
Automating Feature Modeling in Product Line Engineering for
Systems Engineering: The Application of Natural Language
Processing
José Lameh
1,2 a
, Alexandra Dubray
2
and Marija Jankovic
1b
1
Université Paris Saclay - CentraleSupélec, Laboratoire Genie Industriel, Gif-sur-Yvette, France
2
Renault Group - Ampère, Technocentre, 1 Av. du Golf 78288 Guyancourt, France
Keywords: Product Line Engineering, Feature Models, MBSE, Modeling, Artificial Intelligence, Natural Language
Processing.
Abstract: This paper explores the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI), particularly Natural Language Processing
(NLP), with feature modeling (FM) in Product Line Engineering (PLE) for Systems Engineering. By
leveraging AI to formalize and model variability, the study proposes an algorithm to assist subsystem owners
in describing variability, generating prompts, and producing feature models. The results demonstrate AI’s
ability to detect and resolve common modeling issues, such as dead features, false optional features, and
constraint inconsistencies, while enhancing model validation and anomaly detection. Although the approach
is promising, limitations in scalability, conflict resolution, and integration across subsystems highlight the
need for future research to establish a comprehensive and scalable methodology. This work underscores AI's
potential to streamline feature modeling and improve the consistency and efficiency of variability
management in complex systems.
1 INTRODUCTION
Feature modeling is the major mean of representing
variability in Product Line Engineering (Oliinyk et
al., 2017). The hierarchical structure and constraints
of Feature Models (FM) effectively capture the
diverse configurations of complex systems, enabling
systematic variability management (Krueger &
Clements, 2017). In our previous work, we proposed
a novel approach to integrate systems engineering
principles into product line engineering (PLE)
(Lameh et al., 2025). This was based on two studies
done: Systematic Literature Review (Lameh et al.,
2024a) and Interviews (Lameh et al., 2024b). This
integration resulted in a multi-layered PLE
framework, where FMs serve as a central modeling
artifact for representing variability across multiple
domains.
The increasing complexity of modern systems has
underscored the need for advanced techniques to
manage variability. Artificial Intelligence (AI), and
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9762-663X
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3870-0331
particularly Natural Language Processing (NLP), has
emerged as a promising approach to enhance
variability management processes, where FMs are
foundational (Felfernig et al., 2024). AI methods,
especially NLP, can be leveraged to automate and
augment various aspects of FM creation, analysis, and
maintenance, offering significant improvements in
scalability and precision (Benavides et al., 2010). The
challenges that we aim to address in this paper include
detecting anomalies in FM, as well as managing
complexity in large-scale systems (Felfernig et al.,
2024). By leveraging generative AI technologies, this
study demonstrates how NLP used for automation can
streamline variability modeling, reduce error-prone
manual tasks, and enable faster, more reliable model
generation. The central research question is: How can
AI-driven approaches enhance the efficiency,
accuracy, and scalability variability modeling while
considering SE’s viewpoints (Lameh et al., 2025)?
After the current introduction, section 2 presents a
literature review on automated analysis and AI-driven
approaches in feature modeling. Section 3 outlines
450
Lameh, J., Dubray, A. and Jankovic, M.
Automating Feature Modeling in Product Line Engineering for Systems Engineering: The Application of Natural Language Processing.
DOI: 10.5220/0013442900003896
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Model-Based Software and Systems Engineering (MODELSWARD 2025), pages 450-457
ISBN: 978-989-758-729-0; ISSN: 2184-4348
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

the methodology employed, and Section 4 discusses
the results and identifies challenges and opportunities
for further enhancement of AI-based FM automation.
2 BACKGROUND
The integration of AI into Model-Based Systems
Engineering (MBSE) has garnered significant
attention in recent years, aiming to enhance system
design, analysis, and decision-making processes
(Schneider et al., 2022). AI's capabilities in handling
complex datasets and automating intricate tasks align
seamlessly with the objectives of MBSE, which
focuses on using models to support system
requirements, design, analysis, verification, and
validation activities throughout the system lifecycle.
