
Use of Radiomics in Low Dose Chest CT: A Proposal for a Phantom
Multi-Centric Study
Maria Irene Tenerani
1,2 a
, Silvia Arezzini
2
, Antonino Formuso
2
, Francesca Lizzi
2 b
,
Enrico Mazzoni
2
, Stefania Pallotta
3,4,5
, Alessandra Retico
2 c
, Camilla Scapicchio
2 d
,
Cinzia Talamonti
3,4,5
and Maria Evelina Fantacci
1,2 e
1
Department of Physics, University of Pisa, Pisa, Italy
2
National Institute for Nuclear Physics, Pisa, Italy
3
University of Florence, Department of Experimental and Clinical Biomedical Sciences ”Mario Serio”, Florence, Italy
4
Medical Physics Unit, AOU Careggi, Florence, Italy
5
National Institute for Nuclear Physics, Florence, Italy
Keywords:
Lung Cancer Screening, Low-Dose Computed Tomography, Computed Tomography Acquisition Protocol,
Phantom, Multi-Centric Study, Radiomics, Medical Data Sharing Platform.
Abstract:
Radiomics is a quantitative biomedical image analysis tool involving the mathematical extraction of image
features that can be used, particularly in oncology, to build predictive models based on artificial intelligence for
diagnosis and treatment outcome prediction. In Lung cancer screening via Low-Dose Computed Tomography
(LDCT), radiomics-based models could increase lung nodules detectability simplifying the implementation
of large-scale screening. However, their transposition into clinical practice is slowed by the instability that
radiomic feature values show in changes in CT image acquisition and reconstruction parameters. To build
more robust models, it is essential to conduct multi-centric radiomic studies leveraging the use of various types
of phantoms to overcome the challenges associated with patient data complexity. However, many difficulties
may arise related to both the image acquisition and reconstruction process and the extraction and analysis of
radiomic features. In this paper, from the results of a pilot study conducted with two phantoms, guidelines for
a multi-centric radiomic study on phantoms LDCTs are proposed, focusing on crucial aspects such as phantom
positioning, image acquisition and reconstruction protocol, and radiomic feature extraction pipeline. Finally, a
XNAT-based platform for data sharing and management, image quality control implementation and radiomic
feature extraction automation is proposed.
1 INTRODUCTION
Radiomics is a quantitative analysis tool based on
the assumption that biomedical images contain more
information than can be directly perceived by hu-
man vision. These additional data are obtained
through mathematical extraction of high-dimensional
radiomic features by considering images voxel by
voxel. Radiomics has enormous potential in devel-
oping precision medicine, particularly in cancer de-
tection, diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment evalua-
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0000-6230-7858
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0900-0421
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5135-4472
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5984-0408
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2130-4372
tion. The development of radiomics-based models,
for example in lung disease, could lead to improve-
ments in clinical workflow in diagnosis, prognosis,
management, follow-up, and monitoring of treatment
response. Indeed, numerous radiomics-based mod-
els and combined radiomics and Deep Learning (DL)
models have been developed for the detection and
classification of pulmonary nodules and for predict-
ing or monitoring treatment response (Louis et al.,
2024; Frix et al., 2021). Their use in clinical decision
support systems could simplify the identification of
nodules, mitigate the problems associated with small
lesions, ease the work of radiologists resulting in im-
proved accuracy of diagnosis, and thus facilitate the
implementation of large-scale lung cancer screening
programs on the at-risk population while simultane-
Tenerani, M. I., Arezzini, S., Formuso, A., Lizzi, F., Mazzoni, E., Pallotta, S., Retico, A., Scapicchio, C., Talamonti, C. and Fantacci, M. E.
Use of Radiomics in Low Dose Chest CT: A Proposal for a Phantom Multi-Centric Study.
DOI: 10.5220/0013377300003911
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 18th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2025) - Volume 1, pages 403-412
ISBN: 978-989-758-731-3; ISSN: 2184-4305
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
403

ously decreasing their costs (Saied et al., 2023). How-
ever, the translation of radiomics-based models to
clinical practice is complicated by the lack of repeata-
bility and robustness of Computed Tomography (CT)
derived radiomic features due to their dependence
on image acquisition and reconstruction parameters,
such as tube current [mA], tube voltage [kVp], expo-
sure [mAs], slice thickness, and voxel size (Shafiq-ul
Hassan et al., 2017; Traverso et al., 2018). Moreover,
the data analysis is strongly affected by the variability
in scanner models, specific clinical acquisition proto-
cols with different acquisition parameters, and recon-
struction settings that are often unavoidable in current
clinical practice. Large multi-centric studies are es-
sential to build more robust models. However, this
type of study is challenging as the collection of patient
data from different centers for centralized analysis is
complex, and sometimes impossible, for dosimetric,
legal, ethical, administrative, and technical reasons.
One way to overcome these difficulties is to employ
CT phantoms which, although not capable of fully
representing the extreme complexity of the human
anatomy, allow the extraction of plausible CT-derived
radiomic features and conduct repeatability studies
without having to consider the radiation dose deliv-
ered (Mackin et al., 2015). A preliminary study al-
ready conducted by acquiring CT images of two phan-
toms with two different scanners, different dose val-
ues, and numerous iterative reconstruction blending
levels, to study the repeatability and robustness of CT
radiomic features, revealed some acquisition-related
difficulties due to the variability in scanners, acqui-
sition protocols, and reconstruction settings (Scapic-
chio et al., 2024c; Scapicchio et al., 2024b; Tenerani
et al., 2024). Some of these difficulties were solved by
repeating the acquisitions, which, however, resulted
in the need for additional machine time, which was
already limited for CT scanners used daily in clinical
practice. Other difficulties, however, were not fully
resolved, leading to the exclusion of some data from
the study or to the need to resort to post-processing
techniques, which were also time-consuming. To im-
prove the efficiency of data collection and the qual-
ity of the dataset, it is important to define a standard
CT image acquisition and reconstruction protocol and
a well-defined radiomic feature extraction pipeline.
Therefore, the aim of this paper is to outline the steps
of acquisition and reconstruction of phantom CT im-
ages, starting from the experience gained at the San
Luca hospital in Lucca, Italy, during the preliminary
study, and to define a standard procedure for the ex-
traction and analysis of radiomic features.
