
Communication and Negotiation to Improve Agent-Based Models
Alejandro Rodr
´
ıguez-Arias
a
, Noelia S
´
anchez-Maro
˜
no
b
and Bertha Guijarro-Berdi
˜
nas
c
Universidade da Coru
˜
na, CITIC, Campus de Elvi
˜
na, s/n, 15008 A Coru
˜
na, Spain
Keywords:
Agent-Based Modeling, Multi-Agent System, Agent Communication Language, HUMAT, Sustainability.
Abstract:
Agent-based models (ABM) play a fundamental role in studying and modeling complex real-world systems,
primarily relying on reactive agents. Despite their simplicity, the interactions between agents and their envi-
ronment enable the simulation of diverse systems, contributing to their widespread adoption, particularly in
the social sciences. Similarly, though distinct in purpose, multi-agent systems (MAS) are designed to tackle
complex, diverse, and distributed problems by leveraging communication, negotiation, and coordination capa-
bilities. Both types of approaches have been used successfully in numerous areas; the power of ABM lies in
thousands of interacting agents, while MAS usually employs a smaller number of agents with more capabil-
ities. Including MAS agents’ capabilities in ABM agents allows the generation of more realistic simulations
that aid in the study of the modeled systems. In this paper, we present a generic ABM model whose agents
possess more capabilities, such as communication and negotiation, allowing this enhanced ABM to address
more complex modeling problems. To exemplify the usefulness of this enhanced ABM, we propose to use it as
a sandbox-tool to test “case-if” scenarios in a model that studies the evolution of a society’s opinion on a given
subject, specifically in this example, the implantation of superblocks in the city of Vitoria-Gasteiz (Spain).
1 INTRODUCTION
Science aims to understand real-world systems, their
patterns, and responses to various conditions. Direct
analysis is often slow, costly, or impractical, mak-
ing virtual systems essential for experimentation via
modeling.
In AI, agent-based modeling (ABM) is a key
method to represent complex systems. ABM depicts
real-world phenomena through agents, their environ-
ment, and their interactions. Agents are defined by
unique variables, actions, and environmental inter-
pretations, enabling the creation of diverse, heteroge-
neous societies that mirror real-world systems (Rails-
back and Grimm, 2019; Wilensky and Rand, 2015).
Multi-agent systems (MAS) (Dignum, 2017;
Wooldridge, 2009) address complex, distributed
problems by enabling collaborative strategies among
agent groups, facilitating realistic interactions for
solving real-world challenges. To support this, inter-
agent communication languages (ACLs) have been
developed (Soon et al., 2019).
While ABM focuses on social sciences and MAS
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0140-7473
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4025-1405
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8901-5441
on engineering, the demand for advanced ABM in so-
cial sciences is growing (Steinbacher et al., 2021). Ta-
ble 1 summarizes their key differences. In this paper
we will focus on the difference in agent complexity,
and the negotiation, coordination, and cooperation ca-
pabilities associated with MAS.
Table 1: Key differences between ABM and MAS.
Aspect ABM MAS
Purpose
Study emergent
behaviors.
Solve practical,
problems.
Field
Research and
simulation.
AI, engineering
Focus
Emergent phe-
nomena.
Agent coopera-
tion/competition.
Complexity
of Agents
Simple rule-
based behaviors.
Advanced
decision-
making.
Environment
Static or simpli-
fied.
Dynamic and
real-time.
An ABM example requiring more complex agents
is a forest fire propagation model. Fires act as agents,
with the system simulating their evolution under vary-
ing atmospheric conditions. Adding agents like fire-
fighters or fire trucks would enable analysis of their
1388
Rodríguez-Arias, A., Sánchez-Maroño, N. and Guijarro-Berdiñas, B.
Communication and Negotiation to Improve Agent-Based Models.
DOI: 10.5220/0013377500003890
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2025) - Volume 3, pages 1388-1395
ISBN: 978-989-758-737-5; ISSN: 2184-433X
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

effectiveness in extinguishing fires, necessitating ad-
vanced communication, cooperation, and coordina-
tion capabilities to optimize resource management.
Another example is modeling local fauna in an ABM,
where invasive species are agents. Incorporating
hunter agents who negotiate and coordinate to eradi-
cate invasive species introduces MAS functionalities.
In both cases, starting from a standard ABM with re-
active agents, adding MAS-like agents (firefighters or
hunters) enhances the model’s ability to address com-
plex real-world problems.
In this work, we build on a conceptual ABM de-
veloped in prior studies (Antosz et al., 2019; Antosz
et al., 2020; Bouman et al., 2021; Rodr
´
ıguez-Arias
et al., 2024). The model represents societies based on
sociodemographic characteristics and personal needs,
enabling the analysis of opinion evolution on specific
topics. It also highlights the influence of key group
entities or individual agents whose impact on opinion
dynamics is particularly significant.
The ABM was implemented using NetLogo
(Wilensky and Rand, 2015), a popular platform for
agent-based models but lacking MAS functionalities
and goal-oriented architectures (e.g., Belief-Desire-
Intention). This work enhances the ABM by: (a)
equipping NetLogo agents with basic communica-
tion, negotiation skills, and interaction protocols; (b)
integrating these agents into the model to enable com-
plex behaviors; and (c) showcasing these features
through a use case. The example used is citizen ac-
ceptance of a superblock project
1
. However, the en-
hanced ABM is adaptable to various problems and so-
cieties (Bouman et al., 2021; Rodr
´
ıguez-Arias et al.,
2024).