Recent studies have explored various AI
applications within MBSE. For instance, AI-based
assistants have been developed to support MBSE
adoption in practice, providing an overview of
existing and potential application areas for AI in
MBSE (Anacker et al., 2024). These assistants can
augment human decision-making and improve the
overall efficiency of the MBSE process. Machine
learning algorithms, in particular, have been applied
to analyze large amounts of data generated during
system development, offering insights that can
optimize system design and performance (Visure
Solutions, 2023).
The convergence of MBSE and AI has also been
recognized as a platform for unlocking the power of
systems thinking throughout systems design,
increasing the ability to manage disruptive and
emergent system behaviors. Generative AI tools, such
as large language models, are impacting the systems
engineering lifecycle, serving as platforms for
innovation and understanding through model-based
systems engineering standardization and artificial
intelligence (Aerospace America, 2023).
Concerning feature modeling, AI-driven
approaches have demonstrated significant potential.
Feature models are essential in representing
variability and commonality within software product
lines, facilitating the configuration of diverse system
variants from a shared set of features. The integration
of AI methods with feature modeling has been
explored to enhance design, analysis, and application
processes (Lopez-Herrejon et al., 2023). An open
access book provides a basic introduction to feature
modeling and analysis, as well as the integration of
AI methods with feature modeling, serving as an
introduction for researchers and practitioners new to
the field (Felfernig et al., 2024). AI-driven
approaches, particularly those utilizing machine
learning and recommender systems, have shown great
promise in feature modeling. These approaches assist
human decision-making during the analysis phase,
effectively detecting anomalies, proposing solutions,
and generating configurations that satisfy a given set
of constraints. Such methods can significantly reduce
manual effort while improving the reliability of the
models. For example, AI can assist in anomaly
detection, solver support for satisfiability checking,
and the generation of consistent configurations.
Although full automation in modeling is challenging
due to the need for human oversight, AI's role in
analysis and validation is particularly noteworthy
(Sundermann et al., 2024). In this context, the focus
is on AI's application to the modeling and analysis
phases, rather than configuration generation.
Furthermore, AI aspects such as knowledge
representation, reasoning, explainable AI, and
machine learning have been linked to feature model-
related tasks, including modeling, analysis, and
configurators. This linkage underscores AI's potential
in automating model generation and analysis,
enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of feature
modeling processes (Felfernig et al., 2024).
In summary, the integration of AI into MBSE and
feature modeling presents a promising avenue for
enhancing system engineering processes. AI-driven
approaches can automate and improve various
aspects of modeling and analysis, leading to more
efficient and reliable system development. As
research and development in this area continue to
evolve, the collaboration between AI and MBSE is
expected to yield innovative solutions to complex
engineering challenges.
3 METHODOLOGY
Our methodology utilized the Feature IDE tool, an
open academic software platform for feature
modeling. We integrated an NLP-based AI model,
specifically ChatGPT, to automate the generation of
feature models. The technology already exists, and
the goal was not to create something new but to make
effective use of it. It wasn’t just about using ChatGPT
directly; instead, we provided ChatGPT with our
specific modeling approach. The aim was to use
ChatGPT to connect the answers to the questions and
leverage its existing capabilities to formalize the
entire process. The process involved:
Formulating Variability: Variability was
described based on the input provided by subsystem
owners and the feature descriptions in our previous
Automating Feature Modeling in Product Line Engineering for Systems Engineering: The Application of Natural Language Processing
451

work. Our approach focuses on capturing all
variability as described by the subsystem owner,
transforming this input into a structured feature
model. Currently, this process involves manual
meetings between system engineers and domain
experts to extract variability information. By
leveraging AI, we propose automating this
interaction. The AI system would engage directly
with stakeholders through guided questioning,
helping to formalize their inputs into structured
variability descriptions. Once the information is
captured, the AI would process it to automatically
generate a feature model, reducing reliance on
manual interpretation and ensuring a more precise
and efficient modeling process.
AI Prompting and Output with Iterative
Refinement: Initial prompts were formulated to
describe the system’s variability. As the AI-generated
models occasionally included errors or
inconsistencies (e.g., special characters incompatible
with FeatureIDE), iterative refinements were applied.