2 PHANTOMS
The phantoms considered for the multi-centric study
are a commercial phantom and a custom phantom, de-
veloped specifically to conduct radiomic studies, and
already employed in the preliminary study.
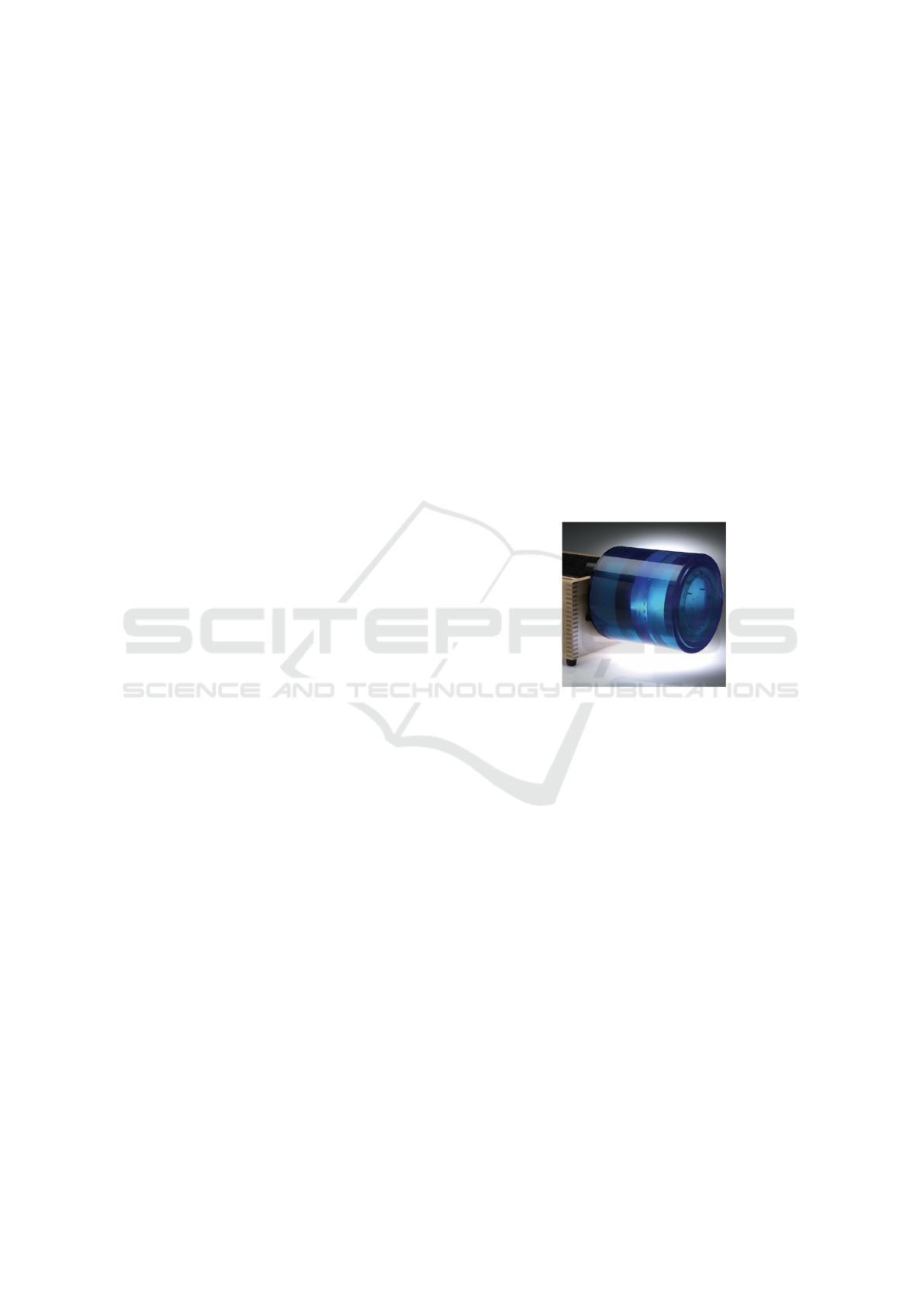
The Catphan-500® (The Phantom Laboratory,
NY, USA) (Mail, 2013) is a commercially available
phantom, commonly employed in clinical procedures
for quality control. It has a cylindrical shape with a di-
ameter of 20 cm and consists of four modules to study
several image properties at different contrast levels,
as can be seen in Fig. 1. Specifically, the CTP404
module, used in the preliminary radiomic study, in-
cludes seven cylindrical inserts of 15-mm diameter
and 25-mm thickness, made of different materials, i.e.
Acrylic, Polystyrene, LDPE, PMP, Air, Teflon and
Delrin and a vial of the same dimension which can
be filled with water, all embedded in a uniform back-
ground.
Figure 1: Illustration of the Catphan-500® phantom
model (Mail, 2013).
The custom phantom has an irregular elliptical
shape with axes measuring approximately 29 cm and
19 cm and the lower edge is cut to allow correct po-
sitioning within the CT system, also aided by the two
black markings on the phantom. Inside the phantom,
twenty five inserts are present embedded in a layer
of epoxy resin and made of different materials, tex-
tures, shapes and sizes in order to produce a wide
range of radiomic features values capable of mimick-
ing those of clinical CT images (Pallotta et al., 2020).
Six inserts are made of homogeneous materials such
as lung tissue, bone tissue and water and have a cylin-
drical or cubic shape. The three cubic inserts have
a side of approximately 9 mm, one cylinder has a
diameter of approximately 15 mm and height of 10
mm while the other two have a diameter and height
of approximately 9 mm. The other nineteen inserts,
also with cylindrical or cubic shape and with differ-
ent filling percentages, were fabricated employing a
3D printer using PLA, FLEX, and PETG with paral-
lel, triesacube, triangle, 1/4 cube and gyroid patterns.
BIOIMAGING 2025 - 12th International Conference on Bioimaging
404

The cubic inserts have a side of approximately 17 mm
while the cylindrical ones have a diameter and height
of approximately 17 mm. The exact structure of the
phantom is shown in Figure 2 and 3.
(a) (b)
Figure 2: Pictures of the custom phantom in the frontal (a)
and transverse (b) planes.
