
Predicting Respiratory Depression in Neonates Using Deep Learning
Neural Networks
Aleksandar Jeremic
1
and Dejan Nikolic
2
1
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, McMaster University, Hamilton, ON, Canada
2
Faculty of Medicine, University of Belgrade, Belgrade, Serbia
Keywords:
Inter-Arterial Pressure Measurements, Signal Models.
Abstract:
Respiratory problems are one of the most common reasons for neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) admis-
sion of newborns. It has been estimated that as much as 29% of late preterm infants develop high respiratory
morbidity. To this purpose invasive ventilation is often necessary for their treatment in NICU. These patients
usually have underdeveloped respiratory system with deficiencies such as small airway caliber, few collateral
airways, compliant chest wall, poor airway stability, and low functional residual capacity. Consequently ven-
tilation control has been subject of considerable research interest. In this paper we propose an algorithm for
detection of respiratory depression by predicting the onset of pO
2
depressions using physiological measure-
ments. We train deep neural network using previously obtained data set from NICU, McMaster University
Hospital with intra-arterial pressure measurements and evaluate its performance. Preliminary results indicate
that adequate performance can be achieved if sufficient number of measurements is available.
1 INTRODUCTION
Newborn intensive care is one of the great medical
success of the last 20 years. Current emphasis is upon
allowing infants to survive with the expectation of
normal life without handicap. Clinical data from fol-
low up studies of infants who received neonatal in-
tensive care show high rates of long-term respiratory
and neurodevelopment morbidity. As a consequence,
current research efforts are being focused on refine-
ment of ventilated respiratory support given to infants
during intensive care (Revow et al., 1989).
The main task of the ventilated support is to
maintain the concentration level of oxygen (O
2
) and
carbon-dioxide (CO
2
) in the blood within the phys-
iological range until the maturation of lungs occur.
Failure to meet this objective can lead to various
pathophysiological conditions. Therefore one of the
most critical components in the neonatal intensive
care units (NICU) is an adequate ventilation control.
In addition, due to a fragile state of neonatal lungs
the ventilation control has to be designed very care-
fully as neither hyperventilation nor hypoventilation
are acceptable.
In our previous work (Jeremic and Tan, 2007)
we developed a deterministic inverse mathematical
model of the CO
2
partial pressure variations in the ar-
terial blood of a ventilated neonate. We evaluated the
applicability of the proposed model using clinical data
sets obtained from neonatal multi-parameter intra-
arterial sensor which enables intra-arterial measure-
ments of partial pressures. Using this model we de-
veloped statistical signal processing model (Jeremic
and Tan, 2009) that predicts both inter-arterial pres-
sure measurements and corresponding confidence in-
tervals. In (Jeremic and Nikolic, 2019) we proposed
an algorithm for prediction of clinical depression
in neonates using parametric model based approach.
The proposed algorithms performs detection of pO
2
depression events using intra-arterial pressure mea-
surements and parametric model based on the log-
Riemannian distance between sample covariance ma-
trix measurements. However, intra-arterial pressure
measurements are administered only in rare cases that
warrant more intensive style of patient monitoring. To
this purpose in this paper we design a deep neural net-
work and use available data-set and intra-arterial pres-
sure measurements as ground truth in order to train
the network.
Deep neural networks are becoming increasingly
popular in the biomedical signal processing due to
the fact that they do not rely on the parametric model
which may be beneficial due to patient-to-patient vari-
ability. In Section 2 we outline the structure of the
1054
Jeremic, A. and Nikolic, D.
Predicting Respiratory Depression in Neonates Using Deep Learning Neural Networks.
DOI: 10.5220/0013385400003911
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 18th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2025) - Volume 1, pages 1054-1057
ISBN: 978-989-758-731-3; ISSN: 2184-4305
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
0 500 1000 1500 2000 2500
Time[ms]
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
p
O
2 [kPa]
Figure 1: Sample of intra-arterial pressure measurements.
deep neural network and the corresponding signal
processing algorithms. In Section 3 we illustrate the
applicability of the proposed techniques by evaluat-
ing the performance of the proposed network using
a validation set that was not used as a part of train-
ing. Our preliminary results indicate that the onset of
oxygen depression can be predicted with potentially
useful accuracy sufficient to alarm the clinical staff
of the NICU. In Section 4 we provide concluding re-
marks and discuss further directions.
2 SIGNAL PROCESSING
MODELS
To examine the applicability of the proposed algo-
rithms we apply them to the data set obtained in the
Neonatal Unit at McMaster University Hospital. The
data set consists of intra-arterial partial pressure mea-
surements obtained from 91 ventilated neonates. The
sampling time was set to 10s and the expiratory rate
was set to 1 breath per second. In Figure 1 we illus-
trate a sample of intra-arterial pressure measurements.
