
Time Series Prediction Models for Diabetes: A Systematic Literature
Review
Wissem Mbarek, Nesrine Khabou
a
, Lotfi Souifi
b
and Ismael Bouassida Rodriguez
c
ReDCAD Laboratory, ENIS, University of Sfax, Tunisia
fi fi
Keywords:
AI, Time Series, Prediction Models, Diabetes, Systematic Literature Review, SLR.
Abstract:
Diabetes is a highly prevalent chronic disease that imposes significant health and economic burdens globally.
Early and accurate prediction, along with timely intervention, is crucial to prevent or delay the onset of diabetes
and its complications. Various techniques have been used to forecast this disease, one of them is time series
analysis, which has shown promise in the field of diabetes research prediction. This comprehensive review
examines the existing literature on time series prediction models for diabetes, identifying the various machine
learning and statistical methods employed, including recurrent neural networks, long short-term memory net-
works, integrated auto-regressive moving average models and hybrid approaches. The review highlights key
time series parameters, such as glucose levels, insulin dosage, diet, physical activity, and other physiological
metrics, that significantly impact predictive precision and overall performance of these models. The findings
of this review provide valuable insight into the current state of time series prediction models for diabetes,
underscoring the strengths and limitations of each approach.
1 INTRODUCTION
Diabetes is a chronic and widespread medical condi-
tion characterized by the body’s impaired ability to
regulate blood glucose levels, leading to severe long-
term health complications if not effectively managed.
As the prevalence of diabetes continues to increase
globally, there is a pressing need for advanced tools
that can monitor and predict blood sugar levels with
high precision. Time series prediction models have
emerged as a critical component in this endeavor, uti-
lizing historical health data to forecast future glucose
levels and other relevant metrics. These models ana-
lyze data collected at consistent intervals, such as con-
tinuous glucose monitoring (CGM) readings, to iden-
tify underlying patterns, trends, and seasonal fluctua-
tions.
In the literature, various predictive models have
been used to forecast blood glucose levels in diabetic
patients, each offering unique strengths. Time-series
models, such as ARIMA and LSTM, are designed to
analyze and predict temporal trends. Regression mod-
els, including linear and logistic regression, estimate
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0461-8820
b
https://orcid.org/0009-0001-9810-4806
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5605-7415
glucose levels based on explanatory variables or the
likelihood of crossing certain thresholds. Decision
tree models, such as random forests and XGBoost,
improve prediction accuracy by aggregating multiple
decision trees or models. Deep learning techniques,
such as CNNs and ANNs, capture intricate patterns
and relationships within the data. Probabilistic mod-
els, such as Gaussian Processes and Bayesian Net-
works, address uncertainties and model probabilistic
relationships. Hybrid models, which integrate various
approaches, aim to improve overall predictive per-
formance. The selection of a model depends on the
specific characteristics of the data and the objectives
of the prediction. The integration of artificial intelli-
gence (AI) with time series models significantly en-
hances their predictive capabilities. Machine learning
algorithms and neural networks, particularly Long-
Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks, have shown
exceptional proficiency in capturing long-term depen-
dencies and temporal dynamics in glucose data. This
allows for more accurate and reliable forecasting of
blood glucose levels, facilitating timely interventions
and personalized treatment plans. AI-driven time se-
ries models can provide real-time alerts for potential
hypoglycemic or hyperglycemic events, optimize in-
sulin dosing, and offer valuable insights into the ef-
fects of lifestyle factors on blood sugar control.
1352
Mbarek, W., Khabou, N., Souifi, L. and Rodriguez, I. B.
Time Series Prediction Models for Diabetes: A Systematic Literature Review.
DOI: 10.5220/0013368400003890
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2025) - Volume 3, pages 1352-1359
ISBN: 978-989-758-737-5; ISSN: 2184-433X
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

In this context of a systematic review of the litera-
ture on time series prediction models for diabetes, it is
essential to explore and evaluate the diverse method-
ologies, AI techniques, and statistical models that
have been applied to this domain. By synthesizing the
findings of various studies, the review aims to identify
the most effective models and approaches for predict-
ing diabetes-related outcomes. This comprehensive
analysis will not only highlight the current state of
research, but also uncover gaps and opportunities for
future advancements in diabetes management. Ulti-
mately, the adoption of sophisticated time series pre-
diction models can empower patients and healthcare
providers with proactive tools for better diabetes care,
improving the quality of life of people living with this
chronic disease.
This paper is structured to offer a comprehensive
analysis of time series prediction models for the treat-
ment of diabetes. It opens with an introduction that
highlights the importance of diabetes as a chronic
disease and the pressing need for effective predictive
tools. The subsequent SLR Process section details the
methodology of the systematic literature review, in-
cluding the formulation of research questions, search
strategy, selection criteria, and data extraction meth-
ods. In the Findings section, the results are organized
into categories: statistical models, machine learning
models, and deep learning models, each addressing
specific research questions. The Learned Lessons sec-
tion reflects on the insights gained during the review
and their implications for future research and prac-
tice. Finally, the article concludes with a summary
of key findings, emphasizing the importance of ad-
vanced predictive models and offering suggestions for
further exploration in the management of diabetes.
