
Proposal for Formalization Using Description Logic of Undesirable
Models in Business Process Management
Jean Elder Santana Ara
´
ujo
a
and Cleyton M
´
ario de Oliveira Rodrigues
b
PPGEC, Universidade de Pernambuco, Benfica, 455, Recife/PE, Brazil
Keywords:
Description Logic, Business Process Management, Modeling, BPMN.
Abstract:
Proposal of a method to detect and correct errors in BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation) models
using ontologies and Descriptive Logic reasoning to formalize and identify common errors related to the use
of gateways, elements that control the flow and decisions in a process. The research highlights how the misuse
of gateways can lead to inefficiencies and failures in process execution. Gateways are explored in the article
as a demonstration of an experimental structure with a focus on expanding the application of the method to
other elements of BPM modeling.
1 INTRODUCTION
Business Process Management (BPM) is essential
for companies to achieve their objectives efficiently.
Business process modeling is crucial for organiza-
tions, and in this context, BPMN has established it-
self as the most relevant notation because of its ex-
pressiveness and simplicity. However, the modeling
process can present errors that compromise the effi-
ciency of the process (Weske, 2019).
Analyzing the literature on approaches to optimiz-
ing business process management supported by on-
tologies, we identified some studies that focus on two
main fields (Cos¸kunc¸ay and Demir
¨
ors, 2022) (Mejri
and Ghannouchi, 2023) (Cherfi et al., 2013) (Ternai
et al., 2015) (Pham and Thanh, 2016) (Yingbo and
Xia, 2019) (Fengel, 2014):
Integration. In this field, ontologies are used to im-
prove some process of integration of systems or
data related to business processes;
Compliance. Understanding compliance as the ade-
quacy of processes or systems to rules, policies,
requirements of some business segment.
The importance of error detection and correction
in business modeling is already consolidated in the lit-
erature, for example, (Chinosi and Trombetta, 2012)
which reports how BPMN stands out in the recording
of business process modeling, ensuring consistency of
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2084-617X
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3816-656X
representation in contrast to the use of case descrip-
tions and documentation of complex procedures that
are often very difficult to understand and prone to er-
rors.
This paper addresses the formalization of the log-
ical description of business process modeling errors
with the aim of improving consistency gains with the
use of BPMN. In order to demonstrate its potential, it
will focus on the use of gateways, an essential element
in BPMN to control the divergence and convergence
of flows. Inadequate use of gateways can lead to un-
expected behaviors and errors in the process model,
resulting in loss of efficiency.
The objective of this study is to present a pro-
posed solution to increase the efficiency and accuracy
of BPM through the detection and correction of errors
in gateway modeling. The research utilizes the BBO
(BPMN 2.0 Based Ontology) ontology and logic de-
scription language to formalize errors and infer solu-
tions.
This article also describes how the proposed for-
malization can be applied using jBPM, a process exe-
cution engine. The approach includes reading a jBPM
XML file, converting it to OWL format, and then us-
ing Prot
´
eg
´
e to infer and present the results.
The formalization of error detection and correc-
tion in BPMN models benefits the creation of more
accurate, flexible, and efficient models, significantly
influencing the efficiency of business process man-
agement.
Araújo, J. E. S. and Rodrigues, C. M. O.
Proposal for Formalization Using Description Logic of Undesirable Models in Business Process Management.
DOI: 10.5220/0013437200003929
In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2025) - Volume 2, pages 891-898
ISBN: 978-989-758-749-8; ISSN: 2184-4992
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
891

2 BACKGROUND
This section will address the theoretical foundation of
the knowledge groups that support the proposed solu-
tion to be described in the article, namely: Business
Process Management in BPMN notation, ontologies,
and description logics.
2.1 BPMN (Business Process Model and
Notation)
A standardized graphical notation for modeling busi-
ness processes. Using symbols, it represents different
stages of a process such as:
• Events: Circles that represent something that hap-
pens in the process (start, end, receiving a mes-
sage, etc.).
• Activities: Rounded rectangles that represent
tasks to be performed
• Gateways: Diamonds that represent decision
points or branching in the process flow.
• Sequence flows: Arrows that indicate the order in
which activities are performed.
BPMN offers significant advantages in facilitating
the understanding of complex processes, communica-
tion between different areas and levels of the organi-
zation, and process improvement, as the representa-
tion makes it easier to identify bottlenecks and auto-
mate tasks. Its application is diverse across various
areas, such as sales, in mapping the initial customer
contact to product invoicing, in the healthcare sector,
in recording the flow of care upon a patient’s admis-
sion to the ICU, and in software development.
2.2 Description Logics
Description Logics (DLs) are formal languages for
representing knowledge and enabling automated rea-
soning. They combine concept descriptions with a
rigorous logical semantics. This combination allows
for efficient querying of a knowledge base, providing
timely answers. The problem-solving capabilities and
complexity of the inferences depend on the expressiv-
ity of the DL used.
There are various types of Description Logics,
each with varying expressivity, depending on the logi-
cal elements it offers. The family of description logics
explored in this paper is A L that allows the nega-
tion of atomic propositions, intersection of concepts,
and universal restrictions, offering limited existential
quantification, namely, only the concept ⊤ can be
used within the scope of the existential quantifier.
