
Toward a Quantum Fuzzy Approach for
Emotion Modeling in Parent-Child Interactivity
Cec
´
ılia Botelho
1 a
, Larissa Schonhofen
1 b
, Helida Santos
2 c
, Giancarlo Lucca
3 d
,
Adenauer Correa Yamin
1 e
and Renata Hax Sander Reiser
1 f
1
Federal University of Pelotas, LUPS, Pelotas, RS, Brazil
2
Federal University of Rio Grande, C3, Rio Grande, RS, Brazil
3
Catholic University of Pelotas, PGEEC, Pelotas, RS, Brazil
Keywords:
Quantum Computing, Fuzzy Systems, Emotion Modeling, Parent-Child Interaction, Qiskit.
Abstract:
This study presents an integrated framework combining Quantum Fuzzy computing concepts with emotion
modeling and simulations of intelligent agents. It explores the distinctions between Quantum Fuzzy and
Classical Computing, focusing on parent-child relationships. Simulations performed on the Qiskit platform
highlight significant differences in the results produced by these two approaches. The research emphasizes
how membership degrees(MD) are represented in the quantum circuit model by interpreting fuzzy operations
through unitary quantum transformations. Established fuzzy connectives, such as the exclusive OR, serve as
an algebraic basis for constructing quantum operators and circuit representations. The algorithms demonstrate
substantial potential for extension, allowing for modeling interactions among multiple agents using multi-
dimensional quantum registers. Simulations within Qiskit offer a solid foundation for implementing these
algorithms on real quantum platforms, paving the way for further exploration in this interdisciplinary field.
1 INTRODUCTION
Quantum Computing (QC) introduces a revolution for
solving classical complex problems, offering an expo-
nentially superior processing capability compared to
classical computers. Using qubits, the fundamental
units of information in quantum systems, this tech-
nology enables the simultaneous execution of multi-
ple entangled and parallel operations. Based on the
principles of Quantum Mechanics, such as entangle-
ment and superposition, quantum algorithms promise
to solve computational challenges more efficiently,
transforming sectors such as finance, logistics, and ar-
tificial intelligence.
Fuzzy Logic (FL) handles concepts beyond binary
values. By dealing with incomplete and imprecise
information, FL enables the manipulation of multi-
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2167-7139
b
https://orcid.org/0009-0003-8243-686X
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2994-2862
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3776-0260
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7333-244X
f
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9934-3115
valued fuzzy sets, reflecting the complexity of natu-
ral language. Flexible algorithms provide a gradual
representation of knowledge, facilitating flexibility in
decision-making processes, especially in expert sys-
tems where ambiguity and uncertainty are frequent.
These characteristics make fuzzy logic particularly
effective for modeling human emotional interactions,
as it captures the inherent ambiguity and fluidity of
emotions. Unlike binary models, which overly re-
duce emotions into fixed states, fuzzy logic represents
them as a continuum, allowing gradual transitions and
intertwined states such as apprehension, fear, or ter-
ror. This allows for a more refined approach to dy-
namic and context-dependent relationships. Conse-
quently, systems based on fuzzy rules promote the in-
terpretability of computational outcomes.
The quantum technology market is expanding,
with a projected compound annual growth rate of
25% between 2024 and 2034 (IDTechEx Research,
2023). This growth is driven by advancements in
three main areas: computing, sensors, and quantum
communications. The development of hardware for
quantum computing is expanding in research centers
and data centers, while quantum sensors are finding
Botelho, C., Schonhofen, L., Santos, H., Lucca, G., Yamin, A. C. and Reiser, R. H. S.
Toward a Quantum Fuzzy Approach for Emotion Modeling in Parent-Child Interactivity.
DOI: 10.5220/0013323700003890
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2025) - Volume 3, pages 1297-1303
ISBN: 978-989-758-737-5; ISSN: 2184-433X
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
1297

applications in sectors such as precision navigation
and medicine. In this context, the interrelationship
between quantum technologies, such as lasers, scan-
ners, and sensors, and quantum-fuzzy applications be-
comes evident.
Following recent scientific literature, we can ex-
plore the interaction between QC and FL. One ex-
ample is the fuzzy connectives modeling via the ex-
tension of quantum operators (de Avila et al., 2019).
Quantum implementations of fuzzy connectives us-
ing multi-qubit gates have also been investigated (Yo-
geesh et al., 2023), along with studies discussing the
use of quantum movements in representing emotions
in humanoid robots modeling (Deng et al., 2021). Ad-
ditionally, the concept of entropy has been applied
in the analysis of inference systems based on the
quantum-neuro-fuzzy perspective, demonstrating the
relevance of this approach for complex data analysis
related to emotion modeling (Ferreira and Almeida,
2020).
