
Randomizing Forger Selection to Improve Decentralization in Proof of
Stake Consensus Protocol
Syed Badruddoja
1
, Sasi Kiran Kanduri
1
and Ram Dantu
2
1
Dept. of Computer Science, California State University, Sacramento, 6000 J Street, Sacramento, California, 95819, U.S.A.
2
Dept. of Computer Science, University of North Texas, 3940 N. Elm Street, Denton, Texas, 76207, U.S.A.
Keywords:
Consensus Protocol, Blockchain, Proof-of-Stake, Decentralization.
Abstract:
In proof-of-stake consensus protocols, the inherent design often favors wealthier participants, perpetuating a
cycle where the rich become richer, thereby consolidating control over validation and block creation. This
dynamic discourages broader participation, as lower-stake nodes are discouraged from contributing to block
creation and transaction processing, undermining the fundamental principle of equitable decentralization. This
research introduces a hash power-based consensus protocol that provides opportunities to low-stakes valida-
tors. We extend an existing work of hash-power-based consensus protocol to increase randomization of val-
idator selection. Moreover, we raise the decentralization factor by extending a ’hash power’ metric, which is
calculated from the minted and native stakes of a participant. The proposed consensus algorithm enhances the
network’s forgers and validators selection mechanism, raising the entropy of the validator selection to 0.80
and fairness to 0.45, which is a significant improvement to coinage-based validator selection.
1 INTRODUCTION
Blockchain (Nakamoto, 2008) is a decentralized and
distributed ledger system that records transactions
across a network with a consensus-based voting
mechanism. The ledger is immutable and distributed
across the network, ensuring that nodes are updated
and the transactions are tamper-proof. Moreover,
blockchain eliminates the need for a single central-
ized entity and validates transactions with the help of
consensus protocols. Proof of Stake (PoS) (Saad and
Radzi, 2020) is one of the popular consensus proto-
cols used by many applications for security and scal-
ability purposes (Swan, 2015). However, decentral-
ization is curbed in PoS protocols due to the nature
of the selection process. Hence, it does not guarantee
true randomness in selecting nodes (Motepalli and Ja-
cobsen, 2024).
Proof of Stake (PoS) (Saad and Radzi, 2020)
emerges as an efficient consensus protocol, select-
ing validators for new blocks based on their cryp-
tocurrency holdings and ”stake.” This method is more
energy-efficient and secures the network through eco-
nomic incentives. However, PoS faces centralization
challenges, with factors showing that stake concen-
tration is encouraged (He et al., 2020). The argument
about centralization has been a pressing one in PoS-
based blockchain systems. PoS protocol inadvertently
leads to a concentration of control among a few par-
ticipants, potentially threatening the decentralized na-
ture of the blockchain.
Not Selected
Due to Low Stake
Selected Validators With High Stake
ForgerValidatorValidatorValidator
Blockchain Consensus Validator
Figure 1: Validator node on the left is not selected due to
low stake. Others with high stakes are selected for the con-
sensus process.
He et al. (He et al., 2020) mentioned that higher-
stakes validators have more probability of being cho-
sen for the block validation process in a PoS consen-
sus protocol. This can create an imbalance in the
validators and make rich participants richer. Inno-
vations like Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), uti-
lized by platforms like EOS and TRON, introduce
a delegate system where token holders vote for rep-
resentatives to validate transactions on their behalf,
enhancing scalability and efficiency (Nair and Do-
rai, 2021; Pan et al., 2021). Byzantine Fault Tol-
erance (BFT) algorithms, including Practical Byzan-
260
Badruddoja, S., Kanduri, S. K. and Dantu, R.
Randomizing Forger Selection to Improve Decentralization in Proof of Stake Consensus Protocol.
DOI: 10.5220/0013317200003899
In Proceedings of the 11th Inter national Conference on Information Systems Secur ity and Privacy (ICISSP 2025) - Volume 2, pages 260-267
ISBN: 978-989-758-735-1; ISSN: 2184-4356
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
tine Fault Tolerance (PBFT) and Tendermint, priori-
tize fault tolerance in distributed systems by tolerat-
ing malicious nodes and maintaining consensus even
in faulty nodes. These ideas effectively make the
blockchain network more scalable, but the core prob-
lem of favoring high-staking nodes remains an is-
sue, causing low decentralization. Figure 1 shows an
overview of the decentralization problem.
Figure 2: Showing the centralization behavior of the exist-
ing Stake-based consensus protocols.
