
Understanding Intention to Adopt Smart Thermostats: The Role of
Individual Predictors and Social Beliefs Across Five EU Countries
Mona Bielig
1,2 a
, Florian Kutzner
1
, Sonja Klingert
3b
and Celina Kacperski
1,2 c
1
Seeburg Castle University, Seeburgstraße 8, 5201 Seekirchen am Wallersee, Austria
2
University of Konstanz, Universitätsstraße 10, 78464 Konstanz, Germany
3
University of Stuttgart, Keplerstraße 7, 70174 Stuttgart, Germany
Keywords: Technology Acceptance, Smart Thermostats, Social Beliefs.
Abstract: Heating of buildings represents a significant share of the energy consumption in Europe. Smart thermostats
that capitalize on the data-driven analysis of heating patterns in order to optimize heat supply are a very
promising part of building energy management technology. However, factors driving their acceptance by
buildings’ inhabitants are poorly understood although being a prerequisite for fully tapping on their potential.
In order to understand the driving forces of technology adoption in this use case, a large survey (N = 2250)
was conducted in five EU countries (Austria, Belgium, Estonia, Germany, Greece). For the data analysis
structural equation modelling based on the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT)
was employed, which was extended by adding social beliefs, including descriptive social norms, collective
efficacy, social identity and trust. As a result, performance expectancy, price value, and effort expectancy
proved to be the most important predictors overall, with variations across countries. In sum, the adoption of
smart thermostats appears more strongly associated with individual beliefs about their functioning, potentially
reducing their adoption. At the end of the paper, implications for policy making and marketing of smart
heating technologies are discussed.
1 INTRODUCTION
Around 40% of energy in the EU is consumed in
buildings, and of building energy consumption about
80% is used for heating
1
. In order to meet the 2030
target of a 55% reduction in emissions compared to
1990, which heavily involves the building sector
(European Environment Agency (EEA), 2021), there
has been a push for the adoption of smart home
technologies, including smart energy management
technologies (European Commission, 2022). A smart
thermostat, a specific type of smart heating
technology (SHT), connects to the existing heating
system and detects behavioral patterns of residents, in
some cases allows for smart controls, and can save up
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7535-8961
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0653-003X
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8844-5164
1
https://energy.ec.europa.eu/topics/energy-efficiency/
energy-efficient-buildings/energy-performance-
buildings-directive_en
to 30% energy, depending on the type (Lu et al., 2010;
Wang et al., 2020).
In principal, smart thermostats work in a loop of
detection of behavioral patterns through sensors, and
potentially with the prediction of external events or
temperature, in order to predict dynamic heating
needs under comfort constraints and then provide
optimal requirement to heating supply, as shown in
Figure 1 (Haji Hosseinloo et al., 2020).
36
Bielig, M., Kutzner, F., Klingert, S. and Kacperski, C.
Understanding Intention to Adopt Smart Thermostats: The Role of Individual Predictors and Social Beliefs Across Five EU Countries.
DOI: 10.5220/0013356200003953
In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Smart Cities and Green ICT Systems (SMARTGREENS 2025), pages 36-47
ISBN: 978-989-758-751-1; ISSN: 2184-4968
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

Figure 1: Design of smart thermostats (Haji Hosseinloo et
al., 2020).
Smart home technology may not yet be widely
perceived as mainstream (Chang & Nam, 2021), and
its rate of adoption has been characterized as
relatively slow (Marikyan et al., 2019). However,
market trends suggest a gradual expansion in the
sector (Sovacool & Furszyfer Del Rio, 2020).
Eurostat figures from 2022 reveal that about 10% of
European households have incorporated smart home
technologies, including but not limited to energy
management systems.
Figure 2: Left: Smart heating technology used as the basis
for technical design. Right: General technology picture
shown to participants.
Notably, the widespread rollout of smart
thermostats not only requires the availability of
technical equipment, but also households’
willingness to adopt the smart thermostats, and a
consent to give up some control. In order to test
technology acceptance, a real life example was used
(see Figure 2) to describe the way that a smart
thermostats works to non-scientific participants of a
survey. In the following, we will first describe the
underlying theoretical models and related work on
predictors for smart thermostat adoption, resulting in
our proposed model and hypotheses. We will then
describe our study design to understand intentions to
adopt smart thermostats in five European Countries,
followed by an overview on our most important
2
We will further refer to the UTAUT-model comprising
research based on both UTAUT and UTAUT2.
results. We end with discussions and conclusions of
our work, including limitations and strengths as well
as policy implications.
2 RELATED WORK
Previous acceptance research has focused mainly on
smart home technologies in general (for a review, see
Li et al., 2021), with research on smart heating
technologies in particular under-represented. This is
problematic, as behavioral flexibility in heating is
lower than for other appliances (Spence et al., 2015).
The existing research on acceptance of smart heating
technology concentrates on individual and technical
factors (e.g., Girod et al., 2017); social drivers for
acceptance are either absent or results inconsistent
(Große-Kreul, 2022). As both the diffusion of
innovative technologies, and pro-environmental
decisions have been shown to be driven by social
aspects (Fritsche et al., 2018; Rogers, 2003), the
current research deepens the understanding of
acceptance of a smart heating technology, smart
thermostats, combining individual and social aspects
in one model.
2.1 UTAUT and Smart Technology
Acceptance
The Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of
Technology (UTAUT) (Venkatesh et al., 2003) was
developed to summarize eight different technology
acceptance models and has been successfully
employed across multiple contexts such as mobility,
IoT in health care or mobile payment (Abrahão et al.,
2016; Arfi et al., 2021; Nordhoff et al., 2021). It was
extended to the UTAUT2 (Venkatesh et al., 2012) to
better align with a consumer context. The full model
includes seven predictors for behavioral intention to
use a technology, which only then translates into
actual user behavior. The seven predictors are
performance expectancy, effort expectancy, social
influence, facilitating conditions, hedonic motivation,
price value and habit.
While the UTAUT
2
, or sometimes a subset of its
predictors, have been studied in the context of
acceptance of different smart home technologies, the
predictive capacity of its components has been
inconsistent across studies, with the exception of
performance expectancy, which has repeatedly been
shown to best predict intention to adopt, both for
Understanding Intention to Adopt Smart Thermostats: The Role of Individual Predictors and Social Beliefs Across Five EU Countries
37

smart energy technologies in general (Gimpel et al.,
2020), and for smart thermostats in particular (Ahn et
al., 2016; Girod et al., 2017; Große-Kreul, 2022;
Mamonov & Koufaris, 2020).
