
Qandle: Accelerating State Vector Simulation Using Gate-Matrix
Caching and Circuit Splitting
Gerhard Stenzel
a
, Sebastian Zielinski, Michael K
¨
olle, Philipp Altmann, Jonas N
¨
ußlein
and Thomas Gabor
LMU Munich, Munich, Germany
fi
Keywords:
Quantum Computing, Quantum Machine Learning, State Vector Simulation, Hybrid Machine Learning,
Quantum-Classical Machine Learning, PyTorch.
Abstract:
To address the computational complexity associated with state-vector simulation for quantum circuits, we
propose a combination of advanced techniques to accelerate circuit execution. Quantum gate matrix caching
reduces the overhead of repeated applications of the Kronecker product when applying a gate matrix to the
state vector by storing decomposed partial matrices for each gate. Circuit splitting divides the circuit into
sub-circuits with fewer gates by constructing a dependency graph, enabling parallel or sequential execution
on disjoint subsets of the state vector. These techniques are implemented using the PyTorch machine learning
framework. We demonstrate the performance of our approach by comparing it to other PyTorch-compatible
quantum state-vector simulators. Our implementation, named Qandle, is designed to seamlessly integrate with
existing machine learning workflows, providing a user-friendly API and compatibility with the OpenQASM
format. Qandle is an open-source project hosted on GitHub and PyPI.
1 INTRODUCTION
Quantum machine learning (QML) is a rapidly ex-
panding field that aims to combine the computational
power of quantum computing with the flexibility and
scalability of classical machine learning algorithms
(Nielsen and Chuang, 2001; K
¨
olle et al., 2024; Stam-
atopoulos et al., 2020; Zoufal et al., 2019). In re-
cent years, machine learning has gained significant
popularity and has been widely applied in various do-
mains, including image and speech recognition, nat-
ural language processing, and recommendation sys-
tems. These applications often rely on deep learning
models, which are trained on large datasets using sub-
stantial computational resources (Cerezo et al., 2021;
Farhi et al., 2022; Rebentrost et al., 2014; Schuld and
Petruccione, 2021; Bauckhage et al., 2022; Nielsen
and Chuang, 2001).
Quantum machine learning seeks to harness the
potential of quantum computing to solve complex op-
timization problems currently intractable for classical
computers. By doing so, it offers a novel approach
to addressing intricate challenges in machine learn-
ing and other disciplines (Nielsen and Chuang, 2001).
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0009-0280-4911
However, existing quantum hardware still faces sev-
eral limitations, such as hardware noise without suffi-
cient error mitigation and correction (Preskill, 2018),
limited qubit connectivity (Wang et al., 2022), and
a restricted number of qubits. These limitations im-
pact the real-world performance of quantum machine
learning algorithms and models.
To overcome these challenges, hybrid quantum-
classical machine learning models have been devel-
oped. These models consist of classical and quan-
tum layers, enabling training on either real hardware
(with reduced noise impact due to their smaller scale)
or simulators (Schuld and Petruccione, 2021). These
simulators, which run on classical hardware such as
CPUs or GPUs, are used to mimic the behavior of
quantum circuits. They facilitate the rapid develop-
ment and training of quantum machine learning mod-
els (Preskill, 2018).
The classical simulation of quantum circuits plays
a crucial role in the development and testing of quan-
tum machine learning models. Although the ulti-
mate goal is to utilize quantum hardware to exploit
quantum mechanical advantages, the current limita-
tions of quantum computers make classical simula-
tion an indispensable tool. It allows researchers to de-
sign, debug, and optimize quantum circuits in a con-
Stenzel, G., Zielinski, S., Kölle, M., Altmann, P., Nüßlein, J. and Gabor, T.
Qandle: Accelerating State Vector Simulation Using Gate-Matrix Caching and Circuit Splitting.
DOI: 10.5220/0013343500003890
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2025) - Volume 1, pages 715-723
ISBN: 978-989-758-737-5; ISSN: 2184-433X
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
715

trolled environment. Moreover, simulators facilitate
the integration of quantum layers into classical ma-
chine learning models, enabling hybrid approaches
that can be experimentally explored even when the
use of quantum hardware is not accessible or prac-
tical. Thus, classical simulation serves as a valuable
means to advance research in quantum machine learn-
ing despite the challenges of implementing it on real
quantum computers.
As the computational complexity of quantum cir-
cuits increases exponentially with the number of
qubits, the efficient performance of simulators plays a
crucial role in advancing quantum machine learning.
This paper introduces two novel methods, namely
quantum gate matrix caching and circuit splitting,
to accelerate the execution of quantum circuit sim-
ulation. We implement these methods in Qandle, a
state-vector simulator we specifically designed for hy-
brid quantum-classical machine learning applications
in conjunction with the widely adopted PyTorch li-
brary. Through a comparative analysis with existing
PyTorch-compatible quantum state-vector simulators,
Qandle demonstrates superior performance in terms
of execution time and memory usage.
Our contributions are
1. the introduction of two novel methods, namely
gate matrix caching and circuit splitting,
2. the implementation of these methods in a new
simulator and
3. a performance comparison to existing approaches.
This paper is structured as follows: in Section 2,
we introduce the required symbols and background.
In Section 3, we analyze related work and elab-
orate our contribution. We then present our pro-
posed performance enhancing techniques of gate ma-
trix caching and circuit splitting in Section 4 and eval-
uate their implementation in Section 5. Our conclu-
sion can be found in Section 6.
2 PRELIMINARIES
2.1 Symbols
In this paper, we adopt the most significant bit first
(MSb 0) notation for representing quantum states.
Under this notation, the state |0000⟩ corresponds to
all qubits being in the state 0, while the state |0001⟩
represents all qubits being in the state 0 except for
the last qubit, which is in the state 1. This notation
allows for a consistent and unambiguous representa-
tion of quantum states throughout our analysis. Other
symbols used include S for the state vector of |ϕ⟩, W
the total number of qubits, w is the current qubit. R
d
is the (matrix representation of the) gate for a rotation
around axis d, and R
d
the matrix representation of R
d
on W qubits.
