
Transfer Learning in Deep Reinforcement Learning: Actor-Critic Model
Reuse for Changed State-Action Space
Feline Malin Barg
1 a
, Eric Veith
2 b
and Lasse Hammer
1 c
1
OFFIS e.V., Escherweg 2, 26121 Oldenburg, Germany
2
Carl von Ossietzky Universit
¨
at, Ammerl
¨
ander Heerstraße 114-118, 26129, Oldenburg, Germany
fi
Keywords:
Reinforecment Learning, Soft-Actor-Critic, Transfer Learning, State-Action Space Change, Model Reuse.
Abstract:
Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) is a leading method for control in high-dimensional environments, ex-
celling in complex tasks. However, adapting DRL agents to sudden changes, such as reduced sensors or
actuators, poses challenges to learning stability and efficiency. While Transfer Learning (TL) can reduce
retraining time, its application in environments with sudden state-action space modifications remains underex-
plored. Resilient, time-efficient strategies for adapting DRL agents to structural changes in state-action space
dimension are still needed. This paper introduces Actor-Critic Model Reuse (ACMR), a novel TL-based algo-
rithm for tasks with altered state-action spaces. ACMR enables agents to leverage pre-trained models to speed
up learning in modified environments, using hidden layer reuse, layer freezing, and network layer expansion.
The results show that ACMR significantly reduces adaptation times while maintaining strong performance
with changed state-action space dimensions. The study also provides insights into adaptation performance
across different ACMR configurations.
1 INTRODUCTION
Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) has emerged as
a powerful tool for solving complex control problems
in dynamic environments (Henderson et al., 2018).
DRL combines Reinforcement Learning (RL) princi-
ples with the power of deep neural networks, enabling
agents to make decisions and learn adaptive strate-
gies in high-dimensional state-action spaces. This ca-
pacity has led to remarkable achievements in areas
like robotics with continuous control tasks (Arulku-
maran et al., 2017), and complex systems including
real-world infrastructure such as the power grid (Omi-
taomu and Niu, 2021). A key challenge with these
systems is the need not only for stable control un-
der normal conditions but also for adaptability when
components are added or removed. In the case of the
power grid, for example, when new components like
like a PV system are introduced or existing ones are
decommissioned, the agent’s state and action spaces
change, and it may lose or gain access to certain sen-
sors and actuators (Wolgast and Nieße, 2024). This
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8753-7430
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2487-7475
c
https://orcid.org/0009-0000-5202-5574
can severely impair the agent’s ability to perceive and
control its environment as it normally would. Simi-
larly, in robotics, the failure or addition of limbs can
dramatically alter the control task, requiring agents to
adjust their strategies to the new state-action space.
Adapting to these new conditions typically requires
extensive retraining, which can be time-consuming.
However, in the context of critical infrastructure or
or autonomous systems, there is often no time for
lengthy retraining processes (Nguyen et al., 2020).
Transfer Learning (TL) offers a potential solu-
tion by allowing DRL agents to reuse knowledge
from previously encountered environments to acceler-
ate learning in modified conditions (Taylor and Stone,
2009). While the power grid provides a compelling
application domain, current benchmarks for power
grid control often lack standardized testing frame-
works required to systematically evaluate advanced
DRL methods like TL. In contrast, robotic control
benchmarks such as Gymnasium’s Humanoid envi-
ronment (Towers et al., 2024) offer well-established,
high-dimensional testbeds with the ability to create
custom environments. This paper focuses on ap-
plying TL in a challenging DRL control environ-
ment: Gymnasium’s Humanoid environment. The
Humanoid environment requires an agent to control a
682
Barg, F. M., Veith, E. and Hammer, L.
Transfer Learning in Deep Reinforcement Learning: Actor-Critic Model Reuse for Changed State-Action Space.
DOI: 10.5220/0013304900003890
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2025) - Volume 2, pages 682-692
ISBN: 978-989-758-737-5; ISSN: 2184-433X
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

complex multi-jointed figure, learning balance, loco-
motion, and continuous forward movement in a high-
dimensional state-action space. This task is particu-
larly sensitive to changes in the agent’s available con-
trols, making it an ideal testbed for investigating TL’s
efficacy in environments with reduced sensory or ac-
tuator capacities. By leveraging the robust evaluation
framework provided by Gymnasium, we can derive
insights that are broadly applicable to other domains,
including critical infrastructure like the power grid.
To address the challenge of adapting a trained
agent to new environmental changes without lengthy
retraining, this paper introduces the Actor-Critic
Model Reuse (ACMR) algorithm. ACMR leverages
TL by reusing pre-trained models, and is demon-
strated here using the Soft Actor-Critic (SAC) algo-
rithm as an example. SAC, which is well-suited for
continuous control tasks (Haarnoja et al., 2018), com-
bines an actor-critic architecture with entropy maxi-
mization to provide both stability and robust explo-
ration—qualities that are crucial in environments with
modified state-action spaces.
In this study, several configurations of ACMR are
examined, each designed to adapt the agent’s policy
and value function efficiently to a target environment
with fewer available control inputs. The configura-
tions include hidden layer reuse, layer freezing, and
the addition of new network layers to match the mod-
ified input-output dimensions of the Humanoid envi-
ronment. The aim is to assess how these transfer con-
figurations impact the agent’s adaptability and learn-
ing speed in the modified environment.
This paper is organized as follows: The Related
Work section reviews DRL and TL, highlighting chal-
lenges like distribution shifts. The Methods section
introduces ACMR for adapting to changes in state-
action spaces. The Testing ACMR chapter describes
the experimental setup, followed by the Results sec-
tion, which presents the findings. The Discussion
compares the ACMR configurations, and the Conclu-
sion outlines our contributions and future directions.
The main contribution of this paper is to introduce
and demonstrate the effectiveness of ACMR in accel-
erating adaptation to modified environments with re-
duced sensors and actuators.