This structure aims to guide the reader through the
research process while underscoring the critical role
of predictive modeling in improving diabetes care.
2 THE SLR PROCESS
The research methodology for this paper follows a
systematic literature review (SLR) approach, which
involves the following three key steps:
• Definition of Research Questions: In this initial
step, research questions are formulated. These
questions guide the review process throughout
and help focus the search for relevant studies.
• Identification of Search Strategy: A systematic
search strategy is developed to identify relevant
articles. This involves systematically searching
various databases and other sources to locate stud-
ies related to the research questions.
• Selection of articles based on specific criteria:
Once the search results are obtained, the articles
are selected based on predefined inclusion and ex-
clusion criteria. These criteria ensure that only
relevant and high-quality studies are included in
the review.
2.1 Research Questions
Defining the research questions is considered a cru-
cial step in any systematic review. A systematic re-
view achieves its goals when it can answer research
questions. The research questions for this systematic
review study are as follows:
RQ1. What prediction models are used for the case of
diabetes?
RQ2. What are the different time series parameters
for diabetes prediction models?
2.2 Search Strategy
We identified the initial studies in the database ac-
cording to the following keywords that are divided
into three groups.
• Group1: (“prediction”).
• Group2: (“time Serie”),
• Group3: (“diabetes”).
To get relevant results, the search method inte-
grates the essential concepts in our search query.
Both sets of keywords were combined with a Boolean
search (AND), in the article search process. The fi-
nal search string in this study is (“Prediction”) AND
(“Time Series”) AND (“Diabetes”).
2.2.1 Selection Criteria
After obtaining search results from various databases,
the articles were meticulously selected based on a
set of Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria. These crite-
ria were instrumental in identifying relevant primary
studies and ensuring the precision, objectivity and
significance of the results of the study.
The Inclusion Criteria encompassed several key as-
pects:
• The presence of predetermined keywords
throughout the paper particularly in the title,
keywords, or abstract section
• Publication in a scientific peer-reviewed journal
• Inclusion of research studies published between
January 2017 and March 2024
• Articles written in the English language
Time Series Prediction Models for Diabetes: A Systematic Literature Review
1353

However, the exclusion criteria aimed to filter out ir-
relevant studies and included:
• Publications not aligned with the research ques-
tion keywords
• Review papers, book chapters, master, and Ph.D.
dissertations
• Publications published before or on December 31,
2016
• Articles written in languages other than English.
These criteria were systematically applied to ensure
the selection of studies that met the specific require-
ments of the investigation, improving the quality and
relevance of the study’s findings.
2.3 Data Extraction
For this systematic literature review (SLR), we used a
comprehensive set of five research databases, includ-
ing HAL, IEEE, ACM, Science Direct, and Springer.
The search period spanned from 2017 to 2024. Upon
executing the predefined research query, we identified
a total of 160 articles from various sources, as detailed
in Table 1. Subsequently, we applied the filtering pro-
cess to find 49 papers’ results for further analysis and
consideration.
3 FINDINGS
In this section, we answer the research questions of
our SLR. In the following part, we discuss the predic-
tion models used for the prediction of diabetes.
3.1 Statistical Models
Jose et al. (Velasco et al., 2017) devised a method
that merges grammatical evolution with a geometric
semantic framework to predict glucose levels in indi-
viduals with type 1 diabetes mellitus. This predictive
model incorporates the symbolic aggregate approxi-
mation (SAX) to refine the representation of glucose
time-series data, thus facilitating the efficient use of
semantic operations. The resultant model capitalizes
on these enhanced representations to make precise
glucose-level predictions, blending both symbolic and
semantic dimensions in data analysis. This approach
employs SAX to boost the representation of glucose
time series, enabling the effective application of se-
mantic operators. Mohammad et al. (Askari et al.,
2020) introduced an adaptive learning model predic-
tive control (AL-MPC) framework, which improves
automated insulin delivery control systems in diabetes
management. Implements the dynamic low-rank and
variable selection regression (DrLVR) algorithm for
analyzing historical data to anticipate future fluctua-
tions and constructs a robust control path. The frame-
work also modifies setpoint parameters and penalty
factors to enhance system performance despite feed-
back delays and variable conditions.
3.2 Machine Learning Models
SSergio et al. (Contador et al., 2019) introduced an in-
novative technique to improve glucose prediction by
integrating Genetic Programming (GP) models with
clustering methods. They used the Chi-square auto-
matic interaction detection (CHAID) algorithm to cat-
egorize glucose time series data into various profiles
based on the weekday and time of day. Fan et al. (Hou
et al., 2020) developed a new methodology to im-
prove glucose prediction using genetic programming
(GP) models with the addition of clustering strategies.