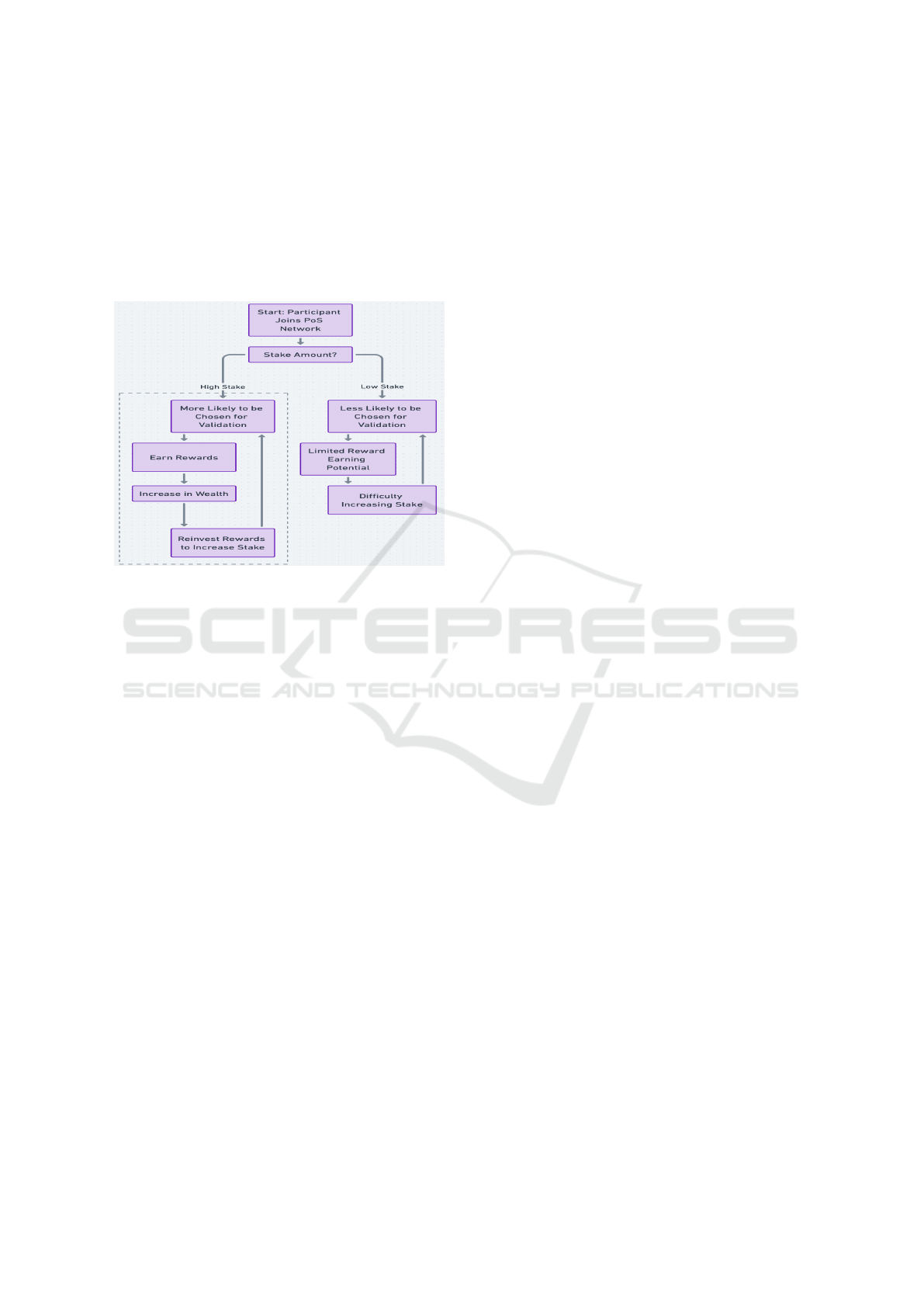
Figure 2 shows how decentralization could shrink
due to a lack of stake participation. A participant joins
the PoS consensus network and deposits a stake. If the
participant has a high stake, the participant will likely
be selected for being a forger or validator of the block.
However, if the participant has a low stake, there is a
low chance that the participant will be selected.
Liquid staking pool platforms such as Lido (Hord,
2024) help users pool their assets for staking on proof-
of-stake (PoS) networks and incentivize users with
liquid tokens. Moreover, staking pools offer various
advantages for users, such as making participation
more accessible, minimizing technical complexities,
and enabling earning staking rewards even with small
ETH contributions. However, these pools can become
centralized if a few large pools dominate staking, con-
centrating validation power and governance influence
(Hord, 2024). This undermines decentralization by
creating reliance on a small number of entities, in-
creasing risks of collusion or censorship.
2 PROBLEM STATEMENT
Proof of Stake (PoS) originated as an alternative to
the energy-intensive Proof of Work (PoW) consen-
sus mechanism, aiming to address the limitations of
PoW-based blockchain networks like Bitcoin. PoS
was conceived to create a more energy-efficient and
sustainable model for achieving consensus within de-
centralized systems. It operates on the principle
that validators, or participants responsible for validat-
ing transactions and creating new blocks, are chosen
based on the amount of cryptocurrency they hold and
are willing to stake as collateral. Despite the bene-
fits of the Proof of Stake protocol, decentralization
remains a concern, and the algorithm favors nodes
with high stakes. Since incentives come from partic-
ipation in elections for forging/validating blocks, the
wealthier nodes naturally stake more to increase their
chances of participation. This can lead to the concen-
tration of wealth among a few participants with sig-
nificant stakes, centralizing power and influence over
the network.
3 CONTRIBUTION
• Our work builds upon and extends the method-
ologies proposed by Gurram et al. (Gurram et al.,
2023) using a weighted hash power-based selec-
tion.
• We extended the hash power-based consensus
protocol and proposed methodology to develop
a consensus algorithm that can be incorporated
to increase randomization in the validator selec-
tion process while also considering the size of the
stake.
• Our experiment demonstrates an improvement in
the fairness of the consensus protocol, increas-
ing from 0.11 with the coinage validator selection
process to 0.45 using the proposed protocol.
• Our experiment demonstrates an improvement in
the entropy of the consensus protocol, increas-
ing from 0.51 with the coinage validator selection
process to 0.80 using the proposed protocol.
