
A Model-Based Approach to Experiment-Driven Evolution of ML
Workflows
Petr Hn
ˇ
etynka
1 a
, Tomáš Bureš
1 b
, Ilias Gerostathopoulos
2 c
, Milad Abdullah
1 d
and Keerthiga Rajenthiram
2 e
1
Charles Univesity, Prague, Czech Republic
2
Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam, The Netherlands
Keywords:
Experiments, Workflows, Machine Learning, Model-Based.
Abstract:
Machine Learning (ML) has advanced significantly, yet the development of ML workflows still relies heavily
on expert intuition, limiting standardization. MLOps integrates ML workflows for reliability, while AutoML
automates tasks like hyperparameter tuning. However, these approaches often overlook the iterative and ex-
perimental nature of the development of ML workflows. Within the ongoing ExtremeXP project (Horizon
Europe), we propose an experiment-driven approach where systematic experimentation becomes central to
ML workflow evolution. The framework created within the project supports transparent, reproducible, and
adaptive experimentation through a formal metamodel and related domain-specific language. Key principles
include traceable experiments for transparency, empowered decision-making for data scientists, and adaptive
evolution through continuous feedback. In this paper, we present the framework from the model-based ap-
proach perspective. We discuss the lessons learned from the use of the metamodel-centric approach within the
project—especially with use-case partners without prior modeling expertise.
1 INTRODUCTION
Machine Learning (ML) has made significant strides
in most fields. However, the processes of designing,
developing, and maintaining ML workflows continue
to rely heavily on the intuition and expertise of in-
dividual data scientists, rendering these efforts more
akin to an art form than a standardized engineering
discipline (Jung-Lin Lee et al., 2019; Xin et al., 2021).
To address the challenges of the development
and evolution of ML workflows, two prominent
paradigms have emerged: MLOps and AutoML.
MLOps focuses on integrating the various stages of
ML workflows, from model training to operational
deployment, emphasizing reliability and maintain-
ability (Kreuzberger et al., 2023). AutoML, on the
other hand, aims to automate tasks such as hyperpa-
rameter tuning, data preprocessing, and feature selec-
tion, making ML techniques more accessible to non-
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1008-6886
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3622-9918
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9333-7101
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0696-6354
e
https://orcid.org/0009-0007-0885-5264
experts (Xanthopoulos et al., 2020; Xin et al., 2021).
Although these paradigms have significantly stream-
lined ML workflow development, they often fail to
address the inherently iterative and experimental na-
ture of ML workflow optimization.
Data scientists frequently engage in cycles of hy-
pothesis formulation, execution, and evaluation to re-
fine their ML workflows. However, existing tools pro-
vide limited support for managing and learning from
these experimental cycles. To address this gap, in the
ExtremeXP project
1
(Horizon Europe), we propose
reframing ML workflows as explicitly experiment-
driven processes, where experiments are systemati-
cally defined, executed, and iterated. Thus, an ex-
periment is the backbone of the evolution of an ML
workflow.
In the project, we propose rethinking the evolution
of an ML workflow as a series of structured exper-
iments, each explicitly designed to address specific
optimization and evolution challenges. Inspired by
Bosch and Olsson, 2016 vision of autonomous, self-
improving systems, this approach is guided by three
principles:
1
https://extremexp.eu/
354
Hn
ˇ
etynka, P., Bureš, T., Gerostathopoulos, I., Abdullah, M. and Rajenthiram, K.
A Model-Based Approach to Experiment-Driven Evolution of ML Workflows.
DOI: 10.5220/0013380500003896
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Model-Based Software and Systems Engineering (MODELSWARD 2025), pages 354-362
ISBN: 978-989-758-729-0; ISSN: 2184-4348
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

• Traceable and Reproducible Experiments. Ev-
ery experiment is meticulously documented, en-
suring transparency, reproducibility, and efficient
knowledge reuse.
• Empowered Decision-Making. Data scientists
actively shape the experimentation process, lever-
aging their expertise rather than merely initiating
or observing automated workflows.
• Adaptive Evolution. Feedback from produc-
tion environments is systematically integrated into
experimental cycles, enabling continuous perfor-
mance enhancement.
In order to provide sufficient support for such an
approach, every experiment needs to be formally de-
fined. In our approach, we heavily rely on meta-
modeling and use of models at runtime.
In this paper, we highlight the modeling-related
challenges and describe how modeling serves as the
backbone of our approach. We provide (i) a formal
metamodel for describing experiments, (ii) a domain-
specific language for creating metamodel instances,
and (iii) an overview of the whole process and plat-
form for model-based development and evolution of
ML systems.
The paper is structured as follows. Section 2 gives
more details on the experimentation approach as it
is understood within the project and also provides a
motivating example. Section 3 presents the created
framework from the model-based development per-
spective. In Section 4, the framework and lessons
learned are discussed, together with related work.
Section 5 concludes the paper.
2 EXPERIMENT-BASED ML
WORKFLOW EVOLUTION
The broader context of our work and of ExtremeXP
is a novel way of rethinking the evolution of ML sys-
tems as a series of structured experiments, each ex-
plicitly designed to address specific optimization and
evolution challenges. The ultimate goal is to provide
a complete framework that supports data scientists in
the preparation, execution, evaluation, and mainte-
nance of such experiments. This is based on two core
concepts: Experiment and Complex Analytics Work-
flow (CAW).
An Experiment is a systematic, user-focused pro-
cess aimed at optimization. Its goal includes creating
an enhanced ML model using data and insights de-
rived from similar past experiments. Each experiment
comprises multiple CAWs and leverages prior knowl-
edge to execute CAWs for training different model
variants, fine-tuning the model, and simultaneously
accumulating insights for future experiments. The ex-
plicit use of previous knowledge collected in previ-
ous experiments is the key novelty that sets our work
apart from existing MLOps and AutoML approaches.
