Towards AI-Based Kinematic Data Analysis in Hand Function
Assessment: An Exploratory Approach
Eveline Prochaska
a
and Martin Sedlmayr
b
Institute for Medical Informatics and Biometry, Faculty of Medicine and University Hospital Carl Gustav Carus,
TUD Dresden University of Technology, Dresden, Germany
Keywords: Artificial Intelligence, Hand Function Assessment, Kinematic Data, Nine Hole Peg Test.
Abstract: Neurological diseases, such as multiple sclerosis (MS), significantly affect hand function, impacting patients'
independence and quality of life. The Nine Hole Peg Test (NHPT) is a standardized tool widely used to assess
upper limb motor function. This paper explores the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine
learning (ML) in the analysis of kinematic data obtained from a digitized NHPT prototype. The digital NHPT
captures detailed motion data, including timestamps for each action, movement patterns, and filling
sequences, enabling advanced analyses of motor and cognitive processes. AI-driven methods, such as
clustering, anomaly detection, and pattern recognition, provide innovative ways to evaluate fine motor skills,
detect subtle anomalies, and monitor disease progression. The combination of enhanced data collection and
AI-based analytics offers a comprehensive and objective approach to understanding hand function, supporting
individualized therapy development, and improving clinical diagnostics. This integration represents a
significant advancement in the evaluation and management of neurological diseases.
1 INTRODUCTION
Neurological diseases such as Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
are associated with upper limb dysfunction (Lamers et
al., 2014). This dysfunction, which is based on sensory
and/or motor deficits, has a negative impact on quality
of life and independence. Typical upper limb
disabilities in MS include a decline in the ability to
precisely control grip force, decreased movement
speed, muscle weakness and sensory deficits
(Lambercy et al., 2013). There is a clear correlation
between hand function and the different stages of MS
(Balaceanu et al., 2024). Since MS is a progressive
disease of the central nervous system in which the
immune system attacks the myelin sheaths of nerves,
there is an increasing impairment of motor functions,
including hand motor skills. The degree of impairment
of hand function varies depending on the severity and
progression of the disease, which is due to the different
stages of MS (Koch et al., 2023). Understanding and
quantifying the extent of upper limb disability is
critical to the care of people with MS (Lamers et al.,
2014) and other neurological diseases.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7609-1565