This included avoiding parentheses in feature names,
clarifying constraints, and ensuring the parent-child
hierarchy was accurately represented. The prompt
was constructed using a structured framework,
integrating key elements such as system context,
variability dimensions, and expected outputs. To
ensure its quality, the prompt underwent iterative
refinement based on subsystem owner feedback and
trial runs. The GenAI model used was ChatGPT-4,
chosen for its advanced language comprehension,
context retention, and capacity to handle complex
prompts effectively.
In our methodology, we build upon the example
developed in our previous work, which focused on
Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS),
specifically the Park Assist feature. In that study, we
demonstrated how to formalize and model an FM in
the context of PLE for SE. This approach emphasized
maintaining the three essential SE perspectives:
operational, functional, and organic (constructional).
By structuring the variability model around these
viewpoints, we ensured that the FM accurately
captured the system's mission diversity (operational),
functional variations (functional), and constructional
components (organic). This example serves as a
foundation for illustrating how AI-driven methods
can further enhance the formalization and modeling
processes, providing a structured approach to
managing variability while aligning with SE
principles.
Validation was performed by comparing AI-
generated models with manually constructed feature
models for the same subsystem. The intuitive nature
of the GenAI-driven process, particularly its ability to
capture implicit variability details was highlighted.
Suggestions for improvement included enhancing AI
explanations for identified constraints and anomalies,
which will guide future iterations of the approach.
4 RESULTS
In this section, we present the outcomes of applying
the proposed algorithm for detecting and formalizing
variability using AI. This algorithm serves as a
structured framework to guide subsystem owners in
articulating variability and ensures that the captured
information can be systematically translated into a
feature model. By focusing on variability detection
and formalization, the algorithm reduces ambiguity
and bridges the gap between informal descriptions
and formalized outputs. We begin by introducing the
algorithm designed to detect and formalize variability
in subsystem descriptions. The algorithm employs a
question-driven approach, structured around
variability dimensions such as operational,
functional, and component diversity. It incorporates
mechanisms to validate the necessity of component
variability, prompting subsystem owners to justify
distinctions based on operational requirements or
functional differences. This systematic process
ensures that only relevant variability is modeled,
avoiding unnecessary complexity. The results are
then organized into three main parts.
4.1 Proposed Algorithm
This section provides a detailed breakdown of the
proposed algorithm for capturing variability in
feature modeling with component rationalization.
The following algorithm ensures that component
diversity is justified by identifying whether
variability arises from operational or functional
differences, avoiding unnecessary complexity. Key
steps are outlined to enhance clarity and
reproducibility. The section addresses challenges
such as inconsistency detection, conflict resolution,
and scalability, demonstrating how the approach
automates manual tasks.
This algorithm was proposed after working on
several projects at Renault. Through these projects,
we refined the questions by applying the model and
improving it based on interactions. The goal was to
replace manual meetings with subsystem teams by
using AI to make the process easier and more
efficient. The usual process involved many
interactions and several meetings, which took a lot of
MBSE-AI Integration 2025 - 2nd Workshop on Model-based System Engineering and Artificial Intelligence
452

time. This approach was applied to over 25
perimeters, and we found that the questions were
mostly the same. Based on this, we formalized the
algorithm to simplify and standardize the process.
Step 1: Identify Mission-Level Variability
1. Ask: What are the different missions or services
proposed to the client? List distinct options or
variations in the missions offered.
2. For each mission: Are there optional extensions or
customizations? Record additional mission-
specific options.
Step 2: Capture Functional Variability
1. For each mission: What are the core functions
required to achieve this mission? Focus on
variable functions only.
2. Ask: Are there alternative ways to implement any
function? Document functional diversity and
optional implementations.
3. Ask: Are there extra or optional features offered
for any function? Note additional capabilities as
optional features.
Step 3: Analyze Component-Level Variability
1. For each function: Are there variable components
or configurations used to deliver this function?
Focus only on components with variability.
2. Rationalize Component Variability: Ask: Why do
we need this component diversity if it performs
the same function? If a cheaper alternative exists
and performs the same, avoid adding variability.
Ask: Does the difference indicate operational or
functional variability instead? If so, reclassify as
operational or functional variability and update
the model.