Effort expectancy, that is the perceived ease of
use, was amongst the strongest predictors for
behavioral intention to adopt smart energy
technologies, i.e. energy-saving technologies
comprising sensors and automatic control in a Danish
sample (Billanes & Enevoldsen, 2022), and smart
homes in a sample from Jordan (Shuhaiber & Mashal,
2019). However, it showed no effects for the intention
to adopt smart thermostats in an US sample (Ahn et
al., 2016). Hedonic motivations were important for
the adoption of smart thermostats in a German sample
(Girod et al., 2017), while in a different German
study, they were irrelevant (Große-Kreul, 2022).
Similar inconsistencies can be found for price value,
which had no effect on intention to adopt a smart
thermostat (Girod et al., 2017), but was found
relevant in a discrete choice experiment (Tu et al.,
2021).
The UTAUT also includes the factor social
influence, i.e., the belief that important others think
an individual should use the technology, which will
be discussed in the next section (2.2). Beyond the
UTAUT, other technology acceptance factors such as
privacy concerns or compatibility have been
examined in studies on intention to use or adopt smart
thermostats, smart homes, or smart meters.
2.2 Social Beliefs as Predictors of
Smart Technology Acceptance
Within the UTAUT, the factor of “social influence”
depicts the belief that important others think an
individual should use the technology (Venkatesh et
al., 2003). Social influence is thus understood as a
social norm in the sense of the Theory of Planned
Behavior (TPB; Ajzen, 1985). This type of norm
describes an individual’s perception of what others
expect them do and reflects the normative belief or
social pressure of ‘ought’ of (important) others,
which is also labeled as an injunctive norm (Cialdini,
2007; Cialdini et al., 1990; Göckeritz et al., 2009;
Rivis & Sheeran, 2003). Studies for acceptance of
smart thermostats that included social influence
found varying effects (Ahn et al., 2016; Billanes &
Enevoldsen, 2022; Gimpel et al., 2020; Girod et al.,
2017): While it has predicted smart thermostat
3
Supplementary material can be found under
https://osf.io/ba2vf/?view_only=986065e170584cad90
98d0a2937e216b
adoption intention in Germany (Große-Kreul, 2022)
and smart meter adoption in Brazil (Gumz et al.,
2022), there were very small or no significant effects
in other studies (Ahn et al., 2016; Gimpel et al., 2020;
Girod et al., 2017). In the two studies in which social
influence had the strongest effect on behavioral
intention to adopt smart thermostats and smart meters
(Gumz et al., 2022), the operationalization included
additional aspects less reminiscent of an injunctive
norm, such as sheer perceptions of presence of smart
thermostats in media, or recommendations by the
government. An overview is given in the
supplementary material of our article (SM1)
3
.
The perception of what other do or believe
corresponds to the psychological social norm
approach (Berkowitz, 2004), which differentiates
between injunctive and descriptive norms. While
injunctive norms capture the priorly mentioned
normative belief of social pressure, descriptive norms
refer to an individual’s belief about the prevalence of
a behavior, i.e. of what is “normal”, therefore the
perception of others' own attitudes and behaviors in
the domain (Cialdini, 2007; Rivis & Sheeran, 2003).
Further, research shows that descriptive and
injunctive norms might differ in their effects in
changing behavior (e.g. Park & Smith, 2007; White
et al., 2009). As prior research failed to demonstrate
an effect of injunctive social norms for smart
thermostat uptake, e.g. in Ahn et al. (2016) or Girod
et al. (2017), we aim to investigate descriptive social
norm perceptions as a possible driver of technology
acceptance for smart heating.
Beyond descriptive social norms, there are several
other social beliefs that have been shown to influence
pro-environmental behavior, which might
complement or interact with social norms to promote
the adoption of smart thermostats. Prominently, the
social identity model of pro-environmental action
(SIMPEA) (Fritsche et al., 2018) depicts the influence
of social identity processes for pro-environmental
behavior, also related to the adoption of “green”
technologies. Relevant predictors are collective
efficacy beliefs, i.e. people’s beliefs in the
effectiveness of their combined ability to achieve
goals, and social identification, i.e. the degree to
which relevant group memberships are considered
important for the individual. Further, generalized
social trust, referring to general trust in others across
groups, and trust in the state, i.e. government and
institutions were found decisive for intentions of pro-
SMARTGREENS 2025 - 14th International Conference on Smart Cities and Green ICT Systems
38

environmental behavior (Cologna & Siegrist, 2020),
and individual energy-saving behavior (Caferra et al.,
2021). We therefore explore whether these social
beliefs might drive the adoption of smart heating
technology. The following section will explicate the
definition of our predictors, the prior findings we
build them on, then form our hypotheses.
3 MODEL PREDICTORS AND
HYPOTHESES
We examine predictors of the intention to adopt smart
heating technology, specifically combining
individual beliefs incorporated in the UTAUT, and
different social beliefs which have been shown to
affect pro-environmental behavior decisions, energy
saving intentions and uptake of smart technologies in
prior research. Our goal is to examine whether social
beliefs can explain the intention to adopt smart
heating technology in addition to beliefs about
technical aspects. We decided to exclude habit,
facilitating conditions and hedonic motivation from
our model, as no experience with the technology is
expected, no active usage is required, and no
additional infrastructure beyond the thermostat itself
is necessary.
Behavioral intention (BI) is our key dependent
variable, reflecting the willingness to adopt smart
heating technologies, and is the strongest predictor of
technology use, especially for technologies with
limited consumer experience (Venkatesh et al., 2012).
To explain behavioral intention, we consider the
following predictors, both based on literature of
technology adoption and wider pro-environmental
behaviors:
Performance expectancy (PE) refers to the
perceived usefulness of the technology in achieving
specific goals and was found to be a significant
predictor of intention to adopt smart energy
technologies in multiple studies (Venkatesh et al.,
2012; Gimpel et al., 2020; Ahn et al., 2016). Effort
expectancy (EE), another core UTAUT construct,
captures the perceived ease of use and technical
efficacy of the technology (Venkatesh et al., 2003),
and evidence suggests it plays a role in smart energy
technology adoption (Billanes & Enevoldsen, 2022;
Ahn et al., 2016). Price Value (PV) is the perceived
trade-off between the cost of technology and its
benefits, which has been shown to influence
technology adoption (Venkatesh et al., 2012; Tu et
al., 2021).
Social norms (SN) reflect the influence of others'
perceived behavior on individual intentions.
