
Regaining Control: Enabling Educators to Build Specialized AI Chat
Bots with Retrieval Augmented Generation
Barbara Pampel
1 a
, Simon Martin
1 b
and Ulrike Pad
´
o
2 c
1
University of Konstanz, Universitaetsstrasse 10, Konstanz, Germany
2
Hochschule f
¨
ur Technik Stuttgart, Schellingstr. 24, 70174 Stuttgart, Germany
Keywords:
Retrieval-Augmented Generation, Large Language Models, Education.
Abstract:
Conversational AI (chat) bots are powerful and helpful tools, but are not suited for the unrestricted use in many
classrooms: They may hallucinate, easily veer from the topic of instruction, and are vulnerable to malicious
prompting. Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) is a technique that allows educators to constrain chat bots
to a specific area of expertise, reducing hallucinations and vulnerability to mis-use. We are working on a
low-code solution that enables tech-savvy educators to build such a RAG-based chat bot system themselves,
thus retaining full control over the content and behavior of their bot. We present the first version of this system
and promising initial feedback from educators and students on its suitability, reliability and flexibility.
1 INTRODUCTION
Recent studies show the growing use of AI chat bots
based on Large Language Models (LLMs) among
school and university students, but raise concerns
about unsupervised and unreflective use without con-
sidering ethical or academic risks – not just pla-
giarism, but also a growing dependence on support
systems that may lead to bypassing critical thinking
processes (Medienp
¨
adagogischer Forschungsverbund
S
¨
udwest, 2024; Abbas et al., 2024; S
¨
uße and Kobert,
2023; Ng et al., 2024). For example, students might
exploit these tools to complete assignments without
engaging in the learning process (Chang et al., 2023).
Further, the lack of connection between AI systems
and established educational theories creates a gap in
aligning these tools with curriculum-specific goals
and desired learning paths(Ouyang and Jiao, 2021).
Adding to the known problem of hallucinations in
LLM-generated text (Maynez et al., 2020), the level
of detail in the bot’s output can be inappropriate for
a specific course or teaching session, as an educator
usually does not have control over the output. This
can lead educators to completely ban AI tools.
On the other hand, there are various benefits that
AI systems can offer learners, such as chat bots sup-
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6492-0381
b
https://orcid.org/0009-0000-4149-7189
c
https://orcid.org/0009-0000-0664-7487
porting self-regulated learning (Chang et al., 2023).
In addition, we need to promote future-oriented learn-
ing. Educators and students must acquire skills in
handling cutting-edge technologies and prepare for
the demand in higher education and the workplace,
where AI systems will increasingly support various
tasks. Although several initiatives are currently be-
ing implemented, there still is a long road ahead (for
Germany, see Budde et al. (2024)).
With the technique of Retrieval-Augmented Gen-
eration (RAG, Lewis et al. 2020), AI systems can be
customized not only to meet students’ support needs
(e.g., learning level, language, subject matter) but also
to reflect educators’ decisions about what information
the system should contain and how it should react to
specific requests (e.g., for solving homework). This
also means that a RAG-based system is much less
vulnerable to malicious queries (prompt injection at-
tacks, e.g., Perez and Ribeiro 2022), because these
will not match the system’s knowledge. Further, using
locally hosted Open Source solutions can safeguard
sensitive student data and reduce cost.
Learners can access knowledge through these AI
systems interactively and without external restric-
tions, which has the potential to increase their engage-
ment and can encourage independent learning and re-
duce educators’ workload on routine questions.
For educators, active involvement in the develop-
ment of the RAG systems promotes both media lit-
eracy and critical engagement with AI systems. Us-
Pampel, B., Martin, S. and Padó, U.
Regaining Control: Enabling Educators to Build Specialized AI Chat Bots with Retrieval Augmented Generation.
DOI: 10.5220/0013425500003932
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2025) - Volume 2, pages 371-378
ISBN: 978-989-758-746-7; ISSN: 2184-5026
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
371
ing custom AI systems ensures transparency and con-
trol over the information provided to students, and
designing system prompts allows tailoring the AI’s
role (e.g., tutor vs. discussion partner). We would
like educators to be more than passive users and in-
stead actively shaping the future of teaching with
and about AI technologies and enriching the teach-
ing landscape. We therefore designed a no-code RAG
system template that tech-savvy educators should be
able to recreate after a brief introduction, and example
use cases including the design of the knowledge base
and system prompts, that can be adapted to individual
needs (see Section 2).