In order to predict the onset of respiratory de-
pression (hypo-ventilating) condition in (Jeremic and
Nikolic, 2019) we calculated the sample covariance
matrix we propose to use Frechet mean (Jahromi,
2014) which is given as the point which minimizes
the sum of the squared distances (Barbaresco, 2008):
and the log-Riemannian distance measure given by
(Moakher, 2005):
d
l
(A, B) =
log(A
−
1
2
BA
−
1
2
)
2
=
s
M
∑
i=1
log
2
(L
i
)
(1)
where the L
i
’s are the eigenvalues of the matrix A
−1
B
(Absil et al., 2009) where A and B are arbitrary M × M
matrices whose distance is being calculated. The de-
tails of this algorithm are provided in the aforemen-
tioned reference (Jeremic and Nikolic, 2019).
Figure 2: The schematic of the artificial neural network
(ANN).
Figure 3: Validation results for ANN training for different
scenarios.
In this paper we propose to use deep learn-
ing neural network (DNN) illustrated in Figure 2.
We use the four dimensional physiological measure-
ments consisting of partial pressure measurements
of oxygen, breathing rate, electrocardiography mea-
surements and intra-arterial pressure measurements
(available only for some patients). The covariance
matrix on the temporal window of N samples is cal-
culated of the physiological signals is calculated ( 4 x
4 ) and provided as a time-series input to DNN. The
training of the network is provided as an additional
input of the critical event (respiratory depression) is
labeled by a critical event triggered by an alarm which
is used as a ground truth. In Figure 3 we illustrate the
performance of the DNN to adequately predict the fu-
ture values of the distance measure (i.e. distance be-
tween sample covariance matrix of the physiological
signals). To illustrate the applicability of the proposed
method and evaluate the need for intra-arterial pres-
sure measurements we utilize two different designs
which differ with respect to input dimensions with
and without the presence of the intra-arterial pressure
measurements. The orange line represents validation
error in the absence of the intra-arterial pressure. The
purple, red and blue lines represent validation errors
