
Quantum Approaches to the 0/1 Multi-Knapsack Problem: QUBO
Formulation, Penalty Parameter Characterization and Analysis
Evren Guney
1 a
, Joachim Ehrenthal
2 b
and Thomas Hanne
2 c
1
Department of Industrial Engineering, MEF University, Maslak, Istanbul, Turkey
2
School of Business, University of Applied Sciences and Arts Northwestern Switzerland FHNW, Brugg, Switzerland
Keywords:
Multi-Knapsack Problem, Quadratic Unconstrained Binary Optimization, Gate-Based Quantum Computing,
Quantum Annealing, Quantum Simulation, Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm.
Abstract:
The 0/1 Multi-Knapsack Problem (MKP) is a combinatorial optimization problem with applications in lo-
gistics, finance, and resource management. Advances in quantum computing have enabled the exploration
of problems like the 0/1 MKP through Quadratic Unconstrained Binary Optimization (QUBO) formulations.
This work develops QUBO formulations for the 0/1 MKP, with a focus on optimizing penalty parameters for
encoding constraints. Using simulation experiments across quantum platforms, we evaluate the feasibility of
solving small-scale instances of the 0/1 MKP. The results provide insights into the challenges and opportuni-
ties associated with applying quantum optimization methods for constrained resource allocation problems.
1 INTRODUCTION
The 0/1 Multi-Knapsack Problem (MKP) extends the
classical knapsack problem to involve multiple knap-
sacks, each with its own capacity constraints. In this
problem, a set of items is available, each characterized
by a profit and weight. The objective is to determine
how to assign these items to knapsacks such that the
total profit is maximized while ensuring that the total
weight in each knapsack does not exceed its capacity.
Additionally, each item can be placed in at most one
knapsack.
The 0/1 MKP is a well-known NP-hard problem,
presenting computational challenges as the number
of items and knapsacks increases. Classical opti-
mization methods, such as exact algorithms, heuris-
tics, and meta-heuristics, have been effective for
solving small- to medium-scale instances. How-
ever, larger problem instances, particularly those
with more complex constraints, require alternative
approaches to address scalability and computational
limitations—despite the recent growth in compute
power.
Quantum computing offers an alternative to clas-
sical optimization by using quantum principles such
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7572-8627
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2195-1465
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5636-1660
as superposition and entanglement to explore solution
spaces more efficiently. Advances in quantum hard-
ware and algorithms have enabled early investigations
into solving combinatorial optimization problems on
quantum simulators and devices. These devices pre-
dominantly operate on Quadratic Unconstrained Bi-
nary Optimization (QUBO) models, making them
well-suited for initial research into problems such as
0/1 MKP alongside classical optimization approaches
(Lucas (2014); Glover et al. (2022)).
A fundamental distinction between classical and
quantum methods, such as those using QUBO, lies in
their handling of constraints. Classical methods typi-
cally model constraints explicitly, ensuring feasibility
through structured formulations. In contrast, QUBO
models incorporate constraints directly into the ob-
jective function via penalty parameters. The effec-
tiveness of solving the 0/1 MKP on quantum devices
depends on the calibration of these penalty parame-
ters, as they influence both the feasibility of solutions
and algorithmic performance. These parameters may
need to be adjusted according to the quantum plat-
form or specific characteristics of the device, intro-
ducing additional complexity (Glover et al. (2019);
Pecyna and R
´
o
˙
zycki (2024)).
Today’s dominant platforms are annealing and
gate-based systems. Quantum annealers (e.g., D-
Wave) natively support QUBO formulations and offer
a direct mapping of optimization problems (Pusey-
Guney, E., Ehrenthal, J. and Hanne, T.
Quantum Approaches to the 0/1 Multi-Knapsack Problem: QUBO Formulation, Penalty Parameter Characterization and Analysis.
DOI: 10.5220/0013387700003890
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2025) - Volume 1, pages 815-823
ISBN: 978-989-758-737-5; ISSN: 2184-433X
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
815

Nazzaro and Date (2020)), while gate-based quan-
tum computers (e.g., IBM, Google, Quantinuum,
IonQ) implement them through parameterized circuits
(Arute et al. (2019)). These platforms differ in how
they handle QUBO constraints and penalty parame-
ters. By examining these differences experimentally,
this work aims to provide practical insights into the
current applicability and limitations of quantum plat-
forms and their role alongside classical optimization
methods.
Characterizing and optimizing penalty parameters
in QUBO formulations is an under-explored area in
quantum optimization. In earlier work, Boros and
Hammer (2002) introduced the sum of coefficients
method for pseudo-Boolean optimization problems
and refined it through posiform transformations of
QUBO formulations (Boros et al. (2006)). In the
context of quantum computing, initial characteriza-
tions of penalty parameters for various QUBO prob-
lems are provided by Lucas (2014) and Glover et al.
(2022). For knapsack problems specifically, Quin-
tero and Zuluaga (2021) offered a characterization of
penalty parameters, while recent studies by Awasthi
et al. Awasthi et al. (2023) explored quantum com-
puting techniques for the MKP without focusing on
the characterization of the penalty parameters, where
similar penalty coefficients to our work are proposed.
Further, the work by Verma and Lewis (2022)
presents a general method for determining effective
penalty parameter values in QUBO problems. As-
suming minimization problems, the authors devel-
oped a heuristic to derive suitable lower bounds for
penalty parameters. Building on this, Garc
´
ıa et al.
(2022) introduced a sequential algorithm to refine
penalty parameters and validated their approach on
classical optimization problems. These studies pro-
vide a foundation for our research into penalty param-
eter characterization in quantum optimization.
