
A Systematic Method to Derive Software Services and Requirements
from Business Models
Abderrahmane Leshob
1 a
, Raqeebir Rab
2
and Omar K. Hussain
3 b
1
University of Quebec at Montreal, Montreal, Canada
2
Ahsanullah University of Science & Technology, Dhaka, Bangladesh
3
School of Business, University of New South Wales, Canberra, Australia
Keywords:
Business Model, Service-Oriented Architecture, Model Transformation, Requirements Engineering, Goal
Model, Business Pattern.
Abstract:
Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) is an established architectural style to design modular, flexible and scal-
able software solutions. It provides design principles based on the service concept. Organizations use SOA
to design software solutions to support their business models, including business process models and value
models. Creating such software is a challenging endeavor that demands expertise in both software and busi-
ness (process) engineering. On the other hand, Requirements Engineering (RE) plays a key role in building
SOA-based solutions. RE ensures that the services are aligned with stakeholders’ needs. This research pro-
poses a transformational approach to i) identify SOA services that automate the collaboration between business
partners through their business models and ii) design a goal-based model that connects identified services to
the functional requirements they implement and the business and non-functional requirements they satisfy.
The obtained model allows to compute a score that measures the effectiveness of the services in satisfying
the requirements. The contribution of this work is twofold. First, it generates services that can be used to
build software from business models. Second, it builds a model that computes satisfaction scores, allowing
architecture and business analysis practitioners to i) measure the effectiveness of the services and ii) compare
and select the most appropriate services from various implementation based on the satisfaction of the require-
ments.
1 INTRODUCTION
Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) is a well-
established architectural style to design service-based
software solutions. It emphasizes the concept of mod-
ularity to develop robust solutions. SOA offers sev-
eral advantages such as reusability, flexibility, scala-
bility, and improved maintainability. SOA-based so-
lutions are decomposed into loosely coupled, interop-
erable services that encapsulate business functions.
SOA is used by organizations for packaging busi-
ness functionalities as services. The services can be
used to design and develop SOA-based software or
automate business processes using, for example, En-
terprise Resource Planning (ERP) software, the Busi-
ness Process Management (BPM) approach with a
BPMS (Business Process Management System), or
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4066-3111
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5738-6560
RPA (Robotic Process Automation) technology.
In the other hand, Requirements Engineering (RE)
is a key phase of the software development process. It
plays a crucial role in building SOA-based solutions
that automate business processes, business functions,
and business services while ensuring that the SOA
services are aligned with stakeholders (e.g., users,
customers and sponsors) needs. One way to ensure
that services are aligned with the stakeholders’ needs
is to: i) link the services to the requirements and ii)
measures their effectiveness in satisfying the require-
ments.
Many research efforts have tried to design SOA-
based solutions from business models, such as (Bian-
chini et al., 2014; Azevedo et al., 2013; Delgado
et al., 2018; Nikaj et al., 2019; Daghaghzadeh and
Babamir, 2021). However, to the best of our knowl-
edge, no work has been done in the current literature
that proposes to i) design SOA services from business
models, ii) connect identified services to the solutions
330
Leshob, A., Rab, R. and Hussain, O. K.
A Systematic Method to Derive Software Services and Requirements from Business Models.
DOI: 10.5220/0013372200003896
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Model-Based Software and Systems Engineering (MODELSWARD 2025), pages 330-337
ISBN: 978-989-758-729-0; ISSN: 2184-4348
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

requirements (functional and non-functional require-
ments) and business requirements, and iii) measure
the effectiveness of the identified services in the sat-
isfaction of the requirements.
This paper provides architecture practitioners and
business analysts with a method to i) identify SOA
services from business models and ii) design a goal-
based model that connects identified services to the
functional requirements they implement and business,
and non-functional requirements (NFR) they satisfy.
The obtained goal model allows to compute a score
that measures the effectiveness of the services in sat-
isfying the requirements, which contributes to the de-
sign and implementation of effective SOA-based soft-
ware solutions.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows.
Section 2 introduces the underlying background for
business modeling. Section 3 describes the proposed
method. We conclude in Section 4.
2 PRELIMINARIES
Business models are real-world representation of
business aspects that captures, analyzes, designs, and
communicates the business logic of the organizations.
Business models provide a holistic perspective on
an organization’s strategy and operations to gener-
ate value. Such models are Computation-Independent
Models. Indeed, business models focus on describ-
ing how an organization creates and delivers value,
but they do not specify the information systems that
enable their execution. Business process models and
value models are largely used in business modeling
to describe various aspects of the organizations’ busi-
ness (Andersson et al., 2009).
