
Virtual Kitchen: Using a Touch Table for Cognitive
Rehabilitation in Activities of Daily Living
Paul Richard
a
, Emmanuelle Richard
b
, Maxime Mac
´
e
c
and Teddy Louisy
d
LARIS SFR Mathstic, University of Angers, 62 Av. Notre Dame du Lac, 49000 Angers, France
Keywords:
Virtual Reality, Touch Table, Rehabilitation, Errorless Learning, Activities of Daily Living.
Abstract:
A tool designed to assess and rehabilitate memory in patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) or
People with Dementia (PwD) is presented. This tool includes a touch table equipped with a 3D camera on top
for motion capture and a 3D Virtual Kitchen application. The aim is to assess and strengthen their ability to
memorize and reproduce the activity of preparing a cup of sweetened coffee with milk. An errorless learning
method has been implemented to prevent the user from performing and remembering any erroneous actions
while performing the task. We conducted a preliminary study with eight healthy participants to investigate
the usability of the solution. The results suggest that Virtual Kitchen on H
ˆ
osea touch table is user-friendly,
motivating, and requires a moderate workload. We assume that the use of the touch table to interact with the
virtual objects will optimize the rehabilitation process for instrumental activities of daily living (IADLs).
1 INTRODUCTION
With virtual reality (VR), a human can be immersed
in a virtual environment (VE) in which he can interact
in real time using 3D techniques based on our natural
abilities of action, perception and expression (Fuchs
et al., 2001; Burdea and Coiffet, 2024). In the con-
text of motor and cognitive rehabilitation, VEs allow
the acquisition of a large quantity of data, minimizing
errors and improving the reliability of results. Addi-
tionally, measurements can be improved, allowing the
examination of parameters that are difficult to capture
with traditional ”paper-and-pencil” tasks (Chae and
Lee, 2023). Virtual reality provides an ecosystem ca-
pable of dynamically adjusting the difficulty of cogni-
tive and sensorimotor tasks for each patient. Specif-
ically, VR devices facilitate the personalization and
adaptation of therapeutic interventions. However, vi-
sualizing, selecting, and manipulating virtual objects
typically relies on fully immersive setups and 3D in-
teraction devices, which can present challenges for
older adults. In fact, immersion achieved with head-
mounted displays (HMDs) or Cave Automatic Virtual
Environments (CAVEs) can lead to problems such as
simulator sickness (Cherniack, 2011).
The main objective of the work presented in this
paper is to offer an easy to use and high performance
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9905-847X
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9592-6150
c
https://orcid.org/0009-0008-0939-8146
d
https://orcid.org/0009-0004-3832-9482
tool to reinforce the ability to carry out an activity
of daily living in people with Mild Cognitive Impair-
ment (MCI) and People with Dementia (PwD). In
the following section, we present some work based
on VR setup and techniques but also on some touch
tables with their use in cognitive rehabilitation. In
section 3, we present our experimental device called
H
ˆ
osea and the Virtual Kitchen application including
the task, the interaction technique, and the proposed
error-free learning method. Finally, we present our
preliminary usability results, and then the article ends
with a conclusion and presents future work.
2 RELATED WORK
2.1 VR Techniques
Virtual reality techniques have been used in cogni-
tive neuropsychology since the early 2000s. In 2004,
a comprehensive study was conducted by Rizzo et
al., (Rizzo et al., 2004). More recently, reviews
have been conducted by Smith et al., (Smith, 2023)
and Catania et al. (Catania et al., 2024). In a study
by Brooks et al., VE enabled an amnesic patient to
learn to move around his rehabilitation center (Brooks
et al., 1999). Before training, the patient was unable
to navigate 10 simple routes within the real unit, all
involving locations he visited regularly. Initially, the
patient was unable to find simple routes in places he
had previously visited. The VE training sessions sig-
666
Richard, P., Richard, E., Macé, M. and Louisy, T.
Virtual Kitchen: Using a Touch Table for Cognitive Rehabilitation in Activities of Daily Living.
DOI: 10.5220/0013356700003912
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 20th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2025) - Volume 1: GRAPP, HUCAPP
and IVAPP, pages 666-673
ISBN: 978-989-758-728-3; ISSN: 2184-4321
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

nificantly improved his ability to move around on his
own.