2 STATE OF THE ART
Agent-Based Models (ABMs) are widely used for
modeling and simulation across various fields. In
health, Escudero et al. (Escudero et al., 2016) mod-
eled HIV transmission in New York City (1996–2012)
using an ABM. In sociology, Crooks (Crooks, 2010)
used ABMs with vector GIS to study residential seg-
regation in urban settings. In emergency manage-
ment, Dawson et al. (Dawson et al., 2011) developed
an ABM for policy analysis to improve flood incident
management.
Agents in agent-based models typically use a reac-
tive architecture, relying on simple stimulus-response
rules (Kaelbling et al., 1987). These agents perceive
1
A superblock is a group of city blocks reorganized to
prioritize pedestrians over vehicles
their environment and act without memory or plan-
ning. This approach suits models where emergent
phenomena arise from numerous simple interactions,
enabling the observation of collective patterns with-
out complex individual behaviors.
Cognitive architectures mimic human cognitive
processes through three components: 1) the agent’s
perception of the world and its ability to sense
it, 2) memory for storing information, and 3) a
decision-making model. A popular example is the
Belief–Desire–Intention (BDI) architecture, where
agents operate based on beliefs (assumed truths), de-
sires (goals), and intentions (committed actions) (Rao
and Georgeff, 1997).
Some ABMs use hybrid architectures, blending
cognitive and reactive elements. This allows agents
to plan and make decisions deliberatively while react-
ing to immediate stimuli. Hybrid architectures com-
bine the strengths of both approaches, providing flex-
ibility and adaptability for simulating complex sys-
tems (Guessoum, 1997). For instance, Bussmann et
al. propose a hybrid architecture for autonomous mo-
bile robots (Chin et al., 2014).
Our goal is to implement an enhanced hybrid ar-
chitecture that incorporates MAS communication lan-
guages, aiming to increase the complexity and capac-
ity of traditional ABMs.
3 THE STANDARD ABM
The original ABM (Antosz et al., 2019; Antosz et al.,
2020; Bouman et al., 2021; Rodr
´
ıguez-Arias et al.,
2024) consists of two distinct agent types: 1) Humats,
representing individuals in the society under study,
based on the HUMAT architecture (Antosz et al.,
2018); and 2) critical nodes, representing entities or
individuals with a significant influence on the opinion
dynamics of the Humats. The following subsections
detail both agent types.
3.1 Humat Agents
A Humat must make a decision regarding the topic
under study, using sociodemographic characteristics
and psychosocial needs. At least three psychologi-
cal needs are considered: (1) experiential needs (e.g.,
personal well-being), (2) values (e.g., concern for en-
vironmental quality), and (3) belongingness (e.g., so-
cial group affiliation). Each need is defined by two
factors: (1) the importance I the Humat places on it,
and (2) the satisfaction S it derives from it. For in-
stance, COVID-19 measures like mask use and social
distancing reduce virus spread but complicate social-
Communication and Negotiation to Improve Agent-Based Models
1389

ization and family visits. The importance individuals
assign to these needs influences their decision to ad-
here to preventive health measures.
To represent societal heterogeneity, each Humat
has sociodemographic properties that, along with psy-
chosocial needs, define it. The HUMAT architecture
is flexible enough to accommodate different sociode-
mographic properties and needs, depending on the
problem being modeled (e.g., (Antosz et al., 2020;
Bouman et al., 2021)).
Each Humat is placed in a virtual environment,
which can be geographical, social, or a combination
of both. By default, the model creates a 2D virtual
space that can represent various settings (e.g., an of-
fice, city, or forest). Additionally, each Humat is part
of one or more social networks, allowing it to influ-
ence and be influenced by other Humats.
The life cycle of a Humat can be divided into two
main phases: (1) self-evaluation and (2) information
exchange.
Phase 1. Self-Evaluation. In each life cycle a Hu-
mat agent must assess its internal needs in order to
choose a decision or behavioural alternative that best
satisfies its individual needs. This is done by calcu-
lating the overall satisfaction (O) expected from each
behavioural alternative using the equation (1).
O
b
=
∑
N
n=1
S
b,n
∗ I
n
N
∈ [−1, 1], b = 1, 2 (1)
where S is the satisfaction value of an Humat for a
need n and a behavioural alternative b and I is the im-
portance that the Humat attaches to the need n. N
is the number of needs that motivate the decision-
making. Humats will choose the behavioural alter-
native with the highest expected overall satisfaction.
After choosing the behavioural alternative that
most satisfies their needs, Humats evaluate whether
this alternative generates any cognitive dissonance in
them. A dissonance occurs when a behavioural alter-
native generates positive or negative evaluations for
one need and the opposite sign for the others, where
the evaluation E of a particular need is calculated as
E
b,n
= S
b,n
∗ I
n
∈ [−1, 1] n = 1. . . N, b = 1, 2
(2)
resulting in a positive (E
+
) or negative (E
−
) evalua-
tion. The strength of an Humat’s dissonance is calcu-
lated following the equation (3).