They specifically used decision trees, more precisely
the CHAID algorithm, to partition glucose time series
data into distinct profiles according to the week and
time schedule. Hasan et al. (Mahmud et al., 2018)
introduced a detailed framework called Diabetes Pre-
diction, Monitoring, and Application (DPMA), which
applies machine learning to real-time diabetes pre-
diction and monitoring. It incorporates six classifi-
cation techniques: Artificial Neural Network (ANN),
Support Vector Machine (SVM), Decision Tree (DT),
Random Forest (RF), Logistic Regression (LR) and
Naive Bayes (NB). Sergio et al. (Contador et al.,
2020) devised an innovative approach for precise pre-
diction of subcutaneous glucose levels in diabetic in-
dividuals by merging genetic programming with clus-
tering methods. Their goal is to develop predictive
models adapted to different glucose profiles identi-
fied through clustering, using CHAID for classifica-
tion. Sterling et al. (Ramroach et al., 2019) made
a vital contribution by using CUDA and C++ to im-
prove neural network training to predict blood glu-
cose levels (HbA1c) from non-invasive markers. This
optimization takes advantage of the parallel process-
ing capabilities of Nvidia GPUs, achieving a signif-
icant speedup in training time compared to standard
CPU-based techniques. Shadman et al. (Sakib et al.,
2021) conducted a research study applying various
machine learning methods, such as logistic regres-
sion, decision tree, XGBoost, support vector machine,
nearest neighbor, and random forest, on the PIMA
Indian Diabetes Dataset to predict diabetes. Takwa
et al. (Hamdi et al., 2018) proposed a novel ap-
proach to accurately predict continuous blood glu-
cose levels using only continuous glucose monitor-
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
1354
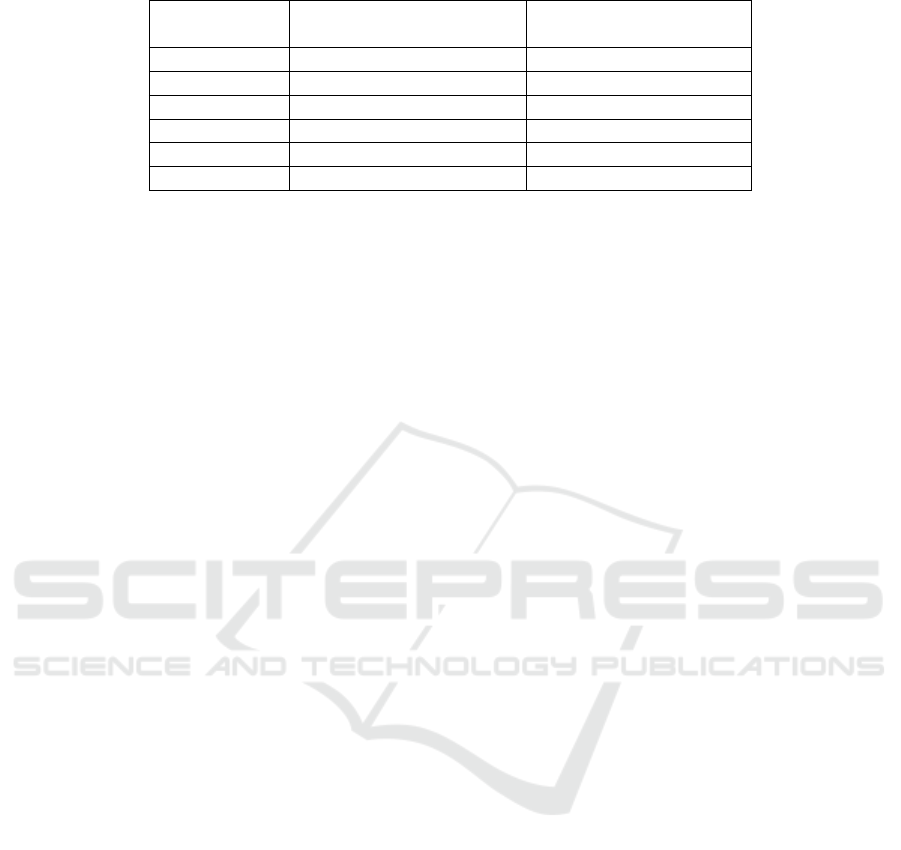
Table 1: Search results for each used database.
Source
Number of papers before
title-abstract filtering
Number of papers after
title-abstract filtering
Springer 82 7
IEEE Xplore
21 17
ACM 27 7
Science Direct 28 16
HAL 3 2
Total 160 49
ing (CGM) data, without relying on additional fac-
tors such as meal intake, insulin injection, or emo-
tional states. This method employs support vector
regression (SVR) and differential evolution (DE) al-
gorithms. Ignacio et al. (Hidalgo et al., 2020) in-
troduced an innovative method for predicting glucose
levels that integrates Markov chain-based data en-
hancement, random grammatical evolution (Random-
GE), and bagging techniques to enhance the precision
and reliability of blood glucose forecasts for diabetic
individuals.
