
A LLM-Powered Agent for Summarizing Critical Information in the
Swine Certification Process
Gabriel Rodrigues da Silva
a
, Alencar Machado
b
and Vinícius Maran
c
Laboratory of Ubiquitous, Mobile and Applied Computing (LUMAC), Federal University of Santa Maria,
Santa Maria, Brazil
Keywords:
LLM-Powered Agent, Conversational Assistant, Animal Farm Certification.
Abstract:
Animal production farms play an essential role in sanitary control by serving as the first line of defense
against disease outbreaks, thus safeguarding both the national food supply and public health. In the state of
Rio Grande do Sul, one of Brazil’s leading regions for livestock production, swine farming holds particular
economic importance and requires rigorous oversight to maintain herd health and compliance with regulatory
standards. Recognizing this critical need, this paper presents the development of a virtual assistant aimed at
supporting swine certification processes within the Animal Health Defense Platform of Rio Grande do Sul
(PDSA-RS), a system integral to monitoring and preserving swine health in the region. The virtual assistant
was implemented in Java using Spring Boot and the Spring AI library, with large language models (LLMs)
executed locally through Ollama to ensure data privacy and provide contextualized responses. To improve
response accuracy and relevance, retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) was employed, enriching user queries
with external data on swine health regulations, standard operating procedures, and relevant certifications.
A case study was conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of the prototype in real-world swine certification
scenarios. Results indicated that the virtual assistant showed promise in improving the speed and accuracy
of the certification process, offering timely and relevant information to users. This highlights the system’s
potential to streamline workflows and facilitate better decision-making among technicians and veterinarians
involved in sanitary control measures.
1 INTRODUCTION
Swine certification in Brazil is pivotal to maintain-
ing and expanding the nation’s standing as one of
the world’s top pork exporters. By ensuring com-
pliance with strict global standards for quality, food
safety, and animal welfare, certification fosters trust
among trading partners and consumers, significantly
contributing to the growth of the swine industry. In
2022 alone, Brazil’s gross production value for swine
reached about R$ 34.175 billion, with the state of Rio
Grande do Sul accounting for nearly 20% of national
slaughter (ABPA, 2024).
In recent years, artificial intelligence (AI) has ac-
celerated rapidly, fueled by advancements in data
processing and increasingly sophisticated algorithms.
Large-scale language models, such as EcoAssistant,
have gained prominence for performing complex nat-
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0000-2705-2810
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2462-7353
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1916-8893
ural language processing tasks more efficiently and
accurately, while reducing operational costs (Zhang
et al., 2023). Various architectures—autoregressive
models (GPT-3), encoder-decoder (BERT), and mul-
timodal models (CLIP)—demonstrate the remarkable
versatility of LLMs in applications beyond natural
language processing (Raffel et al., 2020; Radford
et al., 2021). Notably, GPT-3.5 has shown state-
of-the-art performance in generating coherent, high-
quality text from large datasets (Brown et al., 2020),
while LLaMA caters to contexts where computational
resources are constrained (Touvron et al., 2023).
LLMs have already been adopted across many do-
mains, from virtual assistants to livestock manage-
ment. Ávila (2022) discusses how LLMs and related
AI tools can optimize herd management, reduce ani-
mal stress, and enhance efficiency (Shi et al., 2021).
In customer service, LLM-powered virtual assistants
demonstrate more natural and personalized interac-
tions than traditional chatbots, which handle only ba-
sic queries (Peters et al., 2018). Nonetheless, chal-
Rodrigues da Silva, G., Machado, A. and Maran, V.
A LLM-Powered Agent for Summarizing Critical Information in the Swine Certification Process.
DOI: 10.5220/0013473400003929
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2025) - Volume 1, pages 965-972
ISBN: 978-989-758-749-8; ISSN: 2184-4992
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
965

lenges remain in addressing diverse cultural and lin-
guistic contexts and ensuring users fully understand
model outputs (Brown et al., 2020; Touvron et al.,
2023). Further development is critical, particularly
for precision livestock farming and related industries.
