
Explainable AI in Labor Market Applications
Gabriel Bicharra Santini Pinto, Carlos Eduardo Mello and Ana Cristina Bicharra Garcia
Federal University of Rio de Janeiro (UNIRIO), PPGI, Av. Pasteur, 458, Urca, RJ, Brazil
Keywords:
Explainable Artificial Intelligence, Labor Market, Human Resource Systems, Fairness.
Abstract:
The adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) applications has been accelerating in the labor market, driving
productivity gains, scalability, and efficiency in human resource management. This progress has also raised
concerns about AI’s negative impacts, such as flawed decisions, biases, and inaccurate recommendations. In
this context, explainable AI (XAI) plays a crucial role in enhancing users’ understanding, satisfaction, and
trust. This systematic review provides a segmented overview of explainability methods applied in the labor
market. A total of 266 eligible studies were identified during the search and evaluation process, with 29 studies
selected for in-depth analysis. The review highlights the different explainability requirements expressed by
users of human resource systems. Additionally, it identifies the processes, tasks, and corresponding explain-
ability methods implemented.
1 INTRODUCTION
Artificial Intelligence (AI)-enabled applications are
increasingly automating and enhancing decision-
making processes in human resource management
within organizations, becoming a core component of
corporate investment strategies (Chowdhury et al.,
2023). The adoption of AI in the labor market is
driven by its potential to boost efficiency, minimize
human errors, and forecast future behaviors through
data pattern analysis (Lukacik et al., 2022).
As AI adoption progresses in the labor market, im-
portant issues must be addressed to ensure its ethical
and fair application (Chowdhury et al., 2023). Con-
cerns about AI’s negative impacts, such as flawed
decisions, biases, and inaccurate recommendations,
gain prominence as these technologies become em-
bedded in organizational routines. Despite its poten-
tial to reduce biases, documented discriminatory inci-
dents continue to raise concerns (Tambe et al., 2019).
Simultaneously, human workers face fears and skep-
ticism about potential job losses due to automation
(Webb, 2019).
In this context, Explainable AI (XAI) is essen-
tial to ensure that decisions made by ”black-box”
models are understandable to users (Bertrand et al.,
2022). XAI helps identify and correct biases in train-
ing data, preventing unfair or flawed decisions — a
critical factor for maintaining user trust and the ef-
fectiveness of AI applications across various domains
(Fidel et al., 2020). Clear and comprehensible expla-
nations strengthen the acceptance and credibility of
AI systems from both user and regulatory compliance
perspectives, ensuring that decisions are grounded in
logical and justifiable reasoning (Ali et al., 2023a).
The article is organized as follows: Section 2
presents the theoretical framework, providing con-
text for the research problem. Section 3 describes
the methods and procedures employed in conducting
the systematic literature review (SLR), including a de-
tailed explanation of the search terms and criteria used
for selecting relevant studies. Section 4 outlines the
results obtained from applying the search and selec-
tion protocol. In Section 5, the evaluation of qual-
ity criteria for the selected studies is discussed, along
with answers to the research questions. Finally, Sec-
tion 6 summarizes the study’s conclusions, highlights
the work conducted, and offers suggestions for future
research directions.
2 THEORETICAL BACKGROUND
This section presents the literature review addressing
topics influencing the development of explainability
methods in the labor market. The section is organized
as follows. First, topics related to the application
of artificial intelligence in the labor market are dis-
cussed. Next, explainability methods for artificial in-
telligence are presented. Finally, related works found
1450
Pinto, G. B. S., Mello, C. E. and Garcia, A. C. B.
Explainable AI in Labor Market Applications.
DOI: 10.5220/0013384100003890
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2025) - Volume 3, pages 1450-1457
ISBN: 978-989-758-737-5; ISSN: 2184-433X
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

in the literature are reviewed.
2.1 Artificial Intelligence in the Job
Market
The application of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in la-
bor market processes has been transforming the job
market while simultaneously provoking an important
ethical debate about its applications. In recruitment,
AI technologies have improved processes across four
different stages: job advertisement, screening, eval-
uation, and facilitation (Black and van Esch, 2020).
The benefits include a larger audience for job postings
with better candidate-job fit (Bogen, 2019), analysis
of large volumes of resumes (Lukacik et al., 2022)
with automatic pattern identification based on pre-
defined criteria (Vasconcelos et al., 2018), and in-
creased accuracy (Roemmich et al., 2023). In em-
ployee management, machine learning models are
used to prevent employee attrition, improving reten-
tion strategies and reducing turnover costs (Al-Alawi
and Ghanem, 2024). At the same time, automatic
and personalized skill recommendations make profes-
sional development more informed and suited to ca-
reer paths (B
¨
ohm et al., 2024).
Human resource management is recognized for
high levels of bias and prejudice as they are devel-
oped and manipulated according to human perspec-
tives (Olckers and Walsh, 2024). Consequently, ma-
chine learning models trained on biased employee
databases can perpetuate and magnify discriminatory
practices, privacy issues, and transparency concerns
as they achieve scalability. Ethical application con-
cerns, decision-making biases, discriminatory inci-
dents, and potential job losses due to automation
(Chowdhury et al., 2023) are driving the demand for
explainability in these systems.