Business process models are important corporate
assets that depict the set of actions that should be per-
formed, the performers, and in what order they should
be performed (Blal et al., 2023). Such models are of-
ten described as workflows. Business process mod-
els encapsulate the underlying rationale of the busi-
ness process (i.e., why the resources/values are ex-
changed). Business process models can be expressed
using various modeling languages, such as Unified
Modeling Language (UML) (OMG, 2011b), Busi-
ness Process Model and Notation (BPMN) (OMG,
2011a), and Event-driven Process Chains (Scheer
et al., 2005).
Value models encapsulate the value creation from
business activities (Andersson et al., 2009). Such
models illustrate the value an organization provides
and how it is created, exchanged, and delivered
among business actors (Geerts and McCarthy, 2002).
The design of value model must illustrate the value
creation and exchanges. Business ontologies, such
as Resources, Events, Agents (REA) (McCarthy,
1982), e3-value (Gordijn and Akkermans, 2001), and
E-Business Model Ontology (e-BMO) (Osterwalder
and Pigneur, 2004) are commonly used to design
value models.
In this paper, business process models are ex-
pressed in BPMN while value models are expressed
in the REA ontology.
3 A TRANSFORMATIONAL
METHOD TO EXTRACT SOA
SERVICES AND
REQUIREMENTS FROM
BUSINESS MODELS
Our goal is to design a model-driven transforma-
tional method to help organizations implement effec-
tive SOA-based solutions that support their business
models. Our contribution is twofold: i) designing
SOA-based software solutions that support organiza-
tion business (process) models and ii) creating a goal
model that connects obtained SOA services to the re-
quirements, allowing to compute satisfaction scores
that measure the effectiveness of the identified ser-
vices.
To attain our objective, we are considering a six-
step method (see Figure 1). Step 1 builds the busi-
ness model. Step 2 extracts the collaborative activi-
ties and corresponding services that automate the ex-
change. Step 3 maps the services to business patterns.
Step 4 eliminates duplicate services. Step 5 identi-
fies business, functional, and non-functional require-
ments. Step 6 connects requirements to the identified
services through a goal model.
3.1 Build the Business Model
During the first step of the method, the modeler (e.g.,
business architect, solutions architect, business ana-
lyst) designs the business model (Business process
model or value model). The obtained model high-
lights the exchanges of resources/values between the
business partners.
To illustrate the method, let us consider a B2B
collaboration between a healthcare provider and ISO-
9001 QMS (Quality Management System) software
vendor. The Healthcare provider (HCP) needs to ac-
quire a QMS software to implement quality man-
agement system according to the ISO-9001 standard.
HCP publishes a Request For Quote (RFQ) intended