This paper is structured as follows: Section 2 cov-
ers the fundamental concepts behind our research.
Section 3 presents the related work, examining pre-
vious studies and solutions relevant to this domain.
In Section 4, we introduce our LLM-powered agent
for the swine certification process. Section 5 focuses
on the evaluation of our approach, and Section 6 con-
cludes the paper.
2 BACKGROUND
2.1 Domain-Specific Agents
Domain-specific agents are specialized software sys-
tems designed to leverage focused knowledge bases
and processes relevant to a particular field. In vet-
erinary certification, for instance, these agents must
manage and interpret legislation, health records, im-
munization data, and inspection guidelines with pre-
cision (Peters et al., 2018). Unlike general chat-
bots, which often rely on generic language models or
rule-based flows, domain-specific agents—especially
those powered by LLMs—deliver more nuanced dia-
logues and can adapt to rapidly changing regulations.
These agents may integrate external data sources,
such as official veterinary databases, to implement ro-
bust Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) strate-
gies. This connection ensures that the agent’s answers
remain accurate and authoritative, reducing the poten-
tial for misinformation. However, creating and main-
taining high-quality, domain-relevant training data
poses significant challenges, requiring collaboration
between domain experts and AI developers. Despite
these hurdles, ongoing advances in natural language
processing and knowledge representation promise to
further enhance the reliability and impact of domain-
specific agents in veterinary public health and animal
certification
2.2 LLM
Large Language Models represent a major break-
through in AI, particularly in natural language pro-
cessing. Their development is part of a long-standing
evolution in the field, where researchers have endeav-
ored to create machines capable of understanding and
generating human language automatically. Early ef-
forts with neural networks and transformers, such as
GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer), paved the
way for GPT-2. Released in 2019 by OpenAI, GPT-2
gained attention by producing coherent and persua-
sive text from simple prompts (Brown et al., 2020).
Currently, LLMs permeate everyday applications,
such as Alexa, Siri, and Google Assistant, enabling
more natural language interactions (Radford et al.,
2019). They also underpin large-scale operations,
from automated customer support and content gener-
ation to medical data analysis (Raffel et al., 2020). A
key factor behind their capabilities lies in billions of
adjustable parameters, which allow models like GPT-
3 to capture linguistic nuances. However, increasing
the number of parameters also raises computational
costs, both during training and inference, and requires
extensive datasets to avoid overfitting (Brown et al.,
2020).
Training methods vary. A typical approach is
to first pre-train the model on vast amounts of gen-
eral data, imparting broad language skills. Fine-
tuning then adapts these skills to domain-specific
tasks, such as translation or customer service (Brown
et al., 2020), while in-context learning further refines
models based on a few specialized examples. Fig-
ure 1 illustrates how an LLM can shift from generic
language tasks to targeted applications.
Figure 1: Example of a model’s adaptability (Bommasani
et al., 2021).
Nonetheless, these architectures bring certain
challenges, especially regarding computational re-
sources and data privacy. Balancing model complex-
ity with efficiency is therefore a central concern for
applying LLMs in real-world solutions.
2.2.1 Fine-Tuning
Unlike pre-training with large, general-purpose
datasets, fine-tuning adjusts the model using a
smaller, domain-specific set of labeled data. This
technique is particularly useful for tasks requiring
specialized language understanding (e.g., sentiment
ICEIS 2025 - 27th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
966

analysis or legal text generation), as it optimizes
weights for domain-specific nuances (Howard and
Ruder, 2018). In a simplified workflow, a pre-trained
model undergoes additional training on a specialized
dataset, leveraging prior knowledge while reducing
overall computational cost (Devlin, 2018).
However, fine-tuning also presents challenges. If
the labeled dataset is insufficient or biased, the model
may inherit these flaws, resulting in skewed or overly
specialized responses. Additionally, fine-tuned mod-
els risk over-fitting, losing the ability to generalize to
new data (Raffel et al., 2020). Maintaining a careful
balance between specialization and broader applica-
bility is therefore essential for successful fine-tuning.