2.2 State Vector Simulation
The quantum state |ϕ⟩ of a system with W qubits can
be represented as a vector of size 2
W
. This vector
contains the complex probability amplitudes of each
of the 2
W
possible states, ranging from |00 ... 0⟩ to
|11. ..1⟩. Thus, it fully describes the system’s state at
any given time.
Quantum gates, represented by unitary matrices,
are applied to the quantum state to transform it. On
real quantum hardware, the state vector is not directly
accessible. Instead, it can be inferred from the proba-
bilistic measurement results of the quantum system.
However, these measurements only provide an ap-
proximation of the state vector due to the inherent
noisiness of the hardware in the NISQ era (Preskill,
2018; Nielsen and Chuang, 2001).
In contrast, simulators that work with the full state
vector can provide the exact state of the system at any
given time. However, these simulators face a chal-
lenge when dealing with large circuits due to the ex-
ponential growth of the state vector with the number
of qubits. Due to their deterministic nature, simula-
tors excel in building, debugging, and training varia-
tional quantum circuits.
2.3 Hybrid Machine Learning
In the context of quantum machine learning, hybrid
machine learning refers to integrating classical and
quantum machine learning algorithms. This integra-
tion can be achieved by incorporating trainable quan-
tum circuits into larger machine learning models or
by applying classical machine learning techniques to
optimize quantum circuits.
Typically, quantum models in this context take the
form of quantum variational circuits, which consist of
several groups of gates:
1. Embedding layers, which encode classical data
into the quantum state of the circuit. Different
embedding methods offer varying trade-offs be-
tween the expressiveness of the quantum state and
the number of required qubits. Some circuit archi-
tectures employ ”data re-uploading” techniques to
enhance the expressiveness of the quantum state
by embedding the same data points at multiple lo-
cations within the circuit, effectively reinforcing
the circuit’s memory of the input data.
QAIO 2025 - Workshop on Quantum Artificial Intelligence and Optimization 2025
716

2. Trainable layers, which are parameterized gates
whose parameters serve as the trainable weights
of the quantum model. These parameters, often
represented as angles of rotational gates, can be
optimized using classical optimization algorithms
such as gradient descent or its variants.
3. Measurement layers, which extract relevant infor-
mation encoded in the quantum state and map it
to a classical output. This output can then be fur-
ther processed or optimized. While simulators al-
low measurements at any point in the circuit, real
quantum hardware typically only permits mea-
surements as the final operation on a qubit due to
its destructive nature.
These quantum models can be treated as black boxes,
enabling seamless integration into existing machine
learning workflows. They can be applied to a wide
range of tasks, including classification, regression,
clustering, and generative modeling.
During training, the weights of the quantum
models are optimized using methods such as the
parameter-shift rule or classical backpropagation.
The parameter-shift rule enables the calculation of
the gradient of the loss function without requiring
knowledge of the internal workings of the quantum
circuit, making it suitable for both real quantum hard-
ware and simulators. It approximates the gradient us-
ing the finite difference method. On the other hand,
classical backpropagation, which can be efficiently
deployed on state-vector simulators, treats the quan-
tum and classical parts of the machine learning model
separately and allows for different optimization al-
gorithms and learning rates, while allowing the use
of classical optimization algorithms on the quantum
weights, too.
2.4 Concept of Shapes
The concept of shapes is employed in accordance with
the notion of shape in PyTorch (Paszke et al., 2019)
tensors. A tensor is a potentially high-dimensional
matrix, where the shape specifies the number of el-
ements or sub-tensors in each dimension. For in-
stance, a tensor with shape (2,3,4) consists of two
sub-matrices, each with three rows and four columns,
resulting in a total of 2 · 3 · 4 elements. In the con-
text of quantum circuits, the quantum state S of a
system with W qubits can be represented as a ten-
sor of shape 2
W
, containing the complex probability
amplitudes of each of the 2
W
possible states |00 ...0⟩
to |11 ...1⟩. This can be formulated as a complex
vector S ∈ C
2
W
. By employing isomorphic trans-
formations, we can reshape the tensor to a shape of
(d
1
,d
2
,. ..,d
W
), where all d
i
are equal to two and W
is the number of qubits. This changes the represen-
tation of the state from S ∈ C
2
W
to S ∈ C
2×2×···×2
.
Intuitively, each dimension of this tensor represents a
qubit of the quantum circuit. For example, the prob-
ability amplitude of the state |010⟩ is stored in the
tensor at position (0, 1,0), which corresponds to the
first element of the first dimension, the second ele-
ment of the second dimension, and the first element
of the third dimension.
When applying a single qubit gate, represented by
a G ∈ C
2×2
matrix, to the w-th qubit, we can reshape
the shape of the quantum state from (2
W
) to (d
0
×
d
1
× · ·· × d
w−1
× d
w
× d
w+1
× · ·· × d
W
) (with all di-
mensions being 2), and then further rearrange the ele-
ments to ((d
0
× d
1
× ·· ·×d
w−1
× d
w+1
× .. .d
W
),d
w
).
This results in a tensor shape of (2
W −1
,2), which can
be multiplied with the gate matrix G and then re-
shaped back to the original S ∈ C
2
W
.
In the context of machine learning, the tensor is
typically extended by an additional dimension repre-
senting the batch size of the data, expanding the shape
to (B,2
W
) or (B,2,2, ...,2) (with B being the batch
size, e.g., 16). This allows for processing multiple
data points simultaneously during the same forward
and backward passes.