Enhancing the interpretability of automated de-
cisions promotes greater trust and fairness, ensuring
decisions are based on accurate and justifiable data
while supporting more efficient and equitable hir-
ing, evaluation, and professional development prac-
tices. In fields where explainability is critical, such
as healthcare and finance, systematic reviews have
examined XAI methods and the sociotechnical re-
quirements for their applications (
ˇ
Cernevi
ˇ
cien
˙
e and
Kaba
ˇ
sinskas, 2024; Ali et al., 2023b).
2.2 Explainable Artificial Intelligence
(XAI)
Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) encom-
passes various methods aimed at making machine
learning models more interpretable. A central
approach is feature relevance explanation, exem-
plified by Shapley Additive Explanations (SHAP),
which quantifies each feature’s contribution to a
model’s prediction (Lundberg, 2017). While effec-
tive, SHAP’s reliance on individual feature contri-
butions can overlook feature dependencies. Simpli-
fication methods like decision trees and rule-based
learners approximate complex models through sim-
pler representations, aiding interpretability without
sacrificing performance. Local explanations focus on
specific instances, with Local Interpretable Model-
Agnostic Explanations (LIME) offering insights by
locally approximating predictions through perturbed
inputs (Ribeiro et al., 2016). Counterfactual expla-
nations further support understanding by highlighting
how different inputs could change outcomes, offering
actionable insights (Johansson et al., 2016).
Transparent models like linear regression and de-
cision trees inherently allow interpretability by ex-
posing how input features influence predictions (Ar-
rieta et al., 2020). Finally, XAI frameworks integrate
multiple methods to enhance overall explainability.
These frameworks combine feature relevance, local
and global explanations, and visualization techniques,
creating comprehensive interpretation systems that
improve decision-making transparency and user trust
(Linardatos et al., 2020).
2.3 Related Works
(Bujold et al., 2024) highlight the multidisciplinary
nature of AI in Human Resource Management
(HRM), noting that many studies rely on experimental
frameworks without real-world validation. Similarly,
(Trinh and Elbanna, 2023) observe that AI research
in HRM remains fragmented across management dis-
ciplines, limiting comprehensive knowledge build-
ing. In recruitment and selection, (Rigotti and Fosch-
Villaronga, 2024) stress the need for fairness-driven
system design balancing ethical, legal, and technical
aspects. They recommend cross-disciplinary collab-
oration and participatory research to address power
asymmetries between applicants and HR practition-
ers.
3 METHODS AND PROCEDURE
Conducting a Systematic Literature Review (SLR) is
a well-established approach in Software Engineering
for comprehensively surveying existing research on
a specific topic following the protocol proposed by
(Kitchenham et al., 2015). The following sections
detail this process: Section 3.1 defines the research
Explainable AI in Labor Market Applications
1451
questions; Section 3.2 outlines the search strategy;
Section 3.3 presents the screening process.
3.1 Research Questions
The primary objective of this review is to provide
valuable insights into models, frameworks, and ap-
proaches of explainable AI applied in the labor mar-
ket, emphasizing key topics, design challenges, and
socio-technical requirements for their effective imple-
mentation. To achieve this objective, the following
research questions were formulated:
• RQ1: What are the socio-technical requirements
and the design, implementation, and evaluation
challenges of explainable artificial intelligence
models?
• RQ2: Which labor market AI applications have
benefited from the implementation of XAI?
• RQ3: What are the novel XAI approaches that
have been developed and implemented?
• RQ4: How can machine learning and AI-based
frameworks be designed to promote fairness and
reduce bias in automated recruitment and job eval-
uation systems?
3.2 Search Strategy
The search strategy began with a review of the most
relevant systematic literature on explainable artifi-
cial intelligence (XAI) and its pioneering systematic
reviews in specific domains such as healthcare and
credit scoring. Following this, an initial search was
conducted on Google Scholar using cross-referencing
terms related to the labor market and XAI. This pre-
liminary exploration provided a clearer understanding
of the topic, enabling the definition of search terms as
outlined in Table 1.