Descriptive neighborhood social norms have been
found to influence pro-environmental behaviors
(Farrow et al., 2017; Allcott, 2011). Social
identification (SI), can moderate this effect of social
norms on pro-environmental behavior, i.e. it interacts
with the originally expected influence of social norms
and might modify it (Cialdini & Jacobson, 2021;
Masson & Fritsche, 2014). Collective efficacy (CE),
or the belief in the collective ability to achieve
environmental outcomes, is another key predictor of
pro-environmental behavior (Bandura, 2000; Wang,
2018), and can compensate for low individual
efficacy (Jugert et al., 2016).
Lastly, trust is a significant predictor of pro-
environmental behavior, encompassing both general
trust in people (TP) and trust in state institutions (TS).
Higher trust in others and in institutions has been
shown to influence pro-environmental behaviors,
particularly energy-saving intentions (Cologna &
Siegrist, 2020; Caferra et al., 2021). Demographic
variables like age and gender are also considered as
control variables, given their influence on smart home
adoption (Shin et al., 2018; Sovacool et al., 2020).
This leads us to the following Hypotheses:
H1 Performance expectancy has a positive effect on
BI to adopt smart heating technology.
H2 Effort expectancy has a positive effect on BI to
adopt smart heating technology.
H3 Price value has a positive effect on BI to adopt
smart heating technology.
H4 Social norms within the neighborhood have a
positive effect on BI to adopt smart heating
technology.
H5 Social identification moderates the effect of
social norms, with stronger effects on BI in case of
higher neighborhood identification.
H6 Collective efficacy beliefs have a positive effect
on BI to adopt smart heating technology.
H7 General trust in people has a positive effect on
BI to adopt smart heating technology.
H8 General trust in state has a positive effect on BI
to adopt smart heating technology.
Understanding Intention to Adopt Smart Thermostats: The Role of Individual Predictors and Social Beliefs Across Five EU Countries
39

3.1 Model
Figure 3 depicts our research model, including both
the structural and measurement model. Predictors are
split into ‘individual (left) and ‘social’ (right) beliefs.
Figure 3: Research model, including both structural and
measurement model. All item abbreviations correspond to
the item codes in the supplementary material.
4 METHOD
Our survey consisted of items related to a smart
heating thermostat, its acceptance and the individual
and social beliefs that might influence intention to
adopt. The survey started with an introduction, a short
description of a smart heating device together with an
image (see Figure 1), and consent procedures.
Afterwards, participants were asked to answer all
items included in the questionnaire, ending with
demographic details
4
.
4.1 Sample Description
Our sample of N = 3227 was recruited by a
professional panel provider and stratified by age and
gender for five European countries (Austria,
Belgium, Estonia, Germany, Greece). Renumeration
was based on the provider’s usual rates. Data was
gathered through an online survey link between
21.07.2021 and 10.08.2021. Data collection was
anonymous and in line with the ethical guidelines of
the DGPs (DPGs, 2016). All items were translated
into each country’s native language by native
speakers and back-translated to check for accuracy;
4
Together with the device image, we randomly assigned
participants to a control group, and groups with financial
and environmental (CO2) savings information, and a
group that was presented an app that would facilitate
control of the smart device. We did not find any
significant differences between these groups on any of
our model or dependent variables and therefore will not
discuss this intervention further.
each translation was reviewed by a researcher with a
native speaker multiple times.
We excluded participants who did not finish the
survey, failed the attention check, had an average
relative speed index of >2, and used the careless
package (Yentes & Chevallier, 2021) to exclude
participants with a longstring > 25
5
. This led to a final
sample of N = 2250 (51.3% women) from five
different countries, with Austria N = 465 (49.7%
women), Belgium N = 414 (52.9% women), Estonia
N = 510 (52.5% women), Germany N = 425 (50.6%
women), and Greece N = 436 (50.7% women).
Overall sample size, distributed similarly between
countries, was chosen to enable both an overall
structural equation modeling (SEM, Hair et al., 2021),
as well as country-specific analyses
6
. Participants’
distribution across age brackets was 21.7% 18-30
years old, 34.6% between 30-50 years old, 42.1%
between 50-70 years old, and 0.4% over 70 years old.
Regarding their living situation, 1393 participants
(62%) owned their home, while 853 participants
(38%) indicated to rent their living space. Most
survey participants lived in households between two
to four people (87%), with 37% of the households
having children. 34% of participants reported heating
with a boiler, 22% reported district heating, 17%
reported electric heating, and 27% reported using
other ways of heating.
4.2 Measurements and Scales
We examined predictors of acceptance of smart
heating technology, specifically combining in one
model UTAUT predictors and social beliefs that have
been shown in the past to affect technology adoption
and/or pro-environmental decisions, in-line with the
model shown in Figure 1. Items were surveyed on a
seven-point Likert scale ranging from “strongly
disagree” to “strongly agree” unless indicated
otherwise. We measured Behavioral Intention with
four items, e.g., "If I had the opportunity, I would opt
for a smart heating appliance" (Abrahão et al., 2016;
Venkatesh et al., 2003). Performance Expectancy was
assessed with four items, e.g., "I believe by using such
a smart appliance, I would save a meaningful amount
of greenhouse gases" (Girod et al., 2017; Venkatesh
5
The cut-off criterion is number of items until the first item
was reverse recoded.
6
Based on an A-priori Sample Size Calculator for
Structural Equation Models, with the specifications of
our model, with a desired statistical power level of 0.8
and an estimated effect size of 0.2, we needed N = 425
observations to find an effect.
SMARTGREENS 2025 - 14th International Conference on Smart Cities and Green ICT Systems
40

et al., 2003). Effort Expectancy was measured using
four items, e.g., "I believe that using such smart
heating control would be: difficult – easy" on a 7-
point scale (Venkatesh et al., 2012, 2003). Price
Value included two items, e.g., "Such a smart heating
appliance is good value for the money" (Venkatesh et
al., 2012). Collective Efficacy was measured with one
item, "If a large portion of the population used the
smart device, we would have a positive effect on
society and the climate" (Chen, 2015; Wang, 2018).
Social Norms were assessed with three items, e.g., "I
believe most of my neighbours will adopt such a
technology" (Lazaro et al., 2020; White et al., 2009).
Social Identification was measured with a pictorial
representation to assess the relationship with the
community, based on the "Inclusion of the Other in
the Self" scale (Aron et al., 1992; Gächter et al.,
2015), ranging 5 points. Trust in People was
measured using two items, e.g., "Generally speaking,
most people can be trusted" (European Value Study
(EVS); Caferra et al., 2021), and Trust in State with
two items, e.g., "Please rate how much you trust in
your legal system" (EVS; Caferra et al., 2021).