We built our template with the Will, Skill, Tool,
Pedagogy (SWTP) model by Knezek and Christensen
(2015) in mind, which provides a framework for un-
derstanding the factors that influence how technology
is used in teaching. The aspect Will relates to the mo-
tivation and positive disposition of educators to adopt
technological innovations. Importantly, it refers to
a general readiness to experiment and test new ap-
proaches. The Skill dimension encompasses the tech-
nical competencies and confidence needed to effec-
tively use and integrate technology, which means pro-
ficiency in using tools and adjusting them to differ-
ent educational contexts. The Tool dimension refers
to the availability and accessibility of necessary tech-
nological resources, such as platforms, software, and
devices. Finally, the Pedagogy dimension addresses
the teaching strategies and instructional approaches
that incorporate technology to enhance learning out-
comes. Various studies (Velazquez, 2006; Chris-
tensen and Knezek, 1999; Knezek and Christensen,
2015) found different strengths of these aspects in
predicting Technology Integration using slightly dif-
ferent models for different groups of educators (re-
garding country and skill level). We address all four
aspects: We gather motivated educators in our work-
shops and show them the potential of such systems
(Will), teach them the basic concepts of Generative
AI and RAG and how to use and adapt such systems
(Skill) with prototypes we developed in a no-code
framework using Open Source LLMs (Tool) and rec-
ommend initial typical use-cases (Pedagogy).
Due to the current high interest and growing
demand for AI-powered educational tools, we fol-
low an agile development approach accompanied by
a Design-Based Research methodology (Reimann,
2010). At different stages of development, we have so
far made various iterations of the RAG system avail-
able to students, monitored and evaluated its use, and
collected detailed feedback from participants to guide
further improvements (see Section 3).
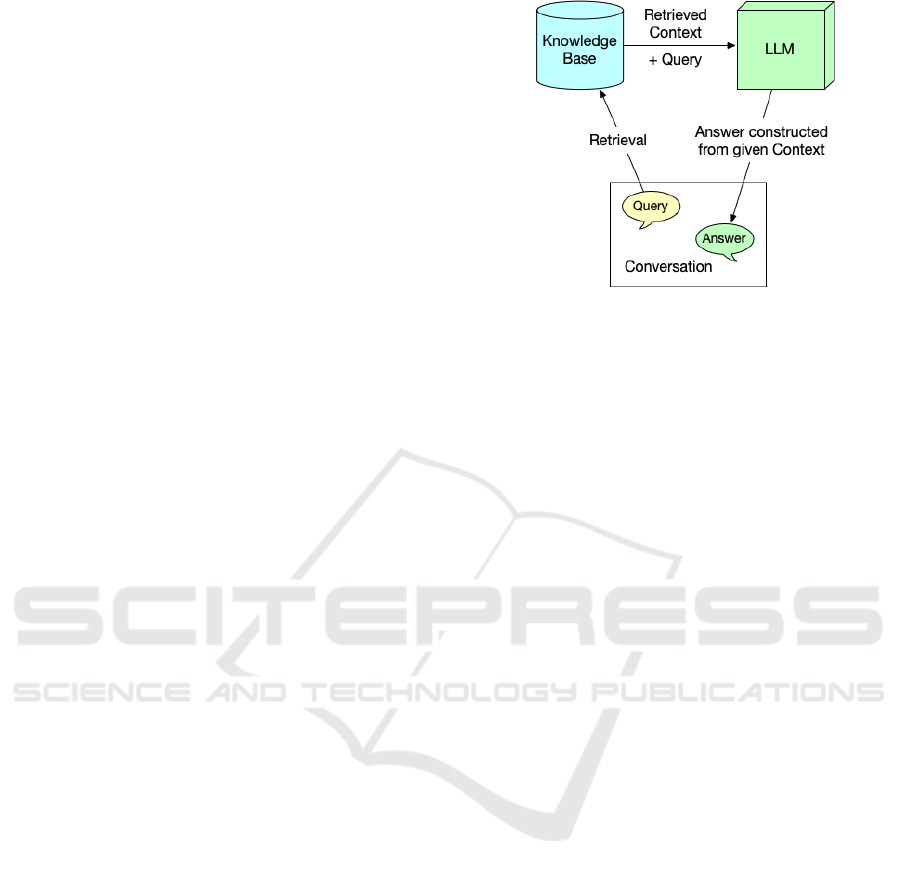
Figure 1: Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Dialogue
(simplified).
1.1 Retrieval-Augmented Generation
(RAG)
LLM-based chat bots have inherent factual knowl-
edge from the training process (Petroni et al., 2019) as
well as knowledge of the desired behavior in conver-
sation through fine-tuning for the dialogue task. How-
ever, the inherent knowledge of LLMs may be out-
dated or at the wrong level of detail for the use case.
In addition, utterances may include plausible halluci-
nations (Maynez et al., 2020) – erroneous statements
that are hard to identify for the user.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (Lewis et al.
2020, see, e.g. Fan et al. 2024 for an overview), en-
hances and defines the relevant context for the con-
versation, thus strictly delimiting the facts used in
conversation. Figure 1 shows a (simplified) example:
The user query is initially matched against documents
relevant to the intended use case that have been col-
lected in a Knowledge Base. These are preprocessed
into snippets that can be retrieved, e.g., by specialized
language models (Fan et al., 2024) whenever they are
relevant to the user’s query. The LLM is then given
not just the user query, but also the relevant context
information needed to reliably answer it. This means
that it is only tasked with phrasing the given informa-
tion coherently (and appropriately for the context).
