
Trust-Centric Blockchain Framework: A Three-Layered Architecture
for Securing Open and Private Systems
Jihen Bennaceur
1, 2 a
, Wissem Zouaghi
3
, Kawouther Thabet
4
, Aziza Bennour
1
, Roudha Ben Jemaa
4
and Ali Mabrouk
3
1
Mediterranean Institute of Technology, Tunis, Tunisia
2
National School of Computer Science, Manouba, Tunisia
3
SAMA PARTNERS Business Solutions GmbH, Mannheim, Germany
4
Higher Institute of Computer Science and Communication Technologies, University of Sousse, Tunisia
Keywords:
Open Architectures, Cyber Threats, Blockchain, Trust, Reputation Management, Evaluation, Testing.
Abstract:
Cybersecurity threats are becoming increasingly sophisticated, posing significant risks to both open and private
architectures. Open architectures, such as open-source ecosystems, collaborative platforms, and information-
sharing frameworks, thrive on transparency and accessibility but face challenges in maintaining trust, data
integrity, and security. Conversely, private architectures, while operating within controlled environments, are
not immune to internal threats or compromised trust mechanisms. Blockchain technology has emerged as a
transformative solution to address these challenges by leveraging decentralization, immutability, and trans-
parency. This paper introduces a dual Blockchain-based trust framework tailored to the unique needs of both
open and private architectures. For open systems, the framework enhances trust and security through trans-
parent trust modeling, Blockchain-based validation, and tamper-proof accountability mechanisms. For private
systems, it strengthens internal trust evaluation and mitigates risks by securing interactions in a closed, per-
missioned environment. The proposed solution integrates three layers—trust modeling, Blockchain-enabled
validation, and adaptive penalty mechanisms—to ensure robust security and participant accountability. Exten-
sive simulations and security validations demonstrate the effectiveness of this approach across diverse open
and private architecture scenarios, providing a comprehensive strategy to mitigate threats and reinforce trust
in these critical ecosystems.
1 INTRODUCTION
Architectures, whether open or private, serve as
foundational frameworks for modern technological
ecosystems. Open architectures, such as threat infor-
mation sharing (TIS) (Mohaisen et al., 2017) frame-
works and open-source ecosystems (Gil et al., 2024),
foster innovation and collaboration by enabling di-
verse communities to co-develop adaptable systems
and share critical data. However, the very openness
that drives their success also introduces vulnerabili-
ties. In TIS, for example, malicious actors can tar-
get the integrity of shared data or exploit trust mech-
anisms to impersonate legitimate participants. Simi-
larly, in open-source environments, vulnerabilities in
code or compromised contributors can jeopardize se-
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8584-5253
curity and reliability.
On the other hand, private architectures operate
in controlled, closed environments that restrict access
and collaboration to authorized entities. While this
design minimizes exposure to external threats, it in-
troduces unique challenges related to trust manage-
ment within a limited and often hierarchical set of
participants. Internal malicious actors or errors in the
trust assessment can compromise the architecture, af-
fecting its security and functionality.
Trust and reputation management systems (Ben-
naceur et al., 2020)(Z. et al., 2018) have become cru-
cial for securing both open and private architectures.
These systems aim to evaluate and maintain the trust-
worthiness of participants, mitigate malicious behav-
ior, and ensure reliable collaboration. However, exist-
ing mechanisms face limitations. Attackers can ma-
nipulate trust values, elevate their reputation through
Bennaceur, J., Zouaghi, W., Thabet, K., Bennour, A., Ben Jemaa, R. and Mabrouk, A.
Trust-Centric Blockchain Framework: A Three-Layered Architecture for Securing Open and Private Systems.
DOI: 10.5220/0013446900003929
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2025) - Volume 1, pages 1097-1109
ISBN: 978-989-758-749-8; ISSN: 2184-4992
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
1097

falsification, or discredit legitimate contributors, un-
dermining the integrity of the system.
To address these challenges, this paper pro-
poses leveraging blockchain technology (Chowdhury
et al., 2016) to enhance trust and reputation man-
agement systems. The properties of the blockchain,
namely immutability, decentralization, and trans-
parency, make it an ideal solution for both open and
private architectures. For open systems, blockchain
can secure trust values against tampering, ensure
transparency in contributions, and deter malicious
behavior with historical accountability. In private
systems, blockchain can enforce strict trust policies
through immutable records and smart contracts, en-
hancing internal security and operational reliability.
By designing and implementing tailored
blockchain solutions for both open and private
architectures, this approach bridges critical gaps
in trust management. It addresses the risks posed
by malicious actors while enhancing the security
and reliability of collaborative systems, whether in
dynamic open-source ecosystems, tightly controlled
private platforms, or hybrid environments.
1.1 Contributions
The increasing reliance on open and private archi-
tectures necessitates robust solutions to secure trust
and reputation in both collaborative and controlled
environments. The vulnerabilities inherent in open
architectures, such as falsified reputation scores and
malicious contributions, demand a transparent and
tamper-proof trust management mechanism. Pri-
vate architectures, while inherently more secure, re-
quire enhanced trust assessment systems to protect
against internal threats and ensure operational relia-
bility. Contributions This work presents the following
key innovations:
• Design of a public blockchain architecture to se-
cure trust in open systems, such as open-source
platforms.
• Design of a private blockchain architecture to en-
hance trust in targeted and controlled environ-
ments, such as closed-source systems.
• Implementation and validation of both solutions
to demonstrate their effectiveness in securing trust
and reputation across diverse architectural frame-
works.
The structure of this research is indicated in Fig.
1; Section 2 describes the trust model for the open
and private architectures. Section 3 indicates the de-
sign of blockchain-based trust. Section 4 describes
the two Blockchain architectures: Private and Public.
Sections 5 and 6 discuss the implementation and an-
alyze the results. Section 6 describes the conclusion
of this research work. The abbreviations used in this
paper are indicated in Table 1.
Figure 1: Paper structure.
2 TRUST AND REPUTATION
MANAGEMENT FOR OPEN
AND PRIVATE
ARCHITECTURES
2.1 Model for Trust Initialization
During trust initialization, newly joined entities are
assigned a first level of trust, defined as the trust ini-
tialization model (Bennaceur et al., 2025). Values are
calculated based on the various dimensions specified
(see Fig2).
• Pre-trust: In this context, it denotes the initial
level of trust attributed to a newly participating en-
tity. This trust rating is determined following the
aggregation of recommendations, often referred
to as reputation, from existing entities within a
specific community. This reputation is then con-
verted into a numerical value within the threat-
sharing platform and subsequently forwarded to
the Blockchain layer for the initial trust assess-
ment. The magnitude of the pre-trust value as-
signed to an entity is directly correlated with
the quality and quantity of recommendations it
receives from the community. In essence, the
more favorable recommendations an entity gar-
ners from its peers, the higher its pre-trust score
will be.
