
Heating up Interactions in an Agent-Based Simulation
to Ensure Narrative Interest
Gonzalo M
´
endez
a
and Pablo Gerv
´
as
b
Facultad de Inform
´
atica, Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Madrid 28040, Spain
Keywords:
Agent-Based Simulation, Affinity Driven, Narrative Generation, Story Sifting, Romantic Interest.
Abstract:
Multi-agent systems have become important sources of inspiration for narrative generation systems, with
significant growth in solutions based on story sifting: identifying the subset of events generated by such
a system that is worthy of being told as a story. Existing systems simulate the romantic behaviour of agents
based on simple rules that consider models of social norms and relations, and the evolution of affinities between
agents. The present paper describes an extension to one such simulation that inserts several sources of conflict
between characters to induce more interesting situations that allows the creation of more engaging stories. The
system is empirically shown to give rise with much higher scores on metrics for narrative interest.
1 INTRODUCTION
One of the challenges of Artificial Intelligence during
the last decades has focused on the generation of qual-
ity narrative texts. With the development of LLMs,
the appearance of the generated texts has improved
dramatically, but the quality of the stories created by
these models still has much room for improvement.
One possible approach to generate interesting stories
is to run agent-based simulations to model human be-
haviour and then pick out of the resulting set of events
a subset that constitutes an interesting story. This
would be equivalent to simply observing how peo-
ple behave around us and identifying the particular
situations that make for an interesting story. How-
ever, in real life the percentage of events that happen
around us that is valuable as material for stories is
considerably low. If the simulation chosen as object
of our study models real human behaviour closely, we
may be faced with a similar situation. Human au-
thors more often apply different strategies, either ex-
agerating or extrapolating beyond the behaviours they
do observe in real life, or merging together remark-
able fragments of ordinary lives into fictional lifes that
pack more interest than real humans usually observe.
The present paper explores measures for enriching
or tuning an agent-based simulation to ensure that the
logs of events that result contain material that may be
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7659-1482
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4906-9837
valuable to inspire an interesting story. As a relevant
case study, the simulation on which we operate fol-
lows a set of characters that interact, focusing on the
evolution of affinities and romantic relations between
them.
2 RELATED WORK
Two topics need to be reviewed to inform the work
in this paper: existing simulations that contemplate
affinities and relations between characters, and efforts
to sift through the logs of simulations in search of in-
teresting stories.
2.1 Simulations Involving Romance
There have been several computational systems that
model situations of affective engagement between
characters. Some of them have been developed as in-
teractive fiction applications (Mateas and Stern, 2005;
Szilas, 2003), some as models of social interaction
(McCoy et al., 2014) to support games (McCoy et al.,
2010) or narratives (Porteous et al., 2013a), some as
models of emotional response to support training en-
vironments (Gratch, 2000), some directly aimed to
support the generation of narratives, whether based on
evolving affinities between characters (P
´
erez y P
´
erez,
1999; Theune et al., 2003; M
´
endez et al., 2014) or
conflict (Ware et al., 2014; Fendt and Young, 2017).
Méndez, G. and Gervás, P.
Heating up Interactions in an Agent-Based Simulation to Ensure Narrative Interest.
DOI: 10.5220/0013308800003890
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2025) - Volume 2, pages 693-703
ISBN: 978-989-758-737-5; ISSN: 2184-433X
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
693

The Fac¸ade system (Mateas and Stern, 2005;
Strong and Mateas, 2008) was an interactive narra-
tive in which the participates in a dinner party at a
couple’s home, gets to participate in the conversa-
tions, and partly experiences and partly determines
the evolution of tensions between the couple. Fac¸ade
was a very realistic system based on a pre-determined
scripts structured as a set of beats, with the system
choosing among them based on the typed contribu-
tions by the user. The system modelled the affinities
between the characters and relied on elaborate models
of how dialogue contributions influenced them.
The IDTENSION system (Szilas, 2003) was also
an interactive narrative engine designed to construct
interesting behaviour for a set of characters, relying
on a model that accounted for character goals, obsta-
cles on their path, and the moral values that sustained
them. To attain interest, the system faced characters
with potential actions that conflicted with their moral
values.
The Comme il Faut (CiF) (McCoy et al., 2014)
system was a knowledge-based model of social in-
teractions that attempted to account for the complex
interplay between social norms, character desires and
cultural background. It considered a micro-theory of
friendship and it proposed a set of rules to capture the
possible behaviours of characters faced with partic-
ular social situations. The Comme il faut system has
been used to build the game PromWeek (McCoy et al.,
2010; McCoy et al., 2013a; McCoy et al., 2013b), in
which players live out the week before the prom and
have to achieve a particular set of goals in that time.
The game evolved from an initial version focused on
the pyschological needs of individuals within the so-
cial context to a later version that focused on the logic
of social statuses and relationships between charac-
ters.
The NetworkING (social Network for Interactive
Narrative Generation) system (Porteous et al., 2013a;
Porteous et al., 2013b; Porteous et al., 2015) was a
system for interactive narrative for a medical drama
with a cast of doctors, nurses and patients. It relies
on a representation of the social relationships between
characters as a network, and it has the story evolve as
these relations change dramatically over time. The
relationships considered are affective (six graded cat-
egories: friend, close-friend, long-term-close-friend,
antagonist, extreme-antagonist, long-term-extreme-
antagonist, professional-rival), romantic (five cate-
gories with subtle differences: long-term-partner,
dating, secretly-dating, attracted-to, romantic-rival)
and a default relationship that covers indifference. A
planner is used to determine the actions each char-
acter takes, based on and affecting the relationships
between them.
The
´
Emile system (Gratch, 2000) was also an in-
teractive system that relied on a model of affective re-
sponse to situations, in this case applied to simulation
for military training and pedagogical agents. Agents
in the system monitor the environment and periodi-
cally update a model of their emotional state, which is
taken into account when determining their behaviour.
The model for Emile considers significant psycholog-
ical theories of emotional appraisal. However, it stops
short of considering issues of romantic attachment be-
tween characters.
The MEXICA system (P
´
erez y P
´
erez, 1999) gen-
erated short sequential narratives about the Mexicas,
ancient inhabitants of Mexico City. To do this it re-
lied on a representation of the affinities and tensions
between characters, which are used to drive the con-
struction of the story based on knowledge structures
that capture examples of evolution of affinities and
tensions over existing prior stories.