2 RELATED WORK
2.1 Deep Reinforcement Learning
DRL combines RL with Deep Neural Networks
(DNN) to enable agents to make high-level decisions
in complex, high-dimensional spaces. At its core, RL
studies how an agent interacts with its environment
through trial and error to learn a policy π that maxi-
mizes cumulative rewards. (Arulkumaran et al., 2017)
In DRL, we define a state space S ∈ R
n
such that
s
t
∈ S represents the state of the environment at time
t, and an action space A ∈ R
n
such that a
t
∈ A repre-
sents actions taken by the agent. The agent’s policy is
expressed as a distribution over actions given a state,
denoted as a
t
∼ π
∗
θ
(·|s
t
) The goal is to maximize the
cumulative reward, where the reward function R de-
fines the reward r
t
as follows:
r
t
= R(s
t
, a
t
, s
t+1
). (1)
The structure and dimensionality of the state-
action space S × A play a fundamental role in
defining the agent’s capacity to perceive and act
within its environment. Significant modifications to
this space—such as the loss of sensors or actua-
tors—affect the learned policy. This can be repre-
sented as a dimensional shift, where the state-action
space in a new environment S‘ × A‘ may have differ-
ent dimensions. Mathematically, if d(S × A) repre-
sents the dimensions of the state-action space, then
d(S × A) ̸= d(S‘ × A‘). (2)
Since the originally learned policy π
∗
θ
is condi-
tioned on states and actions from the original space
S × A, it cannot directly adapt to the modified state-
action space S‘ × A‘, as the dimensionality mismatch
leaves the policy undefined in regions outside the ini-
tial space. Formally, this incompatibility can be ex-
pressed as:
π
∗
θ
(a|s) undefined for (s, a) ∈ S × A‘. (3)
Therefore, the DRL agent must adapt or retrain, as
the initial policy cannot operate effectively in the new
state-action space. A central challenge in DRL lies in
enabling efficient adaptation to such changes without
requiring full retraining, which is resource-intensive
and time-consuming (Amodei et al., 2018).
Some prior work has explored approaches to re-
duce training times, such as pre-trained models (Ce-
liberto Jr et al., 2010), but these studies typically
assume consistent state-action spaces between train-
ing and deployment environments. Consequently, a
gap remains in the applicability of DRL to dynami-
cally changing domains, such as in critical infrastruc-
tures and robotics, where state-action space dimen-
sions may vary significantly (Nguyen et al., 2020).
In conclusion, a research gap exists in the limited
methods for DRL adaptation to modified state-action
spaces without substantial retraining.
Transfer Learning in Deep Reinforcement Learning: Actor-Critic Model Reuse for Changed State-Action Space
683

2.2 Transfer Learning in Deep
Reinforcement Learning
TL is a strategy that leverages knowledge from a
source domain to improve learning in a related tar-
get domain, which is especially valuable when the tar-
get domain lacks sufficient training data (Weiss et al.,
2016). In TL, each domain has a distinct feature space
and marginal probability distribution: the source do-
main is represented by X
S
and P (X
S
), while the tar-
get domain is represented by X
T
and P (X
T
). Effec-
tive transfer is achievable when there are differences
between these feature spaces or distributions, specif-
ically when X
S
̸= X
T
or P (X
S
) ̸= P (X
T
) (Pan and
Yang, 2010).
In the context of DRL, TL techniques often in-
volve reusing components such as policies, value
functions, or pre-trained hidden layers from source
domains to target domains (Fern
´
andez and Veloso,
2006b). A common assumption is that the dimen-
sionality of the state-action spaces remains consistent
between the source and target environments, which
allows for a direct transfer of learned knowledge
without requiring structural modifications (Zhu et al.,
2023).
However, in more dynamic environments, such
as critical infrastructure management or robotics, the
state-action space of an agent can undergo signifi-
cant dimensional changes, posing challenges to tra-
ditional TL approaches. In such cases, knowledge
must be transferred from a source domain with one
state-action space dimension to a target domain with
a different state-action space dimension. Formally, let
the source domain have a state space S
s
⊆ R
n
s
and ac-
tion space A
s
⊆ R
m
s
, while the target domain has a
state space S
t
⊆ R
n
t
and action space A
t
⊆ R
m
t
. TL
requires adapting the actor and critic models of a pol-
icy π
s
: S
s
→ A
s
from the source domain to a policy
π
t
: S
t
→ A
t
in the target domain, where:
n
s
̸= n
t
or m
s
̸= m
t
. (4)
This adaptation involves a mapping or transfor-
mation T applied to both the actor and critic models
to handle the dimensional or structural mismatch be-
tween the source and target domains:
π
t
(s
t
) = T
actor
(π
s
(s
s
)), Q
t
(s
t
, a
t
) = T
critic
(Q
s
(s
s
, a
s
)),
(5)
where s
s
∈ S
s
, s
t
∈ S
t
, a
s
∈ A
s
, and a
t
∈ A
t
. Since
direct transfer is not feasible in this case, new ap-
proaches are needed to enable TL across differing
state-action space dimensions.
Although TL in DRL has been extensively stud-
ied across domains such as gaming (Tan et al., 2022),
robotics (Nair et al., 2018), and traffic engineering
(Xu et al., 2020), limited research addresses the chal-
lenge of adapting to these dimensional shifts in state-
action spaces. For instance, (Beck et al., 2022) ex-
plore reduced action spaces within the same dimen-
sionality, while (Parisotto et al., 2015) examine model
transfer across different video games. There is sub-
stantial work on policy transfer, particularly through
policy distillation methods (Zhu et al., 2023), but
research on policy reuse is comparatively limited.
An example of policy reuse is the probabilistic pol-
icy reuse framework introduced in (Fern
´
andez and
Veloso, 2006b), yet no existing approaches tackle
the problem of adapting to significant shifts in state-
action space dimensions as described above. This gap
highlights a need for TL reuse methodologies tailored
to enable DRL adaptation in environments with sub-
stantially altered state-action space dimensions.
