
Measuring Fall Risk Using the Internet-of-Things Chair
Alexander W. Lee
1a
, Melissa S. Lee
1b
, Chelsea Yeh
2c
and Kyle Yeh
3d
1
Chino Premier Surgery Center, Chino, CA 91710, U.S.A.
2
Yale University, New Haven, CT, 06520, U.S.A.
3
Brown University, Providence, RI, 02912, U.S.A.
Keywords: Lower Extremity Strength, Leg Strength, Falls, 30 Second Chair Stand Test, 5 Times Sit-to-Stand Test,
Internet of Things, Automatic Chair, Wireless Chair, Clinical Study.
Abstract: Falls are one of the leading causes of injuries and deaths for U.S. adults ages 65 and older. People can fall
because of imbalance and leg weakness. Fall risks are evaluated by standardized tests, including the 30-
Second Chair Stand Test (30CST) and 5x Sit-to-Stand Test (5xSST). These tests are conducted by visual
observation of the participant and manual counting, which can be inaccurate and tedious. This study clinically
tested an Internet of Things Chair (IoT) on how well it performed on the 30CST and 5xSST. A clinical study
was performed on 224 participants. The results of the IoT Chair were found to be similar to the traditional,
visually observed method. The IoT Chair required less manual work and provided information that was not
obtainable with the observer method. The IoT Chair was able to calculate the weight exerted on the individual
chair legs, rate of weight change, lag time between each sit-stand cycle, the amount of time spent standing
during each cycle, and the amount of time each sit-stand cycle required. This additional information can allow
for a better understanding of a person's leg strength and improves the prediction for falls, which can save lives
and lower healthcare costs.
1 INTRODUCTION
Falls in adults over 65 years old are the leading cause
of injury-related deaths in the United States (CDC,
2020). The rate of age-adjusted deaths due to falls has
increased by 41% from 2012 to 2022 (CDC, 2024). In
a 2016 National Study of Long-Term Care Providers
conducted by the National Center for Health
Statistics, they found that 22% of adults living in an
assisted-living facility or residential care
communities had fallen in the prior 90 days. Of the
individuals who fell, 19% had to go to the hospital,
and 15% had sustained injuries (Harris-Kojetin &
Sengupta, 2018).
Impairments in vision (Jin et al., 2024), hearing
(Riska et al., 2021), muscle strength (Rodrigues et al.,
2023), reflexes (Marigold et al., 2005), cognition
(Chantanachai et al., 2021), balance (Papalia et al.,
2020), side effects of medications (Hartikainen et al.,
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7809-8181
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3975-821X
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0502-8235
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2979-7143
2007), and environmental hazards can all cause falls
(Campani et al., 2020), (National Institute on Aging,
2022). Preventing these falls is critical in keeping
older adults healthy and active. The 30-Second Chair
Stand Test (30CST) (Jones et al., 1999) (Chan-Mei
Ho-Henriksson et al., 2024), and 5-Time Sit-to-Stand
Test (5xSST) (Muñoz-Bermejo et al., 2021), (Albalwi
& Alharbi, 2023) are well-established tests that
objectively evaluate lower extremity strength,
balance, and fall risks. In the 30CST, patients are
evaluated on how many times they can change from
sitting to standing in 30 seconds, with the observer
visually counting. Their arms are crossed across the
chest and cannot be used during the test. If the person
performs less than what is established for their age
group and gender, then they are at higher risk for falls
(CDC, 2017). The 5xSST is performed in the same
manner as the 30CST with the participant's arms
crossed at the chest and cannot be used during the test.
For the 5xSST, the longer the person takes to
Lee, A. W., Lee, M. S., Yeh, C. and Yeh, K.
Measuring Fall Risk Using the Inter net-of-Things Chair.
DOI: 10.5220/0013404500003944
In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Internet of Things, Big Data and Security (IoTBDS 2025), pages 353-360
ISBN: 978-989-758-750-4; ISSN: 2184-4976
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
353

complete the test, the higher their fall risk (5 Times
Sit to Stand Test (FTSST), n.d.). There are no
standardized cut-off ranges published by the Center
for Disease Control (CDC) for the 5xSST. Buatois et
al. studied 1,618 community-dwelling people over
the age of 65 and found that if they took longer than
15 seconds to complete their 5xSST, their risk of falls
would double. This study is cited in many tests as the
cut-off number (Buatois et al., 2010).
Experimental studies have evaluated the use of
electronics applied to the sit-to-stand test. For
instance, a study by Collado-Mateo et al. used an
automatic chronometer developed by Chronopic to
evaluate the patient during the 30CST trial (Collado-
Mateo et al., 2019). The participant had to wear a vest
with metallic tape. That metallic tape would have to
come into contact with the Chronopic device attached
to the chair seat. The Chronopic device could detect
the time the tape was in contact, thereby establishing
the amount of time the patient was sitting or standing.
If the person was not sitting correctly and the metallic
tape on the vest did not come into contact with the
Chronopic device, the change to the sitting position
would not be recorded.
Yeh et. al. (Yeh, C. et al., 2022) developed an
Internet of Things (IoT) Chair designed to evaluate
patient movement from the chair. A pressure pad
placed on the chair could detect the movement of
patients changing from a sitting position on the chair
to a standing position by detecting pressure and
motion changes. This data would then be transmitted
to a cellular phone app. A significant limitation of that
study was that the chair was not tested for accuracy.