D
b
=
2d
b
d
b
+ c
b
∈ [0, 1] (3)
where
d
b
= min
N
∑
n=1
E
+
b,n
,
N
∑
n=1
E
−
b,n
!
,
c
b
= max
N
∑
n=1
E
+
b,n
,
N
∑
n=1
E
−
b,n
!
When the strength of the dissonance exceeds a
certain tolerance threshold, the Humat will try to act
to resolve it by communicating with other Humats in
its same social network, as described below.
Phase 2. Information Exchange. When an agent
faces a dilemma due to dissonance exceeding their
tolerance threshold, they seek resolution by commu-
nicating with their social network.
The persuasiveness (P) of one Humat over another
during communication depends on: (a) the weight α,
which balances an individual’s opinion against exter-
nal influence, (b) the trust (T ) of the influenced Humat
in the communicator, and (c) the similarity of needs
(C) between them. After communication, the influ-
enced agent’s satisfaction is updated using equation
(4). The α weight ranges from 0 to 0.4, ensuring an
individual’s opinion always outweighs external influ-
ence.
P
b,n
= α ∗ T ∗C
b,n
(4)
Respect to similarity C, if the evaluation of a need
n (see equation (2)) has a different sign in both agents,
then the similarity of that need is 0, otherwise, it fol-
lows equation (5):
C
b,n
= 1 − |I
b,n,e
− I
b,n,o
| (5)
where I is the importance of the need, b is the be-
havioural alternative, o is the agent that influences.
After the communication, the new satisfaction
value of the influenced agent e is calculated as shown
in equation (6).
S
b,n,e
(t + 1) = (1 − P
b,n
) ∗ S
b,n,e
(t) + P
b,n
∗ S
b,n,o
(t)
(6)
3.2 Critical Nodes
The second type of agent is the critical node, which
represents influential collectives or key agents shap-
ing opinion evolution. Examples include local media,
influencers, or academic figures like professors.
Critical nodes hold individual opinions on the
topic being modeled (e.g., promoting sustainable
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
1390

Table 2: Critical node communication act parameters.
Parameter Value
Behaviour Supporter/Opponent
Reach
Integer in [0,100]
Start month Integer in [1,12]
Start year Integer in [1,12]
End month Integer in [1,12]
End year Integer in [1,12]
Frequency per month Integer in [1,2]
Primary critical node Any critical node
Secondary critical node Any critical node
transportation), which can evolve over time. They in-
fluence Humats through communication actions, op-
erating based on a communication plan rather than
seeking to reduce cognitive dissonance.
Each critical node is defined by parameters such as
the percentage of Humats it can reach, its geograph-
ical coordinates, and a communication plan. The so-
cial network of a critical node is determined by the
Humats it can influence.
A communication plan consists of a series of
dated communicative acts, each characterized by
scope (percentage of the social network affected), fre-
quency, and date parameters (as shown in table 2). A
communicative act can be for or against one of the
decisions that the Humats can take. Up to two critical
nodes can be involved in a communication: the pri-
mary node initiates the process, while the secondary
node carries out the communication through its net-
work. An example of a communication plan in the
superblock modeling case is provided in section 5.
3.3 Model Limitations
Humats are purely reactive agents, receiving commu-
nications from other Humats or critical nodes, updat-
ing their internal state, and responding accordingly.
In contrast, critical nodes exhibit a more proactive
behavior by following a fixed communication plan
throughout the simulation.
While this setup allows for the analysis of simple
opinion dynamics, it limits the model’s ability to rep-
resent complex and adaptive behaviors. This is par-
ticularly challenging when studying scenarios requir-
ing collaboration, negotiation, or strategic planning.
For example, the current model cannot capture how
agents might adapt strategies, form coalitions, or en-
gage in negotiation. As a result, it struggles to repre-
sent real-world dynamics where agents must balance
personal interests with community goals, respond to
unforeseen events, or adjust based on feedback. To
address these limitations, agents need communication
and reaction capabilities typical of MAS.
4 ENDOWING AGENTS WITH
NEGOTIATION CAPABILITIES
The goal of this work is to enhance ABM agents, en-
abling them to create and execute more complex plans
and behaviors. This requires hybridizing the model
with multi-agent system features by equipping agents
with intelligence, a new architecture, and a more so-
phisticated communication language, as detailed be-
low.
4.1 BDI-Like Agents in Netlogo
The first step is to convert some agents into more
complex agents by implementing a BDI-like architec-
ture. The BDI architecture consists of 3 main compo-
nents (Rao and Georgeff, 1997; De Silva et al., 2020):
• Beliefs, which represent information about the
state of the world held by the agent.
• Desires, that are the agent’s design objectives, i.e.
those goals to be achieved.
• Intentions, which are the tasks that are part of the
agents’ plan to achieve certain objectives.
Since NetLogo does not natively support BDI
agents, we propose a table-based implementa-
tion where each agent maintains beliefs as “con-
cept”–“value” pairs in a table, representing its per-
ceptions of the world. Desires are defined by a set
of beliefs the agent intends to be true.