• Community Type: The category of community
represents the second dimension in initiating trust,
as it significantly influences the trust-building
process. In a public community marked by an un-
trusted environment, trust initiation is determined
BEST 2025 - Special Session on Blockchain and Enhanced Security for a New Era of Trust
1098
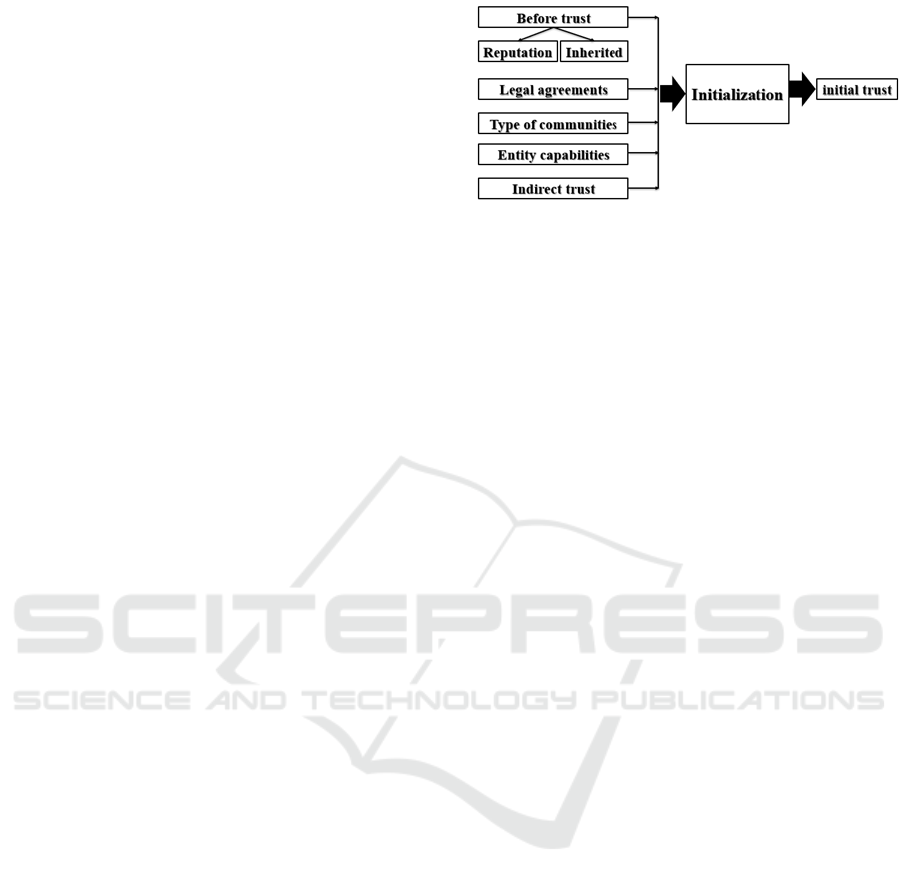
using the zero-trust concept as the basis for calcu-
lation.
• Legal Contract: Upon becoming a member of
the community, participants will enter into a for-
mal contract with the system. This contractual
arrangement serves as a safeguard for the rights
of both the threat information-sharing platform
and the participating entity. It establishes the
terms and conditions governing community mem-
bership and the utilization of platform benefits.
The jurisdiction for the legal contract will align
with the location of the participating entity, and
its enforceability will be assessed on a scale rang-
ing from low to high, depending on the extent to
which the agreement adheres to legal procedures
in that particular country.
• Capabilities: The entity’s capability will be cate-
gorized on a scale from low to high, determined
by its expertise and experience in the field of cy-
bersecurity. This factor will significantly influ-
ence the level of trust, as the reliability of the
shared information will hinge on the extent of the
entity’s experience in this domain.
• Indirect trust pertains to the geographical context
in which participants operate, and it involves the
assessment of trustworthiness based on the partic-
ipant’s country of origin. This facet of trust com-
prises three sub-dimensions:
1. Data Privacy Regulations: This sub-dimension
evaluates the extent to which data privacy laws
are upheld in the participant’s country and the
legal repercussions for any breaches of data pri-
vacy.
2. Copyright Protection: Within this sub-
dimension, an assessment is made regarding
the level of protection afforded to individual
copyrights in the participant’s country, along
with the legal consequences associated with
copyright infringement.
3. Cyber crimes: These are assessed based on a
country’s susceptibility to cyberattacks, a sub-
dimension that encompasses not only the fre-
quency of attacks but also factors in the coun-
try’s cybersecurity strength index.
2.2 Model for Trust Evolution
Trust within a system evolves gradually based on the
nature and quality of the actions performed by enti-
ties, and it is shaped by the specific requirements of
the environment—whether public or private. The cri-
teria for establishing trust depend on the type of hon-
est and benign actions necessary within the system.
Figure 2: Trust initialization model dimensions.
In private environments, such as threat
information-sharing frameworks, trust is calcu-
lated based on the quality, relevance, and accuracy of
the data shared by entities. Entities are evaluated on
their ability to provide actionable insights regarding
threats, vulnerabilities, and incidents that enhance
the security and resilience of the network. In public
environments, such as open-source platforms, trust is
determined by the quality, originality, and reliability
of the contributions made by entities. Actions such
as adhering to coding standards, addressing issues,
and improving functionality play a significant role in
shaping trust scores. By tailoring the trust evaluation
model to the specific actions and contributions
required in each environment, this approach ensures
that trust evolves naturally and accurately reflects the
entity’s value within the system.
Consequently, the assessment and adjustment of
trust levels hinge on several critical factors tailored
to the environment and the type of contributions be-
ing evaluated. These factors ensure that the system
remains secure, fair, and trustworthy, regardless of
whether it operates in a private or public architecture.
Key elements include:
• Quality: In both private and public environments,
the quality of the shared contributions is crucial.
For private systems like threat information shar-
ing, this involves evaluating the accuracy, rele-
vance, and reliability of the shared data. In public
systems like open-source platforms, quality per-
tains to the correctness, originality, and function-
ality of the submitted code or resources.
• Quantity: The volume of contributions is an im-
portant indicator of an entity’s activity and will-
ingness to engage with the system. In threat in-
formation sharing, this could mean the number of
threat reports or vulnerabilities shared. In open-
source platforms, it may reflect the frequency
of code commits, bug fixes, or feature enhance-
ments.
• Integrity: This dimension ensures that the shared
content is honest, accurate, and free from mali-
cious intent. For private systems, it verifies that
Trust-Centric Blockchain Framework: A Three-Layered Architecture for Securing Open and Private Systems
1099

threat data is not manipulated or falsified. In pub-
lic systems, it ensures that code contributions do
not introduce vulnerabilities or other malicious el-
ements.
• Intent: The intent behind contributions is critical
to maintaining trust within the system. For private
architectures, this involves evaluating the motiva-
tion behind shared reputation values and detect-
ing any malicious attempts to discredit trustwor-
thy entities. In public systems, intent is assessed
by analyzing behavior patterns, such as whether
contributions genuinely aim to improve the sys-
tem or to gain undue advantage.
These trust dimensions ensure that the system
adapts to the specific requirements of both private and
public architectures, fostering a secure and collabora-
tive environment. Trust evolves dynamically as these
metrics are continuously monitored and updated, re-
flecting the entity’s ongoing behavior and contribu-
tions.
2.3 Penalty Mechanism
In the process of evaluating contributions and inter-
actions within a system, any entity that raises suspi-
cion—whether in a private or public environment—is
flagged for review. The system leverages a collective
decision-making process to determine the credibility
of the entity, ensuring that trust and integrity are pre-
served.
• Community Feedback Aggregation: Once an en-
tity is flagged, feedback is collected from all
members of the network to evaluate the credibil-
ity of the suspicious entity. This collaborative ap-
proach ensures transparency and fairness in the
decision-making process.
Two scenarios typically follow:
1. Expulsion from the System: If the community de-
termines, through aggregated feedback and cen-
tralized validation, that the flagged entity exhibits
malicious behavior or breaches trust, the entity is
removed from the system. This decision is then
communicated to all users, ensuring that the mali-
cious actor can no longer compromise the system.
2. Affirmation of Trustworthiness: If the investiga-
tion concludes that the flagged entity is trustwor-
thy, the centralized entity dismisses the request
to expel it and communicates this decision to the
community. This ensures that the entity remains
engaged in the system without reputational dam-
age. However, an inquiry is conducted with the
party that initiated the request to investigate any
potential misuse of the reporting mechanism.