Lastly, the 0/1 MKP, characterized by discrete
variables and multiple constraints, naturally aligns
with the QUBO formulations. This property, cou-
pled with the non-fractional structure of the prob-
lem, makes it an ideal candidate for exploring the po-
tential of quantum optimization. Beyond its intrin-
sic optimization challenges, the MKP may also serve
as a benchmark for platform-agnostic testing of op-
timization techniques on the competing current and
near-term quantum device architectures (Dam et al.
(2021)).
This work contributes to the foundational under-
standing of applying quantum computing to the MKP
by:
• Developing a QUBO formulation for the 0/1
MKP, addressing practical scenarios and con-
straints to enhance the applicability and accuracy
of these models in quantum settings.
• Providing a detailed analysis of penalty parame-
ters, which are used to encode constraints within
MKP-QUBO models. We expect the proper char-
acterization of these parameters to impact the fea-
sibility of solutions and the efficiency of optimiza-
tion algorithms.
• Conducting simulation experiments to evaluate
the proposed formulations on current quantum
platforms. These experiments offer insights into
the practical performance and limitations of the
models across different quantum computing plat-
forms, providing benchmarks against a current
state-of-the-art solver and for future studies.
The remainder of the paper is structured as fol-
lows: Section 2 outlines the mathematical formu-
lation of the 0/1 MKP and the characterization of
penalty parameters essential for constraint encoding.
Section 3 presents the quantum optimization methods
employed in this study. Section 4 describes the exper-
imental setup and discusses the results obtained from
implementing the formulations on available quantum
devices. Finally, Section 5 concludes with a sum-
mary of findings and potential directions for future
research.
2 MATHEMATICAL MODELS
The 0/1 MKP is among the most extensively studied
variations of the classical knapsack problem, distin-
guished by involving multiple knapsacks rather than
a single one. The objective is to allocate a set of items
across multiple knapsacks, each with its own capacity,
to maximize the total profit while ensuring the weight
assigned to any knapsack does not exceed its capac-
ity. Formally, given a set of items N , where each
item has a profit c
ik
specific to a particular knapsack
and a weight d
i
, and a set of knapsacks K , each with
a capacity E
k
, the problem is to determine the opti-
mal distribution of items across the knapsacks. To
achieve this, binary decision variables x
ik
are intro-
duced, where x
ik
= 1 if item i is assigned to knap-
sack k, and x
ik
= 0 otherwise. Without loss of gen-
erality, all parameters c, d, and E are assumed to be
non-negative integers.
The 0/1 MKP can be mathematically formulated
as follows:
QAIO 2025 - Workshop on Quantum Artificial Intelligence and Optimization 2025
816

MKP:
max f (x) =
K
∑
k=1
N
∑
i=1
c
ik
x
ik
(1)
s.t.
N
∑
i=1
d
i
x
ik
≤ E
k
, k ∈ K (2)
K
∑
k=1
x
ik
≤ 1, i ∈ N (3)
x
ik
∈ {0, 1}, i ∈ N ,k ∈ K (4)
In this formulation, the objective function (1) is de-
signed to maximize the total profit of the selected
items. The knapsack capacity constraints (2) ensure
that the total weight assigned to each knapsack k does
not exceed its capacity E
k
. Additionally, a second set
of constraints (3) prevents any item from being placed
in more than one knapsack. Finally, the binary restric-
tions on the decision variables are specified in (4).
To construct the QUBO formulation of the MKP,
slack variables u ∈ {0,1}
E
k
×K
are introduced for the
constraints in (2), while another set of slack variables
v ∈ {0,1}
N
is introduced for the constraints in (3).
These constraints are then incorporated into the ob-
jective function by scaling them with penalty param-
eters λ
1
and λ
2
, respectively, resulting in the penalty
function P(x,u,v).
P(x,u,v) = λ
1
K
∑
k=1
N
∑
i=1
d
i
x
ik
−
M
k
−1
∑
t=0
2
t
u
tk
− α
k
u
M
k
K
!
2
+ λ
2
N
∑
i=1
K
∑
k=1
x
ik
+ v
i
− 1
!
2
(5)
Here, M
k
= ⌊log
2
E
k
⌋ and α
k
= E
k
+ 1 − 2
M
k
, k ∈
K . It is important to note that when the polynomi-
als are expanded, the penalty function P(x, u,v) in-
cludes a constant term Nλ
2
due to the 1 present in
the second penalty term. However, as the removal of
constant terms does not affect the optimal solution,
we proceed under the assumption that P(x, u,v) con-
tains only variable-dependent terms, with the constant
term omitted. The resulting QUBO formulation for
the MKP is presented below.
MKP-QUBO:
max g(x,u,v) =
K
∑
k=1
N
∑
i=1
c
ik
x
ik
− P(x,u,v)
x
ik
,u
tk
,v
i
∈ {0,1},i ∈ N , k ∈ K ,t ∈ M
k
(6)
(7)
Theorem 1. For any penalty constant λ
1
and λ
2
such
that λ
1
≥ C
∗
and λ
2
≥ C
∗
, where C
∗
= max{c
ik
: i ∈
N , k ∈ K } ,(MKP-QUBO) is a valid reformulation of
the 0/1 multi-knapsack problem (MKP).
Proof. Let x
∗
be an optimal solution for (MKP). Let α
denote the set of coefficients for u in its binary expan-
sion form. Since x
∗
is a feasible solution for (MKP),
there exists u
∗
such that d
T
x
∗
= α
T
t
u
∗
for each k ∈ K ,
satisfying the constraints in (2). Similarly, there exists
v
∗
such that the constraints in (3) are satisfied, leading
to g(x
∗
,u
∗
,v
∗
) = c
T
x
∗
= f (x
∗
).
