
Assessing the Attention Layers in Convolutional Neural Networks for
Penile Cancer Detection in Histopathological Images
Joana Kuelvia de Ara
´
ujo Silva
a
, Geraldo Braz J
´
unior
b
, Anselmo Cardoso de Paiva
c
,
Italo Francyles Santos da Silva
d
and Alexandre C
´
esar Pinto Pessoa
e
N
´
ucleo de Computac
˜
ao Aplicada, Universidade Federal do Maranh
˜
ao (UFMA), S
˜
ao Lu
´
ıs, MA, Brazil
Keywords:
Penile Cancer, Histopathological Images, Convolutional Neural Networks, Attention Mechanisms.
Abstract:
Penile cancer, with its high incidence in Brazil, stands out due to the need for early diagnosis and avoiding in-
vasive surgical procedures with physical and psychological implications. Although histopathological analysis
is the standard approach, its complexity and delay motivate the search for faster and more accurate alternatives
to aid the process. This study proposes a methodology for classifying penile cancer in histopathological im-
ages using Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) coupled with Attention Mechanisms. Experiments were
conducted using a data set of 194 samples at magnifications of 40× and 100×. As a result, the method achieved
an accuracy of 95% for cancer detection.
1 INTRODUCTION
Cancer, a condition characterized by the uncontrolled
growth of cells in the body, is a global concern as it
is one of the leading causes of death worldwide, re-
sponsible for an average of 9 million deaths in 2022
(World Health Organization, 2024), with an estimated
increase in mortality by over 2 million by 2030 (In-
ternational Agency for Research on Cancer, 2024).
Developing countries have a significant incidence of
various types of cancer. In this context, penile cancer
emerges as a particular concern, accounting for ap-
proximately 20% of malignant diseases in men (Paner
et al., 2018). In Brazil, the rates are high, especially in
the Northern and Northeastern regions, with the state
of Maranh
˜
ao having the highest occurrence, approxi-
mately 6.1 cases per 100,000 inhabitants (Vieira et al.,
2020).
Among the main risk factors associated with the
development of the disease are the presence of a fore-
skin, accumulation of smegma, phimosis, lack of hy-
giene, tobacco exposure, and human papillomavirus
(HPV) infections (Bleeker et al., 2009; Rosas et al.,
2021). Diagnosis, in most cases, is established at ad-
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0004-2216-357X
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3731-6431
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4921-0626
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2041-7538
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4995-8909
vanced stages of the condition, leading to often inva-
sive treatments that have profound physical and psy-
chological effects on patients, commonly resulting
in a reluctance to continue with treatment and dis-
ease monitoring within the healthcare setting (Fon-
seca et al., 2010; Gomes et al., 2019).
Assessing cancer prognosis usually requires the
collaboration of professionals from different special-
ties. For a more in-depth analysis, invasive methods
are conducted. These examinations involve taking
biopsies from the tissue area to obtain detailed infor-
mation about the lesion. The analysis of histopatho-
logical images evaluates the histopathological and
molecular characteristics of the disease (Hunt et al.,
2008). Despite being an essential tool, the interpreta-
tion of histopathological analysis remains a challenge,
even for experienced pathologists.
In this scenario, deep learning models, such as
convolutional neural networks (CNNs), have shown
remarkable progress in classification tasks, achieving
great success in computer vision (Shorten and Khosh-
goftaar, 2019). They can automatically learn discrim-
inative characteristics of images through convolution
layers, enabling the detection of subtle patterns that
may escape human observation, including histopatho-
logical images (Shin et al., 2016). Recently, the appli-
cation of attention mechanisms in deep learning mod-
els has allowed the models to focus on specific regions
of the images, highlighting areas of interest that may
be crucial for identifying (Zhang et al., 2023) patterns.
654
Silva, J. K. A., Braz Júnior, G., Cardoso de Paiva, A., Santos da Silva, I. F. and Pessoa, A. C. P.
Assessing the Attention Layers in Convolutional Neural Networks for Penile Cancer Detection in Histopathological Images.
DOI: 10.5220/0013472900003929
In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2025) - Volume 1, pages 654-661
ISBN: 978-989-758-749-8; ISSN: 2184-4992
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

By incorporating these mechanisms into CNNs, sen-
sitivity in detecting relevant features has been signif-
icantly improved, contributing to more accurate diag-
noses.
Given the importance of efficient diagnosis, this
work aims to classify penile histopathological images
as those of a patient with a tumor or a healthy pa-
tient using CNN models with attention mechanisms.
Section 2 presents the work related to the study. Sec-
tion 3 describes the proposed methodology. Section
4 presents the experiments and results obtained. Fi-
nally, Section 5 discusses the conclusions of the work.
2 RELATED WORK
Recent analysis of histopathological images has ben-
efited from advances in machine learning techniques,
especially convolutional neural networks (CNNs),
which classify and detect patterns in medical images.
They also highlight the role of attention mechanisms
in optimizing the results of histopathological image
classification models (Brancati et al., 2021). This sec-
tion examines the research and studies that served as
a reference for developing the proposed method for
classifying cancers from histopathological images us-
ing convolutional neural networks (CNNs) combined
with attention mechanisms.
Chen et al. (Chen et al., 2022b) present a
multiscale visual transformer model, called GasHis-
Transformer, for detecting gastric histopathology im-
ages. It consists of an architecture that combines
blocks inspired by the Bot-Net with residual blocks,
incorporating an attention layer between the convolu-
tional ones to enhance the features along the network.
It has two main modules designed to extract global
and local information using a position-coded trans-
former model and a convolutional neural network
with local convolutions. In addition, a lightweight
network based on the Dropconnect strategy is pro-
posed to reduce its size and training time, making
it more suitable for clinical applications with greater
confidence.