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9888-8460
Measuring hand function is an important part of
neurological diagnosis and rehabilitation for
neurogenerative diseases. These tests provide
valuable information about motor abilities, disease
progression and treatment effects. Hand and arm
function is commonly assessed in clinical practice
using the Nine Hole Peg Test (NPHT).
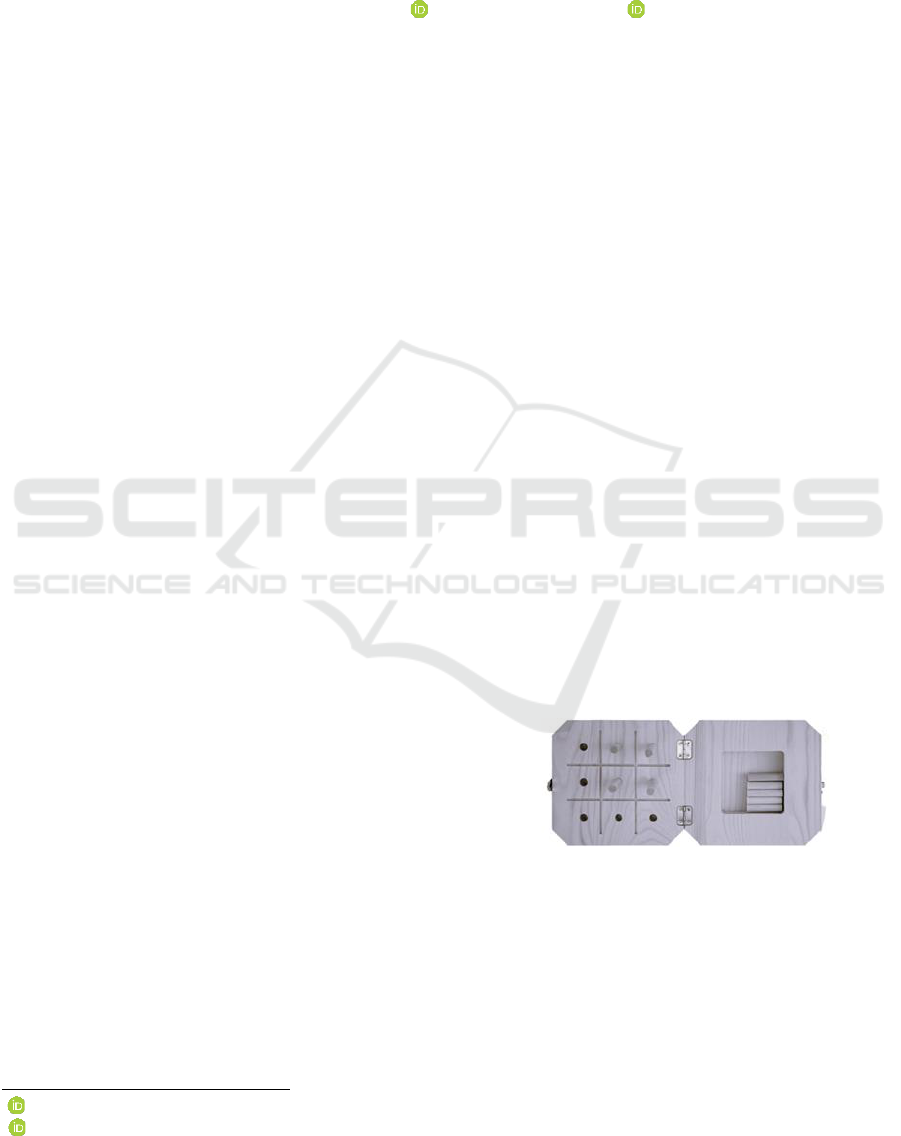
Figure 1: Commercial NHPT made of wood.
The NHPT is a standardized clinical assessment
for neurological diseases to evaluate the motor
function of the upper extremities (Feys et al., 2017).
The NHPT consists of a test board with two areas
(see Fig. 1). One side consists of a container in which
nine pegs are placed before the test begins. The
second side consists of a test board with nine holes.
Prochaska, E. and Sedlmayr, M.
Towards AI-Based Kinematic Data Analysis in Hand Function Assessment: An Exploratory Approach.
DOI: 10.5220/0013376200003911
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 18th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2025) - Volume 1, pages 205-209
ISBN: 978-989-758-731-3; ISSN: 2184-4305
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
205

The task consists of two subtasks: picking up nine
pegs individually from a container and inserting them
into a board with nine holes, and then returning the
pegs individually from the holes back to the
container. The total time required for this task is the
result. The test is simple, time-efficient and used
worldwide in a clinical context.
The integration of modern technologies into the
digital Nine Hole Peg Test can offer numerous
innovative possibilities to enable precise, objective,
and automated evaluations (Balaceanu et al., 2024;
Temporiti et al., 2022). These technologies can help
to identify subtle changes in motor function through
the additional data collected, to monitor the course of
the disease, and to evaluate the effects of therapy.
This paper focuses on the application of artificial
intelligence (AI), particularly machine learning
(ML), to analyse movement patterns in hand function
tests, using the example of multiple sclerosis (MS)
and the digital Nine Hole Peg Test (dNHPT). Unlike
other kinematic data collection methods, the dNHPT
eliminates the need for additional technical
equipment, such as cameras or portable sensors, while
still capturing comprehensive kinematic data. This
streamlined approach ensures ease of use without
compromising the accuracy or depth of the data
collected.
2 DIGITIZED ASSESSMENT
In an earlier study, we digitized and evaluated the
digital Nine Hole Peg Test (dNHPT) (Prochaska &
Ammenwerth, 2023). Figure 2 show the test board of
the dNHPT.
Figure 2: Test board of the dNHPT.
