an instance of the
Localisation Pre-text with a fixed sub-environment
and a varying goal across episodes. Ideally, we would
like to have them both change. However, this is not
trivial for our agent at this stage. The experimental
design incorporates three levels of magnification (see
Figure 3 top-left) where the agent can move. The low-
est magnification level consists of a low-resolution
image that represents the sub-environment. Goals are
randomly selected from the two higher magnification
levels, with an increased probability assigned to the
highest magnification level. This approach is chosen
because patches at higher magnifications are more
abundant, and the larger movement space makes
them more challenging to reach. Additionally, the
initial position of the agent is randomly determined
across all three levels. All of the images in the state
are of size 224× 224 × 3. It is noteworthy that for the
results presented, extensive hyper-parameter tuning
of the agent was not performed.
4.2 Results and Discussion
As reported by the training curve, the agent shows sig-
nificant improvement, increasing from an average re-
ward of approximately 0.01 to 0.23. The average re-
ward is computed by aggregating rewards across nu-
merous steps over multiple episodes. Notably, the
model nearly achieves the optimal policy’s perfor-
mance, which yields a mean reward of 0.245, cal-
culated over 12 randomly generated episodes. The
agent’s learned behavior is particularly promising, as
demonstrated by the episodes visualized in Figure 4.
The first row of images shows the initial timestep of
each episode, with the green box marking the goal and
the orange box indicating the agent’s position. The in-
termediate images illustrate the agent’s trajectory as
it progresses through the episode, while the final row
displays the last timestep. The model demonstrates
a strong ability to act upon visual cues, consistently
reaching the goal in all trials. A particularly inter-
esting behavior emerges in episodes A and B, where
the agent learns to use the ”zoom-out” action to take
larger steps. This behavior aligns with the optimal
policy and is a critical step toward efficient naviga-
tion. However, the agent’s use of the zoom-out action
remains imperfect; its probability of selecting this ac-
Investigating Reinforcement Learning for Histopathological Image Analysis
373

Figure 4: Results.Figure 1 illustrates the average reward achieved by the agent during training, compared to an optimal
policy. The reward steadily increases throughout training, narrowing the gap between the agent and optimal policy. Figure 2
depicts the value functions estimated by the model for two specific states during a single episode. The results show that the
estimated value is higher when the agent is closer to the goal. Figure 3 highlights three episodes (A, B, and C) at the end of the
optimization process. The green box denotes the goal while the orange box indicates the actor’s current position. The first row
shows the starting states for each episode, while the last row displays the corresponding end states. The intermediate images,
captured sequentially over time, provide insight into the agent’s behavior and the transitions through significant states.
tion is not yet sufficiently high in the relevant cases,
and the behavior is absent in episode C. This high-
lights room for improvement in the agent’s policy re-
finement. Additionally, the value function estimates
across different states demonstrate logical patterns:
states closer to the goal have higher estimated val-
ues than those farther away. In summary, while the
model is still under development, its ability to learn,
improve, and navigate effectively within the WSI en-
vironment demonstrates both its potential and feasi-
bility for further advancement.
5 CONCLUSIONS
We presented our work of modeling WSI as an RL
problem, established a versatile environment for WSI
applications, and trained an agent for a navigation
task. Our results demonstrate the potential of RL
in histopathological image navigation and highlight
the interesting navigational behaviors that can be ef-
fectively learned. However, this study remains pre-
liminary and does not yet address the challenges of
generalization across different environments and pa-
tients. Such a problem is inherently more complex
and requires further optimization. Our future work
focuses on tackling the generalization problem and in-
creasing task complexity by incorporating larger sub-
environments and introducing additional zoom levels.
Additionally, we aim to apply the algorithm to a real-
world case study, where we can showcase the primary
advantage of our formulation of reducing the infer-
ence time required by the agent.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work has been supported by the ANR Mor-
pheus (263702) funding and the France 2030 invest-
ment plan managed by the Agence Nationale de la
Recherche, as part of the ”UCA DS4H” project, ref-
erence ANR-17-EURE-0004.
REFERENCES
Bou, A., Bettini, M., Dittert, S., Kumar, V., Sodhani, S.,
Yang, X., De Fabritiis, G., and Moens, V. (2023).
Torchrl: A data-driven decision-making library for py-
torch. arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.00577.
Brockman, G. (2016). Openai gym. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1606.01540.
BIOIMAGING 2025 - 12th International Conference on Bioimaging
374

Chen, R. J., Ding, T., Lu, M. Y., Williamson, D. F., Jaume,
G., Song, A. H., Chen, B., Zhang, A., Shao, D., Sha-
ban, M., et al. (2024a). Towards a general-purpose
foundation model for computational pathology. Na-
ture Medicine, 30(3):850–862.
Chen, W., Liu, J., Chow, T. W., and Yuan, Y. (2024b).
Star-rl: Spatial-temporal hierarchical reinforcement
learning for interpretable pathology image super-
resolution. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging.
Cornish, T. C., Swapp, R. E., and Kaplan, K. J. (2012).
Whole-slide imaging: routine pathologic diagnosis.
Advances in anatomic pathology, 19(3):152–159.
Cui, M. and Zhang, D. Y. (2021). Artificial intelligence and
computational pathology. Laboratory Investigation,
101(4):412–422.
