
Investigating Parameter-Efficiency of Hybrid QuGANs Based on
Geometric Properties of Generated Sea Route Graphs
Tobias Rohe , Florian Burger, Michael K
¨
olle , Sebastian W
¨
olckert, Maximilian Zorn
and Claudia Linnhoff-Popien
Mobile and Distributed Systems Group, LMU Munich, Germany
fi
Keywords:
Quantum Computing, Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), Graph Generation, Quantum-Classical
Hybrid Algorithms, Geometric Data Analysis.
Abstract:
The demand for artificially generated data for the development, training and testing of new algorithms is om-
nipresent. Quantum computing (QC), does offer the hope that its inherent probabilistic functionality can be
utilised in this field of generative artificial intelligence. In this study, we use quantum-classical hybrid gener-
ative adversarial networks (QuGANs) to artificially generate graphs of shipping routes. We create a training
dataset based on real shipping data and investigate to what extent QuGANs are able to learn and reproduce
inherent distributions and geometric features of this data. We compare hybrid QuGANs with classical Gen-
erative Adversarial Networks (GANs), with a special focus on their parameter efficiency. Our results indicate
that QuGANs are indeed able to quickly learn and represent underlying geometric properties and distributions,
although they seem to have difficulties in introducing variance into the sampled data. Compared to classical
GANs of greater size, measured in the number of parameters used, some QuGANs show similar result quality.
Our reference to concrete use cases, such as the generation of shipping data, provides an illustrative example
and demonstrate the potential and diversity in which QC can be used.
1 INTRODUCTION
QC with its probabilistic character and generative AI
are two topics of our time that go together surpris-
ingly well. In the event that Moore’s Law comes to
an end, QC could be a real alternative - assuming im-
proved QC hardware - as many methods of classical
generative AI can be transferred to the field of QC.
In this study, we look at the successful concept
of GANs and how these can be implemented in hy-
brid form on both classical and QC hardware. Al-
though literature on classical GANs is already ex-
tensive (Goodfellow et al., 2014; Wang et al., 2017;
Creswell et al., 2018; Goodfellow et al., 2020), and
their use cases are diverse, examples are the gener-
ation of brain images (Islam and Zhang, 2020), the
enhancement of image quality (Chen et al., 2018), or
the estimation of road-traffic (Xu et al., 2020), there
is a lack of literature that looks at the functionalities
and abilities of its quantum-classical hybrid version,
so-called QuGANs. Like classical GANs, QuGANs
consist of a discriminator and a generator, but at least
one of the two components is implemented using QC.
In our study, we implement the generator of the
GAN on a QC-simulator, which then subsequently
interacts with a classically implemented discrimina-
tor. We learn and generate artificial shipping routes
that are geometrically subject to the triangle inequal-
ity, which must never be broken. Our primary focus is
on the question of how well and how efficiently such
hybrid QuGANs can recognise the underlying, sim-
plest geometric structures and reproduce them in the
generated data, while approximating with the sam-
pled port distances a bimodal distribution. To learn
and represent the underlying geometric structures in
the generated data is thereby an ability which is cru-
cial for the successfully execution of many generative
tasks (De Cao and Kipf, 2018). Artificial generated
data in general can be used as training and / or test
instances to develop new tools and algorithms (Islam
and Zhang, 2020). Here, for example, a future use
of our artificially created realistic shipping routes as
problem instances for the travelling salesman prob-
lem is conceivable. We evaluate the efficiency of
our QuGAN implementations with that of a classical
GAN with similar, even slightly higher, number of pa-
rameters, while we also benchmark the results against
a random baseline. This research should help to shed
724
Rohe, T., Burger, F., Kölle, M., Wölckert, S., Zorn, M. and Linnhoff-Popien, C.
Investigating Parameter-Efficiency of Hybrid QuGANs Based on Geometric Properties of Generated Sea Route Graphs.
DOI: 10.5220/0013350200003890
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2025) - Volume 1, pages 724-730
ISBN: 978-989-758-737-5; ISSN: 2184-433X
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

more light on the inherent functioning and capabili-
ties of hybrid QuGANs - motivating further research
into this area.