The Virtual Storyteller system (Theune et al.,
2003) was a multi-agent system designed to gener-
ate short fairy tales. It has an underlying storyworld
in which agents interact to achieve goals. In so doing
they experience emotions, which affect their subse-
quent actions. To ensure the resulting storyworld in-
cludes material useful for telling stories about it, two
different mechanisms are overlaid on agent simula-
tion: (1) the actions of agents are constrained by a
model of plot (to ensure that stories are consistent)
and (2) a special director agent is added to guide the
actions of the other agents towards a well-structured
plot. The director agent can intervene in the simula-
tion in one of three ways: by inserting new characters
or objects into the story world, by infusing charac-
ters with new goals, by blocking actions that a char-
acter intends to do. The Virtual Storyteller was built
as a multi-agent framework running on JADE (Java
Agent Development Environment (Bellifemine et al.,
2005)).
Further systems that rely on elaborate models of
agent behaviour rely on conflict between agents, mod-
elled as clashes between agents plans modelled ex-
plicitly by means of planners. One such system was
the Glaive system (Ware et al., 2014), which informed
an interactive game where the user would come up
with a plan to carry out a simple task and then the sys-
tem would attempt to find ways of thwarting that plan.
A similar mechanism was employed by the IRIS sys-
tem (Fendt and Young, 2017) which constructed plots
featuring conflict by iterating over a cycle in an orig-
inal plan for the protagonist was built, then come up
with countermeasures that would thwart the plan so
that the protagonist would need to replan. The IRIS
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
694

system relied on a belief desire intention (BDI) model
of the protagonist. However, none of these systems
based on planning considers situations of romantic in-
terest.
Charade (M
´
endez et al., 2016) is a multi-agent
simulation (also based on JADE (Bellifemine et al.,
2005)) driven by a model of interpersonal affinities
between characters and how they evolve over time.
The system represents affinities on a scale of foe, in-
different, friend and mate. The system explicitly con-
siders situations of romantic interest between pairs of
characters, and models how affinities between them
evolve based on how they respond to proposals for
joint activities. A set of rules governs how agents be-
have based on their standing set of affinities and how
these affinities change based on character behaviour.
A simulation is run with 15 agents who do not all
know each other. Each agent may or may not have
a partner, a small set of friends (between 2 and 4) and
may or may not have any enemies (1 or 2 at the start).
Interactions are driven by affinities between charac-
ters, and also act upon them. Probability of interac-
tion is highest for partners, lower for friends, and low-
est for enemies. Acceptance of proposals raises affin-
ity between the characters, rejections and inactivity
lower it. The result is a log of interactions and evo-
lutions of affinity levels which are subsequently used
to generate episodes within a narrative (Concepci
´
on
et al., 2018).
Affinities between two agents A and B are di-
rected, so what A feels for B may differ from what
B feels for A. They are represented on a scale be-
tween 0 and 100, with 0 representing strong dislike
and 100 representing passionate love. The Charade
system considers a classification of relations between
agents in terms of the affinities between them: foe
affinity between 0 and 40, neutral affinity between 40
and 60, friend affinity between 60 and 80 and mate
affinity between 80 and 100.
The type of relation that holds between two agents
determines the subset of activities that they may con-
sider together.
Each agent contributes to the general evolution of
the simulation by: (a) proactively proposing inter-
actions to other agents or reacting to proposals re-
ceived, and (b) by registering changes in affinity to-
wards other agents in response to proposals or reac-
tions. The behaviour of agents is informed by the
affinities between them, and it also has the potential
to alter the affinities between them.
2.2 Story Sifting
The idea of generating narrative by telling about se-
lected subsets of events arising from an agent-based
simulation evolved over time into a research line
specifically focused on modelling this process of se-
lection of interesting events to tell. This research line
has come to be known as story sifting. The term was
proposed in James Ryan’s PhD thesis (Ryan, 2018)
as the task of curating interesting narratives out of the
logs for simulations, usually agent-based. Many of
the early approaches to this task relied on procedures
for trawling through the available events in search for
subsequences that satisfy patterns of plot known to be
interesting (Kreminski et al., 2019; Kreminski et al.,
2021).
The application of evolutionary solutions for sift-
ing interesting stories about romantic entanglements
(Gerv
´
as and M
´
endez, 2023) from the Charade agent-
based simulation (M
´
endez et al., 2016) operated by
developing a set of metric on relative narrative in-
terest from the point of view of romance to a se-
lection of events made over a log of a system run.
The described algorithm was shown to achieve rela-
tively good scores on those metrics, but the overall
values were seen to be restricted by the level of inter-
est achieved by the simulation. Runs of the system
were shown to have a relative variation of affinities
between agents at the start but eventually converge to
rather low values of affinity between all couples tak-
ing part in the simulation. Although this may appear
to be realistic in terms of modelling personal experi-
ence of individuals (Alsawalqa, 2019), it leads to sto-
ries that are not as interesting as we could have hoped.
We therefore consider that the agent-based sim-
ulation might produce more interesting material for
subsequent selection aimed at obtaining interesting
narratives if the behaviour of agents could somehow
be tweaked towards situation more interesting from
the point of view of narrative. To inform such a
task, we consider candidate theories that might pro-
vide clues as to what situations among romantic part-
ners may lead to interesting narratives.