3 RELATED WORK
3.1 PennyLane
PennyLane is a Python 3 software framework for
differentiable programming of quantum computers
(Bergholm et al., 2022). It provides support for a
wide range of quantum hardware and simulators, and
seamlessly integrates with machine learning libraries
such as PyTorch (Paszke et al., 2019) and Tensorflow
(Abadi et al., 2015), as well as other quantum soft-
ware platforms including Qiskit (Qiskit contributors,
2023) (see also Section 3.2) and Cirq (Cirq develop-
ers, 2023). PennyLane distinguishes between quan-
tum nodes and classical nodes, where quantum nodes
represent the parts of the execution graph that run on
a quantum device or simulator. The framework of-
fers an extensive collection of quantum operations,
encompassing single- and multi-qubit gates, measure-
ments, and non-unitary operations such as the Reset
operation. Furthermore, PennyLane provides built-in
support for quantum chemistry simulations.
The performance of PennyLane is primarily de-
pendent on the underlying quantum simulators, with
different backend implementations offering varying
trade-offs between computational speed and sup-
ported operations. Some simulators even support ex-
Qandle: Accelerating State Vector Simulation Using Gate-Matrix Caching and Circuit Splitting
717

ecution on NVIDIA GPUs to further enhance perfor-
mance. To expedite the execution of the same quan-
tum circuit with different parameters, PennyLane em-
ploys caching techniques. These caches are however
only effective for executing the same circuit with the
same parameters multiple times. Additionally, most
gates and simulators support batching (albeit not all),
a common technique in machine learning. Penny-
Lane’s circuit cutting allows for executing parts of
a circuit independently, allowing to run big circuits
on smaller hardware. However, this process comes at
huge overhead in simulation time and memory usage.
PennyLane also offers circuit visualization methods
and supports importing and exporting circuits in the
OpenQASM 2.0 format (Cross et al., 2017; Bergholm
et al., 2022).
3.2 Qiskit
Qiskit is a comprehensive framework for quantum
computing developed by IBM (Qiskit contributors,
2023; Wille et al., 2019). It offers a wide range
of quantum operations, including single- and multi-
qubit gates, measurements, and non-unitary opera-
tions. Qiskit provides access to real quantum hard-
ware through the IBMQ Experience, allowing users
to run their quantum circuits on IBM’s quantum com-
puters or simulators in the cloud. Local simulators are
also available without the need for registration.
To optimize quantum circuits for specific quan-
tum devices, Qiskit offers a transpiler. The transpiler
adapts the circuit to hardware-specific coupling con-
straints, which determine the allowed combinations
of qubits for CNOT gates and their directions. It
also handles gate restrictions by decomposing unsup-
ported gates into the supported set of gates for the
target hardware. Additionally, gate-fusing and gate-
cancellation techniques are employed to reduce the
total number of gates, resulting in improved execu-
tion time and mitigating hardware noise and errors.
It is important to note that Qiskit uses the least
significant bit as the first bit (LSb 0), while most other
frameworks use the most significant bit as the first bit
(MSb 0). This distinction can lead to confusion when
using multiple frameworks simultaneously.
Qiskit’s integration with the IBMQ Experience
provides researchers and developers with valuable re-
sources for exploring and experimenting with quan-
tum computing. The combination of its extensive
quantum operations, transpiler capabilities, and ac-
cess to real quantum hardware makes Qiskit a power-
ful tool for quantum algorithm development and exe-
cution.
3.3 TorchQuantum
TorchQuantum (Wang et al., 2022) is a recently de-
veloped framework based on PyTorch, with a focus
on execution speed and parallelization. It offers seam-
less integration with IBM’s Qiskit, allowing for easy
conversion of its models to Qiskit circuits. These cir-
cuits can then be executed on real quantum hardware
using IBMQ or exported to the OpenQASM format.
TorchQuantum leverages distributed GPU com-
puting to handle large-scale circuits and batch sizes,
resulting in significant performance improvements
compared to PennyLane. In fact, TorchQuantum has
been reported to achieve execution time improve-
ments of up to 1000 times (Wang et al., 2022). The
framework inherits the support for backpropagation
and batching from the PyTorch library, enabling ef-
ficient scaling with the number of qubits and batch
size.
One notable feature of TorchQuantum is its de-
sign as a tool for running QuantumNAS, a noise-
adaptive search for robust quantum circuits (Wang
et al., 2022). This is achieved by dividing circuits
into smaller sub-circuits and optimizing them inde-
pendently. The sub-circuits are then combined using
an evolutionary algorithm. This approach minimizes
the impact of hardware noise and therefore maximizes
performance on real quantum hardware, making it
highly beneficial for quantum machine learning ap-
plications.
3.4 Contribution
Our contribution lies in the proposal and combina-
tion of advanced techniques aimed at accelerating
the execution of quantum circuits. As a result, we
have developed a high-performance state-vector sim-
ulator called Qandle, which offers seamless integra-
tion into PyTorch-based machine learning workflows.
Qandle demonstrates significant improvements in ex-
ecution times and memory usage compared to ex-
isting frameworks such as PennyLane, Qiskit, and
TorchQuantum. Notably, both of our methods are
matrix-based, making them highly compatible with
PyTorch’s torch.compile function, thereby further
enhancing performance.
It is important to emphasize that our simulator
does not aim to replace PennyLane or Qiskit. Instead,
it serves as a valuable tool for quantum machine learn-
ing applications within the PyTorch ecosystem, simi-
larly to TorchQuantum. Our simulator prioritizes effi-
cient execution of quantum circuits on both CPU and
GPU platforms, focusing on performance rather than
providing advanced visualization tools or direct ac-
QAIO 2025 - Workshop on Quantum Artificial Intelligence and Optimization 2025
718

cess to quantum hardware, unlike more mature frame-
works such as PennyLane, Qiskit and TorchQuantum.
By leveraging the presented techniques gate ma-
trix caching (Section 4.1) and partial matrix decom-
position (Section 4.2), our simulator optimizes the ex-
ecution of gate operations on the state vector. This re-
sults in reduced computation (Section 5.2) and mem-
ory requirements (Section 5.3) during the forward
pass of the quantum circuit.
