
Large-Scale Group Brainstorming and Deliberation Using
Swarm Intelligence and Generative AI
Louis Rosenberg
1a
, Hans Schumann
1
, Christopher Dishop
2
, Gregg Willcox
1
, Anita Woolley
2b
,
and Ganesh Mani
2c
1
Unanimous AI, 2200 North George Mason Dr, Arlington, VA, U.S.A.
2
Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, U.S.A.
Keywords: Collaboration, Deliberation, Collective Intelligence, Generative Ai, Conversational Swarm Intelligence,
Deliberative Problem Solving, Large Language Models, Brainstorming, Alternative Use Tasks.
Abstract: Conversational Swarm Intelligence (CSI) is an GenAI-based method for enabling real-time conversational
deliberations among networked human groups of potentially unlimited size. Based on the biological principle
of Swarm Intelligence and modelled on the decision-making dynamics of fish schools, CSI has been shown
in prior studies to enable thoughtful conversations among hundreds of real-time participants while amplifying
group intelligence. It works by dividing a large population into a set of subgroups that are woven together by
real-time AI agents called Conversational Surrogates. The present study focuses on the use of a CSI platform
called Thinkscape to enable real-time brainstorming and prioritization among groups of 75 networked users.
The study employed a variant of a common brainstorming intervention called an Alternative Use Task (AUT)
and compared brainstorming using a CSI platform to a traditional text-chat environment. This comparison
revealed that participants significantly preferred using CSI, reporting that it felt (i) more collaborative, (ii)
more productive, and (iii) was better at surfacing quality answers. In addition, participants using CSI reported
(iv) feeling more ownership and more buy-in in the top answers the group converged on and (v) reported
feeling more heard as compared to a traditional chat environment. Overall, the results suggest that CSI is a
promising GenAI-based method for brainstorming and prioritization at large scale.
1 INTRODUCTION
Humans are not the only species that deliberate in
groups to reach decisions. Fish schools, bird flocks,
and bee swarms are well known examples of natural
groups that can reach rapid decisions to life-or-death
issues, often converging upon the optimal solution.
Biologists refer to this collaborative decision-making
process as Swarm Intelligence (SI) and it enables
many social organisms to make decisions that are
significantly smarter than the individual members
could achieve on their own (Krause, et. al, 2010).
Artificial Swarm Intelligence (ASI) is a novel
technology developed in 2014 to enable networked
human groups to converge on collaborative decisions
by deliberating in systems modelled on biological
swarms (Rosenberg, 2015). ASI has been shown to
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3457-1429
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0620-4744
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2170-7414
amplify the accuracy of group decisions across a wide
range of applications, from financial forecasting and
business prioritization to medical diagnosis (Askay,
et. al., 2019. Rosenberg, 2016. Willcox et. Al., 2021).
While ASI has proven effective, initial versions
required users to choose among a pre-defined set of
options. This works well for narrow applications such
as group prioritization, probabilistic forecasting and
numerical estimation, but is not effective for solving
complex problems that require groups to deliberate,
brainstorm, prioritize and converge. To address this,
a next-generation technology called Conversational
Swarm Intelligence (CSI) was developed in 2023 that
combines the principles of ASI with the power of
large language models (Rosenberg, et al., 2023).
The goal of CSI is to enable large, networked
human groups (25 to 500 people) to hold thoughtful
Rosenberg, L., Schumann, H., Dishop, C., Willcox, G., Woolley, A. and Mani, G.
Large-Scale Group Brainstorming and Deliberation Using Swarm Intelligence and Generative AI.
DOI: 10.5220/0013379800003929
In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2025) - Volume 1, pages 867-872
ISBN: 978-989-758-749-8; ISSN: 2184-4992
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
867

conversational deliberations in real-time that rapidly
converge on optimal solutions based on the combined
knowledge, views, and opinions of the participants.
To make this viable, researchers had to overcome
several fundamental barriers related to basic human
conversations. First and foremost, research shows
that deliberative conversations are most effective in
small groups of only 4 to 7 individuals and rapidly
lose effectiveness with increasing size (Cooney, et.
al., 2020). With additional members, all participants
are afforded less and less airtime to express their
views, and longer and longer wait times to respond to
others. When a group reaches sizes larger than 10 to
12 people, it ceases to be a true deliberation and
devolves into a series of monologues.