2.2.2 Prompt Engineering
Creating and structuring the instructions provided
to LLMs is an essential practice for optimizing the
responses these systems generate, ensuring that an
LLM’s outputs align with the specific needs of the
user. With the growing influence of LLMs, such
as GPT-3, small variations in instruction design
can significantly affect model performance (Brown
et al., 2020), underscoring the importance of carefully
crafted prompts.
Beyond guiding the model toward desired behav-
iors, prompt engineering can also adapt the model to
different contexts and audiences without additional
training. This flexibility is particularly useful when
computational resources or domain-specific data are
limited. By refining prompts, LLMs can perform
complex tasks more efficiently and in a more person-
alized manner, reinforcing the value of prompt engi-
neering in real-world AI solutions (Reynolds and Mc-
Donell, 2021).
2.2.3 Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) significantly
advances the integration of language models with in-
formation retrieval, enhancing both accuracy and rel-
evance in generated answers (Lewis et al., 2020). By
combining text generation with external data, RAG
expands the context and applicability of LLMs be-
yond their internal knowledge. As shown in Figure 2,
a prompt and query first retrieve relevant information
from external sources, such as legislative or special-
ized databases, which is then integrated into the initial
context before the LLM generates a final textual an-
swer. This process allows the model to align text gen-
eration with up-to-date data, overcoming limitations
of pre-trained-only approaches.
RAG typically involves two collaborative mod-
ules: (1) an information retrieval system, essential
Figure 2: How RAG works (Gupta et al., 2024).
for expanding the model’s context and improving re-
sponse accuracy, and (2) a text generation model
that incorporates retrieved data to produce contex-
tualized answers (Brown et al., 2020). This design
adapts quickly to regulatory changes without frequent
re-training, reducing computational costs (Touvron
et al., 2023; Raffel et al., 2020).
Despite its advantages, RAG depends heavily
on the organization and accuracy of external data
sources—poorly maintained or outdated databases
can undermine answer quality (Lewis et al., 2020).
Response time may also increase when large volumes
of data or high query loads are involved (Zhang et al.,
2023). Lastly, security measures become critical in
sensitive domains, such as sanitary certification, to
protect both user data and generated outputs (Brown
et al., 2020).
2.2.4 Embedding Process
Embedding transforms text into dense vectors, cap-
turing semantic and contextual relationships (Reimers
and Gurevych, 2019). In the swine certification con-
text, embedding helps retrieve legislative paragraphs
closely aligned with user queries.
2.3 Animal Farm Certification
Ensuring swine health in Brazil is vital for global mar-
ket competitiveness. Certification processes require
detailed tracking of vaccinations, compliance with
biosafety norms, and continuous monitoring (Brown
et al., 2020). As Brazil is a major pork exporter, these
certifications uphold both national regulations and in-
ternational standards (Descovi et al., 2021).
2.3.1 The PDSA-RS Platform
The PDSA-RS platform streamlines poultry and
swine certification (Descovi et al., 2021). It originally
supported four main portals:
Previously, the PDSA-RS offered only four of its
five main portals, as shown in Figure 3:
• RT Portal. Aimed at veterinarians accredited by
the SVO, enabling them to perform and represent
the legal activities of farms;