It also creates a number of modeling challenges. The
previous knowledge comprises facts and measure-
ments about how much computing the ML training
needed, what was the achieved accuracy, which ML
approaches provided improvements, what data and
data augmentation yielded good or bad results, etc.
Experiments are always designed with a clear in-
tent and are guided by a specific experimentation
strategy. The intent is the concept that binds related
experiments together. We conjecture that the knowl-
edge created in previous experiments can be reused as
long as the intent remains the same (or is similar).
The experimentation process can be thus seen as
a series of experiments with the same intent, where
each experiment uses previous knowledge to formu-
late the best strategy to achieve the intent. The previ-
ous knowledge also allows for predicting how many
resources the experiment will need, and thus trade-
offs (e.g., with expected improvement) can be done
before even starting the experiment. Previous knowl-
edge also allows one to understand whether the ex-
periment progresses as expected and flag experiments
that seem underperforming before completion.
A CAW comprises multiple tasks (e.g., “load
data,” “train,” “evaluate”) orchestrated by a control
flow. Tasks may either be automated or require man-
ual input, such as user feedback (e.g., labeling a re-
sult).
CAWs are, in fact, templates that can have multi-
ple variables (VP), i.e. places where the CAW can
be “parametrized”. VPs include (i) various imple-
mentations of tasks (e.g. different ML algorithms),
(ii) distinct task inputs, (iii) diverse hyperparameter
settings, and (iv) deployment choices (e.g., CPU vs.
GPU). Executing a CAW generates multiple metrics,
which measure (i) overall CAW performance (e.g., to-
tal execution time), (ii) individual task characteristics
(e.g., memory usage during training), or (iii) task out-
puts (e.g., ML model accuracy or user satisfaction).
CAW’s control flow (and data flow) cannot serve as a
VP to limit variability to a manageable degree.
The framework takes an experiment specification,
generates actual workflows from its CAWs, and ex-
ecutes them. Which workflows are generated and in
which order, depends on the experimentation strategy
included in the experiment. The strategy can be fully
automated (e.g., a plain grid search exploring all the
combinations of values for VPs) or semi-automated
when the data analyst is included “in-the-loop” and,
A Model-Based Approach to Experiment-Driven Evolution of ML Workflows
355

based on results of previous executions, can select pa-
rameters for the next executions.
The strong emphasis on the user in-the-loop is
another key novelty of our approach. We specifi-
cally include users in different roles and allow explic-
itly incorporating them in the experimentation pro-
cess (including the ability to provide task-specific
user interfaces). This modeling of user involvement
makes it possible to formalize the experimentation
process from the perspective of potentially multiple
human stakeholders, which is especially important
when working in safety-critical domains (like auto-
motive or avionics), which require explicit descrip-
tions of processes in order to align them with neces-
sary standards.
2.1 Experiment Example
As a motivating example, we use one of the use-cases
of the project related to the predictive maintenance
of machines in a factory. A goal is to predict equip-
ment failures using sensor data streamed from vari-
ous machines and start maintenance before the actual
failure occurs. However, since maintenance requires
both stopping the factory and requiring an additional
budget, too frequent maintenance means unnecessar-
ily losing money. On the other hand, delaying main-
tenance too much may result in a machine failure and
a substantial loss of money. Thus, the ultimate goal is
to minimize downtime while optimizing operational
costs. There are multiple ML algorithms suitable for
this task. Thus, the intent of the experiment is to find
the workflow that yields the best predictions by eval-
uating both these algorithms and also the different al-
gorithms’ parameters and hyper-parameters, different
ways to preprocess input data, etc. For simplicity, in
this paper, the experiment contains only a single CAW
composed of tasks for reading data, preparing data,
training a model, and evaluating the resulting model,
and we consider only a single VP—the task for train-
ing the ML model.
The whole experiment procedure is as follows:
(i) A scientist chooses several ML algorithms to train
the ML model. (ii) She runs the designed CAW
multiple times, each time with a different training
algorithm, and only roughly set (hyper)parameters.
(iii) Based on the results, she chooses the best
training algorithm. (iv) She runs the CAW with
the chosen training algorithm to precisely tune (hy-
per)parameters. The experiment thus directly in-
volves a user in the loop.
3 PROCESS AND FRAMEWORK
FROM THE MODEL-BASED
DEVELOPMENT
PERSPECTIVE
Figure 1 provides an overview of the main compo-
nents of the framework we have developed to support
this experimentation-based approach. The heart of
the framework is the Knowledge Repository (KR). It
stores not only all the designed experiments, but also
all the history of executed experiments plus the trace-
ability links among the experiments and input and
generated data, metrics, and user-in-the-loop feed-
back and decisions.
Execution
engine
Experimentation
engine
Knowledge Repository
DMS
Visual editor
DSL editor
Design tools
Figure 1: Framework architecture.
All other parts of the framework interact with
KR. These are, the tools for designing experiments—
textual and graphical, and the Experimentation en-
gine that generates particular workflows and executes
them within the Execution engine. The design tools
also interact with the Design Model Storage (DMS),
which stores reusable elements of experiments’ mod-
els (namely, experiment templates and CAWs).
3.1 Metamodel
In order to keep all the parts of the framework aligned
and interoperable, we have designed a metamodel
defining the experiment and CAW concepts. For bet-
ter readability of the text in this section, we omit the
“meta” prefix when describing the metamodel ele-
ments (i.e., meta-class is referred to as a class, etc.).
3.1.1 CAW Metamodel
Figure 2 shows the part of the metamodel describing
CAW. Due to space limitations, only the important
parts are shown and technical details are omitted.
