
Development of a Big Data Mechanism for AutoML
Roberto S
´
a Barreto Paiva da Cunha
1 a
, Jairson Barbosa Rodrigues
2 b
and Alexandre M. A. Maciel
1 c
1
Universidade de Pernambuco, Recife, Brazil
2
Universidade Federal do Vale do S
˜
ao Francisco, Juazeiro, Brazil
Keywords:
Big Data, AutoML, Machine Learning.
Abstract:
This paper introduces the development of an AutoML mechanism explicitly designed for large-scale data pro-
cessing. First, the paper presents a comprehensive technological benchmark of current AutoML frameworks.
According to the gaps found, the paper proposes integrating consolidated Big Data technologies into an open-
source AutoML framework, emphasizing enhanced usability and scalability in processing capabilities. The
entire methodology of this paper was based on Design Science Research - DSR, commonly used in studies
that seek to to develop innovative artifacts, such as systems, methods or theoretical models, to address prac-
tical challenges. The developed architecture enhances the AutoML FMD - Framework of Data Mining. This
integration allowed the efficient management of large datasets and supported distributed machine learning al-
gorithms training. An expert opinion evaluation demonstrated the effectiveness in reducing the learning curve
for non-experts and improving scalability and data handling. Integration tests were adopted to validate all
FMD components.This work significantly advanced FMD by broadening its applicability to large datasets and
various domains while making open-source collaboration and ongoing innovation possible.
1 INTRODUCTION
In recent years, the volume of data has grown expo-
nentially with the increase of mobile device availabil-
ity, the Internet of Things (IoT) applications, and so-
cial network popularization. The term Big Data ap-
peared in this context of increased data generation.
Some definitions can be found in the literature: ”Big
Data is a massive volume of structured and unstruc-
tured data that is so large that it’s difficult to process
using traditional database and software techniques”
(Frank, 2013).
Changes in the storage and processing paradigms
are needed to support the complexity of manipulat-
ing these demands. In this context, arisen technolo-
gies can deal with scalability problems, often in real-
time, with support for redundancy and fault tolerance.
These characteristics are viable through distributed
parallel computing, taking advantage of the comput-
ing power of clusters of machines, usually made up of
low-cost hardware managed by an open-source oper-
ating system (Rodrigues, 2020).
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0006-1710-7869
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1176-3903
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4348-9291
As a consequence of this availability of data, we
can see an increase in machine learning research and
applications. However, the performance of many ma-
chine learning methods is susceptible to a plethora
of design decisions, which constitutes a consider-
able barrier for new users. In this scenario, AutoML
frameworks emerged to make these decisions in a
data-driven, objective, and automated way. There-
fore, AutoML makes state-of-the-art machine learn-
ing approaches accessible to domain specialists in-
terested in applying machine learning but lacking the
necessary expertise.
Primarily, the AutoML frameworks focused on
solving CASH and Hyperparameter Optimization
(HPO) problems, but some offer functionalities for
attribute selection and data pre-processing. Solving
these problems is difficult because the solution space
is highly dimensional and involves continuous cat-
egorical choices (Hutter et al., 2019). Thus, these
frameworks can make machine learning accessible to
domain specialists fluent in the domain where ML is
applied but with minimal knowledge of how machine
learning works, (Santu et al., 2021).
We started our research with the following ques-
tion: Considering the technological benchmark, how
294
Paiva da Cunha, R. S. B., Rodrigues, J. B. and Maciel, A. M. A.
Development of a Big Data Mechanism for AutoML.
DOI: 10.5220/0013348700003929
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2025) - Volume 1, pages 294-300
ISBN: 978-989-758-749-8; ISSN: 2184-4992
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

can the use of Big Data technologies increase the pro-
cessing capacity of an AutoML system? This work
aims to develop an AutoML mechanism for large-
scale data processing. For this, a technological bench-
mark was realized, and a mechanism to integrate Big
Data elements into an open-source AutoML was de-
veloped. Finally, an expert opinion experiment was
carried out to validate the results in conjunction with
integration software tests.