A LLM-Powered Agent for Summarizing Critical Information in the Swine Certification Process
967
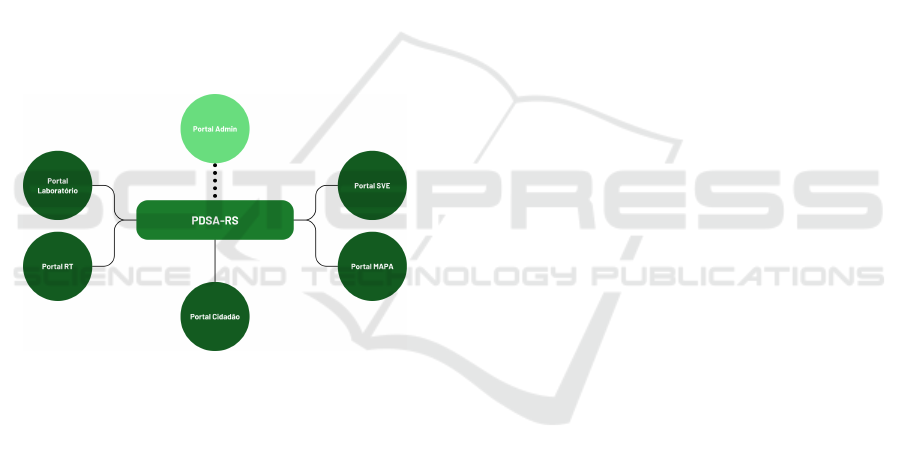
• Laboratory Portal. Equipped with explicit func-
tionalities for sample reception routines, process-
ing, registration, and the issuance of authenticated
reports by veterinarians and staff from private, ac-
credited, and federal laboratories;
• SVE Portal. Geared toward agents of the Sec-
retariat of Agriculture, Livestock, and Irrigation
of Rio Grande do Sul, handling farm registration,
poultry and swine genetic certification, warehouse
management, and other related tasks;
• MAPA Portal. Designed for final certification ac-
tivities involving all parties in certificate issuance,
result analysis, farm history tracking, and other
responsibilities under Brazil’s Ministry of Agri-
culture, Livestock, and Food Supply.
As new demands arose and additional projects
were implemented within PDSA-RS, the platform ex-
panded its known portals by adding the new Citizen
Portal. This portal is intended for use by any individ-
ual, with streamlined access through gov.br authenti-
cation.
Figure 3: Structure of the PDSA-RS platform.
3 RELATED WORK
The application of AI in livestock management has
seen increasing research interest, particularly in pre-
dictive analytics and automated monitoring systems.
Ávila (2022) explored neural networks for herd op-
timization, demonstrating improvements in health
monitoring and resource allocation (Shi et al., 2021).
Similarly, Mallinger et al. (2024) examined how Ex-
plainable AI (XAI) can facilitate the adoption of smart
farming technologies by improving requirement anal-
ysis and technology design, ensuring that AI-driven
solutions are transparent and user-friendly (Mallinger
et al., 2024). However, most studies focus on struc-
tured data analysis rather than language-based AI
models.
LLMs have been extensively used in customer ser-
vice (Peters et al., 2018) and healthcare applications
(Esteva et al., 2019), yet their role in regulatory com-
pliance for animal certification remains underdevel-
oped. Research on AI-driven automation in legal
and administrative fields has demonstrated the po-
tential of LLMs in document processing and compli-
ance validation (Zhong et al., 2020). The integration
of RAG has further improved accuracy in generat-
ing responses based on external regulatory databases
(Lewis et al., 2020).
Despite advancements in AI-driven certification,
existing solutions in livestock management remain
largely manual or rule-based, lacking the contextual
adaptability that LLMs can provide. Our work aims
to bridge this gap by leveraging domain-specific AI
models to enhance the swine certification process
through real-time legal interpretation and compliance
validation.
4 A LLM-POWERED AGENT FOR
SWINE CERTIFICATION
PROCESS
This section describes how we developed and in-
tegrated an LLM-based agent within the PDSA-RS
to aid official veterinaries in swine certification pro-
cesses. We detail the software architecture, agent def-
inition, and the steps involved in ensuring contextu-
ally relevant responses.
4.1 Software Architecture Definition
The architecture of the swine certification assis-
tant integrates seamlessly with the PDSA-RS plat-
form, leveraging existing client portals and backend
APIs while introducing new components to support
the LLM-powered assistant. The system uses Java
(Spring Boot) for a stable REST backend, Spring
AI for connecting to LLM services, and Ollama
for the local execution of open-source models (e.g.,
LLaMA). By running LLMs locally, the system en-
sures data privacy—critical for sensitive veterinary
records—while reducing reliance on external APIs.