This work applies a Quantum Fuzzy strategy to
interpret family interactions, focusing on modeling
emotions through membership degrees represented by
the U quantum gate. To implement this approach, we
developed quantum circuits that utilize the principles
of superposition and entanglement in a quantum sim-
ulation environment. The simulations formally repre-
sent the membership values, reflecting the intensity of
the behaviors between the parent-child agents.
The paper is organized as follows: Section II ex-
plores the fundamental concepts of FL and how it re-
lates to quantum computing. In Section III, we dis-
cuss the modeling and simulation of emotions in fam-
ily dynamics using fuzzy logic applied to quantum
circuits. Section IV describes a case study that models
emotions in a family context. Lastly, we present the
final considerations and proposals for future research
in Section V.
2 PRELIMINARIES
2.1 Basic Concepts of Fuzzy Logic
FL is a mathematical extension of traditional Boolean
logic, providing a logical foundation for dealing with
imprecise or uncertain data. Fuzzy set theory gen-
eralizes the classical one, by smooth transitions be-
tween associated classes (Zadeh, 1965). Further-
more, their multivalued generalizations, later formal-
ized in (Zadeh, 1975), enabled new applications in
many fields.
Let U ̸=
/
0 be the universal set. Classical set the-
ory is based on the characteristic function f
A
: U →
{0,1}, where f
A
(x) = 1 if x ∈ A, and f
A
(x) = 0 if
x /∈ A, with U being the universal set. This function
associates each element x ∈U ̸=
/
0 with a value in the
discrete set {0,1}.
A fuzzy set A in U is characterized by the mem-
bership function f
A
: U →[0,1] where, for each x ∈U,
f
A
(x) indicates the MD of each element x in the fuzzy
set A.
A fuzzy set A in U can also be described as a set
of ordered pairs, where each element x ∈ U is asso-
ciated with its respective MD f
A
(x) ∈ [0,1], that is,
A = {(x, f
A
(x)) | x ∈ U}. Extending this context, a
multivalued fuzzy set can be defined by n-tuples in
the multivalued logic approach.
Let A and B be fuzzy sets in U ̸=
/
0, represented
by the membership functions f
A
, f
B
: U → [0,1], re-
spectively. Taking f
∪
, f
∩
: U → [0, 1], the union and
intersection between A and B are, respectively, given
as:
A∪B={(x, f
∪
(x)) |x ∈U}, f
∪
(x) =max{f
A
(x), f
B
(x)};
A∩B={(x, f
∩
(x)) |x ∈U}, f
∩
(x) =min{f
A
(x), f
B
(x)}.
The operators max,min : [0,1]
2
→ [0,1] represent
triangular norms and conorms and can be replaced by
other functions of the corresponding classes, as seen
in (Klement and Navara, 1999).
Moreover, according to (Bustince et al., 2003), let
f
A
′
: U → [0,1]. The fuzzy set A
′
expresses the fuzzy
complement of A in U considering the standard nega-
tion N
S
: [0,1] → [0,1] given by N
S
(x) = 1 −x, and is
defined by:
A
′
= {(x, f
A
′
(x)) |x ∈U }, and f
A
′
(x) = 1− f
A
(x).
A function E : [0,1]
2
→ [0, 1] is called exclusive
OR (or XOR) if, for all x,y ∈ [0, 1], it satisfies the
properties:
E1: E(0, 0) = E(1,1) = 0 and E(1,0) = E(0,1) = 1
(boundary conditions);
E2: E(x, y) = E(y,x) (symmetry);
E3: x ≤y ⇒E(0,x) ≤ E(0,y) (0-partial isotonicity);
E4: x ≤y ⇒E(1,x) ≥ E(1,y) (1-partial antitonicity).
Example 1. Let E
P
: [0,1]
2
→ [0,1] be the Xor class,
E
P
(x,y) = x + y −2xy, (1)
extending the binary classical operation expressed as
A ⊗B = (A ∪B) −(A ∩B).
An aggregation function A : [0,1]
2
→ [0,1] veri-
fies, for all x,y,x
′
,y
′
∈ [0,1], the following properties:
A1 A(0, 0) = 0 and A(1,1) = 1;
A2 x ≤ x
′
and y ≤ y
′
⇒ A(x, y) < A(x
′
,y
′
) (strict iso-
tonicity).
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
1298

Additional properties can also be demanded:
A3 A(x, y) = A(y,x) (symmetry);
A4 A(x, x) = x (idempotence);
A5 A(0, 1) =
1
2
;
A6 A(λx, λy) = λA(x,y), for all λ ∈[0, 1] (homogene-
ity);
A7 A(λ + x,λ + y) = λ + A(x, y) for all λ ∈[0, 1] (lin-
earity).