Step 4: Formalize Constraints and Relationships
1. For each variability point: Define constraints
(e.g., "if mission X, then mission Y must exist").
Map dependencies (e.g., "function A requires
mission B").
2. Validate: Check for redundancies, false options,
or unnecessary conflicts.
Step 5: Review and Simplify
1. Review: Does the variability model accurately
reflect client needs? Ensure all variability adds
value and aligns with operational or functional
requirements.
2. Verify: Is the variability clear, justified, and cost-
effective? Remove unjustified diversity or
redundancies.
This algorithm, should give us as an output, a refined
variability model structured as:
- Mission-Level Variability: Client-focused
operational differences.
- Functional Variability: Alternative
implementations and extra features.
- Component-Level Variability: Rationalized
with clear justification or reclassified if
operational or functional.
- Constraints and Dependencies: Rules ensuring
consistency and reducing complexity.
This approach minimizes unnecessary variability,
ensuring the model is both practical and cost-
effective.
4.2 Input for Modeling
The proposed algorithm systematically retrieves and
formalizes variability information from subsystem
owners, ensuring alignment with PLE and feature
modeling principles. Its design reflects a structured
approach, leveraging NLP capabilities for variability
extraction while adhering to the operational,
functional, and organic SE perspectives. The
rationale stems from the need to streamline the
elicitation process and minimize variability errors,
which are common challenges in PLE. Completeness
was achieved through iterative GenAI interactions,
employing the “5 Whys” technique to probe deeper
into responses. A checklist of mandatory variability
dimensions (e.g., operational constraints, feature
dependencies) ensured no critical information was
omitted.
Using the proposed algorithm, we captured the
variability as described by the subsystem owner. This
input reflects the subsystem’s missions, functional
diversity, and specific features offered to the client.
The structured representation highlights how the
algorithm transformed a potentially vague and
unstructured description into a comprehensive and
clear variability framework. This input forms the
foundation for generating the feature model.
Automating Feature Modeling in Product Line Engineering for Systems Engineering: The Application of Natural Language Processing
453
PROMPT:
According to feature modeling rules,
create a feature model for ADAS Park
Assist System. This is the description
of variability: ADAS Park Assist system
can offer different park assist
missions: (i) Ultrasonic Park Assist
(UPA): This can exist in two variants:
rear-only or rear-and-front. These
variants are formed by incremental
elementary missions, (ii) Camera Park
Assist (CPA): It can come in two
variants: rear-view camera or around-
view camera, where only one variant is
installed on the vehicle, representing
alternative missions, and (iii)
Automatic Park Assist (APA): This can
also exist in two variants: hands-free
parking and/or remote parking. A vehicle
could have one or both variants,
representing different elementary
missions that form the overall mission.
As an example of constraints, the
dependency of APA REMOTE on CPA
AROUNDVIEW for optimal operation is a
technical constraint, modeled as a
logical condition to ensure system
compatibility. In contrast, the decision
to avoid offering UPA FRONT without UPA
REAR, while technically feasible, is a
marketing constraint defined in the
product structure.
Once done, create an .xml file so it can
be used for FeatureIDE tool.
End.
Algorithm 1: AI prompt used.
4.3 Output of the AI-Driven Process
The variability input was processed by an AI-driven
prompt to produce a detailed feature model. This
model encapsulates the identified variability and
associated constraints, ensuring consistency and
alignment with the subsystem owner’s requirements.
Logical constraints, such as the dependency of certain
features on others, were accurately included in the
output. Additionally, the feature model was exported
as an .xml script for direct use in FeatureIDE. This
script was validated for compatibility and correctness
within FeatureIDE, showcasing the seamless
integration of the generated model into existing feature
modeling tools. Note that, before presenting the script
and feature model, we also provide a preparatory
document explaining the fundamentals of feature
modeling and the functionalities of FeatureIDE. This
ensures that readers unfamiliar with these tools can
fully understand the process and outcomes.
