
Eudaily: Supporting University Students in Daily Eudaimonic Reflection
Using the Reflective Play Framework
Julian Marvin Joers
a
and Ernesto William De Luca
b
Human-Centred Design, University Magdeburg, Universit
¨
atsplatz 2, Magdeburg, Germany
Keywords:
Virtual Philosophy Education, Learning of Reasoning, Eudaimonic Learning Environment, Slow Technology.
Abstract:
Since introducing “slow technology” and “reflective informatics” in human-computer interaction (HCI) re-
search, developing prototypes for eudaimonic activities (such as learning and critical thinking) has gained
attention. With ’eudaily’, students are encouraged to reflect on philosophical ideas playfully. Using the frame-
work of reflective play, a database of 22,216 perspectives across 1,507 philosophical ideas, and a measure for
reflective activities in interaction with technology, this prototype was designed and evaluated by 21 students in
an initial use case. Five practical implications to support reflection in HCI can be derived: (1) creating positive
disruption is a design template for disruptions and (2) diversity of perspectives can serve as a design blueprint
for positive disruption. Furthermore, (3) the importance of enabling the customization of the reflective process
and (4) creating a balance between instruction and exploration have been identified. Finally, (5) users demand
a variety of self-expression mechanisms during the interaction.
1 INTRODUCTION
Beyond the doctrine of simplicity or usability in HCI
(Sarkar, 2023), we can create spaces for humans to
engage with profound questions and activities, to fos-
ter deeper self-exploration, and to ’dwell more in this
world’. “Slow Technology” (Halln
¨
as and Redstr
¨
om,
2001) was the first call for an alternative develop-
ment doctrine for technology that does not focus on
task accomplishment but on the creation of space for
reflection and thinking. Perceiving “slow technol-
ogy” remaining “somewhat vague as to what consti-
tutes reflection” (Baumer, 2015, p. 587), Baumer in-
troduced the term “reflective informatics” (Baumer,
2015), i.e. a conceptual formulation of designing for
reflection in HCI. Several applications of these con-
cepts can be found today in a large number of proto-
types that have been published in the last two years
alone (Li et al., 2023; Behzad, 2023; Pasumarthy
et al., 2024; Cremaschi et al., 2024; Sathya and Naka-
gaki, 2024; Kwon et al., 2024; Liedgren et al., 2023).
Betran et al. state: “[...] we argue that, in a world
where technology is increasingly present, functional
and productive; it is equally important to also support
the socio-emotional value of play” (Altarriba Bertran
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8943-6307
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3621-4118
et al., 2020, p. 3). In 2024, Miller et al. developed
the “Design Framework for Reflective Play” (Miller
et al., 2024) presenting a procedural design guideline
for reflective activities in interaction with games. The
ideas of abstract thinking and perspective-taking are
often referred to as eudaimonic habits (Huta, 2016).
Consequently, contributions in HCI often refer to eu-
daimonic perspectives when addressing these activi-
ties (Schrier, 2024; Joers and De Luca, 2024; Mekler
and Hornbæk, 2016). For example, Cole & Gillies
describe the eudaimonic (play) experience as one that
aims to encourage reflection and self-development
of the activity afterward (Cole and Gillies, 2022).
Strengthening these critical thinking skills is an im-
portant component for the development of students
in the 21st century (Soffel, 2016). This use case ap-
plies the new framework for reflective play to foster
the reflective processes of students within a playful
environment. In this context, the prototype ’eudaily’
was developed using a wordplay of eudaimonia and
daily. This use case is the first application of this
novel framework, thus no state of practice does yet
exist. Furthermore, it contains practical implications
for the development of reflection-enhancing interac-
tive systems. ’Eudaily’ is also a contribution to the ex-
isting challenge of fostering eudaimonic activities and
enhancing eudaimonic well-being in HCI (Stephani-
dis et al., 2019). Thus, beyond the mere application
484
Joers, J. M. and William De Luca, E.
Eudaily: Supporting University Students in Daily Eudaimonic Reflection Using the Reflective Play Framework.
DOI: 10.5220/0013347000003932
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2025) - Volume 1, pages 484-491
ISBN: 978-989-758-746-7; ISSN: 2184-5026
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

of this model, important practical implications can be
deduced in the specific context of technology design
for eudaimonic reflection and eudaimonic well-being.