In a teaching context, this combined strategy al-
lows the educator to specify reliable and up-to-date
information at the right level of detail. Hallucinations
are significantly reduced (Shuster et al., 2021), and
conversation can no longer drift away from the in-
tended topic, avoiding hacking attempts by prompting
or attempts to generate inappropriate output (prompt
injection, Yu et al. 2023) – a real concern in a teach-
ing setting (see Section 3.2). At the same time, the
LLM contributes fluent and coherent output using the
retrieved information snippets.
CSEDU 2025 - 17th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
372

1.2 RAG in Education
Some projects take first steps to integrate RAG in
teaching, but prototypes are rarely ready to use with
students in more than a pilot setting, and even fewer
systematic evaluations can be found in the literature.
Dong et al. (2023) used the OpenAI Assistants
API to build a RAG system where educators can up-
load course materials and tested it with a group of stu-
dents. The feedback for this trial was very positive
regarding ease of use and relevance of the answers,
but mixed regarding the level of detail of the answers.
In addition, the use of a commercial system raised
concerns about costs and data privacy. Mullins et al.
(2024) tried to address this by using Open Source sys-
tems. They tested a RAG system using a Llama LLM
and a Chroma vector database and Reddit as a data
source. This last point was problematic, resulting in a
low correctness rate of the output (below 50%). Kahl
et al. (2024) used chat bots for robotics education and
tried prompt engineering, LLM fine-tuning and RAG
systems to improve factual accuracy. Here, especially
RAG was found to be suitable to improve the educa-
tional utility of LLMs in specialized domains.
In some projects custom RAG-based chat bot pro-
totypes were developed for (Higher) Education and
evaluated by educators. Dakshit (2024) for exam-
ple received positive feedback from computer science
faculty members on the potential of an RAG system
serving as a teaching aid for lecturers and as teach-
ing assistants answering students questions. Still, the
participants highlighted the need for careful consid-
eration of ethical implications and appropriate safe-
guards to ensure that the implementation of such sys-
tems is responsible and effective.
Most systems we found do not have an interface
for learners yet, so they are not ready to be deployed
as safeguarded AI-teaching assistants. Much further
advanced is the OwlMentor by Th
¨
us et al. (2024),
which has a complex user interface with a chat func-
tion including RAG. It has been evaluated quite exten-
sively with positive results for its usability, but for the
task of helping students with understanding scientific
papers, no direct correlation between the use of the
system and learning gains was found. Additionally,
it relies on OpenAI’s GPT-3.5 Turbo model, a cost-
incurring component. Similarly, the now regularly
used CS50 Duck, developed by Liu et al. (2024) for
Harvard’s CS50 course, was tested to be very reliable
and received very positive feedback from students.
However, it uses the more expensive OpenAI GPT-
4 model. Furthermore, both OwlMentor and CS50
Duck were developed specifically for these courses
and, while the results highlight the potential of RAG
in education, they cannot be replicated without exten-
sive technical expertise.
Our focus is not only on the usability and effec-
tiveness of RAG in higher education but also on how
feasible it is for tech-savvy educators to recreate and
adapt a system themselves – this seems as yet implau-
sible for all of the systems mentioned above.
There already are some online platforms (gen-
erally requiring paid subscriptions) offering no-code
custom chat bots including the possibility to upload
own material and define a system prompt, among
them Custom GPT
1
by OpenAI, but the control over
their behavior is limited. In our tests, we could easily
lead the chat bots away from the knowledge base, trig-
ger hallucinations, and found them very vulnerable to
prompt injection. Further, using these web interfaces
with just text fields for prompts and buttons to upload
files, the structure and functionality of such systems
remain completely hidden, so educators would only
learn how to use them and not how they work.
2 TECHNICAL SETUP
2.1 Langchain, Flowise and Our Flow
The central part of creating a custom RAG system
is setting up the interaction with the LLM of choice.
But direct interaction with LLMs is often not possible
without deeper understanding of programming con-
cepts, API integration, and managing computational
resources to effectively query and deploy these mod-
els in applications.
LangChain
2
is a framework designed for building
applications that integrate LLMs and can significantly
simplify several aspects of working with LLMs.
LangChain provides high-level abstractions that re-
duce the need for extensive programming knowl-
edge. Developers can use prebuilt components in-
stead of writing complex logic from scratch. While
LangChain lowers the entry barrier, effective use still
requires substantial programming and computer sci-
ence knowledge, including API configuration, work-
flow design, and integration of external tools.