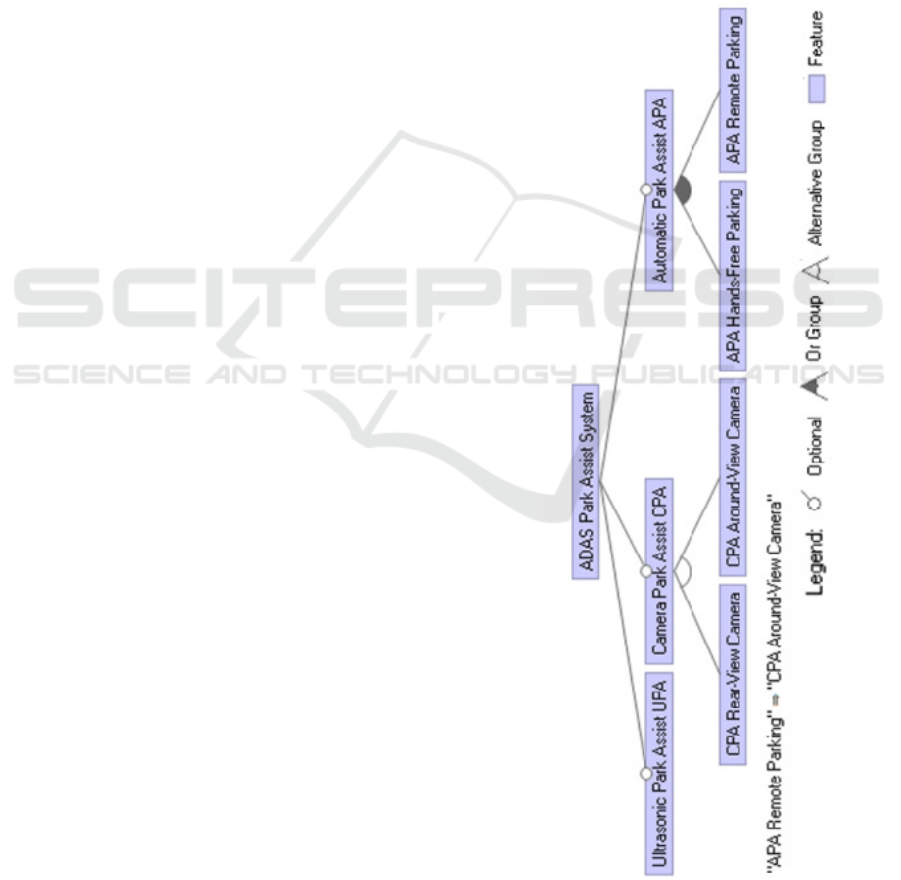
ADAS Park Assist System
├── Ultrasonic Park Assist (UPA)
[Optional]
│ ├── Rear-Only [Mandatory Child]
│ │ └── Rear-and-Front [Optional]
├── Camera Park Assist (CPA) [Optional]
│ ├── Rear-View Camera [Alternative]
│ └── Around-View Camera [Alternative]
└── Automatic Park Assist (APA)
[Optional]
├── Hands-Free Parking [OR Group]
└── Remote Parking [OR Group]
Constraints:
UPA implies UPA Rear-Only.
Algorithm 2: FM model output generated by AI.
Figure 1: FM model generated by AI.
MBSE-AI Integration 2025 - 2nd Workshop on Model-based System Engineering and Artificial Intelligence
454

The generated feature model closely resembled the
one we created manually, demonstrating comparable
accuracy while significantly reducing the time
required for modeling. Although establishing the
process initially required effort, we believe that once
fully implemented, it will save substantial time by
minimizing meetings and automating repetitive tasks,
allowing engineers to focus on higher-value
activities.
These results highlight the algorithm’s
effectiveness in detecting and formalizing variability,
demonstrating how AI can streamline the creation of
feature models while maintaining accuracy and
relevance.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"
standalone="no"?>
<featureModel>
<struct>
<and name="ADAS Park Assist System">
<!-- Ultrasonic Park Assist -->
<and name="Ultrasonic Park
Assist UPA">
<mandatory name="UPA Rear-
Only"/>
<optional name="UPA Rear-
and-Front"/>
</and>
<!-- Camera Park Assist -->
<alt name="Camera Park Assist
CPA">
<feature name="CPA Rear-View
Camera"/>
<feature name="CPA Around-
View Camera"/>
</alt>
<!-- Automatic Park Assist -->
<or name="Automatic Park Assist
APA">
<feature name="APA Hands-
Free Parking"/>
<feature name="APA Remote
Parking"/>
</or>
</and>
</struct>
<constraints>
<!-- APA Remote Parking requires CPA
Around-View Camera -->
<rule>
<imp>
<var>APA Remote
Parking</var>
<var>CPA Around-View
Camera</var>
</imp>
</rule>
</constraints>
</featureModel>
Algorithm 3: .xml of FM model output generated by AI.