3.3 Screening Process
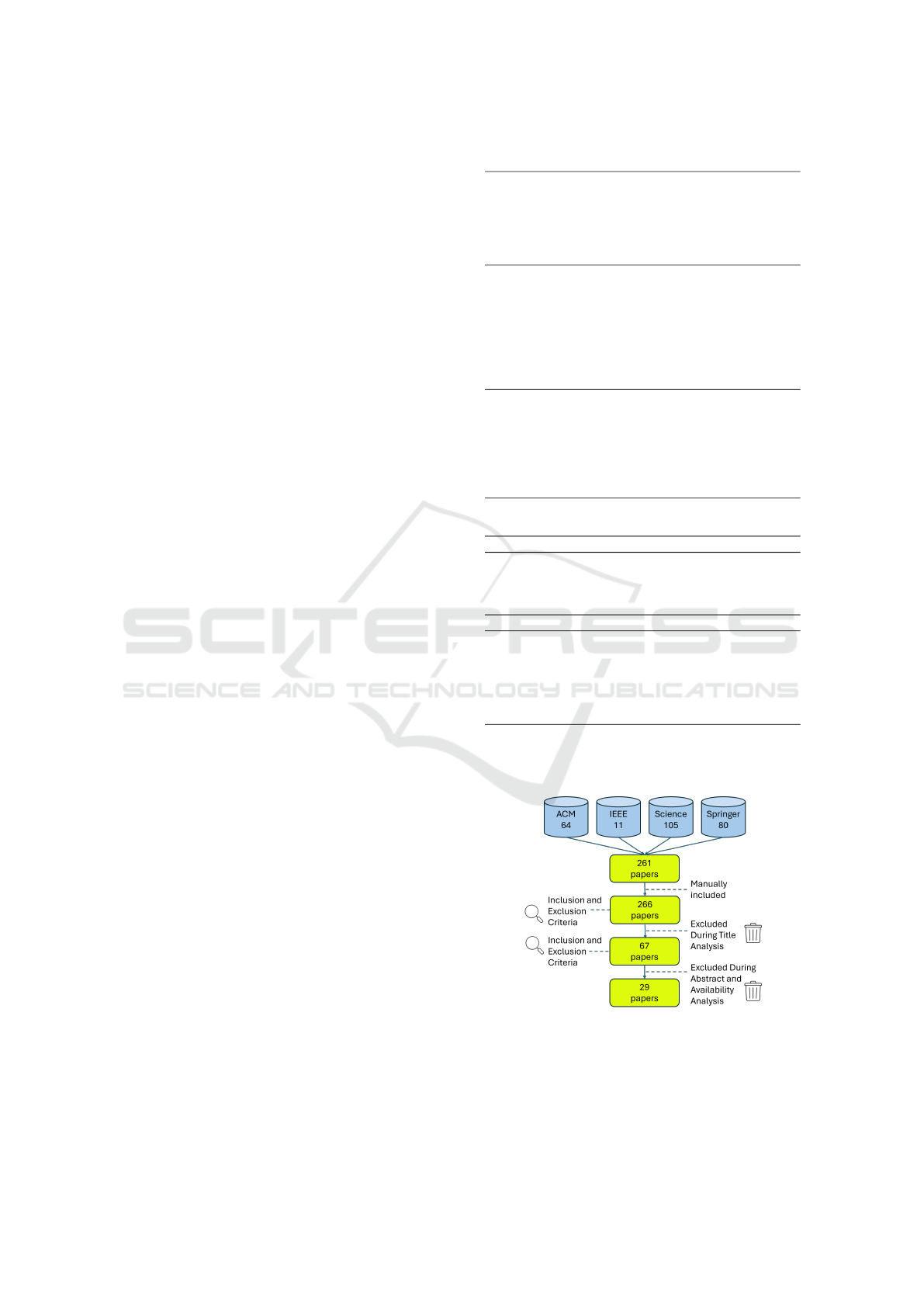
Searches were conducted across four major
databases: ACM Digital Library, IEEE Xplore,
ScienceDirect, and Springer Link, focusing on arti-
cles classified under the Computer Science domain.
The review timeframe covers publications from 2019
to 2024, emphasizing recent advancements in the
field. The initial search retrieved 261 papers. Ad-
ditionally, five manually selected articles identified
during the search strategy development phase were
included. During the title screening process, 199
articles were excluded based on predefined selection
criteria. Subsequently, 67 papers were reviewed
by analyzing their abstracts and assessing their
Table 1: Search Query.
Population
”Employee Verification” OR ”Attrition” OR ”Career
Development” OR ”Employability” OR ”Employee
Retention” OR ”Future of Work” OR ”Human Re-
source Management” OR ”Human Resources” OR
”Job Market” OR ”Labor Market”
Intervention
”Explainable AI” OR ”AI Transparency” OR ”Al-
gorithmic Transparency” OR ”Bias Mitigation” OR
”Explainability” OR ”Explainable Artificial Intelli-
gence” OR ”Fairness in AI” OR ”Interpretability” OR
”LIME” OR ”Model Interpretation” OR ”Post-Hoc
Explanation” OR ”SHAP” OR ”Shapley Additive Ex-
planations” OR ”XAI”
Outcome
”Hiring Process” OR ”Automatic Recruitment” OR
”Career Recommendation Systems” OR ”Job Match-
ing Algorithms” OR ”Performance Evaluation” OR
”Recruitment Automation” OR ”Talent Acquisition”
OR ”Workforce Management” OR ”Workplace Au-
tomation”
Table 2: Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria.
Inclusion Criteria
• Studies with identified black-box models
• Studies addressing research on artificial intelligence
responsibility in the job market
• Studies presenting methods to build explainability
Exclusion Criteria
• Papers that do not answer the research questions
• Studies outside the job market application domain
• Studies not written in English
• Studies that do not present a clear methodology
• Studies that do not investigate explainable artificial
intelligence
availability through institutional access. Ultimately,
29 articles were included in this systematic review, as
illustrated in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Study Selection Flow Diagram.