Now consider ( ˆx, ˆu, ˆv), an optimal solution
to (MKP-QUBO). By construction, g( ˆx, ˆu, ˆv) ≥
g(x
∗
,u
∗
,v
∗
) = f (x
∗
), as (x
∗
,u
∗
,v
∗
) is also a feasible
solution to (MKP-QUBO).
To complete the proof, we need to demonstrate
that g( ˆx, ˆu, ˆv) ≤ g(x
∗
,u
∗
,v
∗
) = f (x
∗
) by establishing
that ˆx is also a feasible solution to (MKP). We will
do so by contradiction, showing that an infeasible so-
lution x
′
, which is feasible for MKP-QUBO but not
for MKP, cannot yield a higher objective value. In
this sense, our proof strategy differs from the one
in (Quintero and Zuluaga (2021)). Assume x
∗
is
the optimal solution to (MKP). We construct an in-
feasible solution x
′
for (MKP) and demonstrate that
g(x
′
,u
′
,v
′
) ≤ g(x
∗
,u
∗
,v
∗
) = f (x
∗
) always holds.
Select an index pair ( j,m) from the complement
of the support of x
∗
, that is, ( j,m) ∈ supp
c
(x) =
{(i,k) | x
∗
ik
= 0}. Set x
jm
= 1. By doing so, we are
adding an extra item j to knapsack m, which results
in an infeasible solution for (MKP). Let x
′
denote this
modified solution.
Next, we construct the corresponding (MKP-
QUBO) objective by isolating x
jm
in the objective
function. We explicitly display the penalty terms as-
sociated with the m-th and j-th constraints, while in-
troducing P
C
to represent the remaining penalty terms
of P:
Set x
jm
= 1. In this case, we are adding an extra
item j into knapsack m, which should result in an in-
feasible solution for (MKP). Let’s represent the new
(extended) solution as x
′
. Next, one can construct the
following (MKP-QUBO) by simply separating x
jm
from the objective function and also displaying ex-
plicitly the m-th and j-th penalty terms corresponding
to respective constraints and thus introducing P
C
as
the rest of the penalty function P:
g(x
′
,u
′
,v
′
) =
K
∑
k=1
N
∑
i=1
c
ik
x
′
ik
− λ
1
K
∑
k=1
N
∑
i=1
d
i
x
′
ik
−
M
k
∑
t=0
α
t
u
′
tk
!
2
− λ
2
N
∑
i=1
K
∑
k=1
x
′
ik
+ v
′
i
− 1
!
2
=g(x
∗
,u
∗
,v
∗
) + c
jm
x
′
jm
− λ
1
N
∑
i=1
d
i
x
′
im
−
M
m
∑
t=0
α
t
u
′
tm
!
2
− λ
2
K
∑
k=1
x
′
jk
+ v
′
j
− 1
!
2
− P
C
(x
′
,u
′
,v
′
)
Quantum Approaches to the 0/1 Multi-Knapsack Problem: QUBO Formulation, Penalty Parameter Characterization and Analysis
817

Since x
∗
is optimal for (MKP), it follows that
f (x
∗
) = g(x
∗
,u
∗
,v
∗
). Additionally, P
C
(x
′
,u
′
,v
′
) = 0,
as it does not include any terms involving x
jm
and cor-
responds to constraints that are already satisfied.
Let us define F as the sum of the additional
terms in the last equation, excluding g(x
∗
,u
∗
,v
∗
) and
P
C
(x
′
,u
′
,v
′
). The key question is whether, with the
current choices for λ
1
and λ
2
, it always holds that
F ≤ 0. This ensures that g(x
′
,u
′
,v
′
) ≤ g(x
∗
,u
∗
,v
∗
),
thereby preserving the optimality of the solution
(x
∗
,u
∗
,v
∗
) for (MKP-QUBO).
Since x
′
is infeasible for (MKP), it must violate
either the m-th knapsack capacity constraint or the j-
th knapsack choice constraint, or both. Let us first
assume that only the m-th capacity constraint is vio-
lated.
In this case,
∑
N
i=1
d
i
x
′
im
−
∑
M
m
t=0
α
t
u
′
tm
> 0, with
the minimum magnitude of violation occurring when
∑
M
m
t=0
α
t
u
′
tm
= E
m
, which implies u
′
tm
= 1 for t =
0,.. .,M
m
. Under the assumption that the second con-
straint is not violated, even when x
′
jm
= 1, it must be
the case that
∑
K
k=1
x
∗
jk
= 0. To offset the associated
penalty, we set v
∗
j
= 1.
When x
′
jm
= 1, then
∑
K
k=1
x
′
jk
= 1, and the penalty
can once again be offset by setting v
′
j
= 0. Conse-
quently, the term associated with λ
2
can be omitted,
and the total change in the objective function is given
by:
F = c
jm
− λ
1
N
∑
i=1
d
im
x
′
im
− E
m
!
.
Given that λ
1
≥ C
∗
, the following relationship
holds:
λ
1
N
∑
i=1
d
i
x
′
im
− E
m
!
≥ λ
1
≥ C
∗
≥ c
jm
(8)
Let us now consider the case where adding the ex-
tra item does not cause an overflow in the m-th knap-
sack capacity constraint but instead results in a viola-
tion of the j-th single-choice constraint. In this sce-
nario, we have
∑
N
i=1
d
i
x
′
im
− E
m
≤ 0. Consequently,
there exists a solution u
′
such that
∑
M
m
t=0
α
t
u
′
tm
=
∑
N
i=1
d
i
x
′
im
, which compensates for the penalty term
associated with the first constraint.