2.3 Marginal Distribution Shifts and
Structural Shifts
In dynamic environments, RL agents encounter two
primary types of distributional changes:
Marginal Distribution Shifts. These shifts refer to
changes in the probability distribution over a fixed
state-action space. The dimensional structure of S×A
remains constant, but the distribution changes, which
we can represent as:
P(S × A) ̸= P‘(S × A) (6)
where S × A is unchanged, and only the probabil-
ity distribution shifts from P(S ×A) to P‘(S×A). This
type of shift can typically be addressed with policy
adjustments, as the agent’s observation and action ca-
pabilities remain the same. Approaches like domain-
adversarial training (Ganin et al., 2016) and conser-
vative Q-learning (Kumar et al., 2020) have been
proposed to enhance the stability and adaptability of
agents under these types of distributional changes
Structural Shifts. Structural shifts involve changes
to the dimensionality or components of the state-
action space, such as the addition or removal of sen-
sors or actuators. However, these shifts do not nec-
essarily alter the marginal distribution within any un-
changed subspaces. We represent this as:
S × A ̸= S‘ × A‘ (7)
where S × A represents the original space and
S‘ × A‘ represents the modified space. While ap-
proaches like (Fern
´
andez and Veloso, 2006a) enable
policy transfer across tasks with structural shifts like
the state-action space change, the process of learn-
ing the mapping between differing dimensionalities is
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
684

time-intensive. This highlights the need for methods
that enable faster adaptation to such changes.
2.4 Research Gap and Challenges
Structural shifts pose a significant challenge in RL, as
they involve changes to the dimensional structure of
the state-action space, and mapping methods for such
shifts are often time-intensive. TL offers a promising
solution, as it allows for knowledge transfer between
domains, potentially reducing the need for extensive
retraining. However, existing RL and TL methods
generally assume a stable state-action space structure
(Zhu et al., 2023), limiting their applicability in en-
vironments with frequent structural changes, such as
power grids or robotics. This research gap under-
scores the need for methods that enable RL agents
to adapt effectively across different state-action space
dimensions without exhaustive retraining—a crucial
capability for real-world, dynamically evolving envi-
ronments.
3 METHODS
3.1 The Changed State-Action Space
Problem
In achieving resilience for DRL agents, a primary
challenge is enabling adaptability to unexpected en-
vironmental changes without extensive retraining.
While fully eliminating retraining isn’t feasible, re-
ducing the training time needed for adaptation is a re-
alistic goal. In this work, we address the state-action
space problem directly: the source domain, represent-
ing the original, unchanged environment, provides
transferable knowledge, while the target domain has
a reduced state-action space due to fewer sensors and
actuators.
To select a suitable TL approach, we apply the di-
mensions of comparison (Taylor and Stone, 2009).
Here, the agent’s objective remains consistent be-
tween domains, eliminating the need for additional
domain mapping. Based on its robustness to unex-
pected events and entropy-driven exploration, we use
the SAC algorithm. The transferable knowledge con-
sists of the actor and critic models from the SAC agent
in the source domain, facilitating efficient adaptation
to the target domain.
In summary, leveraging the source domain’s actor
and critic models in the target domain offers an effi-
cient solution for managing state-action space reduc-
tions. This approach is formalized in the Actor-Critic
Table 1: Overview of ACMR configurations.
Freeze Hidden Layer Tra. Layer Expansion
No Conf. 1 Conf. 3
Yes Conf. 2 Conf. 4
Model Reuse (ACMR) algorithm, which we detail in
the following section.
3.2 Actor-Critic Model Reuse
ACMR is a novel TL algorithm that accelerates DRL
agent adaptation to environments with altered state-
action spaces, enabling rapid adaptation using knowl-
edge from a source environment without full retrain-
ing.
3.2.1 Explanation of ACMR
ACMR is based on the actor-critic architecture com-
mon in DRL, where an agent is composed of two main
components:
• The Actor: Responsible for selecting actions
based on the current state using a policy function,
π(a|s).
• The Critic: Evaluates the chosen actions by es-
timating the expected cumulative reward, or Q-
value, using a Q-function, Q(a|s).
In ACMR, these components are transferred from
a pre-trained agent (teacher agent A
1
= (π
1
, Q
1
)) to
a new agent (student agent A
2
= (π
2
, Q
2
)) facing an
altered environment. Rather than discarding learned
models, ACMR selectively reuses the actor and critic
components to speed up learning. However, given the
change in state-action space, a direct transfer of model
weights is typically not feasible. ACMR tackles this
by using flexible transfer configurations that adapt
to dimensional discrepancies between the source and
target environments.
3.2.2 Transfer Configurations in ACMR
Four different configurations were implemented in
ACMR to enable model reuse across different state-
action dimensions. These configurations were com-
pared to identify the optimal one for ACMR and
shown in Table 1:
• Hidden Layer Transfer (Conf. 1): Only hidden
layers are transferred to the target agent, preserv-
ing learned features while adapting input and out-
put layers to the new state-action dimensions.
• Hidden Layer Transfer with Freezing (Conf. 2):
Hidden layers are transferred and frozen, main-
taining pre-trained values while training only the
input/output layers.
Transfer Learning in Deep Reinforcement Learning: Actor-Critic Model Reuse for Changed State-Action Space
685

• Layer Expansion (Conf. 3): Additional layers are
added to the input and output layers, allowing di-
rect transfer of all actor and critic layers by com-
pensating for dimensional differences.
• Layer Expansion with Freezing (Conf. 4): Sim-
ilar to layer expansion, but the transferred layers
are frozen, focusing learning on the newly added
layers.
The figure 1 shows the ACMR algorithm schemat-
ically, including the configurations:
SAC
teacher
SAC
student
Model Libary
Critic NN
Train
Actor NN
Sensors, Actuators, Reward
changed
Environments
Sensors, Actuators, Reward
Environments
Critic NN
Train
add model
use model
Add layer
Freeze layers
Actor NN
Figure 1: Schematic overview of the ACMR algorithm for
Changed State and Action Space.