2 BUILDING EUDAILY
For the conception of ’eudaily’
1
we used a novel
framework for reflective play (Miller et al., 2024),
the design guidelines for slow serious games (Marsh,
2016), and the eudaimonic interaction design princi-
ples (Joers and De Luca, 2024). The design frame-
work for reflective play has five sequential phases:
disruptions, slowdowns, questioning, revisiting, and
enhancers. Design templates are available to the de-
veloper in all process-related design steps to enable
a reflective experience in a game. The aim of this
framework application is not only a reflection during
the interaction (endo-transformation) but also a real
behavior change (exo-transformation). For the devel-
opment of the interaction during the slowdown, the
guidelines for slow serious games were considered.
Marsh defined eleven design guidelines for slow seri-
ous gaming, e.g. avoiding narration and further infor-
mation but creating a space for de-accelerated reflec-
tion (Marsh, 2016). Finally, the eudaimonic interac-
tion design principles call for the reduction of quan-
tification within the interaction, the promotion of the
user flow, and the reduction of informal feedback in-
stead of the gamification of the activity per se (Joers
and De Luca, 2024). These principles were also taken
into account during the development.
The core idea of ’eudaily’ is encouraging students
to reflect on philosophical ideas (e.g. laws of na-
ture, subjective truth, free will, infinity, or love) tak-
ing existing perspectives of philosophers into account.
Accordingly, a database of philosophical perspectives
on topics was used for the development of ’eudaily’.
Through years of preliminary work by Gibson and
Berry, who together maintain the website “Philosophy
Ideas”
2
, we were able to access 22,126 perspectives
on 1,507 topics such as freedom of lifestyle, nature,
and virtue of courage. The students interact playfully
with the existing perspectives on the randomly cho-
sen topic and are supported in his or her eudaimonic
process of reflection. The topic is selected at random
via a web interface and the perspectives are loaded
into ’eudaily’ accordingly. In the following, the exact
course of the interaction is illustrated in detail in the
subsections.
1
http://eudaily.joersi.com/
2
http://www.philosophyideas.com/
2.1 Disruptions
At the beginning of the interaction, the student is
confronted with a random topic and its perspectives
serving as a disruptive moment within ’eudaily’. A
screenshot of the disruptive moment is shown in Fig-
ure 1. In the moment of disruption, we specifi-
cally aim for an uncomfortable, possibly contradic-
tory encounter with perspectives on a philosophical
object, causing a general moment of friction. During
Figure 1: The ’Eudai-Bot’ takes a walk in the rain and re-
flects on the philosophical positions of a construct (phase of
disruption).
the disruptive phase, one “creates an opportunity for
the player to question their own assumptions and re-
evaluate their own systems of thought” (Miller et al.,
2024, p. 5). Thus, the direct confrontation “with the
player in relation to their beliefs and actions” (Miller
et al., 2024, p. 7) has been chosen as a design ap-
proach to create discomfort in the interaction. The
students can change the topic at any time using the re-
fresh button. The perspectives are shown overlapping,
forcing the student to ’solve’ the thought by clicking
on the perspectives and moving on to another state-
ment. Only after all possible thoughts have been re-
solved the student can access the next page by an ac-
tivated next button and thus enter the phase of slow-
down.
2.2 Slowdown
Based on the reflective play framework, it is intended
to implement a speed bump as “attention as a me-
chanic” (Miller et al., 2024, p. 8). (De-)acceleration
through input devices can be a significant mediator
of interaction, such as writing a tweet using an old-
fashioned typewriter (Cremaschi et al., 2024). The
user receives an overview of past statements in order
to leave the chosen cognitive and perceptual load (in-
tended disruption, the ’eudai-bot’ running in an end-
less loop, statements moving up and down) and thus
enter a merely ’calmer’ phase of interaction. An ex-
ample can be seen in Figure 2. Based on the game
Eudaily: Supporting University Students in Daily Eudaimonic Reflection Using the Reflective Play Framework
485

Figure 2: The text statements are displayed again with addi-
tional questions to guide the students (phase of slowdown).
principles of slow serious games (Marsh, 2016, p. 50),
this situation aims to open up opportunities for think-
ing and reflection. In addition, according to number
10 of the design guidelines for slow serious games
(Marsh, 2016, p. 50), the user can use a button to call
up random reflection questions to address the con-
cepts. These are displayed via a random generator
in the respective text boxes.
