
ReflexAI: Optimizing LLMs for Consistent and Constructive Feedback
in Reflective Writing
Anand Bhojan
a
and Tan Li Xin
b
School of Computing, National University of Singapore, Singapore
Keywords:
Pedagogy, Reflective Learning, Automated Reflection Feedback, Large Language Model.
Abstract:
Creative Media courses often require students to iteratively gather peer playtesting feedback, respond to it,
and document their reflections. To streamline this process, iReflect, a web application, was developed in our
previous work. Research indicates that high-quality reflective writing correlates with improved academic per-
formance. To support this, iReflect leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) to provide automated feedback
on students’ reflective writings. However, LLMs face challenges such as inconsistency and inaccuracies in
feedback. This research explores methods to enhance the quality of LLM-generated feedback for reflective
writing. Findings reveal that repeated queries and in-context learning enhance the consistency and accuracy
of feedback scores. Additionally, integrating key elements of constructive feedback into the prompts enhances
the overall effectiveness and utility of the feedback.
1 INTRODUCTION
Iteratively gathering peer playtesting feedback, re-
sponding to it, and documenting reflections is a cru-
cial aspect of many creative media courses, where
students typically make progressive submissions over
multiple milestones. However, no existing tools or
platforms effectively meet these specific needs, and
current alternatives lack convenience and standardiza-
tion. Therefore, a web application tool, iReflect, was
developed at our university, the National University
of Singapore (NUS), to streamline and enhance this
learning process (Tan, 2022).
While iReflect has currently met the requirement
of facilitating critical peer review, discussions over
peer reviews and individual reflections all on one plat-
form, studies also indicate that high-quality reflective
writing correlates with improved academic perfor-
mance (Tsingos et al., 2015; Bhojan and Hu, 2024).
To support this, iReflect further leverages Large Lan-
guage Models (LLMs) to provide automated feedback
on students’ reflective writings (Quek, 2024). Yet,
LLMs face challenges such as inconsistency and in-
accuracies in feedback (Lee et al., 2024b). Therefore,
this research explores methods to enhance the quality
of LLM-generated feedback for reflective writing.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8105-1739
b
https://orcid.org/0009-0009-3440-3215
In summary, this research has the following key
findings:
1. Repeated queries and in-context learning (the in-
tegration of examples into the prompt) enhances
the consistency and accuracy of feedback scores.
2. Integrating key elements of constructive feedback
into prompts enhances the overall effectiveness
and utility of the feedback generated.
The study’s findings align with established educa-
tional theories emphasizing scaffolded learning, for-
mative assessment, and feedback loops. Vygotsky’s
Zone of Proximal Development (1978) highlights the
role of adaptive feedback in advancing student ca-
pabilities, while Kolb’s Experiential Learning Cycle
(1984) emphasizes reflection as key to deep learning.
This is reinforced by Hattie and Timperley’s model
(2007), which advocates for clear goals, progress
tracking, and actionable next steps. By integrating
few-shot learning, repeated evaluation, and construc-
tivist feedback strategies, this research aligns with
Sadler’s (1989) formative assessment principles em-
phasizing timely, specific, and actionable feedback.
Additionally, iReflect’s structured feedback mirrors
gamified learning environments (Gee, 2003), promot-
ing engagement and self-regulated learning. These
findings suggest that AI-enhanced reflection tools can
deepen metacognitive engagement, reduce instructor
workload, and be applied across disciplines requir-
Bhojan, A. and Xin, T. L.
ReflexAI: Optimizing LLMs for Consistent and Constructive Feedback in Reflective Writing.
DOI: 10.5220/0013430800003932
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2025) - Volume 2, pages 387-394
ISBN: 978-989-758-746-7; ISSN: 2184-5026
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
387

ing self-reflective learning, such as medical educa-
tion, engineering design, and leadership training.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Role of Reflective Writing
Research has consistently highlighted the significance
of reflective writing in education. This practice en-
ables students to articulate their thoughts and expe-
riences in a structured and purposeful way, fostering
critical thinking and deeper self-awareness (Kember
et al., 2008). Such reflection aids in making better-
informed judgments and more effective decisions in
future practices (Chen and Bonner, 2020; Allan and
Driscoll, 2014). Studies have also demonstrated a
strong link between the quality of reflection and the
quality of work produced. For example, Tsingos
et al. (2015) found that students with strong reflective
writing skills in a pharmacy practice course achieved
higher academic performance. Similarly, Bhojan and
Hu (2024) discovered positive correlations between
average reflection scores in a team and team submis-
sion marks across three Creative Media courses.
However, implementing reflective writing in cur-
ricula faces challenges, such as tutors’ limited experi-
ence with grading and the time-intensive task of pro-
viding individualized feedback (Chan and Lee, 2021).
Thus, creating a framework that leverages LLMs to
generate immediate, personalized formative feedback
for student reflections is essential. This would sup-
port students in refining their reflective writing skills
and improving their academic outcomes.
