
Enhancing IoT Interactions with Large Language Models: A Progressive
Approach
Daniela Timisica
1,2 a
, Radu Boncea
1 b
, Mariana Mocanu
2 c
, Bogdan Dura
1 d
and Sebastian Balmus
1 e
1
Complex System Engineering Department,ICI Bucuresti, Bucuresti, Romania
2
Computer Science Department, POLITEHNICA Bucuresti, Bucuresti, Romania
Keywords:
Large Language Models, Internet of Things, Home Automation, Smart Home, Telemetry Data Interpretation.
Abstract:
This paper explores the development and implementation of an Intelligent Virtual Assistant (IVA) leveraging
Large Language Models (LLMs) to enhance interactions with Internet of Things (IoT) systems. Our work
demonstrates the initial success in enabling the IVA to perform telemetry readings and basic interpretations,
showcasing the potential of LLMs in transforming Natural Language Processing (NLP) applications within
smart environments. We discuss the future enhancements planned for the IVA, including the ability to sequen-
tially call multiple tools, perform readings from various sources, and execute robust data analysis. Specifically,
we aim to fine-tune the LLM to translate human intentions into Prometheus queries and integrate additional
analytical tools like MindDB to extend the system’s capabilities. These advancements are expected to improve
the IVA’s ability to provide comprehensive responses and deeper insights, ultimately contributing to more in-
telligent and intuitive virtual assistants. Our ongoing research highlights the potential of integrating advanced
NLP, IoT, and data analytics technologies, paving the way for significant improvements in smart home and
vehicle environments.
1 INTRODUCTION
Recent advancements in Natural Language Process-
ing (NLP), especially the development of Large Lan-
guage Models (LLMs), have significantly influenced
academic research and captured public interest. These
advanced AI models demonstrate exceptional profi-
ciency in comprehending, utilizing, and generating
human language, representing a major technologi-
cal leap and transforming human-machine interac-
tions. The emergence of LLMs marks a revolution-
ary milestone in NLP. Traditional NLP models rely
heavily on sequential processing techniques, such as
Named Entity Recognition (NER), Intent Classifica-
tion, and Part-of-Speech Tagging. While effective,
these methods are often limited by their linear ap-
proach to language understanding and generation. In
contrast, LLMs utilize deep learning architectures like
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0003-2193-8372
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0600-7505
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8305-2652
d
https://orcid.org/0009-0008-3145-5776
e
https://orcid.org/0009-0004-7212-8836
transformers, enabling the models to process and gen-
erate text in a manner similar to human cognition.
This paradigm shift has facilitated the development of
AI systems capable of performing complex language-
related tasks with unprecedented accuracy and coher-
ence.
One of the most notable features of LLMs is their
advanced reasoning capabilities. These models are
not only adept at language processing but also capable
of interacting with external information systems via
Application Programming Interfaces (APIs)(Ouyang
and Srivastava, 2024). This functionality enhances
their reasoning and decision-making processes, al-
lowing them to retrieve, process, and integrate in-
formation from various sources in real-time. Conse-
quently, LLMs can perform more sophisticated anal-
yses and provide more accurate and contextually rel-
evant responses.
A key application of LLM technology is its inte-
gration with Internet of Things (IoT) systems. This
integration facilitates a wide range of tasks, including
sensor data interpretation, data analysiss(Liu et al.,
2024), and actuator control(Xu et al., 2024). By lever-
aging LLMs, IoT systems can achieve higher levels
Timisica, D., Boncea, R., Mocanu, M., Dura, B. and Balmus, S.
Enhancing IoT Interactions with Large Language Models: A Progressive Approach.
DOI: 10.5220/0013346700003929
In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2025) - Volume 1, pages 1025-1033
ISBN: 978-989-758-749-8; ISSN: 2184-4992
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
1025

of automation and intelligence. For example, in a
smart home environment, an LLM can analyze data
from various sensors to optimize energy consump-
tion, enhance security, and improve overall user com-
fort. This capability represents a significant advance-
ment over traditional virtual assistants, which typi-
cally rely on predefined rules and sequential process-
ing techniques.
In this paper, we explore the implementation of an
LLM agent-based Intelligent Virtual Assistant (IVA)
designed for interacting with IoT systems. This sys-
tem demonstrates advanced capabilities in retrieving
and generating augmented and correlated information
from IoT systems, encompassing telemetry data, his-
torical data interpretation, actuator control, and sys-
tem state management.
A typical operational information exchange se-
quence for our Virtual Assistant (VA), as seen in Fig-
ure 1 encompasses the following steps:
• User Interaction Initiation. The end-user begins
an interaction by inputting an inquiry or command
into the Virtual Assistant interface, articulated in
natural language. For example, the user might
ask, ”USER/>What is the temperature and hu-
midity in Room A?”
• Semantic Analysis. The VA transmits this in-
quiry to the Large Language Model (LLM) for
semantic analysis. The LLM deduces the req-
uisite toolset operations and their correspond-
ing parameters, subsequently generating an inter-
preted directive. For instance, the LLM might
determine, ”LLM/>I need to use the tools get-
Temperature(unit of measurement = ’C’, loca-
tion = ’RoomA’) and getHumidity (location =
’RoomA’).”
• Execution of Toolset Functions. The VA sequen-
tially executes the specified Toolset API functions
utilizing the parameters delineated by the LLM.
These functions engage with the IoT platform to
retrieve data points, referred to as ’Observations.’
For example,”LLM/>I read a temperature value
of 22°C and a humidity value of 30%.”