This penalty mechanism is essential in both pub-
lic and private environments to maintain a balance
between fostering collaboration and safeguarding the
network from malicious or dishonest entities. It en-
sures that trust is not only established but actively pro-
tected against misuse.
Fig 3 summarizes the trust-based model and the
penalty mechanism.
Figure 3: Trust-based models and penalty mechanism.
2.4 Limitations
The trust model, including the penalty mechanism,
provides a structured approach to evaluating and man-
aging trust within the system. While effective in many
cases, it has inherent limitations that can leave the
system vulnerable to manipulation and inaccuracies.
Addressing these limitations is essential to ensure the
reliability and security of trust and reputation values
such as :
• Trust Violations
1. False Data Injection: Malicious entities may
share misleading or deceptive information, dis-
rupting the trust evaluation process and com-
promising system integrity.
2. Reputation Manipulation: Entities may exploit
vulnerabilities in the model to inflate their trust
scores or discredit honest participants by fabri-
cating false claims.
3. Sybil Attacks: Attackers may create multiple
fake identities to manipulate trust calculations
and dominate the decision-making process.
• Inaccuracy in Trust Evaluation
1. Trust scores based on static or predefined
thresholds may fail to capture complex behav-
ioral patterns, resulting in delayed or incorrect
trust assessments.
2. Scalability Issues: As the number of enti-
ties in the system grows, aggregating feed-
back and applying penalty mechanisms become
BEST 2025 - Special Session on Blockchain and Enhanced Security for a New Era of Trust
1100

resource-intensive, potentially slowing down
the process.
3. Trust Decay and Erosion: Over time, trust val-
ues may become outdated or inaccurate with-
out robust mechanisms for continuous verifica-
tion, leading to potential breaches of trust and
reduced system reliability.
To overcome these limitations, blockchain tech-
nology can be integrated into the trust model to en-
hance the security and robustness of trust and reputa-
tion management.
1. Immutable Trust Records: Blockchain ensures
that all interactions, trust scores, and penalties are
recorded on an immutable ledger, making them
tamper-proof and verifiable.
2. Decentralized Trust Validation: By distribut-
ing the validation process across the network,
blockchain reduces reliance on a single point of
control, ensuring a fair and transparent evaluation
process.
3. Sybil Attack Mitigation: Cryptographic mecha-
nisms within the blockchain enforce unique iden-
tity verification, preventing malicious actors from
creating multiple identities to manipulate trust
values.
4. Dynamic and Automated Trust Management:
Smart contracts can automate trust score adjust-
ments and penalty enforcement based on prede-
fined rules, ensuring consistency and reducing hu-
man intervention.
5. Scalability and Efficiency: Blockchain’s dis-
tributed nature allows for efficient handling of
trust calculations and penalties, even in large-
scale systems, without bottlenecks or perfor-
mance degradation.
By integrating blockchain as a foundational layer
in the trust model, the system gains enhanced re-
silience against trust manipulation and ensures the in-
tegrity of trust and reputation values. This solution
not only addresses existing challenges but also estab-
lishes a scalable, secure, and transparent framework
for trust management in dynamic environments.
3 BLOCKCHAIN-BASED TRUST
DESIGN
Blockchain (Bandara et al., 2021)(Zheng et al., 2017)
is a distributed and immutable ledger that records
transactions in a secure and transparent manner. This
technology is leveraged to create trust in various ap-
plications (Fathi et al., 2020)(Badsha et al., 2020), in-
cluding:
• Transaction Security: Blockchain ensures the se-
curity and integrity of digital transactions by
recording them in a tamper-resistant and time-
stamped manner. This builds trust among parties
that the transaction history is accurate and cannot
be altered.
• Data Transparency: The decentralized nature of
blockchain allows multiple parties to have access
to the same data in a transparent and synchronized
way. This transparency fosters trust by reducing
the need for intermediaries and providing a clear
view of data and processes.
• Smart Contracts: Smart contracts, which are self-
executing contracts with the terms of the agree-
ment written into code, operate on blockchain
platforms. These contracts automatically execute
actions when predefined conditions are met, elim-
inating the need for intermediaries and increasing
trust in contract enforcement.
• Identity Verification: Blockchain can be used for
identity verification and management, allowing
individuals to have more control over their per-
sonal information and who has access to it. This
enhances trust in online interactions and reduces
the risk of identity theft.
• Supply Chain Transparency: In supply chain
management, blockchain can be used to track the
provenance of products from manufacturer to con-
sumer. This transparency builds trust in the au-
thenticity and quality of products.
• Digital Ownership: Blockchain can establish and
verify ownership of digital assets such as art, mu-
sic, or digital collectibles. This ensures that indi-
viduals have true ownership of their digital prop-
erty, fostering trust in digital markets.
The implementation of both public and private ar-
chitectures, such as Threat Information Sharing (TIS)
platforms or open-source systems, offers significant
opportunities for collaboration, innovation, and im-
proved decision-making. However, these architec-
tures also raise critical concerns that must be ad-
dressed to ensure their effectiveness and security:
• Data Trustworthiness: In both public and pri-
vate architectures, ensuring the trustworthiness of
shared data is a major concern. Companies worry
about sensitive information falling into the wrong
hands or being manipulated within the system.
Establishing a basis for trusting other entities, ver-
ifying the authenticity of shared events, and de-
Trust-Centric Blockchain Framework: A Three-Layered Architecture for Securing Open and Private Systems
1101

tecting malicious or fabricated data remain ongo-
ing challenges.
• Selective Data Sharing: Public architectures, such
as open TIS platforms, allow data and events to
be accessible to all members of the community.
However, companies often prefer to share data se-
lectively, limiting access to entities that meet spe-
cific criteria aligned with their interests and trust
levels. Private architectures also face challenges
in implementing granular access controls to en-
sure data reaches only the intended recipients.
• Data Integrity Assurance: Maintaining the in-
tegrity of data shared within both public and pri-
vate architectures is essential. Unauthorized alter-
ations can compromise trust and reliability. While
public platforms rely on their creators’ security
measures, concerns arise regarding the potential
for tampering or modifications for political, gov-
ernmental, or organizational reasons. Similarly,
in private systems, ensuring transparency and ac-
countability in data handling is crucial to prevent
internal misuse or errors.
These challenges represent the core issues faced
by organizations when adopting public or private ar-
chitectures. Key concerns include the lack of pri-
vacy between entities, undefined trustworthiness cri-
teria for participants and data, and the need for en-
hanced transparency and assurance regarding data in-
tegrity beyond the reliance on platform-specific secu-
rity measures or legal agreements. Addressing these
issues requires robust frameworks and technologies to
secure trust, integrity, and accountability in both types
of architectures.
3.1 Blockchain Design Components
• Entity: The main entity inside a community, ei-
ther private or public, will be the organizations.
These entities will represent the holders of the
trust levels of their employees or members. For
that, it will affect positively or negatively the level
of trustworthiness of its members and vice versa,
which means the members will also affect the trust
level of the organization by their behavior and in-
formation. So we design an organization as the
main entity of the system, since later on, the trust
level of a user will be the trust level of his organi-
zation.
• Users: They are the manipulators of actions in-
side the system. In other words, they are the indi-
viduals interacting within the system, performing
actions such as contributing, evaluating, and ex-
changing trust or recommendations. They operate
under the umbrella of their associated entity, and
their trust level is often tied to the collective repu-
tation of that entity. This allows for distinguishing
users from one another and monitoring their ac-
tivities in a secure and transparent manner. Every
user must belong to an organization and they will
be given the same level of trust. For that, compul-
sory data must be gathered from a user and stored
inside the system to distinguish one user from an-
other.