4 BACKGROUND
To mitigate the challenges of PoS, ongoing research
and development efforts focus on designing PoS pro-
tocols that promote fair participation, distribute re-
wards equitably, and uphold the principles of decen-
tralization and security. Several iterations and varia-
tions of PoS have emerged, each with its unique ap-
proach to achieving consensus and ensuring network
security. Bonded Proof of Stake (BPoS), one of the
variants of PoS, enhances security by requiring val-
idators to ”bond” or ”lock up” their stake for a certain
Randomizing Forger Selection to Improve Decentralization in Proof of Stake Consensus Protocol
261
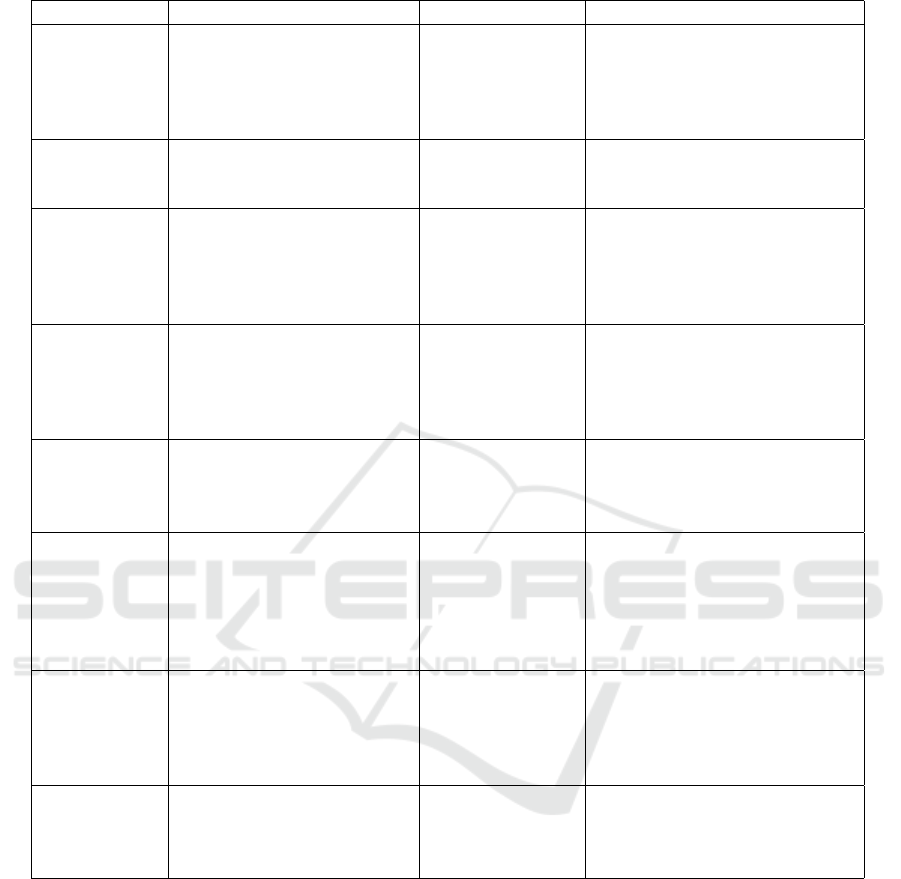
Table 1: Comparison of some of the stake-based consensus protocols that offer decentralization and their limitations.
Consensus Type of Validators Decentralization Limitation
RPoS (Li
et al., 2020)
Uses the number of coins to
select miners and limits the
maximum value of the coin
age to effectively avoid coin
age accumulation attack
Low Does not address decentraliza-
tion problem of the network
DPoS(Pan
et al., 2021)
Validators are elected from a
pre-defined list of block pro-
ducers called delegates
Low Improves scalability but carries
a risk for security and decentral-
ization with fixed delegates
BPoS (Elas-
tos, 2024)
Validators with a certain
amount of stake commit-
ted/locked up in the network
can be selected
Low Minimum stake amounts can in-
crease over time, making the
barrier of entry high, causing
liquidity issues with fewer coins
in circulation
LPoS (Tezos,
2024)
Minimum stake limit (in
coins) is needed to partici-
pate in consensus, can dele-
gate validating rights other-
wise
Medium Increases participation with del-
egation but tends to create a
concentration of few wealthy
validators
PoS (Maung
Maung Thin
et al., 2018)
amount of stake is directly
proportional to opportunities
of participation
Medium Conventional proof of stake
consensus where high staking
participants can centralize over
time
PPoS (Algo-
rand, 2024)
Uses verifiable random
function algorithm (VRF) -
The more algos (cryptocur-
rency) in an account, the
greater chance the account
has of being selected
Medium Promises randomization, but it
is still dependent on coin wealth
EPoS (Saad
et al., 2021)
Executing an immutable
smart contract that imple-
ments the rules of a PoS
auction to support decen-
tralization
Medium Runs a PBFT-based consensus
over the mempool state of PoS,
making it less efficient
This work Based on a ’ hash power’
metric, which is calculated
from the minted and native
stakes of a participant
High -
period. This commitment helps secure the network
by ensuring that validators are vested in maintaining
network integrity, as malicious actions could lead to
losing their bonded stake. In contrast, in LPoS, as op-
posed to DPoS, any user can become a validator with
a certain number of coins. Users can delegate the val-
idation rights if they do not have enough coins. The
idea is to dilute the activity even more and increase
inclusion (Tezos, 2024).
Coinage, another method used in the proof of
stake consensus mechanisms, chooses a validator
based on the product of the tokens staked and the
days they’ve been held, requiring a minimum of 30
days staked to qualify. Winning nodes are excluded
from competition for 30 days, affecting the network’s
scalability. Robust Proof of Stake (RPoS) (Li et al.,
2020) is a proposed consensus algorithm aimed at
improving blockchain sustainability. It elects block
forgers based on coin holdings, limiting the maxi-
mum coinage a node can accumulate to prevent con-
centration. RPoS claims to perform better than tradi-
tional PoW and PoS mechanisms. EPoS (Saad et al.,
2021), another variant of PoS, promises decentral-
ization with random state sharding. Validators with
larger stakes must operate more nodes, maintaining a
balanced control distribution.
