
Dataset Generation for Egyptian Arabic Sign Language
Mariam Ibrahim
1 a
, Milad Ghantous
2 b
and Nada Sharaf
1 c
1
Faculty of Informatics and Computer Science, German International University, Cairo, Egypt
2
Faculty of Media Engineering and Technology, German University in Cairo, Cairo, Egypt
Keywords:
Egyptian Arabic Sign Language (EASL), Sign Language Recognition, Sign Language Datasets, Text-Video
Alignment, Landmark Detection, Skeletal Joint Points, Arabic Sign Languages, Dialect-Specific Sign
Language, Cultural Representation, Machine Learning in Sign Language Translation, Accessibility, Deaf
Community, Gesture Synchronization, Continuous Sign Language Recognition, Computer Vision,
Non-Western Sign Languages, Linguistic Diversity.
Abstract:
This literature review explores the existing body of work related to Egyptian Arabic Sign Language (EASL)
datasets, focusing on translation and text-to-video alignment, and examining relevant hand and face landmark
detection methodologies, including the use of skeletal joint point analysis. With a particular emphasis on the
research gaps in datasets, alignment accuracy, and computer vision models tailored for Arabic dialects, this
review aims to highlight the limitations and challenges within current literature. Despite advancements in
general sign language research, EASL remains understudied, leaving significant gaps in the development of
resources and tools for accurate gesture translation and synchronization. The review concludes by identifying
the need for dialect-specific resources and advanced alignment techniques to support the growth of accessible,
region-specific sign language datasets.
1 INTRODUCTION
The study of sign language recognition and transla-
tion represents a rapidly evolving field at the inter-
section of linguistics, computer vision, and artificial
intelligence. Recent advancements have enabled re-
searchers to bridge critical communication gaps be-
tween Deaf and hearing communities, making infor-
mation and services more accessible worldwide.
Various initiatives have been developed to sup-
port individuals with hearing impairments in differ-
ent settings, particularly in educational environments.
Tools have been developed to automatically annotate
lectures live and provide comprehensive notes espe-
cially for students using Arabic (Nasser et al., 2020;
Mohamed et al., 2021). The availability of relevant
sign language generators can significantly enhance
this support by making lectures more engaging and
accessible. Such technologies would enable hearing-
impaired students to follow along more easily, pro-
moting greater engagement and understanding in the
classroom. Efforts have also been made to digitize
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0006-9560-2312
b
https://orcid.org/0009-0008-1726-6987
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0681-6743
various aspects of the Arabic language and its di-
alects especially with the advancement of the recog-
nition and use of Arabic speech (Nabil et al., 2024;
Safwat et al., 2023). This digitization is crucial in en-
abling users in this digital era to access Arabic tools
across different domains, facilitating broader engage-
ment and utilization of technology in their native lan-
guage (Akila et al., 2015; Kassem et al., 2016).
There are various requirements central to these ad-
vancements including are datasets and models that
aim to capture the linguistic and gestural complex-
ity of various sign languages. While significant
progress has been made in recognizing and trans-
lating widely studied sign languages like American
Sign Language (ASL) and British Sign Language
(BSL), there remains a critical gap in resources and
tools for underrepresented sign languages, particu-
larly those from non-Western contexts. Egyptian
Arabic Sign Language (EASL) is one such underex-
plored language that presents unique challenges and
opportunities for researchers. EASL is uniquely sit-
uated within the linguistic landscape, combining el-
ements of Modern Standard Arabic, Egyptian Ara-
bic dialects, and influences from other sign lan-
guages in the region. This complexity underscores
Ibrahim, M., Ghantous, M. and Sharaf, N.
Dataset Generation for Egyptian Arabic Sign Language.
DOI: 10.5220/0013380100003890
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2025) - Volume 3, pages 1419-1426
ISBN: 978-989-758-737-5; ISSN: 2184-433X
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
1419

the need for specialized datasets and recognition mod-
els that can capture the nuances of EASL’s gram-
matical structure, hand shapes, and facial expres-
sions (Papastratis et al., 2021). Recent studies have
highlighted the importance of developing compre-
hensive datasets and recognition systems for Arabic
Sign Languages. (Aloysius and Geetha, 2020) con-
ducted a thorough review of vision-based continu-
ous sign language recognition, emphasizing recent
deep learning advancements. (Aloysius and Geetha,
2020) introduced a framework using DeepLabv3+
and BiLSTM for Arabic sign language recognition,
yielding promising results (Papastratis et al., 2021).
Additionally, (Elnasharty, 2024a) proposed a real-
time sign language detection model using TensorFlow
and OpenCV, demonstrating the potential for more
dynamic EASL recognition systems. Challenges
in studying EASL are multifaceted, ranging from
linguistic complexities to technological limitations.
EASL gestures often involve unique combinations
of hand shapes, orientations, and facial expressions
that differ significantly from Western sign languages
(Moustafa et al., 2024). These elements are deeply
tied to Egyptian culture and social norms, making
them less amenable to standard models trained on
ASL or BSL datasets (Moustafa et al., 2024). A
promising avenue of research lies in the integration
of advanced machine learning techniques. Methods
like graph convolutional networks (GCNs) and recur-
rent neural networks (RNNs) have shown potential in
capturing the dynamic interactions of hand gestures
and facial expressions, which are central to EASL
communication (Papastratis et al., 2021). Such ap-
proaches not only offer a pathway to more accurate
recognition but also address the limitations of tradi-
tional landmark detection frameworks. This intro-
duction prepares for a detailed review of methods
relevant to Egyptian Arabic Sign Language (EASL),
highlighting advancements in sign language datasets,
alignment technologies, and landmark detection. The
review seeks to identify key gaps in EASL research,
aiming to develop technologies that are inclusive and
responsive to the needs of the Egyptian Deaf commu-
nity, thereby enhancing accessibility and representa-
tion in sign language studies.