4.3 Data & Statistical Procedure
Data was handled with R statistics (R Development
Core Team, 2008). Before conducting the analyses,
all variables were mean-centered. Descriptive
statistics are reported of raw scores. Building on a
recommended two-step approach by Anderson &
Gerbing (1988), we first conducted a Confirmatory
Factor Analysis (CFA) before structural modelling to
assess the fit of the measurement model. This step
aims to estimate the measurement relationships
between the observed variables and their underlying
latent variables that cannot be directly assessed. The
latent variables in our measurement model are
behavioral intention (BI) as dependent variable, and
performance expectancy, price value, effort
expectancy, social norms, trust in state and trust in
people, collective efficacy, and social identification.
To examine the psychometric properties of our
measurement model, we used indicator reliability,
internal consistency reliability, convergent validity,
and discriminant validity as quality criteria. To test
our hypotheses, a SEM was then calculated, which
through the weighting of factors makes it possible to
quantify the strength of the relationship between the
latent variables.
7
We calculated the model with and without trust in people,
which did not change the results.
5 RESULTS
The measurement model consists of the latent
variables and their underlying scale items for
observation. Psychometric properties of our latent
variables including item loadings can be found in the
supplementary material (SM2). All loadings
exceeded the recommended threshold of 0.7 on their
respective scales except the first ‘trust in people’
item. This is further reflected in the results, as both
McDonalds omega (ω, McDonald, 1999) and
Cronbach's alpha (α , Cronbach, 1951) exceeded the
recommended threshold of 0.7 for all cases, which
confirms internal consistency reliability, except for
trust in people. The same is true for the average
variance extracted (AVE), where all values exceeded
the recommended threshold of 0.5 (ranging from .69
to .90), while trust in people just met the minimum
criteria with an AVE of .50. We will therefore
interpret findings regarding trust in people with
caution. Nevertheless, as we assessed trust in people
through a well-established scale (based on the EVS),
we decided to keep it in our model
7
.
5.1 Psychometric Properties of the
Measurement Scales
Building on recommendations of Hair et al. (2018),
we assessed factor loadings for our constructs, as well
as reliability indicators and mean variance extracted
of items loading on the respective construct. We
summarized these results for all model components in
the supplementary material (SM2). Overall, the
reliability of the scales was strong, with Cronbach’s
α ranging from .87 to .94 for key constructs such as
Behavioral Intention, Price Value, Effort Expectancy,
and Performance Expectancy. The Average Variance
Extracted (AVE) values were generally high (.62-
.80), indicating good convergent validity for most
scales, though Trust in People had a lower reliability
(Cronbach's α = .62, AVE = .49). To evaluate overall
model fit, we used two absolute fit indices (RMSEA,
SRMR) and two incremental fit indices (CFI, TLI)
8
which are all recommended for models with large
sample sizes (Hair et al., 2018). The fit indices for
both our CFA model and SEM model showed a good
fit, as depicted in Table 1: All parameters of goodness
exceeded the pre-defined cut-off, based on Hair et al.
(2018).
8
RMSEA – Root Mean Square Error of Approximation;
SRMR – Standardized Root Mean Square Residual; CFI
– Comparative Fit Index; TLI – Tucker Lewis Index
Understanding Intention to Adopt Smart Thermostats: The Role of Individual Predictors and Social Beliefs Across Five EU Countries
41

Table 1: CFA and SEM fit results, including fit cut-off.
Measure CFA SEM Cutoff
CFI 0.928 0.922 >0.9
TLI 0.907 0.906 > 0.9
RMSEA 0.077 0.071 < 0.08
SRMR 0.036 0.043 < 0.08
For discriminant validity, we found that in most
cases, both the Fornell-Lacker Criterion (Fornell &
Larcker, 1981) and in all cases, the conservative
Hetereo-trait-mono-method (HTMT) criterion
(Henseler et al., 2015) were met: The AVE values of
each construct (in cursive) were higher than their
squared correlations and the inter-construct
correlations are below .85. Only for performance
expectancy, we found an AVE which is below the
squared correlations with behavioral intention, price
value and collective efficacy. Still in this case, the
conservative HTMT criterion was met (Henseler et
al., 2015), which is why we accept discriminant
validity to be given. Results are detailed in SM4.
5.2 Descriptive Results
Descriptive statistics of raw scores for the key
constructs are reported in Table 2. BI to accept the
smart heating technology was not normally
distributed (Shapiro-Wilk-test: p < .001), with a mean
value of 5.44 (SD = 1.51) in the overall sample
9
. On
average, participants’ ratings for both social and
smart constructs of our model were quite high. We
found the lowest average ratings for social norms.
Generalized trust in people, and effort expectations
were also above the scale mid-point. Social
identification scores were not as high, with on
average 2.4 on scale of 1 to 5.
Table 2: Descriptive statistics of raw scores.
Scale α M SD
Behavioral Intention .94 5.44 1.51
Price Value .88 5.08 1.49
Effort expectancy .90 5.33 1.43
Performance expectanc
y
.87 4.95 1.37
Social norms .87 4.35 1.50
Trust in
p
eo
p
le .62 5.18 1.98
Trust in state .82 5.01 2.33
Social identification
1
2.39 1.09
Collective efficacy - 5.03 1.49
1 Note that ‘social identification’ was assessed on a scale from 1-5
9
As data cannot be assumed to be drawn from a normally
distributed population, we calculated all models (CFA
& SEM) with a robust estimator, but find no differences
in results.
Country-specific means and standard deviations
for they key constructs can be found in SM5. We find
a significant difference between countries for BI [F(4,
2245) = 46.9, p <.001]. Post hoc comparisons using
the Tukey HSD test indicated that the BI mean score
for Estonia was significantly higher than for Austria
(p < .001, 95% C.I. = [.21, .72]), Belgium (p < .001,
95% C.I. = [.35, .87]) and Germany (p < .001, 95%
C.I. = [.25, .77]), and BI mean score for Greece was
significantly higher than for all other countries
(Greece – Austria: p < .001, 95% C.I. = [.73, 1.26];
Greece – Belgium: p < .001, 95% C.I. = [.87, 1.41];
Greece – Estonia: p < .001, 95% C.I. = [.27, .77];
Greece – Germany: p < .001, 95% C.I. = [.76, 1.31]).
Further, Greek participants showed the highest
average ratings particularly for individual beliefs,
including price value, performance expectancy and
effort expectancy. Higher age was a negative
predictor for BI (ß = -.10, p = .008). We found no
differences between genders for smart heating
technology acceptance (ß = -.04, p = .480).