The quality of the articles was assessed based on
the following criteria, as established by (Kitchenham
et al., 2015): Does the study present clear and unam-
biguous findings? Is the context of the study clearly
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
1452

described? Are the research objectives explicitly de-
fined?
The extracted data were stored using the Parsifal
software. Data extraction followed 24 unique codes
and was analyzed based on the theoretical framework
and the research questions outlined in this study.
4 RESULTS
As a result of applying the proposed methods and pro-
cedures, this systematic review included 29 articles
published between 2019 and 2024 in the field of com-
puter science. Given that this is the first SLR focused
on explainability in the labor market, the number of
identified articles provides a solid foundation for con-
ducting meaningful analyses on the topic. It is im-
portant to note that although the search terms were
specific to the labor market, many of these terms are
commonly used across various application domains,
leading to relevant articles from other fields appear-
ing in the search results.
5 DISCUSSION
The analysis was structured as follows: articles ad-
dressing the first research question include surveys
with XAI users and contributions based on other
qualitative research methodologies. The responses
to research questions 2, 3, and 4 encompass articles
presenting explainability methods validated through
well-defined methodologies.
5.1 What Are the Socio-Technical
Requirements and the Design,
Implementation, and Evaluation
Challenges of Explainable Artificial
Intelligence Models?
Based on the analysis of the studies in this research,
three key requirements were identified to promote
transparency and explainability in artificial intelli-
gence systems applied to the labor market:
Bargaining: AI systems in the labor market can
benefit if they address employees’ desire to express,
negotiate, and contextualize outcomes, thereby bal-
ancing power asymmetries caused by informational
imbalances with employers. In studies on systems de-
signed to digitally monitor employees during task ex-
ecution (Das Swain et al., 2023), employees agreed to
share generated inferences as long as proper negotia-
tion and contextualization occurred. While employ-
ees do not perceive significant differences between
human managers and AI systems regarding objec-
tive aspects such as salaries and bonuses, they expect
greater empathy and emotional support from human
managers in areas like career development (Tomprou
and Lee, 2022). Unmet expectations in these subjec-
tive areas result in greater disappointment when hu-
man interaction is involved, highlighting the impor-
tance of transparent communication in AI-mediated
workplaces.
Job candidates, on the other hand, showed a strong
preference for traditional face-to-face interviews over
those conducted by AI systems (Lashkari and Cheng,
2023; Girona and Yarger, 2024), reflecting the im-
portance of contextual interaction in the candidate
selection process. This need for contextualization
also manifests in candidates’ ability to express their
identities and share their lived experiences and as-
pirations autonomously during interviews (Aizenberg
et al., 2023).
Human Resources Biases: AI systems in the la-
bor market can benefit if they identify and address
historical, conscious, or unconscious biases present
in human resources processes. Corporate data re-
lated to recruitment or performance evaluation often
reflect historical decisions influenced by human bi-
ases. AI tools can help reduce such biases by ap-
plying objective and adjustable criteria, improving
job requirement definitions, structuring interviews,
and conducting skill-based assessments (Lashkari and
Cheng, 2023). Explainability, in this context, helps
both specialists and employees identify errors and bi-
ases in AI outcomes (Park et al., 2022).
However, addressing biases requires particular at-
tention to underrepresented groups. For instance, can-
didates with disabilities face challenges that expose
the need for more equitable and context-sensitive ap-
proaches (Tilmes, 2022). Traditional bias mitigation
strategies often overlook critical differences, under-
scoring the importance of centering candidates’ lived
experiences in achieving algorithmic fairness.
Labor Market Fairness: AI systems in the
labor market can benefit if they incorporate fair-
ness concepts tailored to the context of human re-
sources processes. Issues such as biased predic-
tions, reliance on rigid quantification, and limitations
in identifying groups in computational systems have
faced widespread criticism (S
´
anchez-Monedero et al.,
2020). Using attributes like gender or race to im-
prove predictive performance raises ethical and tech-
nical dilemmas, as well as underlying power dynam-
ics that risk perpetuating structural inequalities unless
participatory approaches are implemented (Park et al.,
Explainable AI in Labor Market Applications
1453

2022).
Defining and measuring algorithmic fairness
poses significant challenges. Professionals working
with responsible AI require organizational support to
drive changes that enable ethical practices (Rakova
et al., 2021). The ethical implementation of AI sys-
tems in recruitment is not inherently unethical; the
associated risks stem from inflated expectations and
the indiscriminate use of automated recruitment tools.
An ethical approach demands a clear definition of
what constitutes a fair AI system (Hunkenschroer and
Kriebitz, 2023). In this regard, counterfactual fair-
ness allows for greater flexibility in decision-making
by considering specific conditions and varied contexts
(Hauer et al., 2021).
These aspects highlight the importance of AI sys-
tems that prioritize transparency, bias mitigation, and
equity in their applications within the labor market.
5.2 Which Labor Market AI
Applications Have Benefited from
the Implementation of XAI?