Example 2. The arithmetic mean, given by:
A(x,y) =
1
2
(x + y), (2)
verifies seven properties, from A1 to A7.
2.2 Basic Concepts of Quantum
Computing
In QC, the qubit is the basic unit of information,
defined by a two-dimensional unit state vector ψ =
(α,β)
t
, usually described in Dirac’s notation (Nielsen
and Chuang, 2000) by the expression: |ψ⟩ = α|0⟩+
β|1⟩, where the coefficients α and β are complex
numbers corresponding to the amplitudes of their re-
spective states, satisfying the normalization condition
|α|
2
+ |β|
2
= 1. So, it ensures the system’s state vec-
tor, represented by (α, β)
t
, is unitary. The amplitudes
configure a state of quantum superposition, giving
rise to the phenomenon of quantum parallelism.
The state space of a multidimensional quantum
system is obtained by the tensor product of the state
spaces of its component systems. Considering a quan-
tum system of two qubits, |ψ⟩ = α
1
|0⟩+ β
1
|1⟩ and
|ϕ⟩ = α
2
|0⟩+ β
2
|1⟩, the related state space is com-
posed by the tensor product:
|ψ⟩ ⊗ |ϕ⟩ = α
1
α
2
|00⟩ + α
1
β
2
|01⟩ + β
1
α
2
|10⟩ +
β
1
β
2
|11⟩.
A state change in a quantum system is performed
via a unitary quantum transformation (QT), repre-
sented by orthogonal square matrices of order 2
N
,
where N is the number of qubits in the transformation.
Taking θ ∈ [0,
π
2
], λ,φ ∈ [0, 2π], an one-dimensional
QT is represented by:
F =
cos
θ
2
−e
iλ
sin
θ
2
e
iφ
sin
θ
2
e
i(φ+λ)
cos
θ
2
. (3)
In particular, when θ =
π
2
, λ = π, and φ = 0, then
F = H, known as the Hadamard gate. The application
of the unitary gate H ⊗H on a classical state |01⟩ gen-
erates a superposition state mathematically described
by:
H⊗H|01⟩=
1
√
2
1 1
1 −1
⊗
1
√
2
1 1
1 −1
|01⟩=
1
2
1
−1
1
−1
.
And when θ = λ = φ = 0, then F = Id represents
the Identity. Furthermore, when θ = π, λ = π, and
φ = 0, then F = X represents the Not gate, referred to
as the Pauli X gate. Additionally, let j =
√
−1 be the
imaginary unit. The QT associated with the quantum
gate V qubit (
√
X) is given by the matrix expression:
V =
1
2
1 + j −1 + j
−1 + j 1 + j
.
The evident exponential growth in the spatial and
temporal complexity of quantum algorithms justifies
the use of simulators to assist in the interpretation and
perform computed algorithms.
The amplitudes of multidimensional quantum
states are governed by the normalization condition,
which is not always achieved through the tensor prod-
uct of the corresponding states of the qubits (the basic
states of the computational basis). In this case, we
have an entangled state (Nielsen and Chuang, 2000).
For a characterization of two-dimensional entan-
gled states, we consider the classical states |00⟩, |01⟩,
|10⟩, and |11⟩ as basic vectors of a two-dimensional
quantum state. The entangled states are the lin-
ear combinations |s
′
⟩ = α
1
|00⟩+ β
1
|11⟩ and |s
′′
⟩ =
α
2
|01⟩+ β
2
|10⟩, with α
1
,β
1
,α
2
,β
2
being normalized
complex amplitudes and α
2
1
+ β
2
1
= α
2
2
+ β
2
2
= 1.
Example 3. The composition of one entangled state
with another generates a new entanglement. See, e.g.,
the three-dimensional quantum state |s
γ
⟩, given as:
|s
γ
⟩ = |s
′
⟩⊗
√
2
2
(|0⟩+ |1⟩)
!
.
So, the entangled qubits are intertwined in such
a way that their individual properties cannot be de-
scribed independently. When an entangled qubit is
subjected to a measurement and its state is deter-
mined, the state of the other entangled qubit is in-
stantly affected, regardless of the distance between
them, known as the “spooky action at a distance”.
The measurement operation on the current state of
a quantum system is defined by a set of linear projec-
tions M
m
, acting on the quantum states (Nielsen and
Chuang, 2000). Let the state be given by |ψ⟩. After
the measurement, the output probability is given by:
p(|ψ⟩) =
M
m
|ψ⟩
q
⟨ψ|M
†
m
M
m
|ψ⟩
.
The measurement operations satisfy the complete-
ness relation given as:
∑
m
M
†
m
M
m
= I. In one-
dimensional systems, we have:
M
0
=
1 0
0 0
= M
†
0
; and M
1
=
0 0
0 1
= M
†
1
.