2 BACKGROUND AND RELATED
WORK
This section provides a comprehensive review of
the existing research in the field of sign language
recognition and translation, with a particular focus
on Egyptian Arabic Sign Language (EASL). It ex-
plores the foundational contributions made in devel-
oping datasets, alignment techniques, and landmark
detection models, which have advanced the study
of sign language recognition globally. While sig-
nificant progress has been made for widely studied
languages like American Sign Language (ASL) and
British Sign Language (BSL), this review highlights
the challenges and gaps in adapting these methods
to culturally and linguistically distinct languages like
EASL.
The subsequent sections address the development
and application of sign language datasets, particularly
for Arabic dialects, and discuss text-video alignment
for translation and advancements in landmark detec-
tion for gesture recognition. The review highlights the
need for culturally tailored resources and innovative
approaches to enhance representation for languages
like EASL, aiming to support future research that fo-
cuses on inclusivity and accessibility in sign language
recognition and translation.
2.1 Egyptian Arabic Sign Language
(EASL)
Egyptian Arabic Sign Language (EASL) is a dis-
tinct and complex language within the broader con-
text of Arabic sign languages. Its unique phono-
logical structure relies on specific hand orientations
and facial expressions to encode grammatical mean-
ing, setting it apart from other sign languages like
ASL or Gulf Arabic Sign Language (Younes et al.,
2023; Mohamed, 2024). Recent research has high-
lighted the importance of capturing the full linguis-
tic richness of EASL, including its regional varia-
tions and continuous signing patterns. The devel-
opment of EASL-specific datasets has seen signifi-
cant progress in recent years. The ArSL2018 dataset,
introduced by (Rastgoo et al., 2020) contains over
54,000 images of Arabic Sign Language gestures,
providing a substantial foundation for research. How-
ever, this dataset primarily focuses on isolated signs
and may not fully capture the complexities of continu-
ous signing in EASL. More recent efforts have aimed
to address these limitations that proposed a real-time
sign language detection model using TensorFlow and
OpenCV, demonstrating the potential for more dy-
namic EASL recognition systems (Bani Baker et al.,
2023). Additionally, (Mosleh et al., 2024) introduced
a vision-based method for identifying Arabic hand
signs and converting them to Arabic speech, achiev-
ing a 90% recognition rate. The multimodal nature of
EASL, combining hand shapes, orientations, move-
ments, and facial expressions, continues to pose chal-
lenges for existing models (Mohamed, 2024). Recent
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
1420

studies have explored various deep learning archi-
tectures to capture these complexities. For instance,
(Latif et al., 2020) utilized transfer learning and deep
CNN fine tuning to enhance the recognition accu-
racy of 32 hand motions in ArSL (Elnasharty, 2024a).
Expanding datasets to include diverse regional varia-
tions and continuous signing remains crucial for ad-
vancing EASL research. Given Egypt’s central role
in the Arab world, advancements in EASL research
could significantly impact the development of inclu-
sive technologies for Arabic-speaking Deaf commu-
nities across the region (Hassan et al., 2024). Fu-
ture research directions should focus on creating more
comprehensive EASL datasets that capture regional
dialects, continuous signing, and the full range of lin-
guistic features. This will enable the development
of more accurate and culturally sensitive recognition
systems, ultimately improving communication acces-
sibility for the Egyptian Deaf community.
2.2 Sign Language Datasets
The development of comprehensive sign language
datasets is foundational to advancing sign language
recognition and translation technologies. Recent ad-
vancements in dataset creation have focused on un-
derrepresented languages, including Egyptian Arabic
Sign Language (EASL). Multimodal datasets incor-
porating RGB-D videos and skeletal joint tracking
have been explored to capture the intricacies of non-
Western sign languages, highlighting the importance
of cultural and linguistic specificity in dataset design
(Adaloglou et al., 2021; Al-Shamayleh et al., 2020).
Pioneering contributions include the American
Sign Language Lexicon Video Dataset (ASLLVD),
which provides a lexicon-based collection of isolated
ASL signs (Neidle et al., 2012; Adaloglou et al.,
2021), and the RWTH-PHOENIX-Weather dataset,
which captures continuous signing in German Sign
Language (GSL) (Koller et al., 2015; Camgoz et al.,
2018). These datasets have advanced understand-
ing of temporal dependencies and syntactic structures
in sign language. However, their language-specific
focus limits applicability to languages with differ-
ing grammar, lexicon, and cultural nuances, such as
EASL (Bakalla, 1975; Tharwat et al., 2021).
Efforts to create datasets tailored to Arabic sign
languages remain sparse but promising. For instance,
the Kafr El Sheikh Dataset offers a small-scale re-
source for EASL, focusing on basic linguistic features
and gestures. Expanding such datasets to address con-
tinuous signing and regional variations will be crucial
for further advancements (Al-Shamayleh et al., 2020;
Luqman and El-Alfy, 2021).
Table 1: Summary of Sign Language Datasets.