Figure 3: Custom phantom structure with the different in-
serts divided by material, filling percentages and texture
types.
3 PRELIMINARY RADIOMIC
STUDY
3.1 Acquisition Procedure
In the preliminary baseline study, two different com-
mercial CT scanners, available at the San Luca hos-
pital, Lucca, Italy, were employed to acquire the CT
images of the two phantoms: the Revolution Evo 64
Slice scanner (GE Healthcare) and the Aquilon CX
128 Slice CT scanner (Toshiba). An initial dataset
of the Catphan® phantom was acquired by starting
with the institutional clinical protocol for diagnostic
tasks in chest imaging and exploring four Computed
Tomography Dose Index (CDTI
vol
) values (IAEA,
2012), ranging from ultra-low to high dose, and four
iterative reconstruction blending levels, for a total
of thirty-two different protocols, each repeated three
times, and ninety-six CT scans. The second custom
phantom dataset consisted of thirty CT images ac-
quired with ten protocols considering two CT scan-
ners, three CDTI
vol
values (from ultra-low-dose to
standard dose), four iterative blending levels, and re-
peating the acquisition three times for each set of pa-
rameters. The acquisition parameters used to produce
the two datasets are described in the Table 1 and Ta-
ble 2.
3.2 Features Repeatability and
Robustness
Eighty-six first- and second-order features were ex-
tracted from each of the homogeneous inserts present
in the CTP404 Catphan® phantom module and from
each of the nineteen textured inserts present in the
custom phantom directly from the original images,
that is without applying any filter. In particular,
radiomic features belonging to first-order statistics,
Gray Level Co-occurrence Matrix (GLCM), Gray
Level Size Zone Matrix (GLSZM), Gray Level Run
Length Matrix (GLRLM) and Gray Level Depen-
dence Matrix (GLDM) classes were calculated using
Pyradiomics. PyRadiomics is a flexible open-source
Python package that enables the processing and the
extraction of a large number of radiomic features
from both 2D and 3D medical images in compliance
with feature definitions as described by the Imaging
Biomarker Standardization Initiative (IBSI) (Van Gri-
ethuysen et al., 2017; Zwanenburg et al., ).
The statistical analysis of the radiomic features
extracted from the Catphan® dataset showed that im-
age quality, assessed by calculating the Detectability
Index (Samei et al., 2019) on the polystyrene insert,
influences the robustness of the radiomic features,
quantified using the two-way mixed effect model with
average raters type and absolute agreement Intraclass
Correlation Coefficient (ICC) (McGraw and Wong,
1996; Koo and Li, 2016). Specifically, a greater per-
centage of radiomic features extracted from the var-
ious inserts are found to be robust when considering
images, and thus protocols, that have similar image
quality than when considering images with widely
varying image quality; In fact, it was already ver-
ified that, when considering protocols with similar
image quality, about 80% of the features extracted
from the polystyrene insert were found to be ro-
bust, where robust features are those that have an
ICC≥75% (Scapicchio et al., 2024c).
This behavior was also confirmed for the textured
inserts present within the custom phantom, where
about 80% robust radiomic features were obtained
for the more homogeneous inserts, while, for the
more defined textured inserts, the percentage of ra-
diomic features considered robust dropped signifi-
cantly, down to approximately 20% (Tenerani et al.,
2024). The percentages of robust features for the
Use of Radiomics in Low Dose Chest CT: A Proposal for a Phantom Multi-Centric Study
405
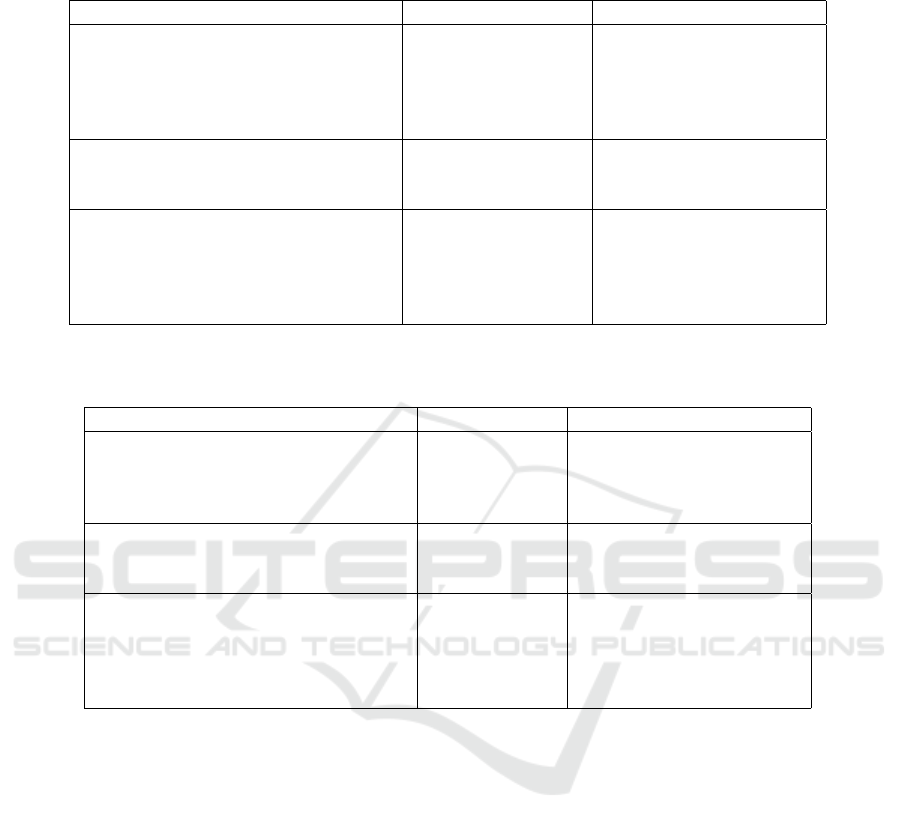
Table 1: Acquisition and reconstruction parameters of the thirty-two protocols used to acquire the Catphan-500® CT images
with the two CT scanners.