The architecture is illustrated in Figure 4, which
highlights the components of the PDSA-RS plat-
form. The existing client portals include MAPA,
SVE, RT, and LAB, each serving specific roles in
swine certification and related processes. Among
these, the MAPA portal is the first to integrate the
LLM-powered assistant, as indicated by the brain icon
in the image. This marks it as the entry point for test-
ing and deploying the assistant.
ICEIS 2025 - 27th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
968

Figure 4: Software architecture of the PDSA-RS platform
with LLM integration.
On the backend, the system includes several APIs
for business and service functionalities. Notably, a
new API, the LLM API, was introduced in the ser-
vices layer to facilitate communication with the LLM
model. This API is responsible for handling queries
sent to the model, managing RAG operations, and
retrieving relevant legislative content from the Post-
greSQL database. The database stores vector em-
beddings of regulatory documents to enable semantic
search, as well as logs of user interactions for analyt-
ics and future improvements.
• Backend (Spring Boot). Exposes endpoints to
handle certification queries, fetch legislative con-
tent, and manage user sessions.
• Spring AI. Orchestrates prompt engineering and
RAG retrieval. Minimal official documentation
posed integration challenges.
• Ollama. Executes LLMs like LLaMA 3.2:3B
locally, ensuring rapid responses for domain-
specific queries (OLLAMA, 2024).
This modular design not only ensures the scalabil-
ity and adaptability of the platform but also positions
it to efficiently incorporate advanced AI features into
existing workflows. The integration with the MAPA
portal demonstrates the potential of the assistant to
enhance certification processes while preserving data
privacy and system autonomy.
4.2 Agent Definition
The agent is a domain-specific virtual assistant de-
signed to streamline the swine certification process by
providing quick and accurate responses to complex
veterinary and regulatory queries. Its primary goal
is to assist veterinarians, inspectors, and other stake-
holders in accessing legislative and procedural infor-
mation necessary for sanitary compliance, thereby
reducing the time and effort required for manual
searches.
The agent operates in a structured manner:
1. Receive a Query. Users, such as veterinarians
or officials, input questions related to sanitary
regulations, certification requirements, or other
domain-specific topics.
2. Retrieve Relevant Data (RAG). The system em-
ploys Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) to
search an embedded database containing regula-
tory documents and legislative data. This ensures
that the query is matched to semantically relevant
content.
3. Integrate and Generate a Response. Retrieved
data is appended to the user’s query and passed
to the Large Language Model (LLM). The LLM
synthesizes this information to generate a context-
rich, domain-specific response.
4. Return Result. The generated response is pre-
sented to the user in an intuitive and accessible
format, providing clear guidance tailored to the
specific query.
The agent was designed with the unique require-
ments of swine certification in mind, ensuring that it
can handle technical terminology, navigate complex
hierarchical regulations, and adapt to evolving leg-
islative standards. However, a notable limitation is
the lack of conversation continuity. Due to the ab-
sence of native multi-turn memory in Spring AI, the
agent processes each query independently. This can
lead to disjointed or repetitive responses in multi-step
interactions, underscoring the need for improved con-
text management mechanisms. Future iterations may
address this limitation by integrating libraries like
Langchain4j or exploring alternative architectures to
support dynamic and continuous dialogue.
By leveraging a combination of advanced in-
formation retrieval and LLM capabilities, the agent
serves as a valuable tool for enhancing decision-
making and operational efficiency in swine certifica-
tion workflows.
4.3 Prototype Definition
The prototype for the swine certification assistant was
developed to integrate seamlessly with the PDSA-
RS platform, leveraging advanced technologies to
provide efficient and privacy-preserving responses to
user queries. Currently at the proof-of-concept (PoC)
stage, the system aims to validate the feasibility and
potential impact of a locally executed LLM for swine
certification.
The software architecture combines a robust back-
end, a curated knowledge base, and a user-friendly in-
terface to streamline the certification process for vet-
erinarians and officials. The backend, implemented
A LLM-Powered Agent for Summarizing Critical Information in the Swine Certification Process
969

using Spring Boot, manages user interactions and pro-
cesses queries through a locally deployed LLM us-
ing Ollama. A PostgreSQL database handles seman-
tic search and logs interactions, enabling RAG for
accurate, context-relevant responses. By embedding
knowledge from domain-specific documents, the sys-
tem ensures quick access to vital information for cer-
tification procedures.