Finally, intentions are managed using a First-In,
First-Out queue structure, where each entry consists
of a pair (”operator to use” and a ”stop condition”).
The operator specifies the function the agent should
execute, and the stop condition determines when the
intention should be removed from the queue.
4.2 Adding Communication Capacity
The second step in enhancing agent intelligence is
to provide more complex communication capabilities.
Currently, agents can only use the inquire/signal ac-
tions of the HUMAT architecture, enabling influence
communications but not real information exchange.
To address this, agents need a structure to manage and
send messages, along with an agent communication
language (ACL) to define them.
An (ACL) is a standard that enables agents to ex-
change information about plans, goals, and beliefs
(Genesereth and Ketchpel, 1994). ACLs define the
types and meanings of messages exchanged between
agents. Most ACLs are based on speech act theory
(Austin, 1975), where messages are communicative
Communication and Negotiation to Improve Agent-Based Models
1391
acts intended to prompt the receiving agent to take
action. In this work, we use the FIPA-ACL commu-
nication language from the Foundation for Intelligent
Physical Agents (FIPA).
FIPA defines a set of performatives that specify
the type of communicative act, indicating the intent
of messages (Wooldridge, 2009). These acts have
a well-defined meaning independent of the message
content (O’Brien and Nicol, 1998), as outlined in the
FIPA communicative acts library specification (FIPA,
2000). The range of performatives varies from sim-
ple information exchange to requests for tasks. Along
with the performative label, a FIPA ACL message
includes a set of parameters, which depend on the
agent’s current situation for effective communication.
NetLogo does not natively support ACLs. To
enable communication, we developed a library
for creating and modifying messages. In NetL-
ogo, a message is represented as a table, with
the ”performative” parameter being the only re-
quired attribute. The library includes functions
to add additional FIPA-defined parameters, such as
sender, receiver, and content, alongside the performa-
tive. This library is available at https://github.com/
alejandrorodriguezarias/EnhancedABM
Each communicating agent must have functional-
ity to manage its conversation structure and handle
message exchange. A conversation records all mes-
sages sent or received under the same conversation
identifier. An agent can engage in multiple conversa-
tions with different agents, or even multiple conversa-
tions with the same agent. When an agent receives a
message, it is added to the existing conversation if the
agent is the intended recipient, or a new conversation
is initiated if it’s the first message in that interaction.
Standardized communication frameworks, known
as communication protocols, enable agents to ex-
change messages, negotiate, and make decisions effi-
ciently. One widely used protocol is the Contract Net
Protocol (CNP) (FIPA, 2002), which manages task
allocation among autonomous agents in a distributed
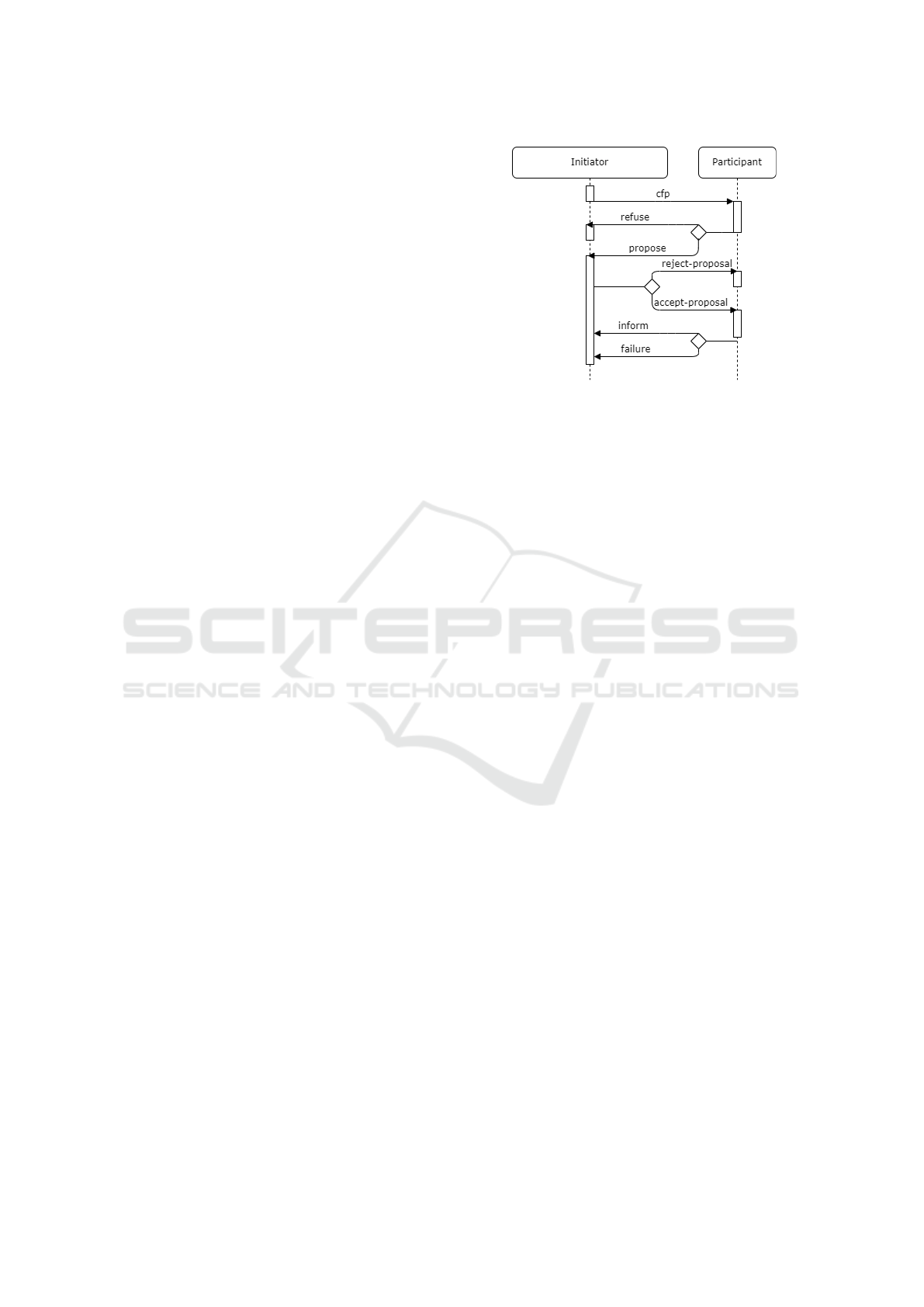
system. In the CNP (illustrated in Figure 1), an initia-
tor agent delegates a task to one or more participants.