Revolution GE Aquilon Toshiba
CTDI
vol
[mGy] (Tube current [mA])
High 13.52 (160) 16.50 (300)
Standard 6.76 (80) 8.30 (150)
Reduced 4.06 (50) 5.00 (90)
Low 2.03 (25) 2.49 (45)
Data acquisition
Tube potential (kVp) 120 120
Pitch 0.984 0.938
Image Reconstruction
Pixel Spacing (mm) 0.406 0.427
Slice thickness (mm) 1.25 1.00
Kernel LUNG FC56
Iterative level 0%, 10%, 40%, 70% 0%, mild, standard, strong
Table 2: Acquisition and reconstruction parameters of the ten protocols used to acquire the custom phantom CT images with
the two CT scanners. The pure Filtered-Back-Projection reconstruction was not applied to the Toshiba low dose acquisitions.
Revolution GE Aquilon Toshiba
CTDI
vol
[mGy] (Tube current [mA])
Standard 7.1 (80) /
Reduced / 4.4 (40)
Low / 2.2 (20)
Data acquisition
Tube potential (kVp) 120 120
Pitch 0.984 0.938
Image Reconstruction
Pixel Spacing (mm) 0.703 0.781
Slice thickness (mm) 1.25 1.00
Kernel LUNG FC56
Iterative level 0%, 10%, 70% 0%*, mild, standard, strong
Catphan® phantom polystyrene insert and the custom
phantom inserts are shown in Table 3. Repeatability
tests conducted with the custom phantom also showed
how the positioning of the phantom and the radiomic
features extraction pipeline, particularly the definition
of the Regions Of Interest (ROIs) from which fea-
tures are extracted, affects their value and thus their
repeatability. Indeed, shifts of a few voxels in the def-
inition of the ROIs (about two in each direction) led
to a percentage of non-repeatable features up to about
25% for some inserts while changes in the volume of
the ROIs caused a percentage of non-repeatable fea-
tures ranging from about 30% to 50%, depending on
the insert considered.
4 DISCUSSION OF
PRELIMINARY WORK AND
COMPARISON WITH
LITERATURE
Although there are some limitations in the prelimi-
nary study, such as the employment of phantoms only,
the limited number of protocols used for the cus-
tomized phantom acquisitions, and the difficulties re-
lated to positioning the phantoms within the gantry,
the results described highlight the need to establish
a standard protocol for image acquisition and recon-
struction to collect data from the various clinical cen-
ters in the context of a multi-centric study. It is there-
fore critical to identify the physical acquisition pa-
rameters such as tube current, tube potential, pitch,
slice thickness and pixel spacing and the ideal itera-
tive reconstruction blending level to reduce the radi-
BIOIMAGING 2025 - 12th International Conference on Bioimaging
406

Table 3: Percentage of robust features extracted from the polystyrene insert of the Catphan® phantom (Scapicchio et al.,
2024c) and on a more homogeneous insert and a more defined textured insert of the custom phantom (Tenerani et al., 2024).
Insert % of robust features
Polystyrene (Catphan®) ∼ 80%
More homogeneous insert (custom phantom) ∼ 80%
More defined textured insert (custom phantom) ∼ 20%
ation dose delivered as much as possible while con-
sidering the different behavior of various commercial
iterative algorithms in suppressing noise and dealing
with interfaces (Samei et al., 2019).
In order to develop and validate a radiomic model
that can be implemented within lung cancer screening
programs, it is essential to use CT acquisition proto-
cols that are as consistent as possible with those com-
monly used in clinical practice. Although several CT
scanners and low-dose CT acquisition protocols have
been used in large lung cancer screening studies, such
as NLST, NELSON, UKLS, and ITALUNG (Team,
2011; Zhao et al., 2011; Baldwin et al., 2011; Pegna
et al., 2009), in which specific reconstruction values
are often not clearly reported (Vonder et al., 2021),
currently more attention is being paid to the choice
of protocols. Indeed, the American College of Ra-
diology (ACR), the Society of Thoracic Radiology
(STR) and the European Society of Thoracic Imag-
ing (ESTI) have provided several guidelines for the
choice of CT acquisition and reconstruction protocols
in lung cancer screening (American College of Ra-
diology (ACR), 2023; European Society of Thoracic
Imaging (ESTI), 2019). In addition, the American
Association of Physicists in Medicine (AAPM) de-
veloped a set of detailed acquisition and reconstruc-
tion protocols of over 30 CT systems of six major
vendors for lung cancer screening purposes (Ameri-
can Association of Physicists in Medicine (AAPM),
2023). Another aspect to consider when planning CT
acquisitions for lung cancer screening is image qual-
ity, which directly affects the detectability of lung
nodules that can be very small, on the order of a few
millimeters, and difficult to detect within the lung tis-
sue (Thakur et al., 2020). The Quantitative Imag-
ing Biomarker Alliance (QIBA) provides six stan-
dard markers for image quality assurance, i.e., mini-
mum requirements for image quality defined by reso-
lution, edge enhancement, HU deviation, voxel noise,
and spatial image distortion (Quantitative Imaging
Biomarkers Alliance (QIBA), 2018). To investigate
the adherence of the protocols suggested by AAPM
to the quality standards proposed by QIBA, in the
study by Iball et al. the use of two different recon-
struction kernels, a sharper kernel as suggested by the
specific AAPM protocol, and a smoother kernel, is
investigated. The authors evaluated the six metrics
suggested by the QIBA guidelines for image qual-
ity using the CTLX1 phantom and found that when
imaging the phantom using the AAPM scan proto-
col with the suggested sharp kernel, the image qual-
ity failed the QIBA specification for two of the six
metrics while, using a smoother kernel, all six image
quality specifications were met (Iball et al., 2021).
These results highlight the importance of the choice
of the reconstruction kernel in defining the acquisi-
tion protocol with regard to both the detectability of
lung nodules and the robustness of radiomic features.
To select a defined CT protocol, it is possible
to start from the guidelines, particularly the individ-
ual CT scanner-specific parameters proposed in the
AAPM guide, then explore also a reduced dose value
and reconstruct the image with different kernels (soft
and sharp) and at least two different iterative recon-
struction blending levels, similar to what was done
for the Reduced and Low Dose protocols in the pre-
liminary study phantom datasets.