So how can a technology enable hundreds of
people hold a productive real-time deliberation in
which participants brainstorm solutions, build on the
ideas of others, debate options and alternatives, and
converge on solutions? To overcome this barrier, CSI
takes its core inspiration from the decision-making
dynamics of large fish schools. That is because large
schools have thousands of members and provide an
interesting analog to human organizations. Consider
the image below which shows a large school facing
three simultaneous threats that require a rapid and
effective response:
Figure 1: Fish School facing simultaneous threats.
In the figure above, three predators approach the
school, creating a complex life-or-death problem that
requires a rapid and effective solution. Like many
human organizations, all members of the school have
limited information. As shown in Fig. 1, three small
pockets of fish (e.g., the circled areas above) are each
aware of a single predator approaching their location.
At the same time, most fish in the school are unaware
of any of the three predators. So how can this large
organization in which all members have limited
information, quickly find an optimal decision as to
which direction the school should move?
Fish schools use a unique form of communication
among neighboring individuals. Each fish has a
specialized organ on the sides of their bodies called a
lateral line that detects faint pressure and vibration
changes in the water as the adjacent fish adjust their
direction and speed. This enables small subgroups of
neighbors to “deliberate” in real-time, establishing a
local tug-o-war that converges on the direction that
small subgroup of fish will go. And because each
subgroup of neighboring fish overlaps other small
subgroups, information quickly propagates across the
full population.
This enables an emergent property that biologists
call Swarm Intelligence, and it allows thousands of
individuals, each with a limited view of the world
around them, to rapidly converge on unified decisions
that are critical for survival (Parish, et. al., 2002.
Rosenberg, et. al., 2023). Fig. 2 below shows this
information propagating across the school, leading to
an efficient and effective collective decision.
Figure 2. Swarm Intelligence enables optimized decisions.
CSI technology takes this natural process and
emulates the dynamics by breaking large human
groups into a network of overlapping subgroups, each
with 4 to 7 members, as that size enables optimal
conversational deliberation. Unfortunately, there is
one more barrier that must be overcome – unlike fish,
humans cannot participate effectively in overlapping
subgroups (i.e. we did not evolve to participate
multiple real-time conversations at once).
This is commonly called the Cocktail Party
Problem – if you engage in a conversation with a
small group at a party and get interested in what a
neighboring group is discussing, you immediately
lose focus on the original group (Bronkhorst, 2000).
So how can hundreds of individuals hold a single
conversation through overlapping subgroups?
To overcome this problem, CSI uses novel
artificial agents called “Conversational Surrogates”
that are powered by Large Language Models (LLMs)
and enable the real-time overlap among deliberating
groups (Rosenberg, 2023). Specifically, CSI breaks a
large population into a series of parallel subgroups
such that an LLM-powered surrogate agent is placed
ICEIS 2025 - 27th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
868

in each subgroup and tasked with observing the
deliberation in that group, distilling the salient
content, and passing critical ideas, insights, opinions
and perspectives to other subgroups where that
subgroup’s local surrogate agent will express those
points as a natural dialog within their ongoing
conversation. With agents in all subgroups
continuously observing insights and passing them to
surrogate agents in other rooms, the full population is
woven together into a single conversation in which
ideas emerge and spread with high efficiency, along
with arguments for and against those ideas. Using this
novel architecture, 50, 500 or even 5,000 people can
hold a real-time conversation in which they
brainstorm ideas, debate alternatives, prioritize
options and converge on solutions.
Figure 3: Conversational Swarm Intelligence Architecture.
An example CSI architecture is shown in Fig. 3
above in which a group of 98 people are divided into
a network of 14 subgroups, each with 7 human users
and one artificial agent. While the image implies that
each subgroup can only pass information to two other
subgroups in the network, the model employed in this
study enabled insights to pass from any subgroup to
any other subgroup (i.e., a fully connected network).