The initiator broadcasts a request for proposals with
evaluation criteria. Participants respond with propos-
als, and the initiator selects the best agent based on
the bids, awarding the contract. The selected agent
performs the task and reports back with the results.
This structured approach allows for efficient task
distribution and coordination in multi-agent systems,
while also promoting a competitive environment
where agents can dynamically evaluate their partici-
pation based on their current state and capabilities.
Figure 1: Contract Net protocol flowchart.
5 USING THE ENHANCED ABM:
THE SUPERBLOCKS PROJECT
The original model, developed for the European
SMARTEES project, has been used to analyze citi-
zens’ responses to various social innovations and sim-
ulate alternative political scenarios, such as new com-
munication strategies by critical nodes to assess their
impact on acceptance. In this paper, we apply the im-
proved model to the case of Superblocks, focusing on
Vitoria-Gasteiz, which was a pioneer in implementing
this urban innovation. The project faced significant
public criticism, particularly regarding policies that
increased on-street parking costs. The model reflects
the project’s implementation (2006-2013) and was
validated by stakeholders and experts in the SMAR-
TEES project.
During the SMARTEES project, numerous pro-
moters and detractors of social innovations con-
tributed to ensuring the model’s reliability. They pro-
posed various scenarios to explore the social inno-
vation from different perspectives. Despite the suc-
cessful outcomes and the interesting model developed
(Antosz et al., 2019; Antosz et al., 2020; Bouman
et al., 2021; Rodr
´
ıguez-Arias et al., 2024), some re-
alistic scenarios could not be implemented due to
the limitations of the agents, which lacked commu-
nication and negotiation capabilities. In the follow-
ing subsections, we will describe the original ABM
adapted to the Vitoria-Gasteiz Superblocks case and
demonstrate how the agents’ new capabilities enable
the exploration of expanded alternative scenarios.
5.1 Virtual Environment
The model includes a virtual environment, consist-
ing of two components: (1) the geographical environ-
ment, represented by the city of Vitoria-Gasteiz using
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
1392

its census sections and a 50x50 2D board (see figure
2), and (2) the social networks of friends and neigh-
bors to which citizens belong.
Figure 2: Vitoria-Gasteiz represented by its census sections.
Citizens are represented by a human silhouette, green if they
are in favour of the project and red if not. Critical nodes are
represented by an image of a building.
Neighbour networks were created using social cir-
cles (Hamill and Gilbert, 2009), based on agent prox-
imity. Friendship networks were generated as random
networks with constraints: (1) a minimum number of
friends per agent and (2) homophily on age and edu-
cation, with a small chance of random links. Humats
(see section 3.1) can communicate and influence oth-
ers within their network.
5.2 Agents of the Model
In the Victoria-Gasteiz case the Humats represents
citizens. Citizens use the HUMAT architecture for
decision-making and influence diffusion (see section
3.1). These agents are initialized using data from sur-
veys conducted in Vitoria-Gasteiz during the SMAR-
TEES project.
As we have explained in the section 3, using HU-
MAT architecture we have enough flexibility to rep-
resent individuals with different sociodemographic
characteristics and needs. In the table 3 we can see the
properties that characterise a citizen in the superblock
model. Different problems may need different char-
acterisation, as seen in (Antosz et al., 2020; Bouman
et al., 2021).
Similarly, the critical nodes are agents (see section
3.2) that represent promoters, and institutions relevant
to the development of the social innovation. In the su-
perblocks case, the following critical nodes were in-
Table 3: Variables defining a Humat agent in the su-
perblock’s project.
Variables Values
Age (years) integer in [18-120]
Gender male/female
Education level
primary/secondary/ tertiary
Economic Activity
employed/jobless /inactive
Location census tract code
Homeowner yes/no
Years in the neigh-
bourhood
<3 / 3- 10/ 10-30 / >30
cluded:
• The city council, as the main promoter of this so-
cial innovation project.