5 DISCUSSION
The integration of Natural Language Processing
(NLP) with feature modeling has provided significant
insights and revealed both opportunities and
challenges. This approach demonstrated that AI can
effectively assist in analyzing and refining feature
models, but it also underscored areas where
improvements are needed to enhance the overall
process.
5.1 Insights and Identified Issues
During the modeling process, several key issues were
detected and addressed. These include but are not
limited to:
i) Dead Features: Features that could not
participate in any valid configuration were
identified, highlighting the importance of
systematic validation during model creation.
ii) False Optional Features: Features
incorrectly marked as optional but required
for consistency were flagged, emphasizing
the necessity of logical verification.
iii) Constraint Inconsistencies: Logical errors
in constraints, such as unsatisfiable or
contradictory rules, were detected, ensuring
model coherence.
iv) Redundant Constraints: Unnecessary or
duplicate constraints were identified and
removed, streamlining the model and
improving its efficiency.
v) Conflict Detection: Faulty constraints and
interdependencies leading to conflicts were
flagged, with the potential for conflict
aggregation and resolution proposed.
These detections not only validated the model but
also provided opportunities for improving its
robustness by addressing errors such as wrong
cardinalities and identifying anomalies. Additionally,
AI-assisted processes could verify product validity
and estimating the number of possible configurations,
further underscoring their utility in model analysis.
5.2 Opportunities for Improvement
While the AI demonstrated substantial promise, the
current approach highlighted several areas for
enhancement:
i) Advanced Anomaly Detection:
Incorporating more sophisticated AI
techniques could enable the identification of
Automating Feature Modeling in Product Line Engineering for Systems Engineering: The Application of Natural Language Processing
455

subtle and complex issues beyond the
current capabilities.
ii) Dynamic Conflict Resolution: Future
development could focus on AI-driven
methods for resolving detected conflicts,
providing practical recommendations for
engineers.
iii) Scalability: Ensuring that the approach is
scalable to accommodate large and complex
feature models remains an essential goal for
broader adoption.
5.3 Limitations and Future Directions
This study's reliance on a direct interaction with an AI
tool, such as ChatGPT, without establishing a
formalized process or methodology, is a noted
limitation. Developing a structured framework for
NLP-driven feature modeling would enhance its
effectiveness and allow for deployment at larger
scales. Additionally, the focus on a limited perimeter
presents challenges in integrating constraints across
multiple subsystems, particularly when features are
interdependent. This highlights the need for a
continuous process where AI not only models’
variability but also adapts dynamically to evolving
system constraints and interactions. While the
integration of NLP into feature modeling is
promising, further advancements are needed to
establish a comprehensive, scalable, and automated
methodology that can be widely applied in PLE. The
other main limits:
i) Data Protection Concerns: Utilizing GenAI
systems like ChatGPT raised questions about
data confidentiality, especially when dealing
with sensitive system requirements. Future
implementations must integrate secure, on-
premise AI models to safeguard proprietary
information.
ii) Variability of Outputs: While the AI
demonstrated consistency in generating
feature models, slight variations were
observed across iterations. These variations
are due to the AI’s process of searching for
additional information to enhance its
responses. To ensure consistent results,
additional tuning and domain-specific
adjustments should be implemented, focusing
on aligning the AI's outputs with predefined
parameters and minimizing unnecessary
deviations.
iii) Generalization of deployment: Applying
this approach to other systems is needed for
further validation. This highlights the need for
customizable templates and modular
algorithms that can generalize across multiple
domains. This approach would allow the
model’s applicability to be extended across
various sectors, insuring integration into
heterogeneous environments.