Algorithm 1 outlines the ACMR algorithm, show-
ing how model parameters are reused based on differ-
ent configurations.
The implementation of ACMR was developed
based on the SAC algorithm provided by CleanRL
(vwxyzjn, 2024) for Gymansium environments on
GitHub. The code can be found on the GitHub reposi-
tory (Barg, 2024). No major adjustments were needed
to transfer the hidden layers, as they have a consistent
dimension. The hidden layers of the target agent (A
2
)
are simply overwritten with those of the source agent
(A
1
) after initialization. To facilitate this process,
functions were added to save all necessary model pa-
rameters and dimension information after training A
1
.
A corresponding load function retrieves the selected
model from memory before starting the simulation,
specifically isolating the layers to be transferred and
using them for overwriting the target model’s layers.
The process is slightly different for configurations
that involve layer expansion. To adjust layer dimen-
sions, the actor and critic networks were modified by
Data: Source environment E
source
, Target
environment E
target
, Transfer option
trans f er type, Freeze option f reeze
Result: Adapted and trained actor-critic
model A
2
in E
target
Train A
1
in E
source
;
Save model parameters of A
1
(hidden layers,
output layers, observation/action space
information);
Initialize A
2
in E
target
;
if trans f er type == ”layer expansion” then
Load entire model parameters from A
1
into A
2
;
Add additional layers to actor and critic
networks in A
2
to match the state-action
space dimensions of E
target
;
end
if trans f er type == ”hidden layer transfer
only” then
Load only the hidden layers from A
1
into
A
2
;
end
foreach layer in A
2
do
if layer was loaded from A
1
then
if f reeze is True then
Disable gradient updates for this
layer to freeze it;
end
end
else
Initialize additional layers with
random weights if trans f er type is
”layer expansion”;
end
end
Train A
2
in E
target
;
Algorithm 1: Actor-Critic Model Reuse.
adding additional layers with flexible dimensions be-
fore the input layer and/or after the output layer, de-
pending on the transferred layers. For the critic net-
work, only one layer was added before the input layer,
as the output layer consistently has a dimension of
1. For freezing, the selected layers were excluded
from future updates directly within the network con-
figuration, ensuring that they retained their pretrained
weights throughout training in the target environment.
4 TESTING ACMR
To evaluate the effectiveness of the ACMR algorithm,
we utilize a well-established benchmark environment
for RL: Humanoid environment from Gymnasium
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
686

(Towers et al., 2024). This environment provides a
high-dimensional, continuous action and state space,
making it ideal for testing the adaptability of DRL
agents to state-action space changes.
4.1 The Environment
The Humanoid is a 2D bipedal robot with an ab-
domen, head, legs, and arms, designed to resemble
a human. The state-action space in this environment
can be modified by removing specific states and ac-
tions, allowing us to replicate scenarios where the
agent’s perception or control capabilities are reduced.
This change aligns with the core ACMR challenge:
Enabling a DRL agent to adapt efficiently to a lower-
dimensional state-action space by reusing the pre-
trained actor and critic models.
Two variations of the environment are used to
test ACMR: a source environment (the original
Humanoid) and a target environment (ArmlessHu-
manoid) with reduced state-action space.
• Humnaoid: The observation space has 367 sen-
sors and the Action space has 17 actuators.
• ArmlessHumanoid: The observation space is re-
duced to 270 sensors and the action space to 11
actuators by removing arm-related components.
The figures 2 and 3 shows pictures from the Hu-
manoid and ArmlessHumanoid simulation:
Figure 2: Visual representation of the Humanoid environ-
ment, automatically generated with Gymnasium.
This structural change in the state-action space
represents a shift beyond typical marginal distribu-
tion changes, as explained in the chapter 2. Marginal
changes can often be handled by incremental updates
or minor adjustments to the policy. However, in sce-
narios like the transition from Humanoid to Arm-
lessHumanoid, we encounter a dimensional reduction
in both the observation and action spaces, requiring a
different adaptation approach.
Figure 3: Visual representation of the ArmlessHumanoid
environment, automatically generated with Gymnaisum.
4.2 Experiment Design
The experimental design for testing ACMR involves
three primary steps to assess its adaptability in a mod-
ified state-action space.
• Baseline Runs in the Source and Target En-
vironment. The teacher SAC agent A
1
is first
trained in the full state-action space of the source
environment, representing the normal, unchanged
conditions (experiment H0). This baseline es-
tablishes the agent’s performance without any
state-action space reduction, serving as the per-
formance benchmark and providing the model
weights to transfer to the student SAC agent A
2
.
In addition, a baseline experiment is conducted
in the ArmlessHumanoid Environment without
ACMR, which serves as performance benchmark
for comparing the experiments (experiment A0).
• Proof of Concept in Source Environment. To
verify that ACMR correctly reuses the transferred
models, a proof-of-concept experiment is con-
ducted in the Humanoid environment with normal
state-action space (experiment H1). Here, the A
1
actor and critic models are transferred to the stu-
dent A
2
agent in the source environment without
additional modifications (not necessary since the
dimensions are the same).
• Testing Configurations. Finally, the ACMR ap-
proach is tested across the four different con-
figurations (as outlined previously) in the modi-
fied environment (ArmlessHumanoid). This stage
evaluates each configuration’s adaptability and ef-
ficiency, quantifying how well each variation ac-
celerates training and preserves learned features
from the source environment. Experiments A1,
A2, A3, A4.
Transfer Learning in Deep Reinforcement Learning: Actor-Critic Model Reuse for Changed State-Action Space
687

Table 2: Experiment overview for the Humanoid environ-
ment.