Our work is structured as follows: In Sec. 2 we
provide theoretical background for the work at hand.
In Sec. 3 we present related work, followed by Sec. 4
and the methodology of our paper. Sec. 5 presents
the results of this work. The paper ends with Sec. 6
Conclusion.
2 BACKGROUND
2.1 Generative Adversarial Networks
(GANs)
GANs represent a framework in the field of machine
learning where two neural network models, the gen-
erator (G) and the discriminator (D), respectively pa-
rameterised by sets of neural network weights θ
G
,
θ
D
, are trained adversarially in a zero-sum game.
G
θ
G
(z) = x
f ake
aims to synthesise fake data x
f ake
from
the latent space z, that is indistinguishable from a set
of real training data x
real
which the model is trying to
replicate. The purpose of training G is thus to newly
generate samples that the discriminator mistakes for
increasingly realistic data. D
θ
D
(x) evaluates the au-
thenticity of both the received real data from the train-
ing set and the fake data generated by G with the aim
of accurately labeling samples as “real” (in the orig-
inal data set) or not. The training process involves
G and D simultaneously adjusting their parameters
θ
G
and θ
D
. The loss of the discriminator D that is
incurred in judging the data generated by G is gen-
erally quantified via the binary cross-entropy (BCE)
loss function:
BCE(y, d) = −(y∗log(d)+(1−y)∗ log(1− d)) (1)
where d ∈ [0; 1] represents the probability estimated
by the discriminator that the sample is real, while y is
the associated ground-truth label (1, real or 0, fake).
Training continues until a Nash equilibrium is
reached where neither G nor D can trivially improve
their strategies, meaning that D is not able to discern
between real and generated data anymore. The gen-
eral dynamic of the mini-max game can be described
by the following value function:
min
G
max
D
V (D, G) = E
x∼p
data
(x)
[logD(x)]
+ E
z∼p
z
(z)
[log(1 − D(G(z)))]
(2)
where z ∼ N (0, 1) is randomly sampled noisy input
and x = G(z) is the latent feature vector generated by
G.
One of the main issues with the GAN architecture is
mode collapse, where G learns to produce a limited
variety of outputs, thus not capturing the full variety
of input data. Here, the training process of GANs is
unstable, which is characterised by oscillations and
non-convergence during the training process. This
instability is due to the balance required between G
and D, where disproportionate gradient updates, pro-
duced by e.g. imbalanced learning rates or model
sizes,cause one to overpower the other and undermine
the training process.
2.2 Quantum Generative Adversarial
Networks (QuGANs)
In a QuGAN, either D and / or G can be replaced
with a variational quantum circuit (VQC) (Sim et al.,
2019). In this setup, classical data is mapped to a
quantum state using a feature map f : R
m
→ H
⊗n
, al-
lowing for the application of parameterised quantum
gates to generate a desired output state Ψ. In the end,
we obtain the classical data by measuring the quan-
tum system, for instance, in the computational basis.
Similar to classical GANs, the parameters are trained
against the BCE loss and the minimising direction is
calculated via gradient based methods.
3 RELATED WORK
In case of the realisation of only one component
of a GAN by means of QC, it is referred to as a
hybrid QuGAN (Ngo et al., 2023). Already early
work has speculated that QuGANs will have more di-
verse representation power than their classical coun-
terparts, particularly for very high-dimensional data
(Dallaire-Demers and Killoran, 2018; Lloyd and
Weedbrook, 2018). Over time, various realisations
of QuGANs such as Tensor-Network-Based GANs
(Huggins et al., 2019), Quantum Conditional GANs
(Dallaire-Demers and Killoran, 2018) and Quan-
tum Wasserstein GANs (Chakrabarti et al., 2019)
have been developed. The application of QuGANs
can be diverse, from approximating quantum states
(Chakrabarti et al., 2019), to generating discrete dis-
tributions (Situ et al., 2020), to learn and load random
distributions (Zoufal et al., 2019), to generating im-
ages (Stein et al., 2021).