2.3 Ontologies
An ontology is an explicit, formal specification of a
shared conceptualization (STUDER, R.; SURE, Y.;
STAAB, S., 2004). They formalize the knowledge of
a domain by defining concepts, their properties, and
relationships. When coupled with reasoners, ontolo-
gies can extract meaning from text, perform complex
inferences, diagnose faults, predict events, or even au-
tomate tasks.
Both Description Logics and ontologies are for-
malisms used to represent knowledge. Description
Logics can be used as a foundation for building on-
tologies, which aim to represent the knowledge of a
specific domain in a way that is understandable to
both humans and machines. Description Logics, on
the other hand, focus on reasoning capabilities, per-
forming inferences, and answering complex questions
that can be posed about the domain represented in an
ontology.
3 BUSINESS PROCESS
MODELING ERRORS
This section will present examples of errors in busi-
ness process modeling that result in a loss of process
flow efficiency. One common error lies in the misuse
of gateways, which are essential elements in BPMN
for controlling the divergence and convergence of se-
quence flows, representing decisions and bifurcations
within the process. However, the improper use of
gateways can lead to unexpected behaviors and errors
in the process model. Below are some common errors
related to the use of gateways in BPMN.
1. OR Gateways without a default flow: Inclusive
(OR) gateways must have a defined default flow
for when none of the conditions of the other flows
are met. The lack of this default flow can cause
the process to stall.
2. XOR Gateways with unconditional flows: This
situation creates ambiguity about which path the
process will take and consequently leads to a loss
of operational efficiency.
3. Lack of synchronization in parallel (AND) gate-
ways: Parallel flows that are not synchronized
correctly: If activities in parallel flows need to
be completed before proceeding, a parallel (AND)
gateway should be used to synchronize the flows.
The undesirable situations in business process model-
ing using BPMN notation are not limited to the cases
listed above, and errors in the use of gateways extend
to other applications.
ICEIS 2025 - 27th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
892
To demonstrate the proposed approach in this on-
going research, the focus is on the above-listed cases
and is further substantiated below.”
3.1 OR Gateways Without Default Path
When used to enable alternative paths in processes,
the OR Gateway becomes problematic when no true
condition exists to direct the process flow. This can
lead to the process becoming blocked or stalled.
For example, consider a credit approval process
that evaluates a customer’s history in different cate-
gories to determine the flow. In the case of a new
customer with no history, the process would be stuck.
Similarly, if the evaluation is based on criteria that
do not fit into any condition, for instance, in a credit
approval process that considers income ranges, if the
customer’s income falls outside all defined ranges, the
process would also be halted.
A solution would be to define a default output that
will be followed if no other condition is true
3.2 XOR Gateways Have Conditionless
Paths
Used to direct a process to a single path, the problem
arises when one or more output paths do not have an
explicitly defined or valid condition.
This situation results in a process error due to am-
biguity, potentially halting the process if the execution
engine is unable to determine the path to follow.
As a solution, in addition to reviewing the model
itself, a default path can be adopted by defining an
else condition that covers all other conditions, ensur-
ing a directed path.
3.3 Lack of Synchronization in Parallel
Gateways (AND)
Used to split the process flow into multiple paths that
are executed concurrently, a lack of synchronization
between paths can result in errors due to incomplete
executions if the process continues without the com-
pletion of a task in any path. Errors can also arise
when these parallel paths share information.
As a solution, the existence of a parallel conver-
gence path that verifies the exit conditions of all paths
would ensure that all paths have fully completed their
tasks before the process continues in a consistent and
correct manner.
4 BBO: BPMN 2.0 BASED
ONTOLOGY FOR BUSINESS
PROCESS REPRESENTATION
The BBO (BPMN 2.0 Based Ontology) (Annane
et al., 2019) is an ontology developed for the repre-
sentation of business processes based on the reuse of
existing ontologies (Falbo and Bertollo, 2009); (Kar-
ray et al., 2012); (Chungoora et al., 2013); (Fraga
et al., 2018) and metamodels such as BPMN 2.0 (Ob-
ject Management Group (OMG), 2013)
This ontology provides a formalization that serves
as a foundation for the construction proposed here.