A Systematic Method to Derive Software Services and Requirements from Business Models
331
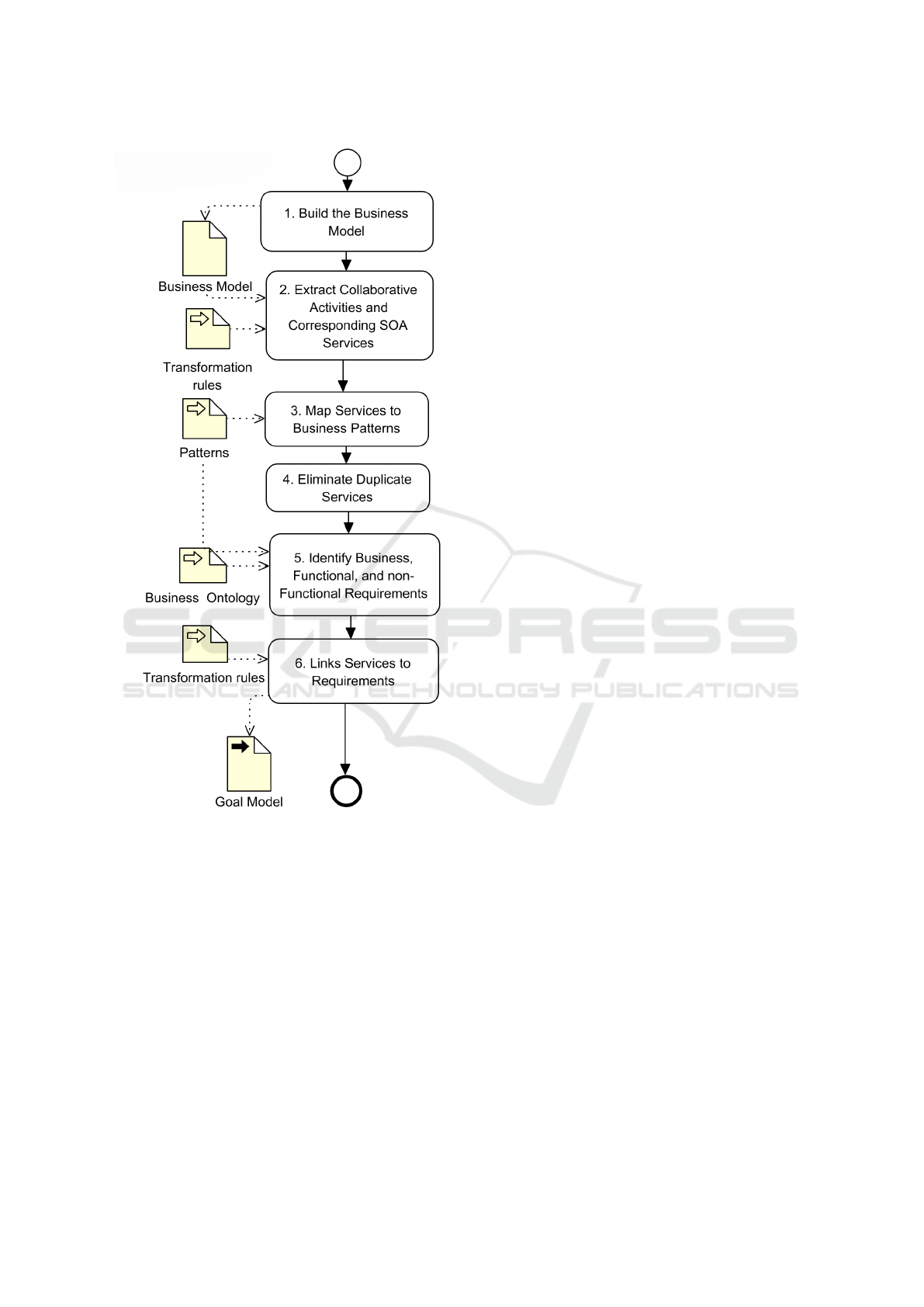
Figure 1: Proposed approach.
for QMS Software Providers. The providers prepare
and send back their quotes. HCP analyzes the quotes,
selects a QMS software provider, and sends a Pur-
chase Order (PO). The selected provider sends an in-
voice to HCP. The latter pays the invoice. The QMS
software provider grants access to the QMS tool. Fig-
ures 2 and 3 illustrate the BPMN process model and
the REA value model of the B2B collaboration, re-
spectively. Economic events in the REA model are
the events involved in the exchange of resources be-
tween the agents (partners). Business events support
the economic events in the exchange.
3.2 Extract Collaborative Activities and
Corresponding Services
We intend to identify collaborative activities by ana-
lyzing the business model as follows.
Collaborative activities are the events (Classes
with economic event and business event stereotypes)
in the value model. These events are provided or re-
ceived by economic agents who own the resources.
Each event in the value model results on a collabora-
tive activity.
In the business process model, collaborative ac-
tivities are obtained from process tasks that exchange
messages. Each set of process tasks linked with mes-
sages result in a collaborative activity. Collaborative
activities correspond to choreography tasks in BPMN.
Figure 4 illustrates the set of collaborative activi-
ties extracted from the BPMN model of the running
example (Figure 2). Each activity shows the provider
of the resource (The initiating actor) and the receiver
(shaded with a light fill). When the exchange is bi-
directional, the activity shows the callback message.
We intend to map a service to each collaborative
activity. Thus, the proposed method identifies five
services to support the collaborative activities, au-
tomating the exchange process. Table 1 shows the
collaboration activities and corresponding services.
The service provider and the consumer are deter-
mined by the resource provider and receiver in the
business model. The provider of Quote Service that
automates the ”Handle QMS Quote” collaborative ac-
tivity is ISO 9001 QMS Provider, while the consumer
is HCP.
We intend to build the set of the collaborative ac-
tivities and corresponding services from the business
models using transformation rules.
3.3 Map Services to Patterns
Business patterns are useful for i) specifying the ser-
vices and ii) designing the goal model that links the
identified SOA services to the requirements they im-
plement and the business requirements and NFR they
satisfy.
The method proposes to map each service to one
or more business pattern(s) according to the specific
business goal of the collaborative activity. The pat-
terns proposed in (Hruby, 2006) represent a source of
business patterns that the method intends to use. We
also plan to design new patterns and/or adapt existing
patterns.