3.3 Deep Learning Models
Wang et al. (Wang et al., 2020) developed a VMD-
IPSO-LSTM model tailored to predict short-term
blood glucose fluctuations. This model tackles the
issue of non-stationary glucose data by initially de-
composing them through variational mode decompo-
sition (VMD) into intrinsic mode functions (IMFs),
each corresponding to different frequencies. An Im-
proved Particle Swarm Optimization (IPSO) algo-
rithm is then employed to fine-tune the hyperparame-
ters of a Long-Short-Term Memory (LSTM) network
for IMF prediction. The ultimate prediction results
from the compilation of the individual IMF forecasts.
Similarly, Kasuri et al. (Balasooriya and
Nanayakkara, 2020) presented a deep learning al-
gorithm aimed at predicting short-term variations in
blood glucose levels among patients with type 2 di-
abetes using non-invasive data. This approach used
time series forecasting with long-short-term memory
(LSTM), which integrates historical glucose readings,
medication doses, dietary intake, and lifestyle details.
In another study, Taiyu et al. (Zhu et al., 2020)
proposed a novel deep learning framework that uses
dilated recurrent neural networks (DRNNs) to predict
glucose levels for patients with type 1 diabetes melli-
tus (DM1). This model capitalized on data from Elec-
tronic Health Records (EHR) and employed a two-
phase transfer learning strategy to surpass existing
techniques in terms of precision and adaptability.
Nora et al. (El-Rashidy et al., 2023) introduced an
innovative framework and model aimed at the early
diagnosis of gestational diabetes in expectant moth-
ers, leveraging fog computing and interpretable deep
learning methods. This framework, named DRPF, is
composed of two main parts: DFM, which surveils
and substitutes data on vital signs, and EPM, which
employs DNN and SHAP to estimate and elucidate
the gestational diabetes risk. The model’s perfor-
mance was assessed using the MIMIC III dataset,
comprised of electronic health records for patients in
intensive care settings.
Shradha et al. (Dubey and Dixit, 2023) provide
a detailed analysis of computer-assisted systems for
identifying diabetic retinopathy (DR), highlighting
both traditional and deep learning approaches. They
emphasize the dominance of deep learning in DR de-
tection, delve into the essential role of feature selec-
tion and fusion methods, and classify datasets into
public and private categories, assisting researchers in
choosing datasets.
Wenqi et al. (Li et al., 2022) introduce a pioneer-
ing model for coronary heart disease prediction. This
model, utilizing data from the Rajaie Cardiovascular
Medical Research Center, merges deep reinforcement
learning, multitask learning, and both soft and hard
parameter-sharing within progressive time-series net-
works.
Hoda et al. (Nemat et al., 2023) examine the
causal relationships affecting blood glucose levels
(BGL) in individuals with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
(DM1). The study employs Convergent Cross Map-
ping (CCM) and Extended CCM (ECCM) to measure
these causal links and identify the most influential
time lags. Sara et al. (Rabhi et al., 2022) made no-
table contributions to predictive analytics in health-
care, notably in the prediction of diabetic retinopa-
thy among patients with type 1 diabetes. This paper
introduces a new application of deep learning meth-
ods, creates a comprehensive framework, fills exist-
ing knowledge gaps, advances methodology, and pri-
oritizes both model performance and interoperability.
On the other hand, Ning et al. (Li et al., 2020) de-
veloped an improved Echo State Network (ESN) al-
gorithm that uses incremental learning and feedback
to predict blood glucose levels with precision. The
Time Series Prediction Models for Diabetes: A Systematic Literature Review
1355

model was trained using clinical trial data and CGMS
records, consisting of a total of 288 data points over
three days.
Wei et al. (Song et al., 2019) introduced a method
to improve the prediction of blood glucose levels
for diabetic patients by combining empirical mode
decomposition (EMD) with long-short-term memory
(LSTM) neural networks. Using continuous glucose
monitoring (CGM) data from 174 diabetic patients,
their approach was trained and evaluated, showing
greater accuracy than conventional LSTM models,
especially at extended prediction intervals. Meliha
et al. (Celik and Varli, 2022) introduced novel data
analysis techniques tailored for wearable health de-
vices, targeting the difficulties in effectively analyz-
ing health data. This research advances health infor-
matics by using the OhioT1DM dataset to extract key
insights, thereby enhancing health outcomes.