The user interface was extended to integrate a chat
component, as shown in Figure 5. This component
allows users to submit queries, receive real-time an-
swers, and interact with the assistant intuitively. By
embedding this functionality directly into the PDSA-
RS platform, the assistant becomes a practical tool
for stakeholders, simplifying the certification work-
flow and improving decision-making efficiency.
Figure 5: Chat component integrated into the PDSA-RS
platform. Source: Author’s own work.
The system’s backend architecture, illustrated in
Figure 6, employs the Reactor project’s Flux class to
enable real-time data exchange through ServerSen-
tEvent (SSE). This design allows responses to be
streamed incrementally, enhancing the user experi-
ence by reducing latency and enabling seamless in-
teraction with the assistant.
This prototype demonstrates the feasibility of
deploying LLM-based solutions for domain-specific
challenges, such as swine certification. By combin-
ing advanced AI with tailored infrastructure, the sys-
tem provides veterinarians and technicians with an ef-
fective, user-friendly tool to navigate complex certifi-
cation requirements. The next section illustrates the
assistant’s practical applications through a real-world
usage scenario, highlighting its benefits and identify-
ing potential areas for future improvement.
Figure 6: REST Controller architecture for managing chat
interactions.
5 EVALUATION AND
DISCUSSION
This section presents a comprehensive evaluation of
the prototype, detailing the implementation, a real-
world usage scenario, and a discussion of the results.
5.1 Usage Scenario
Case: Export Inconsistencies. Suppose a veterinar-
ian named João at MAPA faces an urgent export re-
quest for pigs whose vaccination records are incom-
plete. Unsure which vaccines must be immediately
administered according to Brazil’s swine certification
rules, João queries the integrated assistant:
“What vaccinations are mandatory for breed-
ing swine in Brazil before export?”
The system:
1. Retrieves relevant normative instructions from the
embedded database.
2. Merges the retrieved content with João’s prompt.
3. LLaMA 3.2:3B generates a response summariz-
ing the mandatory vaccines and references official
documents.
4. Answer: "In Brazil, vaccination is mandatory for
pig farming before export. The specific vaccines
required may vary depending on the type of pig
and the destination of the product...".
If João wants to ask a follow-up, like scheduling
details or exceptions for certain export destinations,
the assistant may struggle because each new request
is processed independently. This limitation often re-
sults in partial or repetitive answers. Despite that, it
still saves João time, offering specialized guidance far
more efficiently than manually searching legislation.
ICEIS 2025 - 27th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
970

5.2 Evaluation and Discussion
The evaluation of the swine certification assistant fo-
cused on assessing its performance, usability, and
limitations in real-world scenarios. The prototype
was deployed on a conventional computer equipped
with an AMD Ryzen 5 5600 processor, 48 GB of
RAM, and an NVIDIA 2060 Super graphics card with
8 GB of VRAM. This setup demonstrated the sys-
tem’s capability to achieve efficient local inference
without requiring high-end infrastructure, reinforcing
the feasibility of deploying such solutions in resource-
constrained environments. During testing, the system
was subjected to various queries, including straight-
forward and complex examples, to evaluate its accu-
racy and relevance. For instance, a user might ask:
• "What vaccinations are mandatory for breeding
swine in Brazil before export?": The system re-
trieved relevant regulations from the database,
synthesized the information, and provided a de-
tailed response citing specific normative instruc-
tions.
In a follow-up query, such as:
• "Are there exceptions to these requirements for ex-
ports to specific countries?": The assistant strug-
gled with maintaining context due to the lack of
native multi-turn memory, resulting in responses
that required rephrasing the initial query for clar-
ity. This limitation highlights the need for ad-
vanced context management in future iterations.