The goal of the activity can be obtained by an-
notating either the business model (from step 1) or
the collaborative activity (from step 2) using the busi-
MODELSWARD 2025 - 13th International Conference on Model-Based Software and Systems Engineering
332
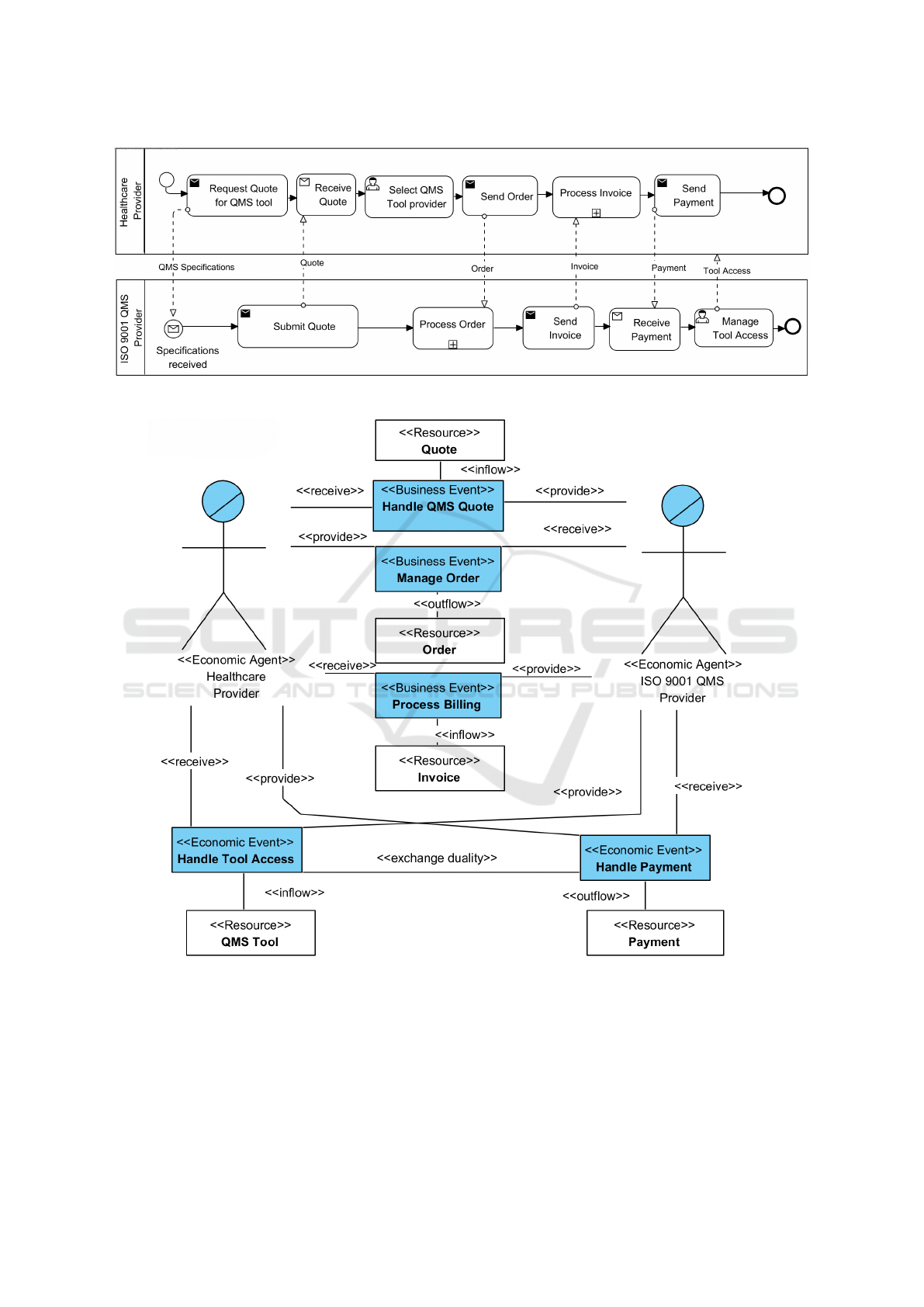
Figure 2: BPMN collaborative business process model.
Figure 3: REA business model.
ness transaction ontology (BTO) (ISO/IEC, 2015).
The latter describe the goal of the activities and the
concepts of collaborative business transactions. BTO
uses REA as an ontological framework for specify-
ing the concepts and relationships involved in busi-
ness transactions (ISO/IEC, 2015).