In a further development, the dNHPT includes
new, more extensive options for data collection
without compromising the standardized test
procedure. This means that the dNHPT supports the
standardized assessment of hand function, which does
not change the manageability compared to the
original NHPT and still allows the comparison of
previously collected follow-up data (reference data,
as well as previously collected data from patients
using the original NHPT.
The digitization of the NHPT offers numerous
advantages beyond the traditional administration of
the test. It expands the possibilities for data
collection, analysis, and application and improves
both the accuracy and efficiency of motor function
diagnostics.
The prototype of our digital NHPTv2 is equipped
with automatic time measurement (between the start
and stop buttons), magnets on the nine pegs, and
sensors in the nine holes. The hall sensors recognize
the magnets on the pins, which allows time stamps to
be recorded at the action level. With the help of the
sensors, a variety of kinematic data can be generated
from the execution of the dNHPTv2. The action
points start, sensor detection in each hole and stop
generate data for the following analyses:
• Movement time (total time in seconds, time
per pin in seconds)
• Speed (average and maximum speed of hand
movement between the actions points: start
event, sensor recognition in each hole and stop
event)
• Acceleration (linear acceleration and
deceleration),
• Coordination (filling patterns of the matrix
may allow conclusions to be drawn about
cognitive abilities): e.g. 1 4 7 2 3 5 6 8 9 (see
Figure 3 with matrix of the dNHPTv2)
• Symmetry of movements (left hand vs. right
hand).
Figure 3: Numbered matrix of dNHPTv2.
2.1 Additional Kinematic Data
The additional digital features of the prototype enable
the precise recording of the time course for all events
(e.g., inserting and removing pegs) and the analysis
of the filling patterns within the 3x3 matrix of the
NHPT test board. These capabilities provide detailed
insights into the motor skills and potential deficits of
patients with neurological diseases, such as multiple
sclerosis (MS).
▪ Timestamp at the action level: Each individual
action such as inserting or removing a peg, is
recorded with a precise timestamp, allowing
for high-resolution temporal analysis.
▪ Motion pattern analysis: The sequence in
which the holes are filled and emptied is
BIODEVICES 2025 - 18th International Conference on Biomedical Electronics and Devices
206
captured, offering insights into movement
strategies and the deviations.
▪ Advanced analyses:
o Detailed time and motion analyses: These
analyses detect subtle deviations in fine
motor skills that may be imperceptible to
the naked eye, enabling a more nuanced
understanding of motor impairments.
o Qualitative analysis: Movement strategies
(e.g., systematic vs. chaotic) are recorded
and analysed, providing valuable insights
into underlying cognitive processes.
o Personalized analysis: Automated
comparisons with normative values or
longitudinal data across multiple time
points allow for the documentation of
individual progress or deterioration.
▪ Visualization:
o Presentation of time and movement
profiles: Temporal development of
movements and actions can be visualized,
along with heat maps to illustrate usage
patterns within the matrix.
o Support for communication: Intuitive
visualizations facilitate the interpretation
of results, improving communication with
patients and healthcare professionals.
The digitization of the NHPT transcends
traditional time measurement, offering a more
accurate, efficient, and comprehensive assessment of
fine motor skills. This approach not only provides
deeper insights into the motor and cognitive processes
of patients but also supports the development of
individualized therapies. Furthermore, it opens new
avenues for research and diagnostics by integrating
modern technologies such as artificial intelligence
(AI), enhancing the NHPT's clinical and scientific
relevance.
2.2 Example Data Set
To illustrate the described idea, synthetic data were
generated by modelling the time courses of NHPT
tests of five individuals. The assumptions for the
sample data were total test times and standard
deviations according to normative values (Grice et al.
2003) of healthy individuals and a uniform
distribution of the data points with few fluctuations
between the data points (i.e., the absence of
impairment of hand function). The data sets were
created and visualized using the Python programming
language and the PyCharm 2024.3 software.