2.3 Questioning
In the sense of “demanding self-explanation”, a
“refection-in-action” is enabled in the questioning
section (Marsh, 2016, p. 10-11), i.e. the student
should translate the confrontation with the perspec-
tives into their own explanations. This process is di-
vided into two parts in the interaction: (1) The stu-
dents formulate their own quotation of the topic so
that their own interpretation and thus a reflection pro-
cess and perspective-taking are initiated. This first
step of questioning can be seen in Figure 3. (2)
Figure 3: The student must become active by providing
their quotation (phase of questioning).
Then, along the design principle of “ambiguous in-
structions” (Miller et al., 2024, p. 11), the students
should express themselves creatively and visually on
a small HTML5 canvas, which they associate with
their interpretation of the topic. This second step can
be seen in Figure 4. We have used a simple edi-
tor (color selection and brush thickness), which, after
saving the artwork, redirects to the page that enables
the revisiting of the experience.
Figure 4: A minimalist painting surface designed to inspire
artistic activities (phase of questioning).
2.4 Revisiting
In the revisting phase, we have chosen a form of re-
flective revisiting, i.e. the user receives a simple vi-
sualization of his or her painting, his or her quote,
and a dwell time within the system. Actively inform-
ing users about their time spent on video platforms
initiates reflection processes (Sathya and Nakagaki,
2024). The times are not stored user-specifically, as
a shift in extrinsic motivation should be prevented
(focus shift to high dwell times in the system, in-
stead of serious engagement with topics). Thus, from
our perspective, there should be no direct reward for
long dwell times in the system. Forms of evaluation
may cause decreases in creativity (Amabile, 1982),
complex problem solving (McGraw and McCullers,
1979), and deep conceptual processing of informa-
tion (Grolnick and Ryan, 1987). However, at the end
of the phase, a small fireworks simulation is played
in the background to acknowledge the time spent in
the system by the student (an example can be seen in
Figure 5). The actual moment of the enhancer takes
place in the last interaction.
Figure 5: The image is displayed with slight transparency in
the background, and the user’s quote definition is displayed
next to the concepts. The user is simply informed positively
about the dwell time in the system (phase of revisiting).
CSEDU 2025 - 17th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
486

2.5 Enhancer
A random generator chooses a slogan from a list of
ready-made motivational statements at the top of the
last page. It is intended to motivate reflection prac-
tices outside of this environment and has been pre-
selected by the author. It is a combination of the
design template, explicit encouragement of reflection
and breaking the fourth wall (Miller et al., 2024), as
the student should be motivated to engage in out-of-
system reflection processes. Furthermore, for the ex-
ploration of multiple perspectives of the game experi-
ence, all user artworks are displayed on the last page
of the interaction - no likes, just text, acronym, and
the artwork, arranged from last to newest timestamp.
It can be seen in Figure 6. We want to emphasize
Figure 6: At the end of the interaction, the user sees the
works of the other users in their variety. A random quota is
intended to reinforce the effectiveness of reflective activities
(phase of enhancer).
this feature of the prototype, as social reflection is
mentioned as an important research object in reflec-
tive play: “Lastly, refective revisiting features can be
made into social learning activities. Instead of re-
viewing your own processes and playbacks, review-
ing your friends’ gameplay can provide opportunities
for comparison, mentorship, and other forms of so-
cial learning.” (Miller et al., 2024, p. 16). However, it
is not only friends with whom one interacts but each
student of the platform and their visual and textual
ideas. In the course of the user study, we are par-
ticularly interested in whether this would contribute
to a more collective enjoyment of the interaction or
whether it would lead to an uncomfortable and thus
unwanted sharing of personal artworks. In the fol-
lowing, we want to discuss the initial results of the
experience with ’eudaily’ and highlight both positive
and negative aspects, as well as further ideas, so that
multiple implications for the development of reflec-
tive play emerge.
3 CASE STUDY
We recruited 21 participants on Prolific who explic-
itly indicate a student status in their profiles. They
had to declare an interest in philosophical activities
and provide a 100% acceptance rate on this platform,
i.e. a submission was never rejected due to suspi-
cious participation. This interest in philosophy was
a prerequisite for authentically analyzing the effec-
tiveness of the prototype. The age range was be-
tween 18 and 46. Eleven men (52.38%), nine women
(42.86%), and one trans man (4.76%) took part in
the study. The participants also shared their nation-
ality (anonymized): Eleven European students, seven
African students, and three students from America.
We collected information consent that allowed the
use of their statements for sharing in a research ar-
ticle. Furthermore, we paid £5 for each participation.