The reviewed articles propose explainability mod-
els applied to three key processes in the labor mar-
ket: candidate selection and recruitment, professional
skill recommendation, and employee performance
evaluation. Each of these automated processes ad-
dresses specific tasks inherent to its domain within
the labor market. In the context of automated re-
cruitment, identified tasks include candidate profile
evaluation (Bhattacharya et al., 2022; Sogancioglu
et al., 2023), interview assessment (Marra and Ku-
biak, 2024; Koutsoumpis et al., 2024), candidate-job
fit prediction (Pessach et al., 2020), resume parsing
(Pe
˜
na et al., 2023), fraud detection in job advertise-
ments (Naud
´
e et al., 2023), and recruitment demand
forecasting (Zhang et al., 2021).
In the area of professional skill recommendation,
two studies presented methods (Akkasi, 2024; Tran
et al., 2021) designed to extract relevant skills from
job descriptions while integrating user feedback to
enhance recommendation systems through reinforce-
ment learning algorithms (Sun et al., 2021; Sun et al.,
2024). Similarly, the automation of employee eval-
uation processes has been applied to measure job
performance (Sampath et al., 2024; Maurya et al.,
2018) and predict potential employee attrition (Das
et al., 2022; Makanga et al., 2024; Sekaran and Shan-
mugam, 2022), contributing to data-driven human re-
source management strategies.
5.3 What Are the Novel XAI
Approaches That Have Been
Developed and Implemented?
Among the 17 different methods for explainability
presented, three stood out for their transparent ap-
proaches aimed at enhancing model interpretability.
In the first approach, explainability was achieved
by applying the Variable-Order Bayesian Network
(VOBN) model to recruitment data (Pessach et al.,
2020). The second method (Tran et al., 2021) uti-
lized counterfactual reasoning to infer the causal ef-
fects of various factors on employment status, rec-
ommending the most effective interventions accord-
ingly. Additionally, the third approach (Maurya et al.,
2018) involved the development of a stylized log-
linear model designed to uncover hidden aspects and
sentiment within an employee peer review corpus.
Another method employed was the use of feature
importance to evaluate the influence of individual fea-
tures on the model’s outcome, representing a signif-
icant contribution to the field. Aiming to identify
fraudulent ads in a comprehensible manner, the most
important features in (Naud
´
e et al., 2023) were ex-
tracted from the best-performing rule-set-based clas-
sifier, the Random Forest with POS tags. Meanwhile,
(Marra and Kubiak, 2024) introduced a novel frame-
work designed to filter user data, detect gender bias,
and implement a feature importance block to enhance
explainability.
Six studies employed SHAP to provide explain-
ability. Two of these focused on candidate profile
evaluation, using SHAP exclusively (Bhattacharya
et al., 2022; Sogancioglu et al., 2023). Addition-
ally, three studies on employee attrition prediction
(Das et al., 2022; Makanga et al., 2024; Sekaran and
Shanmugam, 2022) and one study on employee per-
formance assessment (Sampath et al., 2024) applied
SHAP in combination with the LIME method. An-
other study, centered on recommending professional
skills, relied solely on the LIME method (Akkasi,
2024).
(Sun et al., 2024) proposed a Self-Explaining
Skill Recommendation framework that identifies and
prototypes prevalent market skill sets into represen-
tative exemplars to support decision-making. This
approach quantitatively decomposes the long-term
learning utility of talents into contributions from each
exemplar. It represents an extended and revised ver-
sion of the authors’ previous study, published three
years earlier (Sun et al., 2021). (Zhang et al.,
2021) implemented a data-driven neural sequential
approach called the Talent Demand Attention Net-
work (TDAN), designed to forecast fine-grained tal-
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
1454

ent demand in the recruitment market.
5.4 How Can Machine Learning and
AI-Based Frameworks Be Designed
to Promote Fairness and Reduce
Bias in Automated Recruitment and
Job Evaluation Systems?
(Pe
˜
na et al., 2023) proposed a methodology demon-
strating how to create fairer AI-based tools, partic-
ularly in automated recruitment systems. Similarly,
(Marra and Kubiak, 2024) introduced a framework
leveraging neural networks as an effective strategy for
enhancing fairness in hiring practices with minimal
predictive accuracy loss. Additionally, (Tran et al.,
2021) integrated a machine learning-based framework
to effectively recommend skill upgrades for disabled
job seekers, identifying both the specific skills to im-
prove and the optimal upgrade level to maximize their
employment potential.
In a study on the automatic evaluation of job in-
terviews, (Koutsoumpis et al., 2024) examined bias
issues and emphasized the need for developing ma-
chine learning methodologies specifically designed to
address these challenges.
6 CONCLUSIONS
This study provided a segmented view of explain-
ability methods in the labor market and analyzed the
sociotechnical requirements highlighted by users. A
systematic review was conducted using search strate-
gies applied to major computer science databases.
The search process identified 266 eligible studies,
from which 29 papers were selected after evaluation,
offering a detailed perspective on explainability and
fairness in the labor market.