2.2 Generic Prompt Engineering
Techniques
Prompts are the primary method through which users
interact with LLMs, and the quality of these prompts
has a direct impact on the responses generated. Thus,
Prompt Engineering – the process of crafting effec-
tive prompts – is crucial to obtaining the desired out-
comes from LLMs. Ekin (2023) explored and sum-
marized strategies such as providing clear, specific
instructions, setting explicit constraints (e.g. format,
length, or scope), and including context or examples
to help guide ChatGPT in producing accurate and rel-
evant responses. More advanced techniques involve
adjusting the model’s temperature and token count.
2.3 LLMs for Automated Grading
Many studies have explored the use of LLMs to grade
students’ assignments and essays.
Alnajashi (2024) assessed ChatGPT-4’s accuracy
in grading student paragraphs from a final exam at
an English language institute for foundation year stu-
dents. Each paragraph, along with a grading rubric,
was input into ChatGPT-4, which was then prompted
to score the paragraph based on the rubric. A pre-
cision test followed, comparing ChatGPT-4’s grading
with that of human evaluators to determine its accu-
racy. The findings demonstrated a high level of align-
ment with human ratings, highlighting ChatGPT-4’s
potential in grading assignments using a rubric.
Lee et al. (2024a) explored the use of ChatGPT,
with Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting to score stu-
dent responses on science assessments. The study
found that few-shot learning (where the model is
given a small set of examples) outperformed zero-shot
approaches (where no examples are provided). Addi-
tionally, CoT prompting combined with rubrics no-
tably improved scoring accuracy. These findings un-
derscore the importance of domain-specific reasoning
in enhancing LLM effectiveness for scoring tasks.
Hackl et al. (2023) employed role prompting,
specified criteria, a sample solution, and a step-by-
step task description when using ChatGPT to grade
responses to tasks within the Higher Education (HE)
subject domain of macroeconomics, repeating this
process across 10 separate instances (prompting Chat-
GPT 10 times for each response). The Intraclass Cor-
relation Coefficient (ICC) for absolute agreement was
exceptionally high (0.999), indicating near-perfect
agreement and consistency among raters. Significant
F-tests (p < 0.001) further confirmed reliable con-
sistency and agreement among these ratings. This
demonstrates ChatGPT’s ability to produce consistent
text ratings across multiple iterations.
Similarly, Jukiewicz (2024) assessed ChatGPT’s
consistency in grading programming tasks by examin-
ing variations in task scores across successive queries.
An ICC of approximately 0.95 (with significance be-
low 0.001) indicated nearly perfect agreement across
repeated evaluations. While the results were largely
consistent, Jukiewicz explored the possibility of hav-
ing ChatGPT grade each task multiple times and tak-
ing the mode of these grades as the final result, en-
suring that the evaluation reflects the student’s profi-
ciency without being affected by potential ChatGPT
hallucinations. Each task was graded 15 times and by
comparing the teacher-assigned grades with the mode
of ChatGPT’s grades, Cohen’s d value was calculated.
The agreement initially decreased before stabilizing,
CSEDU 2025 - 17th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
388

leading to the conclusion that hallucination effects on
grading would be minimal after seven iterations.
Stahl et al. (2024) investigated various prompt-
ing strategies within the realm of automated es-
say scoring, which shares many similarities with re-
flective writing. They examined the use of per-
sonas, different instruction patterns (including scor-
ing, feedback, CoT, and combinations of these), as
well as in-context learning. The Teaching Assis-
tant persona and the Educational Researcher per-
sona outperformed both the absence of a persona
and the Creative Writing persona. Among the
instruction patterns, Feedback dCoT+Scoring and
Explanation+Scoring yielded higher mean quadratic
weighted kappa (QWK) scores, suggesting that gener-
ating an explanation for the essay score prior to scor-
ing is beneficial. Lastly, one-shot (where a single
example is provided) and few-shot prompts demon-
strated superior performance compared to the zero-
shot prompt.
2.4 LLMs for Feedback Generation
Given that higher-quality reflective writing correlates
with improved academic performance, providing ac-
tionable feedback is essential for enhancing students’
reflective skills. Thus, it is crucial to understand what
makes feedback effective and how to guide ChatGPT
in generating high-quality responses.
Playfoot et al. (2024) identified feedback quali-
ties that affect students’ intentions to apply teachers’
comments in future work. Multiple regression anal-
yses revealed that students were more inclined to use
comments that were “nice” (supportive, encouraging,
motivating, and positive in tone) and “usable” (clear,
constructive, and helpful).
Meyer et al. (2024) evaluated LLM-generated
feedback on secondary students’ argumentative es-
says. ChatGPT was instructed to provide feedback
that included hints and examples, focusing on struc-
ture, content, and language. The results indicated that
LLM-generated feedback improved revision perfor-
mance, task motivation, and positive emotions com-
pared to unguided revisions. These findings high-
light LLMs’ potential to deliver timely feedback,
which positively influences students’ cognitive and
affective-motivational outcomes.
Yvdal and Bergstr
¨
om (2024) compared ChatGPT-
4’s feedback on argumentative essays with peer feed-
back in higher education. Both assessed essays using
provided criteria, offering constructive feedback and
identifying issues with suggested solutions. Partici-
pants rated feedback based on description, identifica-
tion, justification, and constructiveness. ChatGPT-4’s
feedback was generally more detailed and consistent,
suggesting its potential as a supplemental or alterna-
tive feedback tool in education.