3 UPGRADING THE NARRATIVE
INTEREST OF A SIMULATION
The starting point for the work described in this paper
is the Charade system reported in section 2.1 (M
´
endez
et al., 2016). The simulation is made up of 3 types of
agents that allow the development of the interactions
necessary to simulate an environment of romantic re-
lationships between the characters: The Logger Agent
Heating up Interactions in an Agent-Based Simulation to Ensure Narrative Interest
695
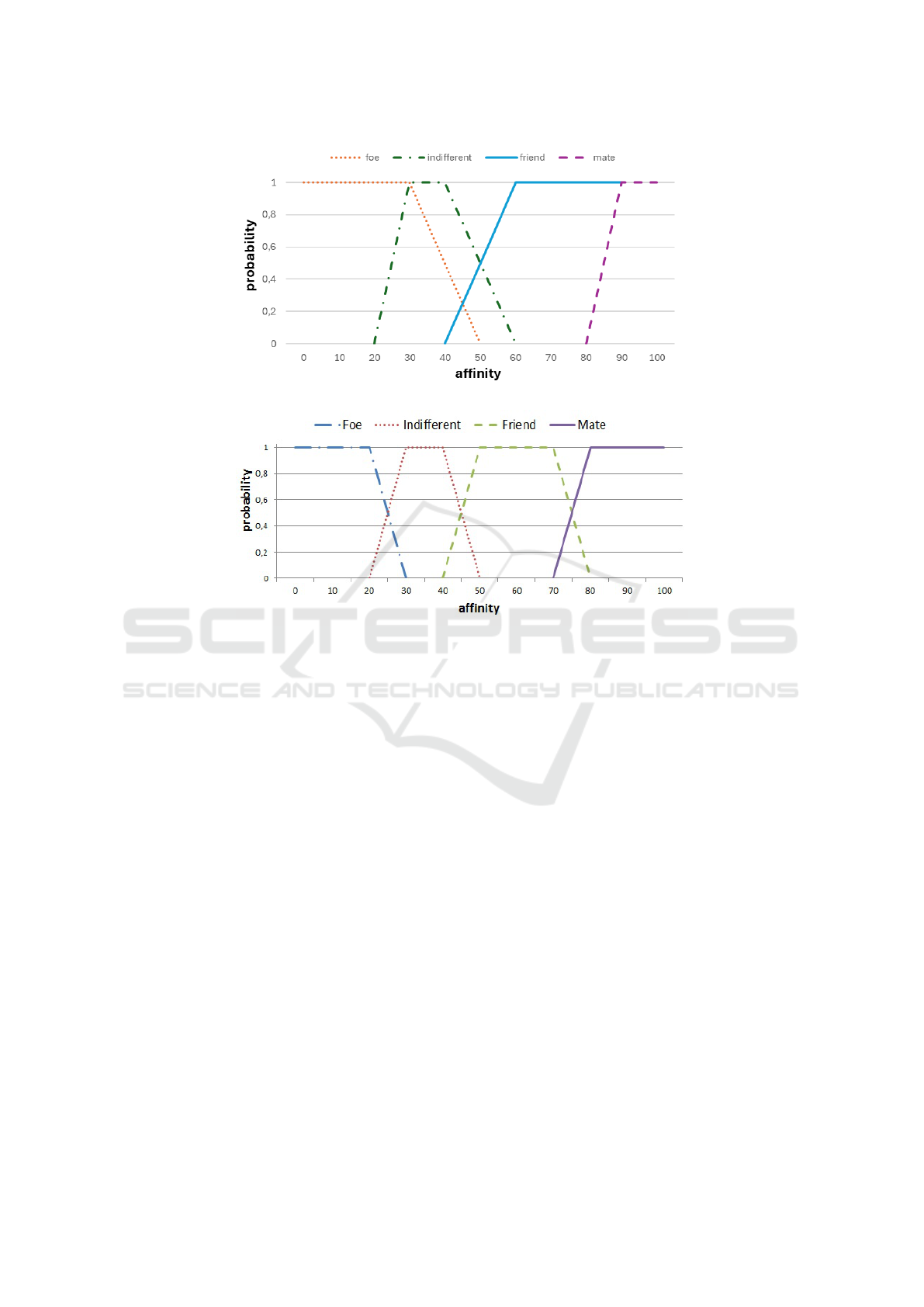
Figure 1: Transition of affinities between characters.
Figure 2: Original transition of affinities between characters.
allows collecting all the events triggered by the rest of
the agents and filtering and formatting those that are
of interest to build the simulation log that is used to
generate the stories; the Director Agent is in charge
of loading the initial situation of the simulation and
creating all the characters that will intervene in it; and
the Character Agents, one for each character in the
plot, whose responsibility is to interpret the state of
the relationships with the other characters and decide
how to interact with them in order to develop the plot
of the story. In turn, these characters are endowed
with a series of behaviors that are executed in a cycli-
cal manner that allow them to send messages to each
other and react to the messages they receive depend-
ing on the relationship they have with the character
sending the message.
A preliminary analysis of the logs generated by
the original simulation shows that of the 23 bidirec-
tional relationships between the 15 characters exist-
ing in the initial situation of the simulation, most
of them decay into a relationship of indifference be-
tween them, which leaves the state of the simula-
tion in a fairly stable situation but which, in narrative
terms, quickly ends up being of no interest. This anal-
ysis is confirmed by the subsequent results described
in (Gerv
´
as and M
´
endez, 2023) where it can be seen
that the story sifting process on the simulation logs
manages to obtain a few interesting events that allow
to extract an attractive narrative from the simulation
logs.
From this starting point, four sources of conflict
have been introduced into the simulation to make it
more dynamic and increase the likelihood of creating
situations that make the narrative more interesting.
3.1 Customising Reaction Thresholds to
Maximize Interest
The first step in achieving greater dynamics in the
relationships between characters has been to empir-
ically modify the thresholds for switching from one
type of affinity to another. The values that have shown
to be most promising, as shown in Figure 1, substan-
tially modify those of the original simulation (see Fig-
ure 2), introducing a greater overlap and a more grad-
ual transition between them, making it possible for
changes between affinities to occur more frequently.
As can be seen by comparing both figures, an at-
tempt has been made to have a greater overlap be-
tween the different affinities, so that the change from
one to the other is not so predictable and there is even
the possibility on occasions of skipping intermediate
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
696

states, such as the possible change from foe to friend
or vice versa. Mate-type relationships used to be too
stable and took away interest from the stories, so their
amplitude has been reduced and, as will be explained
later, the range of actions that make it possible for
a couple to break up and change their status to one
of the other affinities has been widened. This causes
that, with the change of affinity, the actions performed
by the characters have a greater variety and that these,
in turn, cause a greater impact on the variation of the
affinities.
3.2 Adapting Criteria to Prioritize
Reactions to Other Characters
The second change that has been introduced over the
initial simulation is the criterion used by each charac-
ter to decide whether to make a proposal to another
character or to accept or reject one of these proposals
from another character. In the initial simulation, this
decision was made by setting a probability threshold
and generating a random number. If the generated
number exceeds the threshold, then the proposal is
launched or the received proposal is accepted; oth-
erwise, the proposal is not made or the received pro-
posal is rejected, with consequent modifications be-
tween the affinities of the characters.
As a new source for conflict, the thresholds for
deciding to react have been slightly modified to allow
for more interactions between characters. The most
relevant changes that have been made are:
• In the original simulation, the interactions be-
tween friend characters outnumbered by far the
rest of the interactions (about 90% of the inter-
actions took place between friends). The proba-
bility to initiate or accept friend interactions has
been lowered from 0.7 to 0.4, so that less inter-
actions among friends take place and there is a
higher chance that other kinds of interactions take
place.
• The probability of accepting a mate proposal has
been increased from 0.4 to 0.7, so that more pro-
posals are accepted and, as a consequence, more
break-ups with previous mates take place and
more transitions from mate to foe can occur, giv-
ing rise to more dramatic events to take place.
• The probability of getting angry after a break-up
has increased from 0.4 to 0.6. This, together with
the previous change, make it possible for more
couples (but not too many) to dissolve in an un-
friendly manner, which in turn provides a higher
number of dramatic changes that may create more
engaging situations.
• In the first version of the simulation, interactions
with friends and mates were prioritized, so in-
teractions with indifferent characters were almost
nonexistent. The probability to interact with these
characters has increased from 0.4 to 0.7, so that
the chance to meet new characters or interact with
a wider range of them is now higher, therefore
making it possible to interfere in other character’s
lives.