In its core, it is a BPMN-inspired (OMG, 2014a)
workflow model, in which we have interwoven the
ability to (a) reuse tasks and workflows when build-
ing experiments, (b) generate metrics to evaluate the
experiments, (c) interact with user in the loop to col-
lect input and feedback. (For a more detailed list of
MODELSWARD 2025 - 13th International Conference on Model-Based Software and Systems Engineering
356
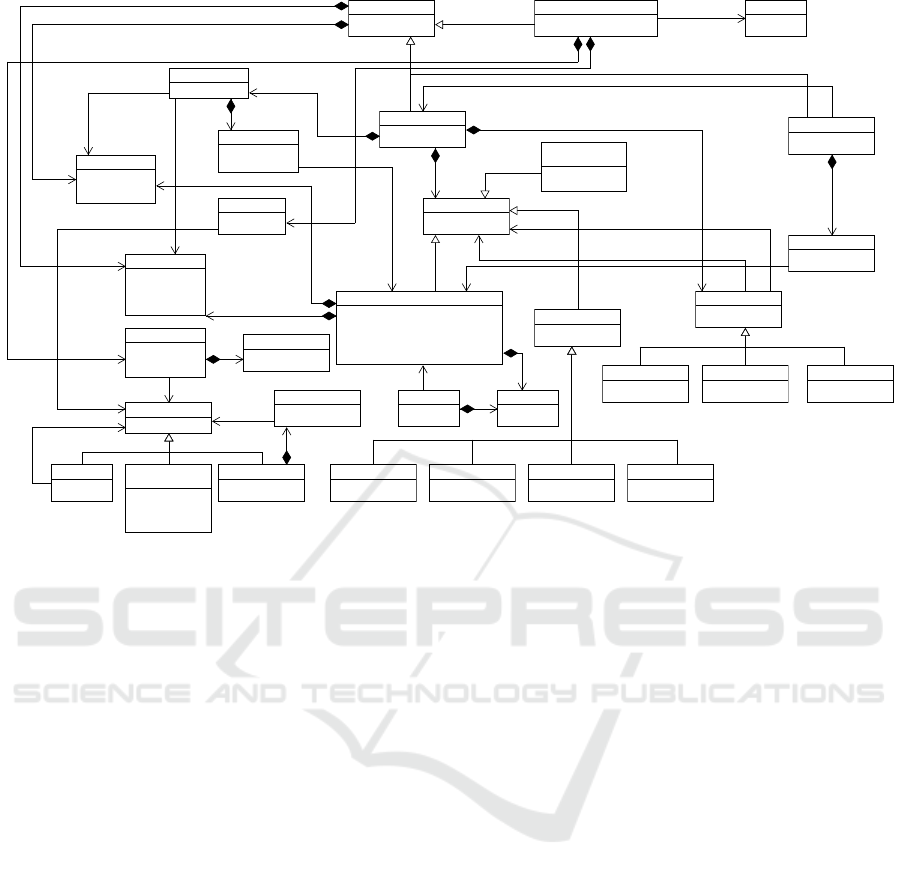
UI
ValueConstraint
+constraint
TaskData
+dataName
DataLink
TaskSpecification
+primitiveImplementation
Workflow
+name
SubstitutedTask
+name
AssembledWorkflow
Metric
MetaData
+name
+value
InputData
+name
Group
+name
Parameter
+name
+defaultValue
OutputData
+name
Array
+length
Field
+name
Structure
«Enum»
Primitive
+NUMBER
+BOOLEAN
+STRING
+BLOB
Join
Inclusive
+condtions[*]
ParameterType
+name
ConditionalLink
+condition
ExceptionalLink
+event
RegularLink
«Enum»
Event
+START
+END
Exclusive
+condition[*]
Parallel
Node
Operator
Link
Task
+name
+description
+isAbstract
+primitiveImplementation
CompositeWorkflow
0..1
*
type
parameters
*
0..1
0..1
0..1
*
generates
inputs
*
outputs
*
task
0..1
*
*
*
*
outputs
*
inputs
*
type
type
fields
*
type
1..*
output
*
input
Figure 2: Metamodel of CAW.
differences see Section 4.)
The Workflow class represents a complete CAW (on
a type level), and is an abstract class with three partic-
ular children classes: TaskSpecification, CompositeWorkflow,
and AssembledWorkflow (described in the following sec-
tions). Each workflow can have specified a number of
the InputData and OutputData (i.e., data that are obtained
by the workflow, and data that are produced by the
workflow). These data are not further modeled and,
from the point of view of the workflows, are opaque.
A common part of the metamodel is in the
ParameterType, which, as its name suggests, models
types of parameters (and similar entities). A parame-
ter type has its name and can be either a Primitive one,
Structure of multiple Fields, or an Array.
The TaskSpecification represents a primitive CAW
with only a single task, which has a direct im-
plementation, e.g., via a Python program. These
TaskSpecifications are reusable between multiple CAWs,
and are stored in DMS.
The TaskSpecification can have a number of Parameters
to parameterize the implementation. Also, the
TaskSpecification can generate a number of Metrics, which
are similar to the OutputData but their structure is mod-
eled. The metrics represent data collected during
the implementation execution (e.g., execution time,
memory consumption, prediction accuracy of trained
model) and can be used within the experiment evalua-
tion. Finally, the TaskSpecification can refer to the UI that
allows for attaching a user interface to those tasks that
are interactive (due to the space limitations, the meta-
model of UI is omitted).
The CompositeWorkflow represents a CAW com-
posed of multiple tasks (represented as Nodes) and
Links. The Node is a common parent of “actions” in
a workflow. They are Events (currently only START
and END of a workflow), Tasks, and Operators. Task
represents a task in the composite workflow and ei-
ther is abstract (will be set in the AssembledWorkflow)
or has specified its implementation through the
TaskSpecification (set via the primitiveImplementation at-
tribute). A task can have a number of the InputData
and OutputData.