Pan (Pan et al., 2021) and Lamriji (Lamriji et al.,
2023) published studies that explain the problem of
ICISSP 2025 - 11th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
262
Election
Round 1
(Timestamp t = 0)
Election
Round 2
(Timestamp t = 10)
Election
Round 3
(Timestamp t = 20)
Node 1
Node 2
Node 3
Participants
Probable Winner
Node 1
TIMELINE
NODES
Intiate
Election
Pool of
participants
with hashpowers
hashpower = h(t, S)
hashpower = h(t, S)
hashpower = h(t, S)
Node 1
Node 2
Node 3
Participants Probable Winner
Node 2
hashpower = h(10, S)
hashpower = h((t + 10) / 2, S)
hashpower = h((t + 10) / 2, S)
Node 1
Node 2
Node 3
Participants Probable Winner
Node 3
hashpower = h((20 + 10) / 2, S)
hashpower = h(20, S)
hashpower = h(t(t + 20) / 2, S)
Update
hash powers
Node 2
Node 3
OR
OR
Node 3
OR
Update
hash powers
Node 1Winner =
Node 2Winner = Node 2Winner =
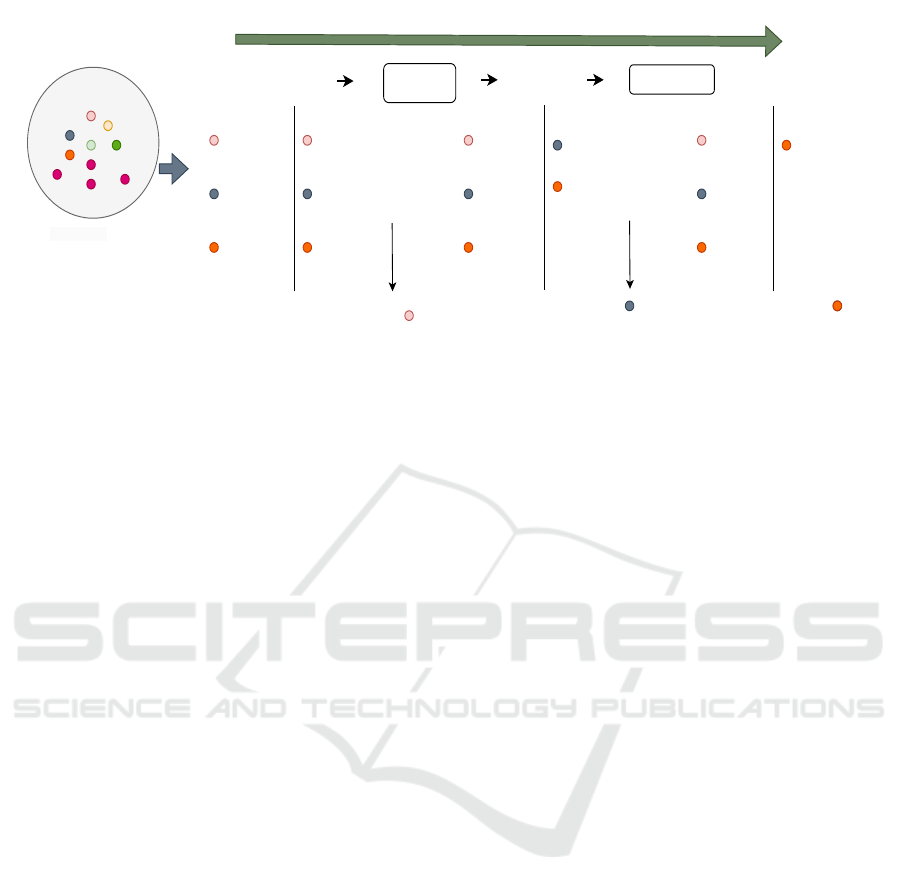
Figure 3: An election process considering three nodes with hash powers. Hashpowers calculated for the nodes at the first
election change over time after every election. In the above figure, the chances of selection for all nodes are equal in election
1, low for node 1, and high for nodes 2 and 3 in election 2. Later, the hash power is high for node 3 in election 3. Hashpowers
are updated based on the assumption that nodes 1, 2, and 3 won elections 1, 2, and 3, respectively.
existing proof-of-stake consensus mechanisms favor-
ing the wealthy, leading to centralization over time.
Extensive analysis indicates that, over a larger scale,
high-staking nodes can easily group together. This
contradicts the purpose of the blockchain as a de-
centralized system (Nair and Dorai, 2021; Pan et al.,
2021). Table 1 shows the comparison of some of the
PoS consensus protocols that indicate the need to im-
prove decentralization.
There have been several approaches to improve
decentralization in blockchain networks. Proof of
Stake and Activity (PoSA) protocol (Kim et al., 2023)
is one such consensus protocol that uses the concept
of Proof of Activity with the traditional Proof of Stake
to reward validators based on both stake capital and
their business contributions, promoting decentraliza-
tion. Khatoon et al. introduce another modified Proof
of Stake mechanism to address the risks of 51% at-
tacks, thus enhancing security and reducing central-
ization by making it more difficult for any single en-
tity to dominate the network validation process (Kha-
toon et al., 2024). Our protocol aims to address the
centralization issue at a lower level, altering the way
block forgers and validators are elected by modifying
the underlying algorithm.
Gurram et al. cite[5] proposed a consensus
methodology that uses stakes with timestamps to cal-
culate what they called hash powers that can be used
to improve randomness in validator selection. How-
ever, their contribution was limited to a mathematical
model and theoretical calculations without practical
implementation or testing of their methodology.