Toward a Quantum Fuzzy Approach for Emotion Modeling in Parent-Child Interactivity
1299

For a qubit |ψ⟩, with α,β ̸= 0, we observe proba-
bilities to measure |0⟩ and |1⟩, resulting in:
• p(|0⟩) = ⟨φ|M
†
0
M
0
|φ⟩ = ⟨φ|M
0
|φ⟩ = |α|
2
.
• p(|1⟩) = ⟨φ|M
†
1
M
1
|φ⟩ = ⟨φ|M
1
|φ⟩ = |β|
2
.
Therefore, after measuring the |ψ⟩ state, we have
|α|
2
as the probability of being in the classical state
|0⟩; and |β|
2
as the probability of being in the other
state, |1⟩.
The Parent-Child algorithm is based on the QC
Model, considering sequential composition. In this
quantum context, the significance of superposition
and entanglement in the representation and the par-
ents’ dynamics of emotions will be discussed. Ad-
ditionally, we will address the implementation of its
quantum circuits using the Qiskit framework, which
is integrated with the Python programming language,
simulating and executing quantum circuits.
Next, we will describe the case study.
3 EMOTION MODELING VIA
QUANTUM FUZZY APPROACH
This section discusses the theoretical foundation from
previous sections for simulating fuzzy systems that
represent the modeling of emotions of effective agents
using quantum computing. The Parent-Child case
study exemplifies this methodology. The principles
of quantum computing, such as superposition and en-
tanglement, are considered to model and analyze such
complex emotions, considering interpretations of un-
certainty through the application of fuzzy logic.
Let U be a universe with cardinality ∥U∥ = n de-
fined in the set of the first natural numbers in N ,
N = {1, 2,. ..,n}. For each element x
i
, we can as-
sociate its MD f
A
(x
i
) and non-membership degree
1 − f
A
(x
i
) to a one-dimensional quantum register ob-
tained from the following superposition state:
|S
f
A
(x
i
)
⟩ = |X
i
⟩ = [
p
f
A
(x
i
)|1⟩+
p
1 − f
A
(x
i
)|0⟩].
(4)
Thus, applying the tensor product, a n-
dimensional quantum state (n-qubits) represents
all the elements x
i
. Let U ̸=
/
0,|U | = n and let A
be a fuzzy set defined by the membership function
f
A
: U → [0,1]. For each x
i
∈ U, a n-dimensional
fuzzy state is given by the expression:
|S
f
A
(x
i
)
⟩ =
O
1≤i≤n
[
p
f
A
(x
i
)|1⟩+
p
1 − f
A
(x
i
)|0⟩].
Highlighting the differences in relation to non-
classical correlations, we can explore the emotional
correlations, applying quantum states and operators.
This research explores the emotion intensities,
expanding on the ideas seen in (Raghuvanshi and
Perkowski, 2010). The angle of the qubit is illus-
trated as meridians in the Bloch sphere (Nielsen and
Chuang, 2000) and the intensity of the emotion is
shown as a point between the north and south poles,
|0⟩and |1⟩. We consider fuzzy interpretations to illus-
trate different types and intensities of emotions, such
as the joy variable, which varies from serenity (low)
to ecstasy (high).
Example 4. In Eq. (3), if λ = π, φ = 0 and
θ = 2arc tan
p
f
A
(x
i
)
p
1 − f
A
(x
i
)
!
,
we have the QT F is given as given by
F
A
=
p
1 − f
A
(x
i
)
p
f
A
(x
i
)
p
f
A
(x
i
)
p
1 − f
A
(x
i
)
, (5)
verifying the following properties:
• F
†
A
= F
−1
A
= F
A
;
• F
A
|0⟩ =
p
1 − f
A
(x
i
)|0⟩+
p
f
A
(x
i
)|1⟩;
• F
A
|1⟩ =
p
f
A
(x
i
)|0⟩−
p
1 − f
A
(x
i
)|1⟩;
• f
A
(x
i
) = 1 ⇒ F
A
= X;
• f
A
(x
i
) =
1
2
⇒ F
A
= H.
The Parent-Child (PC) algorithm is graphically
represented by a quantum circuit considering the se-
quential composition of unitary transformations per-
forming superpositions and entanglements to repre-
sent the dynamics of emotional modeling. Addition-
ally, we analyze the implementation of its quantum
circuits using the Qiskit platform, exploring its fea-
tures in Python library for designing, simulating, and
executing quantum circuits.
4 CASE STUDY:
PC-INTERACTIVITY
The PC-problem models the mood change of a child
based on the level of interactivity of their parents. If
both caregivers are interactive, the child will also be
happy. In other cases, the child will be in a “half
happy” and “half unhappy” state, interpreted as a su-
perposition state
1
√
2
(|0⟩+ |1⟩).