The Operator is a common parent to represent forks
and joins in a workflow. The Parallel operator creates
parallel paths of execution in a workflow. All the
paths are executed potentially simultaneously. The
Exclusive operator creates alternative paths of execution
in a workflow and only a single path is executed based
on the specified condition. Finally, the Inclusive oper-
ator creates alternative (based on the specified condi-
tion) but possibly parallel paths in a workflow. As the
name suggests, the Join is the operator representing a
join of workflow paths created by the fork operators.
Another possible element of a composite work-
flow is the Link via which the control flow is modeled.
It is again a common parent class with three partic-
ular subclasses. The RegularLink is an unconditional
A Model-Based Approach to Experiment-Driven Evolution of ML Workflows
357

flow from one node in a workflow to another. The
ConditionalLink is a flow that is executed when an asso-
ciated condition is satisfied. There must be multiple
links from a particular node so that another flow can
be selected when the condition is not satisfied. The
ConditionalLink is de facto redundant and can be modeled
via the Exclusive operator; however, it is included as
branching in CAWs used within the project are typi-
cally straightforward and is more easily modeled (and
understood by users) via the ConditionalLink. Finally, the
ExceptionalLink is provided to redirect the control flow
when an exception occurs at its source node.
The last element is DataLink for modeling the data
flow of CAW. A data link connects (i) the workflow’s
input data to a task’s input data, or (ii) a task’s output
data to another task’s input data, or (iii) a task’s output
data to the workflow’s output data.
Figure 4 shows a visualization (in the tool de-
veloped within the project—see Section 3.3) of a
CompositeWorkflow representing CAW from the example
in Section 2.1.
The AssembledWorkflow is always based on another
CompositeWorkflow and its intention is to create a fully
specified workflow that can be executed. That is, the
AssembledWorkflow substitutes abstract tasks (tasks with-
out implementations) with specific ones.
3.1.2 Experiment Metamodel
Figure 3 shows the metamodel of an experiment. An
Experiment defines a number of ExperimentSteps of the
experimentation process. These generally fall into
two categories: (i) exploration of an experiment space
(represented by ExperimentSpace) and (ii) user interac-
tion (represented by Interaction ).
The ExperimentSpace is a design space of different
parameterizations of a single AssembledWorkflow. Con-
nected with exploration strategy, it further defines how
the different parameterized workflow variants are to
be traversed. During this traversal, each such param-
eterized workflow is executed and its metrics are col-
lected and stored. In the use cases of the project, this
is used, for example, to explore the effect of hyperpa-
rameters of a neural network to its accuracy.
Examples of the strategy include the grid-search
strategy, which generates all possible combinations of
values; the random-search, which creates a random
combination of values; the bayesian-optimization
strategy, which balances exploration and exploitation
based on expected improvement and minimization of
uncertainty, etc. As a result, a single AssembledWorkflow
results in a number of actually executed workflows.
The Interaction represents an experiment step that
executes a task with a user interface attached. This
step provides a custom task-specific micro-frontend
to a user, intended to collect feedback on the experi-
ment results collected so far and to obtain the user’s
decision on how to continue.
For instance (as shown in Section 3.2), an exper-
iment that trains a prediction model based on either
a regular neural network or a recursive neural net-
work can be formulated to first perform a coarse sam-
pling of a hyperparameter space of the regular NN
(first AssembledWorkflow of the experiment) followed by
a coarse sampling of the hyperparameter space of the
recursive NN (second AssembledWorkflow). Afterward,
it presents the accuracies it was able to achieve dur-
ing training the different variants of NN to the user as
part of the interaction. The user inspects the results
and decides whether to continue with the regular neu-
ral network or whether to prefer the recursive neural
network. Alternatively, the user may also scope the
hyper-parameter search to only a smaller subspace.
Finally, the experiment defines the order in which
the ExperimentSteps are processed. This is modeled via
the Control, Execution, and ControlLink classes (and sub-
classes) that together allow for a simple control spec-
ification.
3.2 DSL
Although the metamodel offers a formal definition of
experiments and CAWs, it is itself not sufficient. It
is necessary to have a way to easily create the meta-
model instances, i.e., the actual experiment and CAW
definitions. Therefore, we designed a Domain Spe-
cific Language (DSL) to create these definitions.
Listing 1 shows an excerpt of the DSL definition
of CAW from the motivating example. The tasks used
in the CAW are first defined (line 2) together with the
control flow (line 3). There is no need to have all the
flow defined in a single declaration (for CAWs with
branching, it is not even possible), and it can be split-
ted into multiple ones. The syntax of the flow defini-
tions is inspired by the DOT language
2
.
1 workflow ExampleWF {
2 define task ReadData, PrepareData, TrainModel, EvaluateModel;
3 START −> ReadData −> PrepareData −> TrainModel −>
EvaluateModel −> END;
4 configure task ReadData {
5 implementation "tasks/factory/read_data.py";
6 }
7 configure task PrepareData {...}
8 configure task EvaluateModel {...}
9 define input data ExternalDataFile;
10 define output data ProducedModel;
11 ExternalDataFile −−> ReadData.ExternalDataFile;
12 ReadData.X −−> PrepareData.X1;
13 ReadData.Y −−> PrepareData.Y1;
14 ...
15 EvaluateModel.TrainedModel −−> ProducedModel;
16 }
Listing 1: CAW definition in DSL.