5 METHODOLOGY
The primary goal of this work is to improve the con-
sensus algorithm to make it fairer and address the cen-
tralization problem. In conventional Proof of Stake
(PoS) protocols, validators deposit native tokens as
stake, and the protocol selects a validator pseudo-
randomly based on the amount staked, as seen in the
coinage protocol. Building upon the methodology
proposed by Gurram et al. (Gurram et al., 2023),
which introduced the concept of staking minted to-
kens backed by native tokens for participation in
the election process, we extended their approach by
adding a behavior rating (W ) to consider reliability
and conduct in achieving consensus. We developed
a practical algorithm based on their work, breaking
it down into steps that the protocol follows to gov-
ern validator elections and block addition throughout
the blockchain’s operation. This approach ensures a
structured mechanism to improve fairness and valid-
ity in the consensus process. We used hash powers
(hP) for all members during the election process and
followed the proposed algorithm to achieve consen-
sus.
hP = S.(|e − m|) (1)
In equation 1, e is the timestamp of the election,
m is the timestamp minted on a token when it was
deposited. S is a node’s valid (unexpired) stake in the
blockchain. Considering that all staked tokens will
not have the same timestamp,
hP =
x
∑
i=1
S
i
· (e − m
i
) (2)
In equation 2, x is the number of records of staked
Randomizing Forger Selection to Improve Decentralization in Proof of Stake Consensus Protocol
263
tokens, and m
i
is the timestamp minted on a token
when it was deposited. The stake tokens are only
valid for x days from the minted date. The limited va-
lidity prevents wealthy nodes from accumulating very
high hash powers and influencing the protocol. If the
minted tokens remain unused, they’re returned to the
node. The value of ’x’ should be adjusted according
to the scale of the network. The calculated hash power
is then adjusted based on behavior rating W .
hP = hP ·W (3)
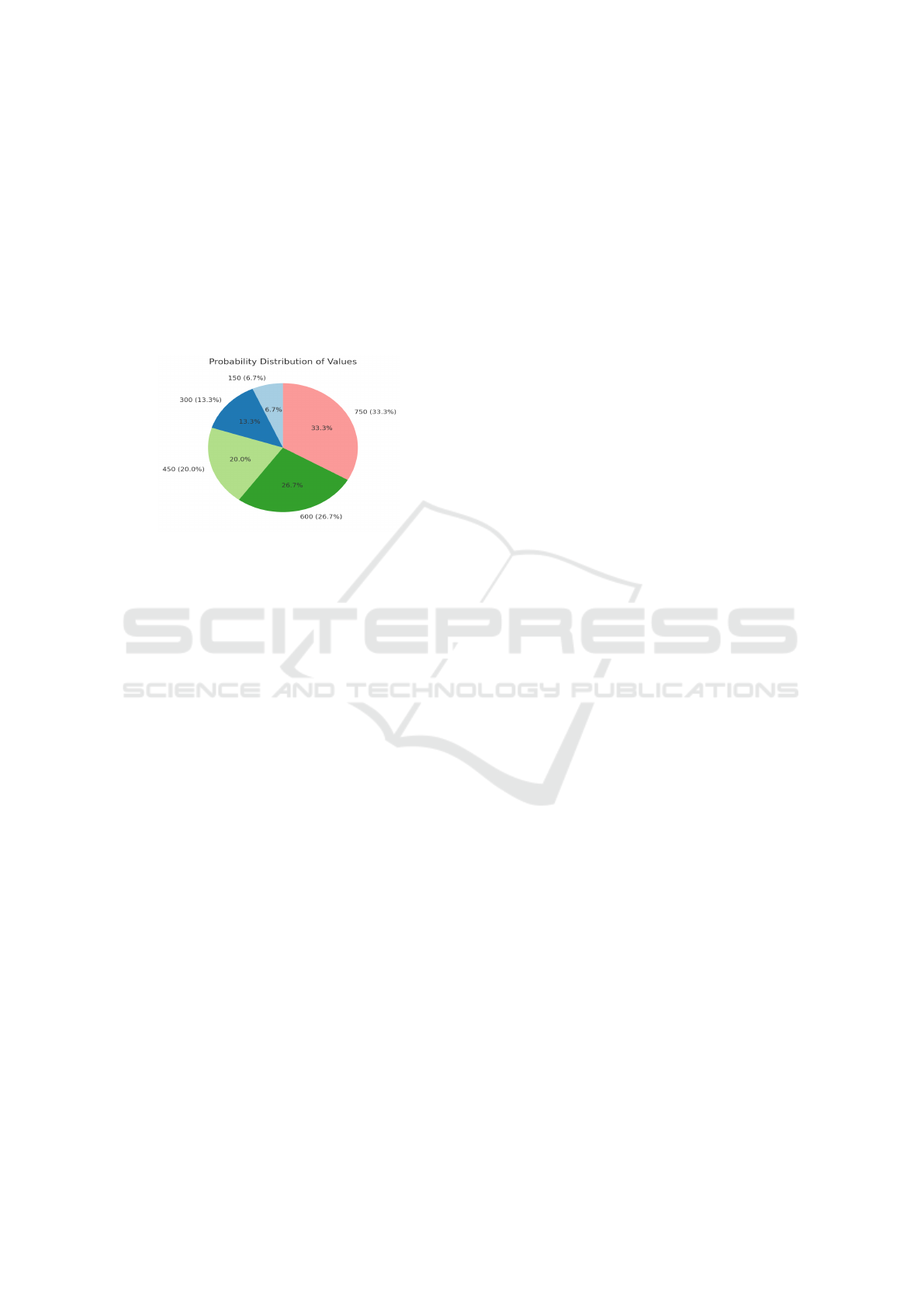
Figure 4: This pie chart represents the probability distri-
bution for being selected as a forger or validator among five
nodes with hash powers assumed as 150, 300, 450, 600, and
750 using Equation 2.
Below is a step-by-step description of the algorithm:
1. Nodes wanting to be a forger/validator can stake
tokens with minted timestamps.