Another problem was that the pressure pad on the
chair could shift with use, decreasing the accuracy of
the measurements. The shifting pad could also cause
patients to slip out of the chair and injure themselves.
The chair only detected whether or not the person was
sitting on the chair. No sensors were detecting the
amount of pressure placed on the chair.
Lee et al. (Lee et al., 2024) improved upon Yeh et
al.'s chair and developed a novel Internet-of-Things
(IoT) Chair utilizing built-in sensors to evaluate fall
risks in adults. This type of sensor technology has
been previously applied to other medical devices (Lee
et al., 2023), (Lee & Yeh, 2022), (Yeh, C. et al.,
2022), (Yeh, C. et al., 2022), (Yeh. K. et al., 2021)
including the measurement of human body movement
(Yeh H.J. et al., 2020), and to computer networking
(Yeh. H.-J. et al., 2019).
Lee et al. designed the entire system as a single
unit so that no sensors were attached to the patients
and no sensors needed to be set up external to the
chair. The participant also did not need to sit in a
particular position in order for the chair to measure
the amount of force exerted on the chair. There were
built-in sensors in the chair which transmitted the data
to a cloud-based server. The chair was designed to
perform the Fullerton Functional Tests, which
included the 30CST and the 5xSST. The technical
aspects of the devices used and their integration into
the chair are detailed in the paper by Lee et al.
This paper examined how well Lee et al.'s IoT
Chair (Lee et al., 2024) performed in test participants
with both the 30CST and the 5xSST. We chose to test
the chair on the 30CST and 5xSST because studies
have shown that they are highly reliable across
different adult populations (Figueiredo et al., 2021),
(Gill et al., 2012), (Goldberg et al., 2012). Prior to
conducting the clinical trials, we received IRB
approval #23-130 from Azusa Pacific University. A
total of 224 people participated in the study. Testing
was conducted over a period of 12 months, from
November 2023 through October 2024.
2 MATERIALS AND METHOD
The use of strain-gauge force sensors for the
measurement of dynamic human weight distribution
is novel and presents significant advantages over
other sensing technologies. Strain gauges are
commonly used to measure static human weight
distribution and are the sensing element in many
commercial and most electronic consumer scales.
Because of their widespread use, economies of scale
in their design and manufacturing have been
achieved, leading to broad availability and low cost.
Designing with these components leads to decreased
end-user costs that offset high equipment costs that
beset the healthcare industry.
The use of weight sensors that are mounted on the
chair provides significant improvements over
previous automatic chair-stand measurement
apparatus. Many of the previous devices, such as
accelerometers or contact sensors, require the
attachment of sensors on the body of the subject
(Cobo et al., 2020), (Hellmers et al., 2019), (Millor et
al., 2013). This can lead to significant complications
during the trial process, increasing preparation time
for each patient and reducing participation.
Additionally, other previous devices using distance
sensors (Takeshima et al., 2019), (Cobo et al., 2020),
(José Gonçalves et al., 2015) require a more
complicated setup, which limits their portability.
Two designs were created for the placement of the
strain gauge weight sensors. Four weight sensors
were integrated into the four corners of common
IoTBDS 2025 - 10th International Conference on Internet of Things, Big Data and Security
354

chairs. For human body scale applications, the four
sensors are typically wired into a single Whetstone
bridge that provides a single reading, which is the
sum of the four weights. In this application, the four
sensors were wired into four separate bridges to
provide four separate channels – right front, right
back, left front, and left back.
For the initial design, the four strain gauges were
mounted on the frame of the chair directly under the
four corners of the seat of the chair. This design had
issues in securing the seat on the chair while
providing accurate measurements. A second design
solved the issue by mounting the sensors under the
four legs of the chair. Since the diameters of typical
chair legs are smaller than the sensors, the chair is
first mounted on a rigid board, and the sensors are
secured to the bottom of the board directly under the
legs (Figure 1).
Figure 1: This picture shows the chair that was designed for
this clinical study.
The completed apparatus directly measures
dynamic weight distribution on the four separate chair
legs as the subject performs each trial. This is not
available with other sensing methodologies. Distance
sensors and accelerometers will be able to provide
velocity data but not measure the weight distribution.
Another improvement over previous work is the
use of a novel network infrastructure that uses cloud
computing. This system architecture provides user-
friendly control and data flow, storage, and retrieval
during data collection and processing. The benefit of
this architecture is that the data collection is highly
scalable and portable; because existing and popular
network protocols are used, migrating or duplicating
the system to different or multiple servers is
extremely simple – often with the simple copying of
the relevant scripts with little or no setup or
provisioning. This design greatly simplifies the
deployment of new systems.
Commands to the system (inputting the patient
number or id, tuning the data collection parameters
such as the collection period or sample rate, and
starting the data collection after the patient is ready)
are done on a web interface that runs on any browser
(Figure 2). The browser runs standard HTML
(hypertext markup language) and JavaScript. The
commands issued from the browser to the chair (red
arrows) and the responses and messages from the
chair to the browser (orange arrows) utilize MQTT
(message queuing telemetry transport), which is the
de facto standard for IoT devices. This allows the user
interface to run on virtually any device – personal
computers, laptops, cell phones, etc.