5.3 Structural Model
Behavioral intention in our structural model had an R
2
value of .707, which exceeded the cutoff value of
0.10 for acceptable explanatory power for
endogenous variable (Falk & Miller, 1992). R
2
values
of all predictor items, reflecting the variance
explained by the corresponding latent variable, were
> 0.5, except for trust in people with .246 Fit indices
for our model confirmed a good fit and Figure 2
shows the model results.
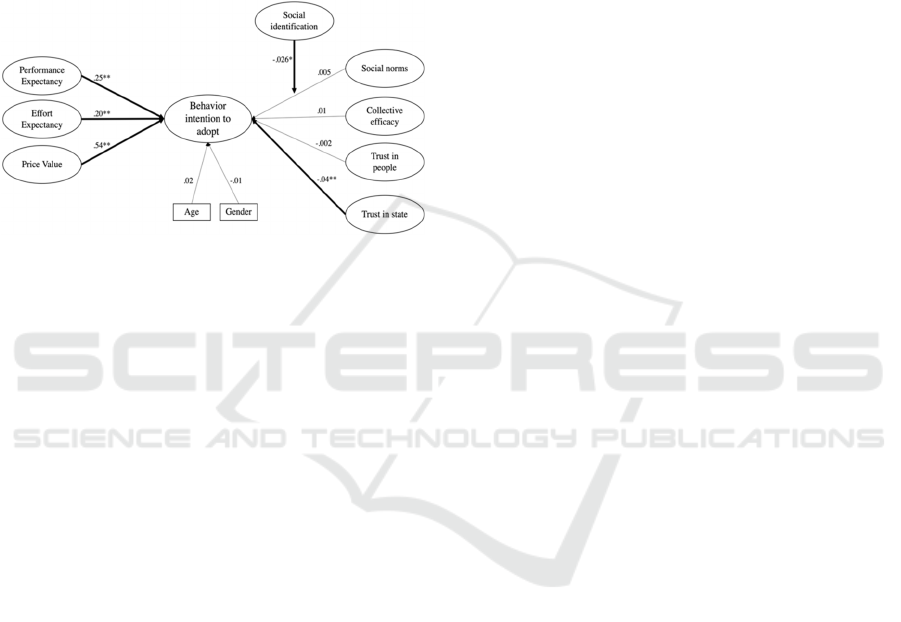
As depicted in Figure 4, for the overall sample,
we found that price value had the strongest positive
influence on BI, followed by performance expectancy
and effort expectancy, in line with H1, H2 and H3. Of
all our included social predictors, only trust in state
had a small negative effect with higher trust levels
reducing the intention to adopt, contradicting our
hypotheses H4, H5 and H6. Additionally, also
contrary to our hypothesis H4, we found a small
negative interaction between social identification and
social norms: social norms had a stronger effect on BI
when people felt less close to their neighbors.
To examine differences between national
samples, we calculated results grouped by country (A
detailed overview of results is in SM7). Across all
five groups, the general pattern was consistent, with
strong significant effects of price value and effort
SMARTGREENS 2025 - 14th International Conference on Smart Cities and Green ICT Systems
42
expectancy. Performance expectancy was a
significant predictor of BI for samples from
Germany, Estonia and Belgium, but not for those
from Austria and Greece. Additionally, collective
efficacy had a significant positive effect on BI for
Austrian participants; trust in state was a negative
predictor for BI for participants from Greece. Finally,
we found that the negative interaction between social
norms and social identification was only found for
our sample from Estonia, and the interaction was not
significant for participants from the other countries.
Figure 4: Model results for SEM.** p < 0.001; * p < 0.05.
6 DISCUSSION
By means of structural equation modelling, we
studied predictors of the intention to adopt a smart
heating technology. The model included the
technologies’ perceived effectiveness, price value,
effort expectancy as well as social beliefs including
social norms, collective efficacy and different types
of trust. Across five countries, the results indicate that
the individual beliefs of the UTAUT model are
suitable to predict the acceptance: price value,
performance expectancy and effort expectancy were
the most relevant predictors. Of the included social
predictors, only trust in state had a small negative
effect, and we found a small negative interaction
between social identification and social norms.
Within the specific country samples, some social
predictors reached significance (e.g., collective
efficacy in Austria) but overall, estimates were very
small. For the aggregated model, we therefore can
only accept H1 – H3, while hypotheses H4 – H6 must
be rejected.
This indicates that individual beliefs currently
better predict the intention to adopt smart heating
thermostats: for the overall sample, and within the
country samples, particularly financial aspects and
technology related beliefs (usefulness, ease of use)
influenced the intention to adopt a smart heating
devices, in line with findings from prior research
(Ahn et al., 2016; Girod et al., 2017; Tu et al., 2021).
Some of our results do not replicate evidence
from previous similar studies, though. For example,
social influence was the strongest predictor for the
intention to adopt a smart thermostat in a
representative consumer study in Germany (Große-
Kreul, 2022), but we do not find any significant
results for social beliefs – neither in the overall
sample, nor in the representative German sample.
One possible explanation lies in how social influence
is operationalized: as we already discussed, the
inconsistent results from social influence or social
norms might be driven by whether the concept is
understood as an injunctive or descriptive social
norm, and who is considered within as norm-related
group. Compared to Große-Kreul (2022), who
assessed social influence as usage in other people and
media presence (see Table 2), we used perceived
descriptive social norms within the neighborhood.
We included collective efficacy, and the
moderating effect of social identification, to broaden
the interpretation of social influence as a singular
construct, based on models and research of social
influences on pro-environmental behavior. Although
we did not find effects for most proposed social
indicators in the overall sample, we found a small
effect of collective efficacy in Austria. This might be
a promising start for future research. In general,
future work should consider the identified differences
between countries, and gain a deeper understanding
of this variations. Interestingly, we further found a
negative interaction between social identification and
social norms, which contradicts most earlier research
(Cialdini & Jacobson, 2021). This might be driven by
our choice of instrument: We used ‘closeness of
relations’ within the neighborhood as indicator for
social identification, which correlates highly with
other relationship indicators, including knowledge of
others’ goals (Gächter et al., 2015). This better
knowledge in turn might have limited the variability
of perceived norms and therefore its potential to
predict intentions. The effect size of the moderation
effect is very small and country-level analysis shows
it to be based in the Estonian sample.