2
https://graphviz.org/docs/layouts/dot/
MODELSWARD 2025 - 13th International Conference on Model-Based Software and Systems Engineering
358
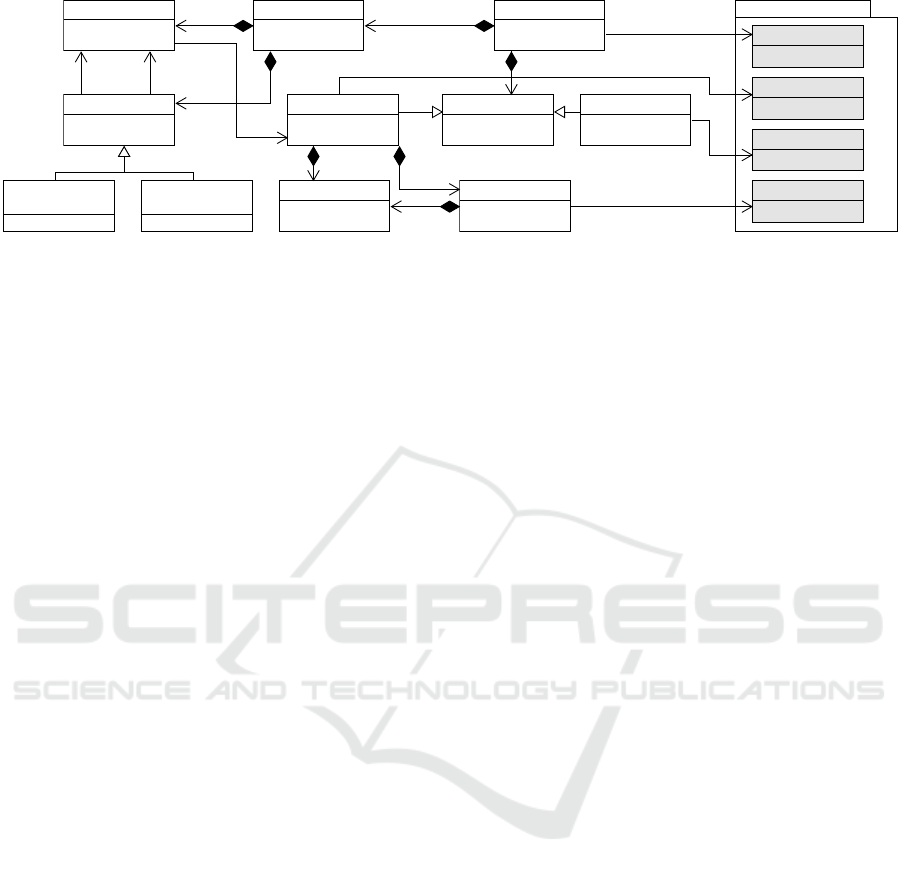
ExperimentStep
+name
TaskSpecification
Interaction
+name
ConditionalControl
Link
RegularControl
Link
From CAW meta-model
ControlLink
Execution
Control
Task
ParameterValue
+name
+value
TaskConfiguration
AssembledWorkflow
Workflow
ExperimentSpace
+strategy
Experiment
+name
uses
output
input
*
*
configures
*
*
*
uses
baseOn
*
*
Figure 3: Metamodel of Experiment.
The semantics of this CAW is according to the ex-
ample. That is, the data are read, they are prepared
for training, a model is trained, and finally the trained
model is evaluated (for accuracy, etc.). All these tasks
run without user interaction.
The defined task can be configured—primarily
with their implementation (lines 4–8). The task
TrainModel is not configured as it is an abstract one, and
configuration is left to the assembled workflow defi-
nition (see Listing 2)—the task is a variation point.
Finally, the data are defined and the data flow is
declared (lines 9–15). The control and data flow dec-
larations differ by simple arrow and double arrow.
Listing 2 shows definitions of two assembled
workflows that differently configure the CAW above.
As mentioned in Section 3.1, the assembled workflow
can configure tasks and replace abstract tasks with im-
plemented ones, but cannot modify the control/data
flows.
1 workflow FDW1 from ExampleWF {
2 configure task TrainModel {
3 implementation "tasks/factory/train_nn.py";
4 }
5 }
6 workflow FDW2 from ExampleWF {
7 configure task TrainModel {
8 implementation "tasks/factory/train_rnn.py";
9 }
10 }
Listing 2: Assembled workflow definitions in DSL.
Here, two variants of the CAW are created—one
with an implementation of the TrainModel task using
neural networks (NN) and the other one with an im-
plementation using recursive neural networks (RNN).
Listing 3 shows an excerpt of the definition of
the experiment according to the motivating exam-
ple. There are four experimentation spaces defined—
a pair for the FDW1 assembled workflow and another
pair for FDW2. The spaces within the pair differ by
choosing values of the parameters of the TrainModel task
in order to achieve a coarse search through the param-
eters’ space and a fine search. Additionally, there is a
definition of an interaction with a human user (starting
at line 12), which executes a task showing a user in-
terface. Finally, there is the definition of the control
flow of the whole experiment (starting at line 17). Its
syntax is, in principle, the same as the control flow in
CAWs.
1 experiment ExampleExperiment {
2 space SNNCoarse of FDW1 { // coarse search over NN
3 strategy gridsearch;
4 param epochs_vp = range(60,120,20);
5 param batch_size_vp = enum(64, 128);
6 configure task TrainModel {
7 param epochs = epochs_vp;
8 param batch_size = batch_size_vp;
9 }
10 }
11 space SRNNCoarse of FDW2 { ... } // coarse search over RNN
12 interaction UserInteraction {
13 task choice(....);
14 }
15 space SNNFine of FDW1 { ... } // fine search over NN
16 space SNNFine of FDW2 { ... } // fine search over NN
17 control {
18 START −> SNNCoarse −> SRNNCoarse −> UI1;
19 UI1 −> SNNFine {condition "choice == NN"};
20 UI1 −> SRNNFine {condition "choice == RNN"};
21 SNNFine −> END;
22 SRNNFine −> END;
23 }
24 }
Listing 3: Experiment definitions in DSL.