Experiment Environment Configuration
H0 Source Baseline
H1 Source POC
A0 Target Baseline
A1 Target Conf. 1
A2 Target Conf. 2
A3 Target Conf. 3
A4 Target Conf. 4
The Table 2 provides an overview of the con-
ducted experiments.
All experiments were performed 3 times with
seeds 1, 2, and 3 to ensure the results reflect true
performance and are not influenced by random vari-
ations. The primary metric used was the episodic re-
turn, which represents the cumulative reward obtained
by an agent from the start to the end of each episode.
The maximum number of steps that the agent can per-
form is limited to 1,000,000, and a maximum of 1,000
steps can be performed per episode. An episode al-
ways ends when the 1,000 steps have expired or if
the agent has already failed. Average episodic returns
across all three seeds were calculated for comparative
analysis. A performance threshold of 4900 was estab-
lished based on visual inspection of performance data
from baseline experiments, representing a significant
level consistently achieved by both baselines. To gain
deeper insights, the ’Step to Threshold’ (StT) metric
was employed, indicating the global steps required
for the agent to reach that predefined performance
threshold. The agents episodic return has to reach
the threshold for five consecutive steps, minimizing
the influence of isolated outliers. Statistical analysis
involved calculating mean values and standard devi-
ations for the steps to threshold across experiments,
as well as T-scores and P-values to assess deviations
from the baseline. A P-value of less than 0.05 was
defined as the significance level, where a negative T-
score indicated that the threshold was reached earlier
than the baseline, while a positive T-score indicated it
was reached later.
The following hyper-parameters were used: A to-
tal of 1,000,000 timesteps (total timesteps) for
the experiments, a replay buffer size of 1 million
(buffer size) to store experience, and a discount
factor (gamma) of 0.99 to prioritize near-term rewards
slightly less than long-term gains. We used a target
smoothing coefficient (tau) of 0.005 for stabilizing
target network updates and a batch size (batch size)
of 256 for sampling from the replay buffer. The agent
began learning after 5,000 steps (learning starts).
The learning rate of the policy network optimizer was
set to 3e-4 (policy lr), while the Q-network opti-
mizer used a rate of 1e-3 (q lr). An entropy reg-
ularization coefficient (alpha) of 0.2 was applied to
encourage exploration during training.
4.3 Results
The results from the ACMR experiments are shown
below. Figure 5 shows the rolling average of episodic
returns over the global steps (total number of steps
across all episodes) for the experiments A0, A1, A2,
A3, A4, averaged over the three seed runs. And Fig-
ure 4 shows the baseline experiments H0 and A0.
The StT shown in the figures is calculated based on
the raw data, which leads to a faster reaching of the
threshold compared to the rolling average curve. The
Table 3 shows the statistical analysis of the StT.
Baseline Experiments (H0 and A0). Figure 4 shows
the rolling average of episodic returns for the baseline
experiments H0 and A0, averaged over the three seed
runs. In the background, the raw episodic return data
for seed 1 is visible, and the dashed lines indicate the
StT. The teacher agent A