6.1 Limitations
Firstly, we investigate how social beliefs relate to
smart heating technology adoption, but causal
conclusions can only be drawn within the limits of the
SEM methodology we used; our assumptions about
the causal impact of social belief predictors are here
not supported by the empirical data, while our
Understanding Intention to Adopt Smart Thermostats: The Role of Individual Predictors and Social Beliefs Across Five EU Countries
43

assumptions about the causal impact of individual
predictors find support in the associations within the
data, in line with prior empirical evidence.
Secondly, we did not measure adoption behavior,
but rather the intention to adopt. The validity of the
findings might be affected by the intention-behavior
gap, which is found widely in pro-environmental
consumer behavior (Carrington et al., 2010; Sheeran
& Webb, 2016). This reflects in our data in the sense
that we find very high adoption intention for smart
technology, but the real adoption rate of smart
thermostats in included countries has not yet reached
full potential
10
.
Lastly, the construct ‘trust in people’ was not
found to exceed critical thresholds, e.g. the AVE and
reliability criteria in our model, and findings
regarding it should be interpreted with caution.
Despite this, our CFA and SEM demonstrated a good
model fit and almost all constructs met reliability and
validity criteria. Thus, as we used a well-established
scale from the EVS we decided for its inclusion in the
final model.
6.2 Conclusion and Policy Implications
Overall, we conclude that the UTAUT model is well
suited to explain behavioral intention to use smart
thermostats. Our data did not yield support for an
extension of the UTAUT model to include social
beliefs derived based on evidence from previous pro-
environmental behavior research; however, this does
not indicate that they don’t play a role. Possible
explanations are the lack of publicness of thermostat
adoption and current marketing practices focusing
mainly on individual benefits. Social effects on pro-
environmental choices are stronger on highly visible
behaviors: studies find that visibility increases the
perception of social status (Uren et al., 2021),
collective efficacy affects public, but not private pro-
environmental behaviors (Hamann & Reese, 2020),
and people imitate visible behavior more (Babutsidze
& Chai, 2018). Visibility has also been found to
strengthen the relationship between a pro-
environmental social identity and behavioral
engagement (Brick et al., 2017). The adoption of a
smart thermostat is invisible behavior, conducted in
the private domain, so this might be a reason why
social beliefs do not impact it greatly. The proposed
model would benefit from implementation of explicit
comparisons of private and public pro-environmental
target variables to differentiate the effects of social
10
https://interpret.la/smart-home-sees-significant-growth-
in-western-europe/
beliefs, specifically with a focus on adoption of novel
technologies.
The conceptualization of smart thermostat
adoption as private sphere behavior also delivers a
potential explanation of the negative significant effect
of trust in state. As part of a meta-analysis, trust in
state has been found to correlate with public pro-
environmental behaviors (Cologna & Siegrist, 2020),
and a study which examined the effect of generalized
trust and trust in governments found that private
behaviors are negatively correlated to trust in
governmental institutions (Taniguchi & Marshall,
2018). This is explained with a theory of overreliance
on the state, which decreases the perceived need or
responsibility for own environmental action. It also
seems worth investigating how the adoption and use
of thermostats is framed across marketing campaigns
and public service announcements. In a previous
extensive qualitative analysis of product reviews for
five commercial smart thermostats, technology or
comfort related content categories were dominant
(Malekpour Koupaei et al., 2020). The marketing
emphasizes individual benefits, i.e. costs savings,
energy efficiency and technology features; this might
be one reason why social beliefs are not prevalent in
people’s cognitions regarding these devices. We
second suggestions by for exampleLi’s review on
smart home adoption (Li et al., (2021)), that
advertisements for such energy-efficiency devices
should consider including broader social benefits,
especially in light of potentially existing rebound
effects (Dütschke et al., 2018; Seebauer, 2018).
Finally, studies on saving devices and efficiency
technology often examine single individual’s
intention to adopt them. However, decisions about
thermal comfort often rely on household decisions
(Sintov et al., 2019). Sovacool et al. (2020)
specifically identified decision-making structures
around smart heating in households, displaying
conflicts between different household members
including between partners, roommates or parents
and children. Care should be taken when interpreting
results from our and previous literature about heating
technology adoption based on individual’s reported
intentions, as in most cases (and in 94% of our
sample), ‘a household is not a person’ (Seebauer &
Wolf, 2017). Future studies should design
measurements of target behaviors that are sensitive to
both individual and household-level decision-
making. Taken these findings into account, it is
imperative to design interventions to better study how
SMARTGREENS 2025 - 14th International Conference on Smart Cities and Green ICT Systems
44

to accelerate the diffusion of smart heating
technologies across Europe to the extent envisioned
by policymakers.
The data, analysis scripts and questionnaire with
stimulus materials can be downloaded at
https://osf.io/ba2vf/?view_only=986065e170584cad
9098d0a2937e216b
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research was supported by a European Union
Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme
grant (RENergetic, grant N957845; DECIDE, grant
N894255) awarded to MB, FK, SK, CK. Conflicts of
interests: none. MB: Conceptualization,
Methodology, Data curation, Formal analysis,
Visualization, Writing – original draft. FK:
Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation,
Funding acquisition, Writing - review & editing. SK:
Conceptualization, Methodology Writing - review &
editing. CK: Conceptualization, Data curation,
Formal analysis, Writing - review & editing,
Supervision, Funding acquisition.
REFERENCES
Abrahão, R. de S., Moriguchi, S. N., & Andrade, D. F.
(2016). Intention of adoption of mobile payment: An
analysis in the light of the Unified Theory of
Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT). RAI
Revista de Administração e Inovação, 13(3), 221–230.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rai.2016.06.003
Ahn, M., Kang, J., & Hustvedt, G. (2016). A model of
sustainable household technology acceptance:
Sustainable household technology acceptance model.
International Journal of Consumer Studies, 40(1), 83–
91. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijcs.12217
Ajzen, I. (1985). From Intentions to Actions: A Theory of
Planned Behavior. In J. Kuhl & J. Beckmann (Hrsg.),
Action Control (S. 11–39). Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-69746-3_2
Arfi, W. B., Nasr, I. B., Kondrateva, G., & Hikkerova, L.
(2021). The role of trust in intention to use the IoT in
eHealth: Application of the modified UTAUT in a
consumer context. Technological Forecasting and
Social Change, 167, 120688. https://doi.org/10.1016/
j.techfore.2021.120688
Babutsidze, Z., & Chai, A. (2018). Look at me Saving the
Planet! The Imitation of Visible Green Behavior and its
Impact on the Climate Value-Action Gap. Ecological
Economics, 146, 290–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/
j.ecolecon.2017.10.017
Berkowitz, A. D. (2004). The social norms approach:
Theory, research, and annotated bibliography.