for the DNN that are trained to predict critical event
in time windows of 1, 5 and 10 minutes respectively.
The above results indicate that in order to achieve
lower validation error we would benefit greatly from
intra-arterial pressure measurements.
Predicting Respiratory Depression in Neonates Using Deep Learning Neural Networks
1055
3 RESULTS
We evaluate the performance of the proposed algo-
rithms using the data set obtained at the Neonatal
Intensive Care Unit, at McMaster University Hospi-
tal. At each cot in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
at the McMaster Children’s Hospital there is a cot-
side monitor displaying the physiological parameters
measured. Moreover, these monitors are linked in a
network with a central station into which data can be
rapidly exported via Draeger Infinity Gateway soft-
ware. Data is stored in the central station for 24 hours.
The final dataset contained 91 patients with the num-
ber of recorded days for each patient varying between
1 and 90 with a mean of 32 days. In order to study
the changes with respect to the length of stay we se-
lected only patients who stayed up to 4 weeks and
performed evaluation for different weeks using cumu-
lative dataset.
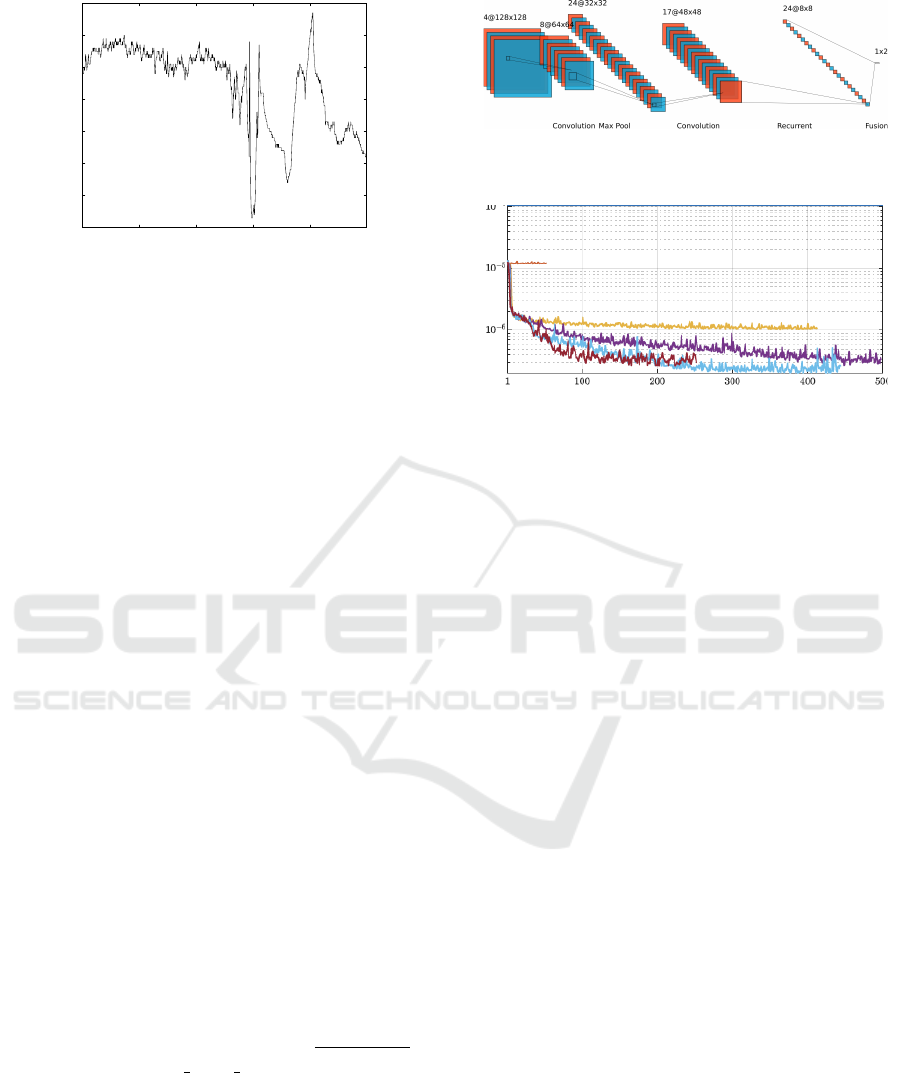
In Figure 4 we illustrate the event corresponding
to the respiratory depression as well as the change in
the covariance matrix distance when calculated com-
pared to the Frechet mean in the absence of respi-
ratory depression. In our previous work (Jeremic
and Nikolic, 2019) we evaluated performance of the
model based approach whose application relies on the
use of one particular distance. We believe that in com-
plex physiological problems we may benefit by allow-
ing the network to learn the processes in an uncon-
strained way as different distances may work better
for different patients. Since the time is of essence
in NICU, we may not have enough time to gather
enough data for a particular patients and thus deep
learning networks may be more useful regardless of
patient to patient variability. To this purpose the orig-
inal DNN was extended to include task of classifica-
tion using the respiratory depression alarms as indi-