The main contributions of this article are: (1)
the development of a new AutoML engine adapted
for large-scale data processing, (2) the integration of
Big Data technologies into an open source AutoML
framework and (3) the development of the proposed
engine using Design Science Research (DSR).
The structure of this paper is as follows: Sec-
tion 2 provides background information on Big Data
technologies and AutoML frameworks. Section 3 de-
scribes the development of the proposed Big Data
mechanism, including the DSR methodology and the
proposed architecture for the FMD. Section 4 presents
the analysis and discussion of results, including in-
tegration tests and expert opinions. Finally, Section
5 concludes the paper, highlighting the contributions
and future work.
2 BACKGROUND
This section provides an overview of the main tech-
nologies and frameworks relevant to this paper, in-
cluding Big Data technologies and AutoML frame-
works.
2.1 Big Data Technologies
In 2004, Google developed a framework called
MapReduce for distributed data processing. MapRe-
duce is a programming model and associated imple-
mentation for processing and generating large data
sets (Dean and Ghemawat, 2008). Most Big Data
tools are based on MapReduce and distributed com-
puting. It enables distributed processing of large data
sets across clusters of computers using across clusters
of computers using simple programming models.
In 2009, Apache Hadoop MapReduce was the
dominant parallel programming engine for clusters
and parallel processing of clustered data of thousands
of nodes but had a challenge due to disk read/write op-
erations that caused high latency (Chambers and Za-
haria, 2018). Apache Hadoop stores data on disks and
needs to read data from them to process, which can be
slower than going directly into the memory.
To improve read/write operations, researchers at
UC Berkeley began the Spark research project to
perform parallel processing using the Resilient Dis-
tributed Dataset (RDDs) abstraction. Their work re-
sulted in open source software called Apache Spark
1
,
which introduces the ability to process large volumes
of data quickly through its programming model that
promotes the execution of processes in memory using
RDDs(Zaharia et al., 2010).
2.2 AutoML Benchmark
To analyze the main AutoML frameworks for the
benchmark, we used those cited by (Z
¨
oller and Hu-
ber, 2021), which took into account the number of
citations in scientific papers and popularity in github
stars for relevance. Table 1 shows the frameworks an-
alyzed and the number of stars on github in Decem-
ber 2024. Table II shows a summary of the frame-
works considering capabilities such as user interface,
data visualization, multiple data inputs, metadata in-
ference and if they can run on a distributed cluster.
TPOT (Tree-based Pipeline Optimization Tool)
runs on the command line or in Python code
and is based on genetic programming (Le et al.,
2019)(Squillero and Burelli, 2016)(Olson et al.,
2016). TPOT does not support distributed cluster pro-
cessing, which supports running on multiple cores of
the same machine.
Auto-Sklearn is based on solving the CASH prob-
lem using the machine learning algorithms from the
Scikit-learn library (Feurer et al., 2015)(Feurer et al.,
2022). According to the documentation, running the
algorithms on large data sets can take several hours,
and Auto-sklearn defaults to using just one core. It
can support core parallelism and execution on more
than one machine if used with a library for distributed
computing in Python called Dask
2
(Auto-Sklearn,
a)(Auto-Sklearn, b).
Hyperopt-sklearn is an AutoML based on Python
code, an extension of the Hyperopt hyperparameter
optimization library. Still, it works with the machine
learning algorithms of the Scikit-learn library (Komer
et al., 2014). According to Z
¨
oller & Huber (2021)
(Z
¨
oller and Huber, 2021), Hyperopt-sklearn has no
parallelization configuration available.
ATM (Auto Tune Models) is developed in Python
and only allows data ingestion in CSV format
(Swearingen et al., 2017). ATM can be run from the
command line or via the REST API using a Flask
3
server that can be located in a distributed computing
1
https://spark.apache.org/
2
https://distributed.dask.org/en/latest/index.html
3
https://flask.palletsprojects.com/en/3.0.x/
Development of a Big Data Mechanism for AutoML
295

Table 1: AutoML Frameworks Benchmark.