• Data Synthesis and User Feedback. After data
acquisition, the VA conveys these Observations
back to the LLM to synthesize an informed in-
terpretation or conclusion, which is then commu-
nicated to the user. This synthesized conclusion
integrates the Observations within the contextual
framework provided by the user’s initial inquiry.
For example, ”VA/>The temperature in Room A
is 22 degrees Celsius, and the humidity is 30%.
These are normal values.”
The proposed solution will integrate with sev-
eral established open-source platforms to enhance its
functionality, scalability, and reliability. This section
elaborates on how the system will utilize Home As-
sistant, Eclipse Mosquitto, and Prometheus.
1.1 Home Assistant as the IoT Platform
Home Assistant is a widely used open-source plat-
form for home automation, enabling users to control
and automate a variety of devices and systems within
their homes. The proposed Intelligent Virtual Assis-
tant (IVA) will leverage Home Assistant for the fol-
lowing key functions:
• Device Management. Home Assistant offers a
unified interface for managing an extensive array
of IoT devices, including sensors, actuators, and
other smart home components. The IVA will uti-
lize Home Assistant’s comprehensive integration
capabilities to seamlessly interact with these de-
vices.
• Automation Scripts. Home Assistant supports
the creation of automation scripts, which allow
for sophisticated behaviors and responses based
on various triggers and conditions. The IVA can
activate these scripts based on user commands or
contextual data, delivering a higher degree of au-
tomation and customization.
• State Monitoring. Home Assistant continuously
monitors the state of all connected devices. The
IVA will access this state information to provide
users with real-time updates and insights about
their IoT systems.
1.2 Eclipse Mosquitto as the MQTT
Message Broker
Eclipse Mosquitto is a lightweight, open-source
MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport) bro-
ker designed for efficient communication, particularly
well-suited for IoT devices. The IVA will integrate
with Eclipse Mosquitto to facilitate several key func-
tionalities:
• Efficient Communication. The IVA will utilize
MQTT to transmit and receive messages between
various IoT devices and the central system, ensur-
ing low-latency communication and efficient use
of network resources.
• Scalability. Eclipse Mosquitto is capable of han-
dling a large number of concurrent connections,
making it ideal for environments with numerous
IoT devices. The IVA can scale its operations
seamlessly without performance degradation.
ICEIS 2025 - 27th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
1026
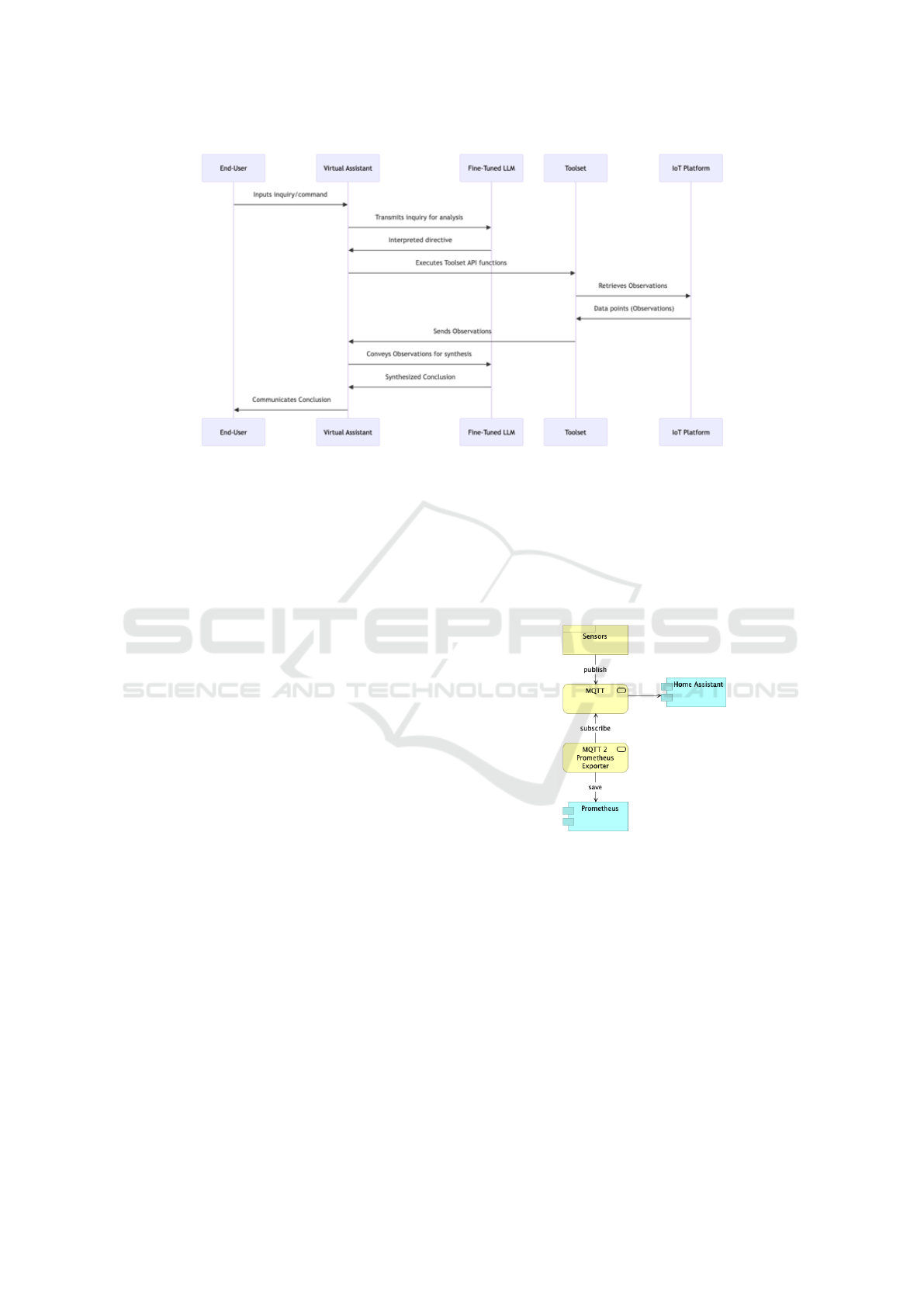
Figure 1: Operational information exchange sequence for IVA.