Dataset Language Features Limitations
ASLLVD ASL Isolated signs,
lexicon-based
Limited to iso-
lated signs
RWTH-
PHOENIX-
Weather
GSL Continuous sign-
ing on temporal
dependencies
does not work
with different
grammar
KafrEl-
Sheikh
Dataset
EASL Small scale re-
source, Basic lin-
guistic
does not ad-
dress regional
variations
General
Multimodal
Datasets
Various RGB-D videos,
skeletal tracking
required to tai-
lor datasets
2.3 Sign Language Translation and
Text-Video Alignment
Recent advancements in dataset generation and align-
ment for sign language recognition have focused on
improving automation and addressing the challenges
of culturally specific sign languages. Here are some
key developments from 2023-2024:
Automated Annotation and Alignment: Recent
studies have explored more efficient methods to an-
notate and align sign language videos with text. (El-
nasharty, 2024b) proposed a real-time sign language
detection model using TensorFlow and OpenCV,
demonstrating potential for dynamic EASL recogni-
tion systems. This approach could significantly re-
duce the manual effort required in annotation.
Cross-Modal Learning: (Aly et al., 2024) intro-
duced a deep learning framework combining CNNs
and LSTMs for Arabic sign language recognition,
achieving high accuracy in capturing both spatial and
temporal features. This method shows promise for
handling the complex multimodal aspects of EASL,
including facial expressions and hand movements.
Large-Scale Datasets: The development of larger,
more diverse datasets has been crucial. (Jiang et al.,
2024) highlighted the importance of expanding sign
language datasets to include regional variations and
continuous signing patterns. While not specific to
EASL, these principles are applicable and essential
for developing robust EASL recognition systems.
Transformer-Based Models: Transformer models
have shown significant potential in sign language pro-
cessing. (Bani Baker et al., 2023) utilized transfer
learning and vision transformer approaches for Ara-
bic Sign Language recognition, demonstrating im-
proved performance in capturing the nuances of Ara-
bic sign languages.
Dataset Generation for Egyptian Arabic Sign Language
1421

2.4 Hand and Face Landmark
Detection in Sign Language Videos
Advancements in hand and face landmark detection
have significantly enhanced sign language recogni-
tion systems by capturing crucial gesture and ex-
pression data, essential for accurate interpretation.
This is particularly impactful for non-Western lan-
guages like Egyptian Arabic Sign Language (EASL).
Google’s MediaPipe framework excels in real-time
gesture recognition and sign language detection by in-
tegrating hand, face, and pose estimation. The frame-
work’s ability to extract 3D hand landmarks from 2D
images has made it particularly useful for sign lan-
guage recognition, offering a cost-effective and effi-
cient solution (Podder et al., 2023). However, chal-
lenges remain when applying these frameworks to
non-Western sign languages like EASL. Cultural dif-
ferences in hand gestures and facial expressions can
lead to misinterpretations or reduced accuracy. To
address this, researchers have proposed hybrid mod-
els that combine deep learning techniques with graph
neural networks (GNNs) to better capture the nuanced
gestures and expressions in EASL (Miah et al., 2023).
Recent studies have explored the use of Convolutional
Neural Networks (CNNs) in conjunction with Long
Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks to improve
the accuracy of sign language recognition. This ap-
proach, known as CNNSa-LSTM, has shown promis-
ing results in capturing both spatial and temporal fea-
tures of sign language gestures(Podder et al., 2023).
The integration of self-attention mechanisms in these
models has further enhanced their ability to focus
on relevant features, improving overall performance
(Baihan et al., 2024). To overcome the limitations of
existing datasets, researchers have begun developing
more comprehensive and diverse datasets specific to
Arabic Sign Languages. For instance, the RGB Ara-
bic Alphabet Sign Language (AASL) dataset, com-
prising 7,857 raw and fully labelled RGB images of
Arabic sign language alphabets, has become a valu-
able resource for training and evaluating recognition
models (Al-Barham et al., 2023). Additionally, ef-
forts are being made to create datasets that capture the
regional variations and continuous signing patterns
unique to EASL (Al-Barham et al., 2023). The devel-
opment of real-time sign language detection models
using frameworks like TensorFlow and OpenCV has
demonstrated the potential for more dynamic EASL
recognition systems (Elnasharty, 2024a). These ad-
vancements, combined with the growing availability
of EASL-specific datasets, are paving the way for
more accurate and culturally sensitive sign language
recognition technologies. As research in this field
continues to evolve, there is a growing focus on devel-
oping models that can adapt to the unique character-
istics of EASL, including its regional variations and
complex grammatical structures. Recent work has ex-
plored the use of YOLOv8, a cutting-edge object de-
tection algorithm, for real-time sign language recog-
nition, achieving high accuracy rates. Furthermore,
the integration of large language models (LLMs) with
sign language recognition systems is opening new
possibilities for more natural and context-aware com-
munication interfaces (Ahmad et al., 2024). These
ongoing advancements promise to enhance commu-
nication accessibility for the Egyptian Deaf commu-
nity and contribute to the broader goals of inclusive
technology development. As the field progresses, we
can expect to see more sophisticated, real-time, and
culturally sensitive sign language recognition systems
that bridge the communication gap between deaf and
hearing individuals.
2.5 Sign Language Recognition
The ability to accurately recognize sign language is a
cornerstone of bridging communication gaps between
deaf and hearing communities. Recent advancements
in sign language recognition leverage cutting-edge
technologies to improve accuracy and scalability, en-
abling applications ranging from real-time translation
to gesture-based human-computer interaction. This
subsection explores two critical aspects of sign lan-
guage recognition: multimodal approaches that inte-
grate various input modalities to enhance recognition
accuracy and real-time systems designed for practical
deployment.