Comprehensive studies have already been carried
out on the efficiency, especially the parameter ef-
ficiency, of QuGANs. These studies have investi-
gated how QuGANs perform in comparison to clas-
sic GANs with the same number of parameters. Kao
Investigating Parameter-Efficiency of Hybrid QuGANs Based on Geometric Properties of Generated Sea Route Graphs
725

et al. (2023) (Kao et al., 2023) and Stein et al.
(2021) (Stein et al., 2021) demonstrate that QuGANs
achieve comparable or superior performance with
substantially fewer parameters. Kao et al. highlight
ongoing challenges in generating unique and valid
molecules. Li et al. (2021) (Li et al., 2021) further
emphasise the efficiency of QuGANs, showing that
their models can learn molecular distributions effec-
tively with a reduced parameter count and improved
training processes through the use of multiple quan-
tum sub-circuits. Additionally, Anand et al. (2021)
(Anand et al., 2021) explore noise resistance in hybrid
quantum-classical setups, finding that QuGANs can
maintain performance despite moderate noise levels,
which is pivotal for practical applications.
However, to the best of our knowledge, there is no
research into the creation of graphs using QuGANs,
although some models do have connections to graphs,
especially the underlying graph structures of their ap-
plication, such as for generative chemistry (De Cao
and Kipf, 2018). In the field of classical GANs, on
the other hand, there is already literature and various
adapted models. A survey by Zhu et al. (2022) (Zhu
et al., 2022) describes the current state of research on
graph generation via deep learning models, also look-
ing at how classical GANs can be used for this pur-
pose.
4 METHODOLOGY
Our methodology builds on a synthesis of concepts
from two foundational pipelines: a pipeline for quan-
tum machine learning (Gabor et al., 2020) and a
pipeline for quantum optimization (Rohe et al., 2024),
ensuring a comprehensive approach to the problem.
4.1 Data Preprocessing
We employed the Python package searoute to cal-
culate realistic sea-routes between different ports
(Halili, 2024). For the underlying training dataset,
we randomly sampled four ports from the 3, 669 ports
of the searoute package and computed the distances
between all pairs sampled, creating a fully connected
graph, where each node represents a port, and the
edge weights denotes the minimum distances between
those ports. To avoid extreme cases where two ports
are directly next to each other, all graphs where two
ports were closer than 100 nautical miles to each other
were excluded. This follows from the logic that the
triangle inequality can be broken particularly easily
in those cases. We sampled a total of 1, 000 graphs
for our training dataset and pre-processed our data by
normalising the sum of edges to one, while preserving
the integrity of the distance relationships.
4.2 Classical GAN
The discriminator used for our classical GAN, but
also for the later described QuGANs, consists of a
fully connected neural network with three linear lay-
ers: an input layer, a hidden layer with 16 neurons,
and an output layer. The network processes tensors
representing graph data, with an input size of 6, cor-
responding to the edges in our fully connected four-
port graphs. Each layer, except for the output layer, is
activated by a LeakyReLU function to mitigate the is-
sue of dying gradients (Maas et al., 2013). The output
layer utilises a sigmoid activation function to classify
the inputs as real or fake. The discriminator has a
total of 129 trainable parameters. The classical gen-
erator mirrors this architecture but includes a hidden
layer of 10 neurons and receives a noise vector sam-
pled from a normal distribution as input. The output is
a tensor matching the dimensions of real graph data,
activated by a ReLU function to ensure non-negative
edge weights. The generator has a total of 136 train-
able parameters.
4.3 QuGAN
For each of the four hyrbid QuGAN models tested, we
employed the classical discriminator described above
and constructed four different quantum generators.
For the quantum generator, the latent variable was
sampled from a standard normal distribution and then
encoded into a quantum state using angle embedding,
leading us to utilise six qubits. We test two differ-
ent quantum circuits (Ans
¨
atze) based on QISKIT’s
efficient SU(2) 2-local circuit, each one with 5 and
with 10 layers, giving us four generator models. The
first circuit consists of layers of one ladder rotational-
X gates and one ladder Pauli-Y gates, followed by
a circular CNOT entanglement. The second circuit
is less restrictive and consists of layers of two lad-
ders of rotational-X and rotational-Y gates, and again
a circular CNOT entanglement. The Ans
¨
atze utiliz-
ing the Pauli-Y gates have 36 and 66 parameters for
the different numbers of layers, while the Ans
¨
atze
with rotational-Y gates have 72 and 132 parameters.