The integration of our simulator with PyTorch en-
ables seamless incorporation of quantum circuits into
machine learning models. This allows researchers
and practitioners to explore the potential of quan-
tum computing in various domains, such as quan-
tum chemistry simulations, optimization problems,
and generative modeling. Furthermore, our simula-
tor’s compatibility with the OpenQASM format fa-
cilitates interoperability with other quantum software
platforms, enabling easy integration with existing
quantum algorithms and libraries, thanks to its user-
friendly yet powerful API (Section 5.1).
In summary, we combine our presented methods
of gate matrix caching and circuit splitting in our pre-
sented high-performance state-vector simulator Qan-
dle, with reduced memory usage and increased ex-
ecution speed and support for just-in-time compila-
tion, making it an attractive choice for researchers and
practitioners seeking to leverage the power of quan-
tum computing in their machine learning workflows.
4 PERFORMANCE ENHANCING
TECHNIQUES
4.1 Gate Matrix Caching
To improve execution times, we employ a technique
we call gate matrix caching, which involves storing
partial matrices of the gates. These partial matrices
are decompositions of the gate matrices into two ma-
trices with the same shape but higher sparsity. For
instance, we can decompose the R
x
(θ) gate into two
matrices, R
xa
and R
xb
, both of shape (2,2), but with
only two non-zero elements each.
The decomposition of the gate matrix is achieved
as follows:
R
x
(θ) =
cos(θ/2) −isin(θ/2)
−isin(θ/2) cos(θ/2)
=
1 0
0 1
· cos(θ/2) +
0 1
1 0
· −i sin(θ/2)
= R
xa
· cos(θ/2) + R
xb
· −i sin(θ/2)
(1)
The advantage of using these partial matrices is
that they require fewer operations during the forward
pass. Instead of allocating and filling the full gate ma-
trix, we can simply multiply the parameters with their
respective partial matrices, add the results together,
and then multiply with the state vector. This reduces
the computational complexity and improves the over-
all efficiency of the circuit.
Furthermore, the benefits of gate matrix caching
are even more pronounced when working with cir-
cuits that involve multiple qubits. To expand the gate
matrix R
x
to the full size of the state vector, we com-
pute the Kronecker product (⊗) of the partial matri-
ces R
xa
and R
xb
with identity matrices, resulting in
R
x
∈ C
2
W
×2
W
.
R
x
(θ) = I
2
w
⊗ R
x
(θ) ⊗ I
2
(W −w)
= I
2
w
⊗ R
xa
⊗ I
2
(W −w)
· cos(θ/2)
+ I
2
w
⊗ R
xb
⊗ I
2
(W −w)
· −isin(θ/2)
= R
xa
· cos(θ/2) + R
xb
− isin(θ/2)
(2)
It is crucial to note the correct execution order
of the Kronecker product concerning the number of
states 2
w
for the qubits before the gate and 2
(W−w)
for
the qubits after the gate. This order is essential for the
proper reshaping of the state vector after the gate ap-
plication. By utilizing the cached partial matrices R
xa
and R
xb
, the application of the expanded matrices R
x
is faster than computing the full gate matrix for each
forward pass, which would necessitate repeated appli-
cations of the Kronecker product.
Gate matrix caching is not limited to single-qubit
gates but also extends to multi-qubit gates such as
CNOT and composed gate structures like the rota-
tional gates for angle embedding layers. For these,
each rotational gate is decomposed into two partial
matrices. For ease of access and better hardware-level
caching, the two groups of partial matrices R
a
and R
b
are stacked into tensors of shape (W,2
W
,2
W
). Dur-
ing embedding, the partial embedding functions (e.g.,
f
ax
(θ) = cos(θ/2) and f
bx
(θ) = −isin(θ/2) for the
R
x
gate) are computed for all inputs, resulting in two
vectors of shape (W). These vectors are then mul-
tiplied with the partial matrices R
a
and R
b
, respec-
tively, along the first axis. The resulting matrices are
added together, forming the full sequence of gate ma-
trices for the embedding layer, which can now be ma-
trix multiplied with the state vector.
The computationally expensive parts of the em-
bedding operation, such as the repeated application of
the Kronecker product, are executed only once during
circuit initialization and cached for future use. Al-
though the cache is computationally fast, it becomes
memory-intensive as the number of qubits increases.
Qandle: Accelerating State Vector Simulation Using Gate-Matrix Caching and Circuit Splitting
719

To mitigate this, we employ circuit splitting (see Sec-
tion 4.2).
While these matrices consist mostly of zeros (the
matrix for W qubits has 2
2W
− 2
W
zeros), it would
be advantageous to use sparse matrix representations,
which are faster to multiply with another. However,
our preliminary tests have shown that due to the con-
stant multiplications with the quantum state (which is
a very dense vector) and the consequent required type
conversions, the overhead greatly outweighs the ben-
efits of sparsity. Therefore, Qandle does not utilize
sparse matrices for the gate matrices.
PennyLane, on the other hand, employs an aggres-
sive caching approach, where the circuit structure,
inputs, and outputs are saved in cache, with struc-
ture and input acting as keys. This caching strategy
enables fast execution times for repeated executions
of the same circuit, particularly when the number of
gates and qubits is low. However, as the number of
qubits increases, the cache becomes less effective. In
many quantum machine learning applications, the in-
put data changes with each forward pass, resulting in
frequent cache misses. This further diminishes the
benefits of PennyLane’s caching mechanism. The im-
pact of PennyLane’s caching can be observed in the
execution speed comparison presented in Figure 1.
4.2 Circuit Splitting
One of the major challenges faced by state vector sim-
ulators is the exponential growth of the state vector
and the corresponding gate matrix size with the num-
ber of qubits. As the number of qubits, denoted by
W , increases, a circuit’s state vector size becomes 2
W
,
and the gate matrices involved in the computations
become 2
W
× 2
W
. Consequently, implementations of
quantum circuits that rely on naive state vector and
gate matrix multiplications struggle to handle larger
circuits efficiently.