Billanes, J., & Enevoldsen, P. (2022). Influential factors to
residential building Occupants’ acceptance and
adoption of smart energy technologies in Denmark.
Energy and Buildings, 276, 112524. https://doi.org/
10.1016/j.enbuild.2022.112524
Brick, C., Sherman, D. K., & Kim, H. S. (2017). “Green to
be seen” and “brown to keep down”: Visibility
moderates the effect of identity on pro-environmental
behavior. Journal of Environmental Psychology, 51,
226–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvp.2017.04.004
Caferra, R., Colasante, A., & Morone, A. (2021). The less
you burn, the more we earn: The role of social and
political trust on energy-saving behaviour in Europe.
Energy Research & Social Science, 71, 101812.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.erss.2020.101812
Carrington, M. J., Neville, B. A., & Whitwell, G. J. (2010).
Why Ethical Consumers Don’t Walk Their Talk:
Towards a Framework for Understanding the Gap
Between the Ethical Purchase Intentions and Actual
Buying Behaviour of Ethically Minded Consumers.
Journal of Business Ethics, 97(1), 139–158.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-010-0501-6
Chang, S., & Nam, K. (2021). Smart Home Adoption: The
Impact of User Characteristics and Differences in
Perception of Benefits. Buildings, 11(9), 393.
https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings11090393
Cialdini, R. B. (2007). Descriptive Social Norms as
Underappreciated Sources of Social Control.
Psychometrika, 72(2), 263–268. https://doi.org/
10.1007/s11336-006-1560-6
Cialdini, R. B., & Jacobson, R. P. (2021). Influences of
social norms on climate change-related behaviors.
Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences, 42, 1–8.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cobeha.2021.01.005
Cialdini, R. B., Reno, R. R., & Kallgren, C. A. (1990). A
focus theory of normative conduct: Recycling the
concept of norms to reduce littering in public places.
Journal of personality and social psychology, 58(6),
1015.
Cologna, V., & Siegrist, M. (2020). The role of trust for
climate change mitigation and adaptation behaviour: A
meta-analysis. Journal of Environmental Psychology,
69, 101428. https://doi.org/10.1016/
j.jenvp.2020.101428
Cronbach, L. J. (1951). Coefficient alpha and the internal
structure of tests. Psychometrika, 16(3), 297–334.
https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02310555
Dütschke, E., Frondel, M., Schleich, J., & Vance, C. (2018).
Moral Licensing—Another Source of Rebound?
Frontiers in Energy Research, 6, 38. https://doi.org/
10.3389/fenrg.2018.00038
European Commission. (2022, Juni 27). Joint Statement by
President von der Leyen and President Biden on
European Energy Security. https://ec.europa.eu/
commission/presscorner/detail/es/statement_22_4149
European Environment Agency (EEA). (2021, Oktober 26).
Greenhouse gas emissions from energy use in buildings
in Europe. https://www.eea.europa.eu/data-and-
maps/indicators/greenhouse-gas-emissions-from-
energy/assessment
Understanding Intention to Adopt Smart Thermostats: The Role of Individual Predictors and Social Beliefs Across Five EU Countries
45

Falk, R. F., & Miller, N. B. (1992). A primer for soft
modeling. University of Akron Press.
Fornell, C., & Larcker, D. F. (1981). Evaluating Structural
Equation Models with unobservable variables and
measurement error. Journal of Marketing Research,
18(1), 39–50.
Fritsche, I., Barth, M., Jugert, P., Masson, T., & Reese, G.
(2018). A Social Identity Model of Pro-Environmental
Action (SIMPEA). Psychological Review, 125(2), 245–
269. https://doi.org/10.1037/rev0000090
Gächter, S., Starmer, C., & Tufano, F. (2015). Measuring
the Closeness of Relationships: A Comprehensive
Evaluation of the „Inclusion of the Other in the Self“
Scale. PLOS ONE, 10(6), e0129478. https://doi.org/
10.1371/journal.pone.0129478
Gimpel, H., Graf, V., & Graf-Drasch, V. (2020). A
comprehensive model for individuals’ acceptance of
smart energy technology – A meta-analysis. Energy
Policy, 138, 111196. https://doi.org/10.1016/
j.enpol.2019.111196
Girod, B., Mayer, S., & Nägele, F. (2017). Economic versus
belief-based models: Shedding light on the adoption of
novel green technologies. Energy Policy, 101, 415–
426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2016.09.065
Göckeritz, S., Schultz, P. W., Rendón, T., Cialdini, R. B.,
Goldstein, N. J., & Griskevicius, V. (2009). Descriptive
normative beliefs and conservation behavior: The
moderating roles of personal involvement and
injunctive normative beliefs. European Journal of
Social Psychology, n/a-n/a. https://doi.org/10.1002/
ejsp.643
Große-Kreul, F. (2022). What will drive household
adoption of smart energy? Insights from a consumer
acceptance study in Germany. Utilities Policy, 75,
101333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jup.2021.101333
Gumz, J., Fettermann, D. C., Sant’Anna, Â. M. O., &
Tortorella, G. L. (2022). Social Influence as a Major
Factor in Smart Meters’ Acceptance: Findings from
Brazil. Results in Engineering, 15, 100510.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rineng.2022.100510
Hair, J. F., Hult, G. T. M., Ringle, C. M., Sarstedt, M.,
Danks, N. P., & Ray, S. (2021). An Introduction to
Structural Equation Modeling. In J. F. Hair Jr., G. T. M.
Hult, C. M. Ringle, M. Sarstedt, N. P. Danks, & S. Ray
(Hrsg.), Partial Least Squares Structural Equation
Modeling (PLS-SEM) Using R: A Workbook (S. 1–29).
Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/
10.1007/978-3-030-80519-7_1
Haji Hosseinloo, A., Ryzhov, A., Bischi, A., Ouerdane, H.,
Turitsyn, K., & Dahleh, M. A. (2020). Data-driven
control of micro-climate in buildings: An event-
triggered reinforcement learning approach. Applied
Energy, 277, 115451. https://doi.org/10.1016/
j.apenergy.2020.115451
Hamann, K. R. S., & Reese, G. (2020). My Influence on the
World (of Others): Goal Efficacy Beliefs and Efficacy
Affect Predict Private, Public, and Activist Pro‐
environmental Behavior. Journal of Social Issues,
76(1), 35–53. https://doi.org/10.1111/josi.12369
Henseler, J., Ringle, C. M., & Sarstedt, M. (2015). A new
criterion for assessing discriminant validity in variance-
based structural equation modeling. Journal of the
Academy of Marketing Science, 43(1), 115–135.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11747-014-0403-8
Li, W., Yigitcanlar, T., Erol, I., & Liu, A. (2021).