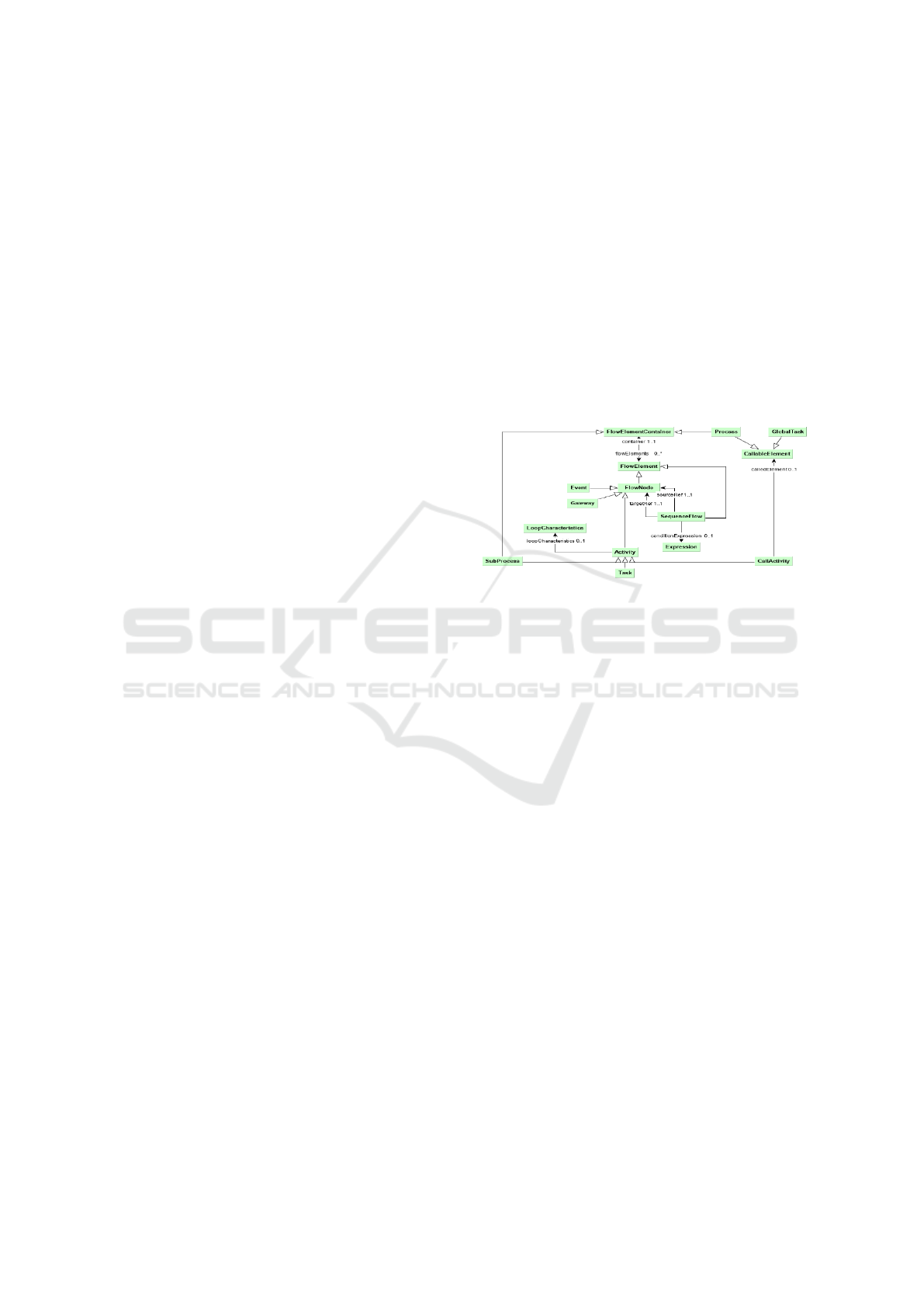
Below is a figure representing a segment of the BBO.
Figure 1: Process class properties and related concepts from
BPMN reused in BBO.
In this context, the main elements of Figure 1 are
described below.
• Activity is the work to be performed. The Activity
class has three subclasses:
1. Task: an atomic task
2. Sub-Process: a complex task that contains mul-
tiple Tasks
3. CallActivity: an activity that calls a
CallableElement which can be a Global-
Task (i.e., a reusable task) or Sub-Process.
• Event is something that ”happens” during the
course of a process. Events affect the flow of the
process and generally have a cause or an impact
and may require or allow a reaction.
• Gateway is used to control how SequenceFlows
interact as they converge or diverge within a Pro-
cess.
Specifically, regarding the Gateway that will be
the focus of this article, we extend the already pre-
sented Gateway concept, exposing that it has an at-
tribute that determines the type of gateway: ”conver-
gent”, ”divergent”, ”multiple”.
The BBO has been extended with elements to en-
compass the formalization and analysis of modeling
errors using Gateway constructs, which have been
presented as illustrative examples.