Jacobsen and Weber (2023) studied prompts for
generating high-quality AI feedback in higher educa-
tion and compared novice, expert, and AI feedback.
Using a theory-based manual, they developed three
prompts of varying quality and coded the feedback us-
ing an adapted scheme from Prilop et al. (2019), Prins
et al. (2006), and Wu and Schunn (2021). Only the
highest-quality prompt consistently produced high-
quality feedback. Pre-service teachers and experts
were given this prompt to generate their feedback.
Both expert and AI feedback outperformed novice
feedback, with AI being faster and excelling in ex-
planation, specificity, and questioning.
Han et al. (2024) examined LLMs as tutors in En-
glish as a Foreign Language (EFL) learning, using
educational metrics — quality, characteristics, and
learning outcomes — to compare standard and score-
based prompting. Score-based prompting, which in-
corporates predicted scores and rubric explanations,
produced more negative, detailed, and straightfor-
ward feedback. These qualities are preferred by stu-
dents and also supported by most teacher annotators.
Likewise, Yuan et al. (2024) found that clear
guidelines and criteria improved model performance
in feedback validity, contextualization, constructive-
ness, and helpfulness for paper introductions. Using
both criteria and demonstrations did not outperform
criteria alone, as models provided fewer critiques and
suggestions when demonstrations are included.
In a manner similar to their investigation into how
different prompting strategies influence the scoring of
essays by LLMs, Stahl et al. (2024) also examined
various prompting strategies for generating helpful
essay feedback. They employed Mistral and Llama-2
for the automated aspect of their feedback evaluation,
instructing these models to assign helpfulness scores
(1-10) to feedback. Both LLMs found that feedback
generated with the Educational Research persona was
the most helpful overall. Strategies prioritizing feed-
back before scoring were generally more effective,
and in-context reasoning provided a modest improve-
ment in feedback helpfulness.
2.5 LLMs for Evaluating Reflective
Writings
While various papers study the possibility of automat-
ing scoring and generating feedback for tasks, few fo-
cused primarily on reviewing reflective writings.
Masikisiki et al. (2024) evaluated the performance
of four language models in grading reflective essays
ReflexAI: Optimizing LLMs for Consistent and Constructive Feedback in Reflective Writing
389
written by third-year medical students. The study uti-
lized CoT prompting, along with a rubric and several
sample essays. Among the models, ChatGPT stands
out as the most effective, achieving a Cohen kappa
score of 0.53 and a correlation of 0.83 when compared
to the scores given by human evaluators.
Awidi (2024) assessed the effectiveness of Chat-
GPT in grading reflective essays and delivering per-
sonalized feedback, comparing its performance to that
of Expert Tutors (ET). The results indicated that Chat-
GPT can reliably score written reflective essays and
provide feedback comparable to that of ETs. How-
ever, both ChatGPT and ETs exhibited inconsisten-
cies and faced challenges in offering sufficiently de-
tailed feedback over time. Nonetheless, ChatGPT
was more consistent in justifying the scores assigned
to each criterion than the ETs. Depending on the
prompt, ChatGPT also provided specific comments
on the writing’s strengths and weaknesses, along with
suggestions for improvement.
3 STUDY AND RESULT
ANALYSIS
Previous studies highlight several common yet essen-
tial prompting strategies, including in-context learn-
ing, providing rubrics, CoT prompting, and specify-
ing an educational persona, to improve the accuracy
and consistency of ChatGPT’s gradings, as well as
to increase the quality of feedback generated. Ad-
ditional considerations might involve using a strategy
where feedback is generated before scoring, and con-
ducting repeated evaluations.
In our previous work (Quek, 2024), the automated
AI feedback in iReflect was implemented using the
GPT-4o model. This version provides score-based
feedback based on rubrics, employs the CoT prompt-
ing technique, and specifies an educational persona.
By incorporating a rubric, ChatGPT can understand
the assessment criteria, resulting in more consistent
scoring and specific feedback for reflective writings.
The reflection assessment rubric chosen, also devel-
oped in our previous work, consists of six categories
(Bhojan and Hu, 2024). CoT prompting enables Chat-
GPT to produce intermediate reasoning steps before
arriving at a final answer, enhancing performance on
complex, multi-step tasks by promoting structured
thinking. Lastly, using an educational persona helps
the model adopt a suitable tone, language, and focus.
As such, our study builds on this implementation
and explores three additional aspects of the prompt:
repeated evaluations, in-context learning, and feed-
back quality.
3.1 Repeated Evaluations
Following Jukiewicz (2024), we investigated whether
ChatGPT should evaluate each reflective writing mul-
tiple times, to increase its accuracy and consistency.
This was tested with the current prompt used in iRe-
flect (Quek, 2024), but the results were largely con-
sistent due to the low temperature value of 0.1.
The temperature parameter is crucial for control-
ling ChatGPT’s output consistency. Ranging from
0 to 2, this setting adjusts the randomness of each
word choice. Davis et al. (2024) demonstrated
that lower temperatures (near 0) favor more pre-
dictable words, enhancing reliability for consistent
tasks, while higher values (above 1) increase random-
ness, fostering creativity, useful for broader audience
engagement on social media platforms.