Flowise
3
is an open-source, low-code tool based
on LangChain for creating customized LLM work-
flows through a drag-and-drop interface. While this
interface simplifies the process, foundational com-
puter science knowledge is still required for tasks like
configuring APIs, managing data flows, and optimiz-
1
https://openai.com/index/introducing-gpts/
2
https://www.langchain.com/
3
https://github.com/FlowiseAI/Flowise
Regaining Control: Enabling Educators to Build Specialized AI Chat Bots with Retrieval Augmented Generation
373
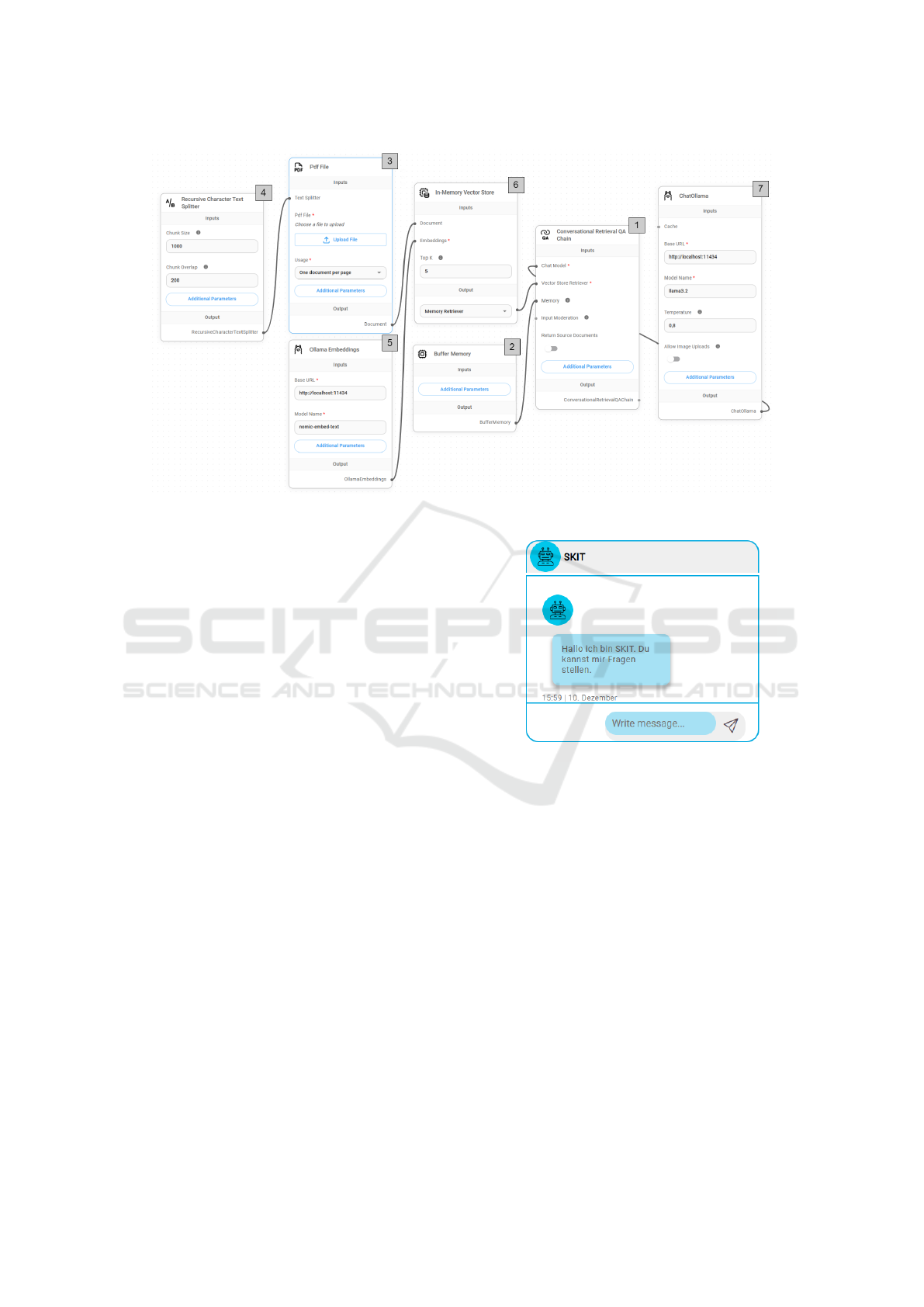
Figure 2: Flowise template for the implementation of an RAG.
ing workflows. However, with the guidance of experts
and a concrete example flow, Flowise can be effec-
tively used by educators to create RAG systems with-
out deep technical expertise.
For this purpose, we designed a Flowise template
for the implementation of an RAG system that can
take on the role of a tutor (shown in Figure 2). The
main component of the template is the Conversa-
tional Retrieval QA Chain (1). Chains serve as the
foundation for building workflows that link inputs,
such as user queries, to outputs like responses or re-
trieved information. For example, a Conversational
Retrieval QA Chain combines conversation history
with external knowledge retrieval, enabling the sys-
tem to maintain context while accurately answering
questions by pulling relevant information from an ex-
ternal source. To maintain context, information is re-
trieved from the Buffer Memory (2) that stores the
conversation history. To use information from an ex-
ternal source (3) like a PDF, pre-processing is re-
quired. The text is extracted from a source and split
into chunks using a Recursive Character Text Split-
ter (4). Then, embeddings (5) for these chunks are
created. The embeddings create high-dimensional nu-
merical vectors that capture semantic and contextual
information. The vectors enable efficient similarity
searches. These vectors are stored in a Vector Store
(6) knowledge base. For each query, the Conver-
sational Retrieval Chain retrieves the most relevant
information chunks based on the stored embeddings
from the Vector Store. The chosen LLM (7) uses
the retrieved information chunks and the conversation
context to generate a natural language response ac-
Figure 3: The user interface of SKIT.
cording to the configurable system prompt that out-
lines the bot’s role and goals.