• Merchants’ associations. Throughout the imple-
mentation of the project they showed a clear re-
jection of the proposed measures to implement the
superblocks. They were the main opponents.
• Other associations, from neighbourhood associa-
tions to cycling associations. Their opinion varied
throughout the implementation of the project.
• Local press: they were the main disseminators of
information about the project.
In the table 4, we can see as an example part of
a communication plan employed in the superblock
modeling problem. In this example, the City Council
acts as a primary critical node, sometimes contracting
an advertising campaign to the press (secondary criti-
cal node) to give support and promote (behavior) the
superblocks project.
Critical nodes implement the BDI architecture
(explained at section 4) and the necessary structure
to communicate using the FIPA-ACL protocols (see
section 4.2). Specifically, in this case they have the
mechanisms to implement the contract net protocol.
5.3 Model Results
After the model was implemented, the lack of detailed
historical data on the evolution of citizen opinion led
to its validation through expert feedback in a series of
workshops conducted during the SMARTEES project
(Dumitru et al., 2021). Calibration and validation of
the model’s parameters can be found in (Rodr
´
ıguez-
Arias et al., 2024).
The timeline (blue curve) in Figure 3 illustrates
the historical evolution of citizen acceptability, as re-
produced by the model, with results averaged over
100 model executions. To develop the communica-
tion plans of the critical nodes, an analysis of the
newspaper library was conducted to ensure their re-
alism. Each cycle of the model represents 15 days in
Communication and Negotiation to Improve Agent-Based Models
1393
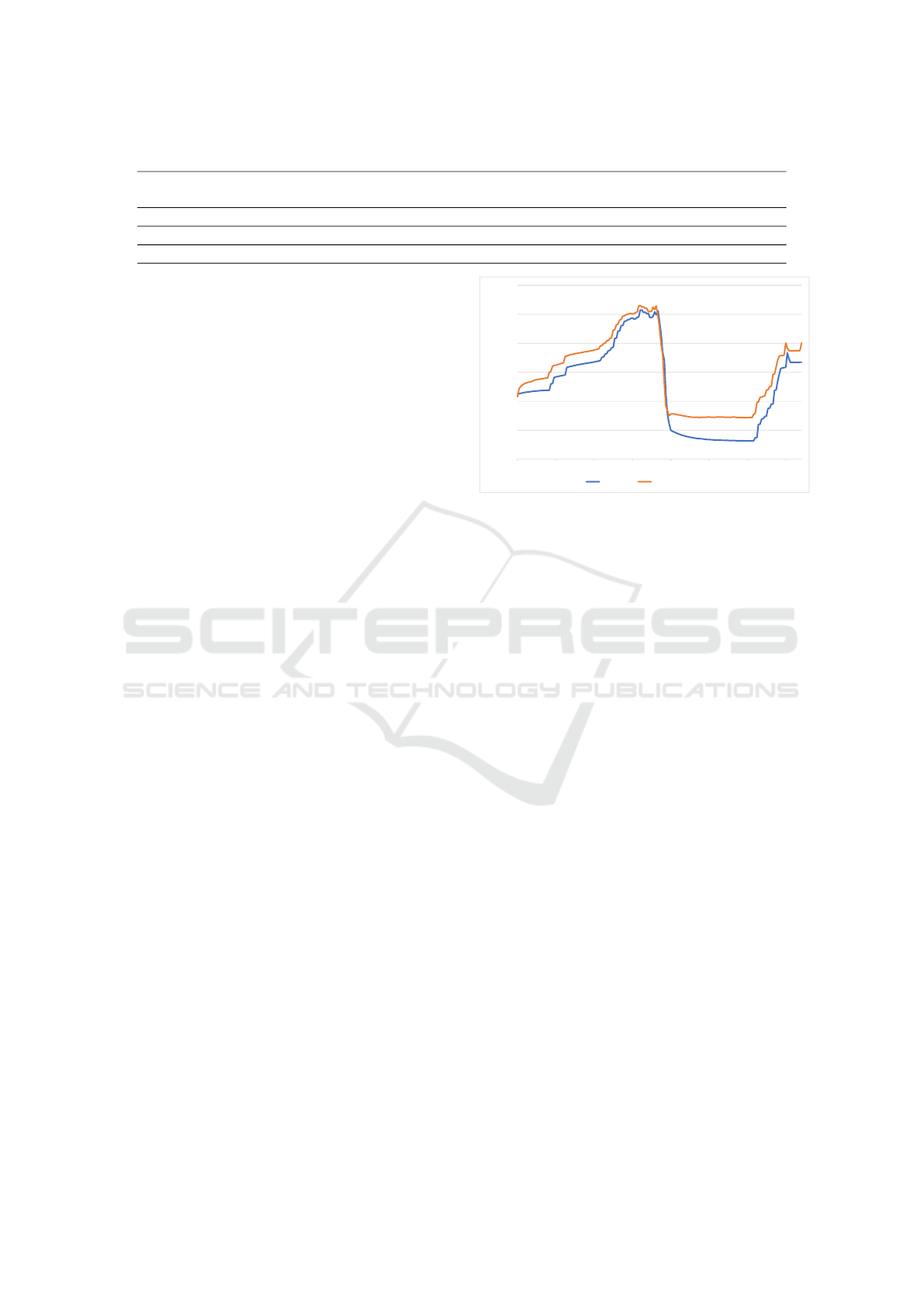
Table 4: Example of a critical node communication plan.