• Reliability. MQTT provides mechanisms to en-
sure message delivery, such as Quality of Service
(QoS) levels. The IVA will leverage these features
to guarantee that critical messages are reliably de-
livered and appropriately acted upon.
Home Assistant provides a native method for integrat-
ing with MQTT brokers. This includes configuring
MQTT components through MQTT discovery as well
as using YAML, a human-readable data serialization
language.
1.3 Prometheus as the Time Series
Database
Prometheus is an open-source monitoring system and
time series database designed for reliability and scal-
ability. It is particularly well-suited for collecting and
storing large volumes of time-stamped data, which is
common in IoT applications. The IVA will utilize
Prometheus for several essential functions:
• Data Collection. Prometheus will gather teleme-
try data from various IoT sensors and devices.
This data includes metrics such as temperature,
humidity, energy consumption, and more.
• Historical Data Analysis. The IVA will access
historical data stored in Prometheus to provide
insights and trend analysis, helping users under-
stand changes in metrics such as temperature and
humidity over time.
• Alerting and Notifications. Prometheus supports
alerting rules that can trigger notifications based
on specific conditions. The IVA can use these
alerts to inform users of critical events or anoma-
lies detected in their IoT systems.
We will utilize a proxy data publisher, leverag-
ing the MQTT2Prometheus exporter, to feed data into
Prometheus(Hikhvar, 2018). This exporter will sub-
scribe to MQTT topics associated with various de-
vices and convert the incoming data into a format
compatible with Prometheus for efficient monitoring
and analysis (see Figure 2).
Figure 2: Prometheus integration with the Home Assistant
and Message Broker.
The remainder of this paper is organized as fol-
lows. Section II presents the state-of-the-art research
and background literature relevant to Large Language
Model (LLM) integration with IoT systems. Section
III introduces our proposed IVA System Architecture,
detailing each component and its function. Section
IV describes the implementation details of our IVA
prototype, including toolset integration and entity res-
olution. Lastly, Section V offers concluding remarks
and outlines potential directions for future work in en-
hancing IVA capabilities and performance.
Enhancing IoT Interactions with Large Language Models: A Progressive Approach
1027

2 STATE-OF-THE-ART
The evolution of Smart Home Personal Assistants
(SPA) has significantly enhanced the capabilities of
home automation systems, allowing users to perform
a wide range of tasks via voice commands. Plat-
forms like Amazon Alexa now support over hundreds
of thousands of third-party skills, enabling function-
alities from smart device management to online shop-
ping and ride booking. However, this expansion raises
significant privacy concerns. A large-scale study with
1,738 participants explored privacy norms in the SPA
ecosystem, revealing that the acceptability of infor-
mation flows between SPA providers, third-party skill
providers, and other entities is crucial(Abdi et al.,
2021). This research emphasizes the need for robust
privacy settings and protocols to protect user data,
suggesting that future IVAs must incorporate strong
privacy frameworks to ensure user trust and compli-
ance with data protection standards.
In the context of Ambient Assisted Living (AAL)
for elderly individuals with dementia, smart home as-
sistants are proving invaluable(Demir et al., 2017).
Dementia-related cognitive decline necessitates sys-
tems that can support independent living through con-
stant monitoring and assistance. Integrated systems
that utilize various sensors to collect, record, and
transmit data about daily activities are being devel-
oped. These IoT-enabled solutions allow for real-time
monitoring and intervention, significantly aiding indi-
viduals in maintaining their independence and reduc-
ing the caregiving burden. For IVAs, this implies a
need for seamless integration with health monitoring
systems and the ability to provide timely alerts and as-
sistance, enhancing the quality of life for the elderly.
The development of virtual home assistants lever-
aging IoT and Natural Language Processing (NLP)
is another significant advancement. For example, the
”JERRY” model(Islam et al., 2022), based on Rasp-
berry Pi, demonstrates how modern computation can
enhance home automation. This system has shown
impressive results in terms of response time and user
satisfaction, outperforming many existing intelligent
assistants. The model’s capability to manage house-
hold tasks, optimize energy consumption, and ensure
security exemplifies the potential of integrating IVAs
into everyday life. These advancements indicate that
future IVAs should focus on improving interaction
efficiency, usability, and real-time responsiveness to
meet user expectations effectively.
Furthermore, recent research on in-vehicle con-
versational assistants (IVCAs) demonstrates the po-
tential of large language models in enhancing proac-
tive interactions(Du et al., 2024). Proactivity in
IVCAs can reduce distractions and improve driving
safety by better meeting users’ cognitive needs. Exist-
ing IVCAs often struggle with user intent recognition
and context awareness, leading to suboptimal inter-
actions. By employing LLMs, proactive interactions
can be significantly improved.