We will refer to them as QuGAN followed by their
respective number of parameters, e.g. QuGAN(36).
The output of these circuits calculate the probability
that each qubit is in the state 0, which represents an
edge weight, therefor the distance between two ports.
We re-normalised the measurement results to the sum
of one, so that the edge-ratios remain the same, but the
QAIO 2025 - Workshop on Quantum Artificial Intelligence and Optimization 2025
726

measurement data do not differ from the real training
data by their sum. Our numerical simulations were
performed without noise.
4.4 Training & Evaluation
All models were trained using the Adam optimiser
over 1, 000 epochs, with a batch size of 32. The learn-
ing rates were set at 0.3 for the discriminator and
0.001 for the generator, optimising against the BCE
loss. This training process was repeated across five
different seeds, and the average outcomes were re-
ported.
To assess the validity of the generated graphs, we
applied the triangle inequality test. Valid graphs were
those where the post-processed edge weights comply
with the triangle inequality. For each vertice triple
A, B, C ∈ V it hold that d(A, B) ≤ d(A, C) + d(C, B),
with a distance function d : R × R → R.
As a further additional baseline, we sampled
1, 000 graphs from the training data’s post-processed
weight distribution using kernel density estimation,
providing a reference for generating random graphs
based on the training dataset. This should help us to
estimate how easy or hard it is to violate the triangle
inequality if the edges are blindly sampled from the
distribution without considering their geometric rela-
tions to each other.
5 RESULT
In the following, we will take a closer look at our re-
sults presented in Fig. 1. We first look at the results
in the light of valid graphs (Fig. 1a), then at the stan-
dard deviation (Fig. 1b) and the density functions of
the sampled edge weights (Fig. 1c), and finally at the
losses achieved by the different generators (Fig. 1d).
At the beginning, all implementations start with
approximately 1000 valid graphs, which then rela-
tively fast decline within the first 100 epochs, but then
recover again. In general, it can be noted that the
QuGANs keep up with the classical implementation
in terms of valid graphs as evaluation metric. The
QuGAN(36) and QuGAN(132) implementation show
very stable and good (approx. 80% valid graphs) re-
sults. The QuGAN(66) and QuGAN(72) implemen-
tations are less stable and show significantly less valid
graphs (approx. 60% valid graphs). The classical
GAN, on the other hand, takes much longer to reach a
solid level and ultimately fluctuates between 60% and
80% valid graphs. However, it should be noted that all
(Qu)GAN implementations clearly outperform ran-
dom sampling with its 27.9% valid graphs baseline.
The standard deviation of the edge weights in the
training dataset was 0.0826, which also should be
observed in our results. However, all implementa-
tions start with a very low standard deviation (close
to zero), and increase it over the subsequent training
process. These results explain the observation of the
development of the valid graphs in Fig. 1a, where
all (Qu)GANs start at around 100% valid graphs and
then drop sharply. At the beginning of the training
process, all (Qu)GAN implementations produce very
monotonous edge weigths without strong variances
and deviate from this behaviour later in the train-
ing process. While the generation of similar edge
weights ensures that the triangle inequality is not bro-
ken, it makes it for the discriminator a simple task
to distinguish between real and fake data. With the
increase of variance of edge weights, the differen-
tiation becomes more difficult, but the triangle in-
equality is also increasingly broken. Our results in-
dicate, that the QuGANs in general seem to have
a harder time in terms of generating variance, with
only implementation QuGAN(66) showing a similar,
even higher standard deviation compared to the clas-
sical GAN towards the end of training. Implemen-
tations QuGAN(36), QuGAN(132) and QuGAN(72)
are clearly behind here.