Yang et al. (Yang et al., 2022) proposed a multi-
task learning strategy to predict hypoglycemic events
and predict glucose levels in diabetic patients. Their
study used CGM data from 112 type 1 diabetic pa-
tients who used CGM devices for 90 days. Data
preprocessing involved breaking down the CGM data
into smaller time series and standardizing glucose lev-
els. Ali et al. (Mohebbi et al., 2020) applied recurrent
neural networks (RNNs) to predict short-term blood
glucose levels using CGM data from 50 diabetes pa-
tients. These data were sourced from the Corner-
stones4Care platform, supported by Glooko, a dia-
betes management application. The data set includes
14 days of CGM data per patient, addressing quality
and missing value concerns in accordance with the in-
ternational CGM consensus guidelines.
Liling et al. (Yu et al., 2022) introduced a
novel technique by integrating the Extreme Learn-
ing Machine (ELM) algorithm with Enhanced Parti-
cle Swarm Optimization (IPSO) to forecast blood glu-
cose levels in diabetic patients for future periods. This
unique combination improves both prediction accu-
racy and generalization capabilities. Using the IPSO
algorithm, they were able to fine-tune input weights
and hidden layer thresholds, eliminating redundant
nodes and improving learning efficiency.
Furthermore. Muhammad et al. (Syafrudin et al.,
2022) developed an innovative model based on an
artificial neural network (ANN) to forecast upcom-
ing glycemic events in patients with type 1 diabetes
(T1D), using real-world data from five data sets of
patients with T1D. This model employs a sliding win-
dow technique for data pre-processing and demon-
strates high performance for prediction horizons of 30
and 60 minutes. Furthermore, the model aims to cat-
egorize all numeric blood glucose outputs into mul-
ticlass labels such as hypoglycemia, hyperglycemia,
and normal. The authors compared their proposed
models with classification models such as Nave Bayes
(NB), Decision Tree (DT), Support Vector Machine
(SVM) and K-Nearest Neighbor (KNN). Heng et al.
(Yang and Li, 2021) developed a new hybrid neural
prediction algorithm called PSONN (Particle Swarm
Optimization Neural Network), which merges parti-
cle swarm optimization with neural networks to en-
hance the accuracy and consistency of traditional neu-
ral networks in the prediction of diabetes.
Aleksandr et al. (Zaitcev et al., 2020) intro-
duced an innovative deep learning approach to predict
HbA1c levels in patients with Type 1 diabetes (T1D)
leveraging SMBG time series data alongside demo-
graphic information. Their model utilizes Convolu-
tional Neural Networks (CNNs) to identify behavioral
patterns in the SMBG data, which are then integrated
with other features using fully connected (FC) layers
to generate a regression output. This model aims to
improve the precision and reliability of HbA1c pre-
dictions, facilitating personalized analyses of behav-
ioral patterns and interventions to improve diabetes
management and quality of life.
Indian et al. (Bhargav et al., 2021a) examined
the application of temporal convolutional networks
(TCNs) to predict blood glucose levels in patients
with Type 1 diabetes. They utilized a dataset sourced
from the AIDA simulator and compared various cali-
bration techniques and hyperparameter tuning strate-
gies for TCNs. The study showcases the benefits of
a generalized model capable of predicting blood glu-
cose levels in previously unseen patients. Muham-
mad et al. (Siddiqui et al., 2022a) developed a novel
LSTM-based framework to forecast blood glucose
levels in diabetic individuals, using a data set that
captures variations in blood glucose over time. This
model employs LSTM, a type of recurring neural net-
work (RNN), to extract insights from the raw time se-
ries and execute sequence classification tasks.
Aashima et al. (Bhargav et al., 2021b) evaluated
the utility of temporal convolutional networks (TCN)
to predict blood glucose levels (BGL) in patients with
Type 1 Diabetes (T1D), transitioning their use from
general sequence modeling efforts to prediction of
BGL. This investigation contrasts the performance
of TCNs with Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs),
maintaining a similar number of trainable parame-
ters for an equitable comparison, thus emphasizing
their respective advantages and limitations. Muham-
mad et al. (Siddiqui et al., 2022b) introduced a novel
LSTM-based approach to forecasting blood sugar lev-
els in diabetic individuals, utilizing a dataset compris-
ing blood glucose measurements over time. This ap-
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
1356

proach employs LSTM, a variant of RNN, to interpret
raw time series data and perform sequence classifi-
cation operations. Federico et al. (D’Antoni et al.,
2020) designed an Auto-Regressive Time Delayed
(ARTiDe) jump neural network to predict blood glu-
cose levels. This neural network integrates feedback
loops and time delays for input-to-hidden, output-to-
hidden, and input-to-output interactions, enabling it
to make use of recent input data along with historical
predictions.
Sadegh et al. (Mirshekarian et al., 2019) devel-
oped advanced prediction frameworks for blood glu-
cose levels (BGL) in cases of Type 1 diabetes. They
examined a double LSTM (Long Short-Term Mem-
ory) setup, compared it with standard models such as
ARIMA, and achieved enhanced predictive accuracy.