The violation of the second constraint, in this case,
is exactly 1, as this constraint has not been previously
violated due to x
∗
jm
= 0. Thus, we can express the
change in the objective function as F = c
jm
− λ
2
. We
conclude that F ≤ 0 through the following relation-
ship:
λ
2
≥ C
∗
≥ c
jm
, (9)
where C
∗
represents the maximum profit coefficient.
If both constraints are violated, we can combine
the individual results to construct the following rela-
tionship, which ensures that F < 0:
λ
1
N
∑
i=1
d
i
x
′
im
− E
m
!
+ λ
2
≥ λ
1
+ λ
2
≥ 2C
∗
> c
jm
.
(10)
Thus, when F < 0, it follows that g(x
∗
,u
∗
,v
∗
) >
g(x
′
,u
′
,v
′
), indicating that an infeasible solution for
(MKP) cannot yield a higher objective value in
(MKP-QUBO). Consequently, this scenario cannot
occur. Therefore, if λ
1
> C
∗
and λ
2
> C
∗
, then x
∗
is both optimal and feasible for (MKP-QUBO).
In the boundary case where λ
1
= C
∗
and λ
2
= C
∗
,
the same conclusion holds. It is possible to construct
a feasible solution ( ˆx, ˆu, ˆv) from (x
′
,u
′
,v
′
), indicat-
ing that ( ˆx, ˆu, ˆv) is an alternative optimal solution for
(MKP-QUBO). Hence, we have:
g(x
′
,u
′
,v
′
) = g( ˆx, ˆu, ˆv) = c
T
ˆx ≤ c
T
x
∗
= f (x
∗
).
An interesting observation arises in the third sce-
nario, where both constraints are violated. In this
case, the condition requiring each penalty parameter
to be at least C
∗
may be overly restrictive. The coef-
ficient of λ
1
can be as large as d
∗
= max{d
i
: i ∈ N}.
Therefore, as long as d
∗
λ
1
+ λ
2
≥ C
∗
, both formula-
tions will produce the same optimal solution, which
depends heavily on the problem data.
3 SOLUTION METHODOLOGY
To address the MKP instances generated for this
study, we employ four distinct solution methods:
(i) solving the classical integer linear programming
(ILP) formulation of MKP using a commercial solver,
(ii) solving the QUBO formulation of MKP with a
commercial solver, (iii) utilizing Quantum Anneal-
ing, and (iv) applying the Quantum Approximate Op-
timization Algorithm (QAOA). State-of-the-art com-
mercial solvers are highly effective at solving both
the ILP and QUBO formulations of MKP by leverag-
ing advanced operations research techniques. These
solvers are mature, well-developed, and fall outside
the primary focus of this work.
In the following, we provide a brief overview of
these two quantum techniques and their relevance to
solving MKP instances.
QAIO 2025 - Workshop on Quantum Artificial Intelligence and Optimization 2025
818

3.1 Quantum Annealing
Quantum annealing exploits the physical properties of
quantum systems to solve optimization problems (Al-
bash and Lidar (2018)). The underlying principle is
rooted in physics: a system will naturally evolve to-
ward its lowest energy state, also known as its ground
state (Das and Chakrabarti (2008)). In quantum an-
nealing, a problem is encoded into an entangled quan-
tum system where each qubit represents a binary vari-
able in the QUBO formulation. The system is config-
ured such that its minimum energy state corresponds
to the optimal solution of the problem. Upon mea-
surement, the quantum system collapses, with each
qubit assuming a binary value of 0 or 1, providing the
solution (D-Wave (2022)).
In practice, quantum annealing maps each binary
variable of the optimization problem onto a qubit. In-
teractions between these variables are represented as
qubit entanglements, forming a network that encodes
the problem’s constraints and objective. The goal is to
structure the quantum system so that its ground state
aligns with the optimal solution of the QUBO. Penalty
parameters are used to enforce constraints by assign-
ing higher energy to infeasible solutions, modifying
the energy landscape to guide the system toward fea-
sible configurations. These parameters must be set
to balance enforcing constraints while preserving the
objective function. This ensures that feasible solu-
tions are energetically favorable compared to infeasi-
ble ones. However, due to the architectural limitations
of quantum hardware, such as restricted qubit connec-
tivity, additional qubits may be required to embed the
problem, which increases resource demands.
The annealing process begins by initializing the
qubits in a superposition state, representing all possi-
ble solutions simultaneously. As the system evolves,
it is guided toward configurations of progressively
lower energy. At the conclusion of the process, the
system is measured, causing the qubits to collapse
into a classical state of either 0 or 1. Each combina-
tion of these states has an associated energy, which re-
flects the value of the QUBO objective function. The
solution with the lowest energy corresponds to the op-
timal configuration.
The energy landscape of a quantum annealer is a
visualization of the energy values across all possible
configurations. For instance, Figure 1 illustrates the
energy landscape for a hypothetical QUBO instance
with four binary variables, resulting in 2
4
= 16 pos-
sible solutions. The height of each state in the land-
scape represents its corresponding energy, including
contributions from penalty terms that distinguish fea-
sible and infeasible solutions. States such as 0011 and
Figure 1: Energy landscape illustration for a hypothetical
QUBO instance with 4 binary variables.
1100 are shown with higher energy, indicating subop-
timal solutions.