• The probability to interact with a foe has been de-
creased from 0.4 to 0.2. Previously, it was less
probable to relax the affinities between two foes,
so once two characters started being foes, their
affinity state rarely changed. This, in some oc-
casions, made the relationships between charac-
ters to get stuck and turned the simulation into an
uninteresting succession of foe events. With this
change, foe relations tend to evolve towards an in-
different state that make it possible for foe charac-
ters to turn into friends or, eventually, form a new
couple.
In addition, the probability on which the decision
of whether to interact with another character is based
in the enhanced version is now computed as the prod-
uct between the value of the random number gener-
ated and the affinity with the character with which one
interacts, so that the probability of interacting with
characters with which one has a higher affinity in-
creases, while the probability of interacting with those
with which one has a lower affinity decreases.
3.3 Monitoring and Intervention to
Avoid Stabilization
The third source of conflict that has been introduced
in the simulation, and the main one, is the intentional-
ity of the characters when deciding with which other
characters they interact and with what objective this
interaction is carried out. For this purpose, the Direc-
tor Agent of the simulation has been provided with
the capacity to supervise the evolution of the affini-
ties between the different characters in the simulation.
This allows, on the one hand, to detect when the ac-
tions taking place in the simulation begin to lose inter-
est because they remain in too stable values. At that
moment, the Director Agent selects a character and
instructs it to increase the probability of interacting
with another character in order to modify its degree
of affinity with that character.
The monitoring and intervention of the Director
Agent is carried out in three steps in order to avoid the
stabilization of the relationships between characters:
Heating up Interactions in an Agent-Based Simulation to Ensure Narrative Interest
697
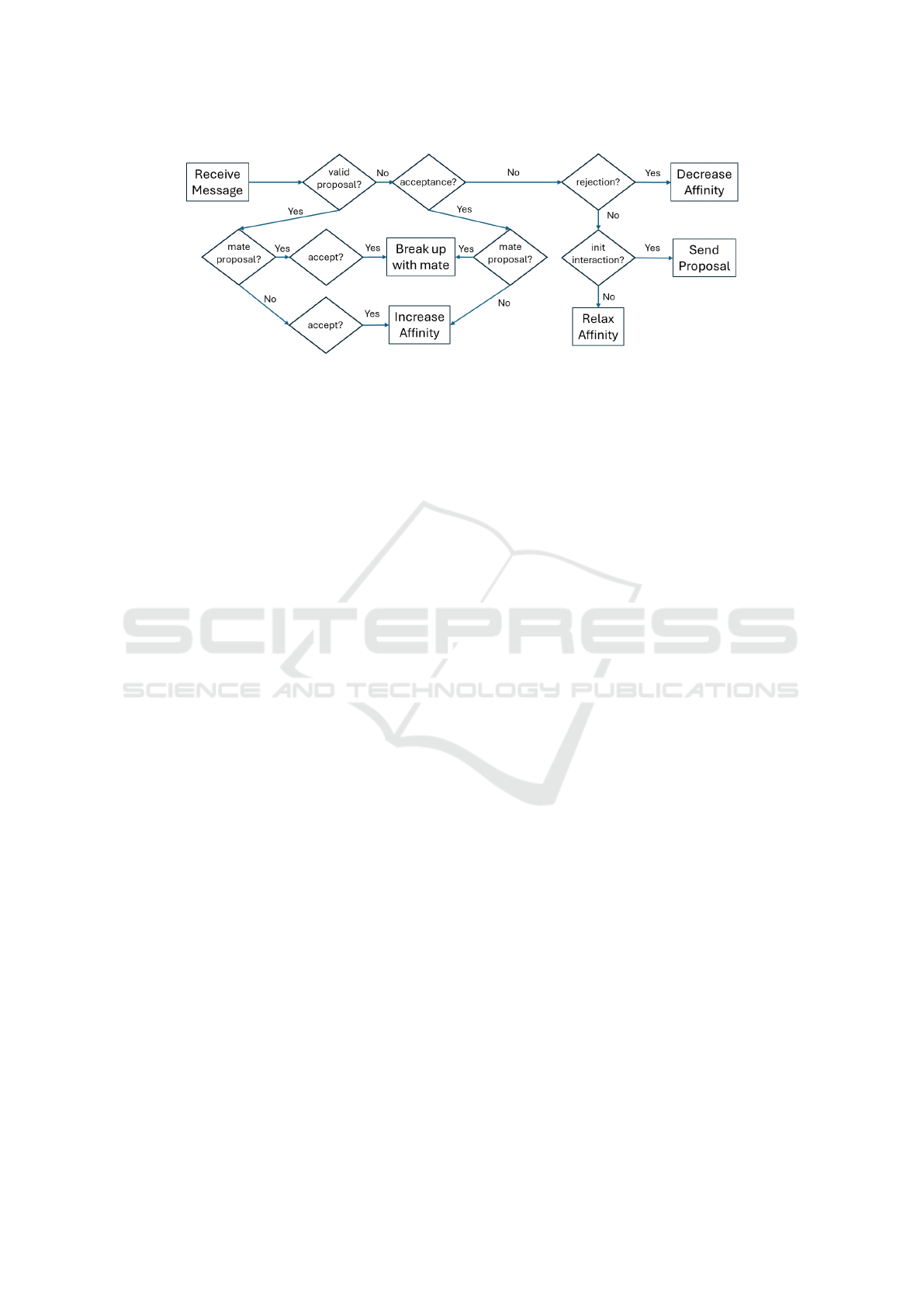
Figure 3: Flow diagram of the Friend Protocol in the enhanced simulation, showing the new possibility of switching from the
preceding partners to a friend with which affinity has reached a sufficiently high value.
1. Supervision: the Director Agent is informed about
all the interactions between each existing pair of
characters - initially, not all characters know each
other, so the number of monitored relationships
depends on the initial configuration of the simu-
lation and the number of new characters that are
met while the simulation runs - and takes note of
all the changes in the affinities. Since affinities in-
crease with interactions and slowly decrease with
the lack of them (or the other way in the case of
foes), it is usually the case that the affinity val-
ues fluctuate between the limits of an affinity level
(e.g. friends) for a long period without anything
exciting happening. To avoid this, the Director
Agent identifies long series of events or periods
of time where the affinity level does not change.
Currently, experimental values are set to 20 inter-
actions or 30 seconds of execution time.
2. Selection: once the described situations are de-
tected, the Director Agent has to select what pair
of characters to act on and where to drive their re-
lationship. In order to do this, the Director Agent
checks the state of the simulation in order to know
how many affinity relations of each kind currently
exist in the simulation and selects the largest one.