The development of LLM-based virtual assistants
for IoT aligns with this direction, focusing on inter-
preting telemetry data and managing actuators. One
such project is ”Home-LLM,”(acon96, 2024) which
exemplifies the integration of IoT systems with a vir-
tual assistant. This initiative acts as a conversational
agent, facilitating user management of smart home
devices via natural language instructions. It employs
refined versions of Microsoft’s Phi model series, tai-
lored for interaction with home devices and basic
query resolution. The refinement process utilizes both
the Cleaned Stanford Alpaca Dataset and a synthetic
dataset, concentrating on functions related to device
management.
These developments collectively illustrate the
transformative potential of combining SPAs, IoT, and
NLP technologies with LLMs to create sophisticated
IVAs. By integrating advanced privacy protections,
health monitoring capabilities, efficient home au-
tomation features, and enhanced proactive interac-
tions, IVAs can significantly improve user interaction,
security, and overall living standards. As the field
progresses, these intelligent systems are poised to be-
come central to managing and enhancing smart home
and vehicle environments.
3 IVA SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE
The reference architecture of the Intelligent Virtual
Assistant consists of several key components (see Fig-
ure 3), each playing a crucial role in ensuring efficient
and effective operation:
3.1 Input Component
• Context. Provides situational data that helps the
IVA understand the environment and conditions
surrounding the user’s request.
• Template. Utilizes predefined formats or struc-
tures to guide the interpretation of user inputs.
• Question/Command. The actual input from the
user, such as a query or instruction (e.g., ”What is
the temperature and humidity in Room A?”).
ICEIS 2025 - 27th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
1028
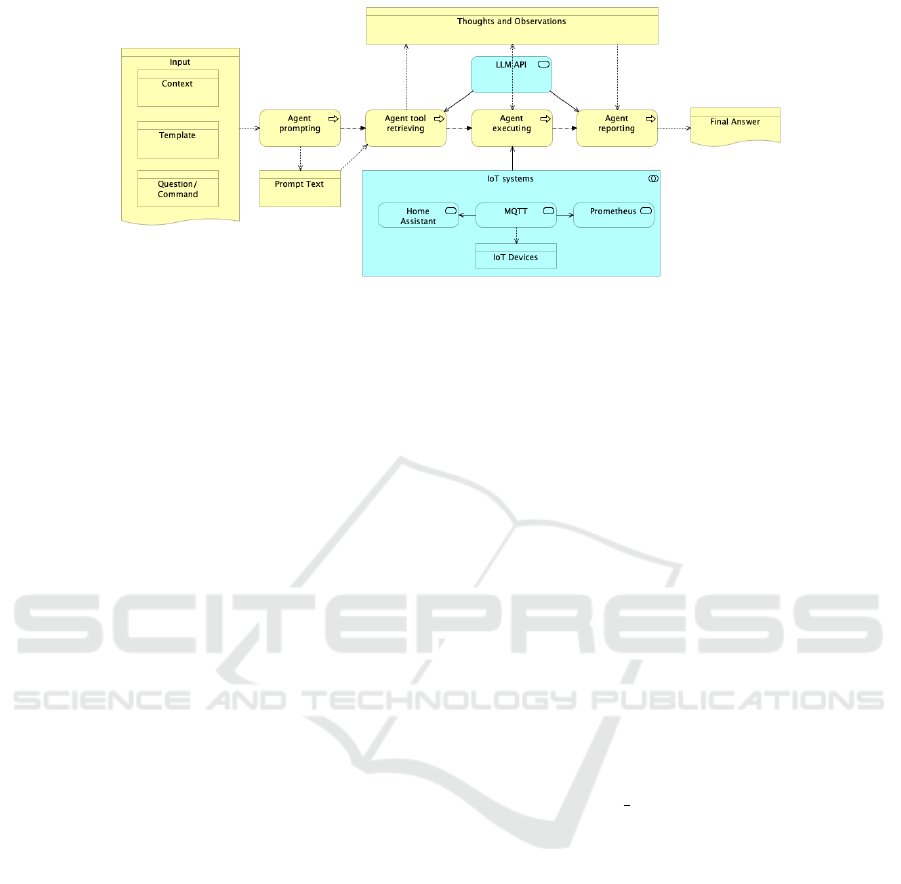
Figure 3: IVA reference architecture.
3.2 Agent Prompting Component
The Agent Prompting component plays a crucial role
in converting user inputs into structured prompt texts,
which serve as formal requests processed by the IVA.
This process of generating structured prompt, in-
volves several sophisticated techniques to ensure that
the user’s intent is clearly understood and effectively
communicated to subsequent components of the IVA
system. The process consists of:
• Formal Request Creation. Converts the parsed
user input into structured prompt text. This
prompt text includes the system prompt, few-shot
examples, and specific guidelines for Chain of
Thoughts (CoT) and other prompt engineering
methods(Chen et al., 2023).
• System Prompt. Sets the overall context and be-
havior expectations for the IVA, guiding the re-
sponse generation process.
• Few-Shot Examples. Provides a few examples to
illustrate how similar requests have been handled,
improving the model’s ability to generate accurate
and relevant responses(Zhou et al., 2023).
• Chain of Thoughts (CoT.) Incorporates CoT
techniques to break down complex queries into
manageable steps, ensuring thorough and logical
reasoning in responses(Kim et al., 2023; Inaba
et al., 2023).