In order to avoid the problems caused by im-
mersion in VE, some works have proposed a non-
immersive approach. This approach relies on using a
simple monitor or a screen with a video projector (Al-
lain et al., 2014; Foloppe et al., 2018; Yamaguchi
et al., 2012; Richard et al., 2018; Lecouvey et al.,
2019; Klinger, 2006; Cogn
´
e et al., 2017). Although
these studies showed some efficacy of the proposed
non-immersive setup, difficulties were mentioned for
some patients regarding the use of the mouse to se-
lect or drag-and-drop the virtual objects. A study
by Plechat
`
a et al. investigated the responsiveness of
a memory task based on a supermarket scenario for
young and senior participants using an immersive in-
terface with a headset and low immersion with a com-
puter. The results suggest that the use of VR is tir-
ing for both groups, but that seniors performed better
with the computer with minimal side effects (Plechat
´
a
et al., 2019).
In a comparative study by Jin et al. on the learning
of traditional art among students, the use of a touch ta-
ble and a VR headset highlighted several aspects. The
table proved to be beneficial for quick handling, play-
ing on the quality of its intuitive interface. This also
facilitated the dialogue between the experimenters.
Conversely, VR has been shown to be more engaging
and attractive in the long term (Jin et al., 2021). From
these comparative studies, we see the advantages of
touch tables in terms of collaboration and accessibil-
ity. The approach we promote in this research is to
use a touch table that allows direct manipulation of
the virtual objects and devices.
2.2 Touch Table Interfaces
Touch tables are present in several industries such as
engineering (Kaya et al., 2017), exhibition (van Dijk
et al., 2012), music (Cossou et al., 2018) and health-
care (Ro et al., 2023). Historically present since the
1990s, touch tables have experienced strong growth
in 2010s (Bruun et al., 2017). Touch table offer an
accessible solution adapted to the varied contexts of
medical-social centers and is a good alternative in
many situations. Different touch table devices coex-
ist. The main differences are characterized by the dis-
play and touch interaction technologies. For the dis-
play mode, touch tables are divided into rear projec-
tion systems and integrated screen systems. Among
the tables using projection, the devices vary accord-
ing to whether they use an external projector or an
internal projection. When it comes to screen display
tables, there are also different design approaches. The
most commonly used are projected capacitive, resis-
tive, infrared, camera optics, and planar scattering
on vision (Sch
¨
oning et al., 2008). Each table of-
fers unique advantages and disadvantages, but most
of them offer a natural interaction interface without
the need for proxies and with multi-touch interaction
capture. This aspect is important for the accessibility
of the interface for profiles subject to cognitive dis-
orders and whose use of the controllers may prove
difficult (Annett et al., 2012). Additionally, the ro-
bustness of the screen provide relative tolerance to
sudden movements and imprecise handling (Augstein
et al., 2016). Furthermore, the enlarged interaction
zone offers freedom of movement and bimanual use
of the interface (Augstein et al., 2015). Finally, fa-
miliarity with traditional tables and touchscreen de-
vices makes touch tables intuitive interfaces, offering
manipulation that closely resembles everyday physi-
cal interactions (Annett et al., 2012).
Some studies have discussed the use of touch ta-
bles with an elderly population. On a European scale,
the ElderGames project has developed a solution to
improve the quality of life of elderly people (Gam-
berini et al., 2009). The device was designed to pre-
serve cognitive functions and help prevent cognitive
dysfunctions associated with aging. In parallel, Mah-
moud et al. identified recommendations for the de-
sign and evaluation of touch table games for older
adults (Al Mahmud et al., 2008). Gundogdu et al.
proposed the use of touch tables for reminiscence
therapy (i.e. an intervention aimed at recalling mem-
ories in older adults) (G
¨
undogdu et al., 2017).
3 MATERIALS
3.1 The H
ˆ
osea Table
Our touch table, called H
ˆ
osea, was designed to be
used in rehabilitation centers and nursing homes. It
is accessible to people with reduced mobility or for
use while standing. A 3D model of our touch table
is shown in Figure 1. It consists of an open-frame
projected capacitive screen with a detection capacity
and a display surface of 43 inches (109.22 cm). The
two miniature jacks allow the screen to be positioned
flat or tilted and the height to be adjusted. The table
is adjustable using buttons to operate the two elec-
tric jacks. The frame is made of aluminum and in-
cludes a side handle at each end to facilitate the move-
ment of the structure. Two columns consisting of two
legs with four directional wheels allow the table to be
moved.