Multimodal systems combine data from hand ges-
tures, facial expressions, skeletal motion, and even
audio cues, creating a richer representation of sign
language input. These approaches are particularly
valuable for addressing the complexities of languages
like Egyptian Arabic Sign Language (EASL), where
non-manual features such as facial expressions play
a critical grammatical role (Tharwat et al., 2021;
Luqman and El-Alfy, 2021). In parallel, real-
time recognition systems are increasingly viable due
to advancements in computational efficiency, such
as lightweight neural architectures and transformer-
based models, which maintain high accuracy with low
latency (Vaswani et al., 2017; Attia et al., 2023). To-
gether, these innovations set the stage for developing
inclusive and culturally specific recognition systems
tailored to the needs of underrepresented languages
like EASL.
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
1422

2.5.1 Multimodal Approaches for Sign
Language Recognition
Multimodal approaches enhance sign language recog-
nition by combining hand gestures, facial expres-
sions, and skeletal motion with advanced RGB-D
cameras and inertial sensors. These methods effec-
tively capture the detailed motions crucial for under-
standing EASL, where hand movements and facial
expressions are closely linked (Tharwat et al., 2021;
Luqman and El-Alfy, 2021).
For instance, studies using depth-based sensors
have demonstrated improvements in gesture segmen-
tation and recognition by providing three-dimensional
spatial data that traditional video methods lack (Ren
et al., 2013; Al-Shamayleh et al., 2020). Addition-
ally, the integration of audio modalities for translating
speech to sign language has opened new avenues for
real-time applications, enabling more accessible tech-
nologies for the hearing-impaired (Cao et al., 2019;
Adaloglou et al., 2021).
2.5.2 Real-Time Sign Language Recognition
Real-time sign language recognition systems have
gained traction with the increasing computational
power of edge devices and advancements in model
optimization. Techniques involving lightweight con-
volutional models and quantized neural networks
have made it feasible to deploy recognition systems
on mobile and embedded platforms (Tharwat et al.,
2021).
For EASL, real-time systems must account for
cultural and linguistic nuances, including rapid ges-
ture transitions and context-dependent facial expres-
sions. Solutions such as attention-based LSTMs and
transformer-based architectures have shown promise
in achieving high accuracy while maintaining low la-
tency (Attia et al., 2023; Luqman and El-Alfy, 2021).
By integrating these approaches with multimodal in-
puts, real-time systems can provide robust perfor-
mance in diverse environments.
2.6 Sign Language Generation
Sign language generation (SLG) complements recog-
nition efforts by producing sign language content in
forms such as animations, avatars, or synthesized
videos. SLG plays a crucial role in accessibility for
Deaf communities by visually representing spoken or
written text. However, SLG faces unique technical
challenges, particularly for non-Western languages
like Egyptian Arabic Sign Language (EASL). The
primary issues include the lack of annotated datasets
that capture cultural nuances and grammatical struc-
tures, and the complexity of replicating EASL’s mul-
timodal nature, where subtle facial expressions and
intricate hand movements convey critical meaning.
Challenges and Opportunities: Existing SLG
systems often rely on datasets and models designed
for Western sign languages such as ASL or German