To address this computational complexity, we pro-
pose a technique called circuit splitting. The idea
behind circuit splitting is to divide the circuit into
smaller sub-circuits, thereby reducing the matrix sizes
and the memory and computation time required. This
splitting can be performed during circuit creation,
eliminating the need to make a trade-off between
splitting quality and execution time. The split cir-
cuits, which are essentially groups of quantum gates,
can then be executed sequentially, operating only on
a subset of the full state vector at a time.
To generate these groups, we interpret the circuit
as a dependency graph, where each CNOT gate repre-
sents a node, ignoring other gates. In this graph, two
CNOT gates are connected by an edge if they share
either a control or a target qubit and are successive
in the circuit. Currently, our implementation utilizes
a simple greedy algorithm. It iterates over all sub-
trees of the dependency graph and introduces a new
group whenever the current group would exceed the
given maximum number of qubits (typically between
three and six). In the final step, the previously ignored
single-qubit gates are added to the nearest group of
CNOT gates on the same qubit.
The previously large circuit has been decomposed
into smaller sub-circuits, which can be treated as uni-
tary gates acting on multiple qubits. During circuit
execution, the state vector is reshaped to match the
dimensions of the sub-circuit. After applying the sub-
circuit, the state vector is reshaped back to its origi-
nal dimensions. In the reshaping process, the qubits
involved in the sub-circuit are stored in a separate di-
mension. For example, if the circuit has five qubits
labeled 0,1, 2,3,4, and the sub-circuit acts on qubits
1 and 2, the reshaping would transform the state vec-
tor from (2
5
) dimensions to (d
0
× d
3
× d
4
,d
1
× d
2
)
dimensions. This allows for matrix multiplication be-
tween the sub-circuit (with a gate matrix G ∈ C
2
2
×2
2
)
and the states over the last dimension. In the case
of batched execution, the additional batch dimension
of the state vector is merged during reshaping, while
storing the original batch size b for reshaping back.
This results in a reshaped state vector of dimensions
(b ×d
0
× d
3
× d
4
,d
1
× d
2
) for batched execution. The
overhead introduced by this reshaping process has a
negligible impact on execution speed compared to the
computational load of matrix multiplications. Addi-
tionally, hardware caching remains unaffected as the
batches are processed independently.
4.3 Additional Optimizations
To enhance the quality of the machine learning pro-
cess, we employ quantum weight remapping tech-
niques (K
¨
olle et al., 2023a; K
¨
olle et al., 2023b). Dur-
ing the remapping process, all quantum weights are
transformed to a new range, such as [−π,π], using
smooth functions like the hyperbolic tangent (tanh).
The additional computational overhead incurred by
the remapping step is negligible compared to the nu-
merous other operations performed during each for-
ward pass. However, it yields noticeable improve-
ments in the training process, including faster con-
vergence and a more stable loss curve (K
¨
olle et al.,
2023a; K
¨
olle et al., 2023b).
In addition, we encourage using PyTorch’s
torch.compile function to further optimize the exe-
cution of our simulator. Since our implementation re-
lies exclusively on PyTorch’s tensor operations, it can
QAIO 2025 - Workshop on Quantum Artificial Intelligence and Optimization 2025
720
be compiled into a single execution graph. This com-
pilation process enables faster execution on both CPU
and GPU by optimizing the execution graph. This op-
timization includes reordering the execution order of
parallelizable operations to improve hardware cache
layout and fusing consecutive reshaping operations
into a single reshaping operation. By reducing the
number of calls to system memory and CPU cycles,
the compilation process can significantly enhance the
overall performance of our simulator (Paszke et al.,
2019).
5 IMPLEMENTATION AND
EVALUATION
5.1 API
We showcase our proposed techniques by implement-
ing a PyTorch-compatible state-vector simulator. It is
designed to ensure compatibility with other quantum
software platforms, facilitating easy exporting to the
OpenQASM format. In addition, we provide a simple
API that closely resembles the standard PyTorch API.
This design choice allows for seamless integration of
our circuits as torch.nn.Modules into existing ma-
chine learning workflows. Similar to conventional
PyTorch modules such as convolutional layers, we
store the quantum weights as parameters, eliminating
the need for manual handling of the quantum weights
and their gradients, as required in PennyLane. If users
still desire to manually access or modify the weights,
they can do so using the parameters method of the
module.
5.2 Execution Time
The execution time of our proposed methods in our
simulator is evaluated by comparing it to the execu-
tion times of PennyLane, Qiskit, and TorchQuantum.
For PennyLane and Qiskit, which offer multiple back-
ends each, the fastest available backend is chosen for
each (determined through pretesting).
To ensure accurate measurements, warm-up runs
are performed to allow on-demand/just-in-time com-
piling of modules, which are then stored in system
memory. Random input data is sampled to simulate
the execution of a larger dataset which exceed the
capacity of CPU caches and system memory. The
weights of the quantum circuit are modified using
a classical optimizer. To minimize the influence of
other components, a trivial loss function and the well-
tested Adam optimizer (Kingma and Ba, 2017) are
employed.