Proposal for Formalization Using Description Logic of Undesirable Models in Business Process Management
893
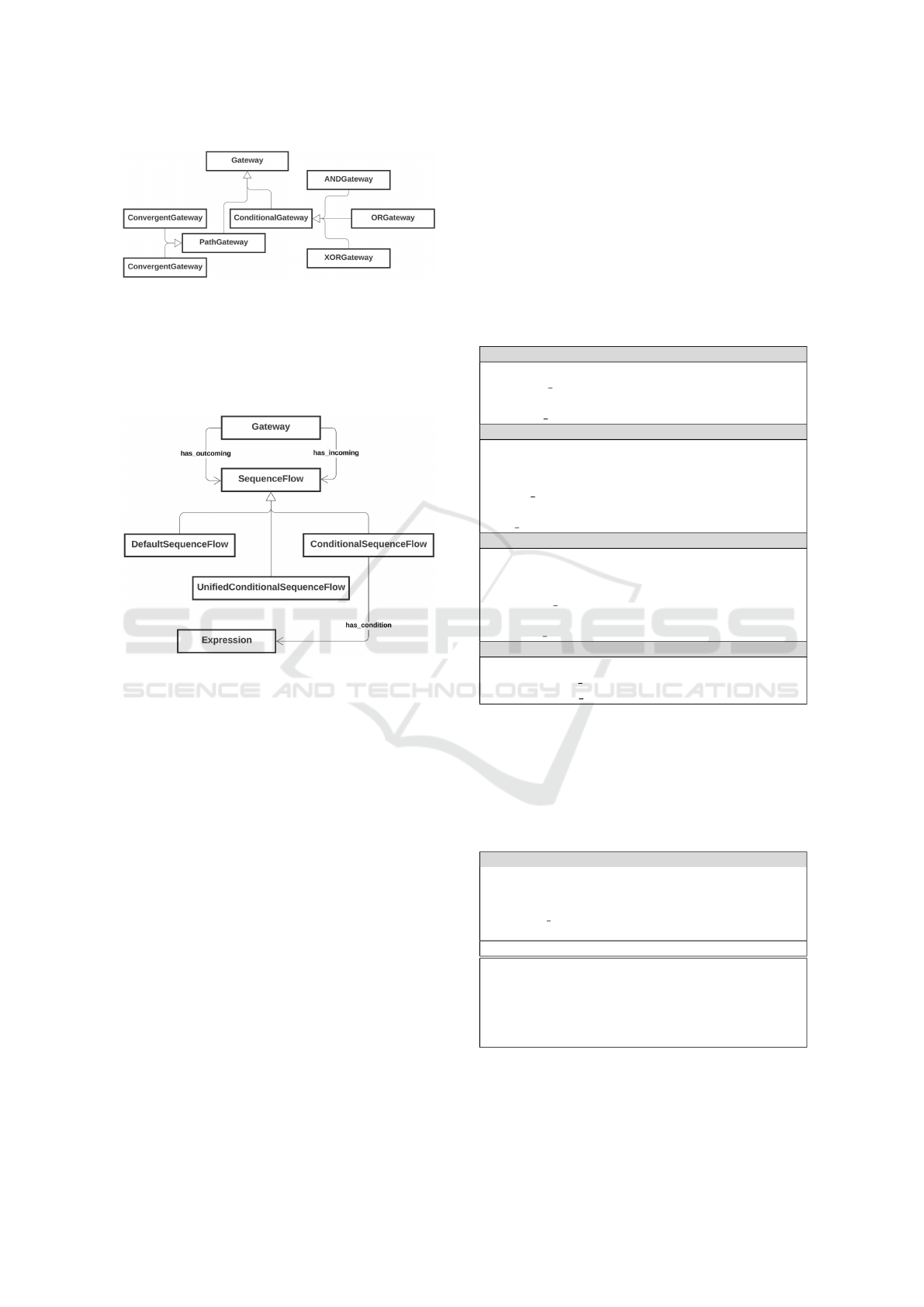
Figure 2: BBO Extension - Gateway Construct (Part 01).
Continuing the extensions for constructing solu-
tions and alternatives to undesirable situations, or
rather, those that impact the efficiency of process flow
in modeling using BPMN notation, the focus is now
differentiated towards Sequence Flows.
Figure 3: BBO Extension - Gateway Construct (Part 02).
5 FORMALIZATION OF BPMN
ELEMENTS IN DESCRIPTION
LOGIC
In extension to the most comprehensive representa-
tion of the BPMN elements, the formalization in De-
scription Logic is called upon for this task.
Focusing mainly on the formulations involving the
Gateways, the following records are presented
5.1 Gateway as the Branches
Throughout the process, there will be branching
points in its flow, and the BPMN element that rep-
resents this phenomenon is the Gateway. Thus, this
branching has two basic behaviors: convergence or
divergence, which already represents the fundamen-
tal characteristic for the use of this element.
A Gateway MUST have either multiple incoming
or multiple outgoing sequence flows. Based on this
combination, it is classified as Convergent, Divergent,
or Multiple.
Convergent. A Gateway with a gatewayDirection of
converging MUST have multiple incoming Se-
quence Flows, but MUST NOT have multiple out-
going Sequence Flows.
Divergent. A Gateway with a gatewayDirection of
diverging MUST have multiple outgoing Se-
quence Flows, but MUST NOT have multiple in-
coming Sequence Flows.
Mixed. A Gateway MUST have either multiple in-
coming and multiple outgoing sequence flows.
Formalization Gateway
Gateway SubClassO f
((has
incoming min2 SequenceFlow)
or
(has outgoing min2 SequenceFlow))
Formalization Converging
ConvergingGateway equivalentTo
Gateway
and
(has incoming min2 SequenceFlow)
and
(has outgoing exactly 1 SequenceFlow)
Formalization Divergent
DivergingGateway equivalentTo
Gateway
and
(has outgoing min2 SequenceFlow)
and
(has incoming exactly 1SequenceFlow)
Formalization Mixed
MixedGateway equivalentTo Gateway
and (has incoming min2 SequenceFlow)
and (has outgoing min2 SequenceFlow)
5.2 Gateway as to the Conditions
Regarding the conditionals of incoming and outgoing
sequence flows at Gateways, their presence or ab-
sence determines the path that the process will follow.
They share the construct ConditionalSequenceFlow,
which is formally defined below.