1
in both the source and tar-
get environments achieved stable performance, estab-
lishing a benchmark that reflects the agent’s optimal
capability in the full state-action space. This baseline
performance serves as the comparison point for each
ACMR configuration in the modified environment in
the following experiments.
Proof of Concept (H1). In the proof-of-concept ex-
periment, the direct transfer of the A
1
actor and critic
models without modifications in the same environ-
ment resulted in an observable jumpstart in initial per-
formance compared to standart initialization (baseline
H0), visible in figure 6. A T-score of -6.875 P-value
of 0.002 confirm that the H1 is significantly faster as
the baseline (see Table 3).
Hidden Layer Transfer (A1). By reusing only the
hidden layers, the student agent A
2
was able to lever-
age learned feature representations from the source
environment while adjusting the input and output lay-
ers for the modified state-action space. Only a very
small difference can be observed in a direct compar-
ison of the mean StT of A1 to the baseline A0, see
figure 5. The rolling averages are not particularly dif-
ferent either. The statistical comparison supports this
visual observation, showing no significant difference
between the StT over the three seeds (P-value of 0.81
see Table 3).
Hidden Layer Transfer with Freezing (A2). When
freezing the transferred hidden layers, the agent A
2
showed an even faster adaptation time. This configu-
ration effectively preserved the learned features, re-
ducing the amount of retraining required for adap-
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
688
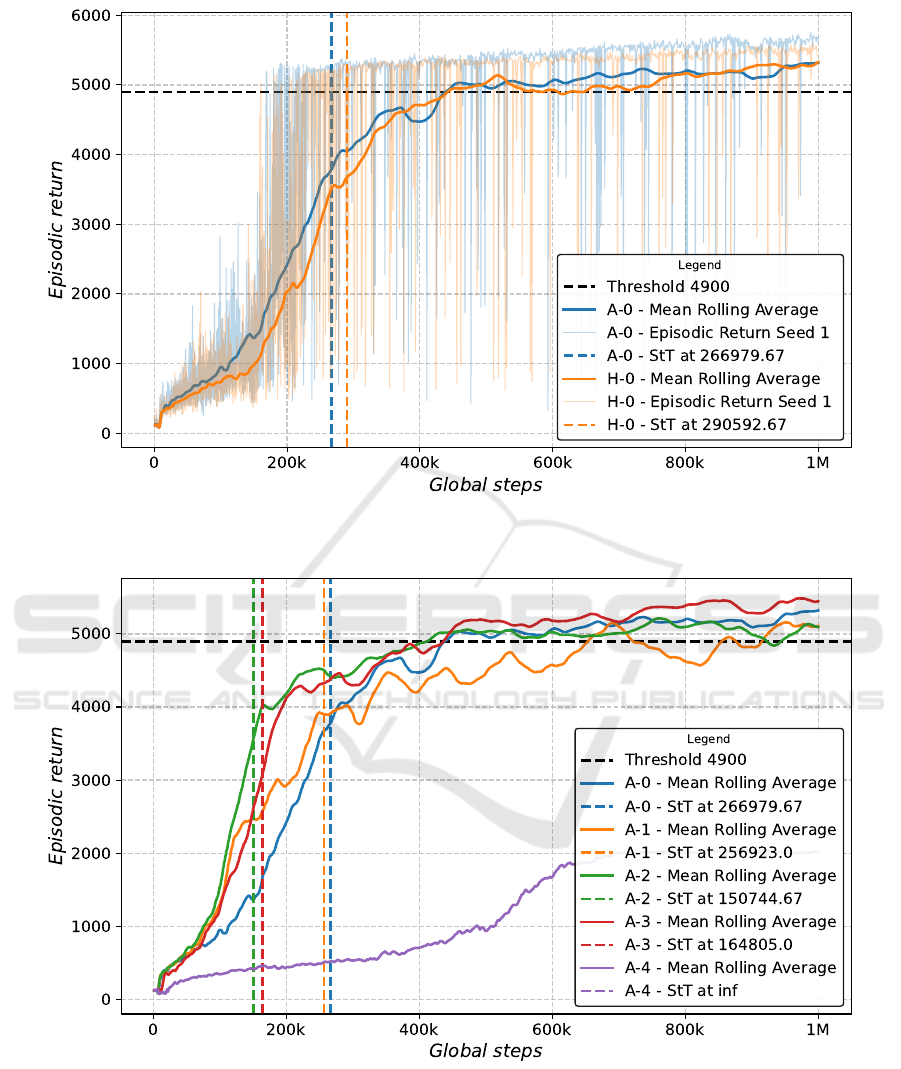
Figure 4: Comparison of baseline experiments A0 (blue) and H0 (orange) without ACMR. Rolling averages (window size
50), threshold (black), and StT (average step threshold) are shown. The background displays raw episodic returns for seed 1.
Figure 5: ACMR experiments in 4 different configurations: A0 - Baseline (blue), A1 - Hidden Layer Transfer (orange), A2 -
Hidden Layer Transfer + Freezing (green), A3 - Layer Expansion (red), A4 - Layer Expansion with Freezing (purple). Rolling
averages (window size 50), threshold (black), and StT (average step threshold) are shown.
tation. The plot shows that A2 StT outperforms the
baseline A1 StT (see Figure 5), this is also significant
with a T-score of -4.129 and P-value of 0.015 (see Ta-
ble 3).
Layer Expansion (A3). The layer expansion ap-
proach allowed for the full transfer of the actor and
critic models with additional layers to bridge dimen-
sional differences. This configuration reaches the
Transfer Learning in Deep Reinforcement Learning: Actor-Critic Model Reuse for Changed State-Action Space
689
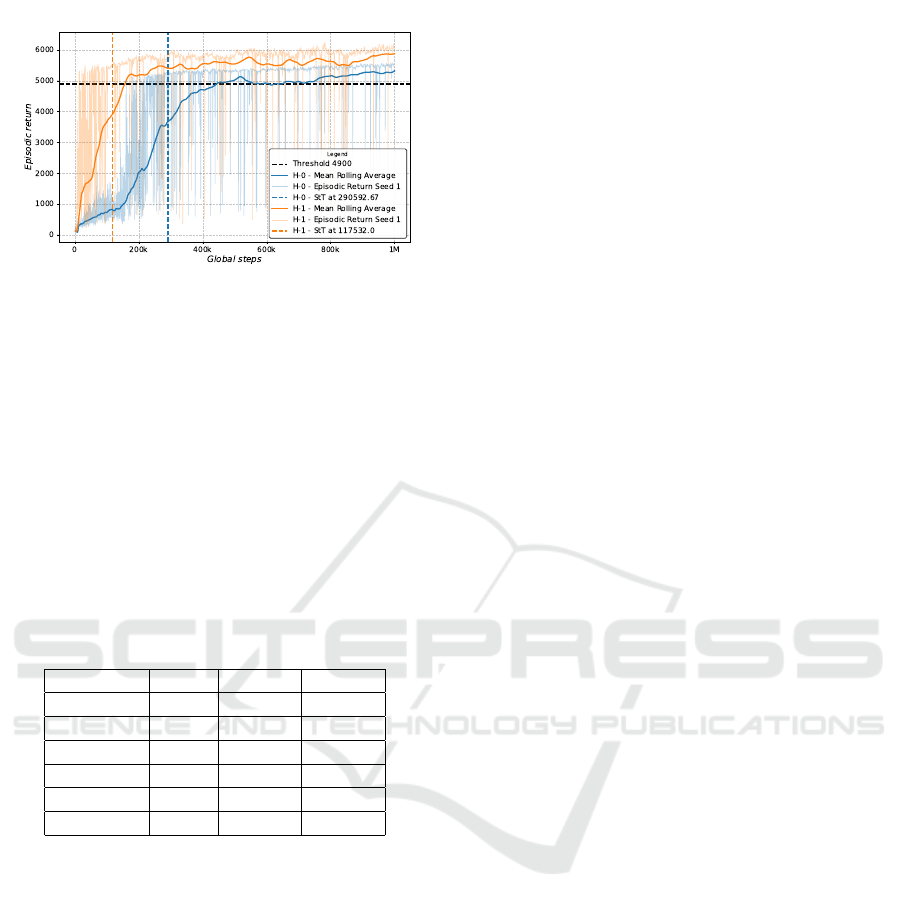
Figure 6: Proof of Concept H-0 (blue) and H-1 (orange)
with direct transfer of actor and critic models. Rolling aver-
ages (window size 50), threshold (black), and StT (average
step threshold) are shown.
threshold faster on average., see Figure 5. Which is
significant with a T-score of -4.377 and P-value of
0.012 (see Table 3).
Layer Expansion with Freezing (A4). In the exper-
iment with ACMR configuration 4, the A
2
agent did
not reach the threshold at all , see Figure 5. Conse-
quently, this means the agents never learned to walk
with the ArmlessHumanoid.