In (Chen et al., 2022a), the IL-MCAM frame-
work was proposed, combining multichannel atten-
tion mechanisms and interactive learning to classify
histopathological images of colorectal cancer. It in-
cludes two phases: Automatic Learning (AL), in
which a multichannel attention mechanism model ex-
tracts multichannel features using convolutional neu-
ral networks, and Interactive Learning (IL), in which
misclassified images are continuously added to the
training set to improve the model’s classification abil-
ity. The experiments carried out obtained classifica-
tion accuracies of 98.98% and 99.77%, respectively.
The results indicate that the framework performs ex-
ceptionally well in classifying histopathological im-
ages of colorectal cancer.
In recent research, a CBAM-VGGNet model was
proposed to classify breast histopathology images,
in which the CBAM (Convolutional Block Attention
Module) is integrated into the network to highlight
crucial features (Ijaz et al., 2023). The results strongly
suggested that CBAM-VGGNet outperformed state-
of-the-art models, achieving an impressive accuracy
of 98.96% and an F1-Score of 97.95% when tested
on 400x BreakHis images. This remarkable perfor-
mance suggests that the addition of the CBAM atten-
tion module contributed significantly to improving the
model’s accuracy and classification capabilities.
On the other hand, when it comes to classify-
ing histological images of penile cancer, studies are
scarce. A pioneering study (Lauande et al., 2022) de-
veloped a method using the DenseNet-201 network
with pre-trained weights to classify images as healthy
or not, Achieving exceptional results. with an F1-
Score of 97.39% for images at 40× magnification
and 97.31% for 100× magnification. Using the same
database as the study above, (Belfort et al., 2023) used
the cascade CNN approach incorporating the Soft-
Attention mechanism to weight relevant image char-
acteristics. Experiments carried out at magnifications
of 40× and 100× show that the method achieves accu-
racies of 93% and 90%, respectively.
Thus, considering the limitations and proposals
for improvement identified in the aforementioned
studies, this work proposes a comprehensive in-
vestigation of the performance of different convo-
lutional neural network architectures with attention
mechanisms in the classification of penile cancer in
histopathological images to explore networks that can
offer a more favourable cost-computational ratio. In
doing so, we aim to contribute not only to advances in
the diagnosis of penile cancer but also to the develop-
ment of more effective and economically viable ap-
proaches to the analysis of histopathological images
in general.
3 METHODOLOGY
The methodology adopted in this study consists
of evaluating the construction of three specialized
networks for diagnosing penile cancer based on
histopathological images (see Fig. 1). In the first
phase, the images were obtained from the database
of the [blind review] Project and the images were
pre-processed. The next stage proposes three mod-
Assessing the Attention Layers in Convolutional Neural Networks for Penile Cancer Detection in Histopathological Images
655
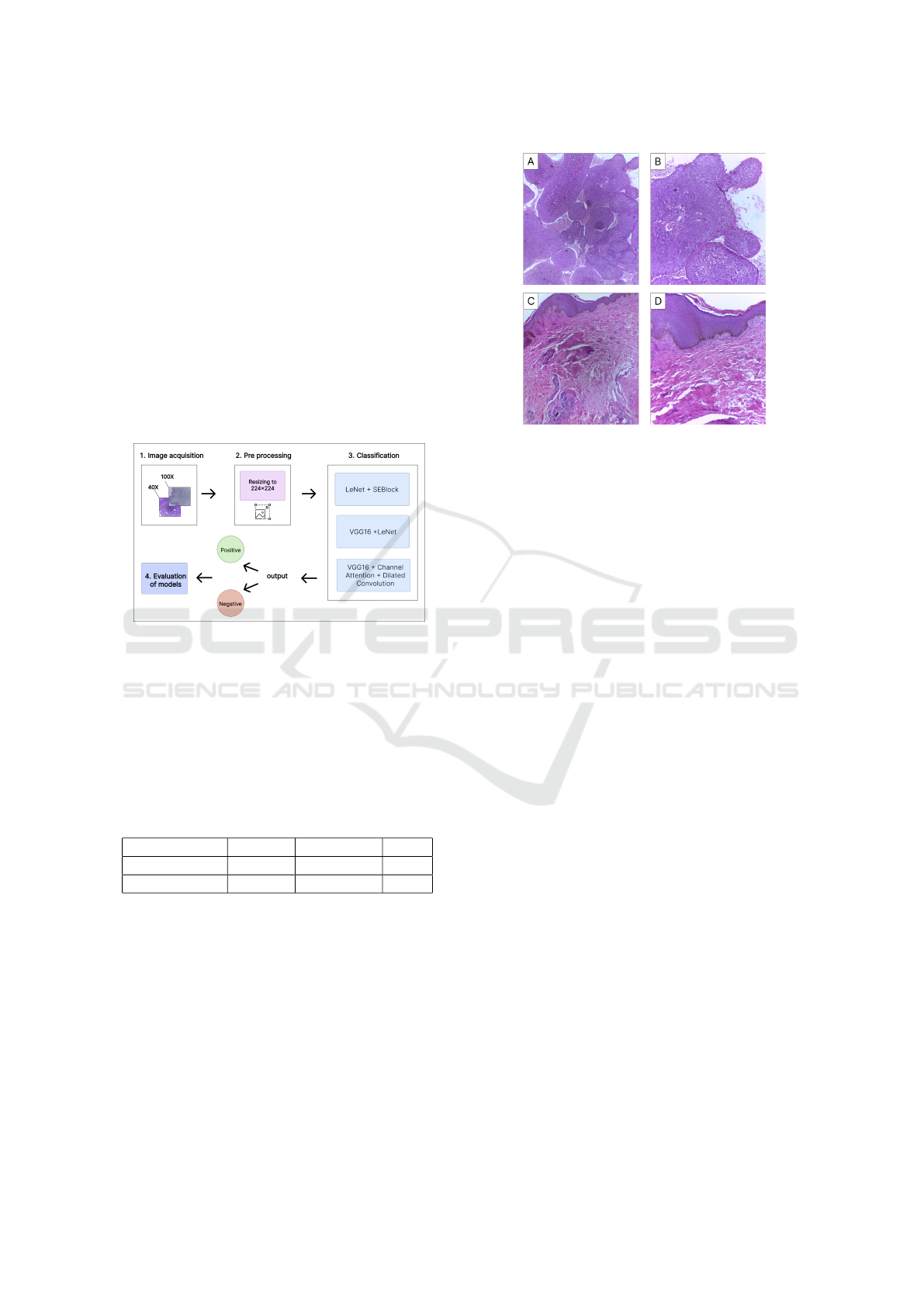
els based on the LeNet and VGG16 architectures,
each with specific modifications to improve per-
formance. LeNet-SE integrates the Squeeze-and-
Excitation block after the second convolution block.