Looking at the edge-weight distribution, the clas-
sical GAN and the hybrid QuGAN(66) implementa-
tion approximate the bimodal nature of the underly-
ing training data (dashed-red line) more effectively
than other models, although they do not sharply repli-
cate the two peaks. These models show a more pro-
nounced but smoother rise towards the second peak,
with a centre slightly offset from the training data. Al-
though these implementations do not match the ex-
act height of the training data peaks, as well as the
variability, they come closest to capturing the over-
all trend, despite the evident shift and reduced peak
magnitude in the first peak. Conversely, the mod-
els represented by the QuGAN(132) and QuGAN(72)
curves depict a unimodal distribution with a peak sit-
uated between the two actual peaks of the training
data, suggesting a simpler but less accurate modeling
of the dataset. The QuGAN(36) model also follows
this trend but with a more pronounced central peak,
indicating a tighter concentration around the median
weigh.
In all our implemented (Qu)GAN versions, we use
the same discriminator, which is why we attribute a
certain significance to the comparison of the average
losses of the generator compared to the other imple-
mentations. The classical GAN performs best here.
This can be interpreted with caution as meaning that
the classical generator is best able to build artificial
Investigating Parameter-Efficiency of Hybrid QuGANs Based on Geometric Properties of Generated Sea Route Graphs
727
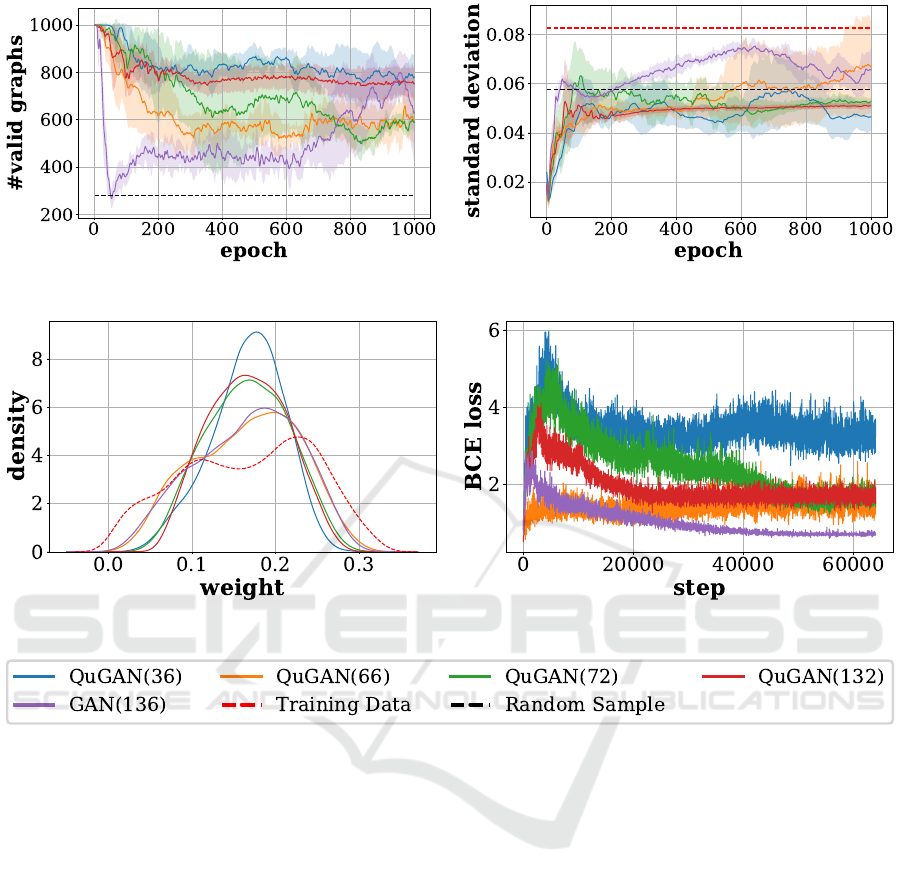
(a) Average Number of Valid Graphs (b) Average Standard Deviation of Edge-Weights
(c) Edge-Weight Distribution (d) Average Loss of Generator
Figure 1: Subgraph a) shows the development of the number of valid graphs over the epochs. Subgraph b) illustrates the
development of the calculated standard deviation of the weights generated over the epochs. Subgraph c) shows the density of
the edge weights, while finally, subgraph d) visualises the loss of the generators.
graphs that cannot be distinguished by the discrimi-
nator, although the feedback loop of the training ef-
fect of D by G must also be mentioned here. The
best quantum implementation is QuGAN(66), closely
followed by QuGAN(72) and QuGAN(132). The
QuGAN(36) implementation performs the worst, al-
though we had the best results here in terms of evalu-
ating the triangle inequality.