The assistant was evaluated on several aspects,
summarized below:
Performance. Running LLaMA 3.2:3B locally via
Ollama delivered near real-time responses, thanks to
the GPU acceleration provided by the NVIDIA 2060
Super. The model’s size was optimized for efficient
inference on this setup, avoiding the need for large-
scale infrastructure while maintaining acceptable re-
sponse times and accuracy
Documentation Limitations. The nascent status
of Spring AI posed challenges during development.
Limited documentation required significant effort to
discover workable configurations and hindered the
customization of prompts to sustain conversational
continuity. This constraint underscored the impor-
tance of community-supported libraries and tools for
future projects.
Context Retention. A notable limitation was the sys-
tem’s inability to retain conversational context across
multiple queries. Each query was processed indepen-
dently, which led to disjointed interactions in scenar-
ios requiring multi-step dialogues. While sufficient
for single-turn queries, the lack of memory negatively
impacted the user experience in more complex use
cases.
Advantages. The prototype demonstrated several key
benefits: - Data Security: All sensitive information,
such as farm records and lab reports, remained on lo-
cal servers, ensuring compliance with privacy stan-
dards. - Faster Development: Leveraging Java and
Spring Boot simplified integration with existing enter-
prise systems, reducing the time required for develop-
ment. - Scalability: The containerized approach with
Docker and Docker Compose facilitated horizontal
scaling, making the system adaptable to increased us-
age demands.
Overall. The results validated the prototype’s poten-
tial to reduce the effort required to access regulatory
information for swine certification. Despite limita-
tions in conversational memory and documentation,
the assistant provided accurate and timely responses
for stand-alone queries. Future improvements should
prioritize enhancing conversational capabilities and
integrating more robust documentation to support de-
velopers and end-users alike
6 CONCLUSION
The integration of LLMs into specific domains, such
as swine certification, addresses the pressing need for
tools that can process and interpret complex, domain-
specific information efficiently. This project pro-
posed and developed a swine certification assistant for
PDSA-RS using Java, Spring Boot, Spring AI, and
Ollama. The objective was to demonstrate how lo-
cally deployed LLMs can provide privacy-preserving,
contextualized, and near real-time responses, cater-
ing to the unique requirements of swine health cer-
tification in Rio Grande do Sul. The proposal was
motivated by the challenges faced in navigating intri-
cate veterinary regulations and processes, which de-
mand precise, timely decisions. By leveraging RAG
and embedding key regulatory documents, the system
enabled rapid access to relevant information. A case
study validated the prototype’s effectiveness in assist-
ing veterinarians with certification tasks, showcasing
its potential to improve decision-making and stream-
line workflows.
Despite these advancements, the project encoun-
tered limitations, particularly in maintaining conver-
sational continuity due to the lack of native support
for multi-turn dialogues in Spring AI. Additionally,
the limited documentation for Spring AI integration
posed challenges during development. These barri-
ers highlight opportunities for future improvements,
such as adopting context-tracking frameworks like
A LLM-Powered Agent for Summarizing Critical Information in the Swine Certification Process
971

Langchain4j, exploring Python-based ecosystems for
broader tool support, and optimizing model perfor-
mance through compression techniques. In conclu-
sion, this work demonstrated the feasibility and value
of integrating LLMs into the swine certification pro-
cess, offering a practical solution for a highly special-
ized domain. Future enhancements to the assistant are
expected to refine its capabilities further, empowering
veterinarians and technicians with accurate, efficient,
and user-friendly tools for managing certification pro-
cedures. This study underscores the broader poten-
tial of LLMs to revolutionize domain-specific appli-
cations, paving the way for innovation in public health
and regulatory compliance.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research is supported by FUNDESA (project
’Combining Process Mapping and Improvement with
BPM and the Application of Data Analytics in the
Context of Animal Health Defense and Inspection
of Animal Origin Products in the State of RS -
UFSM/060496) and FAPERGS, grant n. 24/2551-
0001401-2. The research by Vinícius Maran is par-
tially supported by CNPq, grant 306356/2020-1 -
DT2.
REFERENCES
ABPA (2024). Relatório anual 2024. In Relatório Anual
2024. Associação Brasileira de Proteína Animal.
Bommasani, R., Hudson, D. A., Adeli, E., Altman, R., et al.