2. Calculate hash powers with equations (2) and (3)
3. Select a random hash power for all the calcu-
lated unique hash powers. Let us assume a list
of unique hash powers calculated on the network
in step 2. The list can form a probability distri-
bution as shown below in figure 4, representing
the weight of each hash power value. Nodes with
higher hash power will have a higher probabil-
ity of getting selected as a forger/validator - The
largest hash power, say 750, might have a 33%
chance of getting selected, as shown in figure 4.
This can be imagined as spinning a roulette wheel
where larger hash powers have bigger slices but
are not guaranteed to be selected. Upon selecting
a hash power value, a node with that hash power is
chosen randomly from all nodes sharing the same
value.
4. After selecting the forger, the same steps above
are used to form the validator committee, ex-
cluding the chosen forger’s hash power. This
approach aims to increase the chances for low-
staking nodes with fewer hash powers to partic-
ipate, diversifying forger/validator roles and pre-
venting dominance by high-stake nodes, as having
higher hash power can always result in selection
in subsequent elections.
5. When the election is completed and a block has
been forged, the staked tokens are returned to the
participants with updated timestamps. The times-
tamps are updated differently in the two scenarios.
• Win scenario: When a node wins the election,
the staked tokens are returned with their times-
tamps updated as
m
i
= e (4)
where m
i
is the timestamp mentioned in equa-
tion 1 and e is the timestamp of the election.
• Lose scenario: When a node loses the election,
the staked tokens are returned with their times-
tamps updated as
m
i
= (e + m
i
)/2 (5)
where m
i
is the timestamp, e is the election
timestamp that was just completed.
6. After the selected forger proposes the new block,
the block’s validity is determined with the voting
strategy in (4), where votes are aggregated and
weighted based on the behavior ratings of each
participant.
For simplicity, let’s take an example with three
nodes on a sequence of elections. Figure 3 shows
the timeline of 3 elections. Assume that the three
nodes have equal stakes of 10 with a minted times-
tamp value of zero at the first election. The times-
tamps of the stakes will be updated with the elec-
tion times in the win scenario, the mean of election
time, and the previous timestamps on the token in the
lose scenario after every election. This way, the hash
power’s potency, calculated with equation (2), fluctu-
ates over time, leading to a dynamic shift in the prob-
ability distribution of participation chances.
6 EXPERIMENTAL SETUP
The aim is to simulate a private blockchain that can
be distributed and run across a network of nodes. We
used Python programming language and leveraged
its frameworks to simulate a network of 50 nodes
implementing the proposed consensus protocol. The
network setup consists of peer-to-peer discovery us-
ing Python’s ‘p2pnetwork‘ module and Flask-based
web communication for transaction processing.
Each node is assigned a port, facilitating socket
communication. Key blockchain components include
ICISSP 2025 - 11th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
264

the Block, Transaction, and Blockchain, where each
node maintains a synchronized copy of the chain.
The network implements the proposed proof of stake
protocol across nodes to manage forger/validator
selection and consensus. Additionally, the Account
Model handles participant wallets and nodes, up-
dating wallets post-transaction execution on the
blockchain. Together, these components form a
decentralized and cohesive blockchain network. The
implementation of the abovementioned environment
to simulate a blockchain can be found at the link.
To measure the decentralization of the consensus
protocol, we made some assumptions for a few pa-
rameters in the algorithm.
• The time for the staked token to be valid is as-
sumed to be 5 minutes for the test runs.
• All nodes are assumed to be good nodes with no
malicious behavior so that we can focus on the
randomness in the selection. This means that W is
set to 1 in equation 3.
• Every time a node’s stake expires, the node will
immediately stake the amount it had at that mo-
ment.y
We also measured the decentralization of a
blockchain with Fairness and Entropy metrics. Fair-
ness metrics have been used extensively in resource
allocation in wireless networks. As the objective of a
consensus protocol in blockchain is to be fair among
the miners, we can use the Fairness index to quantify
decentralization (Gochhayat et al., 2020) as shown
below.
F(X) =
∑
N
i=1
p
i
2
N
∑
N
i=1
p
2
i
(6)
pi is the fraction of total blocks mined by a node
i and N is the number of miners. When a system is
completely distributed, when all pis are the same, the
fairness is 1. When it is completely central, the fair-
ness will be N1.
We can then calculate decentrality as normalized
fairness, i.e.,
NF(X ) =
F(X )−
1
N
1 −
1
N
(7)
When a system is completely distributed, the normal-
ized fairness is 1. When it is completely central, the
normalized fairness will be 0.
We used entropy as a metric to measure the ran-
domness in the selection of nodes. The amount of in-
formation from a source is the amount of uncertainty
that existed before the source released the information
(Gochhayat et al., 2020). In Blockchain systems, we
can estimate the probability that a miner will create
the next block based on its ability to add a block in
the past(Gochhayat et al., 2020). With respect to this
model, we can use Shannon’s entropy (Smith, 2011),
H(x), to quantify decentralization as,
H(X) =
N
∑
i=1
−p
i
log(p
i
) (8)
we can calculate normalized entropy as
d(X) =
H(X)
log
2
(N)
(9)
7 PERFORMANCE EVALUATION
We executed the coinage-based and hash power-based
consensus protocol in two scenarios - one where the
stakes are totally random among all the nodes and an-
other where a fixed group of nodes have higher stakes
than all others. The same software setup will be used
to run the blockchain with the coinage algorithm in
the two scenarios with the same set of transactions to
compare the two protocols.