At a low temperature, the grades generated by
ChatGPT remained consistent across multiple evalu-
ations. Thus, increasing the temperature is necessary
to assess the effect of repeated evaluations. Yet, since
evaluating reflective writings does not require much
creativity, a temperature value of 1 was selected.
Using a set of 32 reflections from the course
“CS4350: Game Development Project” at NUS, we
prompted ChatGPT (at a temperature of 1) to grade
each reflection 10 times. The mode score was calcu-
lated for each reflection across 1, 3, 5, 7, and 9 iter-
ations, and these scores were compared to the actual
scores assigned by human raters, using mean squared
error (MSE) and coefficient correlation metrics.
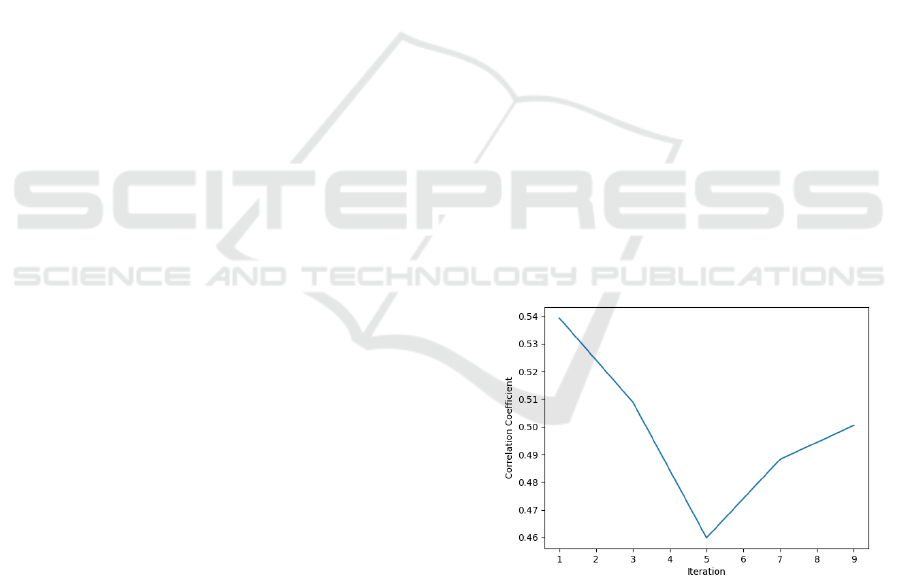
Figure 1: Correlation between mode scores and actual
scores.
Figure 1 and Figure 2 illustrate that as the mode
is calculated from 1 to 5 iterations, the correlation de-
creases while the MSE increases, indicating declining
performance. Beyond 5 iterations, the correlation in-
creases and the MSE decreases, reflecting improving
performance. However, neither graph indicates any
signs of stabilization. Additionally, the coefficient
and MSE after 10 iterations are lower than the initial
CSEDU 2025 - 17th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
390
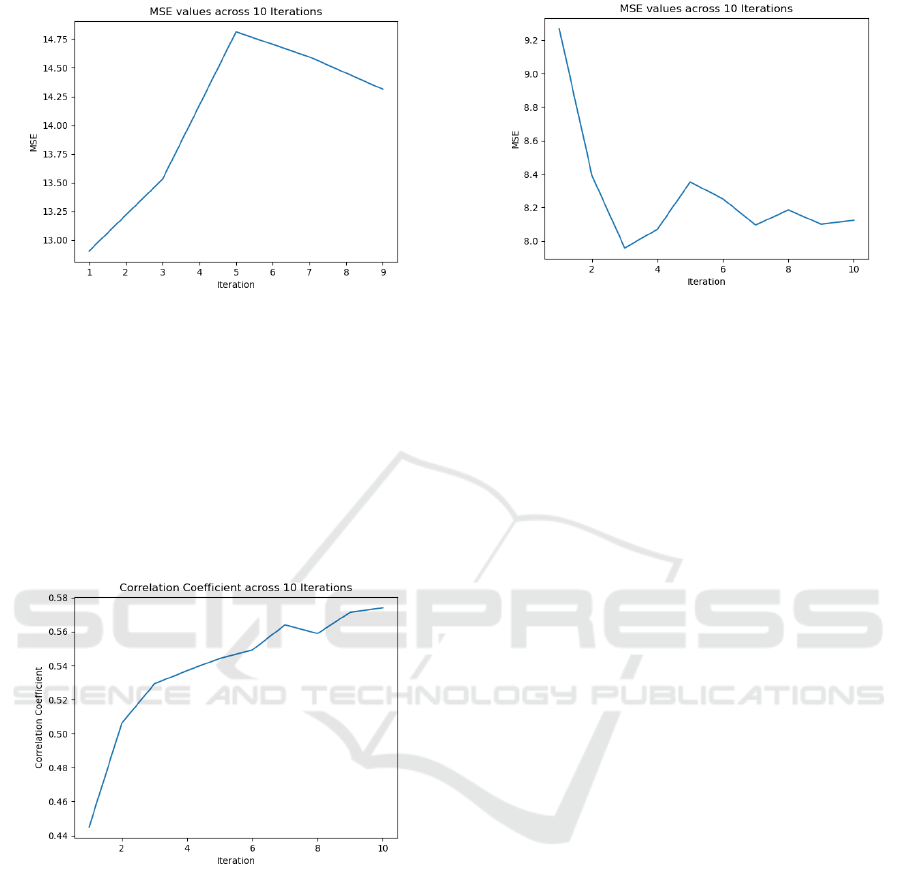
Figure 2: MSE between mode scores and actual scores.