Sign Language, which struggle with EASL’s unique
syntactic and morphological features (Stoll et al.,
2020; Camgoz et al., 2018). Advances in compu-
tational frameworks, such as HamNoSys and neu-
ral motion retargeting, offer promising pathways for
generating linguistically rich content for non-Western
languages like EASL (Prikhodko et al., 2020; Zhang
et al., 2022).
Avatars and Animation: Virtual sign language
avatars are a popular medium in SLG. Motion capture
technology and linguistic rules, as demonstrated by
(McDonald et al., 2016), enable these avatars to pro-
duce sign language gestures. However, their move-
ments often lack the fluidity and cultural authenticity
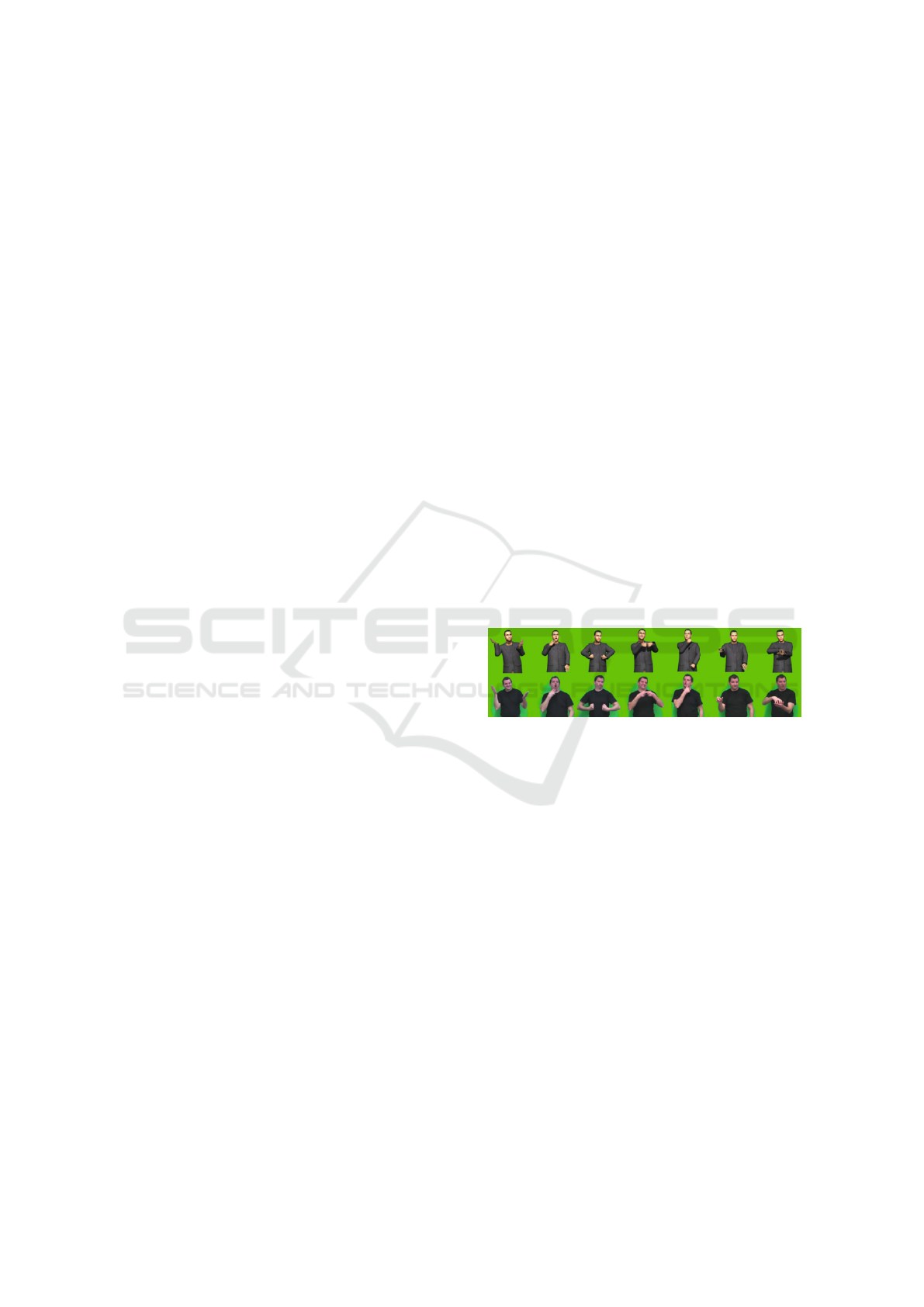
required for natural communication as shown in fig-
ure 1 (Kipp et al., 2011). In contrast, 3D animation
techniques utilize kinematic models to create lifelike
gestures, but they require significant computational
resources and specialized expertise.
Figure 1: Sign Language Avatars: Animation and Compre-
hensibility (from (Kipp et al., 2011)).
Video Synthesis: Recent advancements in deep
learning, such as GAN-based models like SignGAN
(Stoll et al., 2020), have introduced new capabilities
for generating realistic signing videos. Pose-based
representations, such as those proposed by (Natara-
jan and Elakkiya, 2022), enhance temporal consis-
tency and visual accuracy in synthesized videos. For
EASL, these methods hold particular promise due to
their ability to capture gesture variations and cultural
nuances.
Models and Frameworks: Gloss-to-sign
pipelines translate linguistic gloss annotations into
sign language animations or videos. Neural machine
translation techniques, including Transformers, have
been adapted to improve temporal alignment and
naturalness in gloss-to-sign generation (Camgoz
et al., 2018). Text-to-sign pipelines, which extend
this process to raw text input, present broader chal-
lenges, requiring sophisticated parsing and semantic
understanding to produce culturally relevant signs.
Dataset Generation for Egyptian Arabic Sign Language
1423
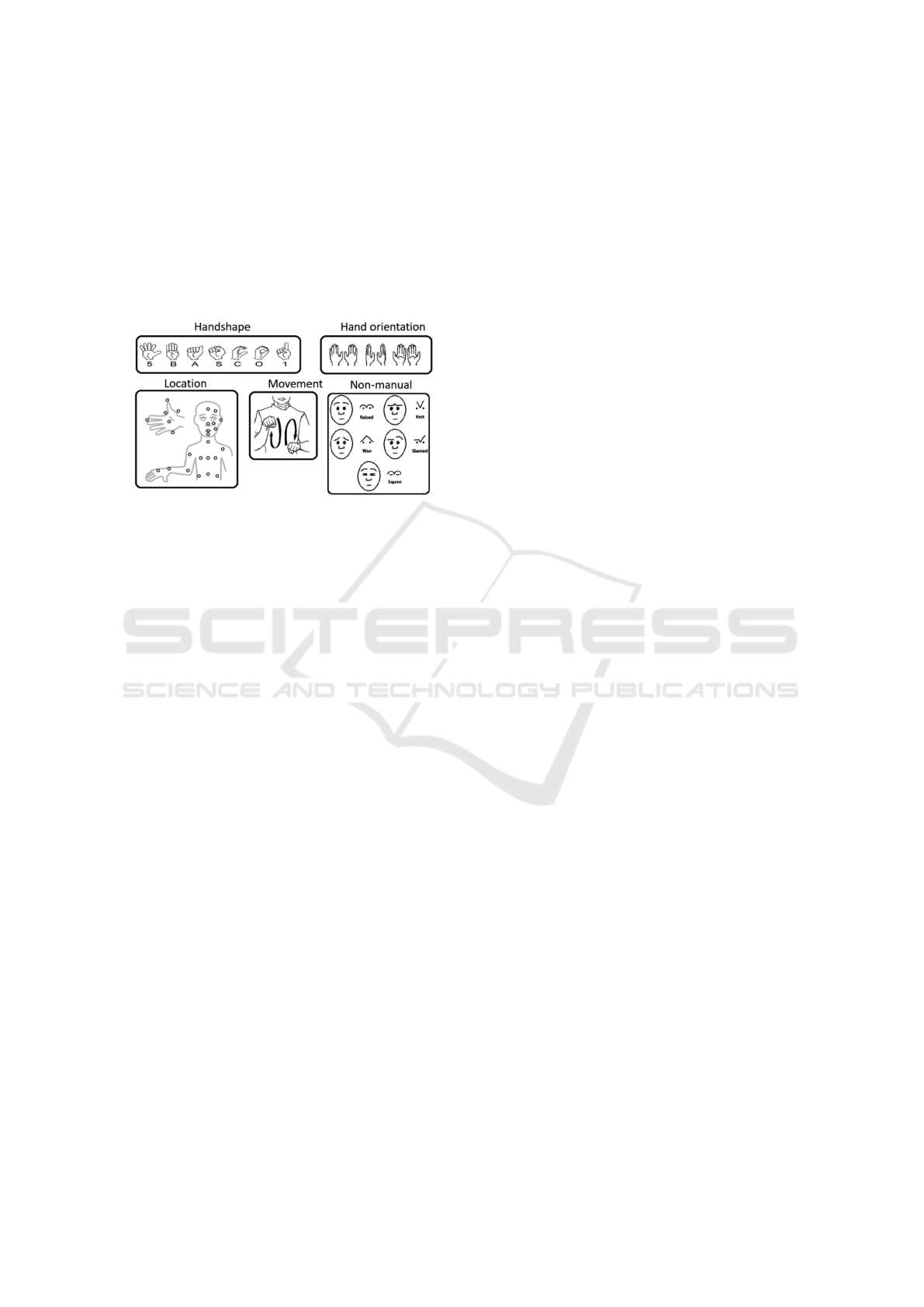
Encoding Systems: Frameworks like HamNoSys
(Prikhodko et al., 2020) and SignWriting (Grushkin,
2017) provide structured ways to encode sign lan-
guage gestures. HamNoSys captures detailed infor-
mation about hand shapes, movements, and orien-
tations, making it valuable for animating avatars as
shown in figure 2. SignWriting, a visually intuitive
method for documenting signs, is increasingly inte-
grated into computational pipelines for SLG.
Figure 2: The five components of signs in sign languages
(from (Prikhodko et al., 2020)).
Hybrid Approaches: Hybrid models that com-
bine avatars with GAN-based video synthesis aim to
balance realism with scalability. These systems gen-
erate lifelike gestures while leveraging the flexibility
of digital avatars to ensure accessibility (Stoll et al.,
2020).
Synthetic Data Generation for Sign Language:
Synthetic data generation using techniques such as
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and 3D
avatar-based simulations has emerged as a promising
solution to address the scarcity of large-scale sign lan-
guage datasets (Natarajan and Elakkiya, 2022). For
EASL, synthetic data generation can mitigate chal-
lenges posed by regional variability and limited data
availability. By simulating culturally specific gestures
and facial expressions, researchers can train mod-
els more effectively, reducing overfitting to Western-
dominated datasets. Recent work has also explored
the use of motion-capture systems to generate high-