The semantics of the experiment is as follows.
First, the model training is executed with a coarse
search through the parameters space for both the
NN and RNN training (the experimentation spaces
SNNCoarse and SRNNCoarse). Then, based on the results
of these two executions, the user selects the imple-
mentation with better results (UserInteraction). Finally,
the selected implementation is executed with a fine
search of the parameters’ space (SNNFine or SRNNFine).
3.3 Visual Tool
Although, especially for advanced users, the DSL of-
fers a quick and easy way to specify experiments and
CAWs, for new users (and users without program-
ming background), DSLs can be intimidating. There-
fore, we have also developed a visual editor. Figure 4
shows a screenshot of the editor with CAW of the mo-
tivating example. The editor offers a palette with all
A Model-Based Approach to Experiment-Driven Evolution of ML Workflows
359
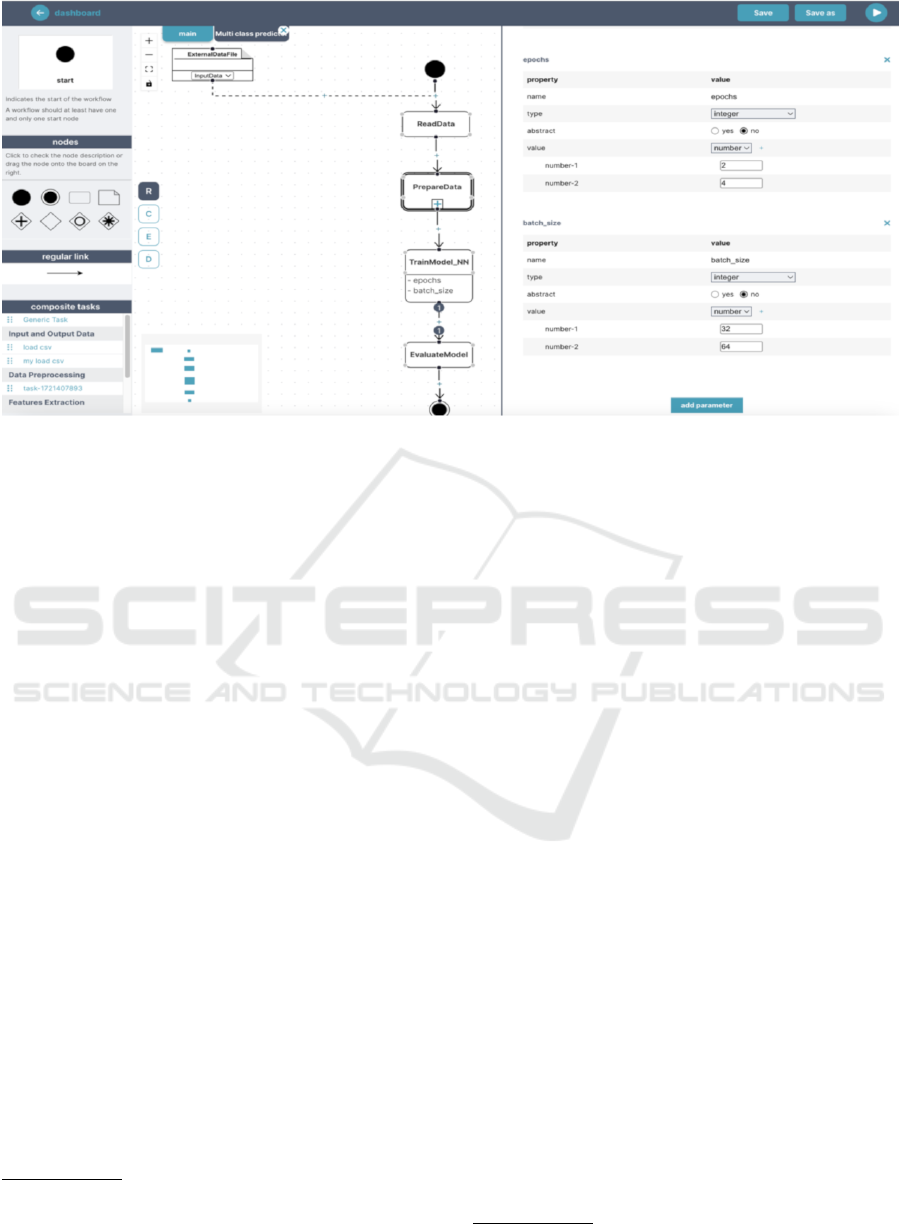
Figure 4: Visual editor of CAWs.
CAW elements (left part of the screenshot; circles for
the start and end, a rounded rectangle for a task, a rect-
angle with a folded corner for data, diamonds for dif-
ferent branching operators, arrows for flow). A user
drags the elements to the canvas (the middle part of
the screenshot) and connects them together. When an
element in the canvas is selected, its details might be
set in the configuration panel (right part of the screen-
shot).
3.4 Framework Implementation
For the metamodel creation, we are using the Eclipse
Modeling Framework (EMF)
3
. To create the DSL, we
are employing the Xtext framework
4
. From grammar,
Xtext can generate a parser, a language server, and
even a web-based application for editing a particular
DSL. Internally, Xtext creates an EMF-based meta-
model that corresponds to the grammar, and the gen-
erated tools use the metamodel. We have prepared the
DSL grammar in a way that the internal DSL meta-
model almost one-to-one corresponds with the “core”
metamodel described in Section 3.1. However, there
are differences between the metamodels, and thus, we
have created a model-to-model transformation to con-
vert models from the DSL to the “core” metamodel
and vice-versa. As for the actual DSL editor, we use
our own instance of VSCode
5
with the integrated lan-
guage server for the DSL generated via Xtext.