For example, Quote Service will be mapped to the
’contract’ business patterns from (Hruby, 2006) as its
goal is to model the promises of the exchange. In-
deed ’Quotes’ have the same structure as contracts.
It is worth noting that the contract pattern uses the
commitment pattern. Table 2 shows the identified
services and their corresponding patterns.
A Systematic Method to Derive Software Services and Requirements from Business Models
333
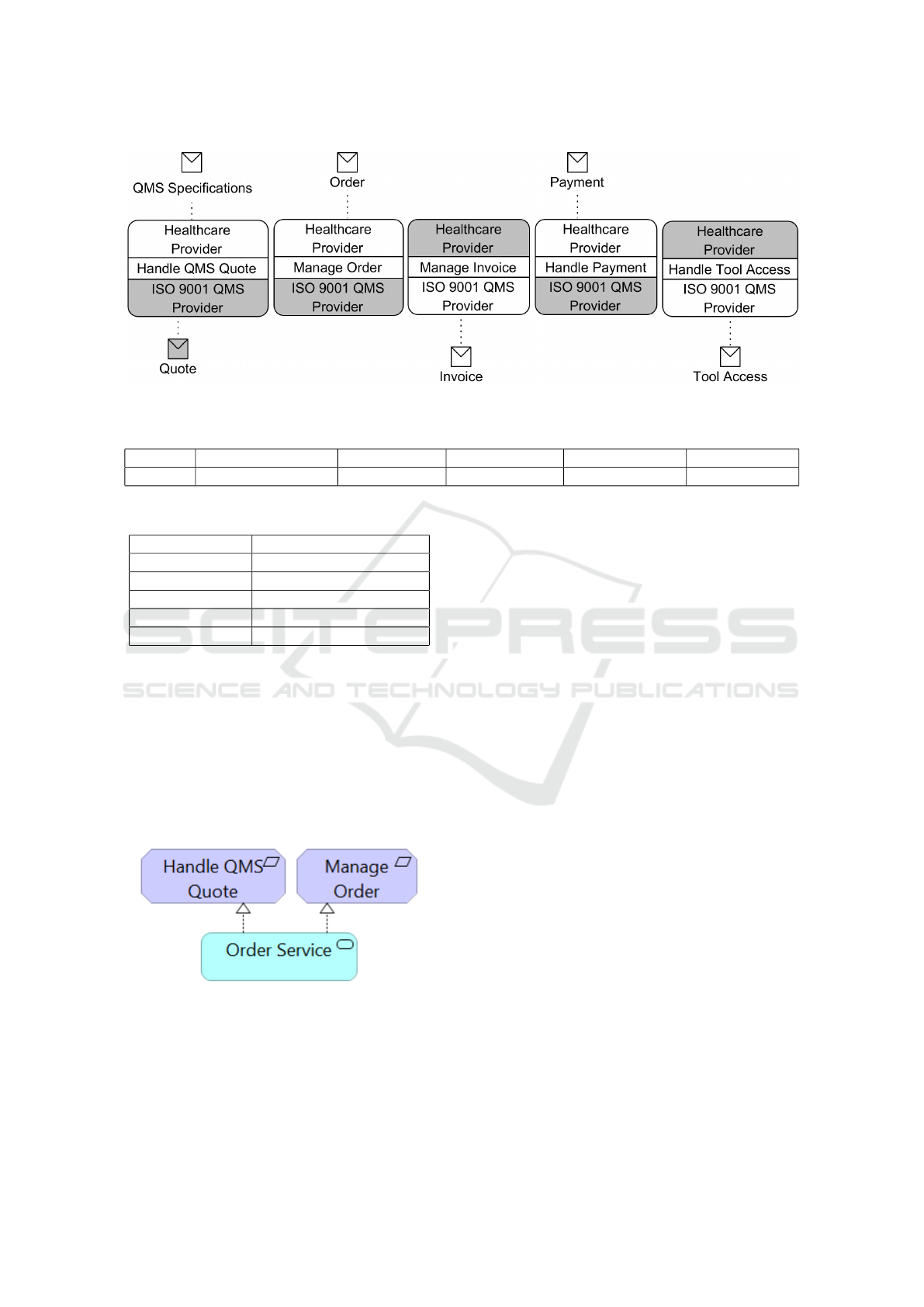
Figure 4: Collaborative activities of the running example.
Table 1: List of services.