fidelity skeletal data that aligns closely with real-
world EASL signing (Adaloglou et al., 2021; Luqman
and El-Alfy, 2021).
3 RESEARCH GAP
The research landscape for Egyptian Arabic Sign
Language (EASL) reveals significant gaps across lin-
guistic, technological, and cultural domains. While
there have been advancements in Arabic Sign Lan-
guage recognition, notably by Aly (2024) and Bani
(2023), EASL-specific challenges persist. The lack
of extensive datasets that capture EASL’s regional
variations and dialectal complexities hinders the de-
velopment of effective recognition models. Current
datasets, like ArSL2018, focus mainly on isolated
signs and do not adequately represent the dynamic na-
ture of natural EASL communication.
Current sign language recognition systems, as
highlighted by Aloysius (2020), show a bias to-
wards analyzing hand gestures alone, overlooking the
critical role of facial expressions and body posture
in EASL. This oversight limits the effectiveness of
recognition models, which fail to capture the full
range of EASL communication. Moreover, the inade-
quacy of existing frameworks like MediaPipe in accu-
rately detecting EASL-specific gestures calls for the
development of culturally adapted computer vision al-
gorithms. Aligning EASL gestures with textual rep-
resentations poses a significant challenge, with cur-
rent methods struggling to capture the unique tim-
ing and non-verbal elements of EASL. This issue
is compounded by regional variations across Egypt,
as Alotaibi (2023) notes, adding variability to ges-
ture execution and interpretation. Additionally, the
potential of using Generative Adversarial Networks
(GANs) to enhance EASL datasets is underexplored.
While promising for addressing data scarcity, their
use must carefully preserve cultural and linguistic
authenticity to accurately reflect natural signing nu-
ances.
The development of real-time EASL recognition
systems, while progressing as demonstrated by (El-
nasharty, 2024b), still faces significant challenges
in terms of efficiency, accuracy, and adaptability
to diverse signing styles and environmental condi-
tions. This gap is particularly pronounced in resource-
constrained settings, where high-performance com-
puting infrastructure may not be readily available.
Addressing these interconnected challenges requires
a multidisciplinary approach that integrates advanced
machine learning techniques, linguistic expertise, and
cultural insights. The resolution of these research
gaps is crucial not only for advancing the field of sign
language recognition but also for developing inclusive
technologies that can significantly enhance communi-
cation accessibility for the Egyptian Deaf community
and potentially serve as a model for other underrepre-
sented sign languages globally.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The studies reviewed highlight advancements in sign
language recognition, especially in datasets, transla-
tion models, and landmark detection for ASL and
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
1424

BSL. Yet, Egyptian Arabic Sign Language (EASL)
remains underexplored. Current tools often under-
perform for EASL due to their reliance on Western
sign language datasets that do not account for EASL’s
unique structures and cultural nuances. Future re-
search should focus on developing comprehensive
EASL datasets, employing multimodal approaches
for gesture analysis, and creating adaptive models
that recognize the linguistic and cultural specifics
of EASL, including its use of facial expressions for
grammatical context.