Primary critical
node
Behaviour
Start
month
Start
year
End
month
End
year
Frequency
per month
Reach
Secondary
critical node
City council Supporter 11 2006 12 2006 1 10% City council
City council
Supporter 1 2008 12 2008 1 1% Local press
City council Supporter 2 2009 2 2009 1 20% Local press
the simulation. As shown, public acceptance was ini-
tially high, consistent with the feedback from promot-
ers and experts. This was due to a general consensus
that led to the underrepresentation of opposing view-
points in the media discourse. Consequently, nega-
tive messages were infrequent (reflected in the limited
number of communicative acts), resulting in a rapid
acceptance of the superblocks. However, in Novem-
ber 2009, a new traffic policy was approved, introduc-
ing traffic and parking restrictions and raising public
parking costs. Resistance to this policy was initially
strong, particularly from the retail sector, but it dimin-
ished as the superblock was fully established and its
benefits became more apparent to the public.
5.4 Alternative Policy Scenarios
The goal of modeling superblock implementation is
to provide a sandbox tool for stakeholders to test poli-
cies or ”what-if” scenarios aimed at improving citizen
acceptance. These scenarios modify the real, expert-
validated case.
For instance, with the enhanced BDI agents, con-
sider a scenario where the critical node ”city coun-
cil” uses this architecture to maintain citizen accep-
tance above 45%. It monitors acceptance levels and, if
they fall below 45%, executes a plan: launching a me-
dia advertising campaign for the superblocks project.
Since multiple media outlets could run the campaign,
the city council uses the Contract Net Protocol to ne-
gotiate and finalize the agreement.
For that, the municipality will launch a commu-
nication to all press agents (critical nodes) request-
ing a two-month advertising campaign in favour of
the project. Each press agent evaluates this request
and communicates a proposal with two parameters:
(1) the scope of the campaign and (2) the cost of the
campaign. The city council will select the proposal it
is most interested in and this press agent will initiate
the campaign.
This scenario evaluates whether a more reactive
developer can mitigate discontent during the project’s
most controversial phase (see Figure 3). The CNP
serves as an example of how the model benefits from
enhanced agents with ACL-based communication,
but other FIPA protocols could be applied. For in-
stance, critical nodes could negotiate between cyclists
0,3
0,4
0,5
0,6
0,7
0,8
0,9
01/01/2006 01/01/2007 01/01/2008 01/01/2009 01/01/2010 01/01/2011 01/01/2012 01/01/2013
% of ci�zens accep�ng social innova�on
Timeline Case-if-scenario
Figure 3: Comparison of the evolution of citizen acceptance
between the real scenario (timeline) of Victoria-Gasteiz and
the new “case-if” scenario.
and merchants opposing the superblocks project. Ad-
ditionally, Humats could adopt BDI features to orga-
nize protest groups or political demonstrations.
6 CONCLUSIONS
Agent-Based Models (ABMs) are powerful tools for
representing complex systems and are widely used in
the social sciences. These models rely on reactive
agents and derive their strength from the interactions
between agents and their environment. However, cer-
tain phenomena require agents with enhanced capa-
bilities to accurately capture the dynamics involved.
For example, while a traditional ABM might predict
the spread of a fire, incorporating agents such as fire-
fighters who can communicate and coordinate their
actions significantly enriches the model’s realism and
predictive power.
We developed a NetLogo library enabling agents
with a hybrid BDI (Beliefs, Desires, Intentions) ar-
chitecture. This includes message generation, stor-
age, modification, and communication via FIPA-
ACL, along with negotiation protocols like FIPA-
ACL Contract Net for collaboration. These agents
were integrated into an ABM framework, expanding
its modeling capabilities. In the presented example,
the enhanced framework supports stakeholders in im-
plementing social innovations by providing deeper in-
sights and facilitating informed decision-making.
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
1394

ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by the Horizon 2020
SMARTEES project (grant no. 7639) of the European
Commission. We also acknowledge funding from the
Xunta de Galicia and ERDF funds of the European
Union through grants for research groups (ED431C
2018/34, ED431C 2022/44), CITIC as a Research
Center of the University System of Galicia (ED431G
2023/01), and the Ministry for Digital Transformation
and Civil Service under ‘Next-GenerationEU’/PRTR
(grant TSI-100925-2023-1).
REFERENCES
Antosz, P., Jager, W., Polhill, G., Jiaqui, G., Salt,
D., Alonso-Betanzos, A., S
´
anchez-Maro
˜
no, N., and
Guijarro-Berdi
˜
nas, B. (2018). Report on the concep-
tual model of the smartees simulation and data types
to be included. Deliverable 7.1, SMARTEES project.
Antosz, P., Jager, W., Polhill, G., Salt, D., Alonso-Betanzos,
A., S
´
anchez-Maro
˜
no, N., Guijarro-Berdi
˜
nas, B., and
Rodr
´
ıguez, A. (2019). Simulation model implement-
ing different relevant layers of social innovation, hu-
man choice behaviour and habitual structures. Deliv-
erable 7.2, SMARTEES project.