The Parent-Child algorithm in (Raghuvanshi and
Perkowski, 2010) is based on the QC model, where
the emotion intensity is modeled as projections on the
Bloch Sphere (Nielsen and Chuang, 2000), a stereo-
graphic representation of qubits, given by a point be-
tween the north and south poles, representing |0⟩ and
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
1300

|1⟩, respectively. Thus, the type of emotion is mod-
eled by the phase angle of the related qubit, geomet-
rically represented by meridians on the Bloch Sphere.
The most positive emotional activity is at |1⟩, and at
|0⟩, the least positive.
In this work, a general interpretation of the Parent-
Child algorithm based on fuzzy aggregations extends
this interpretation to multiple agents, modeling more
complex interactions within the family structure and
considering, e.g., a stepfather and a stepmother.
Figure 1: Fuzzy Modeling Circuit of the Parent-Child Inter-
activity.
Fig. 1 describes the C1 circuit and presents the
fuzzy approach based on f
A1
and f
A2
membership
functions, respectively modeled by F
A
1
and F
A
2
quan-
tum gates, given as matrices obtained from Eq. (5)
that consider controlled gates based on the “Square
Root of the Not” gate V =
√
X.
The sequential composition via controlled opera-
tors includes the following description:
• CV
2
3
, which executes the operator
√
X (V) on the
3
rd
qubit (target) when the 2
nd
qubit is in state |1⟩;
and
• CV
1
3
, which executes the operator
√
X (V) on the
3
rd
qubit when the 2
nd
qubit is in state |1⟩.
Now, the emotional modeling based on a fuzzy ag-
gregation function is formalized in the next proposi-
tion.
Proposition 1. The fuzzy arithmetic mean provides a
behavioral interpretation for the C1 circuit in Fig. (1).
Proof. Consider the fuzzy arithmetic mean opera-
tor, as given by Eq. (2). When f
A
1
(x
1
) = x
1
and
f
A
1
(x
2
) = x
2
, we have F
A
1
|0⟩ =
√
1 −x
1
|0⟩+
√
x
1
|1⟩
and F
A
2
|0⟩ =
√
1 −x
2
|0⟩+
√
x
2
|1⟩. Additionally, tak-
ing x
1
+ x
2
̸= 0 and S
1
= (F
X
1
⊗ F
X
1
⊗ Id)(|X
1
⟩ ⊗
|X
2
⟩⊗|0⟩) as given by Eq. (4), the resulting entan-
gled state S
4
, obtained from the temporal evolution, is
summarized as follows:
S
4
=(M
3
1
⊗C
V
1
3
⊗C
V
2
3
)(S
1
)
=
j−1
p
2(x
1
+x
2
)
p
(1−x
1
)x
2
|011⟩+
j−1
p
2(x
1
+x
2
)
p
(1−x
2
)x
1
|101⟩+
−
√
x
1
x
2
p
2(x
1
+x
2
)
|111⟩ and p
C
2
1
=
x
1
+ x
2
2
.
(6)
Thus, based on the algebraic expressions extracted
from the qFuzzyAnalyser Library (Buss et al., 2024)
and, related to the above measurement, the results
promote the quantum-fuzzy interpretation via the
arithmetic mean, as given by Eq. (2). Thus, inde-
pendently from the membership functions attributions
F
A
1
and F
A
2
, it is interpreted by the quantum gate
given by the M
3
1
(C
V
1
3
⊗C
V
2
3
) composition.
Therefore, the probability of the child’s behavior
changing from |0⟩ to |1⟩ is given by the arithmetic
mean performed by the intensity of the behaviors be-
tween the parents-child agents.
4.1 Classical PC-Interactivity
Table 1 presents an analysis based on classical inputs,
fixing the 3
rd
qubit as |0⟩. In addition, S
0
= S
1
since
F
A1
= F
A2
= Id. Note that the first two qubits, repre-
senting the parents’ mood, do not change during the
evolution from S
0
to S
4
. Furthermore, measuring the
3
rd
qubit (related to the child’s mood) the following
holds:
• In the first row, MD f
A
(x
1
) = f
A
(x
2
) = 0 return the
same initial classical states, with probability p = 0
for the 3
rd
qubit in |1⟩. In these cases, the circuit
interpretation guarantees that, like the parents, the
child’s mood remains in |0⟩;
• In the last row, interpreting the parents’ happy at-
titude as f
A
(x
1
)= f
A
(x
2
)=1 results in a change in
the child’s emotional behavior, from unhappy to
happy;
• In the other rows, modeling only one of the par-
ents as happy, the measure of the 3
rd
qubit always
returns a state in superposition, with probability
p = 0.5 to evaluate whether the child maintains
the same mood or experiences a mood change.