On average, the test participants spent 36.03 minutes
on ’eudaily’ and taking part in the subsequent sur-
vey. Participants were required to write a statement
of at least 50 words detailing the negative and positive
points of use. In addition, participants had to answer
all items of the three subscales (reflection, rumination,
and self-focused thinking) of the “Reflection, Rumi-
nation and Thought in Technology (R2T2)” scale (Lo-
erakker et al., 2024). With the items for reflection, the
consciousness of one’s behavior as well as the sup-
port of reflective activities are measured in interaction
with a technology. The items of the rumination sub-
scale are developed for assessing the amount of creat-
ing negative thought cycles and reflecting on past sit-
uations in interaction with technology. The items of
the self-focused thinking scale measure the influence
of technology on the analysis of one’s feelings and
the origin of thoughts. The subscales should be used
to measure the extent of these aspects in interaction
with ’eudaily’ to determine whether all forms of the
scale-related aspects are addressed in the interaction.
We intended to analyze whether all forms of reflec-
tion are addressed in the interaction. The Cronbach’s
alpha of the subscales were at least satisfactorily con-
sistent (Taber, 2018), so that implications could be de-
veloped on this basis (reflection: α=0.81, rumination:
α=0.66, self-focused thinking: α=0.88).
4 FINDINGS & PRACTICAL
IMPLICATIONS
In general, there are five specific practical implica-
tions based on this use case. However, some general
statements can be derived regarding the overall pleas-
antness of ’eudaily’: The most frequently mentioned
Eudaily: Supporting University Students in Daily Eudaimonic Reflection Using the Reflective Play Framework
487

was the variety of perspectives to be evaluated in the
disruptive phase together with the ’Eudai-Bot’ (n =
5). Four participants share the positive feedback of
an artistic expression on the canvas (19.05%). One
participant (no. 14) positively emphasizes the lack of
pressure for perfection described in the painting pro-
cess. Another participant (no. 2) highlighted the pos-
sibility of being able to focus on the reading process,
which has been evaluated positively. To summarize
and structure each of the five practical implications of
this use case, we will address them in the respective
subsections.
4.1 Positive Disruption
The use case showed that, as assumed by the authors
of the framework (Miller et al., 2024), alternative
mixed-affect experiences can also serve as a design
template during the disruptive phase. The students’
statements showed that engaging with philosophical
perspectives was sufficient for a positive reflective ex-
perience. This is also shown by the quantitative anal-
ysis of the R2T2 subscales that we could not measure
any negative reflection experiences, but significantly
more self-focused thinking and reflection pointing to
reflection based on positive disruption. Low values
were found for rumination, i.e. a t-test for reflection
and rumination shows a significant difference in the
mean values (t=4.939, p¡.000***). This also applies
to the mean values of the subscales of self-focused
thinking and rumination (t=4.546, p¡.000***). The
items for rumination are scored lower in comparison
to each case (the results are illustrated in Figure 7).
This seems logical, as rumination “is considered to
be a negative cognitive process, as it can involve a
focus on loss and failures” (Loerakker et al., 2024,
p. 2). Thus, the use case discovered an additional
form of disruption as previously stated: positive or
morally-elevated dissonance. According to the quan-
titative analyses, confrontation with new, inspiring
perspectives that challenge one’s patterns of thought
also leads to reflection processes and promotes self-
focused thinking. It may be close to feelings such
as awe and moral elevation, which can be assigned
to the eudaimonic emotional field (Landmann, 2021).
Based on the results, these forms of positive eudai-
monic emotions in connection with reflection pro-
cesses are equally design principles of disruptions. In
other words, it may be sufficient to create spaces of
disruption that are not always negative or concern vi-
olation of user expectations, but also to create disrup-
tions with positive eudaimonic emotions.
4.2 Variety During Disruption
The most frequently mentioned positive aspect among
the participants was the variety of perspectives (n =
5, 23.81%), e.g. participant no. 4 wrote: “I really
appreciated the variety of sentences selected and the
possibility of giving my point of view too. I think it’s
something that makes you think”. An alternative in-
terpretation is given by the 21st participant: “I really
liked that many quotes were presented, so we could
tune in to the topic and learn from those who figured it
out in their way”. Other participants also commented
positively on the variety of perspectives, e.g. Partici-
pant No. 17: “I found it interesting to read all of the
different ideas that where being put forward”. Partic-
ipant no. 6 adds: “I really enjoyed the simplicity of
the visuals and how the screen was organized to pro-
vide all different perspectives while not being visually
overwhelming”. Lastly, Participant No. 3 manifests:
“I really appreciated the variety of sentences selected
and the possibility of giving my point of view too”.