A unique matchmaking subsystem is used that
that tracks (i) which groups have a new idea or insight
that is ready to pass to others, (ii) which groups have
not received insights for a threshold amount of time
and are ready to receive another, and (iii) which of the
available insights (across all sending groups) is most
likely to maximally challenge each receiving group,
based on what that group has discussed thus far.
In this way, CSI emulates the basic propagation of
information within fish schools. but does so in a far
more efficient manner. While schools and other
biological swarms pass insights between neighboring
members, CSI can pass insights between any local
groups in the network. This makes CSI a “hyper-
swarm” structure (Willcox, 2021) and it leverages
this hyper-connectivity to challenge each local group
with insights, opinions, and/or rationales that will
most likely evoke the most meaningful responses.
By facilitating large, networked populations to
debate complex issues in real-time, CSI enables
individuals with a wide range of knowledge, wisdom,
and insights to collaboratively deliberate on broad,
open-ended problems. And because every assertion
expressed by every participant is identified and stored
in a real-time taxonomy database by the CSI system,
the system can immediately produce detailed forensic
reports that reveal how each decision was reached,
including a complete assessment of every idea raised,
the reasons that support and reject each ideas, and
impact each idea or reason had on others to sway the
group towards a maximally supported solution.
In addition, CSI solves common biasing problems
that drive deliberating groups to non-optimal
answers. For example, groups can be overly impacted
by individuals with strong personalities, with high
rank within an organization, or who express ideas
very early in a deliberation. This is mitigated by the
CSI structure because points raised by a strong
personality, a high-ranking individual, or an early
talker in the deliberation only impact a small local
subgroup. For those points to gain traction across the
full population, they must stand on their own merits:
either discussed organically in multiple subgroups or
passed into subgroups by surrogate agents. Ideas that
are passed into a group and significantly impact that
group are more likely to pass to other groups, thus
enabling strong insights to propagate quickly.
The effectiveness of CSI has been researched in a
handful of recent studies. In one study conducted at
Carnegie Mellon in 2023, groups of 48 participants
were tasked with debating the future impact of AI on
jobs using a CSI platform called Thinkscape™. The
participants using CSI contributed 51% more content
(p<0.001) compared to those using standard
centralized chat. In addition, CSI showed 37% less
difference in contribution between the most vocal and
least vocal users, indicating that CSI fosters more
balanced deliberations. (Rosenberg, et. al., 2023).
In another recent study, groups of 35 individuals
were tasked with taking a standardized IQ test, either
as individuals on a survey, as a “crowd” by taking the
aggregation of surveys, or as a conversational swarm
inside the CSI-powered Thinkscape platform. The
groups of randomly selected participants using CSI
averaged a collective of score 128 on the IQ test when
Large-Scale Group Brainstorming and Deliberation Using Swarm Intelligence and Generative AI
869

working together in conversational swarms, greatly
outperforming both the average individual participant
(IQ 100, p<0.001) and outperforming traditional
statistical aggregation across groupings of 35
individual tests (IQ 115, p<0.01). In addition, the
score of 128 IQ achieved by the average CSI group
placed its performance in the 97
th
percentile of
individual IQ test takers, achieving “gifted” status by
most metrics (Rosenberg, et. al. 2024).
While prior studies have shown that large groups
using CSI (i) increase conversational participation,
(ii) foster more balanced dialog among participants,
and amplify collective intelligence compared to
traditional methods, no prior study has explored the
ability of large groups to brainstorm collaboratively
and converge on a set of prioritized solutions in real-
time. The following study aimed to test brainstorming
among groups of approximately 75 individuals and
assess their comparative perceptions of brainstorming
with CSI versus brainstorming within a single large
group in a traditional online chat platform.
2 BRAINSTORMING STUDY
To assess if large networked human groups can hold
real-time brainstorming conversations using a CSI
structure and converge on a small set of maximally
supported solutions, two sets of approximately 75
people (sourced from a commercial sample provider)
were assembled in the text-based Thinkscape
platform and tasked with a collaborative
brainstorming problem. As a baseline, the same
groups we also assembled in a single large text-based
chatroom of similar real-time functionality to
Discord, Slack, Google Chat, Microsoft Teams and
other commercial room-based chat environments.