6 CONCLUSION
This paper demonstrated the application of NLP-
based AI to automate feature modeling in PLE. By
leveraging ChatGPT for model generation and
analysis, we reduced manual effort and improved
accuracy. However, further advancements are needed
to address existing challenges and fully realize AI’s
potential in this domain. Future research will focus on
enhancing anomaly detection, conflict resolution, and
the integration of AI-driven methods into the broader
systems engineering process.
REFERENCES
Aerospace America. (2023, novembre). Accelerating
innovation and understanding through model& # x2d ;
based systems engineering standardization and artificial
intelligence. Aerospace America. https://aerospace
america.aiaa.org/year-in-review/accelerating-innovatio
n-and-understanding-through-model-based-systems-en
gineering-standardization-and-artificial-intelligence/
Anacker, H., Wecker, S., & Harting, K. (2024). Artificial
Intelligence (AI) in Model-based Systems Engineering.
Systems Engineering - Innovationen. Mit System.
https://www.selive.de/ai-in-mbse/
Benavides, D., Segura, S., & Ruiz-Cortés, A. (2010).
Automated analysis of feature models 20 years later : A
literature review. Information Systems, 35(6), 615‑636.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.is.2010.01.001
Felfernig, A., Falkner, A., & Benavides, D. (2024). Feature
Models : AI-Driven Design, Analysis and Applications.
Springer Nature.
Krueger, C., & Clements, P. (2017). Enterprise Feature
Ontology for Feature-based Product Line Engineering
and Operations. Proceedings of the 21st International
Systems and Software Product Line Conference -
Volume A, 227‑236. https://doi.org/10.1145/310619
5.3106218
Lameh, J., Dubray, A., & Jankovic, M. (2024a, submitted).
A Systematic Literature Review on Product Line
Engineering Approaches in Systems Engineering :
From Models to Applications (in press). submitted to
INCOSE Systems Engineering Journal (October 2024).
Lameh, J., Dubray, A., & Jankovic, M. (2024b). Variability
in complex product/system design : Case study in
automotive industry. Proceedings of the Design
MBSE-AI Integration 2025 - 2nd Workshop on Model-based System Engineering and Artificial Intelligence
456

Society, 4, 2635‑2644. https://doi.org/10.1017/pds.20
24.266
Lameh, J., Dubray, A., & Jankovic, M. (2025). Modeling
Variability in Product Line Engineering for Systems
Engineering (in press). submitted to ICED25.
Lopez-Herrejon, R. E., Martinez, J., Guez Assunção, W. K.,
Ziadi, T., Acher, M., & Vergilio, S. (Éds.). (2023).
Handbook of Re-Engineering Software Intensive
Systems into Software Product Lines (1st ed. 2023).
Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.10
07/978-3-031-11686-5
Oliinyk, O., Petersen, K., Schoelzke, M., Becker, M., &
Schneickert, S. (2017). Structuring automotive product
lines and feature models : An exploratory study at Opel.
Requirements Engineering, 22(1), 105‑135.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s00766-015-0237-z
Schneider, B., Riedel, O., & Bauer, W. (2022). Review :
Model-based Systems Engineering and Artificial
Intelligence for Engineering of Sustainable Systems –
What contribution can systems engineering and
artificial intelligence provide for the engineering of
sustainable systems as of today? In P. Plapper (Éd.),
Digitization of the work environment for sustainable
production (p. 37‑59). GITO Verlag.
https://doi.org/10.30844/WGAB_2022_3
Sundermann, C., Kuiter, E., Heß, T., Raab, H., Krieter, S.,
& Thüm, T. (2024). On the benefits of knowledge
compilation for feature-model analyses. Annals of
Mathematics and Artificial Intelligence, 92(5),
1013‑1050. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10472-023-09906-6
Visure Solutions. (2023, janvier). Best ALM Tools with
Round Trip integrations with Word & ; Excel. Visure
Solutions. https://visuresolutions.com/mbse-guide/ai-
in-mbse/
Automating Feature Modeling in Product Line Engineering for Systems Engineering: The Application of Natural Language Processing
457