Figure 5 represents a scatter plot of how both the
algorithms behaved in terms of the variable stakes
for node selection. We observed a slight improve-
ment in decentralization with our protocol, but the
overall trend was similar. In a scenario where a
group of nodes has higher stakes than others, our al-
gorithm performed noticeably well, as shown in fig-
ure 6. As the coinage algorithm selected nodes with
higher coinage values in descending order, we see pat-
terns of higher stakes selected across the elections of
the blockchain. Figure 6 also shows that our proto-
col does not have such patterns and is fairly random.
Since the validity of each stake expires after a cer-
tain period of time, the node selection is based on the
stake average over a certain range of stakes, which
increases the randomness of the protocol.
Figures 7, 8 display the selection metrics for all
nodes, showing the frequency with which each node
participated in block forging/validation in the sce-
nario where nodes are grouped by the number of
stakes deposited. The nodes colored in blue have
higher stakes than others, the red-colored nodes have
medium and reasonable amounts of stakes, and the
green-colored nodes have low stakes. Figure 7 shows
the participation opportunities are more equitably dis-
tributed than coinage protocol. However, when nodes
have significantly lower stakes than others in the net-
work, it is natural for any protocol to favor them less.
Figure 9 shows the CPU usage of the coinage-based
and hash power-based consensus protocols; they are
almost at the same level of consumption.
Randomizing Forger Selection to Improve Decentralization in Proof of Stake Consensus Protocol
265
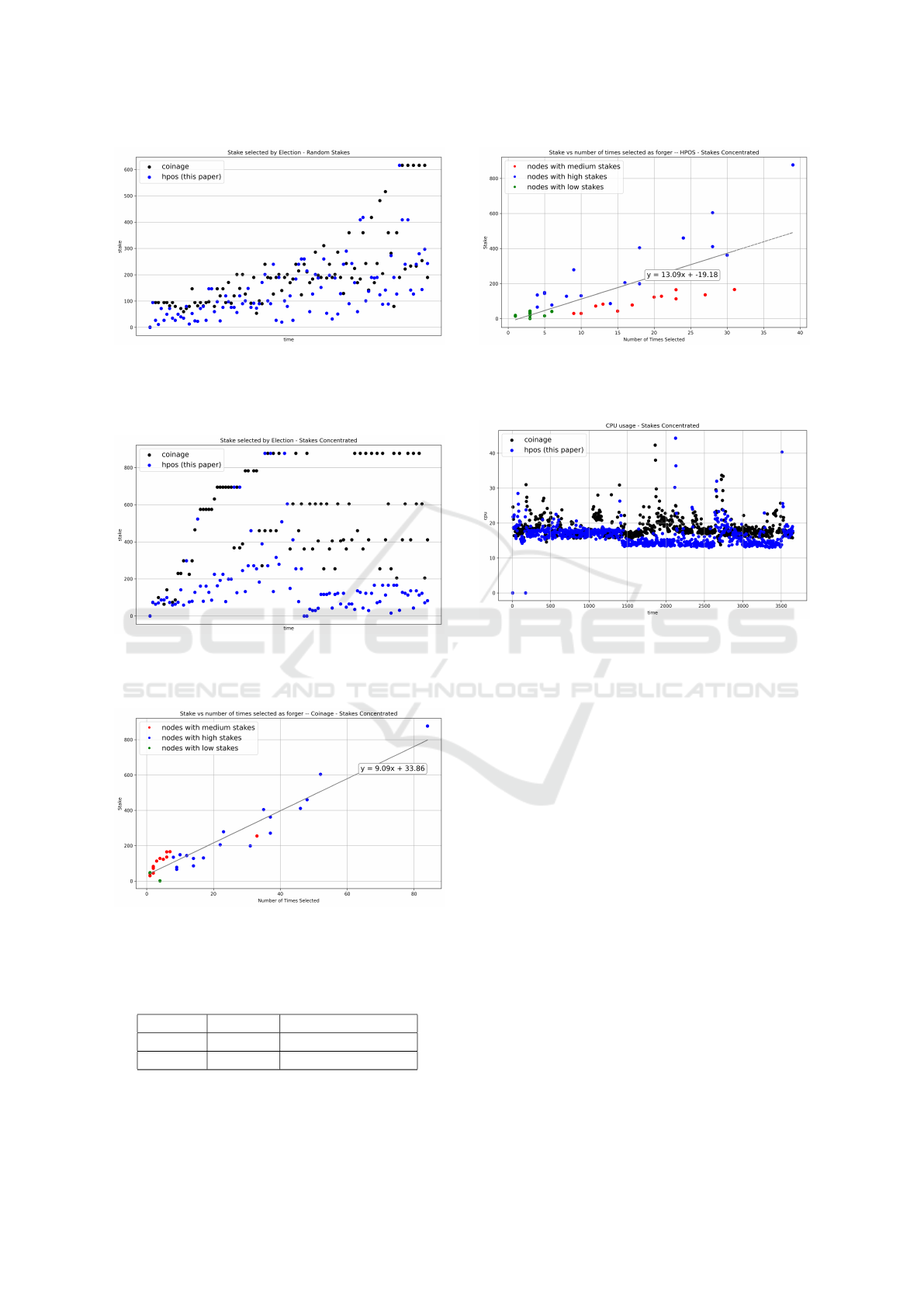
Figure 5: This graph plots the total unexpired stakes of the
nodes selected as forgers at every election. In this scenario,
the transactions and stakes are totally random among all
nodes.
Figure 6: This graph plots the total unexpired stakes of the
nodes selected as forgers at every election. In this scenario,
a few nodes have higher stakes than other nodes.
Figure 7: This graph plots the total number of times a node
with a certain stake was selected as a forger/validator with
the coinage algorithm.
Table 2: Fairness and Entropy metrics for Fig. 6.