VGG16 with LeNet combines features extracted by
the VGG16 architecture with important information
from LeNet, using an attention mechanism to calcu-
late the weights and improve the final representation
of the image. A VGG16 with an additional layer of
channel attention that helps highlight the importance
of the different channels in the convolutional layers.
In addition, a dilated convolution layer widens the re-
ceptive field to capture more extensive contextual in-
formation. Subsequently, the models are trained and
tested on a set of test data, and the results are evalu-
ated in the last phase of the methodology.
Figure 1: Proposed methodology.
3.1 Base Acquisition and pre-processing
The image database used for this study was developed
by the [blind review] Project This database consists
of 194 RGB images with a resolution of 2048x1536
pixels, as shown in Table 1.
Table 1: Distribution of images according to pathological
classification and magnification.
Magnification Tumour Non-tumor Total
40X 56 41 97
100X 41 56 97
During the pre-processing phase, the input images
were first resized to 224×224 due to computational
limitations and then normalized, which is essential
to ensure that the pixel values are on a standardized
scale between 0 and 1. This helps stabilize the model
training and reduces variability in the data, making
the model more robust and less sensitive to variations
in pixel intensities. Examples of images in the dataset
(see Fig. 2).
Figure 2: Examples of histopathological images of penile
cancer by category and enlargement; A tumor 40x; B tumor
100x; C non-tumor 40x; D non-tumor 100x.
3.2 Classification
3.2.1 LeNet-SE
LeNet-SE, shown in Figure 3, is an architecture based
on LeNet (Lecun et al., 1998), one of the first pub-
lished CNNs that gained prominence due to its perfor-
mance in computer vision tasks (Zhang et al., 2023).
It comprises seven layers, each playing a specific role
in feature extraction and image classification. The
first two convolution layers identify the input im-
ages’ edges, contours, and textures. The downsam-
pling layers reduce the extracted features’ size, help-
ing simplify the process. The second convolution and
downsampling layer continues this process, looking
for more abstract features. The two fully connected
layers are responsible for classifying the images into
different categories, while the output layer, a sigmoid
layer, provides the probabilities of each class.
The “SE”(Squeeze-and-Excitation) component
added to LeNet after the second convolution layer
refers to a specific attention technique elaborated by
(Hu et al., 2017), which aims to improve the net-
work’s ability to learn and emphasize essential fea-
tures by adaptively adjusting the characteristics of im-
ages at the channel level and modelling the interde-
pendence between them. In addition, the addition of
SE blocks improves the performance of CNNs with-
out severely compromising computational efficiency.
The term “Squeeze” indicates the compression or
reduction of the dimensionality of spatial informa-
tion. In this process, the global characteristics are
condensed into a vector, providing a more compre-
hensive view of the information present in the im-
age, carried out by Global Average Pooling (GAP).
ICEIS 2025 - 27th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
656
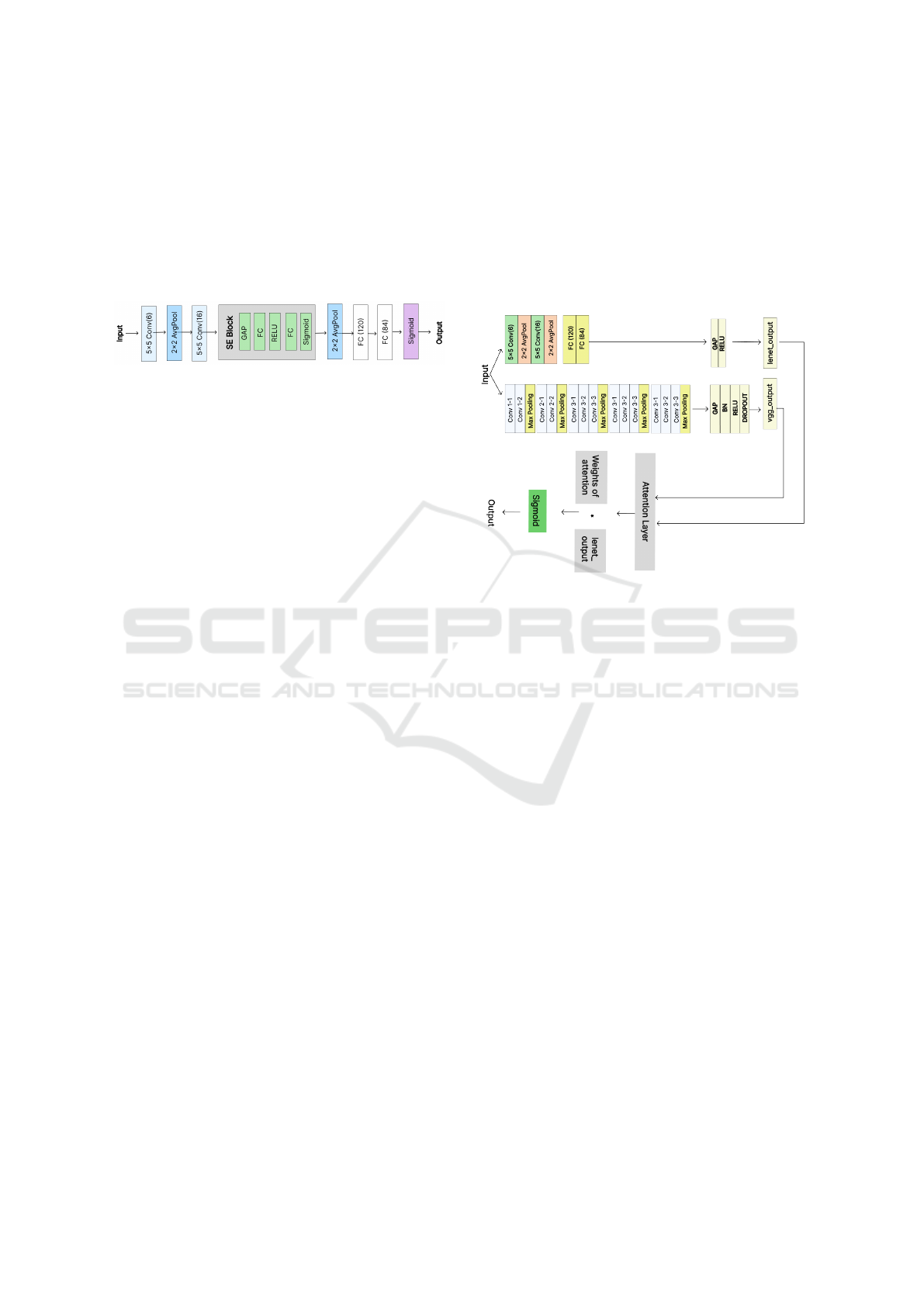
The term “Excitation” refers to the stage in which
the information is recalibrated to give more weight to
the most relevant parts, carried out through two dense
blocks, which learn to weigh each channel based on