Then, among all the relationships that have been
identified as candidates to be modified, it selects
the most stable one in order to act on it.
3. Action: once the pair of characters have been
identified, the Director Agent informs both of
them that they have to modify their interaction cri-
teria until their affinity changes in the following
way:
• they have to stop to select randomly what char-
acter to interact with and they have to focus on
the specific character they have to change the
affinity level
• the probability value to interact with that char-
acter or to accept interactions with that charac-
ter is decreased to 0.1, so that possible interac-
tions are almost nonexistent
• alternatively, if the two characters were close
friends and there are no other restrictions (such
as gender or sexual preferences, which are
taken into account for each character), then the
characters are driven towards trying to become
mates and break up with their current couples,
which automatically generates the possibly in-
teresting sources of conflict (i.e. two break-ups
and a new couple)
• if the existing relation was of indifference, the
characters are driven to change it to friends or
foes, depending on how many relationships of
each kind there are in the simulation
3.4 Increased Affinity with Others
Leading to Couple Break up
The interaction protocol of two characters that are
friends has been modified so that, once a sufficiently
high affinity value is reached between two friends, the
simulation now allows a change of partner between
the characters to occur. To this end, when one char-
acter decides that the level of affinity with another is
sufficiently high, he sends him a proposal to become
his partner. If the other character accepts, each of the
two informs their previous partner that they are break-
ing off their relationship, lowering their affinity level
with them and forming a new partner. In turn, each of
the previous partners decide how much they decrease
their affinity with the partner who has broken the re-
lationship, and can change this affinity to the level of
friend, indifferent or foe. Figure 3 shows the flow di-
agram for the enhanced behaviour.
An example of such an interaction extracted from
the log of one of the simulations can be seen below:
Clark PROPOSE friend_visit_botanical_garden Mary
Mary ACCEPT-PROPOSAL friend_visit_botanical_garden Clark
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
698
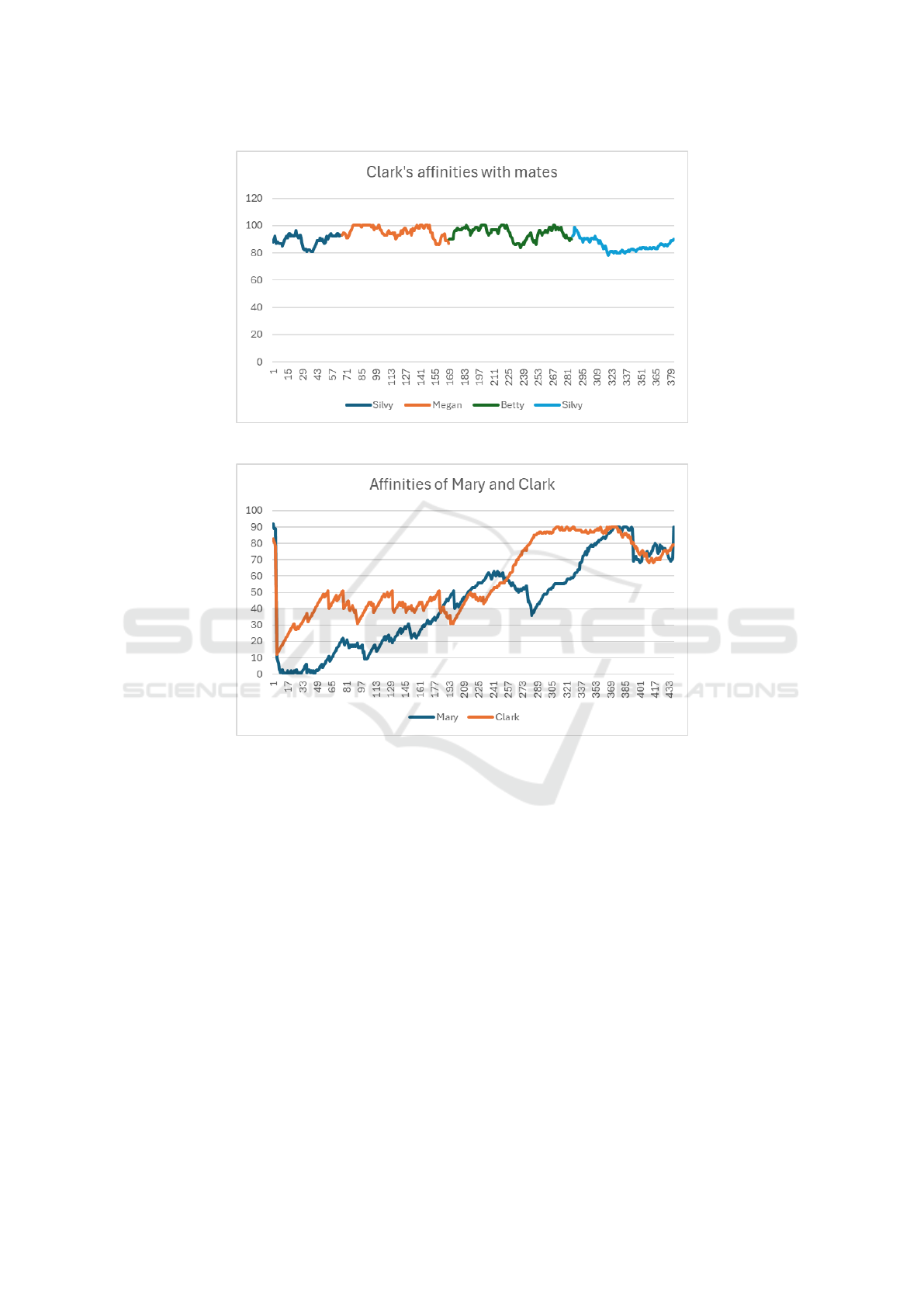
Figure 4: Evolution of the affinities between Clark and his mates.
Figure 5: Evolution of the affinities between characters Mary and Clark.
Mary CHANGE affinity_with Clark 70-->71
Clark CHANGE affinity_with Mary 88-->90
[...]
Clark PROPOSE mate_proposal Mary
Mary ACCEPT-PROPOSAL mate_proposal Clark
Mary CHANGE affinity_with Clark 71-->90
Clark CHANGE affinity_with Mary 90-->90
Clark INFORM mate_break_up Betty
Mary INFORM mate_break_up John
Betty CHANGE affinity_with Clark 92-->15
John CHANGE affinity_with Mary 87-->62
As shown in Figure 4, this new behavior makes
it possible for various changes between existing cou-
ples to occur throughout the simulation, which was
not previously possible. This, in turn, results in that
the relationship between two characters can vary dras-
tically, as can be seen in Figure 5, where, as a conse-
quence of a change of partner of one of the characters,
both change the value of their affinity to be considered
enemies. The relationship between these two charac-
ters evolves in a parallel, but asymmetrical manner,
until eventually they both become friends again.