Different LLMs can be used for this purpose. In
the very early stages of our project, we worked with
GPT-3.5, but later switched to LLMs that can be run
locally, such as Llama, due to data privacy concerns,
increased flexibility, and because it is available at no
cost. At the moment, we primarily use Llama 3.1
SauerkrautLM. Although tests with self-hosted LLMs
were successful, performance was limited due to in-
sufficient computational power on our current virtual
machine. During this research phase, we use the
LLMs hosted by Chat AI (Doosthosseini et al., 2024),
offered by the Gesellschaft f
¨
ur wissenschaftliche
Datenverarbeitung mbH G
¨
ottingen (GDWG), run-
ning on scalable high performance computing sys-
tems with secure cloud access and without storing or
using any user data.
CSEDU 2025 - 17th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
374

To evaluate the created RAG systems, we devel-
oped a small web application called SKIT (Spezial-
isierter KI Tutor, Specialized AI Tutor) that makes
bots powered by different Flowise workflows acces-
sible to test users online, while user interactions are
logged locally for analysis. The user interface of
SKIT is shown in Figure 3. Note that it gives no ac-
cess to the knowledge base or system prompt and is
therefore appropriate for independent use by students.
2.2 Assessing Feasibility in an Educator
Workshop
The template for SKIT is meant to provide an appro-
priate Tool (in the Will, Skill, Tool, Pedagogy frame-
work) that fits the Skills of the intended users. To col-
lect feedback on this goal, the Flowise template (not
including SKIT’s web application) was tested during
a workshop attended by 23 educators and university
members engaged in teacher education. Following
a brief introduction to the fundamental concepts, the
template was presented and participants were given
the opportunity to recreate, test, and customize the
system. At the conclusion of the workshop, partic-
ipants were invited to provide feedback on their ex-
periences and perspectives. The results of the Likert-
scale questions are presented in Figure 4, which also
shows the very promising results: Participants on av-
erage found it likely or very likely that a system like
SKIT can be re-created and used by tech-savvy edu-
cators, in school and especially in higher education,
and that it is more suitable than commercial tools.
Furthermore, participants used a set of open ques-
tions regarding the potential and limitations of such
systems to propose scenarios in which they could
be beneficial. Among the responses (translated from
German) were the following: ”Review tool; first en-
gagement with a topic when students ask initial ques-
tions; its applicability in multilingual teaching would
be interesting; differentiation in teaching”, ”Assign-
ments can potentially be explained more individually.
(Other languages, simplifications, etc.; e.g., when
German is not the student’s native language.)” and
”Students who don’t have support at home can find
help; I think it’s great that the prepared sources can
be integrated.”. One concern was that ”Students pre-
fer open access and often already have ChatGPT in-
stalled privately (e.g., in business schools).”.
Following the workshop, we got several requests
for the use of the SKIT template, not only from lectur-
ers but also from staff in academic advising and writ-
ing support services, as such systems could also be
very helpful in those areas to reliably and accurately
answer students’ questions. Some staff had already
tried commercial systems like OpenAI’s Custom GPT
or poe.com
4
but shared our experience that these chat
bots easily break the character defined by the system
prompts and do not reliably restrict their responses to
the provided knowledge base.
Within the Will, Skill, Tool, Pedagogy framework,
these experiences underscore both the Will of edu-
cators and advisors to use reliable, customized chat
bot systems to support their students, and a perceived
good fit of our Tool with the Skill set of future school
teachers and some current staff in Higher Education.
3 INITIAL USE CASES
Further testing regards the Pedagogy aspect of our
guiding framework. In different iterations of the
Design-Based Research cycle, we experimented with
(a) different types of chat bots with different learning
objectives and (b) exposing learners at different stages
of their studies to the chat bot in parallel to their reg-
ular lectures. These experiments show that the chat
bots can be flexibly tailored to the educators’ objec-
tives, are indeed robust and factually reliable in a real-
world setting, and that students are well-equipped and
motivated by previous experience to use them.
3.1 Different Learning Objectives
We tested two types of bots, tailored to different learn-
ing objectives, in an asynchronous online course on
basic computer science knowledge (CS) for 30 stu-
dent teachers from non-CS subjects. The first, which
we call a knowledge bot, was designed for a unit on
the history of CS, so mainly focusing on knowledge
content. The second version, which we call explain
bot, was designed primarily to describe and explain
procedures and algorithms, i.e., for units on encoding
numbers and encryption. It included a warning (spec-
ified in the system prompt) whenever it was asked
to do calculations, explaining that this is not one of
its strengths and results should be verified carefully.