The visual editor is developed as a web-based ap-
3
https://eclipse.dev/modeling/emf/
4
https://eclipse.dev/Xtext/
5
https://github.com/microsoft/vscode
plication. Internally, for technical reasons, it uses its
own representation of models. As in the case of DSL,
we have created the model-to-model transformation
to and from the “core” metamodel. Thus, it does not
matter if an experiment has been prepared in DSL or
the visual tool and they can be used seamlessly to-
gether. Both the DSL editor and the visual tool use
DMS to store definitions there and reuse the existing
ones.
To execute workflows, we have adopted ProAc-
tive
6
within the project. It is a middleware for
scheduling and executing parallel and distributed
jobs. Nevertheless, the framework is not bound to
ProActive and can be used with other workflow ex-
ecution middleware.
4 DISCUSSION AND RELATED
WORK
As mentioned in Section 3.1, the CAW metamodel
is inspired by BPMN. At the start of the project, we
considered reusing an existing formalism to describe
CAW, and BPMN was the best candidate (since a
business process defines a control flow and data flow
between tasks). However, it soon proved to be in-
sufficient for the project requirements. Unlike exist-
ing workflow languages (such as BPMN), our meta-
model brings several important updates. That is, it
offers support for (i) the reusability of workflows and
tasks (in order to allow users to be able to build ex-
periments out of existing building blocks), (ii) param-
6
https://projects.ow2.org/bin/view/proactive/
MODELSWARD 2025 - 13th International Conference on Model-Based Software and Systems Engineering
360

eterization of workflows (i.e., a possibility to model a
workflow with abstract tasks that are later concretized
in assembled workflows for a particular experiment),
(iii) definition and collection of performance metrics
in order to optimize experiments and also to allow for
meta-analysis over past experiments, (iv) user in the
loop.
We have already mentioned (in Section 2) that, in
our approach, the control flow of a CAW cannot serve
as a variability point (VP), i.e., the control flow of a
CAW is always fixed. The underlying reason for this
decision is to limit variability to a manageable degree.
However, it is important to note that, by allowing the
definition of hierarchical CAWs and task-level VPs,
we can still model variability in control flows (or parts
of them). This can be done, e.g., by having a high-
level CAW that contains an abstract task that is im-
plemented (in different assembled workflows) via dif-
ferent lower-level CAWs with distinct control flows.
This speaks to the versatility and expressiveness of
our metamodels.
Another important aspect of our overall approach
is the role of users in the loop. We have already seen
(in Section 2) that single tasks in a CAW may require
manual input, such as user feedback (e.g., labeling a
result). We have also seen that an experiment step
can be modeled as Interaction , i.e., a task with a user
interface attached. When an experiment is executed,
our framework actually maps the latter to the for-
mer, since it wraps any Interaction steps into single-task
workflows executed by the execution engine. Further-
more, these are both examples of users ‘in-the-loop’:
users that directly interfere with the experimentation
process to validate its progress and steer it in a fine-
grained way.
During the development of the framework, we
also learned several lessons that we believe are in-
teresting and important to share.
First, even though the metamodel offers easy for-
malization of concepts and a core for developing tools
and repositories, by itself (especially in the early
stages of development), it might be hard to under-
stand. Thus, the creation of DSL that offers easy-
to-grasp examples (i.e., models corresponding to the
metamodel) has been mandatory. The downside of it
is that the metamodel went through several rounds of
substantial updates, and it was necessary to update the
DSL with each change to the metamodel. However,
without the DSL, it would not have been possible to
discuss the metamodel with the project partners.
For the same reason (hard to understand the meta-
model without examples), the visual tool is slightly
incompatible with the metamodel as the developer
creating its initial versions understood parts of the
metamodel differently (DSL and the visual editor
have been developed in parallel by different partners
in the project). Such incompatibilities are solved now
via model-to-model transformations.
This leads to another lesson. In model-driven ap-
proaches, e.g., OMG’s MDA (OMG, 2014b), special
languages have been proposed for model-to-model
(and model-to-anything) transformations. For MDA,
prominent examples are QVT (OMG, 2016) and ATL
(Jouault and Kurtev, 2006). Even though these lan-
guages have been designed for transformation, their
usage is not straightforward, and even if they support
bidirectional transformation, for complex transforma-
tions it is necessary to explicitly prepare two one-way
transformations. It also seems that these languages
have not been widely adopted (probably for these rea-
sons). After we considered these languages, we, in the
end, created the transformations in mainstream pro-
gramming languages (Java and Python).
The rest of the section discusses existing related
frameworks and approaches designed to facilitate
experimentation within ML workflows.
For Experiment and Workflow Specifications,
languages like BPMN help define workflows but lack
support for experiment-driven ML system develop-
ment (Section 4). Tools like make.com
7
, offer work-
flow management but also lack traceability and evo-
lution features. Our framework extends these by sup-
porting the entire ML lifecycle.
Regarding MLOps and AutoML frameworks,
John et al., 2021 analyzed MLOps adoption through a
literature review, presenting a framework for MLOps
activities and a maturity model. Tools like MLFlow
8
,
ZenML
9
, and Kubeflow
10
provide features like exper-
iment tracking and replication. Our framework builds
on these, offering reusable blocks and a knowledge
repository for advanced experimentation.