(2021). On the opportunities and risks of foundation
models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2108.07258.
Brown, T., Mann, B., Ryder, N., Subbiah, M., et al.
(2020). Language models are few-shot learners. In
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems,
volume 33, pages 1877–1901. Curran Associates, Inc.
Descovi, G., Maran, V., Ebling, D., and Machado, A.
(2021). Towards a blockchain architecture for animal
sanitary control. In ICEIS (1), pages 305–312.
Devlin, J. (2018). Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirec-
tional transformers for language understanding. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1810.04805.
Esteva, A., Robicquet, A., Ramsundar, B., Kuleshov, V.,
DePristo, M., Chou, K., Cui, C., Corrado, G. S.,
Thrun, S., and Dean, J. (2019). A guide to deep learn-
ing in healthcare. Nature medicine, 25(1):24–29.
Gupta, S., Ranjan, R., and Singh, S. N. (2024). A Com-
prehensive Survey of Retrieval-Augmented Genera-
tion (RAG): Evolution, Current Landscape and Future
Directions.
Howard, J. and Ruder, S. (2018). Universal language model
fine-tuning for text classification. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1801.06146.
Lewis, P., Perez, E., Piktus, A., Petroni, F., et al. (2020).
Retrieval-augmented generation for knowledge-
intensive NLP tasks. In Proceedings of the 34th
International Conference on Neural Information
Processing Systems, NIPS ’20, Red Hook, NY, USA.
Curran Associates Inc.
Mallinger, K., Corpaci, L., Neubauer, T., Tikász, I. E., et al.
(2024). Breaking the barriers of technology adoption:
Explainable ai for requirement analysis and technol-
ogy design in smart farming. Smart Agricultural Tech-
nology, 9:100658.
OLLAMA (2024). Ollama documentation. Acesso em: 07
dez. 2024.
Peters, F. et al. (2018). Design and implementation of a
chatbot in the context of customer support.
Radford, A., Kim, J. W., Hallacy, C., Ramesh, A., et al.
(2021). Learning transferable visual models from nat-
ural language supervision. In International conference
on machine learning, pages 8748–8763. PMLR.
Radford, A., Wu, J., and Child, R. (2019). Language mod-
els are unsupervised multitask learners. OpenAI blog,
1(8):9.
Raffel, C., Shazeer, N., Roberts, A., Lee, K., et al. (2020).
Exploring the limits of transfer learning with a unified
text-to-text transformer. Journal of machine learning
research, 21(140):1–67.
Reimers, N. and Gurevych, I. (2019). Sentence-bert: Sen-
tence embeddings using siamese bert-networks.
Reynolds, L. and McDonell, K. (2021). Prompt program-
ming for large language models: Beyond the few-shot
paradigm. In Extended abstracts of the 2021 CHI con-
ference on human factors in computing systems, pages
1–7.
Shi, Y., Wang, X., Borhan, M. S., Young, J., Newman, D.,
Berg, E., and Sun, X. (2021). A review on meat qual-
ity evaluation methods based on non-destructive com-
puter vision and artificial intelligence technologies.
Food science of animal resources, 41(4):563.
Touvron, H., Lavril, T., Izacard, G., Martinet, X., Lachaux,
M.-A., Lacroix, T., Rozière, B., Goyal, N., Hambro,
E., Azhar, F., et al. (2023). Llama: Open and ef-
ficient foundation language models. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2302.13971.
Zhang, J., Krishnaa, R., Awadallah, A. H., and Wang, C.
(2023). Ecoassistant: Using llm assistant more afford-
ably and accurately. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.03046.
Zhong, H., Xiao, C., Tu, C., Zhang, T., et al. (2020). How
does NLP benefit legal system: A summary of legal
artificial intelligence. In Proceedings of the 58th An-
nual Meeting of the Association for Computational
Linguistics, pages 5218–5230, Online. Association
for Computational Linguistics.
ICEIS 2025 - 27th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
972