Framework User Interface REST API Distributed
Cluster
FMD Yes Yes Yes
Auto-Sklearn No No Yes
Hyperopt-sklearn No No No
TPOT No No No
ATM No Yes Yes
H2O AutoML Yes Yes Yes
infrastructure such as a cluster or the cloud. The al-
gorithms are based on the Scikit-learn library.
H2O AutoML is a framework developed in Java
with Bindings for Python, in this case, a link between
libraries written in Java for direct use by the Python
interpreter. The framework does not use algorithms
from the Scikit-learn library, unlike the other four Au-
toMLs analyzed above, and features support for Big
Data tools such as Apache Hadoop and Apache Spark.
2.3 FMD
In its initial version in 2016, the FMD
4
allowed data
to be mined from the Moodle
5
virtual learning envi-
ronment (VLE), making analysis and graphs available
visually to the user. Initially, FMD used technolo-
gies such as Hypertext Markup Language (HTML),
Cascading Style Sheets (CSS), and JavaScript, and
was integrated into Moodle as an HTML block
(Gonc¸alves et al., 2017).
In 2018, there were additions to the FMD to mod-
ernize the technologies used and enable more func-
tionalities for data mining, even in the educational
context. The framework gained a frontend based on
React
6
and a backend in the programming language
Python
7
using Web Services developed in Flask to
connect with the Moodle database.
In 2020, FMD made a further contribution by
gaining a user-friendly user interface and new tech-
nologies. This contribution meant that FMD was no
longer just a framework for data mining but became
a framework for AutoML. The solution only allowed
the execution of supervised machine learning algo-
rithms and presented the results in the graphical in-
terface of the front end, restricting itself to the educa-
tional context.
In 2024, FMD received an update by adding the
data ingestion layer that allowed for greater flexibility
in the platform’s data inputs, previously limited to di-
4
https://github.com/GPCDA/FMD
5
https://moodle.org/
6
https://react.dev
7
https://www.python.org/
rect connection with the Moodle system database or
education-related CSV files. The data ingestor uses
the PDI-CE
8
tool, which will process requests made
by the FMD Flask backend on the HTTP server called
Carte.
3 DEVELOPMENT OF A BIG
DATA MECHANISM
This section details the development process of the
proposed mechanism, including the Design Science
Research methodology adopted and the architectural
design.
3.1 Design Science Research
According to Freitas et al. (2014), technological re-
search is gaining more and more ground in academia,
especially in areas such as engineering and comput-
ing, fields of human knowledge that encourage the de-
velopment of new artifacts (Junior et al., 2017). The
Design Science Research (DSR) approach is com-
monly used in studies seeking the development of
new artifacts, such as systems, methods, or theoret-
ical models, to address practical challenges (Lacerda
et al., 2012). This methodology was adopted through-
out the development and research of this work.
The first stage of the DSR process is awareness,
which aims to highlight the research problem, seek
a solution, outlining the external environment and its
interaction with the artifact being developed. The de-
velopment phase is the third stage of Design Science
Research (DSR) and is characterized by the justifica-
tion of the choices and tools used in the development
of the artifact, as well as its components and the meth-
ods by which the artifact can be tested (Lacerda et al.,
2012).