3.2 Quantum Approximate
Optimization Algorithm (QAOA)
The Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm
(QAOA) is a widely studied variational quantum algo-
rithm developed to tackle combinatorial optimization
problems that are challenging for classical methods
(Blekos et al. (2024)). QAOA falls under the cate-
gory of hybrid quantum-classical algorithms and op-
erates on gate-based quantum computers. The algo-
rithm constructs a parameterized quantum circuit us-
ing a sequence of quantum gates that encode the opti-
mization problem. This circuit alternates between two
types of gates, each associated with a specific Hamil-
tonian: (i) the Cost Hamiltonian, which represents the
objective function (e.g., a QUBO problem), and (ii)
the Mixer Hamiltonian, which facilitates exploration
of the solution space. Together, these gates form a sin-
gle ”layer” of the QAOA circuit, and multiple layers
can be stacked to improve performance (Farhi et al.
(2014)).
QAOA is designed to run on gate-based quan-
tum devices, including those based on superconduct-
ing qubits (such as IBM and Rigetti systems) or
trapped ions (such as IonQ). The algorithm intro-
duces two tunable parameters, γ (associated with the
Cost Hamiltonian) and β (associated with the Mixer
Hamiltonian), which are iteratively refined using a
classical non-linear optimization routine. γ deter-
mines the system’s alignment with the objective func-
tion, influencing the depth of energy minimization,
while β controls the degree of exploration in the solu-
tion space. Together, these parameters guide the sys-
tem toward an optimal configuration by balancing ex-
ploitation and exploration. This iterative process uses
feedback from quantum measurements to adjust the
circuit parameters, forming a hybrid algorithm that
integrates classical optimization with quantum exe-
Quantum Approaches to the 0/1 Multi-Knapsack Problem: QUBO Formulation, Penalty Parameter Characterization and Analysis
819

Figure 2: Quantum circuit used in QAOA.
cution. While the quantum component (circuit ex-
ecution) is fully gate-based, the overall process in-
corporates a classical optimization loop (Farhi et al.
(2014)).
Figure 2 illustrates the quantum circuit for a small
QUBO instance with four binary variables. The prob-
lem data is directly encoded into the circuit through
specific rotations determined by the coefficients of the
QUBO terms. The Mixer Hamiltonian is then applied,
completing one iteration of the QAOA process. Fol-
lowing the optimization of the parameters γ and β,
the circuit is sampled, ideally with a large number of
shots, to identify the configuration that minimizes the
system’s energy with the expectation of this config-
uration to yield the optimal solution of the original
optimization problem. These parameters hence affect
the quantum state’s evolution during the circuit execu-
tion, shaping the energy landscape such that the sys-
tem is steered toward low-energy configurations cor-
responding to optimal or near-optimal solutions.
QAOA includes several adjustable settings, such
as the number of circuit layers, the method for initial-
izing parameters, and the choice of classical optimiza-
tion technique. The actual circuits used in quantum
hardware are often more complex than the illustrative
example provided here. These variations in settings
and implementation details significantly impact the
performance of the algorithm on practical optimiza-
tion problems.
4 EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS
This section examines how penalty parameter cali-
bration influences the performance of quantum opti-
mization methods for the MKP. Experiments are con-
ducted using a simulation-based approach, enabling
controlled testing of parameter adjustments under
practical constraints. By generating diverse problem
instances and varying penalty parameter values, we
analyze their impact on solution feasibility, quality,
and computational efficiency across different quan-
tum technologies, with classical optimization results
provided for comparison.
4.1 Testbed
Our testbed comprises randomly generated MKP
instances, with the number of items set to N ∈
{3,4,5, 6} and the number of knapsacks varying as
K ∈ {2,3}. The revenue values c are randomly chosen
as integers in the range [1, 10], while the item weights
d are selected as random integers within [1, 5]. The
capacities of the knapsacks, E, are also generated ran-
domly as integers between 60% and 80% of the to-
tal weight of items assignable to that knapsack. This
range ensures that not all items can be placed simul-
taneously.
For the penalty parameters λ, the default value is
set as λ = C
∗
= max{c
ik
}. To evaluate the impact of
penalty parameter scaling, a multiplier ranging from
0.5 to 1.5 is applied to λ, with increments of 0.02,
generating a total of 50 distinct λ values. This setup
allows us to investigate the potential for smaller λ val-
ues to cause infeasibility, as well as to analyze how
the magnitude of λ affects solution times.
In total, 4 × 2 × 50 = 300 problem instances are
created. Note that these instances are relatively
small compared to the size of MKP instances typi-
cally solvable by classical computers. However, due
to the limited number of qubits available in current
Noisy Intermediate-Scale Quantum (NISQ) quantum
devices, solving larger problem instances efficiently
is not feasible with the present state of quantum tech-
nology.
4.2 Experimental Setup and
Implementation Details
To generate the problem instances, we developed a
C# console application using Microsoft Visual Stu-
dio Community 2022. Both the classical MIP for-
mulation and the QUBO formulation of the MKP in-
stances were created using Gurobi callable libraries
and solved using the Gurobi 12.0 Solver (Gurobi Op-
timization, LLC (2024)). For the quantum implemen-
tations, the instances were tested across three primary
quantum technologies: gate-based circuits, trapped-
ion circuits, and quantum annealing.
For the quantum annealing experiments, we uti-
lized D-Wave libraries (D-Wave (2022)). Using D-
Wave’s Python interface, the QUBO formulation of
each instance was transformed into an optimization
problem and solved using the annealer. For gate-
based quantum experiments, we relied on IBM Qiskit
libraries, where the Q matrix representing the co-
QAIO 2025 - Workshop on Quantum Artificial Intelligence and Optimization 2025
820
efficients of the QUBO instance was used to con-
struct quantum circuits. A standard QAOA subrou-
tine was then executed to find the best solution. In the
QAOA implementation, the circuit dept is chosen to
be p = 3 which is the recommended value in many
works (Blekos et al. (2024)). Qiskit implementation
of QAOA uses the COBYLA solver (Powell (1994))
as the default, non-linear, derivative-free solver to op-
timize the circuit parameters. Finally, the trapped-ion
experiments employed IonQ Python libraries. Similar
to the gate-based approach, circuits were generated
from the Q matrix of each instance and solved using
the QAOA algorithm.