After data from a trial has been collected, it is sent
to the cloud-based server via a standard HTML POST
request (blue arrow). The server runs standard PHP
(hypertext processor) to receive, store, and provide
access to the patient trial data. PHP is supported on
virtually all servers without customization, which
provides excellent system portability. The stored data
on the server can be accessed from the browser
interface (green arrow) if the proper permission is
granted. This is important for the confidentiality of
the patient data. The stored data can be graphed, and
various statistics, such as the times of sit-to-stand
transitions, can be computed.
Figure 2: This diagram displays the data and command flow
for the IoT Chair.
We recruited male and female adults ages 18
years and older. Any participants in a wheelchair or
regularly used assistive devices, including canes and
walkers, were excluded from this study. If they had
good leg strength and only occasionally needed the
use of canes or walkers, they were included in this
study. If the participant appeared fatigued, struggling,
or imbalanced, the test was immediately stopped to
prevent a fall. If needed, a walker was also placed in
Measuring Fall Risk Using the Internet-of-Things Chair
355
front of the chair for the participants to hold onto if
they felt fatigued or might fall. Once the participant
required the assistance of the walker, the trial was
immediately ended. The participants could also
voluntarily end the study if they felt tired or unable to
continue by verbally informing us or by raising either
their right or left hand.
A questionnaire was given to all participants, who
recorded their age, use of the assistive walking
devices, history of falls, and any musculoskeletal
pain. Vital signs, including height, weight, body mass
index (BMI), blood pressure, and heart rate, were
measured in all participants.
Participants were given instructions on the 30CST
and the 5xSST. The participant needed to have their
feet flat on the floor, sit in the middle of the chair, and
have their hands on the opposite shoulder with their
arms against the chest. When instructed to “Go,” the
participant needed to go from sitting to a full standing
position and then sit back down again. Data collection
was initiated by clicking a “Start” button on the
custom-designed, secure IoT Chair browser (website)
hosted by the web server. The IoT Chair
programming automatically recorded the number of
sit-stand-sit cycles in 30 seconds. For the 30CST test,
the participants needed to repeat this cycle as many
times as they could in 30 seconds. During the 30CST,
the time required to do the first five sit-stand-sit
cycles was used to record the 5xSST. In essence, the
30 CSST and 5xSST tests were done simultaneously
for efficiency and participant convenience. Besides
automatic recording by the IoT Chair programming,
we manually recorded how long it took to do the first
five sit-stand cycles (5xSST) and the number of sit-
stand cycles completed in 30 seconds (30CST).
3 RESULTS
There were 224 participants in this clinical study.
Fifty-six participants occasionally used assistive
walking devices such as walkers and canes. Seventy-
three participants had fallen within the past year. Two
hundred and eight participants described either some
joint or back pain.
The IoT Chair programming default setting (on
the browser) allowed 30 seconds to complete the
30CST and 5SST tests. Thirty seconds was chosen
because that is the time needed for the 30CST. The
slowest 5xSST completion time cut-off is 10.8
seconds (for people 70 years and above). That means
anyone taking longer than 10.8 seconds is considered
to have failed the 5xSST. Thirty seconds would be
more than sufficient time to test the 5xSST. Test
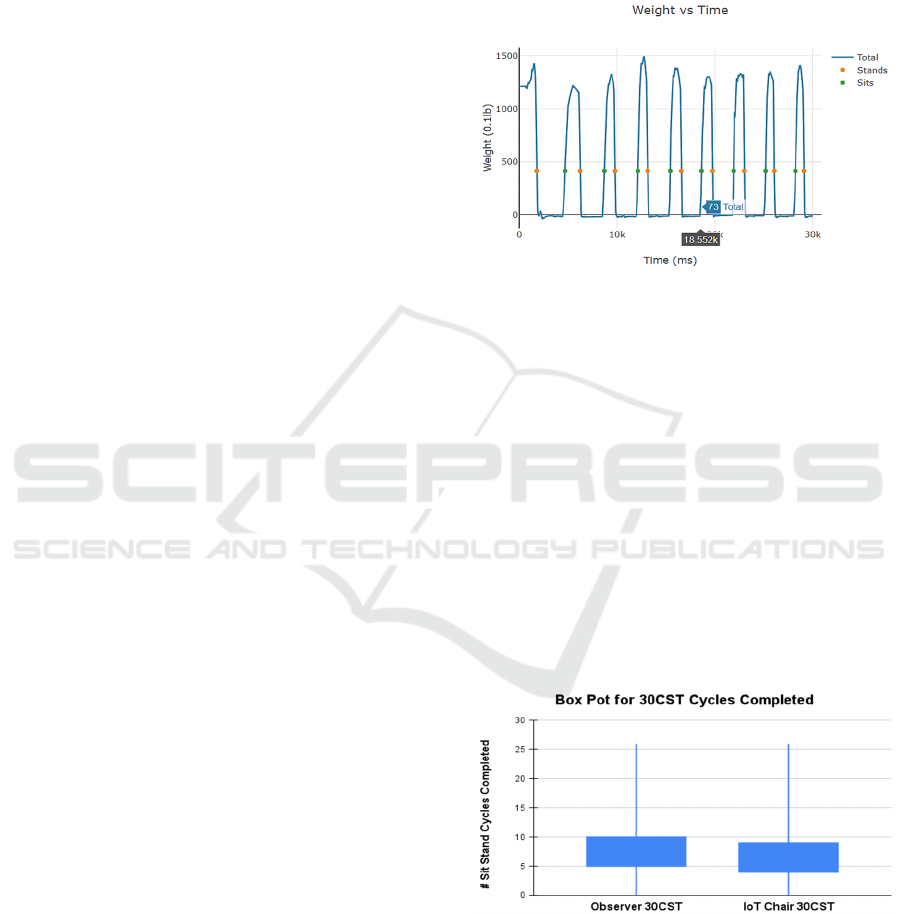
Figure 3 shows the results of a typical 30CST and
5xSST trial. An important note was that the IoT Chair
could automatically record, with a precision of 12.5
milliseconds, how long it took for the person to do 5x
sit-stand cycles. In contrast, the human observer
recordings only measured the 5xSST to the seconds.