• Administrator: The administrator oversees the
proper implementation, maintenance, and security
of the blockchain-based system across both pub-
lic and private architectures. Their responsibilities
include developing, deploying, and maintaining
self-executing contracts on the blockchain. Addi-
tionally, they manage user accounts, permissions,
and access to blockchain applications, ensuring
compliance with organizational policies. In pri-
vate architectures, administrators may also nego-
tiate with service providers, manage service-level
agreements, and enforce adherence to company
policies.
• Records: The user initiates the update process by
submitting the changes they want to make. This
could involve editing existing information, adding
new data, or deleting outdated entries.
• Blockchain: All transactions on the blockchain
are recorded and stored in a chronological and im-
mutable ledger. Trust-related transactions, such
as changes in trust levels or ratings, are added to
this ledger. These transactions serve as a histori-
cal record of trust evolution.
4 BLOCKCHAIN
ARCHITECTURE
Any architecture can adopt either a public or private
design, depending on the use case and target audi-
ence:
• Public Design: These architectures are fully open
and accessible to a broad audience. Examples in-
clude open-source platforms, where code and re-
sources are freely available for collaboration, and
public threat information-sharing systems, where
organizations share data to collectively combat
cyber threats. Public architectures prioritize trans-
parency and community involvement but face
unique challenges in ensuring trust and security.
• Private/Targeted Design: These architectures are
restricted to a specific group of participants and
BEST 2025 - Special Session on Blockchain and Enhanced Security for a New Era of Trust
1102
prioritize confidentiality, control, and targeted
collaboration. Examples include private software
supply chains, where organizations securely man-
age their proprietary software development life-
cycle, or private data-sharing frameworks that re-
quire strict access control and data integrity.
For each type of architecture—public or private—it is
crucial to implement a blockchain framework tailored
to its specific requirements. The blockchain must ad-
dress the unique challenges of the architecture, such
as enhancing transparency and trust in public systems
or ensuring strict access control and tamper-proof in-
teractions in private systems. This adaptability en-
sures that the blockchain solution aligns with the de-
sign principles and security goals of the respective ar-
chitecture.
Figure 4: Global architecture.
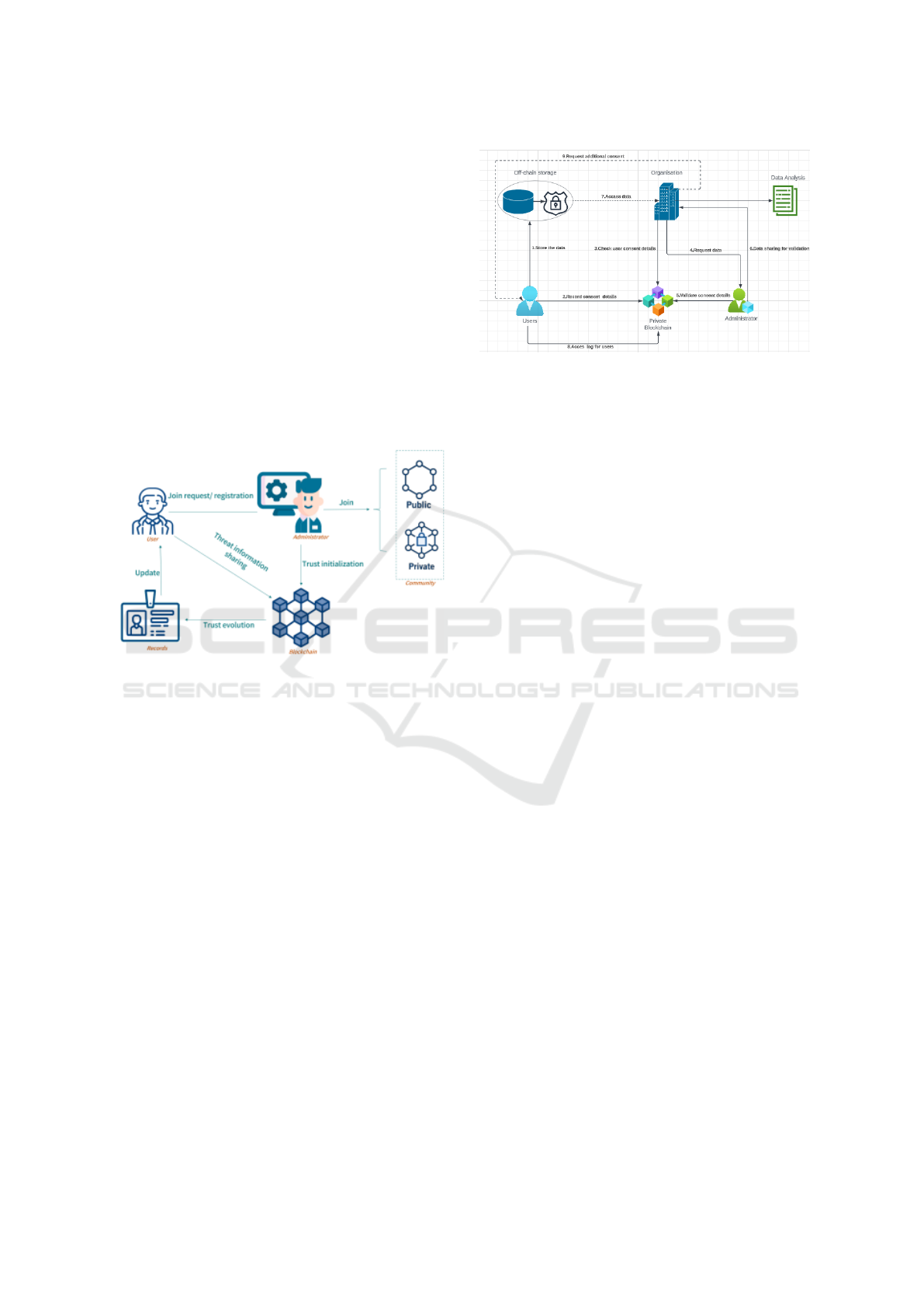
4.1 Private Community Architecture
In the private community architecture, communica-
tion between participants is maintained continuously.
When a new entity joins the community, the data is
sent to the blockchain. The blockchain layer then ver-
ifies the data’s validity, and upon confirmation, the
server sends a permission token to the demonstrator.
Trust initiation is calculated for the new entity, and
a wallet is created for them, with their addition to
the blockchain as a recognized entity. For trust value
updates, the platform sends information consisting of
the entity and the updated trust value. The blockchain
calculates the difference between the old and new
trust values, generating a new block for the transac-
tion. The consensus algorithm validates the creation
of this new block.
4.2 Public Community Architecture
The public community (see fig 6) shares some sim-
ilarities with the private community in terms of its
operation. However, there are distinct differences in
Figure 5: Private Blockchain architecture.
its functioning. Firstly, the public community em-
ploys multiple servers distributed globally to address
network latency. Additionally, authority nodes play
a critical role in validating or reporting newly cre-
ated blocks. These nodes also have the responsibility
of monitoring server statistics and ensuring network
availability.
4.3 Consensus Algorithms
The consensus algorithm plays a pivotal role in val-
idating the creation of each newly generated block.