Thus, the second practical implication of this use case
is that a variety of perspectives during the disruptive
phase may enhance the reflection process instead of a
single event such as a narrative twist. From this, we
conclude that confronting a variety of perspectives,
opinions or interpretations can be sufficient as a dis-
ruptive momentum.
4.3 Customizing the Disruption
A fourth practical implication was drawn from the use
case, namely that the customization of the ambience
and interaction spaces was noticeably demanded. For
example, participant no. 18 stated that he or she “felt
that the overall ‘atmosphere’ was a little too unse-
rious and overly ‘spiritualistic’ for my tastes, which
mainly regards the particular way the content was
presented (e.g. floaty animated UI, walking android
in the backdrop), and not the content itself ”. Par-
ticipant no. 13 mentions the customization of the
theme as a specific point for improvement: “I found
the theme (the color mostly) set a particular mood,
about which I wasn’t sure how to feel. It made me
a little pensive, but in a “gloomy” sense (similar to
how rainy weather may trigger a particular kind of
atmosphere). Overall, I found it a bit distracting and
would prefer the option to choose a theme”. In two
cases there was an explicit wish to add ambient music.
Participant no. 12 writes: “ambient music should be
used to enhance the aspect of focus”. Participant no.
15 adds: “For improvements, I think having some fit-
ting ambience music in the background would further
enhance the experience”. Finally, participant no. 13
CSEDU 2025 - 17th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
488
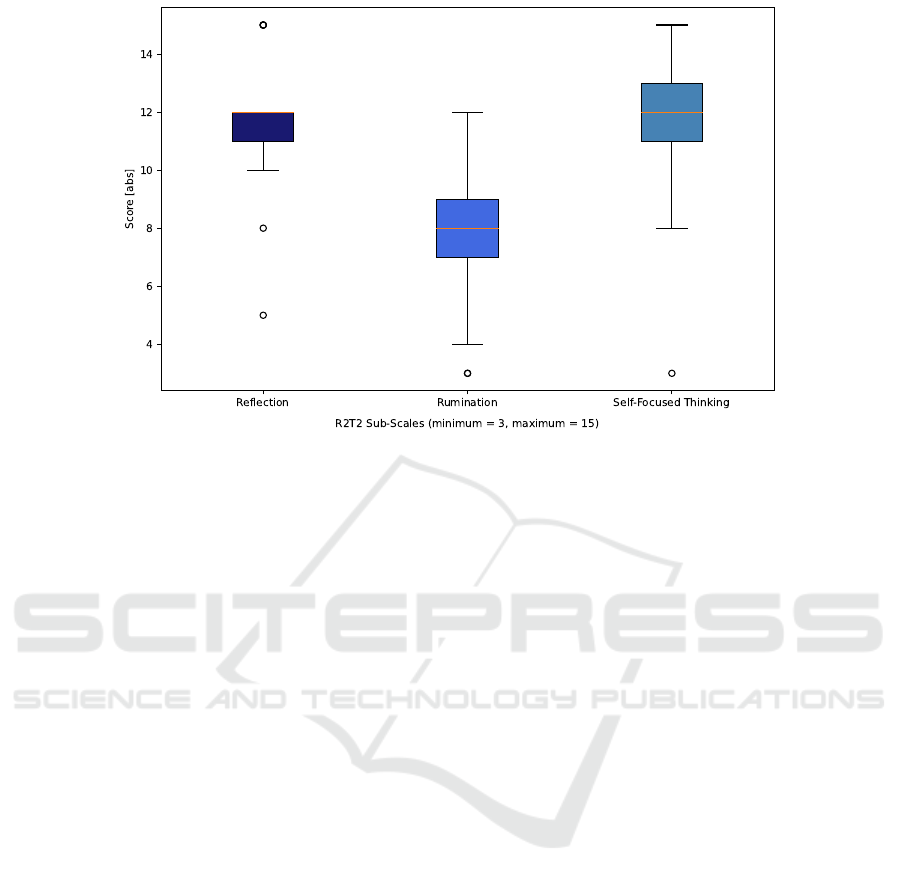
Figure 7: The evaluation of the subscales of the R2T2 scale. The Rumination subscale showed significantly lower scores on
average.
mentioned the capacity to choose the topic in the in-
terface instead of using a randomizer: “At the outset, I
would have preferred an option that listed how many
topics there were from which to choose - I did want
to explore others, [...]”. The supposedly subjective
aspects of interaction design have the practical impli-
cation of wide modification of the disruption such as
the ambience or even the topic. It may indicate that an
overly prefabricated reflection procedure does not al-
low for the desired degree of reflection in the system
for each student. For two students, the ’Eudai-Bot’
was irritating or even annoying in the first step. This
results in the potential importance of influencing the
design of disruptive events and following steps of the
reflective play experience.