Activity Handle QMS Quote Manage Order Manage Invoice Handle Payment Handle Access
Service Quote Service Order Service Invoice Service Payment Service Access Service
Table 2: List of services and corresponding patterns.
Service Pattern
Quote Service Contract, Commitment
Order Service Contract, Commitment
Invoice Service Claim Materialization
Payment Service Exchange, Reconciliation
Access Service Exchange
3.4 Eliminate Duplicate Services
This step of the method consolidates the set of ser-
vices by removing duplicates. Services are duplicated
if they are mapped to the same patterns. Thus, Quote
Service and Order Service designate the same service.
Indeed, ’Quotes’ have the same structure as ’Orders’
that have not been accepted by the partners (parties in
the contract) (Hruby, 2006).
Figure 5: Service-goal model for ’Order Service’.
3.5 Identify Requirements
We are interested on business requirements and so-
lutions requirements (i.e., functional requirements
and NFR). The functional requirements to be im-
plemented by a service are the collaborative ac-
tivities. For example, the Order Service imple-
ments/automates both ’Handle QMS Quote’ and
’Manage Order’ collaborative activities. Thus, ’Han-
dle QMS Quote’ and ’Manage Order’ are functional
requirements.
To identify the business requirements and NFR,
we intend to use the objectives of the correspond-
ing pattern(s) and BTO transaction phase of the col-
laborative activities. For example, the BTO transac-
tion phase of the collaborative activity ’Handle QMS
Quote’ is ’Identification Phase’. This phase aims to
’Identify the most qualified partner(s)’ and ’Obtain
competitive pricing’. The Contract and Commitment
patterns mapped to the Order Service aim to achieve
the following objectives: ’Ensure compliance with
standards’, ’Specify rules (e.g., Security, availabil-
ity)’, and ’Optimize future transactions’.
3.6 Connect Services to Requirements
In this step, we intend to generate a goal model per
service. Each model connects the service to the busi-
ness requirements, functional requirements, and NFR.
Among the goal modeling languages, we have cho-
sen the Goal-oriented Requirement Language (GRL)
(ITU-T, 2012). GRL defines two types of goals:
Hard-goals and Soft-goals.
Hard-Goals are quantifiable elements. We use
them to model functional requirements (collaborative
activities) that the services implement. Figure 5 illus-
trates the service-goal model showing that the Order
Service implements (Realization relationship from
MODELSWARD 2025 - 13th International Conference on Model-Based Software and Systems Engineering
334
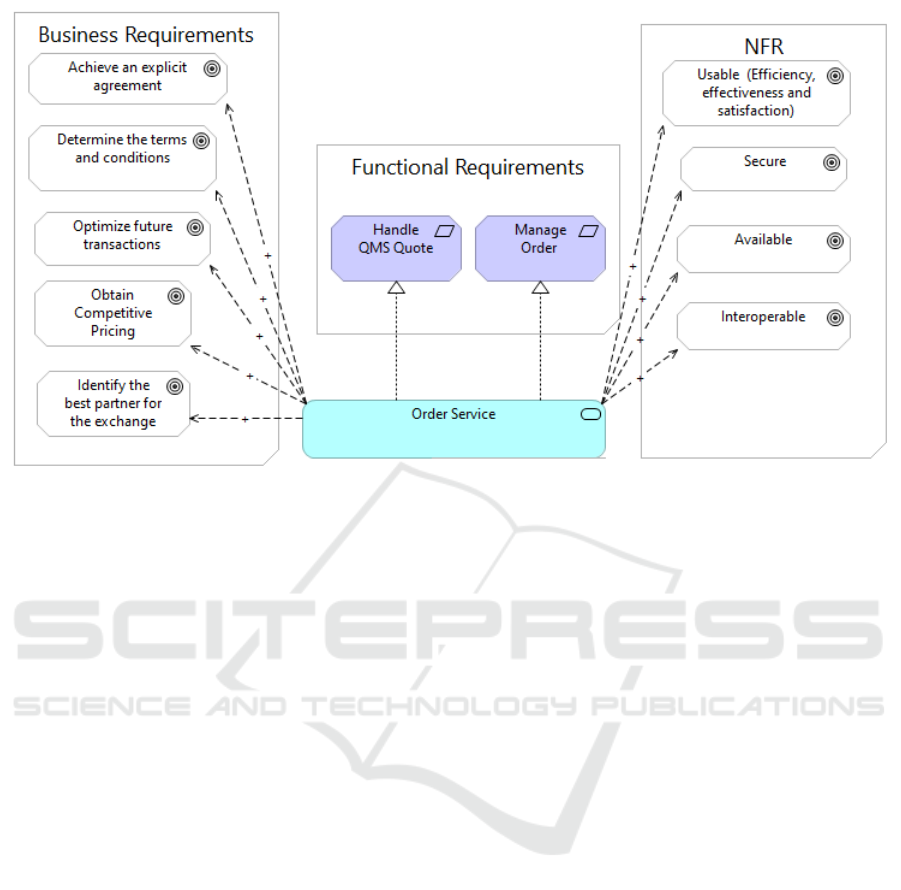
Figure 6: The obtained goal model for ’Order Service’.