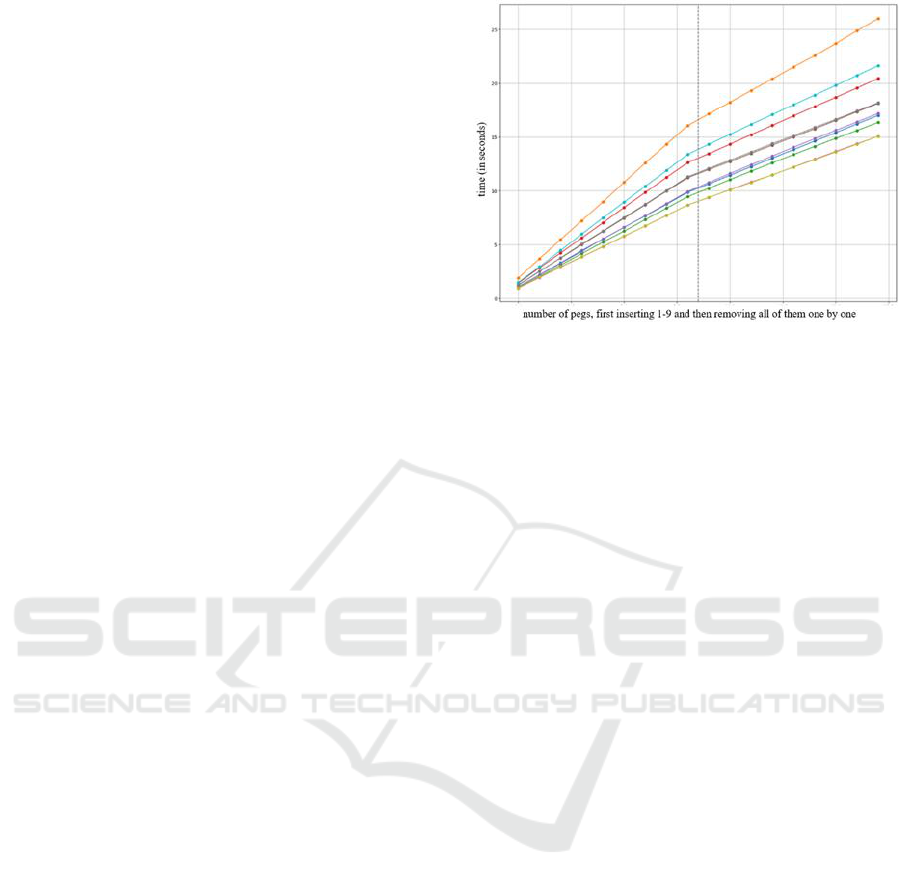
Figure 4: Datasets of five NHPT test runs.
Figure 4 shows the time courses of five tests with
the dNHPTv2. Each data point represents the
insertion of a peg, or after nine peg points, the
removal a peg from the test board. The dashed line
indicates the end of the input phase and the beginning
of the removal phase.
When measuring the hand function with the
dNHPT, a number of data points are collected for
each person tested, in addition to the total time
required for the task. These data points are stored
digitally for further analysis.
2.3 Analysis Using AI
Hand function in MS patients is influenced by a
variety of factors, including neurological damage to
the central nervous system, muscle weakness,
spasticity, tremor, ataxia, fatigue, sensory
disturbances, emotional factors, medications and
their side effects. These symptoms can vary
depending on the stage of the disease and the location
of the lesion, and can significantly affect the ability to
perform activities of daily living. Treatment and
management of these symptoms are critical to
improving hand function and quality of life for
patients.
The kinematic analysis of dNHPTv2 results can
be significantly enhanced through ML, offering
innovative opportunities for precise, objective, and
automated evaluations. The following key areas
highlight the potential of ML in optimizing NHPT
data analysis.
2.3.1 Analysis of Time Series
▪ Clustering: Grouping patients based on
movement profiles to identify common
patterns or subgroups.
Towards AI-Based Kinematic Data Analysis in Hand Function Assessment: An Exploratory Approach
207

▪ Anomaly Detection: Identifying tests with
unusual progressions, such as inconsistent
movements or extended pauses, using time
series analysis.