8
https://www.hitachivantara.com/es-
latam/products/pentaho-platform/data-integration-
analytics/pentaho-community-edition.html
ICEIS 2025 - 27th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
296
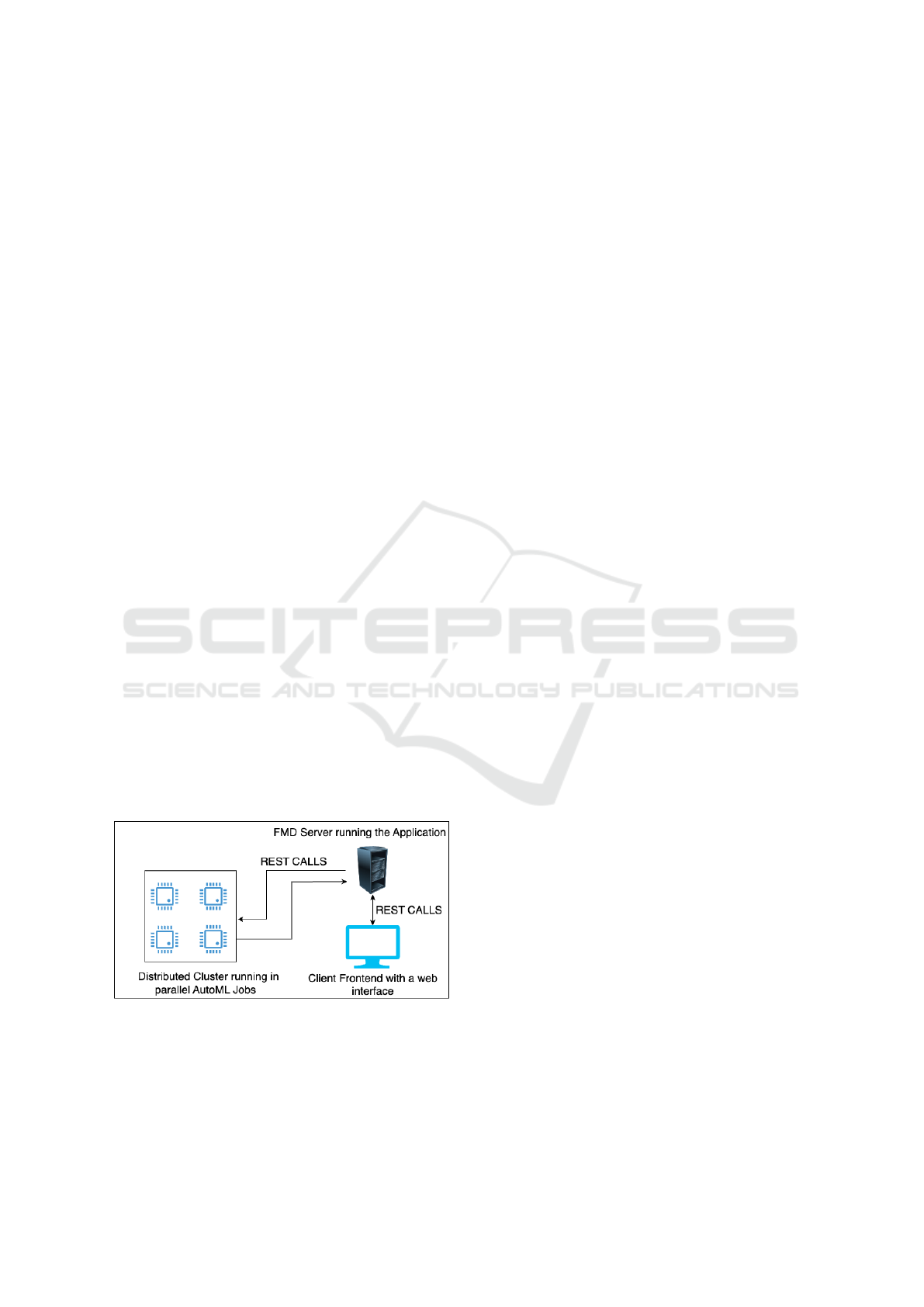
3.2 Proposed Architecture for the FMD
The Frontend layer presents the user interface devel-
oped in React, a JavaScript library used in web ap-
plications. React manipulates the page by dynami-
cally altering its HTML and CSS without the need for
reloading. The graphical components were developed
based on this library. The front end makes HTTP re-
quests using Nginx, a reverse proxy HTTP server, to
facilitate communication between the front and back
end through REST calls.
The original backend was built with Flask using
Gunicorn as the WSGI server (Web Server Gateway
Interface), responsible for receiving requests from
Nginx and sending them to Flask. In the Cluster
layer, a Django Rest server was developed to han-
dle and process requests made through the FMD fron-
tend. The Django Rest service is responsible for read-
ing data from the Hadoop Distributed File System and
executing AutoML training using the H2O library due
to its various algorithms.