Both PoW (Proof of Work) and PoS (Proof of Stake)
consensus algorithms may not be the most suitable
choices for deployment. This is because relying on
miners may not align with the preferred method of
block creation. Instead, the concept of authority
nodes proves beneficial as trusted nodes can exert in-
fluence based on established trust. Another factor in-
fluencing the choice of the appropriate consensus al-
gorithm is the verification of entity identities. En-
suring that at least 75 percent of the entities are not
malicious is a significant consideration. In light of
these factors, the decision has been made to imple-
ment two alternative consensus algorithms. Specif-
ically, the Practical Byzantine fault tolerance (PBft)
algorithm will be employed for private communities,
while the public community will adopt PBft with the
validation of authority nodes.
• For private community: The architecture of pri-
vate communities ensures continuous communi-
cation between the demonstrator and its mem-
bers. When a new entity joins the community, the
demonstrator promptly transmits the participant’s
data. Subsequently, the blockchain layer under-
takes the crucial task of validating this data. Once
the data is confirmed as valid, the server issues
a permission token to the demonstrator. Simulta-
neously, it computes the initial trust level for the
new entity, creates a dedicated wallet for them,
and officially registers them on the blockchain as
Trust-Centric Blockchain Framework: A Three-Layered Architecture for Securing Open and Private Systems
1103
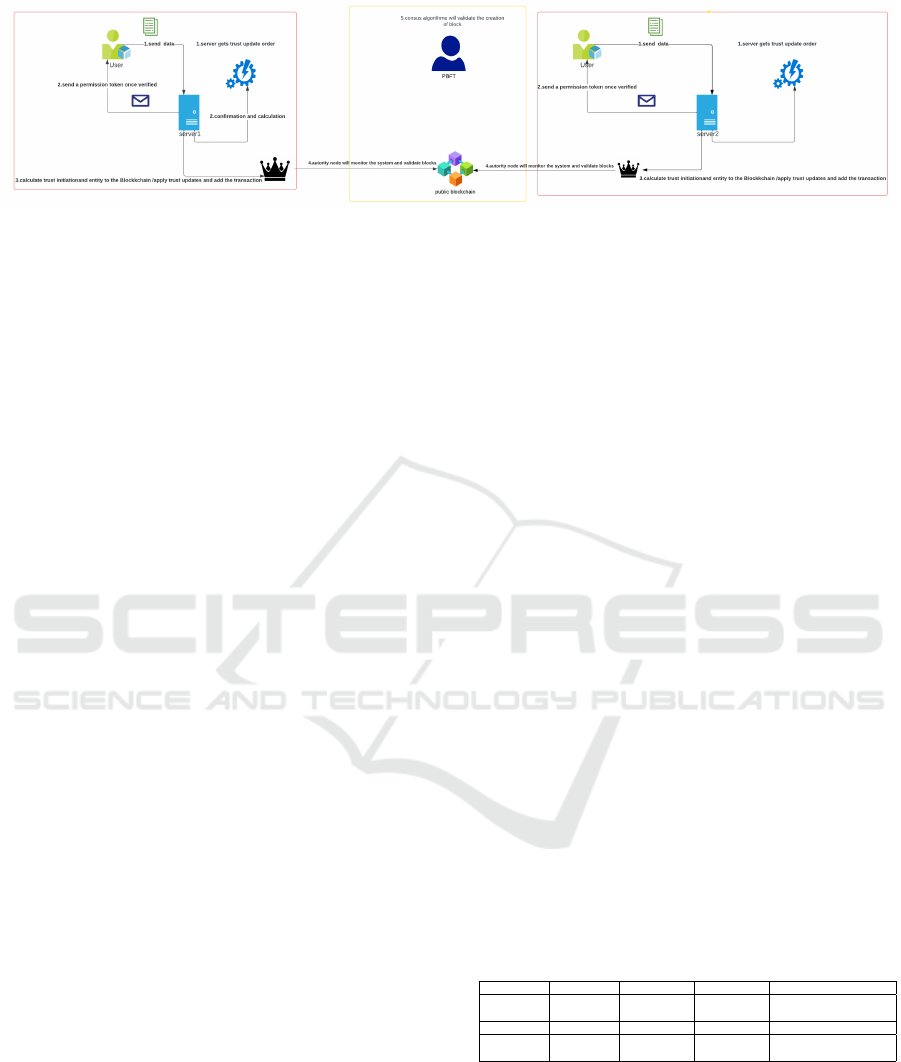
Figure 6: Public Blockchain architecture.
an entity. Regarding trust value updates, the plat-
form is responsible for transmitting relevant infor-
mation, which includes the entity’s identity and
the updated trust value. The blockchain layer then
calculates the difference between the previous and
new trust values, resulting in the generation of a
fresh block for this transaction. The final step in-
volves the consensus algorithm’s validation of the
newly created block.
• Public community: The operation of the public
community shares some commonalities with the
private community, albeit with notable distinc-
tions. One significant difference is the presence
of multiple servers distributed globally to address
network latency efficiently. Additionally, the pub-
lic community introduces the concept of authority
nodes responsible for the validation or reporting
of newly generated blocks. Furthermore, these
authority nodes play a pivotal role in monitor-
ing server statistics and ensuring overall network
availability.
4.4 Technologies
Many technologies were investigated and compared,
so the final ones were chosen.
4.4.1 Blockchain
Researching blockchain technologies provided many
open-source options for the creation of this threat
information-sharing system blockchain. For that,
multiple technologies were tested and they will be
presented in this section and put into a comparative
table to decide what is the best choice.
• Hyperledger fabric: IBM’s Hyperledger Fabric
is a created platform for developing applications
or solutions with an architecture based on mod-
ules. Hyperledger Fabric is used for blockchain
creation and component customization, like con-
sensus and smart contracts, to be plug-and-play.
Its design satisfies a broad range of industrial use
cases. It offers a singular approach to consensus
that permits performance at scale while preserv-
ing scalability and efficiency.
• Hyperledger Sawtooth: IBM’s Hyperledger Saw-
tooth enables a flexible and module-based archi-
tecture that separates the core system from the
application domain. So that the smart contracts
can detail the business rules for the applications
without the need to know the hosted design of the
core system. By default, a variety of consensus
algorithms are implemented in Hyperledger Saw-
tooth, including Practical Byzantine Fault Toler-
ance (PBft) and Proof of Elapsed Time (PoET).
• Hyperledger Besu: IBM’s Hyperledger Besu is
an Ethereum platform that designates a client to
be friendly for enterprises that are used for both
public and private permissioned networks. It can
also be deployed on test networks such as Rinkey,
and G
¨
orli. Hyperledger Besu includes many con-
sensus algorithms such as Proof of Work, and
Proof of Authority (IBFT, IBFT 2.0, Etherhash,
and Clique).
Based on the comparison between the technologies il-
lustrated in Table 1, Hyperledger Sawtooth was the
chosen technology to be implemented in the threat in-
formation sharing system since it provides an imple-
mented Bit consensus algorithm by default, supports
permissioned public and private blockchains and can
be developed in multiple languages.
Table 1: Comparison of Blockchain Technologies.
Technology PBFT Permissions Communities Language
Fabric Unsupported Permissioned Public/Private
js / java / goLang /
python
Besu Unsupported Permissionless Public Solid (Ethereum)
Sawtooth Supported Permissioned Public/Private
Python/java / goLang /
rust/cxx / js
4.4.2 Cryptography
For creating the ledger and securing the information
inside wallets and blockchains. It is necessary to
choose convenient cryptographic algorithms to ensure
these features. For ledger creation, MD5 hashing will
be used for data encryption. It might be changed to
BEST 2025 - Special Session on Blockchain and Enhanced Security for a New Era of Trust
1104

SHA-512 or SHA-256 if it does not prove its effi-
ciency after the simulations. For token creation, the
system will generate JWT tokens for permissions and
access. And for the blockchain blocks that need to
remain non-plain texts. Base 64 cryptography will
encrypt the payloads. And finally, RSA public and
private keys will be the keys to participating as a node
inside the blockchain.