▪ Applications:
o Speed analyses, including time per peg
insertion/removal and acceleration
profiles.
o Examination of consistency and variability
in movement sequences.
o Detection of anomalies, such as irregular
patterns or interruptions.
2.3.2 Pattern Recognition of Sequences
Advanced sequence analysis techniques, such as
hidden Markov models (HMMs) for modeling
common strategies and pattern mining for identifying
frequent or rare behaviours.
Applications:
▪ Analysis of filling and emptying sequences to
identify systematic or chaotic behaviours.
▪ Comparison of filling strategies with clinical
factors, such as hand dominance or
neurological impairments.
▪ Benchmarking results against normative values
(healthy individuals or patients with specific
conditions) or longitudinal follow-up data.
2.3.3 Overall Performance and Cognitive
Aspects
Leveraging feature engineering, regression, and
classification for comprehensive evaluations.
Applications:
▪ Integration of time and sequence data to assess
overall efficiency and precision.
▪ Comparison of filling and removal strategies to
detect performance discrepancies.
▪ Recognition of thought patterns that may guide
sequencing choices, shedding light on
underlying cognitive processes.4. Group and
progression analysis: through time series
analysis or clustering,
2.3.4 Group and Progression Analysis
Time series analysis and clustering to explore broader
trends and disease progression.
Applications:
▪ Comparative analysis between patient groups
(e.g., MS severity levels).
▪ Classification of disease severity based on
movement profiles.
▪ Longitudinal tracking to observe changes
across multiple tests, influenced by therapy,
medication, or disease progression.
2.3.5 Visualization and Reporting
Advanced visualization tools enable intuitive
interpretation of results.
Applications:
▪ Heatmaps to visualize filling or emptying
sequences and their frequencies.
▪ Time diagrams to illustrate the temporal
sequence of actions.
▪ Sequence diagrams, such as arrow plots, for
clear representation of the filling order.
With the extended data provided by the new
NHPT prototype, AI-driven analyses can deliver
comprehensive insights across three critical domains:
motor skills (e.g., timing and efficiency), cognitive
processes (e.g., strategies and thought patterns), and
clinical diagnostics and therapy monitoring. These
capabilities not only advance the precision and depth
of NHPT evaluations but also support the
development of personalized therapeutic strategies
and facilitate long-term patient monitoring.
3 CONCLUSIONS
The digitization of the Nine Hole Peg Test (NHPT)
represents a substantial advancement in the
assessment of hand function for patients with
neurological diseases such as multiple sclerosis (MS).
By capturing detailed kinematic data, the digital
NHPT (dNHPT) facilitates a more comprehensive
understanding of both motor and cognitive processes.
Unlike other kinematic data collection methods, the
dNHPT eliminates the need for additional technical
equipment, such as cameras or portable sensors, thus
maintaining simplicity and ease of use while ensuring
robust data acquisition.
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and
machine learning (ML) into the analytical pipeline
enhances the precision, objectivity, and efficiency of
evaluations. Advanced techniques, including time
series analysis, pattern recognition, and anomaly
detection, enable the identification of subtle motor
deficits that might otherwise go unnoticed, while also
providing novel insights into disease progression and
therapeutic outcomes. While traditional time series
analyses can yield useful indices for tracking the
progression of MS, AI offers distinct advantages: it
recognizes complex patterns, automates personalized
BIODEVICES 2025 - 18th International Conference on Biomedical Electronics and Devices
208

analyses, and integrates data with normative values
and longitudinal trajectories. Moreover, AI-driven
tools enable advanced visualizations such as heat
maps, increase analytical efficiency, and open new
avenues for research and diagnostics in the context of
neurological diseases.
This approach not only reinforces the clinical
relevance of the NHPT but also supports the
development of personalized therapeutic strategies
and facilitates long-term patient monitoring.
Ultimately, the digital NHPT bridges the gap between
conventional clinical assessments and state-of-the-
art, technology-driven diagnostics, thereby advancing
both clinical practice and research in neurological
disease management.