values, suggesting that repeatedly asking ChatGPT to
evaluate the reflections and then taking the mode does
not enhance the accuracy or consistency of its output.
Upon closer examination of the scores for each in-
dividual reflection, a few occurrences of ChatGPT as-
signing two different scores with almost equal proba-
bility were observed. As such, the mode scores con-
tinuously fluctuate and do not stabilize. Hence, the
experiment was repeated using the mean instead of
the mode to better approximate the expected value.
Figure 3: Correlation between mean scores and actual
scores.
From Figure 3 and Figure 4, there is a clearer
trend, where the correlation increases and the MSE
decreases across iterations. The graphs also show that
the values stabilize across the iterations. In fact, there
is little change in the values after 3 iterations. There-
fore, taking the mean score after 3 iterations is suffi-
cient to increase the consistency and accuracy of the
generated scores. This also reduces the processing
time compared to 10 iterations.
An additional step was performed to determine if
this prompting strategy is better than setting a low
temperature which does not require repeated evalu-
ation. Therefore, ChatGPT was prompted to evaluate
the same set of reflections with a temperature of 0,
Figure 4: MSE between mean scores and actual scores.
and the correlation and MSE between the scores gen-
erated and the actual scores were similarly computed.
These values were then compared with the values ob-
tained from taking the mean across 3 iterations.
The correlation and MSE between the scores gen-
erated with a temperature of 0 and the actual scores,
were 0.49 and 10.50 respectively. The correlation and
MSE between the mean scores taken across 3 itera-
tions, generated with a temperature of 1, and the ac-
tual scores were 0.57 and 8.12 respectively. Since the
scores from repeated evaluations show higher correla-
tion and lower MSE with the actual scores, this proves
to be an enhancement to the current implementation.
3.2 In-Context Learning
In-context learning is the incorporation of examples
into the prompt to guide ChatGPT in its response. In
our context, providing ChatGPT with some sample re-
flective writings and their grades can help ChatGPT
learn the differences between reflective writings of
varying quality, hence aligning its grades with those
of the human raters, increasing its accuracy and con-
sistency in grading. Taking reference from Lee et al.
(2024a) and Stahl et al. (2024), we attempted zero-
shot, one-shot, and few-shot learning. While exper-
imenting with a few reflections, there was no differ-
ence in the scores, between using no samples and one
sample, hence we focused on the few-shot technique.
We selected three reflective writings with differ-
ent scores, ensuring there were also variations in the
scores for individual categories, to help ChatGPT bet-
ter associate writing quality with the scores in each
category. The sample reflections and their corre-
sponding scores were included in the prompt, and
ChatGPT was instructed to refer to these examples
before analyzing any new reflective writing. This was
performed using a temperature value of 0, and the
same dataset was used.
ReflexAI: Optimizing LLMs for Consistent and Constructive Feedback in Reflective Writing
391
For zero-shot learning, the correlation and MSE
between the scores generated and the actual scores
were 0.58 and 6.83 respectively. For few-shot learn-
ing, the correlation and MSE between the scores gen-
erated and the actual scores were 0.64 and 3.56 re-
spectively. This indicates that few-shot learning in-
creases the accuracy of the scores produced by Chat-
GPT, which aligns with previous studies.
By combining this with the previous experiment,
few-shot learning was conducted alongside repeated
evaluations (3 iterations), resulting in an even higher
correlation of 0.73 and a lower MSE of 2.98 with the
actual scores, serving as a greater improvement over
the current implementation.
This was tested on a more recent set of 31 re-
flections from the same course, CS4350. The results
(summarized in Table 1) are similar, thus supporting
the conclusions above.
Table 1: Correlation and MSE of LLM-generated scores
and actual scores, across different prompting strategies.
Zero-
Shot,
Temper-
ature 0
Few-
Shot,
Temper-
ature 0
Few-Shot,
Tempera-
ture 1 (3
iterations)
Correlation 0.7721 0.7751 0.7936
MSE 5.3145 4.7984 3.1819
3.3 Improving Feedback Generation
With the current prompt designed by Quek (2024),
feedback is generated for each grading criterion, spec-
ifying strengths and areas for improvement within
each aspect. This approach results in detailed, specific
feedback, as it aligns closely with the rubrics and ad-
dresses each category. However, upon further review,
we noticed that the feedback often adheres too rigidly
to the rubric language, leading to repetitive phrasing,
as illustrated in Table 2. Consequently, the feedback
lacks concrete examples and may be challenging to
translate into actionable steps.