Figure 1 shows the architecture we propose for
distributed AutoML systems in which model train-
ing is carried out on a cluster of distributed machines
based on the horizontal scalability proposed in Big
Data tools, communicating via the REST API with
an application server separate from the cluster. The
main benefit of the training not happening on the
server running the FMD is the possibility of point-
ing the REST calls at any physical cluster or cluster of
cloud computing machines. This approach can reduce
costs and bring greater flexibility to a distributed Au-
toML system. Figure 2 in the appendix shows some
FMD screens such as the data sources that are stored
in HDFS and the screen for selecting indicators and
algorithms The Appendix contains images of some
FMD screens..
Figure 1: Proposal Architecture for distributed AutoML.
4 ANALYSIS AND DISCUSSION
OF RESULTS
This section presents the analysis and discussion of
the results obtained from the integration tests and ex-
pert opinion evaluations.
4.1 Integration Test
In order to evaluate the components of the proposed
architecture, the integration test methodology was
used, whose aim is to validate the communication be-
tween system calls, and can be defined as a test carried
out to integrate components of a system (Jin and Of-
funt, 1998). According to Gouveia (2004), there are
two classic integration testing strategies: bottom-up
and top-down (Gouveia, 2004). The approach used
in this article was bottom-up, which consists of val-
idating the components of the module of the lowest
level, following the hierarchy up to the module with
the highest level. The shows the sequential logical or-
der of the tests from the lowest level to the last, which
trains the AutoML models in the proposed FMD ar-
chitecture. Table 2 summarizes the order of the inte-
gration tests, the endpoints and their descriptions.
4.2 Expert Opinion
In order to select experts, the following factors such
as: proof of experience in the field through publica-
tions, consultancies and project work. All factors are
based on credibility and knowledge in the area of the
problem in question: Integration of an AutoML with
Big Data resources. Data tools. Table 3 summarizes
the experts who participated in the project evaluation
and their experience.
To evaluate the behavior of FMD, an expert opin-
ion experiment was realized based on six questions:
1. How would you rate the preview of distributed
data in FMD?
2. How do you evaluate the visualization of at-
tributes in FMD?
3. Do you consider this framework approach to have
a low learning curve for use?
4. What contributions has the project made?
5. Among Big Data tools, do you consider the ap-
proach used to be the most appropriate for FMD?
6. Considering a distributed cluster architecture with
horizontal scalability (adding more machines), Do
you think the developed integration’s ability to
Development of a Big Data Mechanism for AutoML
297

read data from HDFS and perform distributed Au-
toML training contributes to accelerating scien-
tific research?
Based on the results obtained from the survey’s
first question, a trend suggested that FMD users
should be able to specify how many rows they want
to view in the data preview. Some of the experts con-
sidered the preview implementation in the framework
to be effective and educational. Regarding using the
Python Pandas library
9
for data manipulation and vi-
sualization in the Cluster, Pandas is not used for Big
Data manipulation and processing due to the library
loading the entire dataset into memory.
Regarding the second question about visualization
of dataset attributes, experts found it easy, intuitive,
functional, and beneficial. The design of the selection
interface was aimed at abstracting the complexity that
would be required using command lines or code for
attribute selection in Big Data tools.
The third question asked the experts whether the
framework approach has a low learning curve. If the
user group includes individuals with little data science
knowledge, such as domain experts, explaining some
technical terms, such as cross-validation and cluster-
ing, will be necessary.
The fourth question asked experts about the con-
tributions of the FMD project. One opinion noted that
using a distributed approach for AutoML can reduce
the cost of model training. Considering the FMD per-
sonas, it was mentioned that tools like the framework
make Machine learning more accessible and that the
project’s open-source nature is a significant feature.
In the fifth question, experts were asked if the ap-
proach used in FMD is the most appropriate among
existing open-source Big Data tools. Some opinions
converged to confirm the adopted approach through-
out the project.
The sixth question aimed to evaluate if the capa-
bility to read distributed data and perform training
could accelerate scientific research, and all opinions
confirmed this possibility.
9
https://pandas.pydata.org/
5 CONCLUSIONS
This work contributes to the research field of AutoML
by expanding FMD capabilities, allowing its appli-
cation to large datasets. Implementing a distributed
architecture provides system scalability and also re-
duces algorithms’ processing times. Another signif-
icant contribution was the integration of Big Data
tools, such as Hadoop and Spark, which are widely
used for storing and processing large volumes of data.