Table 1: Temporal Evolution for the Classical Parent-
Child Interactivity.
S
1
S
2
S
3
S
4
|000⟩ |000⟩ |000⟩ p=0, S
f
=|001⟩
|010⟩
j+1
2
|010⟩+
j−1
2
|011⟩
j+1
2
|010⟩+
j−1
2
|011⟩ p=
1
2
, S
f
=|011⟩
|100⟩ |100⟩
j−1
2
|100⟩+
j+1
2
|101⟩ p=
1
2
, S
f
=|101⟩
|110⟩ |111⟩ |110⟩ p=1, S
f
=|111⟩
So, in the emotion modeling of parent-child in-
teraction as described in Fig. (1), the parent’s happi-
ness influences the child to become (or remain) happy.
However, this influence on mood change is not ev-
ident when both parents are unhappy. Whenever at
least one of them is happy, there is a 50% chance of
changing the child’s mood, either to a happy mood
(proactive attitude) or to an unhappy one (passive at-
titude).
Toward a Quantum Fuzzy Approach for Emotion Modeling in Parent-Child Interactivity
1301
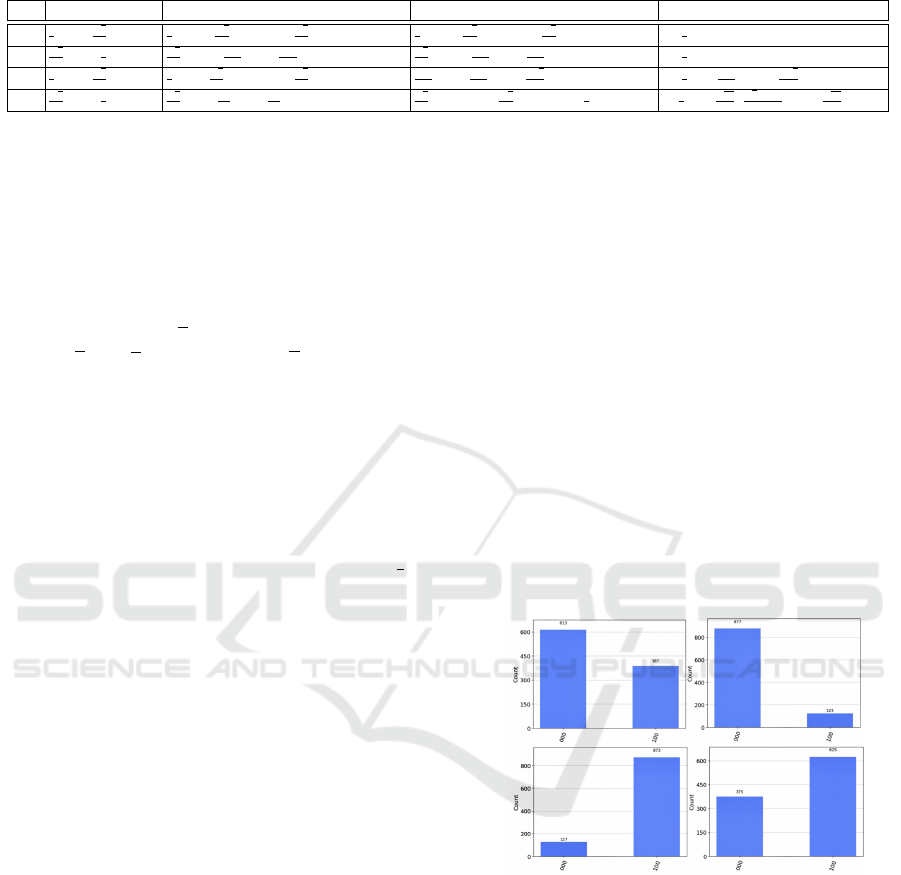
Table 2: Temporal Evolution of the Fuzzy Model of the Parent-Child Interactivity.