its relevance to the task. These layers include dimen-
sionality reduction operations followed by non-linear
activations, such as ReLU, and a sigmoid layer to nor-
malize the weights between 0 and 1.
Figure 3: LeNet-SE Architecture.
3.2.2 VGG16 with LeNet
In this other model, illustrated in Figure 4, the el-
ements of the VGG16 and LeNet architectures are
combined through an attention layer.
The VGG16 model has 13 convolutional layers
and three fully connected layers, using the ReLU ac-
tivation function between them (Simonyan and Zis-
serman, 2014). Thus, the first part of the network
uses it as a basis for feature extraction. In this case,
it is configured without the final fully connected lay-
ers, allowing features to be extracted and used more
flexibly. In this work, the following modifications
were proposed: to reduce dimensionality and pro-
vide a more compact representation of the extracted
features, a fully connected layer (FC) is added with
ReLU activation, followed by batch normalization,
dropout and another fully connected layer. Introduc-
ing dropout aims to mitigate overfitting during train-
ing, helping the model generalize.
The second part of the network incorporates the
LeNet architecture as a complementary approach to
feature extraction. LeNet is useful for identifying
simpler and more localized patterns. The LeNet out-
put is resized to have the same dimensions as the out-
put of VGG16, preparing it for fusion.
Next, an attention layer was proposed to calculate
the attention weights between the output of VGG16
and LeNet. It learns which parts of the features ex-
tracted by VGG16 are most relevant to the task when
combined with the features extracted by LeNet. The
calculated attention weights are used to weight the
LeNet features. This is done by pointwise multiply-
ing the LeNet features by their respective weightings,
using a Multiply layer (Chollet et al., 2015)
In the classification layer, the fused and weighted
features are fed into a classification layer, which is a
dense layer with a single output, activated by a sig-
moid function to generate a continuous output vary-
ing between 0 and 1. This is commonly used in bi-
nary classification problems, where the output indi-
cates the probability of an image belonging to a par-
ticular class.
This architecture aims to explore and combine
features learned at different levels of abstraction, al-
lowing the model to discern discriminative patterns in
histopathological images. This contributes to better
generalization ability and performance on the classi-
fication task.
Figure 4: VGG16 with LeNet Architecture.
3.2.3 VGG16 with Channel Attention and
Dilated Convolution
This proposed model, shown in Figure 5, is an exten-
sion of the VGG16 architecture, which includes two
elements to increase the feature extraction capability
of the network: the channel attention layer that allows
the network to highlight the importance of different
channels in the convolutional layers and the inclusion
of dilated convolution that provides a significant gain
by expanding the receptive field, favouring the net-
work to incorporate broader contextual information
without increasing computational load.
After the first two convolutional blocks, a channel-
type attention mechanism is applied. In this case,
the attention is calculated globally over all the feature
channels of the last convolutional layer. This is done
by calculating the global mean of the features and ap-
plying two fully connected layers to learn the relative
importance of each channel.