4.4.3 Scripting
Since Hyperledger Sawtooth supports multiple lan-
guages, Python represents a suitable solution for de-
veloping the blockchain in the Hyperledger Sawtooth,
for creating both the needed scripts for functionality
deployment and the back-end of the authority engine
and for developing the simulation scripts. Python is
the simplest language in terms of syntax since it pro-
vides multiple modules that will be needed inside the
threat information-sharing system such as cryptogra-
phy, HTTP servers, and mathematical tools. The Au-
thority engine front-end, on the other hand, will be
developed using Angular, which is an open-source
TypeScript-based web application framework created
by Google Inc. Angular is chosen for the Authority
engine front-end.
5 BLOCKCHAIN’S
IMPLEMENTATION
5.1 Private Community
Private communities (Hou and Jansen, 2023) will op-
erate as on-demand blockchains. Any entity within
the blockchain network has the capability to request
the demonstrator to establish a new private commu-
nity and define the entry criteria. This request under-
goes a thorough assessment by the threat information
system, and once it is determined to be suitable for
deployment, the demonstrator initiates the process of
creating the new private community within the host
system.
As previously mentioned, the steps necessary for
setting up a new blockchain will be repeated; how-
ever, this time, the process will be automated. Special
scripts will be employed to generate a new Docker
file in a pristine directory, configure rules and specifi-
cations, and subsequently deploy this blockchain onto
the host machine.
5.2 Public Community
The initial function within the communication layer is
the ”joining” function. To start, this function initiates
a listener to capture the incoming data from newly
joined entities. It performs several checks, such as en-
suring the data’s validation and uniqueness, including
parameters like pre-trust value, geolocation, and ca-
pabilities. A Python function has been implemented
to verify the correctness of these incoming requests.
Subsequently, the function employs the previously
mentioned trust initiation script. This script computes
the initial trust value within the trust model utilized
by the threat information-sharing system, based on
the data provided by the newly joined entity. Upon
calculating the trust initiation, the script generates a
JSON wallet containing the user’s details, including
their trust value. Additionally, it creates a new node
within the blockchain, associating it with the user’s
username and trust value.
Upon successful entry into the community, the
script generates a permission token designed for the
public community. This token is generated using
PYjwt, a Python module for creating JWT tokens.
The token is then transmitted back to the threat
information-sharing demonstrator for delivery to the
user.
After successfully sending the response, the script
proceeds to hash the newly created wallet and add
it to verification ledgers. To verify this process,
blockchain logs are examined. It is observed that each
time a joining request is submitted, the Hyperledger
Sawtooth validator generates a public and private key
for the new user. Additionally, it creates a new block
containing the user’s trust value along with their pub-
lic key. Verification can also be confirmed by visit-
ing the rest-API address with the ”state,” where a new
batch containing the newly created user’s public key
and associated trust value, encrypted using the base-
64 cryptography algorithm, is evident.
6 VALIDATION AND TESTING
The testing results of the simulation will be illustrated
in this section. Six simulations were put to the test to
prove the work of the simulation scripts in the first
place and see the allure of the growth functions in the
second place. The graphs illustrated do not show real
values due to company data confidentiality.
Trust-Centric Blockchain Framework: A Three-Layered Architecture for Securing Open and Private Systems
1105

6.1 Entities Joining
This section presents the analysis of three graphs gen-
erated by blockchain entity joining simulation scripts.
The results provide valuable insights into the behav-
ior and performance of the blockchain system under
varying conditions.
*Data Size Per Node
The first graph (Fig 7. a) demonstrates the relation-
ship between the number of nodes and the size of wal-
lets (in bytes). The results exhibit a clear linear trend,
where each node contributes a predictable amount of
data to the system:
• At 1 node, the size of wallets is approximately 400
bytes.
• At 3 nodes, the size increases to around 1000
bytes.
• At 6 nodes, the size reaches approximately 1800
bytes.
This linear behavior indicates that the system is
scalable with respect to wallet data storage, as the data
size grows proportionally with the number of nodes.
*Blockchain Growth
The second graph (Fig 7. b) illustrates the total size
of the blockchain (in bytes) as new nodes are cre-
ated. Similar to the wallet size, the blockchain size
also grows linearly with the number of nodes:
• At 1 node, the blockchain size starts at around
5600 bytes.
• By 3 nodes, the size increases to approximately
5900 bytes.
• At 6 nodes, the blockchain size grows to about
6200 bytes.
This trend highlights the system’s ability to handle
continuous node creation without exponential growth
in data storage requirements, which is critical for scal-
ability and long-term maintenance.
*Node Creation Delay
The third graph (Fig 7. c) examines the delay asso-
ciated with node creation. Unlike the previous two
metrics, the delay exhibits fluctuations influenced by
external factors such as system load and network la-
tency:
• At 1 node, the delay is approximately 2.66 sec-
onds.
• At 2 nodes, it decreases slightly to 2.64 seconds.
• At 3 nodes, it increases to around 2.70 seconds
before fluctuating in subsequent nodes.
These variations suggest that node creation time is
not constant and depends on the system’s state and ex-
ternal conditions. This unpredictability could impact
performance in real-world applications, necessitating
further optimization to reduce delays and improve re-
liability.
The simulation results highlight the following:
• Scalability: The wallet size and blockchain
growth exhibit linear trends, confirming that the
system is scalable in terms of data storage as
nodes are added.
• Performance Challenges: The fluctuations in node
creation delay reveal potential challenges in sys-
tem performance, influenced by factors such as
network latency and processing efficiency. Ad-
dressing the variability in node creation de-
lay through optimization strategies can enhance
the overall reliability and responsiveness of the
blockchain system.
6.2 Transactions
This section presents an analysis of three performance
graphs generated by blockchain transaction simula-
tion scripts, offering insights into transaction delays
and data scalability.
*Transaction Creation Delays
The first graph ( Fig 8. a) illustrates the delays as-
sociated with the creation of individual transactions.
These delays are influenced by random transaction
amounts and data sizes. Key observations include:
• For a small number of transactions (e.g., 1 to 2
transactions), the delay is relatively low, approxi-
mately 2.64 seconds.
• At 3 transactions, the delay peaks at around 2.70
seconds, before fluctuating as more transactions
are added.
• The delay function demonstrates non-linearity,
with unpredictable spikes and dips caused by fac-
tors such as network latency, hardware conditions,
and the dynamic state of the system.
This variability highlights the challenges in pre-
dicting transaction creation times in real-world sce-
narios, emphasizing the need to account for under-
lying infrastructure when designing blockchain sys-
tems.
*Simultaneous Transaction Creation Delays
The second graph ( Fig 8. b) examines delays
in simultaneous transaction creation, where multiple
transactions are processed concurrently. Similar to
the previous graph:
• Delays range between 2.64 seconds and 2.70 sec-
onds, depending on the number of transactions.