S
0
S
1
S
2
S
3
S
4
|000⟩
1
2
|000⟩+
√
3
2
|010⟩)
1
2
(|000⟩+
√
3
4
( j+1)|010⟩+
√
3
4
( j−1)|011⟩)
1
2
(|000⟩+
√
3
4
( j−1)|010⟩+
√
3
4
( j+1)|011⟩) p=
3
8
, S
f
=|011⟩
|010⟩
√
3
2
|000⟩+
1
2
|001⟩
√
3
2
(|000⟩−
j−1
4
|010⟩+
j−1
4
|011⟩)
√
3
2
(|000⟩−
j−1
4
|010⟩+
j−1
4
|011⟩) p=
1
8
, S
f
=|011⟩
|100⟩
1
2
|100⟩+
√
3
2
|110⟩)
1
2
|100⟩+
√
3
4
( j+1)|110⟩+
√
3
4
( j−1)|111⟩
j+1
4
|100⟩+
j−1
4
|101⟩+
2
√
3
4
|111⟩ p=
7
8
, S
f
=
j−1
4
|101 +
2
√
3
4
|111⟩
|110⟩
√
3
2
|100⟩+
1
2
|110⟩
√
3
2
|100⟩+
j+1
4
|110⟩+
j−1
4
|111⟩)
√
3
4
( j+1)|100⟩+
√
3
4
( j−1)|101⟩+
1
2
|111⟩) p=
5
8
, S
f
=
√
10
5
(
√
3( j−1)
2
|101⟩+
√
10
5
|111⟩)
4.2 Fuzzy PC-Interactivity: Algebraic
Discussion
In this case study, we consider quantum-fuzzy inputs
for one of the parents interpreted by the 2
nd
qubit. The
other agents, related to the qubits 1 and 3, remain in
the classical state |0⟩. Therefore, we consider F
A1
=
Id and
F
A2
=
1
2
1
√
3
√
3 −1
(θ = 2
π
3
rad = 120
◦
).
Table 2 summarizes the results of the Parent-Child
interactivity. In this case study, the resulting prob-
ability of a single measurement on the 3
rd
qubit in
|1⟩, according to the algebraic expression presented
in Eq. (6), results in the following interpretations:
• In the 1
st
row, when the input variable received
MD f
A
(x
1
) = 0 and f
A
(x
2
) = 0.75, the output vari-
able received a membership degree f
B
(y) =
3
8
=
0.375;
• In the 2
nd
row, when the input variable received
MD f
A
(x
1
) = 0 and f
A
(x
2
) = 0.25, the output
variable received the lowest membership degree:
f
B
(y) = 0.125;
• In the 3
rd
row, MD f
A
(x
1
) = 1, and f
A
(x
2
) = 0.75
returning the highest MD f
B
(y) = 0.875;
• And finally, in the last row, the input variable re-
lated to MD f
A
(x
1
) = 1 and f
A
(x
2
) = 0.25, implies
a MD f
B
(y) = 0.625 for the output variable.
The probability distributions seen earlier can also
be obtained through simulations on the Qiskit plat-
form, as shown in the histograms in Fig. 2. Observe
that the best option for changing the child’s mood is
related to the highest degree of the parents in the fuzzy
set, interpreting happiness as the linguistic variable.
4.3 Fuzzy PC-Interactivity: Qiskit
Simulations
The histograms in Fig. 2 illustrate the simulation via
quantum-fuzzy inputs related to the execution of the
quantum circuit. These histograms report results from
Table 2, analyzing the temporal evolution of the fam-
ily dynamics for the four initial states, and the 3
rd
qubit as |0⟩.
The X-axis of the histogram depicts the possible
states of the three qubits after executing the circuit
and measurement. The Y-axis indicates the frequency
of each state, based on a total of 1000 circuit execu-
tions. The frequencies of the |110⟩ and |010⟩ states
are particularly important for our analysis, as they re-
flect distinct scenarios within the family dynamic in
question.
The third qubit starts in the |0⟩ state in the pre-
sented scenarios. The first row of Table 2 corresponds
to the first histogram. After executing the circuit, the
child represented by the third qubit becomes happy
387 times and remains in the initial mood 613 times.
In the second histogram, the child becomes happy 123
times and remains sad 877 times. In the third his-
togram, the child changes the mood 873 times and
stays in the initial state 127 times. Finally, the child’s
mood changes 625 times while keeping it 375 times.
These simulations suggest that happy parents can in-
fluence the child to become or remain satisfied.
Figure 2: Histogram: Fuzzy Approach to the Parent-Child
Interactivity.
5 FINAL CONSIDERATIONS
Based on algebraic expressions integrating fuzzy con-
nectives, including the fuzzy exclusive “or” and fuzzy
arithmetic means, we focused on the parent-child
dilemma as a simple case to investigate the applica-
tion of a generalized quantum gate in the quantum-
fuzzy context. This allows more precise in the model-
ing three agents’ emotions, in a 3-dimensional quan-
tum system.
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
1302

The simulation conducted on the Qiskit platform
revealed distinct patterns in the probability distribu-
tions, providing perceptions of the emotional dynam-
ics of family interactions. Additionally, the imple-
mentation of fuzzy operators, considering the model
of Quantum Circuits, emphasizes the importance of
superposition and entanglement in the emotional rep-
resentation.