Each instance is run 10 times on the quantum plat-
forms, with a sample size (or number of shots) set
to 10,000. For both annealing and gate-based ap-
proaches, increasing the number of shots mitigates er-
rors inherent to quantum mechanics, improving solu-
tion accuracy. In every experiment, we recorded the
best solution, the corresponding objective value, and
the solution time. Since the MIP solver reliably finds
the optimal solutions for both the classical MIP and
QUBO formulations, these serve as a benchmark. Ad-
ditionally, we assessed whether the QUBO solutions
obtained from the solver and the three quantum-based
methods were feasible and/or optimal.
4.3 Computational Results
We began by comparing the running times of the five
methods tested in our experiments, as summarized in
Table 1. These times represent averages over 10 ×
50 = 500 runs (10 randomly generated instances with
50 different values of the penalty parameter) for each
combination of N and K.
In Table 1, the first column lists the number of
items (N) and knapsacks (K) for the generated prob-
lem instances. The next two columns show the aver-
age solution times obtained using Gurobi for the clas-
sical integer programming (MIP) and QUBO formu-
lations of the MKP. The final three columns present
the average solution times for the quantum-based
methods.
As expected, Gurobi achieved the fastest solution
times for the classical integer programming formu-
lation of the MKP, followed closely by the QUBO
version solved with Gurobi. The D-Wave quantum
annealer demonstrated comparable performance to
Gurobi’s quadratic solver, solving nearly all instances
in under one second. It is notable that D-Wave’s av-
erage running time is smaller than Gurobi’s quadratic
solver for the largest instances corresponding to 5/6
item and 3 knapsack scenarios. In contrast, QAOA-
based methods were significantly slower, with solu-
tion times increasing as the problem size grew. For
the largest instances both annealing methods fail to
provide solutions either with out of memory or time-
out errors.
For the IonQ simulator, instances with (N,K) =
(4,3), (5,3), and (6, 3) could not be solved due to
memory limitations, highlighting current hardware
constraints for larger problem sizes.
Table 1: Comparison of running times across different
solvers for varying values of N (number of items) and K
(number of knapsacks).
N,K
Int. Pr. Gur. Qu. Annl. QAOA
IP QUBO D-Wave Qiskit IonQ
3,2 0.003 0.06 0.33 23.1 17.9
4,2 0.003 0.14 0.36 30.5 33.8
5,2 0.012 0.22 0.51 184.1 276.8
6,2 0.124 0.42 0.67 641.1 2075.4
3,3 0.005 0.07 0.40 86.9 209.3
4,3 0.007 0.10 0.44 371.6 -
5,3 0.005 1.15 0.54 - -
6,3 0.005 2.56 0.56 - -
Table 2 compares the solution quality of the
quantum-based methods. Since the optimal solutions
for all instances are known, we evaluate the perfor-
mance of the three quantum-based methods by calcu-