Given the limited machine time usually available
to perform these acquisitions when using CT scanners
employed in daily clinical practice, it is of paramount
importance to establish guidelines on the placement
of the phantom within the scanner to make the image
acquisition process repeatable and efficient. The im-
portance of the phantom positioning step inside the
gantry is accentuated by the different shape of the
patient couch proper to the CT scanners; in fact, in
some scanners, typically for diagnostic use, the couch
is concave while for others, typically used for center-
ing in radiotherapy, the bed is flat. Once the scanning
is done, the quality of image acquisition and recon-
struction should be checked quickly so that it would
be possible, in case of discrepancies, to reconstruct or
reacquire the CT scans immediately.
Another essential aspect to consider, in view of
the expansion of this study to more centers, concerns
the identification of a defined pipeline for feature ex-
traction that minimizes ROIs mismatch problems; in
fact, a further weakness of the preliminary study was
precisely related to the difficulties of positioning the
extraction ROIs within the inserts due to small and
sometimes difficult-to-avoid differences in the posi-
tioning of the phantoms in different scanners. This
could be accomplished by exploring different feature
extraction parameters, such as bin width (Larue et al.,
Use of Radiomics in Low Dose Chest CT: A Proposal for a Phantom Multi-Centric Study
407

2017), and by developing an automatic image coregis-
tration and ROIs placement system that can be easily
replicated on images from different sites. This is es-
pecially important considering that images acquired
on different scanners will have different pixel spac-
ing and slice thickness values, and it may therefore be
necessary to resample the images to isotropic voxels
using interpolations. This aspect is even more pro-
nounced when considering scans of patients where
segmentation of, for example, lung nodules is often
critical. Evaluation of the repeatability of radiomic
features with respect to changes in extraction ROIs,
even if in simplified structures such as those found
within phantoms, could provide insights regarding
how to deal with different segmentations in real pa-
tient scans.
On the basis of the elaborated considerations, we
propose as future work a multi-centric phantom study
for which we suggest some guidelines regarding the
positioning of the phantoms within the CT scanner
gantry, the implementation of quality control checks
on the acquired images, the extraction and processing
pipeline of radiomic features, and we suggest the use
of a dedicated data storage and sharing XNAT-based
platform.
5 GUIDELINES FOR EFFICIENT
DATA COLLECTION
5.1 Phantom Positioning Step
The first key step in conducting a multicenter study
is to ensure the proper positioning of the phantom
within the gantry of the CT scanner. For the com-
mercial Catphan-500® phantom, specific guidelines
for its positioning and alignment can be found within
the manual (Mail, 2013) and an example is shown
in Fig. 4. In contrast, for the custom phantom, no
guidelines are available yet. Here, a procedure is
proposed for the correct and reproducible placement
of the custom phantom that could be easily replicated
with the different CT scanners. In CT scanners
equipped with a flat couch, the custom phantom
can simply be positioned with its base using a level,
while, for CT scanners equipped with a concave
couch, a wooden slab can be used and placed on
the couch and aligned with a level above which
the custom phantom is positioned. To ensure the
correct alignment of the custom phantom with
the center of the imaging system, one positioning
laser of the CT scanner must be aligned with the align-
ment marker marked in the direction of the height of
Figure 4: Catphan-500® phantom acquisition setting. The
phantom is placed on its case leveled and aligned with the
scanner alignment markers.
Figure 5: Custom phantom acquisition setting. The phan-
tom is placed with its base on the wooden slab leveled and
aligned with the scanner alignment markers.
the phantom, while the other positioning laser must
be aligned with the edge of the phantom face itself.
5.2 Quality Control Checks
Inconsistencies in data acquisition and reconstruction
parameters may compromise the stability of radiomic
features and thus deteriorate the generalizability of
radiomics-based models. Improperly acquired im-
ages often require the use of additional image post-
processing or to repeat the reconstruction process thus
requiring additional operator time. In cases where er-
rors in acquisition parameters have occurred, it is nec-
essary to either remove the specific acquisition from
the dataset or repeat it, with relative difficulty in al-
locating additional machine time. Therefore, it is es-
sential to monitor the acquisition and reconstruction
parameters as soon as possible to detect any discrep-
ancies from the chosen protocol and be able to either
reconstruct or repeat the image immediately. It is nec-
essary to check both that the acquisition parameters,
i.e., tube voltage, tube current, activation or deacti-
BIOIMAGING 2025 - 12th International Conference on Bioimaging
408

Figure 6: Feature extraction ROIs on the polystyrene insert
of the Catphan® phantom.
vation of Automatic Exposure Control (AEC), pitch
and voxel size, and reconstruction parameters, e.g.,
image reconstruction kernel and iterative reconstruc-
tion blending level, correspond to those defined in the
chosen protocol for the specific CT scanner. In fact,
difficulties in reconstructing images with a specific it-
erative reconstruction blending level and fixed kernel
may happen when the CT scanner is set to acquire
many subsequent acquisition, as noted in the prelimi-
nary study. It is also important to verify that the posi-
tioning and alignment of the phantom are as expected,
that no reconstruction artifacts are present in the im-
age and that the correct number of repetitions were
acquired.