cated by cot-bed monitors.
In order to evaluate the performance of the pro-
posed DNN we train the network using the available
data for (N-1) i.e. 91 patients and evaluate perfor-
mance on the single patients that was not used for
training. We then repeat these process for all the 92
patients thus effectively performing rotational eval-
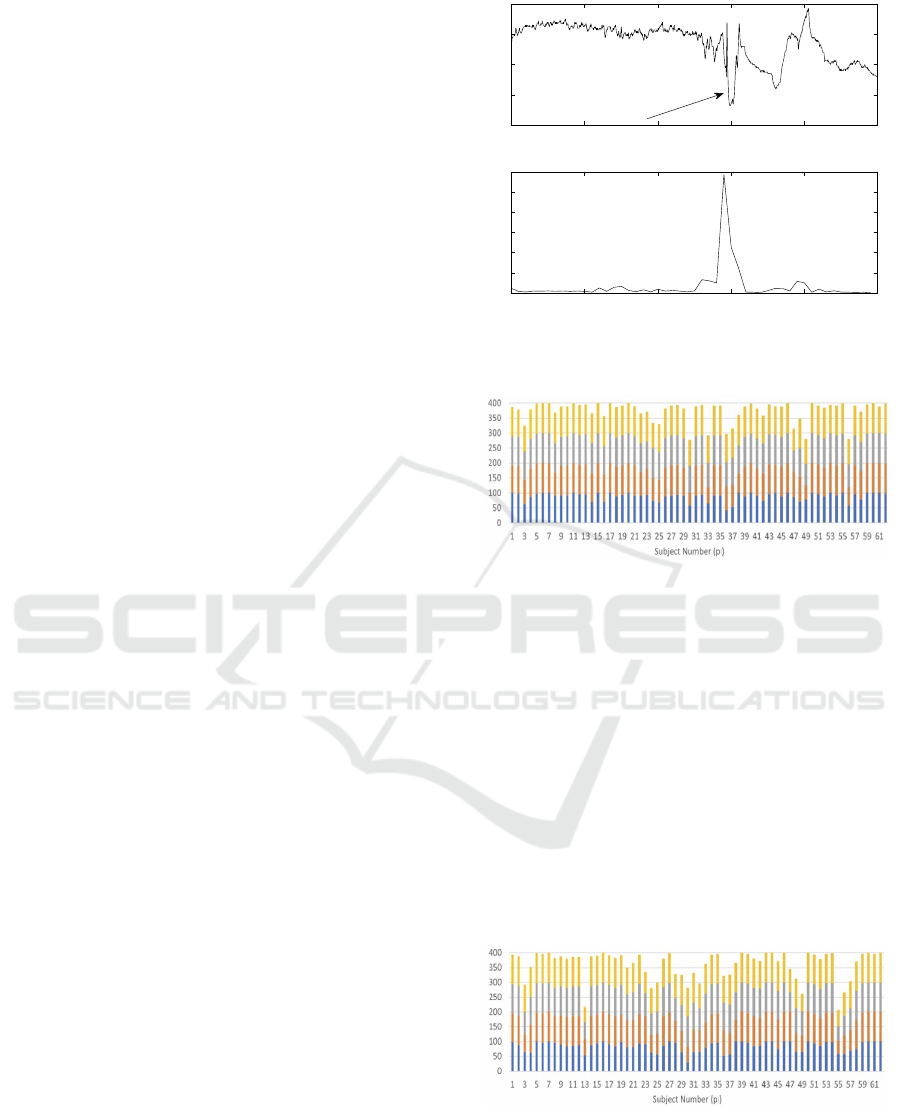
uation of the proposed network. In Figures 5 and
6 we illustrate the respiratory depression detection
for different subjects 5 min and 10 min before res-
piratory depression respectively. The four different
colours represent different weeks of NICU hospital-
ization. Preliminary results indicate that for this par-
ticular set there is not a significant change in our abil-
ity to predict onset of respiratory depression. Please
note that this may be the consequence of the physio-
logical state of the patients which is general correlated
0 500 1000 1500 2000 2500
a) Time [ms]
4
6
8
10
12
p
O
2 [kPa]
0 500 1000 1500 2000 2500
b) Time[ms]
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
Distance
Figure 4: Sample of depression event as perceived by intra-
arterial pressure measurement and breathing rate.
Figure 5: Detection probability as a function of false posi-
tives 5min window.
with the length of stay. In Figure 7 we illustrate the
overall accuracy for all the subjects where the overall
accuracy is defined as inverse of both types of error
(probabilities of false alarm and miss).
Finally in Table 1 we illustrate the precision, re-
call and F-score of the proposed system including all
91 patients. We can observe that the performance sig-
nificantly deteriorates when compared to ”more sta-
ble” patients due to the fact that in the case of long
stay patients the number of respiratory depressions
is much larger. In addition, the statistical variability
of the measurements in these patients may be much
higher.
Figure 6: Detection probability as a function of false posi-
tives 10 min window.
BIOSIGNALS 2025 - 18th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
1056
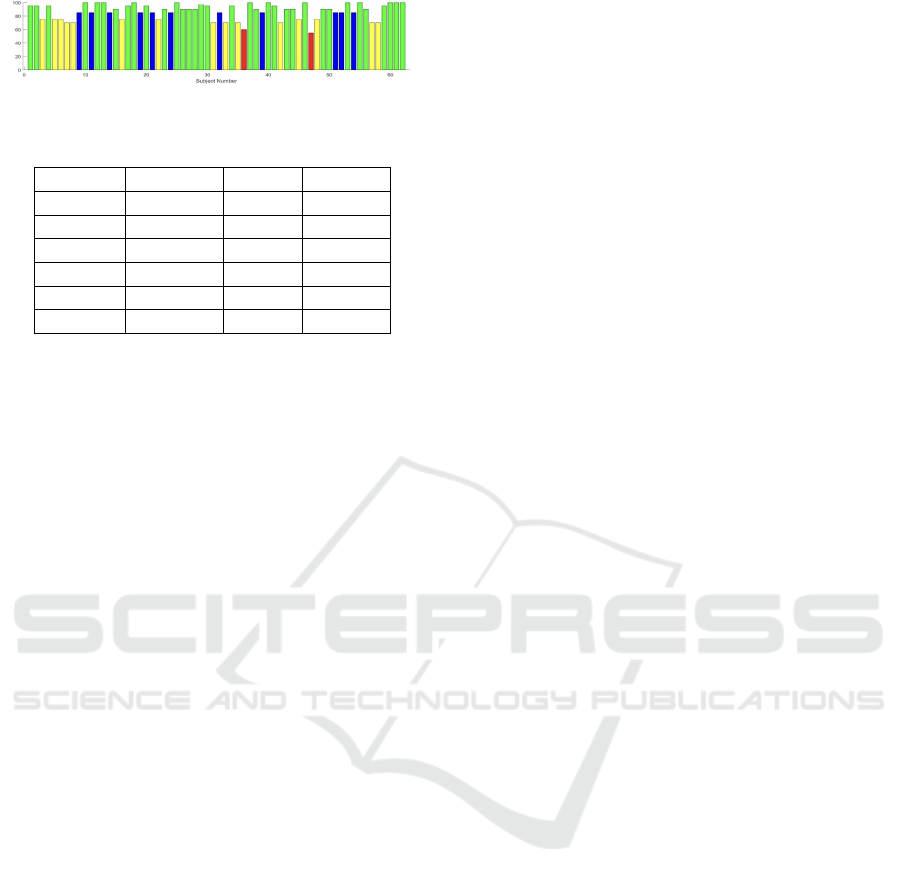
Figure 7: Overall probability of error per subject.