The quantum approach refines the modeling of
interactions between multiple agents. The analysis
of the histograms obtained during the simulation al-
lowed valuable insights into the applicability of quan-
tum computing to tackle complex real-world prob-
lems, especially in the modeling of emotions. Fu-
ture works may explore the fundamentals of quantum-
fuzzy theory in modeling emotions for human-like be-
havior in future intelligent robots. Moreover, the re-
sults can be extended for new research based on data
fusion for artificial intelligent systems (Tiwari et al.,
2024).
Expanding the dimensional model, the natural lan-
guage related to emotional and social contexts can
also essentially improve their practical applicability
on real systems. Besides, applying quantum neural
networks (QNN) and transferring the simulations per-
formed in Qiskit to real quantum hardware (as the
IBM quantum platform) is the next research step, val-
idate our Quantum Fuzzy models in real-world sce-
narios. Thus, when more agents are involved, like
restructured families (stepfather/stepmother and half
brothers/systems) and the Parent-Children Interactive
model will involve more than three agents, justify the
use of quantum simulators. So, further work based
on emerging technologies and combining the poten-
tials of QC and FL, can model emotions collaborates
in relevant scenarios as affective computing, social
robotics, and neurorobotics research areas.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors thank the funding agencies:
CAPES, CNPq (309160/2019-7; 311429/2020-
3, 150160/2023-2), PqG/FAPERGS (21/2551-
0002057-1), FAPERGS/CNPq (23/2551-
0000126-8), and PRONEX (16/2551-0000488-9).
\section*{ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS}
REFERENCES
Buss, J., Novack, B., Botelho, C., Santos, H., Lucca, G.,
Cruz, A., Yamin, A., and Reiser, R. (2024). Fusion
data on fuzzy modality: From algebraic interpreta-
tions to quantum simulations via qiskit platform. In
Lesot, M.-J., Vieira, S., Reformat, M. Z., Carvalho,
J. P., Slezak, D., Batista, F., Bouchon-Meunier, B.,
and Yager, R. R., editors, Information Processing and
Management of Uncertainty in Knowledge-Based Sys-
tems - 20th Int. Conference, IPMU 2024, Lisbon, Por-
tugal, July 22-26, 2024, Proceedings, volume 1176 of
Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, pages 1–6.
Springer.
Bustince, H., Burillo, P., and Soria, F. (2003). Automor-
phisms, negations and implication operators. Fuzzy
Sets Syst., 134(2):209–229.
de Avila, A. B., Reiser, R., Pilla, M. L., and Yamin, A. C.
(2019). Interpreting Xor intuitionistic fuzzy connec-
tives from quantum fuzzy computing. In Guerv
´
os, J.
J. M., Garibaldi, J. M., Linares-Barranco, A., Madani,
K., and Warwick, K., editors, Proc. of the 11th Intl
Joint Conf. on Comp. Intelligence, 2019, Vienna,
pages 288–295. ScitePress.
Deng, R., Huang, Y., and Perkowski, M. A. (2021). Quan-
tum motions and emotions for a humanoid robot actor.
In 51st IEEE International Symposium on Multiple-
Valued Logic, ISMVL 2021, Nur-Sultan, Kazakhstan,
May 25-27, 2021, pages 207–214. IEEE.
Ferreira, A. B. and Almeida, J. M. (2020). Entropic mea-
sures for quantum-neuro fuzzy inference systems.
IDTechEx Research (2023). Quantum technology
market 2024-2034: Trends, players, forecasts.
Available: https://www.idtechex.com/en/research-
report/quantum-technology-market-2024-2034-
trends-players-forecasts/1005. Accessed on Oct. 13,
2024.
Klement, E. P. and Navara, M. (1999). A survey on different
triangular norm-based fuzzy logics. Fuzzy Sets and
Systems, 101(2):241–251.
Nielsen, M. A. and Chuang, I. L. (2000). Quantum Compu-
tation and Quantum Information. Cambridge Univer-
sity Press.
Raghuvanshi, A. and Perkowski, M. (2010). Fuzzy quantum
circuits to model emotional behaviors of humanoid
robots. In IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Compu-
tation, pages 1–8.
Tiwari, P., Zhang, L., Qu, Z., and Muhammad, G. (2024).
Quantum fuzzy neural network for multimodal sen-
timent and sarcasm detection. Information Fusion,
103:102085.
Yogeesh, N., Girija, D. K., Rashmi, M., and Divyashree,
J. (2023). Quantum implementation of fuzzy logic
conjunction and disjunction using multi-qubit gates.
In European Chemical Bulletin, vol. 12, no. 05, pp.
1795–1805.
Zadeh, L. A. (1965). Fuzzy sets. Inf. Control., 8(3):338–
353.
Zadeh, L. A. (1975). The concept of a linguistic variable
and its application to approximate reasoning - I. Inf.
Sci., 8(3):199–249.
Toward a Quantum Fuzzy Approach for Emotion Modeling in Parent-Child Interactivity
1303