The brainstorming task used was a modified
version of a typical Alternative Use Task (AUT) that
is given to assess creative abilities in individuals
and/or groups (Habib, et. al, 2024; Guilford, 1967). In
this case, two alternative use tasks were devised – a
first task which asked groups to imagine they work
for a large company that has been stuck with a
significant inventory of traffic cones. Their task is to
come up with as many alternative uses of traffic cones
as possible (unrelated to traffic) that could be viable
products sold the fictional company and to identify
the best ideas among the proposed alternatives. The
second task was structured the same way, but the item
that the fictional company had in inventory were
toilet plungers.
The protocol for the first group of 75 individuals
was to first brainstorm the traffic cone AUT task first
in a single large chat room and then brainstorm the
toilet plunger AUT task in a CSI structure in which
the 75 individuals were broken up into approximately
15 subgroups of 5 individuals, each sub-group
including one AI agent (i.e., conversational surrogate)
that participated in the local conversation by sharing
ideas received from other subgroups. The second
group of 75 performed the same protocol, but
brainstormed traffic cones first in the CSI structure,
then brainstormed toilet plungers second in a standard
large chat room structure. At the conclusion of the
intervention, both groups were given a survey in
which they were asked a set of subjective judgment
questions to compare each brainstorming experience,
the single large room versus the CSI structure.
For clarity, when using CSI, each participant was
only able to converse with the other 4 members of
their subgroup and with a local AI agent. The agents
did not introduce any AI generated ideas or opinions
into local conversations – they only passed and
received conversational ideas and opinions from
other subgroups (every 30 to 60 seconds). This
weaved the set of 15 subgroups into a single unified
conversion in which individuals could build on ideas
raised in other subgroups and express their support or
opposition to ideas from in subgroups. A time limit of
12 minutes was provided for each brainstorm task.
3 DATA AND ANALYSIS
Each of the two groups of 75 participants took part in
a 30-minute session in which they performed two
AUT brainstorms for 12 minutes each (one using CSI
and one in a traditional chat room) and then
individually completed a subjective feedback survey
to compare the two experiences. The questions asked
on the survey were as follows:
• Which method felt more productive?
• Which method made you feel more heard?
• Which method felt more collaborative?
• Which method was surfaced better answers?
• Which method made you feel more buy-in?
• Which method made you feel more ownership?
• Which method did you prefer overall?
The only substantive difference between the two
groups of participants was that Group 1 brainstormed
in a standard chat room first, then used CSI, while the
participants of Groups 2 brainstormed using CSI first
and then used the standard chat room. This was to
mitigate ordering effects on the subjective feedback.
ICEIS 2025 - 27th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
870
In total we collected 147 surveys, each comparing
brainstorming and prioritization using a CSI structure
versus a traditional chat room. In the CSI structure,
the 75 individuals brainstormed by being divided into
15 subgroups of 5 people, each subgroup including an
AI agent that participated in their local conversation
to link all the subgroups together. In the standard chat
room structure, all 75 people were able to see the
ideas of everyone else and respond to the full group.
The results were highly conclusive, showing that
a significant majority of the 147 survey-responding
participants preferred the CSI structure to the
standard chat room structure in all seven questions
asked. To assess if these results were statistically
significant, a one-proportion z-test was performed on
each question in the surveys to test if the results
showed statistically significant evidence that more
people preferred one method over the other. Because
multiple statistical tests were run, we used a
Bonferroni adjustment to determine significance at
the 1% alpha level and needed to observe a p-
value<0.01/7=0.0014 for each of the 7 questions
tested. This level of significance was observed in each
of the seven questions, meaning we can conclude with
99% confidence that participants preferred the CSI
platform (Thinkscape) for brainstorming and
prioritization as compared to traditional text chat.