6 CONCLUSION
In our, to our knowledge, unique problem setting, we
examined QuGANs for their parameter efficiency. In
particular, we chose a setup where not only the mod-
elling of a density function was in the foreground, but
in each instance several values were sampled from
the distribution, which were all directly connected
and dependent on each other via the triangle inequal-
ity. With the setting applied, not only the sampling,
but also the underlying geometric properties are in-
cluded in the evaluation and comparison. The best-
performing quantum generators were QuGAN(66)
and QuGAN(132), which showed a clear difference
in the learned weight distribution. Both Ans
¨
atze are
built using the same generators, but QuGAN(66) has
fixed Pauli-Y gates. This reduced expressibility al-
lows for easier training while still being capable of ap-
proximating the bimodal distribution of the real data.
Overall, our results suggest that QuGANs struggle to
reflect variance in their generated data. The normali-
sation of the generated graphs plays an important role
in this context. While it reduces the variance of the
generated weights, it also decreases the variance of
the training data. Although GANs are generally dif-
ficult to train, this approach enabled a more stable
training process. At the same time, they can still gen-
QAIO 2025 - Workshop on Quantum Artificial Intelligence and Optimization 2025
728

erate balanced results in the area of tension between
the variation in the edge weights and the fulfilment of
the triangle inequality. For example, the QuGAN(66)
implementation shows equally good results in terms
of variance and valid graphs compared to the clas-
sical GAN, although less than half as many param-
eters were used. This is in line with previous work
on QuGANs and parameter efficiency, although our
work extends this with underlying geometric proper-
ties. In particular, the underlying task chosen here has
great potential for future research. The search for cir-
cuits and implementations that can better reflect the
variance of the training data as well as their geometric
properties should be the main focus of future research.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This paper was partially funded by the German Fed-
eral Ministry of Education and Research through the
funding program ”quantum technologies - from basic
research to market” (contract number: 13N16196).
Furthermore, this paper was also partially funded
by the German Federal Ministry for Economic Af-
fairs and Climate Action through the funding program
”Quantum Computing – Applications for the indus-
try” (contract number: 01MQ22008A).
REFERENCES
Anand, A., Romero, J., Degroote, M., and Aspuru-Guzik,
A. (2021). Noise robustness and experimental demon-
stration of a quantum generative adversarial network
for continuous distributions. Advanced Quantum
Technologies, 4(5):2000069.
Chakrabarti, S., Yiming, H., Li, T., Feizi, S., and Wu, X.
(2019). Quantum wasserstein generative adversarial
networks. Advances in Neural Information Processing
Systems, 32.
Chen, Y., Shi, F., Christodoulou, A. G., Xie, Y., Zhou,
Z., and Li, D. (2018). Efficient and accurate mri
super-resolution using a generative adversarial net-
work and 3d multi-level densely connected network.
In International conference on medical image comput-
ing and computer-assisted intervention, pages 91–99.
Springer.
Creswell, A., White, T., Dumoulin, V., Arulkumaran, K.,
Sengupta, B., and Bharath, A. A. (2018). Generative
adversarial networks: An overview. IEEE signal pro-
cessing magazine, 35(1):53–65.
Dallaire-Demers, P.-L. and Killoran, N. (2018). Quantum
generative adversarial networks. Physical Review A,
98(1):012324.
De Cao, N. and Kipf, T. (2018). Molgan: An implicit gener-
ative model for small molecular graphs. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1805.11973.
Gabor, T., S
¨
unkel, L., Ritz, F., Phan, T., Belzner, L., Roch,
C., Feld, S., and Linnhoff-Popien, C. (2020). The holy
grail of quantum artificial intelligence: major chal-
lenges in accelerating the machine learning pipeline.
In Proceedings of the IEEE/ACM 42nd international
conference on software engineering workshops, pages
456–461.