Efforts to address gaps in sign language recog-
nition should involve collaborative research between
linguists, computer scientists, and the Deaf commu-
nity. This interdisciplinary approach aims to develop
resources that are linguistically precise and culturally
representative. Progress in tackling EASL-specific
challenges could inform similar advancements for
other underrepresented sign languages, setting new
standards for inclusivity and cultural sensitivity. This
would enhance communication access and improve
the quality of life for Deaf communities both in Egypt
and globally.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This paper acknowledges the use of OpenAI’s Chat-
GPT for generating text in sections discussing related
work and proposed research gaps. The AI-generated
content was reviewed and revised to ensure accuracy
and alignment with the paper’s objectives.
REFERENCES
Adaloglou, N., Kouris, L., Theodorakis, S., et al. (2021). A
comprehensive study on deep learning-based methods
for sign language recognition. IEEE Transactions on
Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence.
Ahmad, S. I., Sabir, N., Abid, A., and Hussain, A. (2024).
Sign assist: Real-time isolated sign language recog-
nition and translator model connecting sign language
users with gpt model. In Proc. AVSEC 2024, pages
82–88.
Akila, G., El-Menisy, M., Khaled, O., Sharaf, N., Tarhony,
N., and Abdennadher, S. (2015). Kalema: Digitizing
arabic content for accessibility purposes using crowd-
sourcing. In Computational Linguistics and Intelli-
gent Text Processing: 16th International Conference,
CICLing 2015, Cairo, Egypt, April 14-20, 2015, Pro-
ceedings, Part II 16, pages 655–662. Springer.
Al-Barham, M., Alsharkawi, A., Al-Yaman, M., Al-
Fetyani, M., Elnagar, A., SaAleek, A. A., and Al-
Odat, M. (2023). Rgb arabic alphabets sign language
dataset. arXiv preprint arXiv:2301.11932.
Al-Shamayleh, A. S., Ahmad, R., Jomhari, N., and
Abushariah, M. A. (2020). Automatic arabic sign
language recognition: A review, taxonomy, open
challenges, research roadmap and future directions.
Malaysian Journal of Computer Science, 33(4):306–
343.
Aloysius, N. and Geetha, M. (2020). Understanding vision-
based continuous sign language recognition. Multime-
dia Tools and Applications, 79(31):22177–22209.
Aly, S., Osman, B., Aly, W., and Saber, M. (2024).
Arabic sign language recognition using deep ma-
chine learning. Multimedia Tools and Applications,
80(15):22331–22354.
Attia, N. F., Ahmed, M. T. F. S., and Alshewimy, M. A.
(2023). Efficient deep learning models based on ten-
sion techniques for sign language recognition. Intelli-
gent systems with applications, 20:200284.
Baihan, A., Alutaibi, A. I., Alshehri, M., and Sharma, S. K.
(2024). Sign language recognition using modified
deep learning network and hybrid optimization: a hy-
brid optimizer (ho) based optimized cnnsa-lstm ap-
proach. Scientific Reports, 14(1):26111.
Bakalla, M. H. (1975). Bibliography of Arabic linguistics.
Mansell London.
Bani Baker, Q., Alqudah, N., Alsmadi, T., and Awawdeh,
R. (2023). Image-based arabic sign language recogni-
tion system using transfer deep learning models. Ap-
plied Computational Intelligence and Soft Computing,
2023(1):5195007.
Camgoz, N. C., Koller, O., Hadfield, S., and Bowden, R.
(2018). Neural sign language translation. Proceedings
of CVPR.
Cao, Z., Hidalgo, G., Simon, T., Wei, S.-E., and Sheikh, Y.
(2019). Openpose: Realtime multi-person 2d pose es-
timation using part affinity fields. IEEE Transactions
on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence.
Elnasharty, M. S. (2024a). Using deep learning technology
for real-time sign language detection and recognition
at public libraries in egypt: An experimental study.
Scientific Journal of Library, Archives & Information
(SJLAI), 6(17).
Elnasharty, M. S. (2024b). Using deep learning technology
for real-time sign language detection and recognition
at public libraries in egypt: An experimental study.
Scientific Journal of Libraries, Documents and Infor-
mation, 6(1).
Grushkin, D. A. (2017). Writing signed languages: What
for? what form? American annals of the deaf,
161(5):509–527.
Hassan, M. A., Ali, A. H., and Sabri, A. A. (2024).
Enhancing communication: Deep learning for ara-
bic sign language translation. Open Engineering,
14(1):20240025.
Jiang, X. et al. (2024). Recent advances on deep learning
for sign language recognition. Computer Modeling in
Engineering & Sciences, 139(3):2399–2450.
Kassem, L., Sabty, C., Sharaf, N., Bakry, M., and Abden-
nadher, S. (2016). tashkeelwap: A game with a pur-
pose for digitizing arabic diacritics.
Dataset Generation for Egyptian Arabic Sign Language
1425

Kipp, M., Heloir, A., and Nguyen, Q. (2011). ign language
avatars:animation and comprehensibility. In Intelli-
gent Virtual Agents: 10th International Conference,
IVA 2011, Reykjavik, Iceland, September 15-17, 2011.
Proceedings 11, pages 113–126. Springer.
Koller, O., Zargaran, S., Ney, H., and Bowden, R. (2015).
Continuous sign language recognition: Towards large
vocabulary statistical recognition systems handling
multiple signers. Computer Vision and Image Under-
standing, 141:108–125.