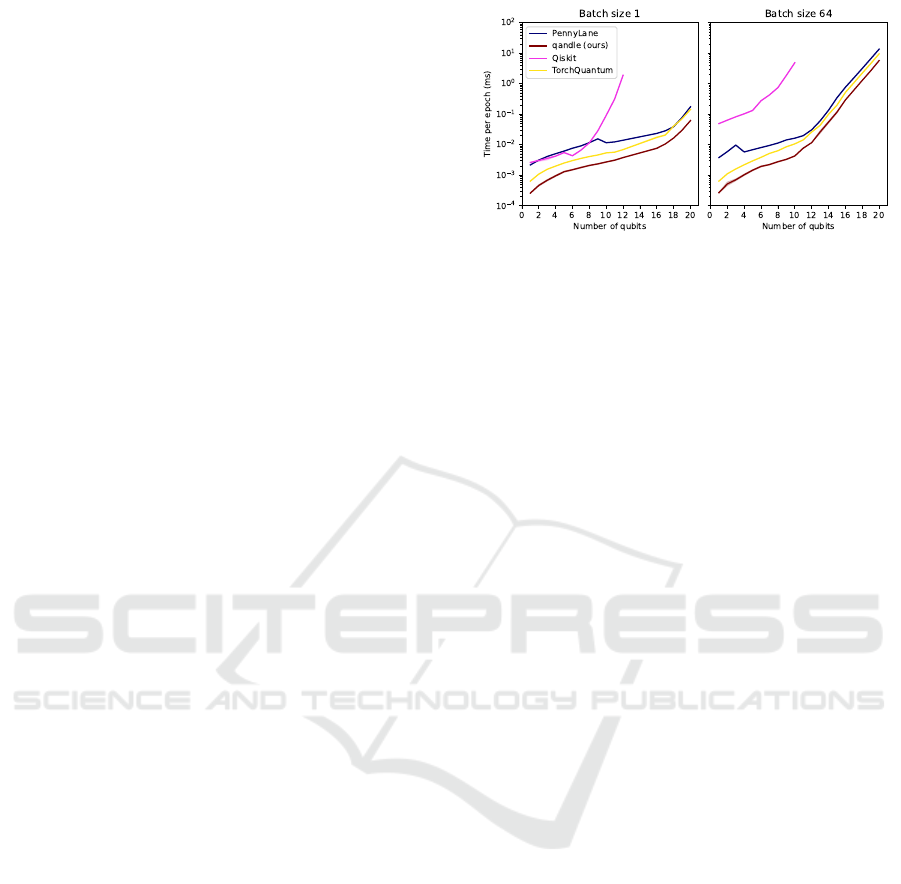
Figure 1: Simulation results for the network.
The evaluation of execution times (mean of 15
runs, other statistics shown in Figure 3) in Figure 1
demonstrates Qandle’s superior performance com-
pared to other simulators. Qandle consistently outper-
forms TorchQuantum, which is specifically designed
for high execution speed.
The speed curve reveals the impact of Penny-
Lane’s caching mechanism. As the number of qubits
increases, the execution times grow until a certain
point, determined by the batch size, where the caching
feature is disabled. At this point, the execution times
briefly decrease before inevitably rising again. This
behavior is a result of our experiment setup, which
uses different inputs (sampled randomly) and weights
(modified by the optimizer) for each forward pass,
leading to cache misses. In scenarios where the same
circuit is repeatedly executed without changes to the
input or weights (e.g., for datasets that fit within the
batch size or during inference), PennyLane’s caching
mechanism would provide better performance than
observed in this evaluation. We however argue that
this is not a realistic scenario for training a quantum
machine learning model.
5.3 Memory Usage
To evaluate memory usage, we executed the same
circuits on different simulators and measured their
peak memory usage. We employed a realistic train-
ing scenario, performing multiple backward passes
with a simple loss function and varying input data
to avoid caching effects. We measured the maxi-
mum resident set size (RSS) of the Python process,
including the loaded simulator libraries and the Py-
Torch library, using the GNU time command. Each
measurement was repeated 15 times, with negligi-
ble variance caused by swapping and other system
processes. All tests were conducted on worksta-
tions with 64 GB of RAM and Intel Core i9-9900
CPUs. Simulators offering multiple backends, such
as PennyLane and Qiskit, were executed with their
fastest backend variants, default.qubit.torch and
Qandle: Accelerating State Vector Simulation Using Gate-Matrix Caching and Circuit Splitting
721
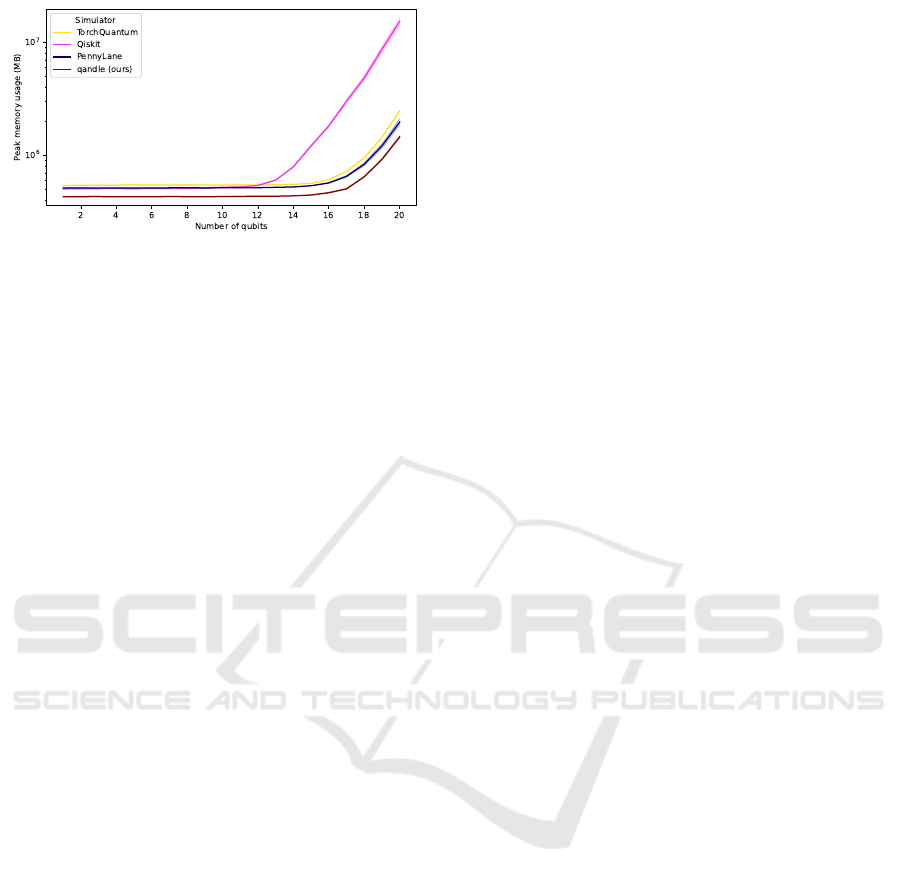
Figure 2: Memory usage for a hardware-efficient SU(2) cir-
cuit with varying numbers of qubits. Qandle exhibits lower
memory usage compared to other simulators.