Prilop et al. (2019) created a coding scheme
to evaluate feedback quality across six cate-
gories: assessment criteria, specificity, suggestions,
questions, first-person perspective, and valence (pos-
itive/negative). High-quality feedback should refer-
ence assessment criteria, be specific, provide sugges-
tions, ask questions, use a first-person perspective,
and balance positive and negative comments. These
criteria for effective feedback are supported by several
studies, and adapted versions of this coding scheme
have been applied across various domains (Playfoot
Table 2: Stage 5 of rubric and a sample ChatGPT feedback.
Stage 5 of the Rubric Sample GPT Feedback
[2 marks] Statement
clearly shows evi-
dence of reflection
and clearly states: (1)
a change in behaviour
or development of
new perspectives as a
result of the task; (2)
ability to reflect on
own task, apply new
knowledge feelings,
thoughts, opinions to
enhance new future
experiences; and (3)
examples
Stage 5: 1 / 2
What was done well:
You showed some self-
reflection on your per-
formance and indicated
a desire to improve by
engaging additional
help.
Improvement: For a
higher score, clearly
outline specific changes
in behavior or new per-
spectives that resulted
from this reflection.
Provide concrete exam-
ples of how you plan
to apply your new un-
derstanding in future
experiences.
et al. (2024),, Han et al. (2024), Mohamad and
Tasir (2023)).
Thus, this coding scheme provides a valuable
framework for enhancing the prompt to generate
higher-quality feedback and for evaluating the gen-
erated feedback itself. Drawing on Jacobsen and We-
ber (2023) ’s work, which also utilized Prilop et al.
(2019) ’s coding scheme, we modified the prompt by
outlining specific criteria for good feedback. Specifi-
cally, we instructed ChatGPT to “give 2 examples for
improvement” in each rubric category, “ask stimulat-
ing questions”, and “phrase feedback in terms of first-
person messages”. Feedback generated on the same
piece of reflective writing, with and without the mod-
ifications are shown in Table 3. The feedback gener-
ated with the modified prompt included questions and
provided suggestions on how the student could apply
new knowledge in future work.
The modified prompt was tested on five reflective
writings, and the resulting feedback was scored us-
ing Prilop et al. (2019) ’s coding scheme, to measure
their effectiveness. For comparison, feedback gener-
ated by the original prompt was also scored. Chat-
GPT assisted in this scoring process, following Stahl
et al. (2024) ’s findings on the effectiveness of LLMs
in evaluating feedback.
Table 4 shows that feedback generated with the
modified prompt consistently scored as well as or
better than feedback from the original prompt, con-
firming that the modified prompt yields higher-quality
feedback.
CSEDU 2025 - 17th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
392
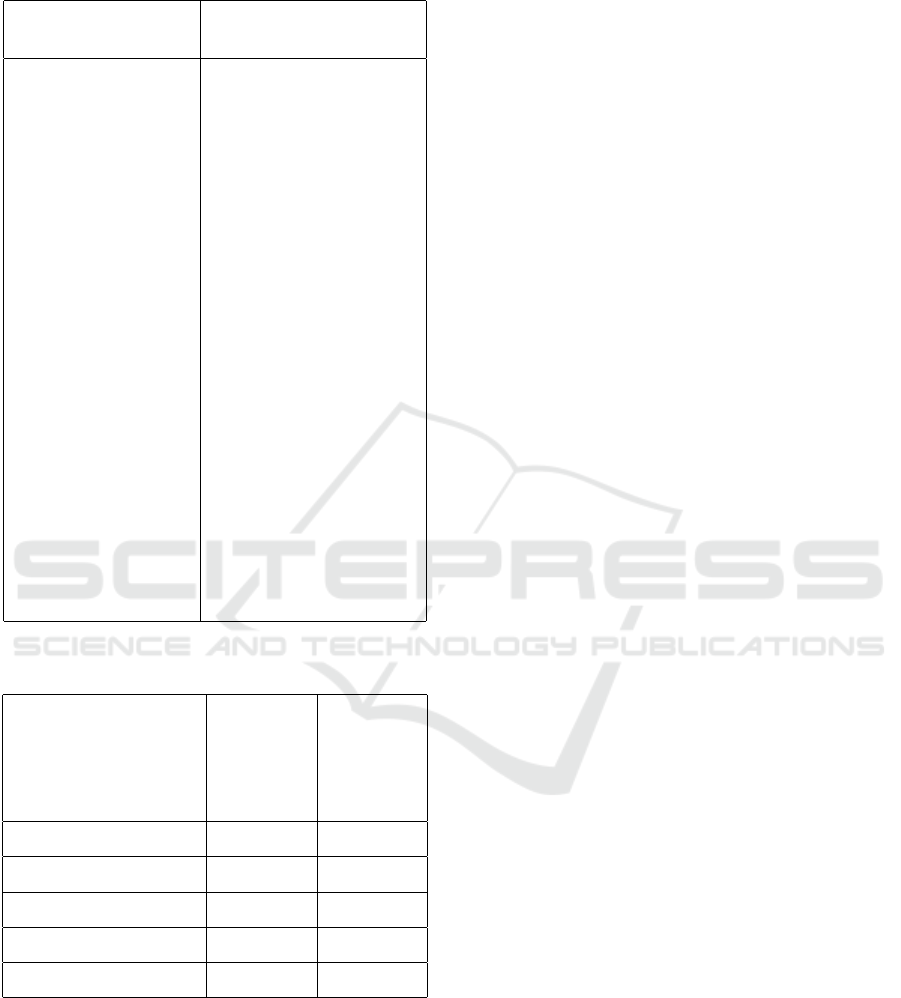
Table 3: ChatGPT’s feedback before and after modifying
prompt.