AI systems in the labor market can benefit from
integrating three fundamental requirements: bargain-
ing, which enables employees and candidates to ex-
press their perspectives, negotiate outcomes, and con-
textualize decisions to balance informational asym-
metries; bias mitigation, which is crucial for identi-
fying and addressing historical biases in human re-
sources processes, fostering greater inclusion and eq-
uity; and fairness, which demands context-specific
approaches to address ethical and structural dilem-
mas, avoiding the perpetuation of inequalities. These
elements are essential for developing transparent, eth-
ical, and trustworthy AI systems that not only opti-
mize processes but also promote fairer and more col-
laborative workplace relationships. Three main labor
market processes emerged as more advanced in terms
of explainability development: recruitment, profes-
sional skill recommendation, and employee perfor-
mance evaluation. Within these processes, specific
tasks involving explainability methods were identi-
fied.
From the perspective of applied explainability
methods, the selected papers included studies where
explainability was integrated by design. Common
explainability techniques and more advanced frame-
works delivering post-hoc explainability were also
frequently used. Notably, none of the papers evalu-
ated user satisfaction.
Overall, the findings clarified key issues, high-
lighted explainability needs, and mapped methods ad-
dressing different labor market processes and tasks.
However, there is still considerable room for progress,
especially when viewed through the lens of explain-
ability literature. Since the labor market is character-
ized by information asymmetry, balancing explana-
tions could enhance the effective adoption of AI sys-
tems by placing users at the center of explainability
method development.
XAI has been advancing across various sectors,
yet significant opportunities remain for its develop-
ment in the labor market. Future research could ex-
plore user perspectives by assessing satisfaction, trust,
and understanding. These measures are essential for
validating proposed methods and fostering greater
adoption of AI systems. Simultaneously, a critical gap
in the literature persists regarding how reducing in-
formational imbalances among different users could
enhance explainability in artificial intelligence.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This study was financed in part by the Coordenac¸
˜
ao
de Aperfeic¸oamento de Pessoal de N
´
ıvel Superior –
Brasil (CAPES) – Finance Code 001. Part of the text
revision and refinement was conducted with the assis-
tance of ChatGPT, an AI-based language model de-
veloped by OpenAI, to enhance clarity and coherence.
REFERENCES
Aizenberg, E., Dennis, M. J., and van den Hoven, J. (2023).
Examining the assumptions of ai hiring assessments
and their impact on job seekers’ autonomy over self-
representation. AI & society, pages 1–9.
Akkasi, A. (2024). Job description parsing with explain-
able transformer based ensemble models to extract the
technical and non-technical skills. Natural Language
Processing Journal, 9:100102.
Explainable AI in Labor Market Applications
1455

Al-Alawi, A. I. and Ghanem, Y. A. (2024). Predicting em-
ployee attrition using machine learning: A systematic
literature review. In 2024 ASU International Confer-
ence in Emerging Technologies for Sustainability and
Intelligent Systems (ICETSIS), pages 526–530. IEEE.
Ali, S., Abuhmed, T., El-Sappagh, S., Muhammad, K.,
Alonso-Moral, J. M., Confalonieri, R., Guidotti, R.,
Del Ser, J., D
´
ıaz-Rodr
´
ıguez, N., and Herrera, F.
(2023a). Explainable artificial intelligence (xai):
What we know and what is left to attain trustworthy
artificial intelligence. Information fusion, 99:101805.
Ali, S., Akhlaq, F., Imran, A. S., Kastrati, Z., Daudpota,
S. M., and Moosa, M. (2023b). The enlightening
role of explainable artificial intelligence in medical
& healthcare domains: A systematic literature review.
Computers in Biology and Medicine, page 107555.
Arrieta, A. B., D
´
ıaz-Rodr
´
ıguez, N., Del Ser, J., Bennetot,
A., Tabik, S., Barbado, A., Garc
´
ıa, S., Gil-L
´
opez, S.,
Molina, D., Benjamins, R., et al. (2020). Explainable
artificial intelligence (xai): Concepts, taxonomies, op-
portunities and challenges toward responsible ai. In-
formation fusion, 58:82–115.
Bertrand, A., Belloum, R., Eagan, J. R., and Maxwell,
W. (2022). How cognitive biases affect xai-assisted
decision-making: A systematic review. In Proceed-
ings of the 2022 AAAI/ACM Conference on AI, Ethics,
and Society, pages 78–91.
Bhattacharya, P., Zuhair, M., Roy, D., Prasad, V. K., and
Savaliya, D. (2022). Aajeevika: Trusted explainable
ai based recruitment scheme in smart organizations. In
2022 5th International Conference on Contemporary
Computing and Informatics (IC3I), pages 1002–1008.
IEEE.
Black, J. S. and van Esch, P. (2020). Ai-enabled recruiting:
What is it and how should a manager use it? Business
Horizons, 63(2):215–226.
Bogen, M. (2019). All the ways hiring algorithms can in-
troduce bias. Harvard Business Review, 6:2019.
B
¨
ohm, M. J., von Gaudecker, H.-M., and Schran, F. (2024).
Occupation growth, skill prices, and wage inequality.
Journal of Labor Economics, 42(1):201–243.