4.4 Instructive Reflection While
Questioning & Slowdowns
There is another important practical implication for
the subsequent steps of slowdowns and questioning.
The principles of slow serious games explicitly de-
mand the avoidance of instructions in two points
(“7. No commentary/narration used/permitted” and
“8. No extra information or text boxes displayed dur-
ing gameplay” (Marsh, 2016, p. 50)). The participants
were sometimes unable to understand the phases and
the corresponding task. Participant no. 19 writes:
“And as for the project itself in general I would add
a bit of an introduction, a really easy task to get me
comfortable or something like that”. Participant no.
4 mentions the importance of additional questions: “I
think It could be improved by adding questions. What
I mean is, instead of just having the quotes, also hav-
ing questions that make people reflect and think by
themselves about the topic”. Participant no. 1 clearly
demands: “I would probably add further explanation
if I where you”. It seems to be not clear from the expe-
riences of the students what exactly needs to be done,
what the next steps are, and what is aimed for within
the interaction. The participants were informed in ad-
vance in the introduction to the study that they would
encounter such a prototype. However, there is still a
certain need for guidance in the process itself. The use
case has shown that this guidance cannot be always
implicitly derived from the events and that textual in-
formation can be useful. Even though they should be
avoided during phases of questioning and slowdowns,
a minimum introduction and help options are recom-
mended.
4.5 Variety of Self-Expressiveness
In the questioning phase, the need for a variety of per-
sonal expressiveness is particularly evident. Two par-
ticipants stated that the reflection is only expressed
by their quotation and minimal painting should be ex-
panded by including other forms of expression. Par-
ticipant no. 10 mentions writing a description and
documenting expressions of feelings: “maybe you
should find a way for the user to be able to ‘paint’
the concept without actually having to draw,- maybe
write a description? explain their feelings regarding
the concept? [...]”. Participant no. 21 states: “How-
Eudaily: Supporting University Students in Daily Eudaimonic Reflection Using the Reflective Play Framework
489

ever, I missed having to write more on the topic in my
own words. Making a quote makes you want to think
philosophically and therefore you miss the important
part of self-reflection. Furthermore the artistic part is
very controversial in my opinion because it’s the kind
of thing that only works for some people”. On the
other hand, participant no. 14 writes: “[...] the art-
work wasn’t perfect but I enjoyed the process”. The
necessity of different forms of expression of reflection
can be derived from these perspectives. In the diver-
sity of statements, some may want to express them-
selves artistically, others may want to avoid it. In the
systems of reflection, a wide range of forms of ex-
pression must be made possible, which also enables
reflection in the final phase of enhancement.
Finally, one statement regarding the presentation of
other artworks and quotes by other students should be
addressed. A participant (no. 20: “It was interest-
ing to see the user(?) generated quotes at the end,
[...]”) briefly commented positively on the viewing
of other participants. However, all other participants
did not mention any concerns or further positive com-
ments. It may therefore not have been perceived as
having any explicit significance in the interaction, but
merely as an ’extra’ to one’s interaction. It may make
sense to anchor these social aspects of reflection in
the interaction at an earlier stage (e.g. questioning).
This research question, which arises from the implicit
derivation of non-mentioning, needs to be analyzed in
an alternative system design.
5 LIMITATIONS
The first limitation of the practical implications is the
reference to only one use case and a limited number
of students participating from three nationalities (Eu-
rope, Africa, and America). In its novelty, however,
it may serve as a useful foundation for future imple-
mentations of the reflective play framework, as it rep-
resents the first application of this framework. The
second limitation is the lack of analysis of the long-
term effect. With the scales, we have only measured
a short-term perception of reflective activities. In the
next step, we aim to analyze the long-term effect by
using well-being metrics, e.g. with the Question-
naire for Eudaimonic Well-Being (QWEB) (Water-
man et al., 2010). The final limitation is the inclusion
of students who are explicitly interested in philoso-
phy (using the profile information on Prolific). For
further research, transfer effects and development of
interest are important for students who are not neces-
sarily enthusiastic about these eudaimonic activities,
but who may be inspired by the interaction. For ex-
ample, one participant (no. 10) comments as follows:
“[...] liked it a lot, and would possibly use it in my
down time, but I must say I have an interest in these
subjects (although not an intense one or anything) so
I don’t know if people that hadn’t taken a class on the
matter would feel the same”. We want to address this
question in further studies.