Figure 3: A typical example of a completed IoT Chair
clinical trial, with the orange dot recording a "stand" and
the green dot recording a "sit". The blue graph showed the
patient's total weight sitting (140 lb) and at full standing (0
lb). The total time elapsed is 30 seconds (i.e. 30,000 ms),
and 8 sit-stand cycles were completed for the 30 CST. The
cursor is on the fifth completed sit-stand cycle, displaying
the amount of time (18.55 seconds) needed to complete the
5xSST test.
In the 30CST trials, the mean in observer-
recorded sit-stand cycles was 7.72 cycles (median
7.0, SD 3.74, 95% CI 0.53) compared to the mean IoT
Chair-recorded sit-stand cycles was 6.93 cycles
(median 7.0, SD 3.76, 95% CI 0.56). This data is
displayed in a box plot analysis in Figure 4, showing
that the two different methods have overlapping 50%
quartiles.
Figure 4: The 30CST Observer (visually) recorded method
and IoT Chair (automatic) recorded method have an
overlapping 50% quartile range.
For the 5xSST, the mean time to complete the test
recorded by the observer was 19.83 seconds (median
18.03, SD 8.83, 95% CI 18.03) compared to the IoT
IoTBDS 2025 - 10th International Conference on Internet of Things, Big Data and Security
356
Chair mean time of 21.33 seconds (median 20.95, SD
6.41, 95% CI 0.98). This data is displayed on a box
plot diagram in Figure 5, showing that the two
different measuring methods are not statistically
different.
Figure 5: The Observer (visually) recorded method and IoT
Chair (automatic) recorded method for the 5xSST have
medians within the comparison 50% quartile box plot,
meaning the difference between these two methods is not
statistically significant. It is important to note that the IoT
Chair was programmed to not record after 30 seconds,
affecting the difference in the IoT Chair vs Observer box
plot range.
4 DISCUSSION
By using the Box Plot analysis, the 50% quartiles for
the observer method and the IoT Chair overlapped on
both the 30CST and 5xSST, meaning that the IoT
chair results were not statistically different compared
to the observer method. That means both methods had
similar results, and the IoT Chair results were just as
reliable as the standard observer method for the
30CST and 5xSST.
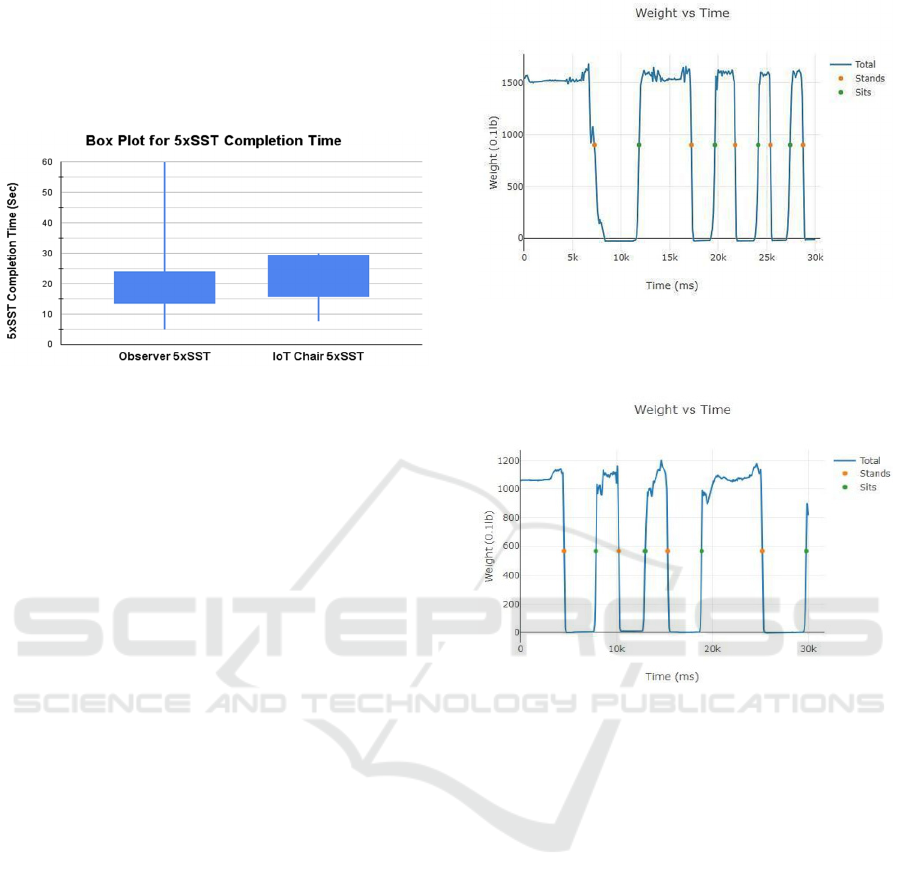
Being able to analyze each sit-stand cycle and its
characteristics is very useful. For instance, the IoT
Chair browser displays the sit-stand cycles as a graph,
showing time on the X-axis and weight on the Y-axis.