Then, after the third block of conventional con-
volutions from VGG16, the last two convolutional
blocks are replaced by dilated convolutions. Dilated
convolution provides a significant gain by expanding
the receptive field, allowing the network to incorpo-
rate broader contextual information without increas-
ing computational load. This is achieved by introduc-
ing a dilation rate parameter in the convolution opera-
Assessing the Attention Layers in Convolutional Neural Networks for Penile Cancer Detection in Histopathological Images
657
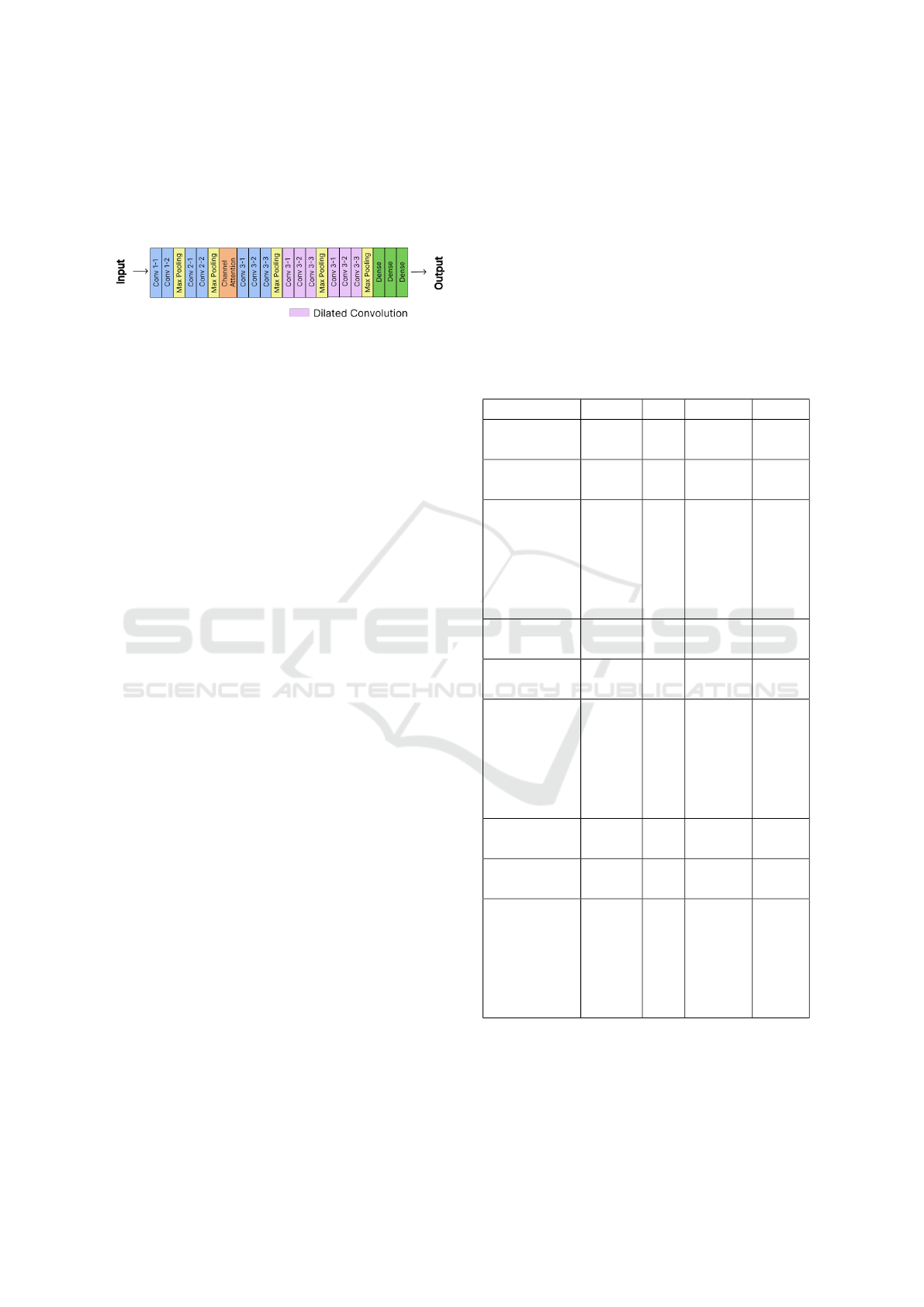
tion, which controls the spacing between the weights
of the convolution mask.
These combined improvements enhance the net-
work’s ability to capture broader contextual informa-
tion and highlight relevant features.
Figure 5: VGG16 with Channel Attention and Dilated Con-
volution Architecture.
4 EXPERIMENTS AND RESULTS
This section provides detailed information about the
experiments conducted, including the configuration
of the computing environment and the libraries used.
In addition, we present the results achieved using the
proposed approaches. All the implementations are
carried out using the Keras(Chollet et al., 2015) and
Tensorflow (Abadi et al., 2016) frameworks, with the
implementation of a patience callback equal to 5 to
prevent training without progress. The optimizer used
is Adam (Kingma and Ba, 2014), with the loss func-
tion being Cross Entropy (DeBoer et al., 2005). The
sigmoid function, generally used in binary classifica-
tion problems (Gaio, 2022), is adopted in this work.
The metrics used to assess performance in the
model evaluation stage include accuracy, recall, f1-
score, and precision. Further details and specific re-
sults for each stage will be presented sequentially.
Of the total of 194 images in the database, 97 were
used, according to Table 1, for each of the two mag-
nifications. The distribution of these images followed
the proportion of 60% for training, 20% for valida-
tion, and 20% for testing, resulting in 57 images des-
tined for training, 20 for validation, and 20 for test-
ing, respectively, for each magnification, already for
the experiments done on the complete dataset with
the two magnifications, the same previous distribution
was made, with 141 images designated for training,
36 for validation and 16 for testing. The data augmen-
tation technique, known as data augmentation, was
employed to expand the training set in both phases of
the method. The applied operations included vertical
and horizontal inversions and rotations in the range of
0° to 160°.
In this phase, three neural networks integrated
with attention mechanisms were tested: LeNet with
SE, VGG16 with LeNet and VGG16 with channel at-
tention and dilated convolution. The networks were
trained on nine hold-outs over 30 epochs each, using
a batch size 32. The final result is determined by the
average of the metrics calculated throughout all hold-
outs. This procedure provides a consolidated view of
the model’s performance, considering the variability
of the test sets used in each iteration.
However, the relatively small number of images
may impact the training of convolutional neural net-
works. In this study, we opted to work with a limited
dataset due to the difficulty in obtaining high-quality
medical images classified by experts. The decision to
use 194 images was based on practical considerations
and the availability of the dataset.
Table 2: Results obtained by the methods proposed in the
penile cancer classification stage.