Motivations, barriers and risks of smart home adoption:
From systematic literature review to conceptual
framework. Energy Research & Social Science, 80,
102211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.erss.2021.102211
Lu, J., Sookoor, T., Srinivasan, V., Gao, G., Holben, B.,
Stankovic, J., Field, E., & Whitehouse, K. (2010). The
smart thermostat: Using occupancy sensors to save
energy in homes. Proceedings of the 8th ACM
Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems,
211–224. https://doi.org/10.1145/1869983.1870005
Malekpour Koupaei, D., Song, T., Cetin, K. S., & Im, J.
(2020). An assessment of opinions and perceptions of
smart thermostats using aspect-based sentiment
analysis of online reviews. Building and Environment,
170, 106603. https://doi.org/10.1016/
j.buildenv.2019.106603
Mamonov, S., & Koufaris, M. (2020). Fulfillment of
higher-order psychological needs through technology:
The case of smart thermostats. International Journal of
Information Management, 52, 102091. https://doi.org/
10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2020.102091
Marikyan, D., Papagiannidis, S., & Alamanos, E. (2019). A
systematic review of the smart home literature: A user
perspective. Technological Forecasting and Social
Change, 138, 139–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/
j.techfore.2018.08.015
McDonald, R. P. (1999). Test Theory: A Unified Treatment
(1st ed.). Psychology Press. https://doi.org/10.4324/
9781410601087
Nordhoff, S., Madigan, R., Van Arem, B., Merat, N., &
Happee, R. (2021). Interrelationships among predictors
of automated vehicle acceptance: A structural equation
modelling approach. Theoretical Issues in Ergonomics
Science, 22(4), 383–408. https://doi.org/10.1080/
1463922X.2020.1814446
Park, H. S., & Smith, S. W. (2007). Distinctiveness and
Influence of Subjective Norms, Personal Descriptive
and Injunctive Norms, and Societal Descriptive and
Injunctive Norms on Behavioral Intent: A Case of Two
Behaviors Critical to Organ Donation. Human
Communication Research, 33(2), 194–218.
https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-2958.2007.00296.x
Rivis, A., & Sheeran, P. (2003). Descriptive norms as an
additional predictor in the theory of planned behaviour:
A meta-analysis. Current Psychology, 22(3), 218–233.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-003-1018-2
Rogers, E. M. (2003). Diffusion of innovations/everett m.
Rogers. NY: Simon and Schuster, 576.
Seebauer, S. (2018). The psychology of rebound effects:
Explaining energy efficiency rebound behaviours with
electric vehicles and building insulation in Austria.
Energy Research & Social Science, 46, 311–320.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.erss.2018.08.006
SMARTGREENS 2025 - 14th International Conference on Smart Cities and Green ICT Systems
46

Seebauer, S., & Wolf, A. (2017). Disentangling household
and individual actors in explaining private electricity
consumption. Energy Efficiency, 10(1), 1–20.
Sheeran, P., & Webb, T. L. (2016). The Intention-Behavior
Gap: The Intention-Behavior Gap. Social and
Personality Psychology Compass, 10(9), 503–518.
https://doi.org/10.1111/spc3.12265
Shuhaiber, A., & Mashal, I. (2019). Understanding users’
acceptance of smart homes. Technology in Society, 58,
101110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2019.01.003
Sintov, N. D., White, L. V., & Walpole, H. (2019).
Thermostat wars? The roles of gender and thermal
comfort negotiations in household energy use behavior.
PLOS ONE, 14(11), e0224198. https://doi.org/10.1371/
journal.pone.0224198
Sovacool, B. K., & Furszyfer Del Rio, D. D. (2020). Smart
home technologies in Europe: A critical review of
concepts, benefits, risks and policies. Renewable and
Sustainable Energy Reviews, 120, 109663.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2019.109663
Sovacool, B. K., Martiskainen, M., Osborn, J., Anaam, A.,
& Lipson, M. (2020). From thermal comfort to conflict:
The contested control and usage of domestic smart
heating in the United Kingdom. Energy Research &
Social Science, 69, 101566. https://doi.org/10.1016/
j.erss.2020.101566
Spence, A., Demski, C., Butler, C., Parkhill, K., & Pidgeon,
N. (2015). Public perceptions of demand-side
management and a smarter energy future. Nature
Climate Change, 5(6), 550–554. https://doi.org/
10.1038/nclimate2610
Taniguchi, H., & Marshall, G. A. (2018). Trust, political
orientation, and environmental behavior.
Environmental Politics, 27(3), 385–410.
https://doi.org/10.1080/09644016.2018.1425275
Tu, G., Faure, C., Schleich, J., & Guetlein, M.-C. (2021).
The heat is off! The role of technology attributes and
individual attitudes in the diffusion of Smart
thermostats – findings from a multi-country survey.
Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 163,
120508.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2020.120508
Uren, H. V., Roberts, L. D., Dzidic, P. L., & Leviston, Z.
(2021). High-Status Pro-Environmental Behaviors:
Costly, Effortful, and Visible. Environment and
Behavior, 53(5), 455–484. https://doi.org/10.1177/
0013916519882773
Venkatesh, Thong, & Xu. (2012). Consumer Acceptance
and Use of Information Technology: Extending the
Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology.
MIS Quarterly, 36(1), 157. https://doi.org/10.2307/
41410412
Venkatesh, V., Morris, M. G., Davis, G. B., & Davis, F. D.
(2003). User acceptance of information technology:
Toward a unified view.
MIS quarterly, 425–478.
Wang, C., Pattawi, K., & Lee, H. (2020). Energy saving
impact of occupancy-driven thermostat for residential
buildings. Energy and Buildings, 211, 109791.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2020.109791
White, K. M., Smith, J. R., Terry, D. J., Greenslade, J. H.,
& McKimmie, B. M. (2009). Social influence in the
theory of planned behaviour: The role of descriptive,
injunctive, and in-group norms. British Journal of
Social Psychology, 48(1), 135–158. https://doi.org/
10.1348/014466608X295207
Yentes, R., & Chevallier, F. (2021). Careless: Procedures
for computing indices of careless responding. R
package version 1.2.1.
Understanding Intention to Adopt Smart Thermostats: The Role of Individual Predictors and Social Beliefs Across Five EU Countries
47