Bujold, A., Roberge-Maltais, I., Parent-Rocheleau, X.,
Boasen, J., S
´
en
´
ecal, S., and L
´
eger, P.-M. (2024). Re-
sponsible artificial intelligence in human resources
management: a review of the empirical literature. AI
and Ethics, 4(4):1185–1200.
ˇ
Cernevi
ˇ
cien
˙
e, J. and Kaba
ˇ
sinskas, A. (2024). Explain-
able artificial intelligence (xai) in finance: A system-
atic literature review. Artificial Intelligence Review,
57(8):216.
Chowdhury, S., Dey, P., Joel-Edgar, S., Bhattacharya, S.,
Rodriguez-Espindola, O., Abadie, A., and Truong, L.
(2023). Unlocking the value of artificial intelligence
in human resource management through ai capabil-
ity framework. Human resource management review,
33(1):100899.
Das, S., Chakraborty, S., Sajjan, G., Majumder, S., Dey,
N., and Tavares, J. M. R. (2022). Explainable ai for
predictive analytics on employee attrition. In Inter-
national Conference on Soft Computing and its Engi-
neering Applications, pages 147–157. Springer.
Das Swain, V., Gao, L., Wood, W. A., Matli, S. C., Abowd,
G. D., and De Choudhury, M. (2023). Algorithmic
power or punishment: Information worker perspec-
tives on passive sensing enabled ai phenotyping of
performance and wellbeing. In Proceedings of the
2023 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Comput-
ing Systems, pages 1–17.
Fidel, G., Bitton, R., and Shabtai, A. (2020). When explain-
ability meets adversarial learning: Detecting adversar-
ial examples using shap signatures. In 2020 interna-
tional joint conference on neural networks (IJCNN),
pages 1–8. IEEE.
Girona, A. E. and Yarger, L. (2024). To impress an algo-
rithm: Minoritized applicants’ perceptions of fairness
in ai hiring systems. In International Conference on
Information, pages 43–61. Springer.
Hauer, M. P., Kevekordes, J., and Haeri, M. A. (2021).
Legal perspective on possible fairness measures–a le-
gal discussion using the example of hiring decisions.
Computer Law & Security Review, 42:105583.
Hunkenschroer, A. L. and Kriebitz, A. (2023). Is ai recruit-
ing (un) ethical? a human rights perspective on the use
of ai for hiring. AI and Ethics, 3(1):199–213.
Johansson, F., Shalit, U., and Sontag, D. (2016). Learn-
ing representations for counterfactual inference. In
International conference on machine learning, pages
3020–3029. PMLR.
Kitchenham, B. A., Budgen, D., and Brereton, P. (2015).
Evidence-based software engineering and systematic
reviews, volume 4. CRC press.
Koutsoumpis, A., Ghassemi, S., Oostrom, J. K., Holtrop,
D., Van Breda, W., Zhang, T., and de Vries, R. E.
(2024). Beyond traditional interviews: Psychomet-
ric analysis of asynchronous video interviews for per-
sonality and interview performance evaluation using
machine learning. Computers in Human Behavior,
154:108128.
Lashkari, M. and Cheng, J. (2023). “finding the magic
sauce”: Exploring perspectives of recruiters and job
seekers on recruitment bias and automated tools. In
Proceedings of the 2023 CHI Conference on Human
Factors in Computing Systems, pages 1–16.
Linardatos, P., Papastefanopoulos, V., and Kotsiantis, S.
(2020). Explainable ai: A review of machine learn-
ing interpretability methods. Entropy, 23(1):18.
Lukacik, E.-R., Bourdage, J. S., and Roulin, N. (2022). Into
the void: A conceptual model and research agenda for
the design and use of asynchronous video interviews.
Human Resource Management Review, 32(1):100789.
Lundberg, S. (2017). A unified approach to interpreting
model predictions. arXiv preprint arXiv:1705.07874.
Makanga, C., Mukwaba, D., Agaba, C. L., Murindanyi, S.,
Joseph, T., Hellen, N., and Marvin, G. (2024). Ex-
plainable machine learning and graph neural network
approaches for predicting employee attrition. In Pro-
ceedings of the 2024 Sixteenth International Confer-
ence on Contemporary Computing, pages 243–255.
Marra, T. and Kubiak, E. (2024). Addressing diversity in
hiring procedures: a generative adversarial network
approach. AI and Ethics, pages 1–25.
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
1456

Maurya, A., Akoglu, L., Krishnan, R., and Bay, D. (2018).
A lens into employee peer reviews via sentiment-
aspect modeling. In 2018 IEEE/ACM International
Conference on Advances in Social Networks Analysis
and Mining (ASONAM), pages 670–677. IEEE.
Naud
´
e, M., Adebayo, K. J., and Nanda, R. (2023). A ma-
chine learning approach to detecting fraudulent job
types. AI & SOCIETY, 38(2):1013–1024.
Olckers, M. and Walsh, T. (2024). Manipulation and peer
mechanisms: A survey. Artificial Intelligence, page
104196.