6 FEATURE EXTRACTION
PIPELINE
Since the CT images will be acquired at different clin-
ical centers using many different CT scanners, even
from different vendors, in order to perform rigid reg-
istration of the images, it is important to resample the
images to isotropic 1 × 1 × 1 mm
3
voxel using cubic
spline interpolation and nearest neighbor interpola-
tion and to convert images intensities to Hounsfield
units (HU) (Louis et al., 2024). Subsequently, the Re-
gions Of Interests (ROIs) from which radiomic fea-
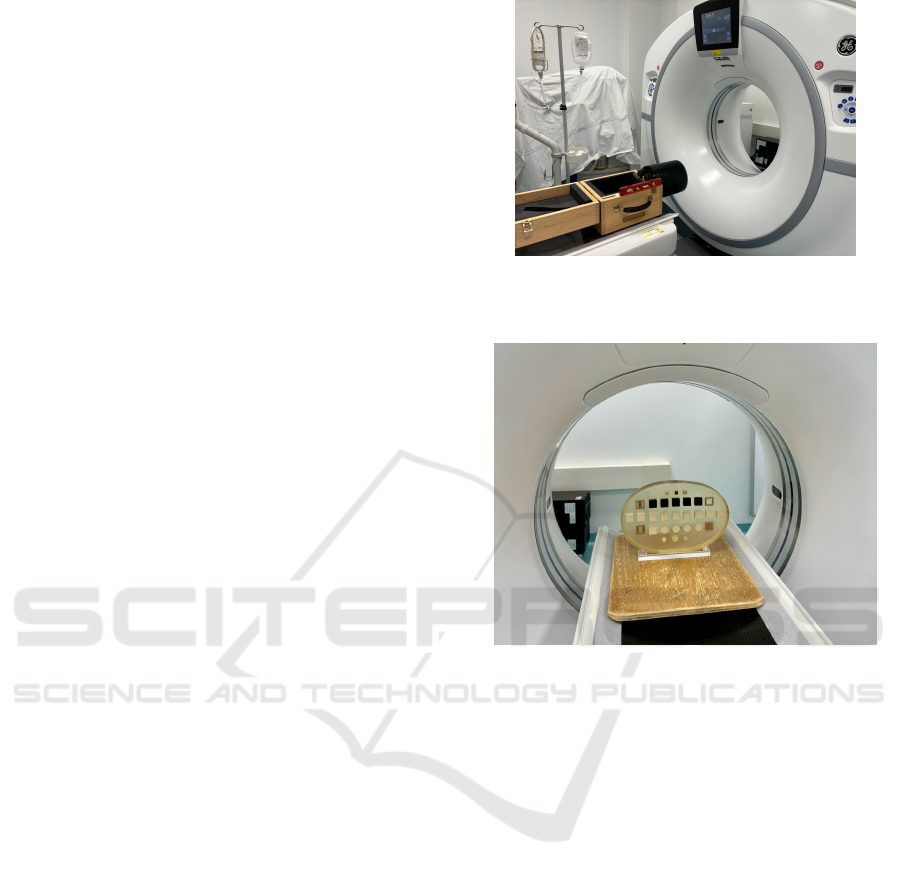
tures will be extracted on the cylindrical inserts of the
Catphan® and those in the custom phantom should be
placed. For the Catphan® phantom, it is sufficient to
choose the cylindrical ROIs centered in the center of
the insert with a distance of about 2 voxels in each
direction from the edge of the insert, as shown in Fig-
ure 6. For the custom phantom, on the other hand, it
is important to keep a greater number of voxels from
the edge of the insert for both the cylindrical and the
cubic ROIs, at least five, because of the presence of a
capsule inside which the insert is contained and resid-
ual glue with which the inserts were glued to a sheet
of plexiglass to anchor them during the construction
of the phantom itself, as shown in Figure 7.
Figure 7: Feature extraction ROIs positioned on the custom
phantom cylindrical and cubic inserts.
Once the ROIs have been defined, it is possible to
proceed with the extraction of first- and second-order
features, excluding shape features, using the Pyra-
diomics open-source python package. PyRadiomics
offers several settings to customize feature extrac-
tion, including the bin width for image gray level dis-
cretization. The default value of this parameter is
set to 25 HU, which can be used as a starting value
for feature extraction, after which two other values,
such as 10 HU and 50 HU, can be used to explore the
dependence of radiomic feature values on bin width.
Of the extracted radiomic features, repeatability and
robustness will then be evaluated through the assess-
ment of specific metrics such as the Intraclass Corre-
lation Coefficient (ICC) and the Coefficient of Vari-
ation (CV). The significance of the robust features
will instead be evaluated through the development of
classifiers either based on Machine Learning and with
the implementation of hybrid models combining ra-
diomic features and Deep Learning. The developed
hybrid classifier could then be translated to chest CT
images for lung nodule classification with the aim of
lowering the amount of false positives, an essential
aspect for the feasibility of large-scale lung cancer
screening.
7 DATA SHARING PLATFORM
Phantom CT images collected by the various clinical
centers could be stored within a platform based on the
Extensible Neuroimaging Archive Toolkit (XNAT)
that is already under development (Scapicchio et al.,
2024a). XNAT is an open source software platform
developed to support FAIR principles, which is a set
of guidelines to ensure the Findability, Accessibil-
ity, Interoperability, and Reusability of data, and to
facilitate the management of medical data. It was
initially developed to store and share neuroimaging
data and was later extended to other areas of medi-
cal imaging (Marcus et al., 2007; Tim
´
on et al., 2017).
XNAT-based platforms can be configured in a vari-
ety of ways to optimize project data management.
Use of Radiomics in Low Dose Chest CT: A Proposal for a Phantom Multi-Centric Study
409

Figure 8: Display of a central slice of the custom phantom
in the OHIF-XNAT viewer.
Data can be uploaded directly in DICOM format and
the images could be visualized through the integrated
OHIF viewer, as shown in Figure 8, as well as orga-
nized, shared, searched and downloaded on the plat-
form while also implementing an access management
mechanism that would allow various clinical centers
to login to the platform. The ability to store and
share heterogeneous data makes the XNAT technol-
ogy effective in multi-centric data storage as it al-
lows interconnected data to be managed across dif-
ferent projects. An added value of using a platform
based on XNAT is the possibility to directly imple-
ment an image quality control pipeline, i.e., an auto-
mated quality control analysis tool on the CT acqui-
sition that would be executed within the platform as
soon as these are uploaded on the platform. Another
potential of this platform concerns the development
of innovative integrated plugins to perform external
analysis such as, for example, the possibility of eval-
uating standard image quality metrics, i.e., Contrast
to Noise Ratio (CNR), Resolution and Noise Power
Spectrum (NPS), but also more complex metrics such
as the Detectability Index. Automated calculation of
these metrics would provide an immediate indication
of the quality of the acquired images by highlighting
the presence of any acquisition, reconstruction or po-
sitioning issues.
The XNAT platform could also be used for the au-
tomation of the radiomic pipeline through the ability
to use OHIF viewer tools for the automatic contour-
ing of ROIs. This would speed up, simplify and auto-
mate the process of defining ROIs within inserts and
extracting features, improving the repeatability of ra-
diomic analysis, a critical aspect of multi-centric stud-
ies. Therefore, the use of the XNAT platform would
not be limited to data storage, but could also become a
tool to optimize the steps of image acquisition and re-
construction parameter control, image quality assess-
ment, and radiomic feature extraction pipeline that
each clinical center could access.