lating the percentage of instances where they success-
fully find the optimal solution.
D-Wave achieves the optimal solution in almost
all cases for the smaller size instances but may de-
crease up to 54.6% for most complex cases. For
smaller instances, QAOA-based methods also per-
form well, with IonQ generally outperforming Qiskit.
However, as the instance size increases, the solution
quality of the QAOA-based methods declines signifi-
cantly.
Table 2: Per-cent of Optimal Solutions found by the
quantum-based method.
N,K
Qu. Annl. QAOA
D-Wave Qiskit IonQ
3,2 100.0% 85.3% 92.7%
4,2 99.7% 86.0% 95.9%
5,2 99.8% 71.9% 85.8%
6,2 99.4% 54.8% 66.8%
3,3 99.2% 63.8% 69.0 %
4,3 99.5% 42.2% -
5,3 68.6% - -
6,3 54.6% - -
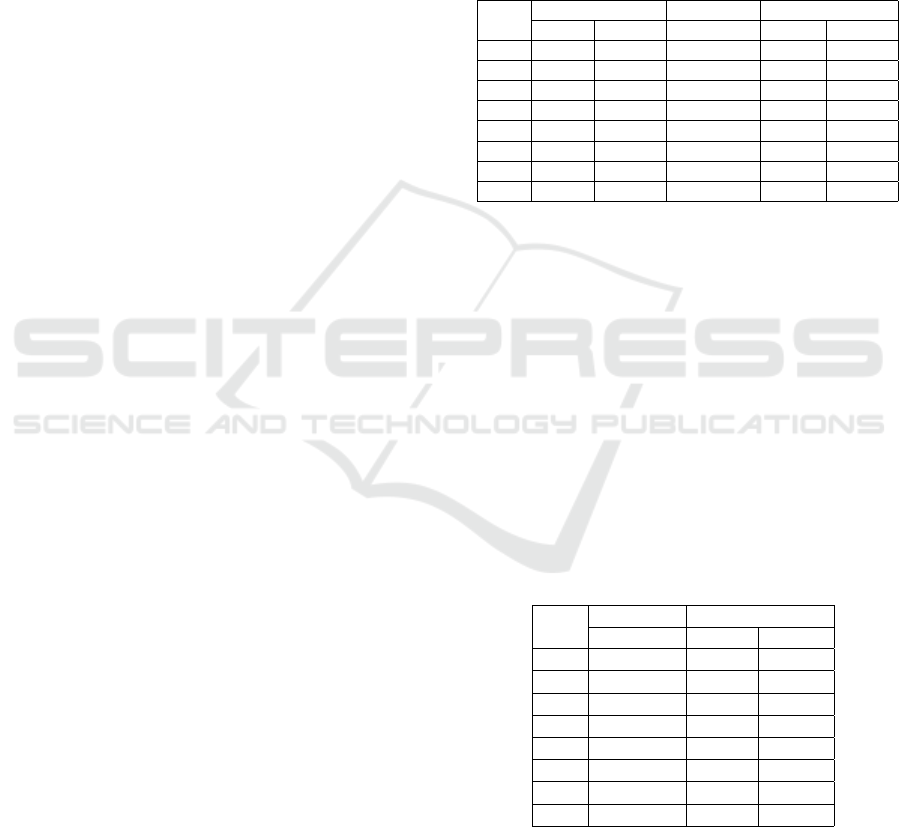
4.4 Effect of Penalty Parameter
Magnitude on Feasibility
In the proof of Theorem-1, we noted that requiring the
penalty parameter λ to be at least λ = C
∗
= max{c
ik
}
Quantum Approaches to the 0/1 Multi-Knapsack Problem: QUBO Formulation, Penalty Parameter Characterization and Analysis
821
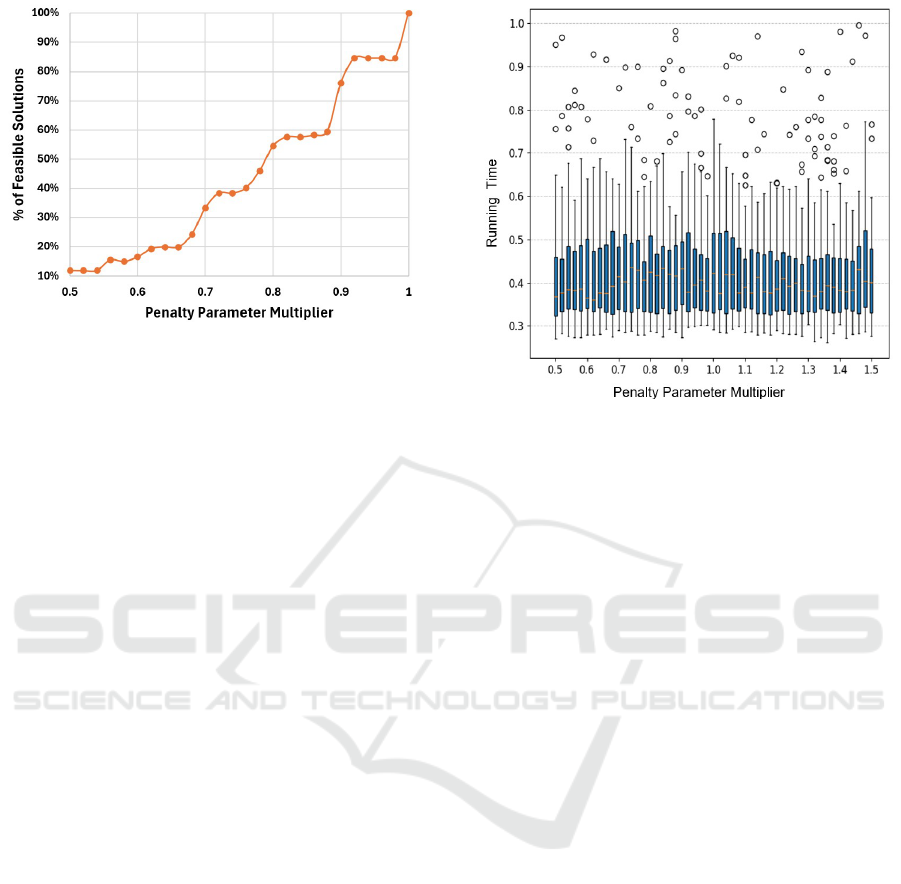
Figure 3: Effect of penalty parameter magnitude on solution
feasibility.
may be overly restrictive for certain instances. To in-
vestigate this, we calibrated the value of λ using a
multiplier ranging from 0.5 to 1.5. Figure 3 illustrates
the average percentage of instances that resulted in
feasible solutions under these varying penalty param-
eter settings.
Each data point in the figure represents the aver-
age results over 10 × 8 = 80 instances (10 random
instances across 8 different combinations of N and
K). When the penalty parameter coefficient is set to
1.00, λ equals C
∗
, and all QUBO instances produce
the same optimal solutions as the original integer pro-
gramming formulation of the MKP.
However, as the penalty parameter is reduced be-
low this theoretical minimum, a gradual decline in
feasibility is observed, with fewer QUBO solutions
satisfying the constraints of the original MKP. Fu-
ture research could focus on deriving tighter bounds
for penalty parameters tailored to specific MKP in-
stances, potentially reducing the need for conservative
parameter settings.
4.5 Effect of Penalty Parameter
Magnitude on Solution Duration
Finally, we evaluate how the magnitude of the penalty
parameter affects the running time of the solution
methods. This analysis is based on normalized run-
ning times for 80 instances across 4 QUBO-based
methods. The results, summarized in the box-whisker
plot in Figure 4, indicate that the magnitude of the
penalty parameter has minimal impact on solution
times. A consistent pattern is observed across all indi-
vidual quantum methods (e.g., annealing and QAOA);
hence, more granular plots for specific methods are
omitted.
Figure 4: Effect of penalty parameter magnitude on running
time.