3.5 Neural Rendering of Selected
Behaviour
The ultimate goal is the ability to create stories from
what happens in the simulation. As we have seen with
the recent development of Large Language Models
(LLMs), these models are capable of generating high
quality text, but it is more complex to be able to con-
trol what these systems generate. This has become
especially apparent in the case of story generation,
where narrative richness and consistency in generat-
ing stories of a certain size has not yet produced the
results that can be seen in other areas. On the other
hand, in the area of story generation, as shown in sec-
tion 2.1, significant progress has been made in gen-
erating stories with great narrative richness, although
Heating up Interactions in an Agent-Based Simulation to Ensure Narrative Interest
699

the quality of the final text, in most cases, was quite
poor.
In the case at hand, we have combined the out-
put generated by our simulation with an LLM, namely
ChatGPT-4o
1
, to generate a story whose development
can be driven in a way by the simulation output and
simultaneously presented in text format with a rich
narrative. A sample prompt we have used for this gen-
eration is
I am going to provide you with the log of a simulation and I need
you to transform it into a short story. The requirements for the
story are:
* Write a brief introduction to the story
* Set the story in some scenario extracted from the log
* Use only the characters and events from the log
This is the log:
<log>
An example with the log shown above is as fol-
lows:
In the heart of the bustling city, nestled amidst towering
skyscrapers, lay the serene Riverside Botanical Garden. A peace-
ful oasis where vibrant blossoms and the soothing rustle of leaves
created a haven away from the urban noise. It was here, on a
warm spring afternoon, that Clark found himself standing by the
entrance, his heart racing with a mix of anticipation and hope.
”Mary,” Clark began, his voice steady but soft, ”would you
like to visit the Botanical Garden with me today?”
Mary’s eyes lit up at the suggestion, and she responded with a
warm smile. “Of course, Clark. I’d love to,” she replied, accept-
ing his invitation. The two friends strolled down the meandering
paths, surrounded by bursts of color from the blooming flowers.
As they wandered through the fragrant air, their bond deepened.
For Mary, her affection for Clark grew just a little stronger, her
feelings blooming like the roses around them. Clark, too, felt the
pull of a stronger connection, and his heart swelled with affection.
Suddenly, a quiet moment by the koi pond turned into some-
thing much more meaningful. Clark took a deep breath and turned
to Mary. “Mary,” he said earnestly, “will you be more than just my
friend?” His voice was sincere, hopeful, and full of vulnerability.
Mary paused, her gaze meeting his, and her heart swirled with
emotions as she gave a gentle nod. “Yes, Clark. I will,” she whis-
pered, sealing their newfound commitment. The garden around
them seemed to glow even brighter as their love blossomed in uni-
son. Their connection was no longer just a friendship but some-
thing richer and deeper. In that magical moment, Mary’s affection
surged, reaching the same height as Clark’s. Their hearts were
fully in sync.
Yet, every new beginning brings change. Knowing what they
had to do, Clark and Mary exchanged difficult messages to their
former partners. Clark informed Betty of their separation, while
Mary had a similar conversation with John. As the news traveled,
old affinities shifted like autumn leaves falling from branches:
Betty’s bond with Clark crumbled, and John’s connection to Mary
dimmed, leaving behind memories of what once was.
And so, amidst the blossoms and the whispering leaves of the
Riverside Botanical Garden, a new chapter began for Clark and
Mary, a story of love born from friendship, growing ever stronger
beneath the open sky.
1
https://openai.com/index/hello-gpt-4o/
The example presented above shows how the text
rendering recounts the basic changes between the af-
fections of the characters that result from the simu-
lation model, while adding a significant amount of
detail on the particular scenes that lead to the differ-
ent changes in affinity. This is considered a valuable
combination of the advantages of the technologies for
agent-based simulation and neural text generation.
4 DISCUSSION
The enhanced simulation proposed in this paper can
be discussed in terms of the advantages it introduces
and in terms of how it compares with previous work
on related topics.
4.1 Advantages of the Enhanced
Simulation
The enhanced simulation, by construction, now
avoids important shortcomings of the original simu-
lation.
Of the modifications introduced in the enhanced
simulation, not all respond to the same motivation.
Some of the changes may be considered as im-
provements that make the simulation more realistic.
The preference for interacting with characters towards
which one has stronger affinity, or the possibility of
dissolving an ongoing romantic relationship when the
affinity with a third party increases beyond a given
threshold, both fall under this category.
Other changes can be considered departures from
real behaviour as observed in human couples, and
they would correspond more to the type of interven-
tion that an author inspired by real life events but de-
siring richer situations might apply in powering up
the situations in her story. The adaptation of reaction
thresholds to obtain richer interactions, or the moni-
toring by the Director Agent of stable situations that
may lead to direct interventions on the probability of
characters interacting would correspond to this sec-
ond category.
Table 1 shows data from different runs of the
simulations grouped by the version of the simula-
tion used (the first four stories were generated with
the original simulation, while the last four were gen-
erated with the version described in this paper) and
sorted by simulation length. The PROPOSE, AC-
CEPT and REJECT rows refer to interactions be-
tween mates, friends and indifferents, while the IN-
FORM row shows interactions between foes. The
break-ups row shows the number of break-ups that oc-
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
700

Table 1: Simulation data sorted by simulation length. The first 4 stories have been generated using the original simulation,
while the last 4 stories include the modifications described in this paper. Column n shows the number of interactions of each
kind, while column % shows the percentage that each type of interaction represents out of the total number of interactions.
story0 story1 story2 story3 story4 story5 story6 story7
n % n % n % n % n % n % n % n %
PROPOSE 317 46,14 667 49,44 1011 24,71 1074 13,78 7976 64,57 8988 48,37 9545 58,36 10585 54,97
ACCEPT 151 21,98 375 27,80 420 10,27 448 5,75 2230 18,05 4064 21,87 3356 20,52 3641 18,91
REJECT 125 18,20 245 18,16 282 6,89 282 3,62 1733 14,03 3346 18,01 2730 16,69 2770 14,39
INFORM 94 13,68 62 4,60 2378 58,13 5992 76,86 414 3,35 2184 11,75 725 4,43 2260 11,74
break-ups 6 7 7 6 7 11 14 17
affinity
changes
652 1,59 1309 1,80 3789 1,12 7458 1,06 11117 1,33 14162 1,27 17546 1,71 24093 1,88
cur, and the affinity changes row shows the number of
affinity changes over the total number of interactions.