Matteo et al. (Gadaleta et al., 2018) focused on
identifying patterns that could lead to risky scenar-
ios, helping patients make therapeutic choices based
on anticipated (predicted) glucose levels. They evalu-
ated regression and classification methods, comparing
static and dynamic training techniques, with a dataset
of 89 continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) time se-
ries from diabetic participants over seven consecu-
tive days. Hoda et al. (Nemat et al., 2022) intro-
duced novel algorithms designed to predict clinical
outcomes in the context of healthcare data analysis.
They used cutting-edge machine learning techniques
to enhance the precision and reliability of these pre-
dictive models.
In a related study, Jaouher et al. (Ben Ali et al.,
2018) developed an innovative method based on arti-
ficial neural networks to forecast blood glucose lev-
els in individuals with Type 1 diabetes, utilizing only
CGM data. This method aligns with the goal of the
biomedical industry for autonomous systems. Mean-
while, Meng et al. (Zhang et al., 2021) presented a
pioneering predictive strategy that combines instance-
based learning with network-based deep transfer to
estimate glucose levels in various subjects. For new
patients who lack extensive historical data, their ap-
proach utilizes dynamic time warping (DTW) to iden-
tify a source domain dataset that closely matches the
new subjects.
4 LEARNED LESSONS
The present review demonstrates that the prediction
of diabetes uses a diverse array of methodologies, en-
compassing machine learning algorithms such as re-
current neural networks (RNN) and long-short-term
memory (LSTM) networks, in conjunction with tradi-
tional approaches such as auto-regressive integrated
moving average (ARIMA) models, often employed
in combination. The precision of these models is
considerably affected by factors that include glucose
levels, insulin dosage, diet intake, and physical ac-
tivity, along with other physiological metrics. Each
methodological approach exhibits distinct advantages
and limitations: Recurrent neural networks (RNNs)
and long-short-term memory (LSTM) networks ex-
cel in handling complex temporal patterns but require
extensive datasets, while Auto-Regressive Integrated
Moving Average (ARIMA) models are more simplis-
tic yet less effective with nonlinear data. Establishing
a collaborative framework that integrates the expertise
of endocrinology, data science, and machine learning
is essential for the development of robust predictive
models. Future investigations should prioritize im-
proving data quality, including more pertinent param-
eters and exploring new hybrid techniques. For these
models to be clinically useful, they must be precise,
interoperable, and user-friendly to facilitate seamless
implementation by healthcare professionals.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This study underscores significant advances and on-
going challenges within this critical healthcare do-
main. Through the examination of various machine
learning and statistical techniques, including recur-
rent neural networks (RNNs), long-short-term mem-
ory networks (LSTMs), autoregressive integrated
moving average (ARIMA) models, and hybrid meth-
ods, an extensive review of the current research land-
scape is presented. The primary findings underscore
the exceptional capabilities of AI-driven models, par-
ticularly LSTM networks, in capturing long-term de-
pendencies and temporal dynamics inherent in glu-
cose data. These models improve prediction accu-
racy and enable real-time monitoring in conjunction
with customized diabetes management. Incorporat-
ing physiological metrics such as glucose levels, in-
sulin dosage, dietary intake, and physical activity into
prediction models is emphasized as critical to improv-
ing performance. Despite these advancements, sev-
eral limitations and areas that require further investi-
gation are identified.
Numerous models persistently encounter chal-
lenges associated with the variability and complexity
of individual patient data, signaling the need for more
robust and adaptable algorithms. In addition, the in-
tegration of diverse data sources and the development
of more comprehensive datasets are imperative to in-
crease the precision and applicability of these mod-
els. In conclusion, although substantial progress has
Time Series Prediction Models for Diabetes: A Systematic Literature Review
1357

been made in time series prediction models for dia-
betes, ongoing research and innovation are imperative
to overcome present limitations and improve the effi-
cacy of these instruments. By refining these models
and exploring novel approaches, it becomes increas-
ingly feasible to achieve better diabetes management
and improved patient outcomes.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was partially supported by the LABEX-TA
project MeFoGL: “M
´
ethodes Formelles pour le G
´
enie
Logiciel”
REFERENCES
Askari, M. R., Hajizadeh, I., Rashid, M., Hobbs, N., Zavala,
V. M., and Cinar, A. (2020). Adaptive-learning model
predictive control for complex physiological systems:
Automated insulin delivery in diabetes. Annual Re-
views in Control, 50:1–12.
Balasooriya, K. and Nanayakkara, N. D. (2020). Predicting
short-term changing blood glucose level of diabetes
patients using noninvasive data. In 2020 IEEE RE-
GION 10 CONFERENCE (TENCON), pages 31–36.
IEEE.