8 CONCLUSIONS
Radiomic-based models and Radiomics and Deep
Learning combined models have huge potential with
regard to aiding diagnosis for lung nodule detection,
particularly in lung cancer screening programs where
a large number of chest LDCT must be analyzed by
detecting even very small lung nodules. However, the
translation to clinical practice of these models is lim-
ited by the poor reproducibility of radiomic features
as the image acquisition and reconstruction parame-
ters and the pipeline of radiomic feature extraction it-
self vary. Multi-centric phantom studies are essential
to enable harmonization of data acquired with differ-
ent CT scanners, define a procedure to identify a sub-
set of stable radiomic features using phantoms specifi-
cally developed for radiomics study that could be gen-
eralized to more heterogeneous datasets, and evaluate
the reliability of the results obtained in clinical tri-
als. In this study, a set of guidelines are proposed
for conducting a multi-centric study with two phan-
toms, one commercial and one custom. Particular at-
tention should be paid to the choice of image acqui-
sition and reconstruction protocols, starting with the
standard for lung nodule detection, and to the posi-
tioning of the phantoms. Image quality checks must
be implemented to verify adherence between the ac-
quired images and the acquisition and reconstruction
parameters required by the protocol. Finally, a spe-
cific feature extraction pipeline must be followed to
allow for reproducibility. The data should be stored
within a platform that allows the sharing among the
various centers. The proposed XNAT-based platform
could facilitate data management by simplifying the
image quality control procedure and automating the
radiomic feature extraction pipeline.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The research leading to these results has received
funding from:
The European Union - NextGenerationEU through
the Italian Ministry of University and Research
under: PNRR - M4C2-I1.3 Project PE 00000019
”HEAL ITALIA” to Maria Evelina Fantacci and
Maria Irene Tenerani – CUP I53C22001440006.
Piano Nazionale di Ripresa e Resilienza
(PNRR), Missione 4, Componente 2, Ecosis-
temi dell’Innovazione–Tuscany Health Ecosystem
(THE), Spoke 1 “Advanced Radiotherapies and
Diagnostics in Oncology”—CUP I53C22000780001.
PNRR - M4C2 - Investimento 1.3, Partenariato
Esteso PE00000013 - ”FAIR - Future Artificial
BIOIMAGING 2025 - 12th International Conference on Bioimaging
410

Intelligence Research” - Spoke 8 ”Pervasive AI”,
funded by the European Commission under the
NextGeneration EU programme.
PNRR - M4C2 - I1.4, CN00000013 - ”ICSC –
Centro Nazionale di Ricerca in High Performance
Computing, Big Data and Quantum Computing”
- Spoke 8 ”In Silico medicine and Omics Data”,
both funded by the European Commission under the
NextGeneration EU programme.
The National Institute for Nuclear Physics (INFN)
within the next AIM (Artificial Intelligence in
Medicine: next steps) research project (INFN-
CSN5), https://www.pi.infn.it/aim.
The views and opinions expressed are those of the
authors only and do not necessarily reflect those of
the European Union or the European Commission.
Neither the European Union nor the European Com-
mission can be held responsible for them.
REFERENCES
American Association of Physicists in Medicine (AAPM)
(2023). Lung Cancer Screening CT Protocols Version
6.0. AAPM. Accessed online.
American College of Radiology (ACR) (2023).
ACR–SABI–SPR–STR Practice Parameter for
the Performance of Thoracic Computed Tomography
(CT). American College of Radiology. Practice
parameters for thoracic CT imaging.
Baldwin, D., Duffy, S., Wald, N., Page, R., Hansell, D.,
and Field, J. (2011). Uk lung screen (ukls) nodule
management protocol: modelling of a single screen
randomised controlled trial of low-dose ct screening
for lung cancer. Thorax, 66(4):308–313.
European Society of Thoracic Imaging (ESTI) (2019).
Chest CT for Lung Cancer Screening: ESTI Techni-
cal Standards. ESTI. Technical standards for lung
cancer screening CT.
Frix, A.-N., Cousin, F., Refaee, T., Bottari, F.,
Vaidyanathan, A., Desir, C., Vos, W., Walsh, S., Oc-
chipinti, M., Lovinfosse, P., et al. (2021). Radiomics
in lung diseases imaging: state-of-the-art for clini-
cians. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 11(7):602.
IAEA (2012). Quality assurance programme for com-
puted tomography: Diagnostic and therapy applica-
tions. IAEA Human Health Series, 19.
Iball, G. R., Darby, M., Gabe, R., Crosbie, P. A., and Callis-
ter, M. E. (2021). Establishing scanning protocols for
a ct lung cancer screening trial in the uk. The British
journal of radiology, 94(1128):20201343.
Koo, T. K. and Li, M. Y. (2016). A guideline of selecting
and reporting intraclass correlation coefficients for re-
liability research. Journal of chiropractic medicine,
15(2):155–163.
Larue, R. T., van Timmeren, J. E., de Jong, E. E., Feliciani,
G., Leijenaar, R. T., Schreurs, W. M., Sosef, M. N.,
Raat, F. H., van der Zande, F. H., Das, M., et al.
(2017). Influence of gray level discretization on ra-
diomic feature stability for different ct scanners, tube
currents and slice thicknesses: a comprehensive phan-
tom study. Acta oncologica, 56(11):1544–1553.
Louis, T., Lucia, F., Cousin, F., Mievis, C., Jansen, N.,
Duysinx, B., Le Pennec, R., Visvikis, D., Neb-
bache, M., Rehn, M., et al. (2024). Identifica-
tion of ct radiomic features robust to acquisition and
segmentation variations for improved prediction of
radiotherapy-treated lung cancer patient recurrence.
Scientific Reports, 14(1):9028.
Mackin, D., Fave, X., Zhang, L., Fried, D., Yang, J., Tay-
lor, B., Rodriguez-Rivera, E., Dodge, C., Jones, A. K.,
et al. (2015). Measuring computed tomography scan-
ner variability of radiomics features. Investigative ra-
diology, 50(11):757–765.