Archimate) both ’Handle QMS Quote’ and ’Manage
Order’ functional requirements.
Soft-goals refers to qualitative aspects. We use
them to model the business requirements (e.g., Iden-
tify the most qualified partner(s)) and NFR (e.g., Se-
curity and usability). Business requirements and NFR
are obtained from the pattern(s) and BTO transaction
phases of the collaborative activities.
The Order Service covers two BTO transaction
phases: ’Identification’ and ’negotiation’ phases cor-
responding to ’Handle QMS Quote’ and ’Manage Or-
der’ activities, respectively. The mains goals of the
’Identification’ phase are ’Obtain Competitive Prices’
and ’Identify the best partner for the exchange’. The
main goals for creating an order (e.g., purchase order,
sales order) in the ’negotiation’ phases are ’Achieve
an explicit agreement upon the goal of the collabora-
tion’ and ’Determine the terms and conditions of the
collaboration’. We also plan to use the goals of the
patterns to identify business requirements. For exam-
ple, the goal of the commitment pattern is to optimize
future transactions.
Regarding NFRs, we intend to use the quality at-
tributes associated with the business patterns. Order
Service is mapped to the contract and commitment
patterns. This service must exchange sensible data
with the exchange-type services e.g., Payment Service
and Access Service, from the running example. Thus,
it must be ’Interoperable’ and ’Secure’. From the us-
ability point of view, the Order Service must be easy
to use by any business partner.
Figure 6 illustrates the goal model for the Order
Service. The goal model is designed with the Archi-
mate language using the GRL language concepts and
rules. ArchiMate is an enterprise architecture model-
ing language (The Open Group, 2022). To create a
goal model with Archimate, we mapped: GRL soft-
goals to Archimate Goals, GRL hard-goals to Archi-
mate Requirements, GRL tasks to Application Ser-
vices, GRL contribution links to Archimate Influence
relationships, and GRL Means-End to Archimate Re-
alization relationships.
The models shows that the service i) automates
two collaborative activities: ’Handle QMS Quote’
and ’Manage Order’ and ii) satisfies a set of business
requirements and NFR obtained from the correspond-
ing pattern(s) and BTO transaction phases of the col-
laborative activities i.e., Identification and negotiation
phases.
As for the step 2 that builds the set of the collabo-
rative activities and services, we plan to use transfor-
mation rules to design the GRL-based goal model.
It is important to note that GRL allows to com-
pute satisfaction scores that measure the effectiveness
of solutions (GRL task) through its evaluation algo-
rithms (Petelo et al., 2022). Thus, obtained GRL-
based goal model can be used to measure the ef-
fectiveness of the identified services in implement-
ing functional requirements and satisfying business
requirements, and NFR. User of the method can use
this score to compare several services (e.g., payment
services) in order to choose the one that is most ap-
propriate in terms of meeting the requirements.
A Systematic Method to Derive Software Services and Requirements from Business Models
335

4 CONCLUSIONS
SOA is a well-established architectural pattern used
by organization to develop robust software solutions
to support their business models, including business
process models, value models and goal models. SOA
paradigm allows, through its principles, the encap-
sulation, composition, re-usability, and integration of
services in order to build effective and efficient soft-
ware solutions. However, designing such software is
a challenging task that requires expertise in both soft-
ware and business (process) engineering.
On the other hand, RE plays a key role to build
SOA-based solutions. Indeed, RE ensures that the
identified and designed services are aligned with busi-
ness requirements, functional requirements, and NFR.
This paper proposed a model-driven transforma-
tional approach to i) design SOA-based software that
support organization business (process) models and
ii) build a goal model that links obtained SOA ser-
vices to the functional requirements they implement
and business requirements and NFR they satisfy. The
obtained GRL-based goal model allows organizations
to compute satisfaction scores that measure the effec-
tiveness of the identified services in automating the
business collaboration through inter-organizational
business processes and/or values exchanges.