3.3 Agent Tool Retrieving
The Agent Tool Retrieving component is a vital part
of the IVA architecture, responsible for identifying
and interacting with the necessary tools or APIs to
fulfill the user’s request. This component ensures
that the IVA can effectively utilize external systems
to gather data, execute actions, and provide accurate
responses. Below is a detailed breakdown of its func-
tions and capabilities:
• Tool Identification. The Agent Tool Retriev-
ing component starts by analyzing the structured
prompt text generated by the Agent Prompting
component. This analysis helps determine the
specific tools or APIs required to address the
user’s request(Qin et al., 2023a; Zhuang et al.,
2023; Qin et al., 2023b).
• Function Calling. Leveraging the sophisticated
capabilities of LLMs like GPT-4, the Agent Tool
Retrieving component excels in accurately detect-
ing when a function needs to be called, including
the required arguments:
– Generate Function Arguments. The compo-
nent creates precise arguments necessary for
executing the functions.
– Entity Resolution for IoT Devices. It effec-
tively maps IoT device names and IDs from
user intentions. For example, the query ”What
is the temperature in Room A” will map ”Room
A” to ”room a”.
– Utilize RAG Methods for Mapping. The
mapping process is based on an entity catalogue
using Retrieved Augmented Generation (RAG)
methods, ensuring accurate and efficient entity
resolution(Lewis et al., 2020; Gao et al., 2023).
3.4 Agent Executing
• Calls the function with the arguments determined
by the Agent Tool Retrieving module. The re-
turned value from the function call becomes an
Observation, which is then used to formulate a
Conclusion or a Final Answer as part of the
Thoughts and Observations process. The Agent
Executing module can chain or consecutively call
multiple functions, appending each returned value
to the Observation.
Enhancing IoT Interactions with Large Language Models: A Progressive Approach
1029

3.5 Agent Reporting Component
• Compiles the results from the Agent Executing
module and prepares a response for the user. This
includes synthesizing data into a comprehensible
format.
3.6 LLM API
• Interfaces with advanced AI models to process
and understand natural language inputs, pro-
vide contextual analysis, and enhance the IVA’s
decision-making capabilities. It ensures that the
responses are accurate and contextually relevant
by interacting with the Agent Tool Retrieving and
Agent Executing modules.
3.7 Thoughts and Observations
• A layer where the LLM API processes and stores
contextual information, observations, and insights
derived from the interactions. This helps refine fu-
ture responses and maintain context over multiple
interactions.
This architecture ensures that the IVA can effi-
ciently process user inputs, interact with various IoT
systems, and provide accurate and contextually rel-
evant responses, thereby enhancing the overall user
experience.
4 IMPLEMENTATION
For the implementation of IVA, we will be uti-
lizing LangChain, a powerful Python software li-
brary and framework specifically designed to as-
sist in the development of applications that uti-
lize language models. The initial code for
IVA has been published and is available at
http://gogs.ici.ro:3000/radu/IoTVirtualAssistant. The
chat application entry point is hachat.py
LangChain offers several features that align per-
fectly with the needs of our IVA system:
• Chains.
– Task Sequencing. LangChain enables the cre-
ation of sequential task chains, which is cru-
cial for workflows requiring multiple steps.
For our IVA, this will facilitate processes such
as data preprocessing, querying the language
model, and post-processing the output, ensur-
ing a smooth and efficient operation.
• Agents.
– Decision Making and Action. LangChain in-
cludes agent functionality, allowing our IVA to
make decisions and take actions based on in-
puts from language models. This is particularly
useful for creating interactive applications and
chatbots that need to respond dynamically to
user inputs.
• Memory.
– Context Retention. LangChain offers memory
management capabilities that allow our IVA to
retain information across interactions. This fea-
ture ensures that the IVA can remember previ-
ous conversations and use that context to en-
hance the relevance and accuracy of future re-
sponses.
• Prompt Templates.
– Standardization and Reusability. The frame-
work provides tools for managing and cus-
tomizing prompts, making it easier to stan-
dardize and reuse prompts throughout the IVA
application. This consistency is essential for
maintaining high-quality interactions.
• Retrievers.
– External Data Integration. LangChain sup-
ports the integration of external data sources,
enabling our IVA to fetch and use relevant in-
formation during processing. This capability
will improve the accuracy and depth of re-
sponses by providing additional context or fac-
tual data.
• Tool Integration.
– Extended Functionality. LangChain can be
extended with various tools and APIs, allow-
ing our IVA to perform functions beyond lan-
guage generation. For example, we can inte-
grate search engines, databases, or other exter-
nal APIs (in our case, the Home Assistant API)
to enhance the assistant’s capabilities.