Formalization
ConditionalSequenceFlow equivalentTo
SequenceFlow
and
(has condition Expression
some Expression)
Expression equivalentTo (True or False)
ConditionalGateway equivalentTo
(ConvergingGateway
or
DivergingGateway)
and
(has only ConditionalSequenceFlow)
The focus of this paper is on Gateways and their
conditional requirements for sequence flow progres-
sion, specifically the Sequence Flows and their corre-
sponding logical values for process continuation
ICEIS 2025 - 27th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
894
AND. All logical values must be true.
OR. At least one logical value must be true.
XOR. Exactly one logical value must be true.
Formalization
ANDGateway equivalentTo
CondicionalGateway
and ∀x ∈ Expression ⊑ True
ORGateway equivalentTo CondicionalGateway
and ∃x ∈ Expression ⊑ True
XORGateway equivalentTo
CondicionalGateway
and ∃!x ∈ Expression ⊑ True
The extension of this formalization for the afore-
mentioned Gateways is presented above.
5.3 Descriptive Logic-Based Solution
Formulation
BPMN notation is a powerful tool for modeling busi-
ness processes; however, some situations may com-
promise the effectiveness of the business process in
question. In Section 3 of this work, some of these sit-
uations were listed within the construct of the Gate-
way and their corresponding associated solutions.
The formalizations in Description Logics pre-
sented in this section are built upon the ontological
structure in conjunction with the BBO extensions.
This enables reasoning and inferences that support
the identification of undesirable situations in model-
ing and the corresponding proposed solutions.
Given that the current scope is limited to con-
structing a proposal with an exemplary focus on Gate-
way constructs (Christiansen et al., 2010), the simpli-
fied ontological structure presented in the following
is restricted to this aspect for now, with the intended
future extension objective.
For illustrative purposes, the figure below depicts
the proposed solution’s structure with a gateway, out-
lining the paths for incorporating future handling of
undesirable situations.
Figure 4: Error structure.
Gateways are essential elements in BPMN model-
ing, serving as decision points and flow control mech-
anisms within a business process (Marin-Castro and
Tello-Leal, 2021). They enable the process to fol-
low different paths based on specific conditions, thus
modeling the logic and behavior of the process more
accurately and comprehensively.
Although formalizations are limited to the use of
gateways, their impact as powerful tools in BPMN
modeling contributes to the creation of more precise,
flexible, and efficient models, significantly influenc-
ing the efficiency of business process management.
At this moment, the formalization of these solu-
tions in Description Logic, which supports the object
of study of this work, will be exposed.
5.3.1 OR Gateways Without Default Path
Solution: Default Path
Formalization
ORGatewayError equivalentToORGateway and
(¬∃x ∈ Expression ⊑ True)
ORGatewayErrorSolved equivalentTo
ORGatewayError and
(has outgoing exactly 1 SequenceFlowDe f ault)
5.3.2 XOR Gateways Have Conditionless Paths
Solution: Default Path
Formalization
XORGatewayError equivalentTo
XORGateway(G) and has Condition(G, x)
and (¬∃x ∈ Expression)
XORGatewayErrorSolved equivalentTo
XORGatewayError and
(has outgoing exactly 1 SequenceFlowDe f ault)
5.3.3 Lack of Synchronization in Parallel
Gateways (AND)
Solution: parallel convergence path
Formalization
ANDGatewayError equivalentTo
ANDGateway and (¬∃x ∈ Expression ⊑ True)
ANDGatewayErrorSolved equivalentTo
ANDGatewayError and
(has outgoing
exactly1 SequenceFlowUni f iedCondition)
SequenceFlowUni f iedCondition(G1) equivalentTo
∀xhas condition(G1, x)andExpression(x)
and ANDGateway(G2) and has condition(G2, x)
6 APLICATION
The approach to applying formalization in the de-
scription logic of errors in BPMN models utilized
adaptations of methods employed in previous re-
search. (Ternai et al., 2015)
Proposal for Formalization Using Description Logic of Undesirable Models in Business Process Management
895

Although there are other tools capable of perform-
ing processes, jBPM seemed to be the most appropri-
ate tool to achieve our goals.
Considering, for the purpose of analysis and cor-
rection, the execution of a fictitious process starting
with flow 1 leading to an inclusive OR gateway that
diverges into two flows, 2 and 3, respectively, which
execute tasks A and B if their conditional expressions
are true. At this point in the execution, flow 4, orig-
inating from the aforementioned gateway, leads to a
join gateway that triggers an end event.
However, if the conditional expressions of flows
2 and 3 are false, neither task A nor task B will be
executed, and the process will terminate without any
action being taken. The solution to this situation, as
already explained, is to define a default flow that is
triggered when all divergent flows from the inclusive
OR gateway are invalid or false.