Ben Ali, J., Hamdi, T., Fnaiech, N., Di Costanzo, V.,
Fnaiech, F., and Ginoux, J. (2018). Continuous blood
glucose level prediction of type 1 diabetes based on
artificial neural network. biocybern biomed eng 38:
828–840. DOI, 10:828–840.
Bhargav, S., Kaushik, S., Dutt, V., et al. (2021a). Tempo-
ral convolutional networks involving multi-patient ap-
proach for blood glucose level predictions. In 2021
International Conference on Computational Perfor-
mance Evaluation (ComPE), pages 288–294. IEEE.
Bhargav, S., Kaushik, S., Dutt, V., et al. (2021b). Tempo-
ral convolutional networks involving multi-patient ap-
proach for blood glucose level predictions. In 2021
International Conference on Computational Perfor-
mance Evaluation (ComPE), pages 288–294. IEEE.
Celik, M. G. and Varli, S. (2022). Deep learning approaches
for type-1 diabetes: Blood glucose prediction. In
2022 7th International Conference on Computer Sci-
ence and Engineering (UBMK), pages 1–5. IEEE.
Contador, S., Hidalgo, J. I., Garnica, O., Velasco, J. M., and
Lanchares, J. (2019). Can clustering improve glucose
forecasting with genetic programming models? In
Proceedings of the Genetic and Evolutionary Compu-
tation Conference Companion, pages 1829–1836.
Contador, S., Velasco, J. M., Garnica, O., and Hidalgo,
J. I. (2020). Profiled glucose forecasting using genetic
programming and clustering. In Proceedings of the
35th Annual ACM Symposium on Applied Computing,
pages 529–536.
Dubey, S. and Dixit, M. (2023). Recent developments
on computer aided systems for diagnosis of diabetic
retinopathy: a review. Multimedia Tools and Applica-
tions, 82(10):14471–14525.
D’Antoni, F., Merone, M., Piemonte, V., Iannello, G., and
Soda, P. (2020). Auto-regressive time delayed jump
neural network for blood glucose levels forecasting.
Knowledge-Based Systems, 203:106134.
El-Rashidy, N., ElSayed, N. E., El-Ghamry, A., and Ta-
laat, F. M. (2023). Utilizing fog computing and ex-
plainable deep learning techniques for gestational dia-
betes prediction. Neural Computing and Applications,
35(10):7423–7442.
Gadaleta, M., Facchinetti, A., Grisan, E., and Rossi, M.
(2018). Prediction of adverse glycemic events from
continuous glucose monitoring signal. IEEE journal
of biomedical and health informatics, 23(2):650–659.
Hamdi, T., Ali, J. B., Di Costanzo, V., Fnaiech, F., Moreau,
E., and Ginoux, J.-M. (2018). Accurate prediction
of continuous blood glucose based on support vector
regression and differential evolution algorithm. Bio-
cybernetics and Biomedical Engineering, 38(2):362–
372.
Hidalgo, J. I., Botella, M., Velasco, J. M., Garnica, O.,
Cervig
´
on, C., Mart
´
ınez, R., Aramendi, A., Maqueda,
E., and Lanchares, J. (2020). Glucose forecasting
combining markov chain based enrichment of data,
random grammatical evolution and bagging. Applied
Soft Computing, 88:105923.
Hou, F., Cheng, Z., Kang, L., and Zheng, W. (2020). Pre-
diction of gestational diabetes based on lightgbm. In
Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Artificial In-
telligence and Healthcare, pages 161–165.
Li, N., Tuo, J., Wang, Y., and Wang, M. (2020). Predic-
tion of blood glucose concentration for type 1 diabetes
based on echo state networks embedded with incre-
mental learning. Neurocomputing, 378:248–259.
Li, W., Zuo, M., Zhao, H., Xu, Q., and Chen, D. (2022).
Prediction of coronary heart disease based on com-
bined reinforcement multitask progressive time-series
networks. Methods, 198:96–106.
Mahmud, S. H., Hossin, M. A., Ahmed, M. R., Noori, S.
R. H., and Sarkar, M. N. I. (2018). Machine learning
based unified framework for diabetes prediction. In
Proceedings of the 2018 international conference on
big data engineering and technology, pages 46–50.
Mirshekarian, S., Shen, H., Bunescu, R., and Marling, C.
(2019). Lstms and neural attention models for blood
glucose prediction: Comparative experiments on real
and synthetic data. In 2019 41st annual international
conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and
biology society (EMBC), pages 706–712. IEEE.
Mohebbi, A., Johansen, A. R., Hansen, N., Christensen,
P. E., Tarp, J. M., Jensen, M. L., Bengtsson, H.,
and Mørup, M. (2020). Short term blood glucose
prediction based on continuous glucose monitoring
data. In 2020 42nd Annual International Conference
of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Soci-
ety (EMBC), pages 5140–5145. IEEE.