• The graph shows irregular trends, reflecting the
impact of system congestion, network conditions,
BEST 2025 - Special Session on Blockchain and Enhanced Security for a New Era of Trust
1106
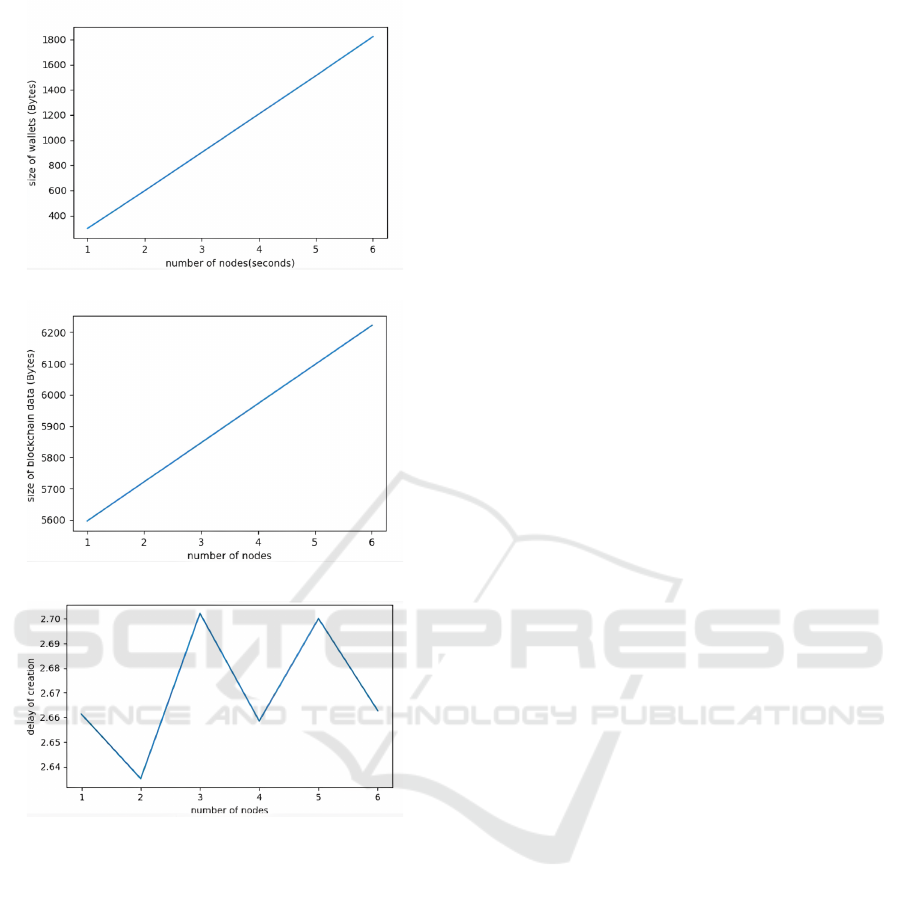
(a) Size of Wallets vs Number of Nodes.
(b) Size of Blockchain Data vs Number of Nodes.
(c) Creation Delay vs Number of Nodes.
Figure 7: Analysis of blockchain performance metrics: (a)
Size of wallets, (b) Size of blockchain data, (c) Delay in
creation.
and the computational overhead of simultaneous
operations.
Both the first and second graphs reveal that
transaction delay metrics exhibit non-linear behav-
ior, underscoring the need for further optimization in
blockchain implementations to reduce delay variabil-
ity and enhance performance.
*Transaction Data Size
The third graph ( Fig 8. c) depicts the total size of
transactions as the number of nodes increases. Un-
like the delay metrics, this graph follows a clear linear
trend:
• For 1 transaction, the data size starts at approxi-
mately 400 bytes.
• At 3 transactions, the size grows to around 1000
bytes, and by 6 transactions, it reaches approxi-
mately 1800 bytes.
This linearity indicates that the blockchain system ef-
ficiently manages transaction data growth, maintain-
ing predictable storage requirements as the number of
transactions increases. Such scalability is critical for
ensuring the system’s ability to handle larger transac-
tion volumes over time.
*Interpretation
The results from the simulation highlight key charac-
teristics of blockchain performance:
• Delay Metrics: Both individual and simultaneous
transaction creation delays exhibit non-linear be-
havior, influenced by external factors like network
latency and system state. This unpredictability
may impact system responsiveness and reliability,
calling for strategies to optimize performance.
• Scalability: The linear growth of transaction data
size demonstrates the system’s scalability, ensur-
ing predictable and manageable storage require-
ments even as transaction volumes increase.
These findings provide a comprehensive under-
standing of the blockchain system’s behavior, iden-
tifying areas for improvement in delay predictabil-
ity while affirming its scalability for future growth.
This analysis serves as a foundation for optimizing
blockchain performance in diverse applications.
6.3 Trust Level Evaluation
• Power consumption: According to information
from the Ehow.com website, the power consump-
tion of a server typically ranges from 500 to 1,200
watts per hour. This averages out to around 850
watts per hour. When considering a full day of
operation (24 hours), this equates to 20,400 watts
per day or 20.4 kilowatts (kW). Over the course
of a year (365 days), this amounts to 7,446 kWh,
based on data from the US Energy Information
Administration.
Taking into account the average commercial elec-
tricity cost in Germany, which is 0.0683 Euros per
kWh, the annual cost to power the server would be
approximately 542.94 Euros.
To make informed decisions about where to host
the threat information sharing system and mini-
mize power consumption costs, an investigation
was conducted by comparing the host server’s
power consumption to the typical usage of a
server. These statistics will guide the corporation
in choosing the most cost-effective hosting loca-
tion.
Trust-Centric Blockchain Framework: A Three-Layered Architecture for Securing Open and Private Systems
1107
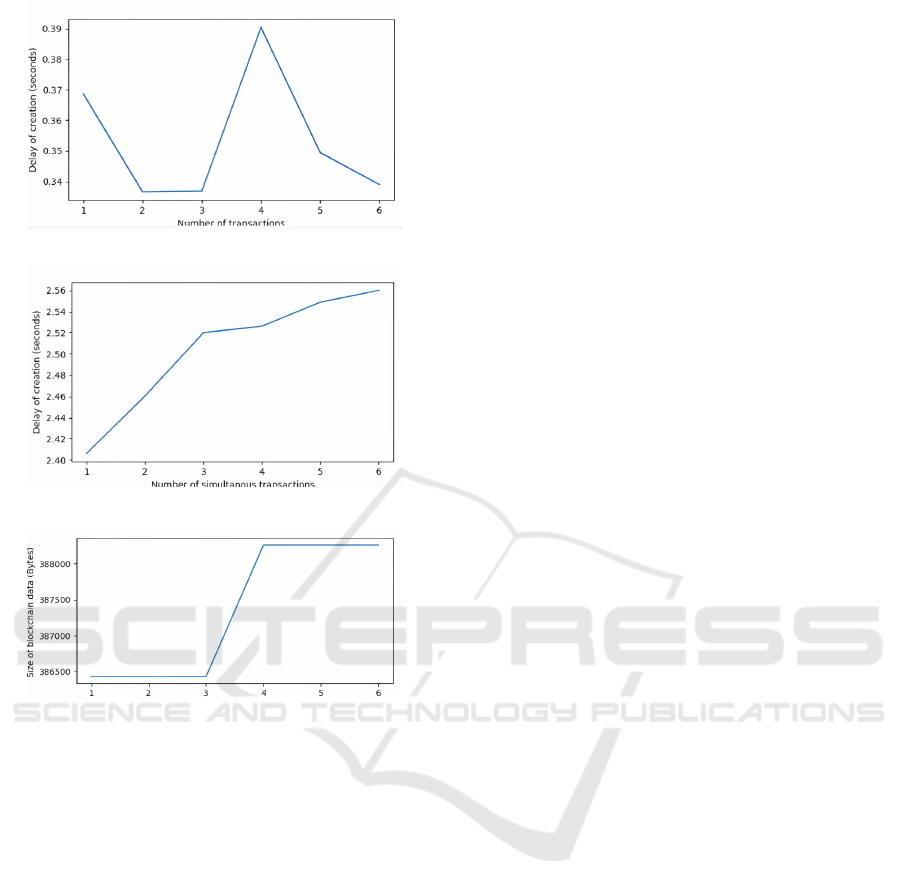
(a) Wallet Size (bytes) vs Transaction Numbers.