In other words, the default flow must be con-
structed with the combination of all conditions of the
diverging flows from the OR gateway. In this exam-
ple, the condition for this default flow would be as
follows:
¬(conditionA OR conditionB)
The solution presented to address the undesir-
able situation described in Section 3.1 is materialized
in the jBPM XML code shown in the figure above
through the defaultFlow. This flow aggregates the
conditions of flow 1 and flow 2:
<process id="myProcess" name="My Process"> 1
<startEvent id="start" /> 2
<sequenceFlow id="flow1" 3
sourceRef="start" 4
targetRef="gateway" /> 5
<inclusiveGateway id="gateway" 6
name="OR Gateway" /> 7
<sequenceFlow id="flow2" 8
sourceRef="gateway" 9
targetRef="taskA"> 10
<conditionExpression 11
xsi:type="tFormalExpression"> 12
#{conditionA} 13
</conditionExpression> 14
</sequenceFlow> 15
<sequenceFlow id="flow3" 16
sourceRef="gateway" 17
targetRef="taskB"> 18
<conditionExpression 19
xsi:type="tFormalExpression"> 20
#{conditionA} 21
</conditionExpression> 22
</sequenceFlow> 23
<sequenceFlow id="flowDefault" 24
sourceRef="gateway" 25
targetRef="taskDefault"> 26
<conditionExpression 27
xsi:type="tFormalExpression"> 28
#{conditionDefault} 29
</conditionExpression> 30
</sequenceFlow> 31
<sequenceFlow id="flow4" 32
sourceRef="gateway" 33
targetRef="join" /> 34
<userTask id="taskA" 35
name="Task A" /> 36
<userTask id="taskB" 37
name="Task B" /> 38
<userTask id="taskDefault" 39
name="Task Default" /> 40
<joinGateway id="join" 41
name="Join" /> 42
<sequenceFlow id="flow5" 43
sourceRef="join" 44
targetRef="end" /> 45
<endEvent id="end" /> 46
</process> 47
Figure 5: Exemple - OR gateway with default.
To detail the XML elements that represent the ex-
ample of using the OR Gateway in the jBPM tool, see
the list below.
Inclusive Gateway. Each outgoing sequenceFlow
from the gateway has an associated condition. If
conditionA is evaluated as true, the flow proceeds
to taskA. If conditionB is true, the flow progresses
to taskB. In particular, both conditions can be true
simultaneously, resulting in the execution of both
tasks.
Join Gateway. This gateway serves to synchronize
the flow after the inclusive gateway. The process
continues only after all tasks activated by the in-
clusive gateway have been completed.
Conditions. The conditions can be any valid
Boolean expression within the context of jBPMN.
An initial step involves populating an ontology
with general data from a Business Process Concep-
tual Model, utilizing an ontology instantiation mecha-
nism. This transforms the process representation into
a formal ontology structure, facilitating reasoning and
inference.
Instantiation entails populating the ontology with
real-world data, thereby creating instances of the
classes defined within the ontology. This involves
creating individuals and assigning properties and re-
lationships based on the structure defined in the ontol-
ogy, which also encompasses the axioms formalized
in Description Logic, as previously discussed. This
process comprises a sequence of steps:
Identify the Individuals Determine which real-
world entities will be represented as instances in
the ontology.
Create Instances Use the chosen tool to create in-
stances of the relevant classes for each individual.
Populate Properties Assign values to the properties
of each instance, describing its characteristics.
ICEIS 2025 - 27th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
896
Define Relationships Establish relationships be-
tween instances that represent the connections
between them.
The data and relationships of the actual processes
would be extracted through analysis using optimized
mechanisms from XML files that record process ele-
ments.
To perform the task of reading the jBPM XML
file, instantiating the ontology, and subsequently per-