This research represents a new step to reach our
goal to provide architecture and business analysis
practitioners, such as solutions architects and busi-
ness architects as well as business analysts with an
easy-to-use method and tools to design SOA-based
software from the specification of business models.
Future work will include empirical experimentation
to validate the approach.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research was supported by the Natural Sci-
ences and Engineering Research Council of Canada
(NSERC).
REFERENCES
Andersson, B., Johannesson, P., and Zdravkovic, J. (2009).
Aligning goals and services through goal and business
modeling. Inf Syst e-Bus Manag, 7(2):143–169.
Azevedo, L. G., Santoro, F., Bai
˜
ao, F., Diirr, T., Souza, A.,
De Souza, J. F., and Sousa, H. P. (2013). A Method for
Bridging the Gap between Business Process Models
and Services. iSys - Brazilian Journal of Information
Systems, 6:62–98.
Bianchini, D., Cappiello, C., De Antonellis, V., and Per-
nici, B. (2014). Service Identification in Interorgani-
zational Process Design. IEEE Transactions on Ser-
vices Computing, 7(2):265–278.
Blal, R., Leshob, A., Benzarti, I., Mili, H., and Hussain,
O. K. (2023). A model-driven method to design soaml
services from BPMN models: Principles, proof-of-
concept, and validation. In Bui, T. X., editor, 56th
Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences,
HICSS 2023, Maui, Hawaii, USA, January 3-6, 2023,
pages 5799–5808. ScholarSpace.
Daghaghzadeh, M. and Babamir, S. M. (2021). A model
driven and clustering method for service identification
directed by metrics. Software - Practice and Experi-
ence, 51(2):449–484.
Delgado, A., Ruiz, F., and Garc
´
ıa-Rodr
´
ıguez de Guzm
´
an, I.
(2018). A reference model-driven Architecture link-
ing Business Processes and Services. In Proceedings
of the 51st Hawaii International Conference on Sys-
tem Sciences, volume January, pages 4651–4660.
Geerts, G. L. and McCarthy, W. E. (2002). An ontological
analysis of the economic primitives of the extended-
REA enterprise information architecture. Interna-
tional Journal of Accounting Information Systems,
3(1):1–16.
Gordijn, J. and Akkermans, H. (2001). Designing and Eval-
uating E-Business Models. IEEE Intelligent Systems,
16(August):11–17.
Hruby, P. (2006). Model-Driven Design Using Business
Patterns. Springer-Verlag, Berlin/Heidelberg.
ISO/IEC (2015). Business transaction scenarios — Ac-
counting and economic ontology - ISO/IEC 15944-
4. Technical report, International Organization for
Standardization/ International Electrotechnical Com-
mission.
ITU-T (2012). ITU-T,User Requirements Notation (URN)–
Language definition.
McCarthy, W. E. (1982). The REA accounting model:
A generalized framework for accounting systems in
a shared data environment. Accounting Review,
57(3):554–578.
Nikaj, A., Weske, M., and Mendling, J. (2019). Semi-
automatic derivation of RESTful choreographies from
business process choreographies. Software and Sys-
tems Modeling, 18(2):1195–1208.
OMG (2011a). Business process model and notation
(BPMN) Version 2.0.
OMG (2011b). Unified Modeling Language (UML) Version
2.5.
Osterwalder, A. and Pigneur, Y. (2004). An ontology for e-
Business models. In Wendy L. Currie, editor, Value
Creation from E-Business Models, chapter 4, pages
65–97. Elsevier Ltd., Butterworth-Heinemann.
Petelo, P., Leshob, A., Benzarti, I., and Mili, H. (2022). To-
wards a goal-oriented method for software solutions
prioritization. In Proceedings of the 10th Interna-
tional Conference on Model-Driven Engineering and
Software Development, MODELSWARD 2022, Febru-
ary 6-8, 2022, pages 287–293. SCITEPRESS.
MODELSWARD 2025 - 13th International Conference on Model-Based Software and Systems Engineering
336

Scheer, A., Thomas, O., and Adam, O. (2005). Process
Modeling using Event-Driven Process Chains. In Du-
mas, M., van der Aalst, W. M. P., and Hofstede, A.
H. M. T., editors, Process-Aware Information Systems,
chapter 6, pages 119–145. John Wiley & Sons, Hobo-
ken, New Jersey.
The Open Group (2022). The Open Group Standard: Archi-
Mate® 3.2 Specification.
A Systematic Method to Derive Software Services and Requirements from Business Models
337