The integration of the toolset relies on implement-
ing the abstract class BaseTool from LangChain (see
Figure 4). The name and description properties of
each tool are appended as context to the prompt, guid-
ing the LLM in identifying the appropriate tool and
the necessary arguments. The run method, which
encapsulates the logic of the tool, is responsible for
retrieving data from sensors via the Home Assis-
tant API or for invoking actuators. In our example,
the HASensorReading class implements the general
logic for reading telemetry data from sensors. In con-
trast, the HATempHumReading and HAGeolocation
ICEIS 2025 - 27th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
1030
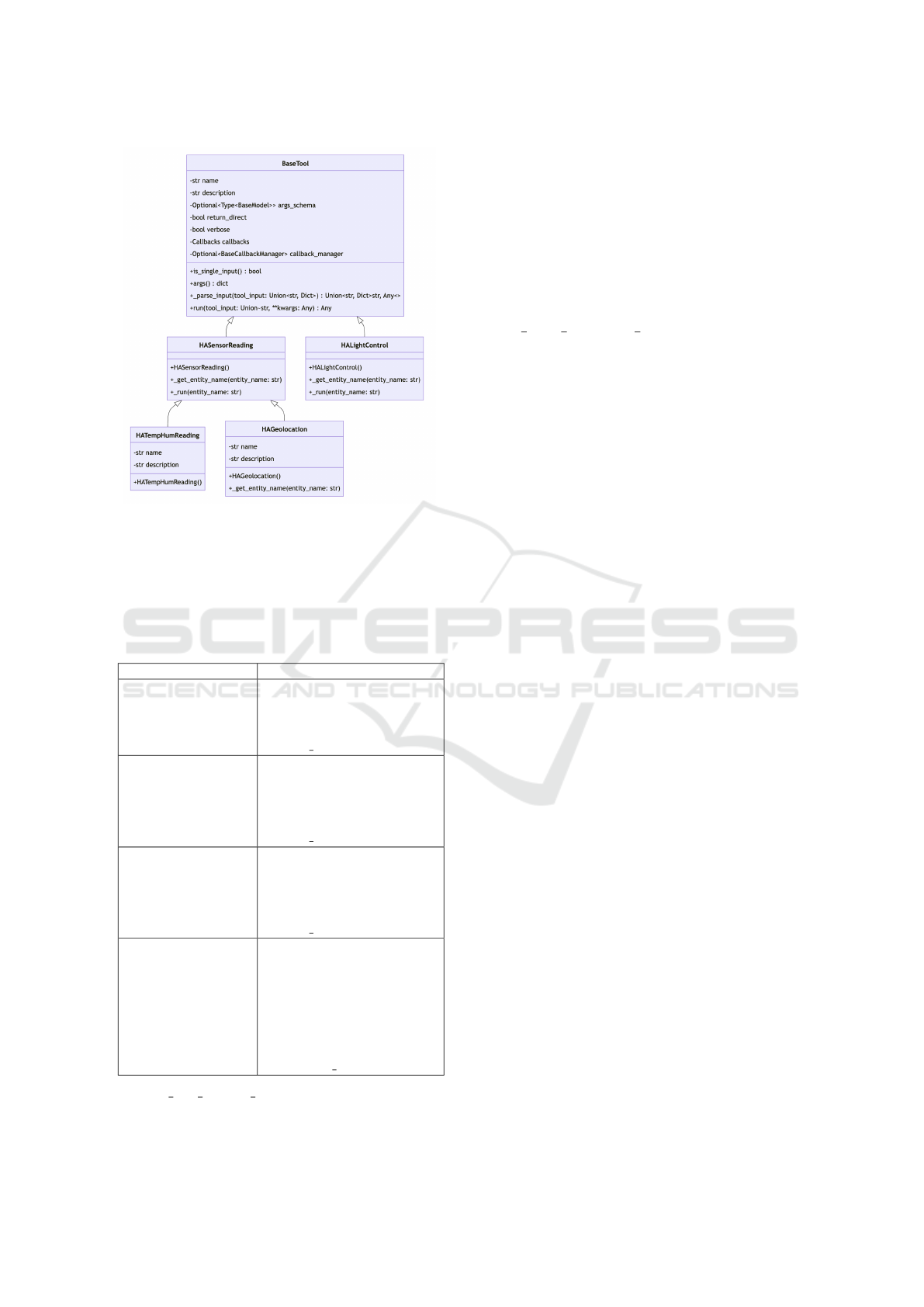
Figure 4: IVA Toolset class diagram.
classes specialize in reading and interpreting specific
types of data, such as temperature and humidity or
GPS coordinates from geolocation devices. Table 1
illustrates the descriptions utilized for the aforemen-
tioned classes.
Table 1: Toolset classes with their descriptions.
Class Description
HASensorReading
use this tool when you need to
read data from a sensor. To use
the tool you must provide ex-
actly the following parameter
entity name
HATempHumReading
use this tool when you need
to get room temperature and
humidity readings. To use
the tool you must provide ex-
actly the following parameter
entity name
HAGeolocation
use this tool when you need
to get geolocation of an en-
tity, person, object. To use
the tool you must provide ex-
actly the following parameter
entity name
HALightControl
use this tool when you need to
turn on or off the light in the
room. Given the light entity
name and an action like turnon
or turnoff, this tool will turn
the lights on or off. To use the
tool you must provide exactly
two of the following parame-
ters entity name, action
The get entity name method plays a crucial
role in entity resolution within the IVA system. This
method implements the logic required to map a user’s
intention, expressed by mentioning the canonical
name of a device, to the corresponding Home Assis-
tant name and ID of the device. Essentially, it trans-
lates user-friendly names into precise identifiers used
by Home Assistant, enabling the system to accurately
retrieve data or control the specified devices.
4.1 Functionality of the
get entity name Method
• User Intention Interpretation. The method in-
terprets the user’s input, identifying the device
mentioned by its canonical name. This involves
understanding the context and extracting the rel-
evant device name from the user’s command or
query.
• Canonical to Home Assistant Name Mapping.
Once the device is identified from the user input,
the method maps this canonical name to the cor-
responding name and ID used within the Home
Assistant environment. This mapping is essential
because the user-friendly names used in queries
often differ from the technical identifiers required
by the Home Assistant API.