ChatGPT Feedback
with original prompt
ChatGPT Feedback with
modified prompt
Stage 5: 1 / 2
What was done well:
You showed some
self-reflection on
your performance
and indicated a de-
sire to improve by
engaging additional
help.
Improvement: For a
higher score, clearly
outline specific
changes in behav-
ior or new perspec-
tives that resulted
from this reflection.
Provide concrete ex-
amples of how you
plan to apply your
new understanding in
future experiences.
Stage 5: 1 / 2
What was done well:
There is evidence of re-
flection on the need for
behavior change, par-
ticularly around dead-
line reminders and team
progress.
Improvement: Deepen
your reflection by dis-
cussing more specific
actions to apply new
knowledge in the future,
for instance, implement-
ing new team structures,
utilizing project man-
agement tools, or setting
personal reminders. De-
tail strategies for effec-
tive communication with
your team. How do you
plan to handle potential
future challenges differ-
ently?
Table 4: Scores of feedback before and after modifying
prompt.
Score of
feedback
(using
original
prompt)
Score of
feedback
(using
modified
prompt)
Reflective Writing 1 9 9
Reflective Writing 2 8 9
Reflective Writing 3 7 9
Reflective Writing 4 8 8
Reflective Writing 5 7 8
We also explored a prompting technique that gen-
erates feedback before scoring, which, according to
Stahl et al. (2024), can enhance feedback quality.
However, the feedback produced did not appear to dif-
fer from that generated with the original prompt.
4 LIMITATIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
While the modified prompt improves the quality of
the generated feedback, some issues still require
prompt refinement. First, the added requirements
make the feedback longer, which can overwhelm and
confuse students, making it harder for them to focus
on key points and take meaningful action. Second,
the generated feedback sometimes still lacks concrete
examples and actionable suggestions. Further experi-
mentation is needed to address these areas.
Additionally, the small number of students in the
course limits the generalizability of the study, since
individual differences in learning styles and engage-
ment may influence the results. Larger and more di-
verse samples will help confirm these findings.
Although this research illustrates that the adopted
methods enhance LLM-generated feedback for reflec-
tive writing, it does not necessarily lead to higher-
quality reflective pieces written by students and bet-
ter academic performance. To address this, we plan
to integrate the improvements directly into iReflect
and evaluate their impact within a specific course in
NUS. Students in the course will be divided into two
groups: one receiving feedback based on the origi-
nal prompt and the other receiving feedback with the
modified prompt. A follow-up study will then assess
the effectiveness of these enhancements by compar-
ing the quality of reflective writing and overall course
performance between the two groups. In addition, a
survey will gather student feedback on the tool, pro-
viding valuable insights into user experience and sat-
isfaction. By combining quantitative data with quali-
tative input, this follow-up study will offer a compre-
hensive evaluation of the changes and their impact on
the tool’s overall effectiveness.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this study, we demonstrate that prompt engineer-
ing techniques, such as in-context learning, repeated
evaluations, and the integration of key elements of
constructive feedback into the prompts, enhance the
accuracy, consistency and overall usefulness of LLM-
generated feedback for reflective writings. Addition-
ally, it shows that repeatedly querying ChatGPT and
taking the mode score does not necessarily stabilize
ChatGPT’s output for all datasets. In our experiment,
taking the mean score proves to be a better alternative
for our dataset.
ReflexAI: Optimizing LLMs for Consistent and Constructive Feedback in Reflective Writing
393

REFERENCES
Allan, E. G. and Driscoll, D. L. (2014). The three-fold ben-
efit of reflective writing: Improving program assess-
ment, student learning, and faculty professional de-
velopment. Assessing Writing, 21:37–55.
Alnajashi, A. (2024). Investigating the accuracy of large
language models ’chatgpt-4’ in grading students’ writ-
ing according to a specific rubric.
Awidi, I. T. (2024). Comparing expert tutor evaluation of
reflective essays with marking by generative artificial
intelligence (ai) tool. Computers and Education: Ar-
tificial Intelligence, 6:100226.
Bhojan, A. and Hu, Y. (2024). Play testing and reflec-
tive learning ai tool for creative media courses. In
Proceedings of the 2024 CSEDU, pages 146–158. IN-
STICC, SciTePress.
Chan, C. and Lee, K. (2021). Reflection literacy: A
multilevel perspective on the challenges of using re-
flections in higher education through a comprehen-
sive literature review. Educational Research Review,
32:100376.
Chen, P. P. and Bonner, S. M. (2020). A framework for
classroom assessment, learning, and self-regulation.