statevector_simulator on the Aer simulator, re-
spectively (Bergholm et al., 2022; Qiskit contribu-
tors, 2023). As PennyLane’s caching mechanism is
not effective in an activate training scenario, and cir-
cuit cutting is focused for execution on real hardware,
neither of these features were enabled for the evalua-
tion (pretesting showed a significant negative impact
on execution time).
The memory scaling behavior exhibits similar
characteristics to other simulators: even with opti-
mizations, memory usage grows exponentially with
the number of qubits. This is due to the large size of
the state vector, which consists of 2
W
complex num-
bers, and the associated memory overhead of matrix
multiplications. Over the tested quantum circuits with
up to 20 qubits (see Figure 2 for an implementation of
a hardware-efficient SU(2) circuit over all qubits), our
simulator demonstrates lower memory usage com-
pared to other simulators, although it still scales ex-
ponentially with the number of qubits. TorchQuan-
tum and PennyLane perform similarly (with a slight
advantage for TorchQuantum), while Qiskit utilizes
the most memory, potentially making it unsuitable for
very large circuits.
6 CONCLUSION
This paper presents advanced techniques, namely
quantum gate matrix caching and circuit split-
ting, to accelerate the execution of quantum cir-
cuits. The showcase implementation, Qandle, is a
high-performance state-vector simulator that seam-
lessly integrates with PyTorch-based machine learn-
ing workflows. Qandle demonstrates significant im-
provements in execution times and memory usage
compared to existing frameworks such as PennyLane,
Qiskit, and TorchQuantum, validating the effective-
ness of the proposed methods. Moreover, Qandle’s
compatibility with PyTorch’s torch.compile func-
tion further enhances its performance. The user-
friendly API of Qandle enables easy integration, even
for users with limited experience in quantum machine
learning and quantum computing, thereby expanding
the accessibility of quantum machine learning to a
wider audience.
Based on the promising performance of the pro-
posed methods, we recommend incorporating them
into other existing simulators.
As part of future work, we plan to expand the
range of supported quantum gates, particularly multi-
qubit gates like the Toffoli gate. This expansion will
enable the simulation of more complex circuits that
are currently not supported by our implementation.
Additionally, we aim to develop a more sophisticated
splitting algorithm based on graph algorithms, lever-
aging the circuit’s dependency graph. This algorithm
will determine the optimal split, reducing the num-
ber of sub-circuits and minimizing the overhead of
reshaping the state vector, while ensuring efficient ex-
ecution. We propose exploring graph coloring tech-
niques or split decomposition algorithms for this pur-
pose.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This paper was partially funded by the German Fed-
eral Ministry of Education and Research through
the funding program “quantum technologies —
from basic research to market” (contract number:
13N16196).
REFERENCES
Abadi, M., Agarwal, A., Barham, P., Brevdo, E., Chen, Z.,
Citro, C., Corrado, G. S., Davis, A., Dean, J., Devin,
M., Ghemawat, S., Goodfellow, I., Harp, A., Irving,
G., Isard, M., Jia, Y., Jozefowicz, R., Kaiser, L., Kud-
lur, M., Levenberg, J., Man
´
e, D., Monga, R., Moore,
S., Murray, D., Olah, C., Schuster, M., Shlens, J.,
Steiner, B., Sutskever, I., Talwar, K., Tucker, P., Van-
houcke, V., Vasudevan, V., Vi
´
egas, F., Vinyals, O.,
Warden, P., Wattenberg, M., Wicke, M., Yu, Y., and
Zheng, X. (2015). TensorFlow: Large-scale machine
learning on heterogeneous systems. Software avail-
able from tensorflow.org.
Bauckhage, C., Bye, R., Knopf, C., Mustafic, M., Pi-
atkowski, N., Reese, B., Stahl, R., and Sultanow, E.
(2022). Quantum machine learning in the context of
it security.
Bergholm, V., Izaac, J., Schuld, M., Gogolin, C., Ahmed,
S., Ajith, V., Alam, M. S., Alonso-Linaje, G., Akash-
Narayanan, B., Asadi, A., Arrazola, J. M., Azad,
U., Banning, S., Blank, C., Bromley, T. R., Cordier,
QAIO 2025 - Workshop on Quantum Artificial Intelligence and Optimization 2025
722
B. A., Ceroni, J., Delgado, A., Matteo, O. D., Dusko,
A., Garg, T., Guala, D., Hayes, A., Hill, R., Ijaz,
A., Isacsson, T., Ittah, D., Jahangiri, S., Jain, P.,
Jiang, E., Khandelwal, A., Kottmann, K., Lang, R. A.,
Lee, C., Loke, T., Lowe, A., McKiernan, K., Meyer,
J. J., Monta
˜
nez-Barrera, J. A., Moyard, R., Niu, Z.,
O’Riordan, L. J., Oud, S., Panigrahi, A., Park, C.-
Y., Polatajko, D., Quesada, N., Roberts, C., S
´
a, N.,
Schoch, I., Shi, B., Shu, S., Sim, S., Singh, A.,
Strandberg, I., Soni, J., Sz
´
ava, A., Thabet, S., Vargas-
Hern
´
andez, R. A., Vincent, T., Vitucci, N., Weber, M.,
Wierichs, D., Wiersema, R., Willmann, M., Wong,
V., Zhang, S., and Killoran, N. (2022). Pennylane:
Automatic differentiation of hybrid quantum-classical
computations.