6 CONCLUSION
To summarize, there are five practical implications for
technologies to enhance reflective practices: (1) Pos-
itive disruption can be a design element, i.e. being
confronted with fragments (even if only textual) can
already generate positive forms of disruption that ini-
tiate reflective processes. (2) Diversity of perspec-
tives can serve as a design concept for positive dis-
ruption. (3) The technology should be customizable
regarding ambience and interaction space for reflec-
tion. (4) Instructions can be helpful during phases of
slowdowns, even if the user’s free exploration has a
higher priority in reflective activities. (5) The user
must be able to develop his or her reflections play-
fully through a variety of self-expressive mechanisms.
To conclude, these five initial implications expand the
development spectrum around the question of eudai-
monic and reflection-enhancing technology and are
more closely analyzed concerning the aforementioned
limitations.
REFERENCES
Altarriba Bertran, F., M
´
arquez Segura, E., and Isbister, K.
(2020). Technology for situated and emergent play:
A bridging concept and design agenda. In Proceed-
ings of the 2020 CHI Conference on Human Factors in
Computing Systems, CHI ’20, page 1–14, New York,
NY, USA. Association for Computing Machinery.
Amabile, T. M. (1982). Social psychology of creativity: A
consensual assessment technique. Journal of Person-
ality and Social Psychology, 43(5):997–1013.
Baumer, E. P. (2015). Reflective informatics: Conceptual
dimensions for designing technologies of reflection.
In Proceedings of the 33rd Annual ACM Conference
on Human Factors in Computing Systems, CHI ’15,
page 585–594, New York, NY, USA. Association for
Computing Machinery.
Behzad, A. (2023). Co-shaping temporality: Mediating
time through an interactive hourglass. In Compan-
ion Publication of the 2023 ACM Designing Interac-
tive Systems Conference, DIS ’23 Companion, page
241–245, New York, NY, USA. Association for Com-
puting Machinery.
CSEDU 2025 - 17th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
490

Cole, T. and Gillies, M. (2022). Emotional exploration and
the eudaimonic gameplay experience: A grounded
theory. In Proceedings of the 2022 CHI Conference
on Human Factors in Computing Systems, CHI ’22,
New York, NY, USA. Association for Computing Ma-
chinery.
Cremaschi, M., Dorfmann, M., and De Angeli, A. (2024).
A steampunk critique of machine learning accelera-
tion. In Proceedings of the 2024 ACM Designing In-
teractive Systems Conference, DIS ’24, page 246–257,
New York, NY, USA. Association for Computing Ma-
chinery.
Grolnick, W. S. and Ryan, R. M. (1987). Autonomy in
children’s learning: An experimental and individual
difference investigation. Journal of Personality and
Social Psychology, 52(5):890–898.
Halln
¨
as, L. and Redstr
¨
om, J. (2001). Slow technology – de-
signing for reflection. Personal Ubiquitous Comput.,
5(3):201–212.
Huta, V. (2016). Eudaimonic and hedonic orienta-
tions: Theoretical considerations and research find-
ings. Handbook of eudaimonic well-being, pages 215–
231.
Joers, J. M. and De Luca, E. W. (2024). Perfect eudai-
monic user experience design that aristotle would have
wanted. In Companion Publication of the 2024 ACM
Designing Interactive Systems Conference, DIS ’24
Companion, page 96–101, New York, NY, USA. As-
sociation for Computing Machinery.
Kwon, S., Yoo, D. W., and Kang, Y. (2024). Spiritual ai:
Exploring the possibilities of a human-ai interaction
beyond productive goals. In Extended Abstracts of the
2024 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Comput-
ing Systems, CHI EA ’24, New York, NY, USA. As-
sociation for Computing Machinery.
Landmann, H. (2021). The bright and dark side of eudai-
monic emotions: A conceptual framework. Media and
Communication, 9(2):191–201.
Li, J., Kwon, N., Pham, H., Shim, R., and Leshed, G.