In use, the medical brakes on each of the wheels
Virtual Kitchen: Using a Touch Table for Cognitive Rehabilitation in Activities of Daily Living
667

(a) (b)
Figure 1: 3D model of the H
ˆ
osea touch table in low position
(a) and high inclined position (b).
guarantee the stability of the structure. The cen-
tral unit integrated in one of the two side boxes is a
compact, non-ventilated industrial computer, also de-
signed in aluminum and used for ecological consider-
ations of energy consumption, recycling and robust-
ness. The operating system embedded in the central
unit is Windows 10 IOT.
3.2 The Virtual Kitchen
The Virtual Kitchen presented here has already been
the subject of publications to which we bring new
perspectives through the use of tactile interactions
with the Multi-touch Table (Yamaguchi et al., 2012;
Allain et al., 2014; Richard et al., 2018; Foloppe
et al., 2018). Cognitive stimulation involves certain
components of cognitive functions, which are higher
functions of the brain: attention, memory, executive
functions, visuospatial functions, and language
(Lumsden et al., 2016). In this work, we study in
particular the rehabilitation of memory and executive
functions such as planning in instrumental activities
of daily living (IADL).
Figure 2: Front view of the Virtual Kitchen.
The choice of a Virtual Kitchen is justified by the
fact that a kitchen occupies an important place in peo-
ple’s daily life activities in their own home. The Vir-
tual Kitchen is illustrated in Figure 2. On the Virtual
Kitchen table are arranged all the elements and in-
gredients necessary for preparing a cup of sweetened
coffee with milk. A coffee machine is also available,
equipped with a water tank and a compartment for
coffee filter and ground coffee. To open the compart-
ment, the touch table allows you to simply touch it
with a finger. A button (at the bottom) allows you to
turn the machine on and off. This button, which is ini-
tially red, turns green to indicate that the machine is
making coffee. During this preparation time, a cof-
fee machine noise is emitted. Another button (at the
top) allows you to open and close the water tank. To
enhance the realism of the task, appropriate sounds
are emitted when the user pours water into the com-
partment, puts ground coffee into the coffee filter, and
pours milk into the cup. The same is true when the
objects (jug, milk carton, water jug, coffee carton) are
put back on the table.
3.2.1 Setup and Procedure
The setup is illustrated in Figure 3. The user sits in
front of the touch table. An Orbbec Astra 3D camera
(IR + RGB) is placed high behind the table. This cam-
era can capture a wide range of behaviors to assess
and support the recovery process. These behaviors
are crucial for both the diagnosis of impairments and
the monitoring of a patient’s progress during rehabil-
itation. In particular, the camera makes it possible to
capture the kinetics of movements in space which per-
mits a better analysis of patient performance. For ex-
ample, we can identify patients’ hesitations, parasitic,
compensatory, and pathological movements.
(a) (b)
Figure 3: User watching the video showing the different
actions to perform (a) and selection of the milk jug (b).
The application was developed using Unity3D
2021 game Engine. A main menu allowing to enter
a user ID is proposed (Fig. 4). The identifier will be
used to name the backup file (CSV). The menu also
allows you to specify the time at which the visual
and sound signals are triggered. In this case, the
application can be used for patient assessment. The
menu also allows you to launch the instruction video
and start or exit the application. The generated CSV
HUCAPP 2025 - 9th International Conference on Human Computer Interaction Theory and Applications
668

file includes the 3D camera movement data, as well
as all relevant events (object selection, errors, number
of cues used) and their timing.
Figure 4: Main menu of the Virtual Kitchen application.
The proposed procedure is as follows. First,
the user must watch a video that shows the differ-
ent actions that must be memorized and reproduced
(Fig. 3a). Once the video is finished, the application
launches. You must then reproduce each action, one
by one, in the same order. At the end of the activity, a
final view allows you to see the necessary assistance
as well as the omissions made. This section provides
an opportunity for discussion between the elder and
their caregiver on the task performed. The list of data
collected during the exercise is given in table 1.
3.2.2 Interaction Techniques
The interaction technique used on the touch table is
very intuitive. The user simply has to touch with any
finger the object or element of the scene to be selected
(Fig. 3b). The corresponding action is then executed
automatically using a predefined 3D animation. For
those able to perform the required arm movements,
a non-automatic mode has also been implemented. In
this mode, to move objects, the user must keep his fin-
ger on the table surface and perform translation move-
ments.
3.2.3 Errorless Learning
Errorless learning could be useful for patients with
cognitive impairments, such as memory disorders or
learning disabilities, where making errors can lead to
frustration or reinforce incorrect learning. Although
this approach has many advantages, such as reduc-
ing anxiety, preventing errors, it also has limitations.