forming inference, it is necessary to utilize a set of
tools. Initially, for demonstration purposes, the fol-
lowing tools appear suitable:
• SAX API (Simple API for XML): For sequential
processing of the file and preparation of the OWL
file for consumption in the instantiation and infer-
ence phase.
• Ontology instantiation: Employ an ontology in-
stantiation tool (Prot
´
eg
´
e) for analysis of instances
in the ontology and subsequent inferences.
As noted above, jBPM utilizes variables to store
process information. These variables persist in a
database. This facilitates the automation process, en-
abling direct reading of process data and conversion
into a format suitable for the ontology and reasoning
tool employed in this work, namely Prot
´
eg
´
e
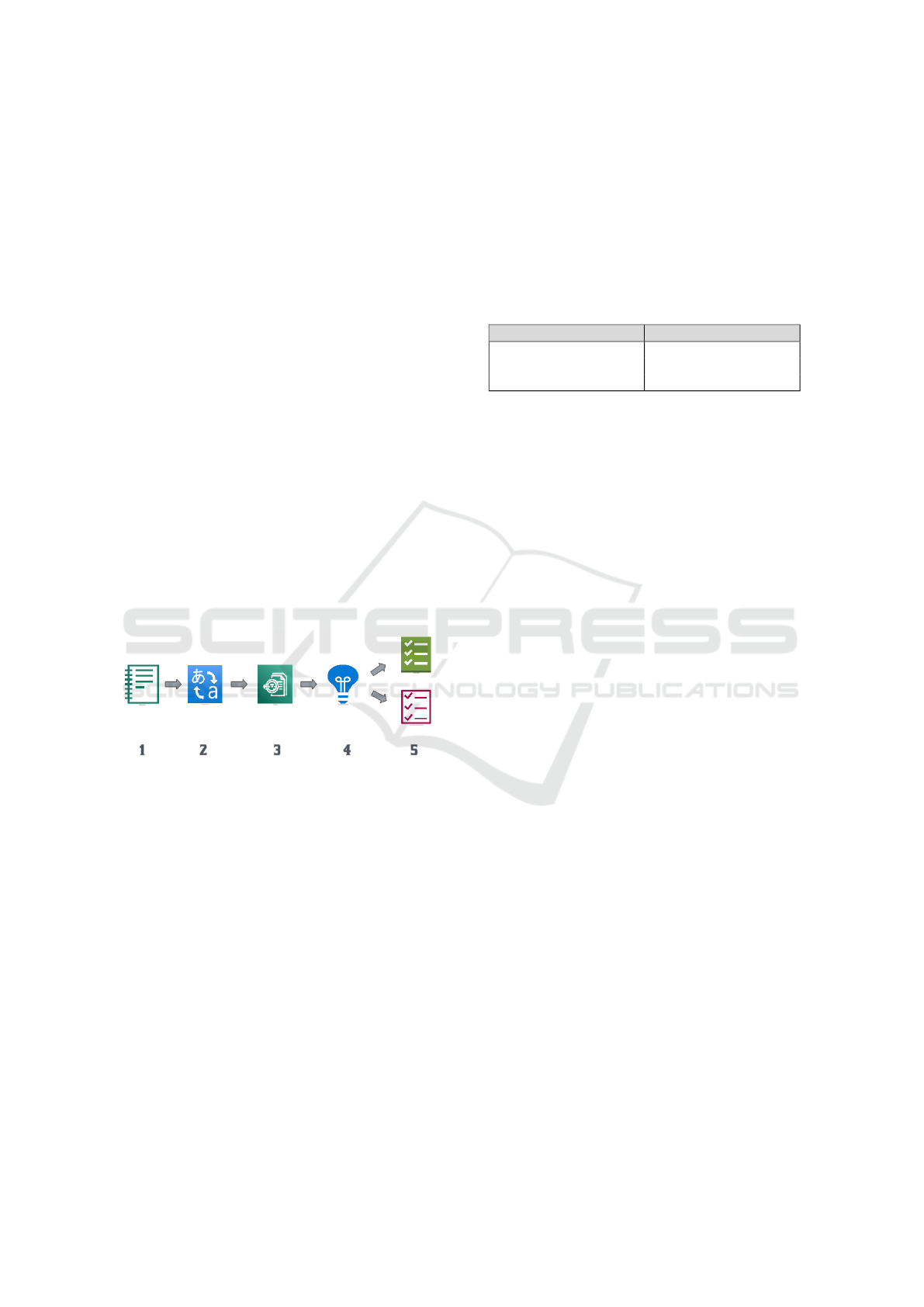
Figure 6: Proposal steps.
Figure 8 illustrates the sequence of steps in the
proposed approach for analyzing BPMN elements to
identify the mapped errors and indicate the corre-
sponding solutions. The five main steps are as fol-
lows:
1. Read the XML file from the jBPM process execu-
tion engine.
2. Convert / treat XML (Nika et al., 2022).
3. Read the OWL file generated in step 2 using the
Prot
´
eg
´
e tool.
4. Execute inference using reasoners within Prot
´
eg
´
e.
5. Present the results, including undesirable situa-
tions and those with solutions already mapped in
the ontology.
The results display will present, as an outcome
of the inference, the signaling classes. For example,
identifying the use of an OR gateway (inclusive) will
signal the possibility of an ErrorORGateway. If the
implementation of the standard flow is identified, it
will signal SolverORGateway, indicating that a cor-
responding treatment measure has been taken to ac-
count for the possibility of error.
Accordingly, two lists are presented below: cases
of possible errors followed by titles indicating the
implemented solution measures.
Errors Solvers
ErrorORGateway SolverORGateway
ErrorANDGateway SolverANDGateway
ErrorXORGateway SolverXORGateway
7 FUTURE WORK
This study has presented a formalization for specify-
ing business processes using Description Logic, with
a focus on identifying and correcting common errors
in BPMN models. However, there are several oppor-
tunities to deepen this research.
Although the errors in the BPMN models pre-
sented here represent only a small sample, there is
a vast field of study to be explored. This includes
the potential to map and consolidate antipatterns in
business process modeling and their corresponding
solutions, similar to the work done on antipatterns
in object-oriented software engineering. (Gamma,
2009) This research would focus specifically on iden-
tifying and addressing recurring problematic patterns
in business process models, ultimately contributing to
improved modeling practices and process quality.
One promising direction is to expand the formal-
ization language to capture more complex aspects of
processes, such as time, resources, and uncertainty.
In addition, integration with machine learning tech-
niques can enable automatic error detection and the
generation of BPMN models from historical data.
Another area of interest is the development of de-
cision support tools that use the proposed formaliza-
tion to assist in process analysis and optimization.
These tools can be used to identify bottlenecks, sim-
ulate different scenarios, and evaluate the impact of
changes in processes.
Furthermore, the ontological segments con-
structed for simulations can be extended to encom-
pass all elements of the BPMN notation, based on a
review of the literature concerning undesirable situ-
ations. Furthermore, the conceptual conformity of a
foundational ontology such as UFO (Guizzardi, 2005)
can be assessed to improve the conceptual validity of
the ontology and the semantic rules mapped from the
literature.