Latif, G., Mohammad, N., AlKhalaf, R., AlKhalaf, R., Al-
ghazo, J., and Khan, M. (2020). An automatic arabic
sign language recognition system based on deep cnn:
An assistive system for the deaf and hard of hearing.
International Journal of Computing and Digital Sys-
tems, 9(4):715–724.
Luqman, H. and El-Alfy, E.-S. M. (2021). Towards hy-
brid multimodal manual and non-manual arabic sign
language recognition: marsl database and pilot study.
Electronics, 10(14):1739.
McDonald, J., Wolfe, R., Schnepp, J., Hochgesang, J., Jam-
rozik, D. G., Stumbo, M., Berke, L., Bialek, M., and
Thomas, F. (2016). An automated technique for real-
time production of lifelike animations of american
sign language. Universal Access in the Information
Society, 15:551–566.
Miah, A. S. M., Hasan, M. A. M., Jang, S.-W., Lee, H.-S.,
and Shin, J. (2023). Multi-stream general and graph-
based deep neural networks for skeleton-based sign
language recognition.
Mohamed, A., Nasser, N., and Sharaf, N. (2021). Auto-
matic code-switched lecture annotation. In Interactive
Mobile Communication, Technologies and Learning,
pages 464–477. Springer.
Mohamed, N. A. E. (2024). Arabic sign language and vi-
tal signs monitoring using smart gloves for the deaf.
Engineering Research Journal (Shoubra), 53(2):185–
191.
Mosleh, M. A., Assiri, A., Gumaei, A. H., Alkhamees,
B. F., and Al-Qahtani, M. (2024). A bidirectional ara-
bic sign language framework using deep learning and
fuzzy matching score. Mathematics, 12(8):1155.
Moustafa, A., Rahim, M. M., Khattab, M. M., Zeki, A. M.,
Matter, S. S., Soliman, A. M., and Ahmed, A. M.
(2024). Arabic sign language recognition systems: A
systematic review. Indian Journal of Computer Sci-
ence and Engineering, 15:1–18.
Nabil, M., Abdalla, A., Sharaf, N., and Sabty, C. (2024).
Bridging the gap: developing an automatic speech
recognition system for egyptian dialect integration
into chatbots. In International Conference on Appli-
cations of Natural Language to Information Systems,
pages 119–125. Springer.
Nasser, N., Salah, J., Sharaf, N., and Abdennadher, S.
(2020). Automatic lecture annotation. In 2020 IEEE
Frontiers in Education Conference (FIE), pages 1–9.
IEEE.
Natarajan, B. and Elakkiya, R. (2022). Dynamic gan
for high-quality sign language video generation from
skeletal poses using generative adversarial networks.
Soft Computing, 26(23):13153–13175.
Neidle, C., Thangali, A., and Sclaroff, S. (2012). Chal-
lenges in development of the american sign language
lexicon video dataset (asllvd) corpus. Proceedings of
LREC.
Papastratis, I., Chatzikonstantinou, C., Konstantinidis, D.,
Dimitropoulos, K., and Daras, P. (2021). Artificial
intelligence technologies for sign language. Sensors,
21(17):5843.
Podder, K. K., Ezeddin, M., Chowdhury, M. E., Sumon, M.
S. I., Tahir, A. M., Ayari, M. A., Dutta, P., Khandakar,
A., Mahbub, Z. B., and Kadir, M. A. (2023). Signer-
independent arabic sign language recognition system
using deep learning model. Sensors, 23(16):7156.
Prikhodko, A., Grif, M., and Bakaev, M. (2020). Sign lan-
guage recognition based on notations and neural net-
works. In Digital Transformation and Global Society:
5th International Conference, DTGS 2020, St. Peters-
burg, Russia, June 17–19, 2020, Revised Selected Pa-
pers 5, pages 463–478. Springer.
Rastgoo, R., Kiani, K., and Escalera, S. (2020). Hand sign
language recognition using multi-view hand skeleton.
Expert Systems with Applications, 150:113336.
Ren, Z., Yuan, J., Meng, Z., and Zhang, J. (2013). Robust
part-based hand gesture recognition using kinect sen-
sor. In IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, volume 15,
pages 1110–1120. IEEE.
Safwat, S., Salem, M. A.-M., and Sharaf, N. (2023). Build-
ing an egyptian-arabic speech corpus for emotion
analysis using deep learning. In Pacific Rim Inter-
national Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pages
320–332. Springer.
Stoll, S., Camgoz, N. C., Hadfield, S., and Bowden, R.
(2020). Text2sign: Towards sign language production
using neural machine translation and generative ad-
versarial networks. In International Journal of Com-
puter Vision (IJCV).
Tharwat, G., Ahmed, A. M., and Bouallegue, B. (2021).
Arabic sign language recognition system for alphabets
using machine learning techniques. Journal of Elec-
trical and Computer Engineering, 2021(1):2995851.
Vaswani, A., Shazeer, N., Parmar, N., et al. (2017). Atten-
tion is all you need. Advances in Neural Information
Processing Systems.
Younes, S. M., Gamalel-Din, S. A., Rohaim, M. A., and
Elnabawy, M. A. (2023). Automatic translation of
arabic text to arabic sign language using deep learn-
ing. Journal of Al-Azhar University Engineering Sec-
tor, 18(68):566–579.
Zhang, H., Li, W., Liu, J., Chen, Z., Cui, Y., Wang, Y., and
Xiong, R. (2022). Kinematic motion retargeting via
neural latent optimization for learning sign language.
IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 7(2):4582–
4589.
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
1426