(b) Blockchain Size (bytes) vs Transaction Numbers.
(c) Node Creation Delay (seconds) vs Transaction
Numbers.
Figure 8: Performance analysis of blockchain metrics: (a)
Wallet size, (b) Blockchain size, (c) Node creation delay, all
as a function of transaction numbers.
• Scalability investigations: To gain a comprehen-
sive understanding of the scalability challenges
faced by blockchain systems, it’s instructive to
delve into the early days of Bitcoin’s operation.
Bitcoin, while a relatively simple blockchain with
a specific use case—sending and receiving digi-
tal currency—experienced scalability issues right
from its inception. The core problem revolved
around ensuring that this decentralized network
could effectively manage a continually increas-
ing user base. This challenge can be likened to a
fundamental computer networking dilemma: the
available bandwidth to process transactions is fi-
nite. Furthermore, each user must validate trans-
actions by referencing the blockchain records, a
process that demands a certain amount of storage
space.
To address this, simulations were conducted to
scale up the number of system entities and trans-
action volumes by deploying millions of them.
This simulated state represents the potential con-
dition of this trust-based blockchain in the years
to come. Subsequently, the system was set
into motion, and all prior simulations were re-
run to calculate updated statistics and observe the
blockchain’s performance on a larger scale. The
aim of this simulation is to provide the organiza-
tion with valuable insights into what can be an-
ticipated after years of blockchain growth. These
insights will enable the organization to formulate
an effective strategy to preemptively address any
impending challenges.
• Trust and reputation management model investi-
gation: The trust model, which is currently un-
der development and not in its final form, will un-
dergo a series of simulations to assess its func-
tionality comprehensively. These simulations will
rigorously test all aspects and values related to
trust. To ensure robustness, organizations in-
volved will identify potential attacks that could
impact the trust and reputation management sys-
tem and subsequently simulate these scenarios
once the system is deployed. The outcome of
these simulations will inform the refinement of
mathematical formulas and weightings within the
trust model of the threat information-sharing sys-
tem. This phase is deemed the most critical sim-
ulation within the entire project, and the organi-
zation has determined that it warrants a separate,
dedicated project for its execution.
7 DISCUSSION
This study sheds light on the challenges and limita-
tions associated with integrating a blockchain-based
trust architecture into threat information-sharing plat-
forms. While the proposed system demonstrates
promise in addressing key issues such as trust man-
agement and data integrity, several limitations were
identified during simulations and security assess-
ments. One significant limitation is the vulnerability
of the system when the proportion of malicious enti-
ties within the network exceeds 50
Another challenge lies in the computational and
storage overhead associated with the implementation.
Blockchain inherently requires significant resources
to maintain an immutable ledger, which becomes in-
creasingly demanding as the system scales. This lim-
itation could hinder its deployment in environments
with limited infrastructure or when handling large
volumes of transactions and data. Furthermore, la-
BEST 2025 - Special Session on Blockchain and Enhanced Security for a New Era of Trust
1108

tency issues observed in the simulations indicate that
the system may face delays during peak operational
periods, which could affect its responsiveness and us-
ability in real-world scenarios. The trust model, while
effective in many cases, also requires refinement to
address sophisticated attacks that attempt to manipu-
late reputation scores or exploit vulnerabilities in the
penalty mechanisms.
Despite these limitations, the system represents a
robust framework for enhancing trust and security in
both private and public architectures. By combining
blockchain with trust modeling and penalty mecha-
nisms, the architecture provides a comprehensive so-
lution for managing and securing shared information.
However, addressing the identified shortcomings is
essential to ensure its effectiveness and scalability in
diverse operational environments.
8 CONCLUSION AND
PERSPECTIVES
This paper presents an emergent approach to address-
ing the growing challenges of cybersecurity by intro-
ducing a blockchain-based trust architecture for pub-
lic and private architectures. The study builds upon
the inherent strengths of blockchain, such as decen-
tralization and immutability, and combines them with
a trust model and penalty mechanisms to create a
multi-dimensional security solution. The proposed
system effectively addresses the needs of both private
and public architectures, ensuring trust and account-
ability among participants while maintaining data in-
tegrity and resilience.
The work highlights the pressing need for robust
cybersecurity solutions in the face of increasingly so-
phisticated threats. By leveraging blockchain and
trust modeling, the proposed architecture represents
a significant step forward in securing shared threat in-
formation. Extensive simulations and security evalu-
ations confirm its potential to enhance system relia-
bility and scalability.
In our future work, to continue advancing this field
and addressing the ever-evolving cybersecurity land-
scape, we will explore methods to improve the scal-
ability and performance of blockchain networks for
handling large volumes of threat information while
maintaining efficiency. Future work in these areas can
contribute to the ongoing improvement and effective-
ness of blockchain-based trust and reputation systems
for threat information sharing, ultimately strengthen-
ing cybersecurity defenses and reducing the impact of
cyberattacks on organizations and society as a whole.
REFERENCES
Badsha, S., Vakilinia, I., and Sengupta, S. (2020).
Blocynfo-share: Blockchain based cybersecurity in-
formation sharing with fine grained access control. In
10th Annual Computing and Communication Work-
shop and Conference (CCWC), Las Vegas, NV, USA.
[Specify Publisher Here].
Bandara, E., Liang, X., Foytik, P., and Shetty, S. (2021).
Blockchain and self-sovereign identity empowered
cyber threat information sharing platform. In Confer-
ence on [Specify Conference Name Here], Irvine, CA,
USA. [Specify Publisher Here].
Bennaceur, J., Zouaghi, W., Hammouda, I., and mabrouk,
A. (2020). Composite multi-dimensional trust-based
schemes for threat information sharing.
Bennaceur, J., Zouaghi, W., Hammouda, I., and Mabrouk,
A. (2025). Multi-dimensional trust model: Towards
multi-layered secure architecture for enhanced threat
information sharing. Journal of Systems Science and
Systems Engineering, pages 1–29.
Chowdhury, M. J. M., Ferdous, M. S., Hoque, M. A., and
W.Colman, A. (2016). Blockchain consensus algo-
rithms: A survey. Online.
Fathi, Z., Rafsanjani, A. J., and Habibi, F. (2020). Anon-
isac: Anonymity-preserving cyber threat information
sharing platform based on permissioned blockchain.
In 28th Iranian Conference on Electrical Engineering
(ICEE), Tabriz, Iran. [Specify Publisher Here].
Gil, S., Mikkelsen, P. H., Gomes, C., and Larsen, P. G.
(2024). Survey on open-source digital twin frame-
works–a case study approach. Software practice and
experience, 54(6):929–960.
Hou, F. and Jansen, S. (2023). A systematic literature re-
view on trust in the software ecosystem. Empirical
Software Engineering, 28(8).
Mohaisen, A., Al-Ibrahim, O., Kamhoua, C., Kwiat, K.,
and Njilla, L. (2017). Assessing quality of contri-
bution in information sharing for threat intelligence.
In IEEE Symposium on Privacy-Aware Computing
(PAC). IEEE.
Z., Y., K., Y., L., L., K., Z., and Leung (2018). Blockchain-
based decentralized trust management in vehicular
networks. Online.
Zheng, Z., Xie, S., Dai, H., Chen, X., and Wang, H. (2017).
An overview of blockchain technology: Architecture,
consensus, and future trends. In IEEE International
Congress on Big Data (BigData Congress). IEEE.
Trust-Centric Blockchain Framework: A Three-Layered Architecture for Securing Open and Private Systems
1109