Thus, the IoT Chair programming can calculate how
long each sit-stand cycle takes. Patients who are
slower with the first or last sit-stand cycle may
indicate leg weakness. Initially, these participants
may need to build momentum going from sitting to
standing. They may initially sit longer or stand
longer. Figure 6 shows an example of a person with
difficulty in the first sit-stand cycle, with a pause in
the standing phase. At the end of the trial, if the
participants are slower in a sit-stand cycle, this may
also indicate increasing fatigue (Figure 7). Increasing
fatigue would be a risk for falls. Again, this nuanced
data would not be recorded via the human observer
method.
Figure 6: In this trial, the graph clearly depicted the initially
slower first sit-stand cycle compared to the other sit-stand-
sit cycles, with a pause in the standing phase.
Figure 7: This graph shows a prolonged sit-stand cycle near
the end, at about 20 seconds.
Since the chair measures the weight placed on
each chair leg, we can make inferences about a
participant's balance issues. For instance, in Figure 8,
the person consistently placed higher pressure on the
left front and left back chair leg. This difference in
chair leg pressure may indicate that the person has a
right-sided weakness and favors his left leg. Some
possibilities for favoring one side may be due to a
history of stroke, vestibular, or balance issues. This
type of information is not available with the
traditional observer counting method. A physician or
physical therapist can use this additional information
to diagnose leg weakness or imbalance better and
improve patient treatments and outcomes.
Measuring Fall Risk Using the Internet-of-Things Chair
357
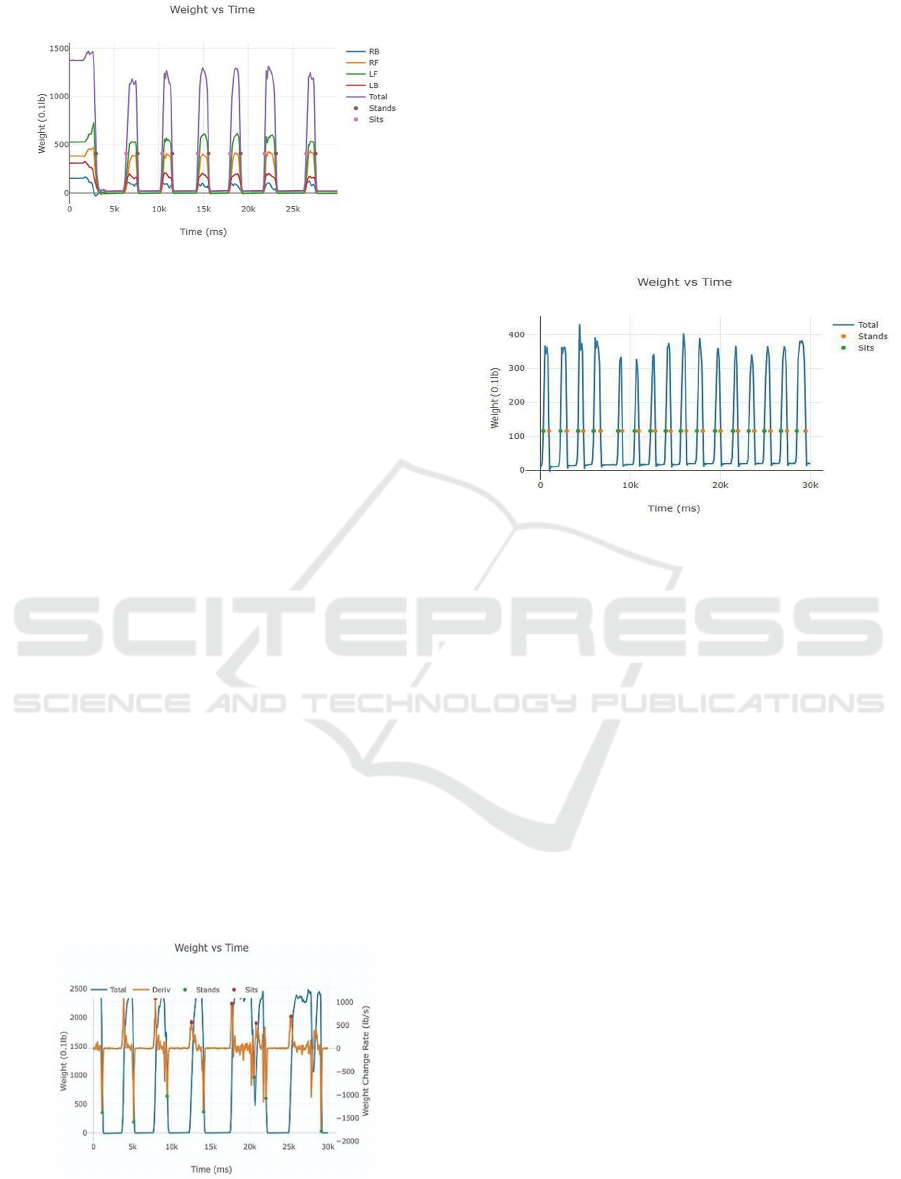
Figure 8: The different color lines indicate the weight
exerted on each chair leg. As the legend describes RB (blue
line)= weight on right back IoT Chair leg, RF (orange line)=
weight on right front leg, LF (green line)= weight on left
front leg, LB (red line)= weight on left back leg, Total
(purple line)= weight on all four legs.