Model Accuracy Recall Precisionn F1 Score
LeNet+SE
(40X/100X)
0.82 0.82 0.85 0.82
VGG16 + LeNet
(40X/100X)
0.91 0.90 0.91 0.90
VGG16 +
Channel
Attention
+ Dilated
Convolution
(40X/100X)
0.92 0.90 0.91 0.90
LeNet+SE
(40X)
0.91 0.91 0.91 0.90
VGG16 + LeNet
(40X)
0.86 0.88 0.88 0.88
VGG16 +
Channel
Attention
+ Dilated
Convolution
(40X)
0.87 0.87 0.86 0.86
LeNet+SE
(100X)
0.95 0.93 0.95 0.93
VGG16 + LeNet
(100X)
0.87 0.90 0.87 0.88
VGG16 +
Channel
Attention
+ Dilated
Convolution
(100X)
0.95 0.93 0.95 0.94
Table 2 shows the results obtained from the ex-
periments carried out for this stage of the proposed
method. In the tests with 40X magnification, the
LeNet + SE network presented one of the best results,
with an accuracy of 0.91. The VGG16 with Channel
ICEIS 2025 - 27th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
658
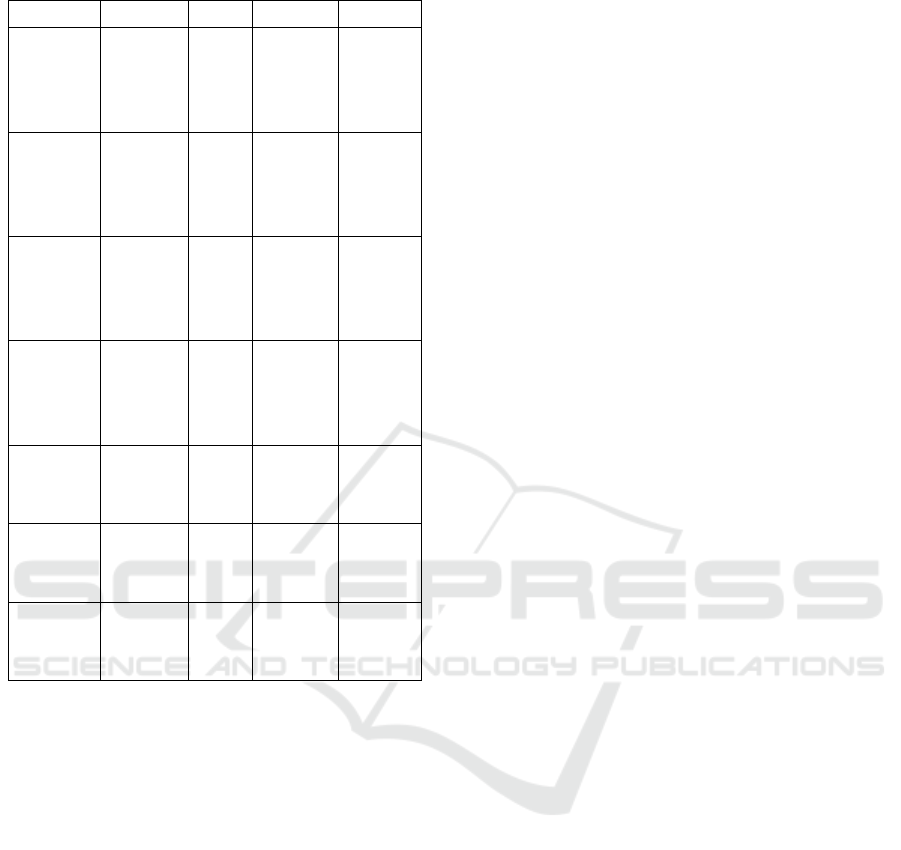
Table 3: Comparison with related models.
Model Accuracy Recall Precision F1 Score
Lauande
et al.
(2022)
40X
96.89
±2.5
98.33
±3.3
96.67
±4.0
97.39
±2.1
Lauande
et al.
(2022)
100X
96.84
±4.2
98.18
±3.6
96.52
±4.2
97.31
±3.6
Belfort
et al.
(2023)
40X
88.60
±3.1
95.80
±7.7
89.40
±3.3
92.40
±1.5
Belfort
et al.
(2023)
100X
91.20
±1.4
97.60
±5.6
88.4
±3.3
92.40
±2.3
Proposed
Model
40X
91.66
±4.4
91.11
±5.0
91.55
±3.5
90.44
±5.0
Proposed
Model
100X
95.71
±4.1
93.87
±6.1
95.43
±3.0
94.06
±5.1
Proposed
Model
40X/100X
92.00
±4.0
90.81
±4.1
91.87
±5.1
90.68
±4.1
Attention and Dilated Convolution stood out in the
tests with 100X and 40X magnification and also only
with 100X, achieving an accuracy of 0.92 and 0.95,
respectively.
Table 3 shows a comparison with related work.
These are the proposal that uses data augmenta-
tion and image pre-processing using a DenseNet-201
network (Lauande et al., 2022) and the experiment
(Belfort et al., 2023) which uses the DenseNet-121
network with Self-Attention. The proposed models
are the ones that obtained the best results in the ex-
periments; at 40X magnification, it was LeNet + SE,
and both at 100x and in the complete dataset at 40X
and 100X, it was VGG16 with channel attention and
dilated convolution. The authors also use the same
database as this work.
The results show that although the related mod-
els were trained with a more complex network,
DenseNet-201 and DenseNet-121, the proposed mod-
els have very similar values in various metrics eval-
uated with less complexity since VGG16 and Lenet
have 16 and 7 layers, respectively. In the proposed
model, at 100X magnification, we observed an accu-
racy of 95.71 ± 4.1, while in the model by Lauande
et al., the accuracy is 96.8 ± 4.2, and in the model, by
Belfort et al., we have 91.2 ± 1.4. At 40X magnifica-
tion, Lauande et al. achieved 96.8 ± 2.5; Belfort et al.
achieved 88.8 ± 3.1 and the proposed model is 91.6 ±
4.4.