For example, errorless learning provides heavy guid-
ance and support, which can cause the patient to be-
come dependent. This can limit the ability to transfer
learned skills to real-world situations where cues are
not present. In addition, for some patients, this high
level of support can inhibit problem solving and inde-
Table 1: Descriptive list of quantitative collected data.
Data Type
Time Number (Secondes)
Actions Categorical (Click on
the button; Opening the
compartment; Incorrect
action; Closing the wa-
ter tank)
Total number of clicks Number
Correct action Categorical (Correct;
Incorrect; With help)
Number of sound cues Number
Number of audio and visual
cues
Number
Automatic movement count Number
Total number of indices Number
Total number of errors Number
Waiting time before cues Number
pendent learning, as they are not encouraged to find
solutions on their own or deal with mistakes. Finally,
by preventing errors, errorless learning may reduce
the cognitive challenge and patient engagement.
Keeping these advantages and drawbacks in mind,
an errorless learning approach has been implemented
to prevent the patient from making mistakes, such as
selecting the wrong object or using the machine at the
wrong time. For example, if the patient selects an ob-
ject or activates the machine when he should not, the
corresponding action is not performed but the error is
logged. If the patient does not perform an expected
action, after a while a human voice indicates the ac-
tion to be performed, for example ‘Place the coffee fil-
ter in the compartment’. Then, if the patient still can-
not perform the expected action after the same amount
of time, the action is repeated verbally and the object
to be selected flashes. Finally, if the patient still does
nothing, the required action is performed automati-
cally and the next one is moved on.
3.2.4 Task Description
The task consists of a series of 12 consecutive actions.
The goal is to prepare a cup of sweetened milk cof-
fee using the proposed ingredients and the coffee ma-
chine. The user simply places his finger on the ma-
chine’s opening/closing and activating/deactivating
buttons. The selected object is animated to automat-
ically perform the associated action. Animations are
also used to open and close the coffee and water com-
Virtual Kitchen: Using a Touch Table for Cognitive Rehabilitation in Activities of Daily Living
669

partments. The sequence of actions is described in
the appendix. To perform each action and trigger the
corresponding predefined animation, a simple touch
is necessary.
4 PRELIMINARY STUDY
A preliminary study was conducted at the Univer-
sity of Angers to investigate the usability of different
application on the touch table including the Virtual
Kitchen application. Each healthy participant (n = 9)
performed a Virtual Kitchen evaluation task, standing
and under the supervision of an experimenter. One
participant was removed because a technical interrup-
tion compromised the validity of his data. The ex-
ercise consisted of performing the task of preparing
a cup of sweetened coffee with milk without having
seen the explanatory video and assistance. The sound
was not kept for this test to focus on visual feedback.
The characteristics of the participants are available in
Table 2.
4.1 Usability Scale
The usability of the Virtual Kitchen application on
the touch table was measured with the F-SUS scale
(French System Usability Scale) (Brooke, 1995;
Gronier, 2021). The test requires answering 10 ques-
tions based on a 5-point Likert scale. The final score
is given by subtracting one point from the answer for
odd-numbered questions and subtracting the answer
value from 5 for even-numbered questions. The sum
of the questions multiplied by 2.5 gives a usability
score out of 100 for each participant. Our result for all
participants is 76.56 (mean: 76.56; std: 11.49) sug-
gesting an acceptable usability of the solution despite
strong variations between users. The other scale used
is the raw version of the NASA-TLX measuring per-
ceived workload (Hart, 1988; Maincent, 2001). This
simplified version does not weight the importance
of each subscale between participants and considers
them as having equal value. The six subscales are
Mental Demand, Physical Demand, Time Demand,
Performance, Effort, and Frustration. One question
is asked per subscale on a 20-point Likert scale. The
overall score is obtained by summing the responses to
the question and dividing by 6 before multiplying by
5. The results of the subscales are Mental Demand
(mean: 7.50; std: 6.37), Physical Demand (mean:
3.25; std: 4.17), Temporal Demand (mean: 3.63; std:
3.20), Performance (mean: 16.50; std: 3.30), Effort
(mean: 5.88; std: 6.60) and Frustration (mean: 15.63;
std: 3.02). The mean score of the participants is 43.65
(mean: 43.65; std: 16.70) suggesting an activity that
only requires subjectively moderate workload for an
healthy population. The low Mental, Physical and Ef-
fort Demand scores for healthy participants suggest
relative simplicity of actions. The Frustration score
can be explained by the need for gameplay improve-
ments, bug fixes, and the short trial period. Finally,
a motivational study was carried out using the SIMS
scale (Situational Intrinsic Motivation Scale) (Guay,
2000). The test consists of 16 items grouped into 4
sub-dimensions and are asked using a 7-point Lik-
ert scale. The four subscales correspond to Intrinsic
Motivation (IM), Identified Regulation (IR), External
Regulation (ER) and Amotivation (A). In our experi-
ment we have as result IM (mean: 5.19; std: 1.59), IR
(mean: 3.88; std: 2.23), ER (mean: 3.00; std: 1.93),
A (mean: 2.31; std: 1.63). These results suggest a
tendency towards personal satisfaction during the task
(IM), a moderate importance of the task is considered
in the motivation of the participants (IR), external fac-
tors play a minor role in the motivation of the partici-
pants to the task (ER) and a low absence of motivation
is felt (A).