Nemat, H., Khadem, H., Eissa, M. R., Elliott, J., and
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
1358

Benaissa, M. (2022). Blood glucose level predic-
tion: advanced deep-ensemble learning approach.
IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics,
26(6):2758–2769.
Nemat, H., Khadem, H., Elliott, J., and Benaissa, M.
(2023). Causality analysis in type 1 diabetes melli-
tus with application to blood glucose level prediction.
Computers in Biology and Medicine, 153:106535.
Rabhi, S., Blanchard, F., Diallo, A. M., Zeghlache, D.,
Lukas, C., Berot, A., Delemer, B., and Barraud,
S. (2022). Temporal deep learning framework for
retinopathy prediction in patients with type 1 diabetes.
Artificial Intelligence in Medicine, 133:102408.
Ramroach, S., Dhanoo, A., Cockburn, B., and Joshi, A.
(2019). Cuda optimized neural network predicts blood
glucose control from quantified joint mobility and an-
thropometrics. In Proceedings of the 2019 3rd Inter-
national Conference on Information System and Data
Mining, pages 32–36.
Sakib, S., Yasmin, N., Tasawar, I. K., Aziz, A., Siddique,
M. A. B., and Khan, M. M. R. (2021). Performance
analysis of machine learning approaches in diabetes
prediction. In 2021 IEEE 9th Region 10 Humanitarian
Technology Conference (R10-HTC), pages 1–6. IEEE.
Siddiqui, M. M., Malick, R. A. S., and Ahmed, G. (2022a).
Lstm based deep learning model for blood sugar pre-
diction. In 2022 Mohammad Ali Jinnah University
International Conference on Computing (MAJICC),
pages 1–4. IEEE.
Siddiqui, M. M., Malick, R. A. S., and Ahmed, G. (2022b).
Lstm based deep learning model for blood sugar pre-
diction. In 2022 Mohammad Ali Jinnah University
International Conference on Computing (MAJICC),
pages 1–4. IEEE.
Song, W., Cai, W., Li, J., Jiang, F., and He, S. (2019). Pre-
dicting blood glucose levels with emd and lstm based
cgm data. In 2019 6th International Conference on
Systems and Informatics (ICSAI), pages 1443–1448.
IEEE.
Syafrudin, M., Alfian, G., Fitriyani, N. L., Hadibarata, T.,
Rhee, J., and Anshari, M. (2022). Future glycemic
events prediction model based on artificial neural net-
work. In 2022 International Conference on Innova-
tion and Intelligence for Informatics, Computing, and
Technologies (3ICT), pages 151–155. IEEE.
Velasco, J. M., Garnica, O., Contador, S., Botella, M., Lan-
chares, J., and Hidalgo, J. I. (2017). Forecasting glu-
cose levels in patients with diabetes mellitus using
semantic grammatical evolution and symbolic aggre-
gate approximation. In Proceedings of the Genetic
and Evolutionary Computation Conference Compan-
ion, pages 1387–1394.
Wang, W., Tong, M., and Yu, M. (2020). Blood glucose
prediction with vmd and lstm optimized by improved
particle swarm optimization. IEEE Access, 8:217908–
217916.
Yang, H.-L. and Li, B.-Y. (2021). A hybrid neural network
based on particle swarm optimization for predicting
the diabetes. In Proceedings of the 2021 10th Interna-
tional Conference on Software and Computer Appli-
cations, pages 302–306.
Yang, M., Dave, D., Erraguntla, M., Cote, G. L., and
Gutierrez-Osuna, R. (2022). Joint hypoglycemia pre-
diction and glucose forecasting via deep multi-task
learning. In ICASSP 2022-2022 IEEE International
Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Process-
ing (ICASSP), pages 1136–1140. IEEE.
Yu, L., Zhang, G., Xu, B., Liu, W., Guo, J., and Chen, Y.
(2022). Extreme learning machine algorithm based on
ipso for prediction of blood glucose concentration in
patients with type 1 diabetes. In 2022 7th Interna-
tional Conference on Computational Intelligence and
Applications (ICCIA), pages 113–117. IEEE.
Zaitcev, A., Eissa, M. R., Hui, Z., Good, T., Elliott, J., and
Benaissa, M. (2020). A deep neural network appli-
cation for improved prediction of backslashtexthba1
in type 1 diabetes. IEEE journal of biomedical and
health informatics, 24(10):2932–2941.
Zhang, M., Flores, K. B., and Tran, H. T. (2021). Deep
learning and regression approaches to forecasting
blood glucose levels for type 1 diabetes. Biomedical
Signal Processing and Control, 69:102923.
Zhu, T., Li, K., Chen, J., Herrero, P., and Georgiou, P.
(2020). Dilated recurrent neural networks for glucose
forecasting in type 1 diabetes. Journal of Healthcare
Informatics Research, 4:308–324.
Time Series Prediction Models for Diabetes: A Systematic Literature Review
1359