Both bots had a knowledge base extracted from our
digital self-learning units for the courses, containing
many textual descriptions and explanations, which
substantially differ from typical lecture slides.
The knowledge bot was rarely used, so we asked
students for reasons (multiple reasons could be se-
lected). The results indicate that 40% of the par-
ticipants managed very well without assistance and
had no questions or problems with the unit. How-
ever, 25.71% admitted they simply forgot they could
4
https://poe.com/
Regaining Control: Enabling Educators to Build Specialized AI Chat Bots with Retrieval Augmented Generation
375

1
1,5
2
2,5
3
3,5
4
4,5
5
I think that such a system...
… can be recreated by (tech-savvy) teachers.
… can be used by (tech-savvy) teachers.
... can be us efully implemented in school-lessons.
... can be us efully implemented in higher education.
… is more suiable than commercial tools.
Figure 4: Responses to Likert-Scale questions from 1 (for ”not at all”) to 5 (for ”very likely”).
use the bot. Other reasons for not using the bot in-
cluded not trusting its ability to help (2.86%), con-
cerns about anonymity (5.71%), bad experiences with
other chat bots (2.86%), or preferring a familiar chat
bot (5.71%). Interestingly, no participants preferred
human tutors over the bot. Additionally, 17.14%
listed other reasons, such as not having seen the pass-
word until later, being unable to log in, not know-
ing about the bot, attempting the task without help,
finding it unnecessary to use the chat bot for the spe-
cific unit, or simply working through the material in-
stead. It is worth mentioning, that the unit already is
designed quite interactively, as it mainly consists of
a digital interactive self-learning unit, including text,
videos, annotated figures and little quizzes, followed
by (graded) assignments. The results for these assign-
ments were very good with an average of 9.06 out of
10 points, so it seems that in fact no additional help
was needed.
The second bot, equipped to explain procedures
and algorithms, was designed for a more difficult unit
on encoding numbers and characters. Here we mon-
itored 14 conversations with a total of 56 interac-
tions. The most common queries asked for explana-
tions (36%), but many users just directly copied ques-
tions from the assignments or quizzes (25%). Only
16% had general questions like the goal of the unit
or a summary, 14% of the questions were not close
enough to the content and 9% were social interac-
tions like ”hi” or ”thanks”. Apart from some tem-
porary technical problems with follow-up questions
which resulted in unanswered requests, the quality of
answers to successful requests was very good. The
bot either gave a correct answer or directed the user
to a specific section of the material. It warned the
user when doing calculations but did not even make
any mistakes here. If it could not generate an answer,
it responded with ”Sorry, I am not sure about this!” or
”I am not prepared for this topic”, just like we speci-
fied in the system prompt. Unfortunately, this was the
case even for some questions about the content, due to
the mentioned problems with the follow-up questions,
but this has been solved in the meantime.
Interestingly, apart from one user asking for a
pizza recipe, none of the users tried to explore fur-
ther abilities of the bot, maliciously distract it from
the knowledge base or hijack it through prompt injec-
tion. Keep in mind that the participants do not study
computer science but only take part in this course for
basic CS knowledge. One user, aware that the con-
versations would be logged for research, directly ad-
dressed ”the researchers” in one message.
3.2 Different Learner Groups
Our second use case employs an instance of the
knowledge bot introduced in Section 3.1. We observe
its use in two different classes (and learner groups).
Setup of the bot comprised collecting the relevant
documents for each course (i.e., the existing lecture
slides) and phrasing a welcome message. The stan-
dard SKIT flow was used otherwise, cutting prepara-
tion time for the educator to the minimum.
The students answered a questionnaire about their
previous experience with chat bots and their expecta-
tions of a custom bot, then they had free access to the
bot for several weeks. Participation was voluntary;
we report on the group of participants only.
One learner group consisted of 60 somputer sci-
ence students from a first-semester Java program-
ming class
5
; the other consisted of 34 computer sci-
ence students in their third and fourth semesters in
an AI class. The students were familiar with chat
bots (like ChatGPT): more than 80% of answers from
both groups reported using tools like this at least once
a week and many, more often than that. However,
both groups of students were worried about the re-
5
All students requested access to the bot, but only 20%
of students answered the questionnaire.
CSEDU 2025 - 17th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
376

liability of chat bot output - half the participants in
each group named this concern (multiple concerns
could be given). This aligns with our motivation for
preparing easy-to-configure RAG bots to increase the
reliability of answers. The most frequently reported
bot uses were searching for information and, for the
younger students, text generation – the older students
listed coding in second place (multiple uses could be
named). Our knowledge bot was configured for infor-
mation search but intentionally offered only limited
coding support (no code generation, just information
about available methods and syntax).