4.2 Qualitative Analysis
We retained the verbal remarks of the participants
during the experiments. Regarding the level of dif-
ficulty of the task, the participants found it relatively
simple with clearly identified problems. For many of
them, it is necessary to have to explain the objectives
of the task beforehand. The main cause of the mis-
understanding of the scenario would be the buttons
of the coffee machine. Several comments highlight
a difficulty in understanding how to act with the but-
tons and when the coffee is ready thanks to the light
feedback. Some comments are about the choice to
limit interactions to a single click. This is a source of
frustration when they want to drag-and-drop. The ap-
plication offers a version that integrates this function-
ality. Another modality of interaction with step-by-
step clicks starting with choosing the object and then
pointing to the target was mentioned. Adding sugar
and milk at the end of the sequence is also confus-
ing. Several experimenters asked to make the choice
of milk and sugar optional or not to define an or-
der between them. Various comments suggested re-
visiting key aspects of the scenario. The playabil-
ity of the scenario is too simple without bringing a
playful aspect. Some testify that the coffee machine
model must be customizable to look more like the
one present in nursing homes. Others point out that
the choice to make coffee discriminates against those
who do not consume it. The need for assistance is also
HUCAPP 2025 - 9th International Conference on Human Computer Interaction Theory and Applications
670

Table 2: Participant characteristics and subjective condition
(mean, standard deviation).
Baseline characteristics (n = 8)
Age 41.63 (10.70)
Sex (% women) 75.00
Laterality (% right) 100.00
Education years 22.38 (3.11)
Years of work 15.50 (9.50)
Subjective condition (10-Likert scale)
Health status 7.88 (0.83)
Physical status 7.38 (1.41)
Mental status 8.00 (0.76)
Digital fluency 7.75 (1.49)
felt at certain stages, and the differentiation between
actionable objects and the decor should be more pro-
nounced. Finally, some technical bugs were recorded
during the experiments and will be corrected before
interventions in nursing homes.
5 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
We presented a Virtual Kitchen application on a touch
table designed for motor and cognitive rehabilitation
in patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI)
and People with Alzheimer (PwD). The aim is to
assess and strengthen their ability to memorize and
reproduce a sequence of an activity of daily living
(preparing a cup of sweetened coffee with milk). The
touch table is equipped with a 3D camera on top for
motion capture. It specifically allows for direct in-
teraction with virtual objects. An errorless learning
method has been implemented to prevent the user
from performing and remembering any erroneous ac-
tions executed during the task. In addition, visual and
sound signals are displayed if the user does not re-
member the required action. The assumption is that
the user will need fewer and fewer hints and will even-
tually be able to perform the task without assistance.
This tool will soon be put into practice in an exper-
iment involving healthy elderly people, elderly people
with MCI and people with Alzheimer’s disease. We
will use usability tests accessible for elders such as
TAM and UTAUT (Davis and Davis, 1989; Venkatesh
et al., 2003). We will propose the activity to two
groups separately, one with a distribution method on a
virtual reality headset, the other on the original touch
table proposal. Subjects will first be assessed without
any visual or auditory cues, then spend a number of
sessions with these aids before being assessed again.
A large amount of data will be collected jointly with
both approaches and analyzed. This data concerns the
evolution of patients during the different sessions of-
fered. In this context, we will study the influence of
visual and auditory cues as well as selection errors
across different attribution modalities. To study trans-
fer of learning, patients will be tested in a real kitchen
and asked to prepare a cup of sweetened coffee with
milk using the same or different ingredients and ma-
chines.