As shown in the table, using the original simula-
tion, as the simulation time increases the percentage
of interactions between mates, friends and indiffer-
ent characters tends to decrease, while the number of
interactions between foes increases notably. On the
contrary, in the stories generated with the simulation
described in this contribution, it can be observed how
the interactions between couples, friends and indif-
ferent people are more numerous and remain more
stable, fluctuating around 60%, while the interactions
between foes fluctuate around 8%.
This has an effect on the number of affinity
changes, which in the case of the original simulation
tends to decrease as the length of the simulation in-
creases while in the case of the new simulation it tends
to double the number of interactions. The latter data
points to a greater tendency to meet new characters
over the course of the simulation and to relax affini-
ties with those characters with whom one character
interacts less. In the case of the initial simulation, this
effect did not occur because the break-ups between
characters led to an increase in interactions between
enemies, which can be appreciated in the increase in
INFORM-type interactions.
Finally, the row relating to break-ups shows how
in the original simulation all or almost all the exist-
ing couples (initially 7) break up due to lack of inter-
est between the members of the couple, while no new
couples are created. In the case of the new simulation,
although the number of break-ups is not very high, the
creation of new couples is a fact that, in due course,
gives rise to new break-ups, so that in the subsequent
story sifting process it is possible to select events that
provide greater interest to the final story.
4.2 Comparison with Prior Work
The Fac¸ade system (Mateas and Stern, 2005; Strong
and Mateas, 2008) differs from the solution presented
in this paper in that it relied on pre-determined scripts.
The Virtual Storyteller system (Theune et al.,
2003) uses a model of plot to constrain the actions of
characters. The system described in this paper differs
from these in that it contemplates a basic set of ac-
tions that can be combined freely to develop complex
behaviours.
The
´
Emile system (Gratch, 2000) operates at a
lower level of representation of relationships, more
concerned with emotional appraisal. The Glaive
(Ware et al., 2014) and IRIS (Fendt and Young, 2017)
systems focus on conflict at the level of the actions
that character want to undertake, but these actions in
general do not involve romantic attachments between
the characters. The system described in this paper op-
erates at a higher level of abstraction, considering ro-
mantic attachments between characters and the social
interactions that may lead to such attachments.
The IDTENSION system (Szilas, 2003) focused
on conflict between actions desired by the charac-
ters and the moral values they aspire to uphold. The
Comme il Faut (CiF) (McCoy et al., 2014) system
evolved from an earlier focus on the psychological
needs of individuals onto the logic of social statuses
and relationships between characters. The simulation
described focuses on romantic relations and it does
not consider conflicting plans, moral values, psycho-
logical needs or social status.
The MEXICA system (P
´
erez y P
´
erez, 1999) relies
on a system for representing affinities between char-
acters, and it drives the construction of its stories by
a set of tensions computed over these affinities. Ten-
sions arise when characters have conflicting values of
affinity to other characters (one character hates and
loves another, or two characters love the same charac-
ter). The system described in this work does not yet
allow us to reflect that type of conflict, although what
it does allow us to reproduce with the new sources of
conflict are situations in which, when a couple breaks
up through the intermediation of a third person, the
characters who have been abandoned have the pos-
sibility of reacting to the breakup in three different
ways: by downgrading their affinity to the level of
friendship and trying to win back their former part-
Heating up Interactions in an Agent-Based Simulation to Ensure Narrative Interest
701

ner, as can be seen in Figure 4; by adopting a position
of indifference; or by displaying a hostile and hateful
attitude and executing actions that reflect this.
The NetworkING (social Network for Interactive
Narrative Generation) system does include romantic
relationships between characters as well as a num-
ber of other possible relations between them, such as
friendship, antagonism or professional rivalry. The
actions of the characters are determined by a plan-
ner that takes into account the network of relations in
which the characters participates. In contrast, the ac-
tions of the characters in the simulation described in
this paper are determined by stochastic process that
operate on the values of affinities between them. This
has been an explicit decision made because, as can
be seen in the analyzed literature (e.g. (Laclaustra
et al., 2014)) and in our own experience developing
story-generating systems (e.g. (Gerv
´
as et al., 2019)),
the use of systems based on rules or planners gen-
erally leads to solutions that tend to always generate
the same story or a very reduced set of them, since
the variability introduced by these solutions is usually
small. In our case, it has been decided to use pseudo-
random decisions to ensure that the variety of situa-
tions that can arise is as wide as possible, since the
subsequent story-sifting process on the log generated
allows us, from among all of them, to select those that
are most interesting depending on the parameters that
are set at any given time. In addition, although appar-
ently the representation of the types of relationships
possible in our system is poorer than the one used in
NetworkING, it seems that the categories used in that
system are closed categories. In our case the affinity
values, although discrete, simulate to be continuous
in comparison, the transitions between categories are
more diffuse and smooth and, above all, the represen-
tation of the affinities used in our system is designed
to make the affinities efficient to calculate, since our
simulation, not being interactive, unlike Networking,
performs many more interactions between characters
per second and needs the calculations of the new val-
ues of the affinities to be performed efficiently.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This paper has shown how four mechanisms have
been successfully introduced to inject conflict into an
agent-based simulation used to create romantic sto-
ries based on the affinity variations that occur between
characters when they interact with each other. These
four mechanisms have been the modification of the
interaction thresholds between characters to achieve
more affinity variations between them; the introduc-
tion of intentionality in the characters when deciding
which character to interact with and what type of in-
teraction to initiate with them; the possibility of hav-
ing the Director Agent directly modify the probability
of interaction between characters to avoid stagnation
into uninteresting situations; and an extension in the
agents’ behavior that allows them to search for a new
partner even at the cost of breaking up with their own
partner and having their new partner break up with
their previous partner as well.
There is still room for improvement in the story
generation system described in this work. As lines
of future work, the following courses of action are
proposed. First, we intend to enrich the representa-
tion of the relationships between characters, introduc-
ing relationships and interactions between more than
two characters and representing the affinities between
them so that contradictory interests may arise (having
a partner with whom one has a low affinity or that a ro-
mantic interest arises with a character one hates). Sec-
ondly, it is proposed to introduce the possibility of the
characters interpreting the existing relationships be-
tween other characters, giving the possibility of mis-
understandings or misinterpretations based on what
one character tells another. Finally, it is also intended
to provide the characters with a more complex model
of personality and emotions, so that each character
can react differently from another to the same situa-
tion, and that this does not depend solely on the gen-
eration of a random value as in the current system.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This paper has been partially funded by the projects
CANTOR: Automated Composition of Personal Nar-
ratives as an aid for Occupational Therapy based on
Reminescence, Grant. No. PID2019-108927RB-
I00 (Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation),
project DARK NITE: Dialogue Agents Relying on
Knowledge-Neural hybrids for Interactive Training
Environments, Grant No. PID2023-146308OB-I00
(Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation) and
the ADARVE (An
´
alisis de Datos de Realidad Vir-
tual para Emergencias Radiol
´
ogicas) Project funded
by the Spanish Consejo de Seguridad Nuclear (CSN).