As seen in Figure 9, the IoT Chair also calculated
and displayed the rate of change in weight or weight
velocity of each sit-stand and stand-sit curve. The
weight velocity measures the weight change placed
on the chair over time, which can be a proxy for how
fast the person goes from sitting to standing and from
standing to sitting. These values can help predict if a
person is at a greater risk of falling. For instance,
participants with a faster change in weight exerted on
the chair indicate they can sit or stand quickly due to
greater lower extremity strength. A slower change in
weight exerted on the chair indicates a slower speed
in sitting or standing, suggesting that the person may
be weaker or have more instability and, thus, are at a
greater risk for falls. Figure 9 shows an overall
decreasing rate of weight change amplitude over
subsequent sit-stand cycles starting at about the
halfway point (15 seconds) of the 30CST. This
decreasing rate of weight change can indicate that the
patient has increasing leg muscle weakness and may
be at higher risk of falls compared to a person with a
consistent rate of weight change amplitudes
throughout the trial.
Figure 9: This graph shows a 30-CST trial with the rate of
weight change (orange line) or weight change rate.
The graphs in the IoT Chair sit-to-stand trials
(Figure 10) even have an interesting pattern
reminiscent of an electrocardiogram (EKG) of the
heart. In reading an EKG, the physician looks at the
rhythm, rate, and type of electrical pattern peaks and
troughs to determine different heart conditions
(Hockstad, n.d.). The IoT Chair data can be viewed
similarly. Each person has a different rhythm, rate,
and pattern of sitting and standing. Future studies can
see if the IoT Chair graph patterns can be used to help
determine the patient's leg strength and fall risks.
Figure 10: This figure shows the pattern of a participant
performing 15 total sit-stand cycles (sit-stand-sit again) and
shows a particular, repetitive pattern.
More clinical tests can be done on the IoT Chair
to gather data that can be applied to a broader patient
population, including patients with certain comorbid
conditions such as pain, obesity, heart disease, and
lung disease. Machine learning has been widely used
in various applications (Yeh & Khan, 2022) and can
be applied to the IoT Chair data. Machine learning
can help determine normal or abnormal rates of
weight changes placed on the chair and how much
uneven pressure on the four different chair legs can
indicate leg weakness. Algorithms can also be
developed to determine how much standing or sitting
time is normal or abnormal.
5 CONCLUSION
Clinical testing for the 30CST and the 5xSST on the
IoT Chair developed by Lee et al. showed that the
chair not only provided automatic data collection and
freed up the work of the observer, but the chair was
easy to use for both observer and participant, just like
a manual chair. Furthermore, the measurements were
accurate and reliable, as shown by the box plot
analysis. The chair also produced additional data that
was unavailable using the manual observer method.
The IoT Chair displayed the completion time for each
IoTBDS 2025 - 10th International Conference on Internet of Things, Big Data and Security
358

sit-stand cycle, the amount of time spent sitting and
standing, the amount of weight placed on each chair
leg, and the rate of weight change placed on the chair.
This additional data, along with the traditional
measurements of time and the number of sit-stand
cycles, can more precisely help doctors give earlier
and better predictions of fall risks and leg weakness
in patients. In turn, preventing falls would improve
quality of life, increase life expectancy in older
Americans, and save on the enormous annual
healthcare costs.
REFERENCES
Albalwi, A. A., & Ahmad Abdullah Alharbi. (2023). Optimal
procedure and characteristics in using five times sit to
stand test among older adults: A systematic review.
Medicine, 102(26), e34160–e34160. https://doi.org/
10.1097/md.0000000000034160
Buatois, S., Perret-Guillaume, C., Gueguen, R., Miget, P.,
Vançon, G., Perrin, P., & Benetos, A. (2010). A Simple
Clinical Scale to Stratify Risk of Recurrent Falls in
Community-Dwelling Adults Aged 65 Years and Older.
Physical Therapy, 90(4), 550–560. https://doi.org/10.25
22/ptj.20090158
Campani, D., Caristia, S., Amariglio, A., Piscone, S., Ferrara,
L. I., Barisone, M., Bortoluzzi, S., Faggiano, F., Dal
Molin, A., Silvia Zanetti, E., Caldara, C., Bellora, A.,
Grantini, L., Lombardi, A., Carimali, C., Miotto, M.,
Pregnolato, A., & Obbia, P. (2020). Home and
environmental hazards modification for fall prevention
among the elderly. Public Health Nursing, 38(3), 493–
501. https://doi.org/10.1111/phn.12852
CDC. (2017). ASSESSMENT Patient Date Time 30-Second
Chair Stand. https://www.cdc.gov/steadi/pdf/STEADI-
Assessment-30Sec-508.pdf
CDC. (2020, October 8). Deaths from Older Adult Falls.
Www.cdc.gov. https://www.cdc.gov/falls/data/fall-
deaths.html
CDC. (2024). Older adult falls data. Older Adult Fall
Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/falls/data-research/in
dex.html
Chan-Mei Ho-Henriksson, Thorstensson, C. A., &
Nordeman, L. (2024). Self-assessment using 30-second
chair stand test for patients with knee osteoarthritis – an
intra- and inter-rater reliability study. European Journal
of Physiotherapy, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1080/21679
169.2024.2337419
Chantanachai, T., Sturnieks, D. L., Lord, S. R., Payne, N.,
Webster, L., & Taylor, M. E. (2021). Risk factors for falls
in older people with cognitive impairment living in the
community: Systematic review and meta-analysis.