REFERENCES
Al Mahmud, A., Mubin, O., Shahid, S., and Martens, J. B.
(2008). Designing and evaluating the tabletop game
experience for senior citizens. In Proceedings of the
5th Nordic Conference on Human-Computer Interac-
tion: Building Bridges, page 403–406, New York, NY,
USA. Association for Computing Machinery.
Allain, P., Foloppe, D., Besnard, J., Yamaguchi, T.,
Etcharry-Bouyx, F., Le Gall, D., Nolin, P., and
Richard, P. (2014). Detecting everyday action deficits
in alzheimer’s disease using a nonimmersive virtual
reality kitchen. Journal of the International Neuropsy-
chological Society, 20(5):468–477.
Annett, M., Anderson, F., and Bischof, W. F. (2012). User
perspectives on tabletop therapy.
Augstein, M., Neumayr, T., Karlhuber, I., Dielacher, S., Alt-
mann, J., and
¨
Ohlinger, S. (2015). Tabletop-supported
rehabilitation with fun.tast.tisch.: Lessons learned.
pages 283–288.
Augstein, M., Neumayr, T., Ruckser-Scherb, R., and
Dielacher, S. (2016). Collaboration around an inter-
active tabletop in rehabilitation settings.
Brooke, J. (1995). Sus: A quick and dirty usability scale.
Usability Eval. Ind, 189.
Brooks, B., McNeil, J., Rose, F., and Greenwood, R., e. a.
(1999). Route learning in a case of amnesia: A pre-
liminary investigation into the efficacy of training in a
virtual environment. Neuropsychol. Rehab., 9:63–76.
Bruun, A., Jensen, K. E., Kristensen, D. H., and Kjeldskov,
J. (2017). Escaping the trough: Towards real-world
impact of tabletop research. International Journal of
Human-Computer Interaction, 33(2):77–93.
Burdea, G. and Coiffet, P. (2024). Virtual Reality Technol-
ogy. N.-Y.: John Wiley & Sons Pub., 3
rd
edition.
Catania, V., Rundo, F., Panerai, S., and Ferri, R. (2024).
Virtual reality for the rehabilitation of acquired cog-
nitive disorders: A narrative review. Bioengineering,
11(1):35.
Chae, H. and Lee, S. (2023). Effectiveness of online-
based cognitive intervention in community-dwelling
older adults with cognitive dysfunction: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry,
38(1):36468299.
Virtual Kitchen: Using a Touch Table for Cognitive Rehabilitation in Activities of Daily Living
671

Cherniack, E. (2011). Not just fun and games: applications
of virtual reality in the identification and rehabilitation
of cognitive disorders of the elderly. Disabil Rehabil
Assist Technol, 6(4):283–9.
Cogn
´
e, M., Auriacombe, S., Vasa, L., Tison, F., Klinger, E.,
Sauz
´
eon, H., Joseph, P., and Bernard, N. (2017). Influ-
ence of visual stimuli on spatial navigation and mem-
ory of mci, alzheimer’s disease patients and healthy
control subjects. volume 60, pages e88–e89.
Cossou, L., Louison, C., Bouchigny, S., and Ammi, M.
(2018). Tangible sounds: An audio system for inter-
active tabletops. In 1st International Conference on
Digital Tools & Uses Congress (DTUC ’18). Associa-
tion for Computing Machinery, volume 1, pages 1–4.
Davis, F. and Davis, F. (1989). Perceived usefulness, per-
ceived ease of use, and user acceptance of information
technology. MIS Quarterly, 13:319–.
Foloppe, D., Richard, P., Yamaguchi, T., Etcharry-Bouyx,
F., and Allain, P. (2018). The potential of virtual
reality-based training to enhance the functional auton-
omy of alzheimer’s disease patients in cooking activ-
ities: A single case study. Neuropsychological Reha-
bilitation, 28(5):709–733.
Fuchs, P., Moreau, G., and Papin, J.-P. (2001). Le trait
´
e de
la r
´
ealit
´
e virtuelle. Les Presses de l’Ecole des Mines
de Paris.
Gamberini, L., Martino, F., Seraglia, B., Spagnolli, A., Fab-
regat, M., Ibanez, F., Alcaniz, M., and Andres, J. M.
(2009). Eldergames project: An innovative mixed re-
ality table-top solution to preserve cognitive functions
in elderly people. In 2009 2nd Conference on Human
System Interactions, pages 164–169.