We analyzed a total of 573 interactions with the
bots. During the initial weeks, students in both groups
explored the bots’ abilities and tried to generate unin-
tended output through prompt injection. There were
200 such interactions in total, and in the AI class,
where students learnt about the technical background
of chat bots, malicious prompts made up 60% of inter-
actions in one week. However, none of these attempts
was successful. Content-based interactions were suc-
cessful (defined as a relevant bot answer to a student
query) in 42% of cases (some of the failures are likely
due to the technical issues reported above). Suc-
cessful bot output was almost always factually cor-
rect (only two of 155 bot answers were found to be
incorrect). Requests for definitions, explanations or
lists of items were more successful on average (be-
tween 74 and 56%), requests for non-covered meta-
information (like the course schedule) or for solutions
to the homework sheets always failed. While failure
on definition or explanation requests is frustrating to
the students, from the educator perspective this be-
havior is preferable to hallucinations.
3.3 Summary of Observations
These use cases highlight the reliability of the output
and the robustness of the RAG approach towards tam-
pering, two of our motivations for promoting RAG for
educational bots. The data also shows that university
students can be expected to be familiar with chat bots
and their drawbacks, which makes them equipped to
use reliable alternatives. However, this also shapes
their expectations, for example for code generation,
which may not fit the educators’ intentions.
We also see that students’ use of the bots strikingly
differs by learner group. Some groups are very inter-
ested in exploring the bot and its robustness towards
malicious prompts, others only use it as intended. If
a learning unit is engaging and well-explained on its
own, the students may even not use the bot at all. In
the second use case, we observed that interest in the
bot waned over time, probably because of initial fail-
ures to answer relevant student requests and because
of the intentionally sparse coding support in the pro-
gramming class. This underscores our intuition that
no single bot is appropriate for all groups, but that ed-
ucators need the freedom to define specialized bots.
4 CONCLUSIONS
We have presented our work on a low-code Retrieval-
Augmented Generation (RAG) template – a Tool (in
the sense of the Will, Skill, Tool, Pedagogy frame-
work by Knezek and Christensen (2015)) that allows
educators to customize chat bots as resources for their
courses. Customization of the bot is possible both re-
garding the extent and depth of the bot’s knowledge
(through filling its knowledge base) and regarding the
bot’s behavior in the conversation with students (for
example, as a source of definitions and explanations
or as a discussion partner). Our goal was to both re-
duce the demands on educators’ skill sets and make it
easier for them to acquire deeper familiarity with AI
tools for teaching, strengthening the Skill dimension.
We have collected first feedback on the tool: Ed-
ucators have attested to a good fit with the Skills that
can be expected from tech-savvy teachers, and have
documented their Will to engage with AI tools and use
them for their students’ advantage. We have also col-
lected insights from classroom use of the tool in order
to inform the Pedagogy dimension of the framework.
We find that our (university-level) students are famil-
iar with chat bots, but share our concerns about the
reliability and appropriateness of general bots. En-
couragingly, we also the bots themselves proved ro-
bust against tampering and accurate in their replies.
Our next goals are to further develop the usage
scenarios, improve technical aspects of the bots, and
also to develop prompting tips for our students to en-
sure they are getting the most out of their chat bot use.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was partially funded by fellowships to Bar-
bara Pampel and Ulrike Pad
´
o in the bwDigiFellow-
ship program 2024-2025 of the Stifterverband and
the Ministry of Science, Research and Arts Baden-
W
¨
urttemberg and by the Federal Ministry of Edu-
cation and Research, project “MINT-ProNeD”, grant
number 01JA23M02K. We also thank the GWDG for
the possibility to use the Chat AI services for our re-
search.
Regaining Control: Enabling Educators to Build Specialized AI Chat Bots with Retrieval Augmented Generation
377

REFERENCES
Abbas, M., Jam, F. A., and Khan, T. I. (2024). Is it harmful
or helpful? examining the causes and consequences of
generative ai usage among university students. Inter-
national Journal of Educational Technology in Higher
Education, 21(1):10.
Budde, J., Tobor, J., and Friedrich, J. (2024). K
¨
unstliche
Intelligenz. Wo stehen die deutschen Hochschulen?
Hochschulforum Digitalisierung.
Chang, D. H., Lin, M. P.-C., Hajian, S., and Wang, Q. Q.
(2023). Educational design principles of using ai chat-
bot that supports self-regulated learning in education:
Goal setting, feedback, and personalization. Sustain-
ability, 15(17):12921.
Christensen, R. and Knezek, G. (1999). Stages of adop-
tion for technology in education. Computers in New
Zealand Schools, 11(3):25–29.
Dakshit, S. (2024). Faculty perspectives on the potential
of rag in computer science higher education. ACM
SIGITE.
Dong, C., Chen, K., Cheng, S., and Wen, C. (2023). How
to build an ai tutor using llms and rag. Unpublished
Manuscript.
Doosthosseini, A., Decker, J., Nolte, H., and Kunkel, J. M.