REFERENCES
Alsawalqa, R. O. (2019). Marriage burnout: When the emo-
tions exhausted quietly quantitative research. Iranian
Journal of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences, 13(2).
Bellifemine, F., Bergenti, F., Caire, G., and Poggi, A.
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
702

(2005). Jade—a java agent development framework.
Multi-agent programming: Languages, platforms and
applications, pages 125–147.
Concepci
´
on, E., Gerv
´
as, P., and M
´
endez, G. (2018). Ines:
A reconstruction of the Charade storytelling system
using the Afanasyev framework. In Proceedings of
the Ninth International Conference on Computational
Creativity, Salamanca, Spain, pages 48–55.
Fendt, M. W. and Young, R. M. (2017). Leveraging inten-
tion revision in narrative planning to create suspense-
ful stories. IEEE Transactions on Computational In-
telligence and AI in Games, 9:381–392.
Gerv
´
as, P., Concepci
´
on, E., Le
´
on, C., M
´
endez, G., and De-
latorre, P. (2019). The long path to narrative gener-
ation. IBM Journal of Research and Development,
63(1):8–1.
Gerv
´
as, P. and M
´
endez, G. (2023). Evolutionary story sift-
ing over the log of a social simulation. In Italian Work-
shop on Artificial Life and Evolutionary Computation,
pages 381–393. Springer.
Gratch, J. (2000).
´
Emile: Marshalling passions in training
and education. In Proceedings of the Fourth Interna-
tional Conference on Autonomous Agents, AGENTS
’00, pages 325–332, New York, NY, USA. ACM.
Kreminski, M., Dickinson, M., and Mateas, M. (2021).
Winnow: A domain-specific language for incremen-
tal story sifting. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference
on Artificial Intelligence and Interactive Digital En-
tertainment, 17(1):156–163.
Kreminski, M., Dickinson, M., and Wardrip-Fruin, N.
(2019). Felt: A simple story sifter. In Interac-
tive Storytelling: 12th International Conference on
Interactive Digital Storytelling, ICIDS 2019, Little
Cottonwood Canyon, UT, USA, November 19–22,
2019, Proceedings, page 267–281, Berlin, Heidel-
berg. Springer-Verlag.
Laclaustra, I. M., Ledesma, J. L., M
´
endez, G., and Gerv
´
as,
P. (2014). Kill the dragon and rescue the princess: De-
signing a plan-based multi-agent story generator. In
5th International Conference on Computational Cre-
ativity, ICCC 2014, Ljubljana, Slovenia.
Mateas, M. and Stern, A. (2005). The interactive drama
fac¸ade. In AIIDE, pages 153–154. AAAI Press.
McCoy, J., Treanor, M., Samuel, B., Reed, A. A., Mateas,
M., and Wardrip-Fruin, N. (2013a). Prom week. In
AIIDE. AAAI.
McCoy, J., Treanor, M., Samuel, B., Reed, A. A., Mateas,
M., and Wardrip-Fruin, N. (2013b). Prom week: De-
signing past the game/story dilemma. In FDG, pages
94–101. Society for the Advancement of the Science
of Digital Games.
McCoy, J., Treanor, M., Samuel, B., Reed, A. A., Mateas,
M., and Wardrip-Fruin, N. (2014). Social story worlds
with comme il faut. IEEE Transactions on Computa-
tional Intelligence and AI in Games, 6(2):97–112.
McCoy, J., Treanor, M., Samuel, B., Tearse, B., Mateas, M.,
and Wardrip-Fruin, N. (2010). Authoring game-based
interactive narrative using social games and comme il
faut. In Proceedings of the 4th International Confer-
ence & Festival of the Electronic Literature Organi-
zation: Archive & Innovate (ELO 2010), Providence,
Rhode Island, USA.
M
´
endez, G., Gerv
´
as, P., and Le
´
on, C. (2014). A model
of character affinity for agent-based story generation.
In 9th International Conference on Knowledge, In-
formation and Creativity Support Systems, Limassol,
Cyprus. Springer-Verlag, Springer-Verlag.
M
´
endez, G., Gerv
´
as, P., and Le
´
on, C. (2016). On the Use
of Character Affinities for Story Plot Generation, vol-
ume 416 of Advances in Intelligent Systems and Com-
puting, chapter 15, pages 211–225. Springer.
P
´
erez y P
´
erez, R. (1999). MEXICA: A Computer Model of
Creativity in Writing. PhD thesis, The University of
Sussex.
Porteous, J., Charles, F., and Cavazza, M. (2013a).
Networking: Using character relationships for in-
teractive narrative generation. In Proceedings of
the 2013 International Conference on Autonomous
Agents and Multi-agent Systems, AAMAS ’13, pages
595–602, Richland, SC. International Foundation for
Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems.
Porteous, J., Charles, F., and Cavazza, M. (2013b). A social
network interface to an interactive narrative. In Pro-
ceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Au-
tonomous Agents and Multi-agent Systems, AAMAS
’13, pages 1399–1400, Richland, SC. International
Foundation for Autonomous Agents and Multiagent
Systems.
Porteous, J., Charles, F., and Cavazza, M. (2015). Using
social relationships to control narrative generation. In
Proceedings of the Twenty-Ninth AAAI Conference on
Artificial Intelligence, January 25-30, 2015, Austin,
Texas, USA., pages 4311–4312.
Ryan, J. (2018). Curating Simulated Storyworlds. PhD the-
sis, University of California Santa Cruz, CA, USa.
Strong, C. R. and Mateas, M. (2008). Talking with npcs:
Towards dynamic generation of discourse structures.
In AIIDE. The AAAI Press.
Szilas, N. (2003). Idtension: a narrative engine for inter-
active drama. In Technologies for Interactive Digital
Storytelling and Entertainment. TIDSE 2003 Proceed-
ings, pages 187–203.
Theune, M., Faas, E., Nijholt, A., and Heylen, D. (2003).
The virtual storyteller: Story creation by intelligent
agents. In Proceedings of the Technologies for Inter-
active Digital Storytelling and Entertainment (TIDSE)
Conference, pages 204–215.
Ware, S. G., Young, R. M., Harrison, B., and Roberts,
D. L. (2014). A computational model of narrative con-
flict at the fabula level. IEEE Transactions on Com-
putational Intelligence and Artificial Intelligence in
Games, 6(3):271–288.
Heating up Interactions in an Agent-Based Simulation to Ensure Narrative Interest
703