Ageing Research Reviews, 71. https://doi.org/10.1016/
j.arr.2021.101452
Cobo, A., Villalba-Mora, E., Hayn, D., Ferre, X., Pérez-
Rodríguez, R., Sánchez-Sánchez, A., Bernabé-Espiga,
R., Sánchez-Sánchez, J.-L., López-Diez-Picazo, A.,
Moral, C., & Rodriguez-Mañas, L. (2020). Portable
Ultrasound-Based Device for Detecting Older Adults’
Sit-to-Stand Transitions in Unsupervised 30-Second
Chair–Stand Tests. Sensors, 20(7), 1975. https://doi.org/
10.3390/s20071975
Cobo, A., Villalba-Mora, E., Pérez-Rodríguez, R., Ferre, X.,
Escalante, W., Moral, C., & Rodriguez-Mañas, L.
(2020). Automatic and Real-Time Computation of the
30-Seconds Chair-Stand Test without Professional
Supervision for Community-Dwelling Older Adults.
Sensors, 20(20), 5813. https://doi.org/10.3390/s202058
13
Collado-Mateo, D., Madeira, P., Dominguez-Muñoz, F. J.,
Villafaina, S., Tomas-Carus, P., & Parraca, J. A. (2019).
The Automatic Assessment of Strength and Mobility in
Older Adults: A Test-Retest Reliability Study. Medicina,
55(6), 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina55060270
Figueiredo, P. H. S., Veloso, L. R. de S., Lima, M. M. O.,
Vieira, C. F. D., Alves, F. L., Lacerda, A. C. R., Lima, V.
P., Rodrigues, V. G. B., Maciel, E. H. B., & Costa, H. S.
(2021). The reliability and validity of the 30-seconds sit-
to-stand test and its capacity for assessment of the
functional status of hemodialysis patients. Journal of
Bodywork and Movement Therapies, 27, 157–164.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbmt.2021.02.020
5 Times Sit to Stand Test (FTSST). (n.d.). APTA. https://
www.apta.org/patient-care/evidence-based-practice-reso
urces/test-measures/5-times-sit-to-stand-test-ftsst-
Gill, S. D., de Morton, N. A., & Mc Burney, H. (2012). An
investigation of the validity of six measures of physical
function in people awaiting joint replacement surgery of
the hip or knee. Clinical Rehabilitation, 26(10), 945–951.
https://doi.org/10.1177/0269215511434993
Goldberg, A., Chavis, M., Watkins, J., & Wilson, T. (2012).
The five-times-sit-to-stand test: validity, reliability and
detectable change in older females. Aging Clinical and
Experimental Research, 24(4), 339–344. https://doi.org/
10.1007/bf03325265
Harris-Kojetin, L., & Sengupta, M. (2018). Falls Among
Assisted Living Residents: Results From the 2016
National Study of Long-Term Care Providers.
Innovation in Aging, 2(suppl_1), 766–766.
https://doi.org/10.1093/geroni/igy023.2833
Hartikainen, S., Lonnroos, E., & Louhivuori, K. (2007).
Medication as a Risk Factor for Falls: Critical Systematic
Review. The Journals of Gerontology Series A:
Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences, 62(10), 1172–
1181. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/62.10.1172
Hellmers, S., Fudickar, S., Lau, S., Elgert, L., Diekmann, R.,
Bauer, J., & Hein, A. (2019). Measurement of the Chair
Rise Performance of Older People Based on Force Plates
and IMUs. Sensors, 19(6), 1370. https://doi.org/10.3390/
s19061370
Hockstad, E. (n.d.). ECG Review 2020 2020 American Heart
Association Virtual Cardiac Symposium. https://www.
heart.org/-/media/files/affiliates/mwa/kansas-city/kc-car
diac-and-stroke-symposium/2020-event-documents/card
iac-presentations/2-ecg-hockstad.pdf?la=en
Jin, H., Zhou, Y., Stagg, B. C., & Ehrlich, J. R. (2024).
Association between vision impairment and increased
Measuring Fall Risk Using the Internet-of-Things Chair
359

prevalence of falls in older US adults. Journal of the
American Geriatrics Society, 72(5), 1373–1383.
https://doi.org/10.1111/jgs.18879
Jones, C. J., Rikli, R. E., & Beam, W. C. (1999). A 30-s
Chair-Stand Test as a Measure of Lower Body Strength
in Community-Residing Older Adults. Research
Quarterly for Exercise and Sport, 70(2), 113–119.
https://doi.org/10.1080/02701367.1999.10608028
José Gonçalves, Batista, J., & Novo, A. (2015). Fully-
Automated “Timed Up and Go” and “30-Second Chair
Stand” Tests Assessment: A Low Cost Approach Based
on Arduino and LabVIEW. Lecture Notes in Electrical
Engineering, 669–678. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-
319-10380-8_64
Lee, A. W., & Yeh, H.-J. J. (2022). Real-Time Monitoring of
Urine Output with Internet-of-Things Connected Foley
Catheters. 2021 International Conference on
Computational Science and Computational Intelligence
(CSCI), 1808–1811. https://doi.org/10.1109/csci581
24.2022.00322
Lee, A., Lee, M., & Yeh, H.-J. J. (2023). An IoT-Based
Automatic and Continuous Urine Measurement System.