Park, H., Ahn, D., Hosanagar, K., and Lee, J. (2022). De-
signing fair ai in human resource management: Un-
derstanding tensions surrounding algorithmic evalu-
ation and envisioning stakeholder-centered solutions.
In Proceedings of the 2022 CHI conference on human
factors in computing systems, pages 1–22.
Pe
˜
na, A., Serna, I., Morales, A., Fierrez, J., Ortega, A., Her-
rarte, A., Alcantara, M., and Ortega-Garcia, J. (2023).
Human-centric multimodal machine learning: Recent
advances and testbed on ai-based recruitment. SN
Computer Science, 4(5):434.
Pessach, D., Singer, G., Avrahami, D., Ben-Gal, H. C.,
Shmueli, E., and Ben-Gal, I. (2020). Employees re-
cruitment: A prescriptive analytics approach via ma-
chine learning and mathematical programming. Deci-
sion Support Systems, 134:113290.
Rakova, B., Yang, J., Cramer, H., and Chowdhury, R.
(2021). Where responsible ai meets reality: Practi-
tioner perspectives on enablers for shifting organiza-
tional practices. Proceedings of the ACM on Human-
Computer Interaction, 5(CSCW1):1–23.
Ribeiro, M. T., Singh, S., and Guestrin, C. (2016). ” why
should i trust you?” explaining the predictions of any
classifier. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD
international conference on knowledge discovery and
data mining, pages 1135–1144.
Rigotti, C. and Fosch-Villaronga, E. (2024). Fairness, ai
& recruitment. Computer Law & Security Review,
53:105966.
Roemmich, K., Rosenberg, T., Fan, S., and Andalibi, N.
(2023). Values in emotion artificial intelligence hiring
services: Technosolutions to organizational problems.
Proceedings of the ACM on Human-Computer Inter-
action, 7(CSCW1):1–28.
Sampath, K., Devi, K., Ambuli, T., and Venkatesan, S.
(2024). Ai-powered employee performance evalua-
tion systems in hr management. In 2024 7th Interna-
tional Conference on Circuit Power and Computing
Technologies (ICCPCT), volume 1, pages 703–708.
IEEE.
S
´
anchez-Monedero, J., Dencik, L., and Edwards, L. (2020).
What does it mean to’solve’the problem of discrimina-
tion in hiring? social, technical and legal perspectives
from the uk on automated hiring systems. In Proceed-
ings of the 2020 conference on fairness, accountabil-
ity, and transparency, pages 458–468.
Sekaran, K. and Shanmugam, S. (2022). Interpreting the
factors of employee attrition using explainable ai.
In 2022 International Conference on Decision Aid
Sciences and Applications (DASA), pages 932–936.
IEEE.
Sogancioglu, G., Kaya, H., and Salah, A. A. (2023). Using
explainability for bias mitigation: A case study for fair
recruitment assessment. In Proceedings of the 25th
International Conference on Multimodal Interaction,
pages 631–639.
Sun, Y., Ji, Y., Zhu, H., Zhuang, F., He, Q., and Xiong, H.
(2024). Market-aware long-term job skill recommen-
dation with explainable deep reinforcement learning.
ACM Transactions on Information Systems.
Sun, Y., Zhuang, F., Zhu, H., He, Q., and Xiong, H. (2021).
Cost-effective and interpretable job skill recommen-
dation with deep reinforcement learning. In Proceed-
ings of the Web Conference 2021, pages 3827–3838.
Tambe, P., Cappelli, P., and Yakubovich, V. (2019). Ar-
tificial intelligence in human resources management:
Challenges and a path forward. California Manage-
ment Review, 61(4):15–42.
Tilmes, N. (2022). Disability, fairness, and algorithmic bias
in ai recruitment. Ethics and Information Technology,
24(2):21.
Tomprou, M. and Lee, M. K. (2022). Employment rela-
tionships in algorithmic management: A psychologi-
cal contract perspective. Computers in Human Behav-
ior, 126:106997.
Tran, H. X., Le, T. D., Li, J., Liu, L., Liu, J., Zhao, Y.,
and Waters, T. (2021). Recommending the most ef-
fective intervention to improve employment for job
seekers with disability. In Proceedings of the 27th
ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery
& Data Mining, pages 3616–3626.
Trinh, N. and Elbanna, A. (2023). Ai and human relation-
ship in the workplace: A literature review and future
research agenda. In International Working Confer-
ence on Transfer and Diffusion of IT, pages 144–156.
Springer.
Vasconcelos, M., Cardonha, C., and Gonc¸alves, B. (2018).
Modeling epistemological principles for bias mitiga-
tion in ai systems: an illustration in hiring decisions.
In Proceedings of the 2018 AAAI/ACM Conference on
AI, Ethics, and Society, pages 323–329.
Webb, M. (2019). The impact of artificial intelligence on
the labor market. Available at SSRN 3482150.
Zhang, Q., Zhu, H., Sun, Y., Liu, H., Zhuang, F., and Xiong,
H. (2021). Talent demand forecasting with attentive
neural sequential model. In Proceedings of the 27th
ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery
& Data Mining, pages 3906–3916.
Explainable AI in Labor Market Applications
1457