Additionally, this work extends FMD applicabil-
ity beyond educational contexts, making it a versa-
tile tool for various areas that require analysis of large
data volumes, such as healthcare and industry. Thus,
this was made possible due to the abstraction of sys-
tem components that allow easy adaptation to dif-
ferent types of data and specific processing require-
ments. One of the key features of the proposed solu-
tion is the ability to read distributed data from HDFS.
This capability is an important step towards the de-
mocratization of Big Data technologies for AutoML
frameworks.
The detailed documentation of the project in the
repository and the availability of the source code in an
open-source manner encourage ongoing collaboration
and improvement of the project within the academic
community (FMD, 2024). The Django Rest service
allowed it to be installed separately from the FMD
application server, enabling it to run on clusters.
5.1 Future Work
For future scientific research, we propose exploring
Apache Spark’s native machine learning
10
library to
build AutoML systems. This approach would al-
low an in-depth investigation of the CASH problem
(Combined Algorithm Selection and Hyperparameter
optimization) problem, by systematically combining
the algorithms available in the library and available
in the library and the optimization of their respective
hyperparameters.
10
https://spark.apache.org/mllib/
Table 2: Integration Test Endpoints.
Order Endpoint Endpoint Description
1 GET http://IP ADDRESS:8000/arquivos Shows files in HDFS
2 GET http://IP ADDRESS:8000/dados Shows firts rows of a file
3 GET http://IP ADDRESS:8000/colunas Shows all columns of a selected file
4 POST http://IP ADDRESS:8000/
treinamento
Train model
5 GET http://IP ADDRESS:8000/modelo Download trained model
ICEIS 2025 - 27th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
298
Table 3: Selected experts and profile.
Expert Education Area of ex-
pertise
Institution Experience
Expert 1 PhD in Computer
Science
Data Science Universidade de Pernam-
buco
20 years
Expert 2 Msc in Computer
Science
Data Science F
´
abrica de Neg
´
ocios 18 years
Expert 3 PhD in Computer
Science
Data Science Universidade Federal Rural
Pernambuco
20 years
Expert 4 Msc in Electrical En-
gineering
Data Science Universidade de Pernam-
buco
10 years
Expert 5 PhD in Computer
Science
Data Science Universidade Federal do
Vale do S˜ao Francisco
20 years
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This paper was financed in part by the Coordenac¸
˜
ao
de Aperfeic¸oamento de Pessoal de N
´
ıvel Superior -
Brazil (CAPES) - Finance Code 001, Fundac¸
˜
ao de
Amparo a Ci
ˆ
encia e Tecnologia do Estado de Pernam-
buco (FACEPE), the Conselho Nacional de Desen-
volvimento Cient
´
ıfico e Tecnol
´
ogico (CNPq) - Brazil-
ian research agencies.
REFERENCES
Auto-Sklearn. Manual — autosklearn 0.15.0 docu-
mentation,automl.github.io. https://automl.github.io/
auto-sklearn/master/manual.html.
Auto-Sklearn. Parallel usage: Spawning workers from
the command line — autosklearn 0.15.0 doc-
umentation,” automl.github.io. https://automl.
github.io/auto-sklearn/master/examples/60search/
exampleparallel\ manual\ spawning\ cli.html\
sphx-glr-examples-60-search-example-parallel-
manual-spawning-cli-py.
Chambers, B. and Zaharia, M. (2018). Spark: The
Definitive Guide Big Data Processing Made Simple.
O’Reilly Media, Inc., 1st edition.
Dean, J. and Ghemawat, S. (2008). Mapreduce: simpli-
fied data processing on large clusters. Commun. ACM,
51(1):107–113.
Feurer, M., Eggensperger, K., Falkner, S., Lindauer, M., and
Hutter, F. (2022). Auto-sklearn 2.0: hands-free automl
via meta-learning. J. Mach. Learn. Res., 23(1).