Note that these results were obtained using classi-
cal quantum system simulators, which may not fully
capture the computational dynamics of actual quan-
tum hardware. Replicating these experiments on real
quantum devices would provide more accurate in-
sights and validate the observations made here.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This study investigates the application of QUBO for-
mulations to the 0/1 Multi-Knapsack Problem (MKP)
using classical and quantum techniques.
Specifically, we characterize and analyze the
penalty parameters, demonstrating that overly con-
servative settings can impact feasibility without sig-
nificantly affecting solution times. Our results high-
light the strengths and limitations of quantum anneal-
ing and QAOA in solving MKP instances on simu-
lators, with annealing showing potential for handling
larger problem sizes, albeit with suboptimal solutions.
Specifically for our investigation, a state-of-the-art
classical solver remains superior.
Further, our research suggests exploring better
ways to configure penalty parameters for annealing,
as well as simplifying quadratic representations to
reduce computational overhead across all platforms,
both quantum and classical. Lastly, testing across a
wider range of simulators and on real quantum de-
vices may further guide scholarly efforts in adopting
quantum techniques for common operations research
problems.
QAIO 2025 - Workshop on Quantum Artificial Intelligence and Optimization 2025
822

REFERENCES
Albash, T. and Lidar, D. A. (2018). Demonstration of a scal-
ing advantage for a quantum annealer over simulated
annealing. Physical Review X, 8(3):031016.
Arute, F. et al. (2019). Quantum supremacy using a
programmable superconducting processor. Nature,
574(7779):505–510.
Awasthi, A., B
¨
ar, F., Doetsch, J., Ehm, H., Erdmann,
M., Hess, M., Klepsch, J., Limacher, P. A., Luckow,
A., Niedermeier, C., Palackal, L., Pfeiffer, R., Ross,
P., Safi, H., Sch
¨
onmeier-Kromer, J., von Sicard, O.,
Wenger, Y., Wintersperger, K., and Yarkoni, S. (2023).
Quantum computing techniques for multi-knapsack
problems. In Arai, K., editor, Intelligent Computing,
pages 264–284. Springer Nature Switzerland.
Blekos, K., Brand, D., Ceschini, A., Chou, C.-H., Li, R.-
H., Pandya, K., and Summer, A. (2024). A review on
quantum approximate optimization algorithm and its
variants. Physics Reports, 1068:1–66. A review on
Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm and
its variants.
Boros, E. and Hammer, P. L. (2002). Pseudo-boolean op-
timization. Discrete Applied Mathematics, 123(1–
3):155–225.
Boros, E., Hammer, P. L., and Tavares, G. (2006). Prepro-
cessing of unconstrained quadratic binary optimiza-
tion. Technical Report RRR 10-2006, Rutgers Univer-
sity, New Jersey, USA. RUTCOR Research Report.
D-Wave (2022). What is quantum annealing? Accessed:
2024-11-11.
Dam, W. v., Eldefrawy, K., Genise, N., and Parham, N.
(2021). Quantum optimization heuristics with an ap-
plication to knapsack problems. In 2021 IEEE Inter-
national Conference on Quantum Computing and En-
gineering (QCE), pages 160–170. IEEE.
Das, A. and Chakrabarti, B. K. (2008). Colloquium: Quan-
tum annealing and analog quantum computation. Rev.
Mod. Phys., 80:1061–1081.
Farhi, E., Goldstone, J., and Gutmann, S. (2014). A quan-
tum approximate optimization algorithm.
Garc
´
ıa, M. D., Ayodele, M., and Moraglio, A. (2022). Ex-
act and sequential penalty weights in quadratic uncon-
strained binary optimisation with a digital annealer. In
Proceedings of the Genetic and Evolutionary Com-
putation Conference Companion, GECCO ’22, page
184–187, New York, NY, USA. Association for Com-
puting Machinery.
Glover, F., Kochenberger, G., and Du, Y. (2019). A tu-
torial on formulating and using qubo models. arXiv
preprint, arXiv:1811.11538.
Glover, F., Kochenberger, G., Hennig, R., Lewis, M., L
¨
u, Z.,
Wang, H., and Wang, Y. (2022). Quantum bridge ana-
lytics i: a tutorial on formulating and using qubo mod-
els. Annals of Operations Research, 314:141–183.
Gurobi Optimization, LLC (2024). Gurobi Optimizer Ref-
erence Manual.
Lucas, A. (2014). Ising formulations of many np problems.
Frontiers in Physics, 2.
Pecyna, T. and R
´
o
˙
zycki, R. (2024). Improving quantum
optimization algorithms by constraint relaxation. Ap-
plied Sciences, 14(18):8099.
Powell, M. J. D. (1994). A direct search optimization
method that models the objective and constraint func-
tions by linear interpolation. Advances in Optimiza-
tion and Numerical Analysis, pages 51–67.
Pusey-Nazzaro, L. and Date, P. (2020). Adiabatic quantum
optimization fails to solve the knapsack problem. Ac-
cessed: 2024-12-04.
Quintero, R. A. and Zuluaga, L. F. (2021). Characterizing
and benchmarking qubo reformulations of the knap-
sack problem. Technical report, Department of In-
dustrial and Systems Engineering, Lehigh University.
Technical Report.
Verma, A. and Lewis, M. (2022). Penalty and partitioning
techniques to improve performance of qubo solvers.
Discrete Optimization, 44:100594. Quadratic Combi-
natorial Optimization Problems.
Quantum Approaches to the 0/1 Multi-Knapsack Problem: QUBO Formulation, Penalty Parameter Characterization and Analysis
823