Table 3: Statistical comparison of average StT from all ex-
periments, including T-score and P-value calculations. The
Index is the condition being compared, and the Reference is
the baseline for comparison.
Reference Index T-score P-value
A0 A1 -0.247 0.817
A0 A2 -4.129 0.015
A0 A3 -4.377 0.012
A0 A4 NaN NaN
A0 H0 0.668 0.540
H0 H1 -6.875 0.002
In summary, the ACMR configurations ’Hidden
Layer Transfer with Freezing’ (A2) and ’Layer Ex-
pansion’ (A3), showed the most promising results,
enabling fast and effective adaptation to a modified
state-action space. These findings highlight the util-
ity of ACMR configurations in reducing training time,
underscoring their applicability in dynamic environ-
ments where rapid adaptation is crucial.
5 DISCUSSION
The experiment compared two environments: Hu-
manoid as the source domain and ArmlessHumanoid
as the target domain, with no significant difference
in the episodic returns despite the reduction in state-
action space. A proof of concept in the source tar-
get humanoid has shown that the expected jumpstart
occurred when transferred to the same unchanged en-
vironment. This clear result was expected, as trans-
ferring a model into the same environment allows the
agent to start with knowledge from step 1M.
Experiment A1 involved only the ACMR of hid-
den layers. Although there was a slight visual indica-
tion of earlier threshold achievement, it was not sta-
tistically significant. This suggests that hidden layer
model transfer alone does not reduce training time,
thus failing to enhance the agent’s responsiveness.
One possible explanation for this result is that the
transferred hidden layers may be direct overwritten
during subsequent training, leading to a loss of the
features learned from the source domain.
Experiment A2 achieved notable success with the
transfer of hidden layers, combined with freezing
these layers. The episodic return showed a signif-
icantly shorter training time to reach the threshold,
suggesting that freezing the transferred layers is cru-
cial. Freezing reduces noisiness in the results, likely
because it forces the agent to adjust the input and out-
put layers rather than re- learning everything.
Transferring the hidden layers as well as the orig-
inal input and output layers and then adding new in-
put and output layers for the target domain proved ef-
fective. Experiment A3 showed significant improve-
ment in reaching the threshold. This approach al-
lows the agent to retain the primary model’s structure,
which aids in faster reward acquisition. The adapta-
tion layers works as translation layers from the cur-
rent reduced sensor and actuator count to the higher
number in the transferred model. Future research
could explore the agent’s behavior when more crucial
body parts are omitted, necessitating different walk-
ing methods.
The experiment A4 yielded unfavorable results.
The agents never reached the threshold, indicating
that the combination of freezing and additional layers
makes the agent becomes too adapted to the source
domain, leading to overfitting.
Thus, it indicates that effective transfer in altered
state-action spaces requires either freezing or addi-
tional layers. Too little transformed knowledge has
no effect, while too much leads to bad performance.
The conclusions drawn in this paper provide in-
sights into the optimal amount of knowledge to trans-
fer (number of transferred layers) and the extent of
behavior to fix (number of frozen layers) for suc-
cessful learning acceleration. The results highlight
that a combination of extensive knowledge transfer
and fixed weights and biases leads to bad perfor-
mance, but the individual application of the tech-
niques achieve excellent results. The ACMR in ex-
periment A2, i.e., the ’Hidden Layer Transfer with
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
690

Freezing’, is the best method overall. The results are
slightly better than the experiment with the ’Layer Ex-
pansion’ (A3). However, while method ’Layer Ex-
pansion’ significantly complicates and enlarges the
neural network, Hidden Layer Transfer with Freez-
ing’ in ACMR is minimally invasive, which is another
advantage. However, this study does not explore how
the agent would respond to different changes in state-
action space that more significantly affect walking
methodology. Moreover, only the pre-trained model
transfer methodology was reviewed, leaving other TL
methodologies to be explored.
6 CONCLUSIONS
This study demonstrates the potential of ACMR as an
effective TL method, particularly in the Hidden Layer
Transfer with Freezing (A2) and Layer Expansion
(A3) configurations, to accelerate SAC agent train-
ing in the Gymnasium Humanoid environment with
changed state-action space dimension. The A2 con-
figuration was the most effective, as freezing trans-
ferred hidden layers reduced training noise and en-
abled efficient adaptation to the new environment
without extensive model changes. While A3 also
achieved significant acceleration, its added model
complexity could reduce efficiency in larger applica-
tions and repeated retrainings.
However, the experiments also highlighted
ACMR’s limitations. Experiment A1 (simple hidden
layer transfer) showed that transferring hidden layers
alone, without freezing, had little impact on train-
ing time, indicating that more directed knowledge
preservation is necessary. Experiment A4, which
combined layer expansion with freezing, led to bad
performance, as excessive transferred knowledge
made the agent overly specific to the source domain,
limiting its adaptability.
Overall, ACMR offers strong potential for re-
silient control in environments with changing state-
action spaces by enabling rapid adaptation.
7 FUTURE WORK
The results presented in this paper pave the way
for further research in TL for evolving state-action
spaces, with significant potential for advancing the
field, particularly through the use of ACMR. Future
studies should explore ACMR in more complex en-
vironments and investigate variations in state-action
spaces, comparing its performance with other TL
methods. A key area of focus will be the application
of ACMR in real-world environments, such as power
grids. Specifically, ACMR will be integrated into the
ARL methodology (Fischer et al., 2019) for resilient
control of power grids, with the goal of enhancing
the responsiveness of learning agents to unforeseen
changes (Veith et al., 2024).
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research was supported by funding from the
German Federal Ministry of Education and Research
(BMBF) under Grant No. 01IS22047C. We extend
our gratitude to ChatGPT, an AI model developed by
OpenAI, for assistance with language refinement and
corrections. Special thanks go to Thomas Wolgast
and Torben Logemann for their thorough internal re-
view, as well as to all our colleagues for their invalu-
able discussions and support throughout this work.