• Database or Configuration Lookup. The
method typically involves looking up a predefined
database or configuration file where the mappings
between canonical names and Home Assistant
identifiers are stored. This lookup ensures that the
correct device is targeted for data retrieval or con-
trol actions.
• Ensuring Accuracy and Consistency. By accu-
rately resolving the entity names, the method en-
sures consistency in device interactions. This pre-
vents errors that could arise from ambiguous or
incorrect device identification, thereby improving
the reliability of the IVA system.
4.2 Functionality of the Run Method
Below, we provide an example implementation of a
generic run method for the HASensorReading class.
This method demonstrates how the system retrieves
the state of a specified sensor by interacting with the
Home Assistant API. The method first resolves the
entity name to ensure accurate identification and then
attempts to obtain the sensor’s current state. Error
handling mechanisms are included to manage poten-
tial issues, such as the sensor not being found or other
unexpected errors.
def _run(self, entity_name: str):
entity = self._get_entity_name(entity_name)
Enhancing IoT Interactions with Large Language Models: A Progressive Approach
1031

try:
sensor = ha_client.get_entity(
entity_id=entity)
state = sensor.get_state()
except EndpointNotFoundError as e:
return "No sensor found with name
{entity_name}".format(
entity_name=entity_name)
except Exception as e:
return "An error occurred while trying
to get the sensor {entity_name}".
format(entity_name=entity_name)
return state
4.3 Case Study: Applying IVA in a
Smart Laboratory Environment
To demonstrate the practical application of our In-
telligent Virtual Assistant (IVA), we conducted a
case study in our laboratory environment, which is
equipped with various IoT sensors. The goal was to
evaluate the IVA’s ability to process natural language
queries, retrieve telemetry data, and provide meaning-
ful insights using Large Language Models (LLMs).
4.3.1 Scenario Overview
The laboratory setup included sensors for humidity,
temperature, light, sound, and air quality, all inte-
grated into a central Prometheus-based data collection
system. Additionally, we had access to statistics re-
lated to our Network-Attached Storage (NAS). A user
could interact with the IVA using voice or text com-
mands, requesting real-time readings or trend analy-
ses.
4.3.2 Implementation and Workflow
1. User Query Processing – The IVA, powered by
an LLM, interpreted user intents such as:
• “What is the current humidity level in the labo-
ratory?”
• “How has air quality changed over the past
week?”
• “What is the current status of our NAS statis-
tics?”
2. Prometheus Query Generation – The LLM
translated user requests into structured PromQL
queries to fetch relevant telemetry data.
3. Data Retrieval & Analysis – The system re-
trieved the requested data and performed basic
statistical analysis to provide useful insights.
4. Response Generation – The IVA structured its
response in natural language, summarizing key
findings and providing actionable insights, such
as optimizing environmental conditions or moni-
toring NAS performance.
4.3.3 Results & Observations
The case study demonstrated that the IVA effectively:
• Understood and processed diverse natural lan-
guage queries related to IoT telemetry and NAS
statistics.
• Generated accurate Prometheus queries without
manual intervention.
• Provided insightful summaries based on retrieved
data.
However, challenges remain, particularly in han-
dling multi-step queries and complex data correla-
tions, which we aim to improve in future iterations.
4.3.4 Future Enhancements
Building on these findings, we plan to enhance the
IVA by:
• Implementing sequential tool execution to han-
dle more complex interactions.
• Expanding data sources beyond Prometheus for
richer analytics.
• Fine-tuning the LLM to improve query translation
accuracy.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The integration of Large Language Models (LLMs)
with IoT systems shows promising potential for en-
hancing Natural Language Processing (NLP) applica-
tions. Our ongoing work on the Intelligent Virtual As-
sistant (IVA) has achieved the ability to call telemetry
readings and perform basic interpretations. However,
this is just a starting point, and several enhancements
are planned to further develop the IVA’s capabilities.
One primary area of future development is en-
abling the IVA to sequentially call multiple tools and
perform readings from various sources. This im-
provement will enhance the system’s ability to man-
age complex tasks and provide more comprehen-
sive responses. Additionally, we aim to develop ro-
bust data analysis features. Beyond reading tabular
data from databases like Prometheus, our goal is to
fine-tune the LLM to translate human intentions into
Prometheus queries effectively.
Furthermore, we plan to incorporate inference
capabilities and integrate additional tools, such as
MindDB, to extend the IVA’s analytical functions.
ICEIS 2025 - 27th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
1032

These enhancements will allow the IVA to perform
more sophisticated data analyses, providing users
with deeper insights and more actionable information.
As we continue to refine and expand the IVA sys-
tem, integrating advanced NLP, IoT, and data analyt-
ics technologies will lead to more intelligent and in-
tuitive virtual assistants. These advancements are ex-
pected to enhance smart home and vehicle environ-
ments, contributing to a more connected and efficient
future. The ongoing research and development efforts
underscore the potential of this integration, setting the
stage for future improvements in intelligent virtual as-
sistant technologies.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research was conducted with the support of the
Core Program under the National Research Develop-
ment and Innovation Plan 2022-2027. The project, ti-
tled “Contributions to the Consolidation of Emerging
Technologies Specific to the Internet of Things and
Complex Systems,” is funded by the Ministry of Re-
search, Innovation and Digitization (MCID), project
number 23 38 01 01.
REFERENCES
Abdi, N., Zhan, X., Ramokapane, K. M., and Such, J.