4 OUTLOOK
Looking ahead, the integration of artificial
intelligence (AI) with the digital NHPT offers
transformative opportunities for research,
diagnostics, and therapeutic applications. Future
developments may include real-time AI models
capable of providing immediate feedback during
testing, advanced visualizations such as interactive
dashboards for enhanced data interpretation, and
seamless integration with telemedicine platforms to
enable remote assessments. Expanding normative
databases through larger-scale studies is essential to
further refine diagnostic thresholds and improve the
accuracy of disease classification.
To support these advancements, additional
studies are planned to collect comprehensive
reference datasets in the form of time series. These
datasets will serve as a robust foundation for training
AI algorithms, facilitating the identification of
movement patterns, detection of subtle motor
deviations, and precise classification of disease states.
As these algorithms evolve, their outputs are expected
to significantly enhance the diagnostic and
monitoring capabilities of the digital NHPT,
equipping clinicians with actionable insights for
personalized care.
Furthermore, integrating NHPT data with
complementary sources, such as wearable sensors or
imaging modalities, could yield a holistic perspective
on patient motor and cognitive health. These
advancements will not only solidify the NHPT’s role
in clinical practice but also advance the broader
understanding of neurological diseases, ultimately
contributing to improved patient outcomes and
quality of life.
REFERENCES
Balaceanu, A., Puertas, I., Alonso de Leciñana, M., Tallón,
A., Gutiérrez-Tenorio, Vargas, P., Torres, G., &
Gutiérrez. (2024). Automatic evaluation of the Nine-
Hole Peg Test in multiple sclerosis patients using
machine learning models. Biomed Sign Proc and
Control, 92, 106128.
https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BSPC.2024.106128
Grice, K. O., Vogel, K. A., Le, V., Mitchell, A., Muniz, S.
& Vollmer, M. A. (2003) Adult Norms for a
commercially available Nine Hole Peg Test for Finger
Dexterity. Am J Occup Ther, 57(5), 570-573.
https://doi.org/10.5014/ AJOT.57.5.570
Feys, P., Lamers, I., Francis, G., Benedict, R., Phillips, G.,
Larocca, N., Hudson, L. D., & Rudick, R. (2017). The
Nine-Hole Peg Test as a manual dexterity performance
measure for multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler, 23(5), 711–
720. https://doi.org/10.1177/1352458517690824
Koch, M. W., Repovic, P., Mostert, J., Bowen, J. D.,
Comtois, J., Strijbis, E., Uitdehaag, B., & Cutter, G.
(2023). The nine hole peg test as an outcome measure
in progressive MS trials. Multiple Sclerosis and
Related Disorders, 69(November 2022), 104433.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msard.2022.104433
Lambercy, O., Fluet, M. C., Lamers, I., Kerkhofs, L., Feys,
P., & Gassert, R. (2013). Assessment of upper limb
motor function with MS using the virtual Peg insertion
test: a pilot study. Int Conf Rehabil Robot, 2013.
https://doi.org/10.1109/ICORR.2013.6650494
Lamers, I., Kelchtermans, S., Baert, I., & Feys, P. (2014).
Upper Limb Assessment in Multiple Sclerosis: A
Systematic Review of Outcome Measures and their
Psychometric Properties. Arch Phys Med Rehabil,
95(6), 1184–1200.
https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APMR.2014.02.023
Prochaska, E., & Ammenwerth, E. (2023). Validity and
Reliability of a new developed digital version of Nine
Hole Peg Test. IEEE Access, 11, 97169–97176.
https://doi.org/10.1109/ ACCESS.2023.3311270
Temporiti, F., Mandaresu, S., Calcagno, A., Coelli, S.,
Bianchi, A. M., Gatti, R., & Galli, M. (2022).
Kinematic evaluation and reliability assessment of the
Nine Hole Peg Test for manual dexterity. J Hand
Therapy, 36(3), 560–567. https://doi.org/10.1016/
j.jht.2022.01.007
Towards AI-Based Kinematic Data Analysis in Hand Function Assessment: An Exploratory Approach
209