BioMedInformatics, 3(2), 446–454. https://doi.org/10.33
90/biomedinformatics3020030
Lee, A. W., Lee, M. S., Yeh, D. P., & Yeh, H.-J. J. (2024).
Sensor-Integrated Chairs for Lower Body Strength and
Endurance Assessment. Sensors, 24(3), 788.
https://doi.org/10.3390/s24030788
Marigold, D. S., Eng, J. J., Dawson, A. S., Inglis, J. T., Harris,
J. E., & GylfadÃ
3
ttir, S. (2005). Exercise Leads to Faster
Postural Reflexes, Improved Balance and Mobility, and
Fewer Falls in Older Persons with Chronic Stroke.
Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, 53(3), 416–
423. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1532-5415.2005.53158.x
Millor, N., Lecumberri, P., Gómez, M., Martínez-Ramírez,
A., & Izquierdo, M. (2013). An evaluation of the 30-s
chair stand test in older adults: frailty detection based on
kinematic parameters from a single inertial unit. Journal
of NeuroEngineering and Rehabilitation, 10(1), 86.
https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-0003-10-86
Muñoz-Bermejo, L., Adsuar, J. C., Mendoza-Muñoz, M.,
Barrios-Fernández, S., Garcia-Gordillo, M. A., Pérez-
Gómez, J., & Carlos-Vivas, J. (2021). Test-Retest
Reliability of Five Times Sit to Stand Test (FTSST) in
Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.
Biology, 10(6). https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10060510
National Institute on Aging. (2022). Falls and Fractures in
Older adults: Causes and Prevention. National Institute
on Aging. https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/falls-and-
fractures-older-adults-causes-and-prevention
Riska, K. M., Peskoe, S. B., Kuchibhatla, M., Gordee, A.,
Pavon, J. M., Kim, S. E., West, J. S., & Smith, S. L.
(2021). Impact of Hearing Aid Use on Falls and Falls-
Related Injury. Ear & Hearing, 43(2). https://doi.org/
10.1097/aud.0000000000001111
Papalia, G. F., Papalia, R., Diaz Balzani, L. A., Torre, G.,
Zampogna, B., Vasta, S., Fossati, C., Alifano, A. M., &
Denaro, V. (2020). The Effects of Physical Exercise on
Balance and Prevention of Falls in Older People: A
Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of
Clinical Medicine, 9(8), 1–19. https://doi.org/10.3390/
jcm9082595
Riska, K. M., Peskoe, S. B., Kuchibhatla, M., Gordee, A.,
Pavon, J. M., Kim, S. E., West, J. S., & Smith, S. L.
(2021). Impact of Hearing Aid Use on Falls and Falls-
Related Injury. Ear & Hearing, 43(2). https://doi.org/
10.1097/aud.0000000000001111
Rodrigues, F., Monteiro, A. M., Forte, P., & Morouço, P.
(2023). Effects of Muscle Strength, Agility, and Fear of
Falling on Risk of Falling in Older Adults. International
Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health,
20(6), 4945. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20064945
Takeshima, N., Kohama, T., Kusunoki, M., Fujita, E., Okada,
S., Kato, Y., Kofuku, K., Islam, M. M., & Brechue, W.
F. (2019). Development of Simple, Objective Chair-
Standing Assessment of Physical Function in Older
Individuals Using a Kinecttm Sensor. The Journal of
Frailty & Aging, 1–6. https://doi.org/10.14283/jfa.2019.
23
Yeh, C., Lee, A., Dy, H., & Li, K. (2022). Internet-of-Things
Management of Medical Chairs and Wheelchairs. 183–
188. https://doi.org/10.5220/0011059600003194
Yeh, C., Lee, A. W., Lee, M. S., & Li, K. C. (2022). Internet-
of-Things Monitoring of Physical Restraint Patients.
2021 International Conference on Computational
Science and Computational Intelligence (CSCI), 1803–
1807. https://doi.org/10.1109/csci58124.2022.00321
Yeh, C., Lee, A., Dy, H., & Li, K. (2022). Internet-of-Things
Management of Medical Chairs and Wheelchairs. 183–
188. https://doi.org/10.5220/0011059600003194
Yeh, C., & Khan, F. H. (2022). Citizen Science Mobile Apps
with Machine Learning for Recyclable Objects. 1539–
1542. https://doi.org/10.1109/csci58124.2022.00273
Yeh, K., Yeh, C., & Li, K. (2021). Internet-of-Things
Management of Hospital Beds for Bed-Rest Patients.
Transactions on Computational Science and
Computational Intelligence, 439–448. https://doi.org/
10.1007/978-3-030-71051-4_33
Yeh, J. H.-J., Bartholio, C., Shackleton, E., Costello, L.,
Perera, M., Yeh, K., & Yeh, C. (2020). Environmentally
Embedded Internet-of-Things for Secondary and Higher
Education. 543–547. https://doi.org/10.1109/icict505
21.2020.00092
Yeh, H.-J. J., Stambaugh, M., Zahnd, A., & Yeh, K. (2019).
IoT Sensing and Control Network for Pico-Hydroelectric
in the Nepal Himalayas. 2021 International Conference
on Computational Science and Computational
Intelligence (CSCI), 1184–1189. https://doi.org/10.1109/
csci49370.2019.00223
IoTBDS 2025 - 10th International Conference on Internet of Things, Big Data and Security
360