Cerezo, M., Arrasmith, A., Babbush, R., Benjamin, S. C.,
Endo, S., Fujii, K., McClean, J. R., Mitarai, K.,
Yuan, X., Cincio, L., and Coles, P. J. (2021). Vari-
ational quantum algorithms. Nature Reviews Physics,
3(9):625–644.
Cirq developers (2023). Cirq.
Cross, A. W., Bishop, L. S., Smolin, J. A., and Gambetta,
J. M. (2017). Open quantum assembly language.
Farhi, E., Goldstone, J., Gutmann, S., and Zhou, L. (2022).
The Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm
and the Sherrington-Kirkpatrick Model at Infinite
Size. Quantum, 6:759.
Kingma, D. P. and Ba, J. (2017). Adam: A method for
stochastic optimization.
K
¨
olle, M., Giovagnoli, A., Stein, J., Mansky, M. B.,
Hager, J., and Linnhoff-Popien, C. (2023a). Improv-
ing convergence for quantum variational classifiers us-
ing weight re-mapping.
K
¨
olle, M., Giovagnoli, A., Stein, J., Mansky, M. B., Hager,
J., Rohe, T., M
¨
uller, R., and Linnhoff-Popien, C.
(2023b). Weight re-mapping for variational quantum
algorithms.
K
¨
olle, M., Stenzel, G., Stein, J., Zielinski, S., Ommer, B.,
and Linnhoff-Popien, C. (2024). Quantum denoising
diffusion models.
Nielsen, M. A. and Chuang, I. L. (2001). Quantum com-
putation and quantum information. Phys. Today,
54(2):60.
Paszke, A., Gross, S., Massa, F., Lerer, A., Bradbury, J.,
Chanan, G., Killeen, T., Lin, Z., Gimelshein, N.,
Antiga, L., Desmaison, A., Kopf, A., Yang, E., De-
Vito, Z., Raison, M., Tejani, A., Chilamkurthy, S.,
Steiner, B., Fang, L., Bai, J., and Chintala, S. (2019).
Pytorch: An imperative style, high-performance deep
learning library. In Advances in Neural Information
Processing Systems 32, pages 8024–8035. Curran As-
sociates, Inc.
Preskill, J. (2018). Quantum computing in the NISQ era
and beyond. Quantum, 2:79.
Qiskit contributors (2023). Qiskit: An open-source frame-
work for quantum computing.
Rebentrost, P., Mohseni, M., and Lloyd, S. (2014). Quan-
tum support vector machine for big data classification.
Physical review letters, 113(13):130503.
Schuld, M. and Petruccione, F. (2021). Machine learning
with quantum computers. Springer.
Stamatopoulos, N., Egger, D. J., Sun, Y., Zoufal, C., Iten,
R., Shen, N., and Woerner, S. (2020). Option pricing
using quantum computers. Quantum, 4:291.
Wang, H., Ding, Y., Gu, J., Li, Z., Lin, Y., Pan, D. Z.,
Chong, F. T., and Han, S. (2022). Quantumnas:
Noise-adaptive search for robust quantum circuits. In
The 28th IEEE International Symposium on High-
Performance Computer Architecture (HPCA-28).
Wille, R., Van Meter, R., and Naveh, Y. (2019). IBM’s
qiskit tool chain: Working with and developing for
real quantum computers. In 2019 Design, Automa-
tion and Test in Europe Conference and Exhibition
(DATE), pages 1234–1240.
Zoufal, C., Lucchi, A., and Woerner, S. (2019). Quantum
generative adversarial networks for learning and load-
ing random distributions. npj Quantum Information,
5(1):103.
APPENDIX
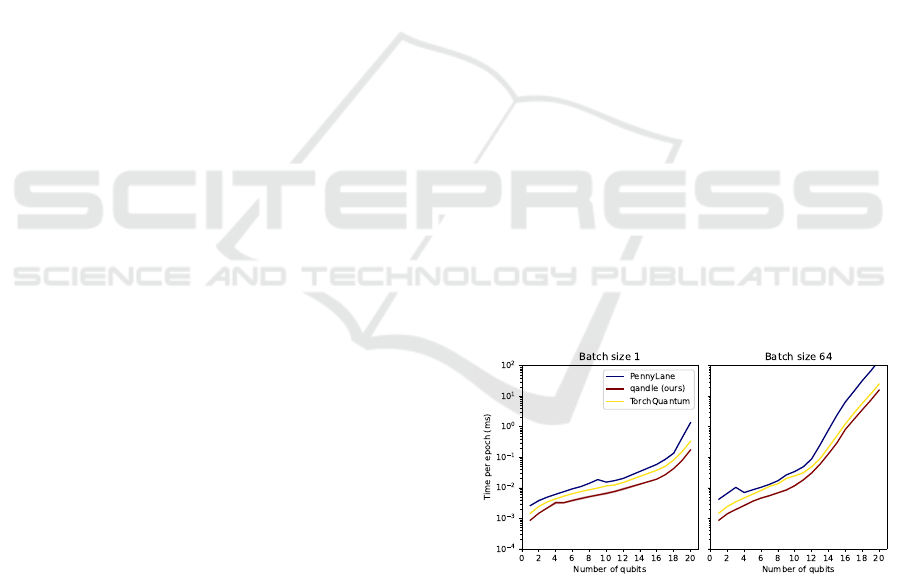
Execution Time
In Figure 3, we show the minimum execution times of
the simulators for the same circuits, employing a full
forward and backward pass. The results are consis-
tent with the mean execution times shown in Figure 1,
showing Qandle as the fastest simulator, followed by
TorchQuantum and PennyLane. Minimal execution
times are more effected by other system processes and
caching mechanisms, and are therefore less reliable to
reproduce.
Figure 3: Simulation results for the network, showing only
the fastest run.
Qandle: Accelerating State Vector Simulation Using Gate-Matrix Caching and Circuit Splitting
723