Table 1: Overall performance for all the patients.
Window Precision Recall F-score
10 min 0.7099 0.6911 0.7003
8 min 0.7492 0.733 0. 741
5 min 0.7846 0.7709 0.7777
3 min 0.7546 0.7411 0.7478
2 min 0.7874 0.7774 0.7824
1 min 0.8294 0.8201 0.8247
4 CONCLUSIONS
One of the most important tasks that affect both long-
and short-term outcomes of neonatal intensive care is
maintaining proper ventilation support. To this pur-
pose in this paper we develop signal processing algo-
rithms for predicting the onset of hypoventilation in
order to increase efficient control of ventilation sys-
tem in timely manner. This is especially important for
neonates due to a fragile state of their lungs and hence
predicting the decrease oxygen levels can potentially
enable us to control the ventilator with smaller dy-
namic range.
In this paper we propose to predict the onset us-
ing second order statistical properties by calculating
sample covariance matrices using Frechet mean. Our
experimental results indicate that the structure of co-
variance matrix is slowly changing once the hypoven-
tilation begins. Due to the fact that the trend changes
of intra-arterial pressure occur continuously they may
not serve as a good indicator due to a large number of
false positives. To this purpose we focus our attention
on the second order properties i.e. covariance matrix
and utilize Frechet mean as it is know to be able to
capture different information about matrix structure
depending on the distance measure used. Due to the
fact that patient-to-patient variability and short length
of stay per patient may prevent utilization of paramet-
ric models we evaluate applicability of deep learning
networks. We illustrate the applicability of the pro-
posed method for patients with the length of stay of
up to four weeks. Our preliminary results indicate that
DNN could be potentially used in a hybrid setting in
which the rough estimate of model parameters could
be obtained using DNN and the fine tuning for a par-
ticular patient could evolve throughout the patient’s
stay at NICU.
REFERENCES
Absil, P.-A., Mahony, R., and Sepulchre, R. (2009). Opti-
mization algorithms on matrix manifolds. Princeton
University Press.
Barbaresco, F. (2008). Innovative tools for radar signal pro-
cessing based on cartan’s geometry of spd matrices &
information geometry. In Radar Conference, 2008.
RADAR’08. IEEE, pages 1–6. IEEE.
Jahromi, M. (2014). Frechet means with respect to rieman-
nian distances: Evaluations and applications. Ma.Sc.
Thesis.
Jeremic, A. and Nikolic, D. (2019). Predicting respira-
tory depression in neonates using intra-arterial pres-
sure measurements. BIOSIGNALS 2019, pages 342–
347–.
Jeremic, A. and Tan, K. (2007). Estimating respiratory pa-
rameters using intra-arterial partial pressure measure-
ments. Asilomar, 2:851–854.
Jeremic, A. and Tan, K. (2009). Estimating respiratory
parameters using intra-arterial partial pressure mea-
surements and stochastic differential equations. 2009
Canadian Conference on Electrical and Computer
Engineering, 2:559–564.
Moakher, M. (2005). A differential geometric approach
to the geometric mean of symmetric positive-definite
matrices. SIAM Journal on Matrix Analysis and Ap-
plications, 26(3):735–747.
Revow, M., England, S., Beirne, H., and Bryan, A. (1989).
A model of the maturation of respiratory control in
the newborn infant. IEEE Trans. on Biomedical Engi-
neering, 36(4):415–423.
Predicting Respiratory Depression in Neonates Using Deep Learning Neural Networks
1057