Gronier, B. (2021). Psychometric evaluation of the f-
sus: Creation and validation of the french version of
the system usability scale. International Journal of
Human-Computer Interaction, page 1–12.
Guay, Vallerand, B. (2000). On the assessment of situa-
tional intrinsic and extrinsic motivation: The situa-
tional motivation scale (sims). Motivation and Emo-
tion, 24.
G
¨
undogdu, R., Bejan, A., Kunze, C., and W
¨
olfel, M.
(2017). Activating people with dementia using nat-
ural user interface interaction on a surface computer.
pages 386–394.
Hart, S. (1988). Development of nasa-tlx (task load in-
dex): Results of empirical and theoretical research.
P. A. Hancock and N. Meshkati (Eds.) Human Men-
tal Workload. Amsterdam: North Holland Press.
Jin, S., Fan, M., and Kadir, A. (2021). Immersive spring
morning in the han palace: Learning traditional chi-
nese art via virtual reality and multi-touch tabletop.
International Journal of Human–Computer Interac-
tion, 38(3):213–226.
Kaya, E., Alac¸am, S., Findik, Y., and Balcisoy, S. (2017).
Low-fidelity prototyping with simple collaborative
tabletop computer-aided design systems. Computers
& Graphics, 70.
Klinger, E. (2006). Apports de la r
´
ealit
´
e virtuelle
`
a la prise
en charge de troubles cognitifs et comportementaux.
PhD thesis, T
´
el
´
ecom ParisTech.
Lecouvey, G., Morand, A., Gonneaud, J., Piolino, P., Or-
riols, E., P
´
elerin, A., and Desgranges, B. (2019).
An impairment of prospective memory in mild
alzheimer’s disease: A ride in a virtual town. Fron-
tiers in Psychology, 10:241.
Lumsden, J., Edwards, E., Lawrence, N., Coyle, D., and
Munaf
`
o, M. (2016). Gamification of cognitive assess-
ment and cognitive training: A systematic review of
applications and efficacy. JMIR serious games, 4:e11.
Maincent (2001). Le nasa tlx, traduit en franc¸ais et adapt
´
e
pour le laboratoire d’etudes et d’analyses de la cogni-
tion et des mod
`
eles, lyon.
Plechat
´
a, A., Sahula, V., Fayette, D., and Fajnerov
´
a, I.
(2019). Age-related differences with immersive and
non-immersive virtual reality in memory assessment.
Frontiers in Psychology, 10.
Richard, P., Foloppe, D., and Allain, P. (2018). A virtual
kitchen for cognitive rehabilitation of alzheimer pa-
tients. In Human Interface and the Management of
Information. Interaction, Visualization, and Analytics,
pages 426–435. Springer International Publishing.
Rizzo, A., Bowerly, T., Shahabi, C., and Buckwalter, J.G.,
e. a. (2004). Diagnosing attention disorders in a virtual
classroom. IEE Computer, 37:87–89.
Ro, D., Lee, J., Lee, G., Shin, S., and Kim, Y. H. (2023).
Effect of interactive multitouch game-based cogni-
tive intervention on cognitive function in older adults:
A randomized controlled trial. DIGITAL HEALTH,
9(205520762311766).
Sch
¨
oning, J., Brandl, P., Daiber, F., Echtler, F., Hilliges, O.,
Hook, J., L
¨
ochtefeld, M., Motamedi, N., Muller, L.,
Olivier, P., Roth, T., and Zadow, U. (2008). Multi-
touch surfaces: A technical guide technical report
tum-i0833.
Smith, J. e. a. (2023). Vis: A systematic review. Journal of
Cognitive Rehabilitation, 12(4):210–225.
van Dijk, B., van der Sluis, F., and Nijholt, A. (2012). De-
signing a museum multi-touch table for children. In-
telligent Technologies for Interactive Entertainment.
INTETAIN 2011. Lecture Notes of the Institute for
Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecom-
munications Engineering, 78.
Venkatesh, V., Morris, M., Davis, G., and Davis, F. (2003).
User acceptance of information technology: toward a
unified view. MIS Quarterly, 27(3):425–478.
Yamaguchi, T., Foloppe, D., Richard, P., Richard, E.,
and Allain, P. (2012). A dual-modal virtual reality
kitchen for (re)learning of everyday cooking activities
in alzheimer’s disease. Presence, 21(1):43–57.
APPENDIX
Figure 5: Opening the coffee compartment of the machine.