Proposal for Formalization Using Description Logic of Undesirable Models in Business Process Management
897

8 CONCLUSION
This study delved into the significance of Business
Process Management (BPM) and the role of BPMN
in business process modeling. While BPMN is a pow-
erful tool, it can be prone to errors, particularly when
dealing with complex processes, especially when the
process flow becomes lost in the ramifications of
flows at their convergences and divergences in the
paths taken by the process. At some point, some
conditional may be poorly evaluated, generating un-
wanted situations and impacting the performance of
business process management.
Thus, this work highlighted common errors in
BPMN modeling, specifically focusing on issues re-
lated to gateways. Errors that can lead to process in-
efficiencies and, ultimately, implementation failures.
To address these challenges, we proposed a formal-
ization approach using Description Logic.
By representing BPMN concepts and constraints
in a formal language, we can increase the accuracy
and consistency of process models. This formaliza-
tion can be used to automate various tasks, such as
model validation, simulation, and analysis, leading to
more reliable and efficient processes.
Future research directions include exploring the
application of advanced reasoning techniques, such
as ontology-based reasoning, to further refine the for-
malization of BPMN. In addition, investigating the in-
tegration of machine learning techniques to automate
error detection and correction is a promising avenue.
In conclusion, the proposed formalization of un-
desirable situations with the application of reasoning
tasks has proven to be an important element in en-
hancing the quality and effectiveness of BPMN mod-
eling, ultimately contributing to improved organiza-
tional performance and decision-making. This, in
turn, can help organizations gain a competitive advan-
tage in their niche.
REFERENCES
Annane, A., Aussenac-Gilles, N., and Kamel, M. (2019).
Bbo: Bpmn 2.0 based ontology for business pro-
cess representation. In 20th European Conference on
Knowledge Management (ECKM 2019), volume 1,
pages 49–59.
Cherfi, S. S.-S., Ayad, S., and Comyn-Wattiau, I. (2013).
Aligning business process models and domain
knowledge: a meta-modeling approach. In Advances
in Databases and Information Systems, pages 45–56.
Springer.
Chinosi, M. and Trombetta, A. (2012). Bpmn: An intro-
duction to the standard. Computer Standards & In-
terfaces, 34(1):124–134.
Christiansen, D. R., Carbone, M., and Hildebrandt, T.
(2010). Formal semantics and implementation of
bpmn 2.0 inclusive gateways. In International Work-
shop on Web Services and Formal Methods, pages
146–160. Springer.
Chungoora, N., Young, R. I., Gunendran, G., Palmer, C.,
Usman, Z., Anjum, N. A., Cutting-Decelle, A.-F.,
Harding, J. A., and Case, K. (2013). A model-driven
ontology approach for manufacturing system inter-
operability and knowledge sharing. Computers in in-
dustry, 64(4):392–401.
Cos¸kunc¸ay, A. and Demir
¨
ors, O. (2022). A method for in-
tegrated business process modeling and ontology de-
velopment. Business Process Management Journal,
28(3):606–629.
Falbo, R. D. A. and Bertollo, G. (2009). A software pro-
cess ontology as a common vocabulary about soft-
ware processes. International Journal of Business
Process Integration and Management, 4(4):239–250.
Fengel, J. (2014). Semantic technologies for aligning het-
erogeneous business process models. Business Pro-
cess Management Journal, 20(4):549–570.
Fraga, A. L., Vegetti, M., and Leone, H. P. (2018). Semantic
interoperability among industrial product data stan-
dards using an ontology network. In ICEIS (2), pages
328–335.
Gamma, E. (2009). Padr
˜
oes de projetos: soluc¸
˜
oes reuti-
liz
´
aveis. Bookman editora.
Guizzardi, G. (2005). Ontological foundations for structural
conceptual models. University of Twente.
Karray, M. H., Chebel-Morello, B., and Zerhouni, N.
(2012). A formal ontology for industrial mainte-
nance. Applied ontology, 7(3):269–310.
Marin-Castro, H. M. and Tello-Leal, E. (2021). An end-to-
end approach and tool for bpmn process discovery.
Expert Systems with Applications, 174:114662.
Mejri, S. and Ghannouchi, S. A. (2023). A proposed
guidance approach for bp performance improvement.
Procedia Computer Science, 225:1425–1437.
Nika, Z. G., Khadivar, A., Dadkhahc, C., and Rahimiand,
S. (2022). Developing an ontology for business pro-
cess management techniques and tools. University of
Twente.
Object Management Group (OMG) (2013). Business Pro-
cess Model and Notation (BPMN) Version 2.0.
Pham, T. A. and Thanh, N. L. (2016). An ontology-based
approach for business process compliance checking.
In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference
on Ubiquitous Information Management and Com-
munication, pages 1–6.
Ternai, K., Khobreh, M., and Ansari, F. (2015). An ontology
matching approach for improvement of business pro-
cess management. Springer International Publishing.
Cited by: 2.
Weske, Mathias Weske, M. (2019). Business Process
Management - Concepts, Languages, Architectures.
Springer, Potsdam, Germany, 4 edition.
Yingbo, D. and Xia, H. (2019). Business modeling and rea-
soning based on process ontology. In Proceedings
of the 5th International Conference on Frontiers of
Educational Technologies, pages 143–147.
ICEIS 2025 - 27th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
898