It is essential to highlight that, even with poten-
tially lower complexity, the proposed models achieve
comparable or superior results to those obtained with
more complex networks, such as DenseNet-121 and
DenseNet-201. For example, VGG16 and LeNet,
used in the proposed models, have fewer layers than
DenseNets. This suggests that the approach adopted
can be more efficient and less complex regarding
network architecture, demonstrating the viability and
robustness of the proposed models relative to more
complicated alternatives.
The F1 score, a metric that combines precision
and recall, shows approximate results. At 40X mag-
nification, Lauande et al., Belfort et al. and the pro-
posed model, respectively, register 97.3 ± 2.1, 92.4 ±
1.5 and 90.4 ± 5.0, which indicates a close correspon-
dence of the results; and for 100x magnification, they
register 97.3 ± 3.6, 92.4 ± 2.3 and 94.0 ± 5.1, with
the proposed model showing slightly more expressive
results than the Belfort et al. model.
When observing recall, we note that all models
show relatively high standard deviations, especially
at 100X magnification. Model Lauande et al. has a
superior recall of 98.3, Model Belfort et al. records
97.60, and Proposed Model is 93.8. At 40X magnifi-
cation, the standard deviations are lower.
In summary, the results indicate that the perfor-
mance of the model proposed in this study is compa-
rable to that of related models, given that less com-
plex networks are used, LeNet and VGG16, with the
addition of the attention mechanism for training. One
of the proposed models also showed exemplary per-
formance with promising results. The implementa-
tion without dividing the magnification proved to be
effective, as in the other models, where the training,
test and validation sets were divided into two magni-
fications (40x, 100x).
5 CONCLUSIONS
This study proposes a method for classifying penile
cancer using CNNs with attention mechanisms in
histopathological images. This method is divided into
distinct stages. The images were resized and normal-
ized in the first stage to suit the available computing
resources. Then, in the second stage, classification
was carried out using the VGG16 and LeNet base net-
Assessing the Attention Layers in Convolutional Neural Networks for Penile Cancer Detection in Histopathological Images
659

works, both approaches using attention mechanisms.
These networks were trained individually at 40x and
100x magnification and at a combination of the two
magnifications. The results obtained were promising,
showing the effectiveness of using the attention mech-
anism integrated into the VGG16 and LeNet networks
to improve classification performance, with the best
performance achieved by VGG16 with channel atten-
tion and dilated convolution.
The evaluation metrics showed satisfactory results
for training configurations, demonstrating the viabil-
ity of the proposed method for classifying penile can-
cer in histopathological images. For 40× magnifica-
tion images, the accuracy of 91%, the precision of
91%, recall of 90%, and F1-Score of 90% were ob-
tained. The following values were obtained for the
100× magnification images: 95% accuracy, 95% pre-
cision, 93% recall and 94% F1-Score. Finally, when
combining the 40X and 100X images, the model
achieved an accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-Score
of 92%, 91%, 90%, and 90%, respectively.
The results found, however, suggest opportuni-
ties for further advances. In future work, we plan
to explore the application of the attention mechanism
in other convolutional neural network architectures,
such as those of the ResNet and EfficientNet family
(He et al., 2016; Tan and Le, 2019). In addition, we
will consider the use of other attention models based
on Vision Transformer (Dosovitskiy et al., 2021) such
as attention based on multiple heads (Vaswani et al.,
2017) or Data-efficient image Transformers (DeiT)
(Touvron et al., 2021), recommended for experiments
with smaller amounts of data.
REFERENCES
Abadi, M., Barham, P., Chen, J., Chen, Z., Davis, A., Dean,
J., Devin, M., Ghemawat, S., Irving, G., Isard, M.,
Kudlur, M., Levenberg, J., Monga, R., Moore, S.,
Murray, D. G., Steiner, B., Tucker, P., Vasudevan,
V., Warden, P., Wicke, M., Yu, Y., and Zheng, X.
(2016). Tensorflow: a system for large-scale machine
learning. In Proceedings of the 12th USENIX confer-
ence on Operating Systems Design and Implementa-
tion (OSDI’16), pages 265–283.
Belfort, F., Silva, I., Silva, A., and Paiva, A. (2023).
Detecc¸
˜
ao de c
ˆ
ancer peniano em imagens histopa-
tol
´
ogicas usando redes neurais convolucionais em cas-
cata. In Anais do XXIII Simp
´
osio Brasileiro de
Computac¸
˜
ao Aplicada
`
a Sa
´
ude, pages 328–339.
Bleeker, M., Heideman, D., Snijders, P., Horenblas, S., Dill-
ner, J., and Meijer, C. (2009). Penile cancer: epidemi-
ology, pathogenesis and prevention. In World Journal
of Urology, volume 27, pages 141–150.
Brancati, N., Pietro, G. D., Riccio, D., and Frucci, M.
(2021). Gigapixel histopathological image analysis
using attention-based neural networks. In IEEE Ac-
cess, volume PP.
Chen, H., Li, C., Li, X., Rahaman, M. M., Hu, W., Li,
Y., Liu, W., Sun, C., Sun, H., Huang, X., and Grze-
gorzek, M. (2022a). Il-mcam: An interactive learning
and multi-channel attention mechanism-based weakly
supervised colorectal histopathology image classifica-
tion approach. In Computers in Biology and Medicine,
volume 143, page 105265.
Chen, H., Li, C., Wang, G., Li, X., Rahaman, M., Sun,
H., Hu, W., Li, Y., Liu, W., Sun, C., Ai, S., and
Grzegorzek, M. (2022b). Gashis-transformer: A
multi-scale visual transformer approach for gastric
histopathological image detection. In Pattern Recog-
nition, volume 130, page 108827.
Chollet, F. et al. (2015). Keras. In GitHub. last accessed
2024/04/25.