For ML Workflow Management and Automa-
tion, Cirrus (Carreira et al., 2019) automates ML
workflows using serverless computing but lacks sup-
port for iterative experimental cycles. Ahmed, 2023
identified patterns for improving MLOps workflows,
focusing on iterative development. Our framework in-
tegrates experimentation cycles with traceability.
cycles. Ahmed, 2023 identified patterns IoT-
based ML workflows using containerized components
but focuses on data orchestration over experimenta-
tion. BPMN4sML BPMN4sML (Tetzlaff, 2022) ex-
tends BPMN for interoperable ML workflow model-
ing. Our platform enhances decision-making by in-
7
https://www.make.com/
8
https://mlflow.org
9
https://docs.zenml.io
10
https://kubeflow.org
A Model-Based Approach to Experiment-Driven Evolution of ML Workflows
361

corporating user participation and meta-modeling.
Regarding DSL for ML and System Monitoring,
Freire et al., 2013 proposed a DSL for devising and
monitoring experiments in software Freire et al., 2013
proposed a DSL for ML performance monitoring with
seamless platform integration. Our approach expands
on these by combining formal meta-modeling, moni-
toring, and iterative experimentation.
Morales et al., 2024 formed a DSL for ML sys-
tems, handling task standardization. Zhao et al., 2024
introduced a DSL for ML workflows in MS research,
blending AutoML and manual methods. We extend
DSLs to embed them within the experimentation life-
cycle and feedback-driven ML development.
5 CONCLUSION
In the ExtremeXP project, we have proposed a novel
approach that reframes ML workflow development as
an experiment-driven process, where experiments are
systematically defined, executed, and evolved over
time. Our approach emphasizes traceability, empow-
ered decision-making, explicit involvement of users-
in-the-loop, and adaptive system evolution by inte-
grating formal modeling and models at runtime. This
structured experimentation paradigm not only en-
hances transparency and reproducibility but also facil-
itates continuous improvement through feedback inte-
gration.
In this paper, we described a platform supporting
the model-driven development and evolution of ML
workflows. Our current work focuses on validating
the framework in real-world ML workflow deploy-
ments and further refining the developed platform.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work has been partially supported by the EU
project ExtremeXP grant agreement 101093164, and
by Charles University institutional funding SVV
260698.
REFERENCES
Ahmed, A. M. A. (2023, July). Exploring MLOps dynam-
ics: An experimental analysis in a real-world machine
learning project. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2307.
13473
Alves, J. M., Honório, L. M., & Capretz, M. A. M. (2019).
ML4iot: A framework to orchestrate machine learning
workflows on internet of things data. IEEE Access,
7, 152953–152967. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.
2019.2948160
Bosch, J., & Olsson, H. H. (2016). Data-driven con-
tinuous evolution of smart systems. Proceedings
of SEAMS 2016, 28–34. https://doi.org/10.1145/
2897053.2897066
Carreira, J., Fonseca, P., Tumanov, A., Zhang, A., & Katz,
R. (2019). Cirrus. Proceedings of the ACM Sympo-
sium on Cloud Computing, 13–24. https://doi.org/10.
1145/3357223.3362711
Freire, M., Accioly, P., Sizílio, G., Campos Neto, E.,
Kulesza, U., Aranha, E., & Borba, P. (2013). A model-
driven approach to specifying and monitoring con-
trolled experiments in software engineering. Product-
Focused Software Process Improvement, 65–79. https:
//doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-39259-7_8
John, M. M., Olsson, H. H., & Bosch, J. (2021). To-
wards MLOps: A framework and maturity model.
SEAA’21, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1109/SEAA53835.
2021.00050
Jouault, F., & Kurtev, I. (2006). On the architectural
alignment of ATL and QVT. Proceedings of SAC
2006, 1188–1195. https://doi.org/10.1145/1141277.
1141561
Jung-Lin Lee, D., Macke, S., Xin, D., Lee, A., Huang, S., &
Parameswaran, A. (2019). A Human-in-theloop Per-
spective on AutoML. IEEE Data(base) Engineering
Bulletin, 42, 59–70.
Kourouklidis, P., Kolovos, D., Noppen, J., & Ma-
tragkas, N. (2023). A domain-specific language for
monitoring ML model performance. MODELS-C,
266–275. https://doi.org/10.1109/MODELS-C59198.
2023.00056
Kreuzberger, D., Kühl, N., & Hirschl, S. (2023). Machine
learning operations (MLOps): Overview, definition,
and architecture. IEEE Access, 11, 31866–31879.
https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3262138
Morales, S., Clarisó, R., & Cabot, J. (2024, August). A
framework to model ML engineering processes. https:
//doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2404.18531
OMG. (2014a). Business process model and notation, ver.
2.0.2 [OMG doc. formal/13-12-09].
OMG. (2014b). Model driven architecture,MDA guide rev.
2.0 [OMG doc. formal/14-06-01].
OMG. (2016). MOF query/view/transformation, ver. 1.3
[OMG doc. formal/16-06-03].
Tetzlaff, L. M. (2022, August). BPMN4sML. https://doi.
org/10.48550/arXiv.2208.02030
Xanthopoulos, I., Tsamardinos, I., Christophides, V., Si-
mon, E., & Salinger, A. (2020). Putting the Human
Back in the AutoML Loop. EDBT/ICDT Workshops.
Xin, D., Wu, E. Y., Lee, D. J.-L., Salehi, N., &
Parameswaran, A. (2021, January). Whither Au-
toML? Understanding the Role of Automation in Ma-
chine Learning Workflows. http://arxiv.org/abs/2101.
04834
Zhao, W., Wendt, K., Ziemssen, T., & Aßmann, U. (2024).
Rule-based DSL for continuous features and ML
models selection in multiple sclerosis research. Ap-
plied Sciences, 14, 6193. https://doi.org/10.3390/
app14146193
MODELSWARD 2025 - 13th International Conference on Model-Based Software and Systems Engineering
362