4 RESULTS
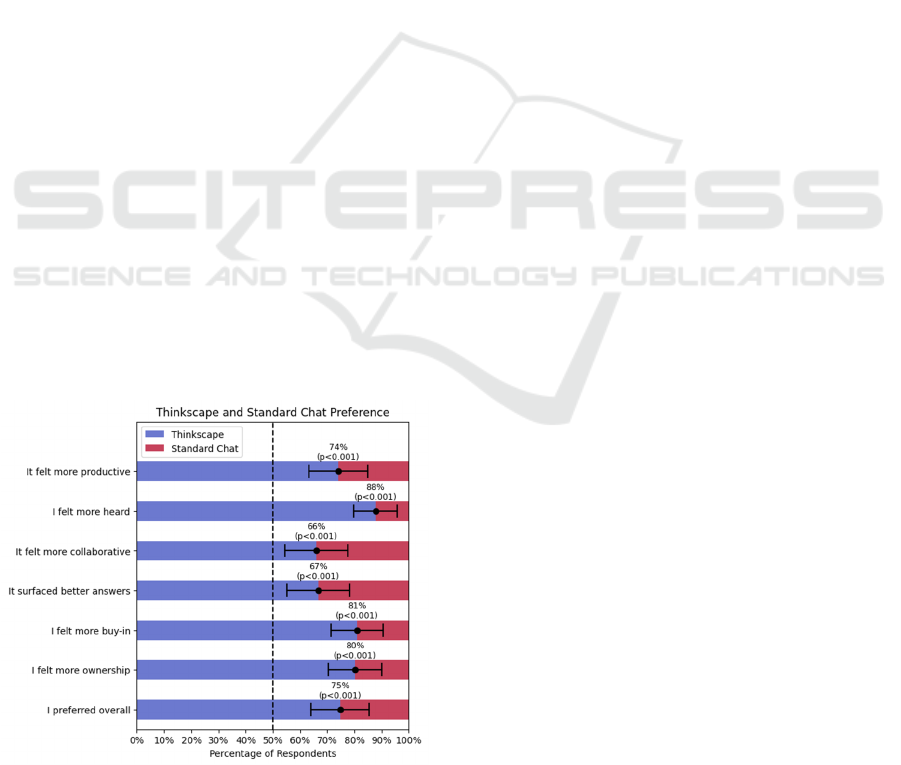
The segmented bar chart in Figure 4 below shows the
proportion of survey respondents that preferred either
Thinkscape or Standard Chat when answering each of
the feedback questions.
Figure 4. Subjective Feedback Results with Error Bars.
We can see in Fig. 4 that a significant majority of
participants preferred Thinkscape with respect to all
seven of the feedback questions, the support ranging
between 66% and 88%, with 75% of respondents
preferring Thinkscape overall. Each question in
Figure 4 also shows error-bars reflecting a 99%
Bonferroni-adjusted confidence interval estimating
the true proportion of all participants who would
prefer Thinkscape over a Standard Chat. None of the
confidence intervals overlap the 50% dotted line,
demonstrating statistical significance in our findings
that Thinkscape is the preferred method.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The results of this study are promising, showing that
groups of 75 individuals can successfully brainstorm
ideas and prioritize options in real-time using a text-
based CSI platform. The results further show that
participants significantly preferred the CSI structure
(which used AI agents to connect conversations in
real-time across many small subgroups) over the
traditional flat structure of a single chatroom.
In particular, they found the CSI structure to be
more productive, more collaborative, and more
effective at surfacing quality answers. In addition,
over 80% of participants in the study reported feeling
“more heard” during each deliberation and came
away feeling “more ownership” and “more buy-in”
with respect to the resulting answers than they did in
a traditional real-time chat environment.
Future studies into CSI should test collaborative
brainstorming and prioritization among significantly
larger groups to validate usage among hundreds or
thousands of simultaneous participants. Considering
that the average Fortune 1000 company has over
30,000 employees, the ability to engage large groups
in real-time discussions, brainstorms, evaluations,
debates, assessments and prioritizations could be a
powerful collaborative method for solving problems,
planning projects, forecasting outcomes, assessing
risks, capturing employee feedback, and fostering the
cross-pollination of ideas across large companies. In
addition, CSI could be useful for promoting buy-in
and fostering feelings of ownership within large and
complex project teams.