DeBoer, P. T., Kroese, D. P., Mannor, S., and Rubinstein,
R. Y. (2005). A tutorial on the cross-entropy method.
volume 134, pages 19–67.
Dosovitskiy, A., Beyer, L., Kolesnikov, A., Weissenborn,
D., Zhai, X., Unterthiner, T., Dehghani, M., Minderer,
M., Heigold, G., Gelly, S., Uszkoreit, J., and Houlsby,
N. (2021). An image is worth 16x16 words: Trans-
formers for image recognition at scale. In Interna-
tional Conference on Learning Representations.
Fonseca, A., Pinto, J., Marques, M., Drosdoski, F., and
Neto, L. (2010). Estudo epidemiol
´
ogico do c
ˆ
ancer
de p
ˆ
enis no estado do par
´
a, brasil. In Revista Pan-
Amaz
ˆ
onica de Sa
´
ude, volume 1.
Gaio, D. E. (2022). An
´
alise comparativa das t
´
ecnicas de
implementac¸
˜
ao de arquiteturas da func¸
˜
ao sigmoide.
Gomes, A., Moraes, J., da S. Ferreira, A., and dos S. Ozela,
C. (2019). Educac¸
˜
ao em sa
´
ude para prevenc¸
˜
ao do
c
ˆ
ancer de p
ˆ
enis: relato de experi
ˆ
encia / health edu-
cation for the prevention of penile cancer: experience
report. In Brazilian Journal of Health Review, vol-
ume 2, pages 2961–2964.
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., and Sun, J. (2016). Deep
residual learning for image recognition. In IEEE Con-
ference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition
(CVPR), pages 770–778.
Hu, J., Shen, L., Albanie, S., Sun, G., and Wu, E. (2017).
Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In 2018 IEEE/CVF
Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recogni-
tion, pages 7132–7141.
Hunt, K. K., Robb, G. L., Strom, E. A., Ueno, N. T., and
(Eds.), J. M. (2008). Breast Cancer, 2nd Edition.
Springer, 2nd edition.
Ijaz, A., Raza, B., Kiran, I., Waheed, A., Raza, A., Shah, H.,
and Aftan, S. (2023). Modality specific cbam-vggnet
model for the classification of breast histopathology
images via transfer learning. In IEEE Access, vol-
ume 11, pages 15750–15762.
International Agency for Research on Cancer (2024). Iarc
global cancer observatory. In International Agency
for Research on Cancer Website. Last accessed
2024/05/14.
ICEIS 2025 - 27th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
660

Kingma, D. P. and Ba, J. (2014). Adam: A method for
stochastic optimization. In CoRR, volume 1412.6980.
Lauande, M. G. M., Junior, G. B., and Almeida, J. D. S.
(2022). Classificac¸
˜
ao de imagens histopatol
´
ogicas de
c
ˆ
ancer de p
ˆ
enis usando redes convolucionais e trans-
fer
ˆ
encia de aprendizagem. In Universidade Federal
do Maranh
˜
ao.
Lecun, Y., Bottou, L., Bengio, Y., and Haffner, P. (1998).
Gradient-based learning applied to document recogni-
tion. In Proceedings of the IEEE, volume 86, pages
2278–2324.
Paner, G., Stadler, W., Hansel, D., Montironi, R., Lin, D.,
and Amin, M. (2018). Updates in the eighth edition
of the tumor-node-metastasis staging classification for
urologic cancers. In European Urology, volume 73,
pages 560–569.
Rosas, N., Souza, P., Bandeira, V., de M.F. Rondon, H.,
Castro, N., Heibel, M., Silva, K., and do C.R. Alves,
V. (2021). Fatores de risco para o c
ˆ
ancer peniano: re-
vis
˜
ao de literatura / risk factors for penile cancer: lit-
erature review. In Brazilian Journal of Health Review,
volume 4, pages 13138–13147.
Shin, H., Roth, H., Gao, M., Lu, L., Xu, Z., Nogues, I.,
Yao, J., Mollura, D., and Summers, R. (2016). Deep
convolutional neural networks for computer-aided de-
tection: Cnn architectures, dataset characteristics and
transfer learning. In IEEE Transactions on Medical
Imaging, volume 35, pages 1285–1298.
Shorten, C. and Khoshgoftaar, T. M. (2019). A survey on
image data augmentation for deep learning. In Journal
of Big Data, volume 6, pages 1–48.
Simonyan, K. and Zisserman, A. (2014). Very deep convo-
lutional networks for large-scale image recognition. In
CoRR, volume 1409.1556.
Tan, M. and Le, Q. V. (2019). Efficientnet: Rethinking
model scaling for convolutional neural networks. In
ArXiv, volume 1905.11946.
Touvron, H., Cord, M., Douze, M., Massa, F., Sablayrolles,
A., and Jegou, H. (2021). Training data-efficient im-
age transformers & distillation through attention. In
Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on
Machine Learning, pages 10347–10357.
Vaswani, A., Shazeer, N. M., Parmar, N., Uszkoreit, J.,
Jones, L., Gomez, A. N., Kaiser, L., and Polosukhin,
I. (2017). Attention is all you need. In Neural Infor-
mation Processing Systems.
Vieira, C., Feitoza, L., Pinho, J., Teixeira-J
´
unior, A., Lages,
J., Calixto, J., Coelho, R., Nogueira, L., Cunha, I.,
Soares, F., and Silva, G. (2020). Profile of pa-
tients with penile cancer in the region with the high-
est worldwide incidence. In Scientific Reports, vol-
ume 10, page 2965.
World Health Organization (2024). Cancer fact sheet. In
World Health Organization Website. Last accessed
2024/02/29.
Zhang, A., Lipton, Z. C., Li, M., and Smola, A. J. (2023).
Dive into Deep Learning. arXiv e-prints.
Assessing the Attention Layers in Convolutional Neural Networks for Penile Cancer Detection in Histopathological Images
661