Assessment in Education: Principles, Policy & Prac-
tice, 27(4):373–393.
Davis, J., Van Bulck, L., Durieux, B. N., and Lindvall, C.
(2024). The temperature feature of chatgpt: Modify-
ing creativity for clinical research. JMIR Hum Fac-
tors, 11:e53559.
Ekin, S. (2023). Prompt engineering for chatgpt: A quick
guide to techniques, tips, and best practices.
Gee, J. (2003). What video games have to teach us about
learning and literacy. Computers in Entertainment,
1:20.
Hackl, V., M
¨
uller, A. E., Granitzer, M., and Sailer, M.
(2023). Is gpt-4 a reliable rater? evaluating consis-
tency in gpt-4’s text ratings. Frontiers in Education,
8.
Han, J., Yoo, H., Myung, J., Kim, M., Lim, H., Kim,
Y., Lee, T. Y., Hong, H., Kim, J., Ahn, S., and
Oh, A. (2024). Llm-as-a-tutor in efl writing educa-
tion: Focusing on evaluation of student-llm interac-
tion. KAIST, South Korea.
Hattie, J. and Timperley, H. (2007). The power of feedback.
Review of Educational Research, 77(1):81–112.
Jacobsen, L. and Weber, K. (2023). The promises and pit-
falls of chatgpt as a feedback provider in higher ed-
ucation: An exploratory study of prompt engineering
and the quality of ai-driven feedback.
Jukiewicz, M. (2024). The future of grading programming
assignments in education: The role of chatgpt in au-
tomating the assessment and feedback process. Think-
ing Skills and Creativity, 52:101522.
Kember, D., McKay, J., Sinclair, K., and Wong, F. K. Y.
(2008). A four-category scheme for coding and as-
sessing the level of reflection in written work. Assess-
ment & Evaluation in Higher Education, 33(4):369–
379.
Kolb, D. (1984). Experiential Learning: Experience As The
Source Of Learning And Development, volume 1.
Lee, G.-G., Latif, E., Wu, X., Liu, N., and Zhai, X. (2024a).
Applying large language models and chain-of-thought
for automatic scoring. Computers and Education: Ar-
tificial Intelligence, 6:100213.
Lee, Y., Son, K., Kim, T. S., Kim, J., Chung, J. J. Y.,
Adar, E., and Kim, J. (2024b). One vs. many: Com-
prehending accurate information from multiple erro-
neous and inconsistent ai generations. FAccT ’24,
page 2518–2531. ACM.
Masikisiki, B., Marivate, V., and Hlophe, Y. (2024). Inves-
tigating the efficacy of large language models in re-
flective assessment methods through chain of thought
prompting. pages 44–49.
Meyer, J., Jansen, T., Schiller, R., Liebenow, L. W., Stein-
bach, M., Horbach, A., and Fleckenstein, J. (2024).
Using llms to bring evidence-based feedback into
the classroom: Ai-generated feedback increases sec-
ondary students’ text revision, motivation, and posi-
tive emotions. Computers and Education: Artificial
Intelligence, 6:100199.
Mohamad, S. K. and Tasir, Z. (2023). Exploring how
feedback through questioning may influence reflective
thinking skills based on association rules mining tech-
nique. Thinking Skills and Creativity, 47:101231.
Playfoot, D., Horry, R., and Pink, A. E. (2024). What’s the
use of being nice? characteristics of feedback com-
ments that students intend to use in improving their
work. Assessment and Evaluation in Higher Educa-
tion, pages 1–12.
Prilop, C., Weber, K., and Kleinknecht, M. (2019).
Entwicklung eines video- und textbasierten Instru-
ments zur Messung kollegialer Feedbackkompetenz
von Lehrkr
¨
aften, pages 153–163.
Quek, S. L. (2024). Play testing and reflective learning tool
with ai/ml based automated feedback for creative me-
dia courses. B. Comp. Dissertation, Project Number
H1352410, 2024/2025.
Sadler, D. R. (1989). Formative assessment and the de-
sign of instructional systems. Instructional Science,
18(2):119–144.
Stahl, M., Biermann, L., Nehring, A., and Wachsmuth, H.
(2024). Exploring llm prompting strategies for joint
essay scoring and feedback generation. Leibniz Uni-
versity Hannover.
Tan, K. Q. J. (2022). Playtesting and reflective learning tool
for creative media courses. B. Comp. Dissertation,
Project Number H1352060, 2021/2022.
Tsingos, C., Bosnic-Anticevich, S., Lonie, J. M., and Smith,
L. (2015). A model for assessing reflective practices
in pharmacy education. American Journal of Pharma-
ceutical Education, 79(8):124.
Vygotsky, L. S. (1978). Mind in society: The development
of higher psychological processes, volume 86. Har-
vard university press.
Yuan, W., Liu, P., and Gall’e, M. (2024). Llmcrit: Teaching
large language models to use criteria. In Annual Meet-
ing of the Association for Computational Linguistics.
Yvdal, A. and Bergstr
¨
om, O. (2024). Chatgpt-4’s effective-
ness in providing feedback on argumentative writing
in higher education : A case study.
CSEDU 2025 - 17th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
394