REFERENCES
Amodei, D., Olah, C., Steinhardt, J., Christiano, P., Schul-
man, J., and Mane, D. (2018). Ai and compute. Ope-
nAI Blog, 8(7):1–9.
Arulkumaran, K., Deisenroth, M. P., Brundage, M., and
Bharath, A. A. (2017). Deep reinforcement learning:
A brief survey. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine,
34(6):26–38.
Barg, F. M. (2024). Actor-critic model reuse for transfer
learning in humanoid environments. https://github.
com/feline-malin/ACMR for Humanoid.
Beck, N., Rajasekharan, A., and Tran, H. (2022).
Transfer reinforcement learning for differing action
spaces via q-network representations. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2202.02442.
Celiberto Jr, L. A., Matsuura, J. P., De M
`
antaras, R. L.,
and Bianchi, R. A. (2010). Using transfer learning to
speed-up reinforcement learning: a cased-based ap-
proach. In 2010 latin american robotics symposium
and intelligent robotics meeting, pages 55–60. IEEE.
Fern
´
andez, F. and Veloso, M. (2006a). Policy reuse for
transfer learning across tasks with different state and
action spaces. In ICML Workshop on Structural
Knowledge Transfer for Machine Learning. Citeseer.
Fern
´
andez, F. and Veloso, M. (2006b). Probabilistic policy
reuse in a reinforcement learning agent. In Proceed-
ings of the fifth international joint conference on Au-
tonomous agents and multiagent systems, pages 720–
727.
Fischer, L., Memmen, J. M., Veith, E. M., and Tr
¨
oschel,
M. (2019). Adversarial resilience learning—towards
systemic vulnerability analysis for large and complex
systems. In ENERGY 2019, The Ninth International
Conference on Smart Grids, Green Communications
Transfer Learning in Deep Reinforcement Learning: Actor-Critic Model Reuse for Changed State-Action Space
691

and IT Energy-aware Technologies, number 9, pages
24–32, Athens, Greece. IARIA XPS Press.
Ganin, Y., Ustinova, E., Ajakan, H., Germain, P.,
Larochelle, H., Laviolette, F., March, M., and Lem-
pitsky, V. (2016). Domain-adversarial training of neu-
ral networks. Journal of machine learning research,
17(59):1–35.
Haarnoja, T., Zhou, A., Abbeel, P., and Levine, S. (2018).
Soft actor-critic: Off-policy maximum entropy deep
reinforcement learning with a stochastic actor. In
International conference on machine learning, pages
1861–1870. PMLR.
Henderson, P., Islam, R., Bachman, P., Pineau, J., Precup,
D., and Meger, D. (2018). Deep reinforcement learn-
ing that matters. In Proceedings of the AAAI confer-
ence on artificial intelligence, volume 32.
Kumar, A., Zhou, A., Tucker, G., and Levine, S. (2020).
Conservative q-learning for offline reinforcement
learning. Advances in Neural Information Processing
Systems, 33:1179–1191.
Nair, A., McGrew, B., Andrychowicz, M., Zaremba, W.,
and Abbeel, P. (2018). Overcoming exploration in re-
inforcement learning with demonstrations. In 2018
IEEE international conference on robotics and au-
tomation (ICRA), pages 6292–6299. IEEE.
Nguyen, T. T., Nguyen, N. D., and Nahavandi, S. (2020).
Deep reinforcement learning for multiagent systems:
A review of challenges, solutions, and applications.
IEEE transactions on cybernetics, 50(9):3826–3839.
Omitaomu, O. A. and Niu, H. (2021). Artificial intelligence
techniques in smart grid: A survey. Smart Cities,
4(2):548–568.
Pan, S. J. and Yang, Q. (2010). A survey on transfer learn-
ing. IEEE Transactions on knowledge and data engi-
neering, 22(10):1345–1359.
Parisotto, E., Ba, J. L., and Salakhutdinov, R. (2015). Actor-
mimic: Deep multitask and transfer reinforcement
learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1511.06342.
Tan, M., Tian, A., and Denoyer, L. (2022). Regularized
soft actor-critic for behavior transfer learning. In 2022
IEEE Conference on Games (CoG), pages 516–519.
IEEE.
Taylor, M. E. and Stone, P. (2009). Transfer learning for
reinforcement learning domains: A survey. Journal of
Machine Learning Research, 10(7).
Towers, M., Kwiatkowski, A., Terry, J., Balis, J. U.,
De Cola, G., Deleu, T., Goul
˜
ao, M., Kallinteris, A.,
Krimmel, M., KG, A., et al. (2024). Gymnasium: A
standard interface for reinforcement learning environ-
ments. arXiv preprint arXiv:2407.17032.
Veith, E. M., Logemann, T., Wellßow, A., and Balduin, S.
(2024). Play with me: Towards explaining the benefits
of autocurriculum training of learning agents. In 2024
IEEE PES Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Eu-
rope (ISGT EUROPE), pages 1–5, Dubrovnik, Croa-
tia. IEEE.
vwxyzjn (2024). sac continuous action.py. https://github.
com/vwxyzjn/cleanrl/blob/master/cleanrl. Accessed:
2024-05-28.
Weiss, K., Khoshgoftaar, T. M., and Wang, D. (2016).
A survey of transfer learning. Journal of Big data,
3(1):1–40.
Wolgast, T. and Nieße, A. (2024). Learning the opti-
mal power flow: Environment design matters. arXiv
preprint arXiv:2403.17831.
Xu, Z., Yang, D., Tang, J., Tang, Y., Yuan, T., Wang,
Y., and Xue, G. (2020). An actor-critic-based trans-
fer learning framework for experience-driven net-
working. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking,
29(1):360–371.
Zhu, Z., Lin, K., Jain, A. K., and Zhou, J. (2023). Trans-
fer learning in deep reinforcement learning: A survey.
IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine
Intelligence.
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
692