Dong, N., Kampffmeyer, M., Liang, X., Wang, Z., Dai, W.,
and Xing, E. (2018). Reinforced auto-zoom net: to-
wards accurate and fast breast cancer segmentation in
whole-slide images. In Deep Learning in Medical
Image Analysis and Multimodal Learning for Clin-
ical Decision Support: 4th International Workshop,
DLMIA 2018, and 8th International Workshop, ML-
CDS 2018, Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2018,
Granada, Spain, September 20, 2018, Proceedings 4,
pages 317–325. Springer.
Han, D., Mulyana, B., Stankovic, V., and Cheng, S. (2023).
A survey on deep reinforcement learning algorithms
for robotic manipulation. Sensors, 23(7):3762.
Ioffe, S. and Szegedy, C. (2015). Batch normalization: Ac-
celerating deep network training by reducing internal
covariate shift. CoRR, abs/1502.03167.
Kiran, B. R., Sobh, I., Talpaert, V., Mannion, P., Al Sallab,
A. A., Yogamani, S., and P
´
erez, P. (2021). Deep rein-
forcement learning for autonomous driving: A survey.
IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Sys-
tems, 23(6):4909–4926.
Liu, Z.-B., Pang, X., Wang, J., Liu, S., and Li, C. (2024).
Histogym: A reinforcement learning environment
for histopathological image analysis. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2408.08847.
Mnih, V. (2013). Playing atari with deep reinforcement
learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1312.5602.
Mnih, V., Kavukcuoglu, K., Silver, D., Rusu, A. A., Ve-
ness, J., Bellemare, M. G., Graves, A., Riedmiller, M.,
Fidjeland, A. K., Ostrovski, G., et al. (2015). Human-
level control through deep reinforcement learning. na-
ture, 518(7540):529–533.
Mohamad, M., Ponzio, F., Di Cataldo, S., Ambrosetti, D.,
and Descombes, X. (2024). Renal cell carcinoma sub-
typing: learning from multi-resolution localization.
arXiv preprint arXiv:2411.09471.
Mukherjee, L., Bui, H. D., Keikhosravi, A., Loeffler, A.,
and Eliceiri, K. W. (2019). Super-resolution recurrent
convolutional neural networks for learning with multi-
resolution whole slide images. Journal of biomedical
optics, 24(12):126003–126003.
Naik, S., Doyle, S., Feldman, M., Tomaszewski, J., and
Madabhushi, A. (2007). Gland segmentation and
computerized gleason grading of prostate histology by
integrating low-, high-level and domain specific infor-
mation. In MIAAB workshop, pages 1–8. Citeseer.
Pantanowitz, L., Valenstein, P. N., Evans, A. J., Kaplan,
K. J., Pfeifer, J. D., Wilbur, D. C., Collins, L. C., and
Colgan, T. J. (2011). Review of the current state of
whole slide imaging in pathology. Journal of pathol-
ogy informatics, 2(1):36.
Ponzio, F., Descombes, X., and Ambrosetti, D. (2023). Im-
proving cnns classification with pathologist-based ex-
pertise: the renal cell carcinoma case study. Scientific
Reports, 13(1):15887.
Qaiser, T. and Rajpoot, N. M. (2019). Learning where to
see: a novel attention model for automated immuno-
histochemical scoring. IEEE transactions on medical
imaging, 38(11):2620–2631.
Schaul, T., Horgan, D., Gregor, K., and Silver, D. (2015).
Universal value function approximators. In Interna-
tional conference on machine learning, pages 1312–
1320. PMLR.
Schulman, J., Wolski, F., Dhariwal, P., Radford, A., and
Klimov, O. (2017). Proximal policy optimization al-
gorithms. arXiv preprint arXiv:1707.06347.
Shao, Z., Bian, H., Chen, Y., Wang, Y., Zhang, J., Ji, X.,
et al. (2021). Transmil: Transformer based correlated
multiple instance learning for whole slide image clas-
sification. Advances in neural information processing
systems, 34:2136–2147.
Sutton, R. S. and Barto, A. G. (2018). Reinforcement learn-
ing: An introduction. MIT press.
Vance, G. H., Barry, T. S., Bloom, K. J., Fitzgibbons, P. L.,
Hicks, D. G., Jenkins, R. B., Persons, D. L., Tubbs,
R. R., and Hammond, M. E. H. (2009). Genetic het-
erogeneity in her2 testing in breast cancer: panel sum-
mary and guidelines. Archives of pathology & labora-
tory medicine, 133(4):611–612.
Wang, Z., Dong, N., Dai, W., Rosario, S. D., and Xing, E. P.
(2018). Classification of breast cancer histopatho-
logical images using convolutional neural networks
with hierarchical loss and global pooling. In Inter-
national conference image analysis and recognition,
pages 745–753. Springer.
Xu, H., Usuyama, N., Bagga, J., Zhang, S., Rao, R., Nau-
mann, T., Wong, C., Gero, Z., Gonz
´
alez, J., Gu, Y.,
et al. (2024). A whole-slide foundation model for dig-
ital pathology from real-world data. Nature, pages 1–
8.
Ziegler, D. M., Stiennon, N., Wu, J., Brown, T. B., Rad-
ford, A., Amodei, D., Christiano, P., and Irving, G.
(2019). Fine-tuning language models from human
preferences. arXiv preprint arXiv:1909.08593.
Investigating Reinforcement Learning for Histopathological Image Analysis
375