Feurer, M., Klein, A., Eggensperger, K., Springenberg,
J. T., Blum, M., and Hutter, F. (2015). Efficient and
robust automated machine learning. In Proceedings
of the 28th International Conference on Neural Infor-
mation Processing Systems - Volume 2, NIPS’15, page
2755–2763, Cambridge, MA, USA. MIT Press.
FMD (2024). Fmdev. https://github.com/GPCDA/FMD.
Frank, C. (2013). The Big Data Long Tail — devx.com.
https://www.devx.com/blog/the-big-data-long-tail.
[Accessed May-09-2024].
Gonc¸alves, A., Maciel, A., and Rodrigues, R. (2017). De-
velopment of a data mining education framework for
visualization of data in distance learning environ-
ments. pages 547–550.
Gouveia, C. C. (2004). Teste de integrac¸
˜
ao para sistemas
baseados em componentes. Master’s thesis, Universi-
dade Federal da Para
´
ıba, Campina Grande, Para
´
ıba.
Hutter, F., Kotthoff, L., and Vanschoren, J. (2019). Auto-
mated Machine Learning: Methods, Systems, Chal-
lenges. Springer Publishing Company, Incorporated,
1st edition.
Jin, Z. and Offunt, A. J. (1998). Coupling-based criteria
for integration testing. SOFTWARE TESTING,
VERIFICATION AND RELIABILITY 8. Dispon
´
ıvel
em: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.
1002/%28SICI%291099-1689%281998090%298%
3A3%3C133%3A%3AAID-STVR162%3E3.0.CO%
3B2-M. Acesso em: 16 mai. 2024.
Junior, V., Ceci, F., WOSZEZENKI, C., and Goncalves,
A. (2017). Design science research methodology as
methodological strategy for technological research.
Espacios, 38:25.
Komer, B., Bergstra, J., and Eliasmith, C. (2014).
Hyperopt-sklearn: Automatic hyperparameter config-
uration for scikit-learn. In SciPy.
Lacerda, D., Dresch, A., Proenc¸a, A., and Antunes J
´
unior,
J. A. V. (2012). Design science research: A re-
search method to production engineering. Gest
˜
ao &
Produc¸
˜
ao, 20:741–761.
Le, T. T., Fu, W., and Moore, J. H. (2019). Scaling
tree-based automated machine learning to biomedical
big data with a feature set selector. Bioinformatics,
36(1):250–256.
Olson, R. S., Bartley, N., Urbanowicz, R. J., and Moore,
J. H. (2016). Evaluation of a tree-based pipeline opti-
mization tool for automating data science.
Rodrigues, J. B. (2020). An
´
alise de fatores relevantes no
desempenho de plataformas para processamento de
Big Data : Uma abordagem baseada em projeto de
Development of a Big Data Mechanism for AutoML
299

experimentos. PhD thesis, Universidade Federal de
Pernambuco.
Santu, S. K. K., Hassan, M. M., Smith, M. J., Xu, L., Zhai,
C., and Veeramachaneni, K. (2021). Automl to date
and beyond: Challenges and opportunities.
Squillero, G. and Burelli, P., editors (2016). Applications of
Evolutionary Computation - 19th European Confer-
ence, EvoApplications 2016, Porto, Portugal, March
30 - April 1, 2016, Proceedings, Part II, volume 9598
of Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Springer.
Swearingen, T., Drevo, W., Cyphers, B., Cuesta-Infante,
A., Ross, A., and Veeramachaneni, K. (2017). Atm:
A distributed, collaborative, scalable system for auto-
mated machine learning. In 2017 IEEE International
Conference on Big Data (Big Data), pages 151–162.
Zaharia, M., Chowdhury, M., Franklin, M. J., Shenker, S.,
and Stoica, I. (2010). Spark: cluster computing with
working sets. In Proceedings of the 2nd USENIX
Conference on Hot Topics in Cloud Computing, Hot-
Cloud’10, page 10, USA. USENIX Association.
Z
¨
oller, M.-A. and Huber, M. F. (2021). Benchmark and
survey of automated machine learning frameworks.
APPENDIX: FMD SCREENS
Figure 2: Screens of FMD.
ICEIS 2025 - 27th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
300