HUCAPP 2025 - 9th International Conference on Human Computer Interaction Theory and Applications
672
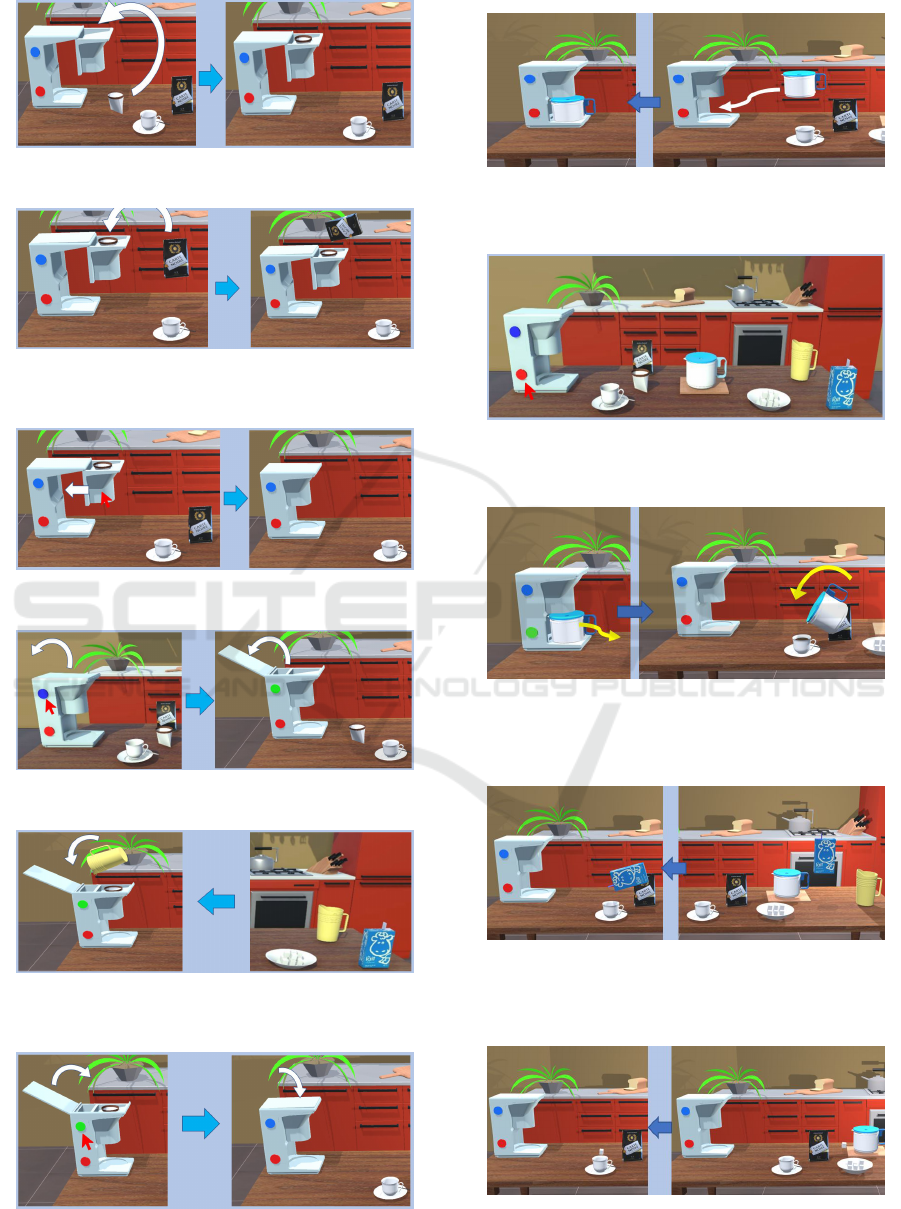
Figure 6: Place the coffee filter in the compartment.
Figure 7: Pour the coffee from the bag into the filter and put
it back in place.
Figure 8: Closing the coffee compartment.
Figure 9: Opening the machine cover.
Figure 10: Pour the water from the carafe into the machine
and replace it.
Figure 11: Closing the machine cover.
Figure 12: Place the jug in the machine.
Figure 13: Press the red button to activate the machine.
Figure 14: Pour the coffee from the carafe into the cup and
return it to its original position.
Figure 15: Pour the milk from the milk pack into the cup
and replace the pack.
Figure 16: Place a sugar cube in the cup.
Virtual Kitchen: Using a Touch Table for Cognitive Rehabilitation in Activities of Daily Living
673