(2023). Co-designing magic machines for everyday
mindfulness with practitioners. In Proceedings of the
2023 ACM Designing Interactive Systems Conference,
DIS ’23, page 1630–1647, New York, NY, USA. As-
sociation for Computing Machinery.
Liedgren, J., Desmet, P. M. A., and Gaggioli, A. (2023).
Liminal design: A conceptual framework and three-
step approach for developing technology that delivers
transcendence and deeper experiences. Frontiers in
Psychology, 14.
Loerakker, M. B., Niess, J., and Wo
´
zniak, P. W. (2024).
Technology which makes you think: The reflection,
rumination and thought in technology scale. Proceed-
ings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and
Ubiquitous Technologies, 8(2).
Marsh, T. (2016). Slow serious games, interactions and
play: Designing for positive and serious experience
and reflection. Entertainment Computing, 14:45–53.
McGraw, K. O. and McCullers, J. C. (1979). Evidence of a
detrimental effect of extrinsic incentives on breaking
a mental set. Journal of Experimental Social Psychol-
ogy, 15(3):285–294.
Mekler, E. D. and Hornbæk, K. (2016). Momentary plea-
sure or lasting meaning? distinguishing eudaimonic
and hedonic user experiences. In Proceedings of the
2016 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Comput-
ing Systems, CHI ’16, page 4509–4520, New York,
NY, USA. Association for Computing Machinery.
Miller, J. A., Gandhi, K., Whitby, M. A., Kosa, M., Cooper,
S., Mekler, E. D., and Iacovides, I. (2024). A design
framework for reflective play. In Proceedings of the
CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Sys-
tems, CHI ’24, New York, NY, USA. Association for
Computing Machinery.
Pasumarthy, N., Nisal, S., Danaher, J., van den Hoven, E.,
and Khot, R. A. (2024). Go-go biome: Evaluation of a
casual game for gut health engagement and reflection.
In Proceedings of the CHI Conference on Human Fac-
tors in Computing Systems, CHI ’24, New York, NY,
USA. Association for Computing Machinery.
Sarkar, A. (2023). Should computers be easy to use? ques-
tioning the doctrine of simplicity in user interface de-
sign. In Extended Abstracts of the 2023 CHI Confer-
ence on Human Factors in Computing Systems, CHI
EA ’23, New York, NY, USA. Association for Com-
puting Machinery.
Sathya, A. and Nakagaki, K. (2024). Attention receipts:
Utilizing the materiality of receipts to improve screen-
time reflection on youtube. In Proceedings of the CHI
Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems,
CHI ’24, New York, NY, USA. Association for Com-
puting Machinery.
Schrier, K. K. (2024). How do we teach eudaimonia through
games? In Proceedings of the 19th International Con-
ference on the Foundations of Digital Games, FDG
’24, New York, NY, USA. Association for Computing
Machinery.
Soffel, J. (2016). Ten 21st-century skills every student
needs. https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2016/03/
21st-century-skills-future-jobs-students/. Accessed:
2024-09-01.
Stephanidis, C., Salvendy, G., Antona, M., Chen, J. Y. C.,
Dong, J., Duffy, V. G., Fang, X., Fidopiastis, C.,
Fragomeni, G., Fu, L. P., Guo, Y., Harris, D., Ioannou,
A., ah (Kate) Jeong, K., Konomi, S., Kr
¨
omker, H.,
Kurosu, M., Lewis, J. R., Marcus, A., Meiselwitz, G.,
Moallem, A., Mori, H., Nah, F. F.-H., Ntoa, S., Rau,
P.-L. P., Schmorrow, D., Siau, K., Streitz, N., Wang,
W., Yamamoto, S., Zaphiris, P., and Zhou, J. (2019).
Seven hci grand challenges. International Journal of
Human–Computer Interaction, 35(14):1229–1269.
Taber, K. S. (2018). The use of cronbach’s alpha when de-
veloping and reporting research instruments in science
education. Research in science education, 48:1273–
1296.
Waterman, A. S., Schwartz, S. J., Zamboanga, B. L., Ravert,
R. D., Williams, M. K., Agocha, V. B., Kim, S. Y.,
and Donnellan, M. B. (2010). The questionnaire for
eudaimonic well-being: Psychometric properties, de-
mographic comparisons, and evidence of validity. The
journal of positive psychology, 5(1):41–61.
Eudaily: Supporting University Students in Daily Eudaimonic Reflection Using the Reflective Play Framework
491