Antosz, P., Jager, W., Polhill, G., Salt, D., Scalco, A.,
Alonso-Betanzos, A., S
´
anchez-Maro
˜
no, N., Guijarro-
Berdi
˜
nas, B., and Rodr
´
ıguez, A. (2020). Smartees
simulation implementations. Deliverable 7.3, SMAR-
TEES project.
Austin, J. L. (1975). How to do things with words, vol-
ume 88. Oxford university press.
Bouman, L., Antosz, P., Jager, W., Polhill, G., Salt, D.,
Scalco, A., Alonso-Betanzos, A., S
´
anchez-Maro
˜
no,
N., Guijarro-Berdi
˜
nas, B., and Rodr
´
ıguez-Arias, A.
(2021). Report on scenario development and exper-
iments for selected cases. Deliverable 7.4, SMAR-
TEES project.
Chin, K. O., Gan, K. S., Alfred, R., Anthony, P., and
Lukose, D. (2014). Agent architecture: An overviews.
Transactions on science and technology, 1(1):18–35.
Crooks, A. T. (2010). Constructing and implementing an
agent-based model of residential segregation through
vector gis. International Journal of Geographical In-
formation Science, 24(5):661–675.
Dawson, R. J., Peppe, R., and Wang, M. (2011). An agent-
based model for risk-based flood incident manage-
ment. Natural hazards, 59:167–189.
De Silva, L., Meneguzzi, F. R., and Logan, B. (2020). Bdi
agent architectures: A survey. In Proceedings of the
29th International Joint Conference on Artificial In-
telligence (IJCAI), 2020, Jap
˜
ao.
Dignum, V. (2017). Social agents: Bridging simula-
tion and engineering. Communications of the ACM,
60(11):32–34.
Dumitru, A., Lema Blanco, I., Albulescu, P., Antosz, P.,
Bouman, L., Colley, K., Craig, T., Jager, W., Mac-
singa, I., Meskovic, E.and Mischkowski, N., Pelle-
grini Masini, G., Polhill, G., Quinti, G., Salt, D.,
Somervail, P., and Wilson, R. (2021). Policy recom-
mendations for each cluster of case-studies of case-
studies. Insights from policy scenario workshops. De-
liverable 5.2, SMARTEES project.
Escudero, D. J., Lurie, M. N., Mayer, K. H., Weinreb, C.,
King, M., Galea, S., Friedman, S. R., and Marshall,
B. D. (2016). Acute hiv infection transmission among
people who inject drugs in a mature epidemic setting.
Aids, 30(16):2537–2544.
FIPA, O. (2002). Fipa contract net interaction protocol
specification. Document no. SC00029H.
FIPA, T. (2000). Fipa communicative act library specifica-
tion. Change, 2000(01/18).
Genesereth, M. and Ketchpel, S. (1994). Communications
of the acm. Software Agents, 37(7):48–54.
Guessoum, Z. (1997). A hybrid agent model: a reactive and
cognitive behavior. In Proceedings of the Third In-
ternational Symposium on Autonomous Decentralized
Systems. ISADS 97, pages 25–32. IEEE.
Hamill, L. and Gilbert, G. (2009). Social circles: A sim-
ple structure for agent-based social network models.
Journal of Artificial Societies and Social Simulation,
12(2).
Kaelbling, L. P. et al. (1987). An architecture for intelligent
reactive systems. Reasoning about actions and plans,
pages 395–410.
O’Brien, P. D. and Nicol, R. C. (1998). Fipa—towards a
standard for software agents. BT Technology Journal,
16(3):51–59.
Railsback, S. F. and Grimm, V. (2019). Agent-based and
individual-based modeling: a practical introduction.
Princeton university press.
Rao, A. S. and Georgeff, M. P. (1997). Modeling rational
agents within a bdi-architecture. Readings in agents,
pages 317–328.
Rodr
´
ıguez-Arias, A., S
´
anchez-Maro
˜
no, N., Guijarro-
Berdi
˜
nas, B., Alonso-Betanzos, A., Lema-Blanco, I.,
and Dumitru, A. (2024). An agent-based model to
simulate the public acceptability of social innovations.
Expert Systems, page e13731.
Soon, G. K., On, C. K., Anthony, P., and Hamdan, A. R.
(2019). A review on agent communication language.
Computational Science and Technology: 5th ICCST
2018, Kota Kinabalu, Malaysia, 29-30 August 2018,
pages 481–491.
Steinbacher, M., Raddant, M., Karimi, F., Camacho Cuena,
E., Alfarano, S., Iori, G., and Lux, T. (2021). Ad-
vances in the agent-based modeling of economic and
social behavior. SN Business & Economics, 1(7):99.
Wilensky, U. and Rand, W. (2015). An introduction to
agent-based modeling: modeling natural, social, and
engineered complex systems with NetLogo. MIT
press.
Wooldridge, M. (2009). An introduction to multiagent sys-
tems. John Wiley & Sons.
Communication and Negotiation to Improve Agent-Based Models
1395