Future studies should also test the value of CSI in
voice-chat and videoconferencing environments. In
addition, future studies should explore the value of
CSI in vertical applications that could benefit from
group deliberation at massive scale. Examples of such
applications include citizen assemblies, deliberative
civic engagement, deliberative democracy, big
Large-Scale Group Brainstorming and Deliberation Using Swarm Intelligence and Generative AI
871

science, decentralized autonomous organizations
(DAOs), political forecasting, and market research.
And finally, future studies of CSI should test its
potential in enabling Collective Superintelligence to
be achieved among large, networked groups.
REFERENCES
Askay, D., Metcalf, L., Rosenberg, L., Willcox, G. (2019)
“Enhancing Group Social Perceptiveness through a
Swarm-based Decision-Making Platform.”
Proceedings of the 52nd Hawaii International
Conference on System Sciences (HICSS-52), IEEE.
Blair, Clancy & Gamson, David & Thorne, Steven &
Baker, David. (2005). Rising Mean IQ: Cognitive
Demand of Mathematics Education for Young
Children, Population Exposure to Formal Schooling,
and the Neurobiology of the Prefrontal Cortex.
Intelligence. 33. 93-106. 10.1016/j.intell.2004.07.008.
Bronkhorst, Adelbert W. (2000). "The Cocktail Party
Phenomenon: A Review on Speech Intelligibility in
Multiple-Talker Conditions". Acta Acustica United
with Acustica. 86: 117–128. Retrieved 2020-11-16.
Cooney, G., et. al. (2023) "The Many Minds Problem:
Disclosure in Dyadic vs. Group Conversation." Special
Issue on Privacy and Disclosure, Online and in Social
Interactions edited by L. John, D. Tamir, M. Slepian.
Current Opinion in Psychology 31 (February 2020):
22–27.
Habib S, Vogel T, Anli X, Thorne E. How does generative
artificial intelligence impact student creativity?. Journal
of Creativity. 2024 Apr 1;34(1):100072.
Guilford, J. P. (1967). The Nature of Human Intelligence.
McGraw-Hill.
Krause, J., Ruxton, G.D., & Krause, S. (2010). Swarm
intelligence in animals and humans. Trends in ecology
& evolution, 25 1, 28-34
Parrish, J. K., Viscido, S. and Grünbaum, D. (2002) “Self-
Organized Fish Schools: An Examination of Emergent
Properties.” Biological Bulletin 202, no. 3: 296–305
Rosenberg, L. (2015) “Human Swarms, a real-time method
for collective intelligence.” Proceedings of the
European Conference on Artificial Life, pp. 658-659
Rosenberg, L. (2016). Artificial Swarm Intelligence vs
human experts. 2016 International Joint Conference on
Neural Networks (IJCNN), 2547-2551.
Rosenberg, L., Willcox, G., Schumann, H. and Mani, G.
(2023) “Conversational Swarm Intelligence (CSI)
Enhances Groupwise Deliberation.” 7th International
Joint Conference on Advances in Computational
Intelligence (IJCACI 2023). Oct 14, 2023. New Delhi.
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-0180-3_1
Rosenberg, L., Schumann, H., Dishop, C., Willcox, G.,
Woolley, A. and Mani, G. (2024). Conversational
Swarms of Humans and AI Agents enable Hybrid
Collaborative Decision-making. IEEE UEMCON
2024. DOI: 10.1109/UEMCON62879.2024.10754763
Rosenberg, L., Willcox, G., Schumann, H. and Mani, G.
(2024). Towards Collective Superintelligence:
Amplifying Group IQ Using Conversational Swarms.
In Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on
Enterprise Information Systems - Volume 1: ICEIS;
ISBN 978-989-758-692-7; SciTePress, pages 759-766.
DOI: 10.5220/0012687500003690
Willcox, G., Rosenberg, L., Domnauer, C. and Schumann,
H., 2021, October. Hyperswarms: a new architecture
for amplifying collective intelligence. In 2021 IEEE
12th Annual Information Technology, Electronics and
Mobile Communication Conference (IEMCON) (pp.
0858-0864). IEEE.
ICEIS 2025 - 27th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
872