(2021). Privacy norms for smart home personal as-
sistants. In Proceedings of the 2021 CHI Conference
on Human Factors in Computing Systems, CHI ’21,
New York, NY, USA. Association for Computing Ma-
chinery.
acon96 (2024). Home-llm. https://github.com/acon96/
home-llm. Accessed: 2024-06-25.
Chen, Z., Zhou, K., Zhang, B., Gong, Z., Zhao, W. X.,
and Wen, J.-R. (2023). Chatcot: Tool-augmented
chain-of-thought reasoning on chat-based large lan-
guage models. arXiv, 2305.14323.
Demir, E., K
¨
oseo
˘
glu, E., Sokullu, R., and S¸eker, B. (2017).
Smart home assistant for ambient assisted living of el-
derly people with dementia. Procedia Computer Sci-
ence, 113:609–614. The 8th International Conference
on Emerging Ubiquitous Systems and Pervasive Net-
works (EUSPN 2017) / The 7th International Confer-
ence on Current and Future Trends of Information and
Communication Technologies in Healthcare (ICTH-
2017) / Affiliated Workshops.
Du, H., Feng, X., Ma, J., Wang, M., Tao, S., Zhong, Y., Li,
Y.-F., and Wang, H. (2024). Towards proactive inter-
actions for in-vehicle conversational assistants utiliz-
ing large language models. arXiv, 2403.09135.
Gao, Y., Xiong, Y., Gao, X., Jia, K., Pan, J., Bi, Y.,
Dai, Y., Sun, J., Guo, Q., Wang, M., and Wang, H.
(2023). Retrieval-augmented generation for large lan-
guage models: A survey. ArXiv, abs/2312.10997.
Hikhvar (2018). Mqtt2prometheus. https://github.com/
hikhvar/mqtt2prometheus. Accessed: 2024-06-25.
Inaba, T., Kiyomaru, H., Cheng, F., and Kurohashi, S.
(2023). Multitool-cot: Gpt-3 can use multiple ex-
ternal tools with chain of thought prompting. arXiv,
2305.16896.
Islam, M. T., Azad, M. S., Ahammed, M. S., Rahman,
M. W., Azad, M. M., and Nasir, M. K. (2022). Iot
enabled virtual home assistant using raspberry pi. In
Majhi, S., Prado, R. P. d., and Dasanapura Nanjunda-
iah, C., editors, Distributed Computing and Optimiza-
tion Techniques, pages 559–570, Singapore. Springer
Nature Singapore.
Kim, S., Joo, S. J., Kim, D., Jang, J., Ye, S., Shin, J., and
Seo, M. (2023). The cot collection: Improving zero-
shot and few-shot learning of language models via
chain-of-thought fine-tuning. arXiv, abs/2305.14045.
Lewis, P., Perez, E., Piktus, A., Petroni, F., Karpukhin,
V., Goyal, N., Kuttler, H., Lewis, M., tau Yih, W.,
Rockt
¨
aschel, T., Riedel, S., and Kiela, D. (2020).
Retrieval-augmented generation for knowledge-
intensive nlp tasks. ArXiv, abs/2005.11401.
Liu, J., Zhang, C., Qian, J., Ma, M., Qin, S., Bansal,
C., Lin, Q., Rajmohan, S., and Zhang, D. (2024).
Large language models can deliver accurate and inter-
pretable time series anomaly detection. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2405.15370.
Ouyang, X. and Srivastava, M. (2024). Llmsense: Harness-
ing llms for high-level reasoning over spatiotemporal
sensor traces.
Qin, Y., Hu, S., Lin, Y., Chen, W., Ding, N., Cui, G., Zeng,
Z., Huang, Y., Xiao, C., Han, C., Fung, Y. R., Su,
Y., Wang, H., Qian, C., Tian, R., Zhu, K., Liang, S.,
Shen, X., Xu, B., Zhang, Z., Ye, Y., Li, B., Tang, Z.,
Yi, J., Zhu, Y., Dai, Z., Yan, L., Cong, X., Lu, Y.,
Zhao, W., Huang, Y., Yan, J., Han, X., Sun, X., Li, D.,
Phang, J., Yang, C., Wu, T., Ji, H., Liu, Z., and Sun,
M. (2023a). Tool learning with foundation models.
arXiv, 2304.08354.
Qin, Y., Liang, S., Ye, Y., Zhu, K., Yan, L., Lu, Y.-T.,
Lin, Y., Cong, X., Tang, X., Qian, B., Zhao, S., Tian,
R., Xie, R., Zhou, J., Gerstein, M. H., Li, D., Liu,
Z., and Sun, M. (2023b). Toolllm: Facilitating large
language models to master 16000+ real-world apis.
ArXiv, abs/2307.16789.
Xu, W., Liu, M., Sokolsky, O., Lee, I., and Kong, F.
(2024). Llm-enabled cyber-physical systems: Survey,
research opportunities, and challenges. International
Workshop on Foundation Models for Cyber-Physical
Systems.
Zhou, Y., Maharjan, S., and Liu, B. (2023). Scalable
prompt generation for semi-supervised learning with
language models. ArXiv, abs/2302.09236.
Zhuang, Y., Yu, Y., Wang, K., Sun, H., and Zhang, C.
(2023). Toolqa: A dataset for llm question answering
with external tools. In Oh, A., Naumann, T., Glober-
son, A., Saenko, K., Hardt, M., and Levine, S., editors,
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems,
volume 36, pages 50117–50143. Curran Associates,
Inc.
Enhancing IoT Interactions with Large Language Models: A Progressive Approach
1033