Goodfellow, I., Pouget-Abadie, J., Mirza, M., Xu, B.,
Warde-Farley, D., Ozair, S., Courville, A., and Ben-
gio, Y. (2014). Generative adversarial nets. Advances
in neural information processing systems, 27.
Goodfellow, I., Pouget-Abadie, J., Mirza, M., Xu, B.,
Warde-Farley, D., Ozair, S., Courville, A., and Ben-
gio, Y. (2020). Generative adversarial networks. Com-
munications of the ACM, 63(11):139–144.
Halili, G. (2024). searoute. https://pypi.org/project/
searoute/. Apache License 2.0.
Huggins, W., Patil, P., Mitchell, B., Whaley, K. B., and
Stoudenmire, E. M. (2019). Towards quantum ma-
chine learning with tensor networks. Quantum Sci-
ence and technology, 4(2):024001.
Islam, J. and Zhang, Y. (2020). Gan-based synthetic brain
pet image generation. Brain informatics, 7(1):3.
Kao, P.-Y., Yang, Y.-C., Chiang, W.-Y., Hsiao, J.-Y., Cao,
Y., Aliper, A., Ren, F., Aspuru-Guzik, A., Zha-
voronkov, A., Hsieh, M.-H., et al. (2023). Exploring
the advantages of quantum generative adversarial net-
works in generative chemistry. Journal of Chemical
Information and Modeling, 63(11):3307–3318.
Li, J., Topaloglu, R. O., and Ghosh, S. (2021). Quantum
generative models for small molecule drug discovery.
IEEE transactions on quantum engineering, 2:1–8.
Lloyd, S. and Weedbrook, C. (2018). Quantum gener-
ative adversarial learning. Physical review letters,
121(4):040502.
Maas, A. L., Hannun, A. Y., Ng, A. Y., et al. (2013). Rec-
tifier nonlinearities improve neural network acoustic
models. In Proc. icml, volume 30, page 3. Atlanta,
GA.
Ngo, T. A., Nguyen, T., and Thang, T. C. (2023). A survey
of recent advances in quantum generative adversarial
networks. Electronics, 12(4):856.
Rohe, T., Gr
¨
atz, S., K
¨
olle, M., Zielinski, S., Stein, J.,
and Linnhoff-Popien, C. (2024). From problem
to solution: A general pipeline to solve optimisa-
tion problems on quantum hardware. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2406.19876.
Sim, S., Johnson, P. D., and Aspuru-Guzik, A. (2019).
Expressibility and entangling capability of parame-
terized quantum circuits for hybrid quantum-classical
algorithms. Advanced Quantum Technologies,
2(12):1900070.
Situ, H., He, Z., Wang, Y., Li, L., and Zheng, S. (2020).
Quantum generative adversarial network for gener-
ating discrete distribution. Information Sciences,
538:193–208.
Stein, S. A., Baheri, B., Chen, D., Mao, Y., Guan, Q., Li, A.,
Fang, B., and Xu, S. (2021). Qugan: A quantum state
fidelity based generative adversarial network. In 2021
Investigating Parameter-Efficiency of Hybrid QuGANs Based on Geometric Properties of Generated Sea Route Graphs
729

IEEE International Conference on Quantum Comput-
ing and Engineering (QCE), pages 71–81. IEEE.
Wang, K., Gou, C., Duan, Y., Lin, Y., Zheng, X., and Wang,
F.-Y. (2017). Generative adversarial networks: intro-
duction and outlook. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automat-
ica Sinica, 4(4):588–598.
Xu, D., Wei, C., Peng, P., Xuan, Q., and Guo, H. (2020).
Ge-gan: A novel deep learning framework for road
traffic state estimation. Transportation Research Part
C: Emerging Technologies, 117:102635.
Zhu, Y., Du, Y., Wang, Y., Xu, Y., Zhang, J., Liu, Q., and
Wu, S. (2022). A survey on deep graph generation:
Methods and applications. In Learning on Graphs
Conference, pages 47–1. PMLR.
Zoufal, C., Lucchi, A., and Woerner, S. (2019). Quantum
generative adversarial networks for learning and load-
ing random distributions. npj Quantum Information,
5(1):103.
QAIO 2025 - Workshop on Quantum Artificial Intelligence and Optimization 2025
730