Mail, T. B. (2013). Catphan® 500 and 600 manual. The
Phantom Laboratory.
Marcus, D. S., Olsen, T. R., Ramaratnam, M., and Buckner,
R. L. (2007). The extensible neuroimaging archive
toolkit: an informatics platform for managing, explor-
ing, and sharing neuroimaging data. Neuroinformat-
ics, 5:11–33.
McGraw, K. O. and Wong, S. P. (1996). Forming inferences
about some intraclass correlation coefficients. Psycho-
logical methods, 1(1):30.
Pallotta, S., Cusumano, D., Taddeucci, A., Benelli, M.,
Sulejmeni, R., Lenkowicz, J., Calusi, S., Marrazzo,
L., Talamonti, C., Belli, G., et al. (2020). Po-1536:
Radiomik: a phantom to test repeatability and repro-
ducibility of ct-derived radiomic features. Radiother-
apy and Oncology, 152:S830–S831.
Pegna, A. L., Picozzi, G., Mascalchi, M., Carozzi, F. M.,
Carrozzi, L., Comin, C., Spinelli, C., Falaschi, F.,
Grazzini, M., Innocenti, F., et al. (2009). Design, re-
cruitment and baseline results of the italung trial for
lung cancer screening with low-dose ct. Lung cancer,
64(1):34–40.
Quantitative Imaging Biomarkers Alliance (QIBA) (2018).
QIBA Profile: Small Lung Nodule Volume Assessment
and Monitoring in Low Dose CT Screening.
Saied, M., Raafat, M., Yehia, S., and Khalil, M. M. (2023).
Efficient pulmonary nodules classification using ra-
diomics and different artificial intelligence strategies.
Insights into Imaging, 14(1):91.
Samei, E., Bakalyar, D., Boedeker, K. L., Brady, S., Fan, J.,
Leng, S., Myers, K. J., Popescu, L. M., Ramirez Gi-
raldo, J. C., Ranallo, F., et al. (2019). Performance
evaluation of computed tomography systems: sum-
mary of aapm task group 233. Medical physics,
46(11):e735–e756.
Scapicchio, C., Arezzini, S., Fantacci, M., Formuso, A.,
Kraan, A., Mazzoni, E., Saponaro, S., Tenerani, M.,
and Retico, A. (2024a). Integration and optimiza-
tion of xnat-based platforms for the management of
heterogeneous and multicenter data in biomedical re-
search. In Proceedings of the 13th International Con-
ference on Data Science, Technology and Applications
- DATA, pages 551–558. INSTICC, SciTePress.
Use of Radiomics in Low Dose Chest CT: A Proposal for a Phantom Multi-Centric Study
411

Scapicchio, C., Imbriani, M., Lizzi, F., Quattrocchi, M.,
Retico, A., Saponaro, S., Tenerani, M. I., Tofani,
A., Zafaranchi, A., and Fantacci, M. E. (2024b).
Characterization and quantification of image qual-
ity in ct imaging systems: A phantom study. In
Proceedings of the 17th International Joint Confer-
ence on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Tech-
nologies - BIOIMAGING, pages 289–296. INSTICC,
SciTePress.
Scapicchio, C., Imbriani, M., Lizzi, F., Quattrocchi, M.,
Retico, A., Saponaro, S., Tenerani, M. I., Tofani, A.,
Zafaranchi, A., and Fantacci, M. E. (2024c). Inves-
tigation of a potential upstream harmonization based
on image appearance matching to improve radiomics
features robustness: a phantom study. Biomedical
Physics & Engineering Express, 10(4):045006.
Shafiq-ul Hassan, M., Zhang, G. G., Latifi, K., Ullah, G.,
Hunt, D. C., Balagurunathan, Y., Abdalah, M. A.,
Schabath, M. B., Goldgof, D. G., Mackin, D., et al.
(2017). Intrinsic dependencies of ct radiomic features
on voxel size and number of gray levels. Medical
physics, 44(3):1050–1062.
Team, N. L. S. T. R. (2011). The national lung screen-
ing trial: overview and study design. Radiology,
258(1):243–253.
Tenerani, M., Imbriani, M., Lizzi, F., Pallotta, S., Quat-
trocchi, M., Retico, A., Saponaro, S., Scapicchio, C.,
Talamonti, C., Tofani, A., Zafaranchi, A., and Fan-
tacci, M. (2024). Sc10.04 evaluation of repeatabil-
ity and robustness of ct-derived radiomic features us-
ing a custom phantom. Physica Medica, 125:103472.
Abstracts of the 5th European Congress of Medical
Physics.
Thakur, S. K., Singh, D. P., and Choudhary, J. (2020). Lung
cancer identification: a review on detection and classi-
fication. Cancer and Metastasis Reviews, 39(3):989–
998.
Tim
´
on, S., Rinc
´
on, M., and Mart
´
ınez-Tom
´
as, R. (2017). Ex-
tending xnat platform with an incremental semantic
framework. Frontiers in neuroinformatics, 11:57.
Traverso, A., Wee, L., Dekker, A., and Gillies, R. (2018).
Repeatability and reproducibility of radiomic fea-
tures: a systematic review. International Journal of
Radiation Oncology* Biology* Physics, 102(4):1143–
1158.
Van Griethuysen, J. J., Fedorov, A., Parmar, C., Hosny, A.,
Aucoin, N., Narayan, V., Beets-Tan, R. G., Fillion-
Robin, J.-C., Pieper, S., and Aerts, H. J. (2017).
Computational radiomics system to decode the radio-
graphic phenotype. Cancer research, 77(21):e104–
e107.
Vonder, M., Dorrius, M. D., and Vliegenthart, R. (2021).
Latest ct technologies in lung cancer screening: proto-
cols and radiation dose reduction. Translational lung
cancer research, 10(2):1154.
Zhao, Y. R., Xie, X., De Koning, H. J., Mali, W. P., Vliegen-
thart, R., and Oudkerk, M. (2011). Nelson lung cancer
screening study. Cancer Imaging, 11(1A):S79.
Zwanenburg, A., Leger, S., Valli
`
eres, M., and Lock, S.
Image biomarker standardisation initiative. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1612.07003.
BIOIMAGING 2025 - 12th International Conference on Bioimaging
412