(2024). Chat ai: A seamless slurm-native solution for
hpc-based services.
Fan, W., Ding, Y., Ning, L., Wang, S., Li, H., Yin, D., Chua,
T.-S., and Li, Q. (2024). A survey on rag meeting llms:
Towards retrieval-augmented large language models.
In Proceedings of the 30th ACM SIGKDD Conference
on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, KDD ’24,
page 6491–6501, New York, NY, USA. Association
for Computing Machinery.
Kahl, S., L
¨
offler, F., Maciol, M., Ridder, F., Schmitz,
M., Spanagel, J., Wienkamp, J., Burgahn, C., and
Schilling, M. (2024). Enhancing ai tutoring in
robotics education: Evaluating the effect of retrieval-
augmented generation and fine-tuning on large lan-
guage models. Autonomous Intelligent Systems
Group.
Knezek, G. and Christensen, R. (2015). The will, skill, tool
model of technology integration: Adding pedagogy as
a new model construct. International Association for
Development of the Information Society.
Lewis, P., Perez, E., Piktus, A., Petroni, F., Karpukhin,
V., Goyal, N., K
¨
uttler, H., Lewis, M., tau
Yih, W., Rockt
¨
aschel, T., Riedel, S., and Kiela,
D. (2020). Retrieval-augmented generation for
knowledge-intensive NLP tasks. In Proceedings of
the 34th Conference on Neural Information Process-
ing Systems (NeurIPS 2020), Vancouver, Canada.
Liu, R., Zenke, C., Liu, C., Holmes, A., Thornton, P., and
Malan, D. J. (2024). Teaching cs50 with ai: leveraging
generative artificial intelligence in computer science
education. In Proceedings of the 55th ACM Techni-
cal Symposium on Computer Science Education V. 1,
pages 750–756.
Maynez, J., Narayan, S., Bohnet, B., and McDonald, R.
(2020). On faithfulness and factuality in abstractive
summarization. In Jurafsky, D., Chai, J., Schluter,
N., and Tetreault, J., editors, Proceedings of the 58th
Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational
Linguistics, pages 1906–1919, Online. Association
for Computational Linguistics.
Medienp
¨
adagogischer Forschungsverbund S
¨
udwest (2024).
Jim-Studie. Jugend, Information,(Multi) Media. Ba-
sisstudie zum Medienumgang.
Mullins, E. A., Portillo, A., Ruiz-Rohena, K., and Piplai, A.
(2024). Enhancing classroom teaching with llms and
rag. In Proceedings of SIGITE 2024, El Paso, TX.
ACM.
Ng, D. T. K., Tan, C. W., and Leung, J. K. L. (2024). Em-
powering student self-regulated learning and science
education through chatgpt: A pioneering pilot study.
British Journal of Educational Technology.
Ouyang, F. and Jiao, P. (2021). Artificial intelligence in
education: The three paradigms. Computers and Ed-
ucation: Artificial Intelligence, 2:100020.
Perez, F. and Ribeiro, I. (2022). Ignore previous prompt:
Attack techniques for language models. In Proceed-
ings of the Workshop on Machine Learning Safety at
NeurIPs.
Petroni, F., Rockt
¨
aschel, T., Riedel, S., Lewis, P., Bakhtin,
A., Wu, Y., and Miller, A. (2019). Language models
as knowledge bases? In Inui, K., Jiang, J., Ng, V.,
and Wan, X., editors, Proceedings of the 2019 Con-
ference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language
Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference
on Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-IJCNLP),
pages 2463–2473, Hong Kong, China. Association for
Computational Linguistics.
Reimann, P. (2010). Design-based research. In Method-
ological choice and design: Scholarship, policy and
practice in social and educational research, pages 37–
50. Springer.
Shuster, K., Poff, S., Chen, M., Kiela, D., and Weston, J.
(2021). Retrieval augmentation reduces hallucination
in conversation. In Moens, M.-F., Huang, X., Specia,
L., and Yih, S. W.-t., editors, Findings of the Associ-
ation for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2021,
pages 3784–3803, Punta Cana, Dominican Republic.
Association for Computational Linguistics.
S
¨
uße, T. and Kobert, M. (2023). Generative ai at school-
insights from a study about german students’ self-
reported usage, the role of students’ action-guiding
characteristics, perceived learning success and the
consideration of contextual factors. Zenodo.
Th
¨
us, D., Malone, S., and Br
¨
unken, R. (2024). Explor-
ing generative ai in higher education: A rag system to
enhance student engagement with scientific literature.
Frontiers in Psychology, 15.
Velazquez, C. M. (2006). Cross-cultural validation of the
will, skill, tool model of technology integration. Uni-
versity of North Texas.
Yu, J., Wu, Y., Shu, D., Jin, M., and Xing, X. (2023). As-
sessing prompt injection risks in 200+ custom gpts.
arXiv preprint arXiv:2311.11538.
CSEDU 2025 - 17th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
378