Coinage HPOS(this paper)
Fairness 0.11 0.45
Entropy 0.51 0.80
Table 2 shows the fairness and entropy compari-
son of the hash power-based consensus protocol ver-
Figure 8: This graph plots the total number of times a node
with a certain stake was selected as a forger/validator with
the proposed algorithm.
Figure 9: This graph plots the CPU usage of both algo-
rithms. Since both algorithms have the same underlying
concept of Proof of Stake, there is not much difference in
CPU usage.
sus the Coinage protocol. The fairness factor in-
creased from 0.11 to 0.45, and entropy increased from
0.51 to 0.80 for hash power-based protocol compared
to the Coinage.
8 CONCLUSION
The proposed consensus protocol in this paper im-
proves the decentralization of stake-based consensus
protocols. The hash power-based algorithm discussed
in this paper enhances randomness and makes the pro-
tocol fairer. By considering timestamps and valid-
ity on the staked currencies, the protocol ensures that
wealthy nodes staking high amounts cannot influence
the network over time. However, evaluating the pro-
posed protocol at a larger scale, with more nodes, is
crucial to test the feasibility and requires further in-
vestigation. Moreover, the experiments conducted as-
sumed that all participating nodes were honest. Proof
of stake consensus mechanisms rely on a voting strat-
egy to validate a block’s authenticity to be added to
the blockchain. This makes the protocol susceptible
ICISSP 2025 - 11th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
266

to malicious or abstaining nodes in the system, as all
nodes are anonymous. Our future work aims to se-
cure the blockchain network from malicious nodes by
assessing node behavior and weighing the nodes ac-
cordingly to protect the validity of consensus.
REFERENCES
Algorand (2024). Pure proof of stake. https://developer.
algorand.org/docs.
Elastos (2024). Bonded proof of stake. https://elastos-wiki.
netlify.app/learn/mainchain/bpos/.
Gochhayat, S. P., Shetty, S., Mukkamala, R., Foytik, P.,
Kamhoua, G. A., and Njilla, L. (2020). Measuring de-
centrality in blockchain based systems. IEEE Access,
8:178372–178390.
Gurram, H. N., Mohamad, H., Sriram, A., and Endurthi, A.
(2023). A strategy to improvise coin-age selection in
the proof of stake consensus algorithm. In 2023 In-
ternational Conference on Software, Telecommunica-
tions and Computer Networks (SoftCOM), pages 1–4.
He, P., Tang, D., and Wang, J. (2020). Staking pool central-
ization in proof-of-stake blockchain network. ERN:
Other Game Theory & Bargaining Theory (Topic).
Hord (2024). Ethereum staking pools: The risks of lido’s
centralization. Accessed: 2024-11-20.
Khatoon, N., Rishu, R., Verma, S., and Pranav, P. (2024).
Proposing a modified proof of stake system to counter
51blockchain. In 2024 2nd International Conference
on Device Intelligence, Computing and Communica-
tion Technologies (DICCT), pages 01–04.
Kim, J., Oh, S., Kim, Y., and Kim, H. (2023). Improving
voting of block producers for delegated proof-of-stake
with quadratic delegate. In 2023 International Confer-
ence on Platform Technology and Service (PlatCon),
pages 13–17.
Lamriji, Y., Kasri, M., Makkaoui, K. E., and Beni-Hssane,
A. (2023). A comparative study of consensus algo-
rithms for blockchain. In 2023 3rd International Con-
ference on Innovative Research in Applied Science,
Engineering and Technology (IRASET), pages 1–8.
Li, A., Wei, X., and He, Z. (2020). Robust proof of stake:
A new consensus protocol for sustainable blockchain
systems. Sustainability, 12(7).
Maung Maung Thin, W. Y., Dong, N., Bai, G., and
Dong, J. S. (2018). Formal analysis of a proof-of-
stake blockchain. In 2018 23rd International Confer-
ence on Engineering of Complex Computer Systems
(ICECCS), pages 197–200.
Motepalli, S. and Jacobsen, H.-A. (2024). How does
stake distribution influence consensus? analyzing
blockchain decentralization. In 2024 IEEE Interna-
tional Conference on Blockchain and Cryptocurrency
(ICBC), pages 343–352. IEEE.
Nair, P. R. and Dorai, D. R. (2021). Evaluation of perfor-
mance and security of proof of work and proof of stake
using blockchain. In 2021 Third International Confer-
ence on Intelligent Communication Technologies and
Virtual Mobile Networks (ICICV), pages 279–283.
Nakamoto, S. (2008). Paper templates. In Bitcoin: A Peer-
to-Peer Electronic Cash System.
Pan, J., Song, Z., and Hao, W. (2021). Development in con-
sensus protocols: From pow to pos to dpos. In 2021
2nd International Conference on Computer Commu-
nication and Network Security (CCNS), pages 59–64.
Saad, M., Qin, Z., Ren, K., Nyang, D., and Mohaisen,
D. (2021). e-pos: Making proof-of-stake decentral-
ized and fair. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Dis-
tributed Systems, 32(8):1961–1973.
Saad, S. M. S. and Radzi, R. Z. R. M. (2020). Compar-
ative review of the blockchain consensus algorithm
between proof of stake (pos) and delegated proof of
stake (dpos). International Journal of Innovative
Computing, 10(2).
Smith, G. (2011). Quantifying information flow using min-
entropy. In 2011 Eighth International Conference on
Quantitative Evaluation of SysTems, pages 159–167.
Swan, M. (2015). Blockchain: Blueprint for a new econ-
omy. OReilly Media.
Tezos, O. (2024). Liquid proof of stake. https://opentezos.
com/tezos-basics/liquid-proof-of-stake#references.
Randomizing Forger Selection to Improve Decentralization in Proof of Stake Consensus Protocol
267
