
The Future of BPM in the Era of Industry 4.0: Exploring New
Opportunities for Innovation
Hadjer Khider
1,2
, Abdelkrim Meziane
2
and Slimane Hammoudi
3
1
Information Systems and Multimedia Systems Department, CERIST, Algiers, Algeria
2
Computer Science Department, Abderrahman Mira University, Bejaia, Algeria
3
MODESTE Team, Computer Science Department – ESEO, Angers, France
Keywords: Business Process Management (BPM), Industry 4.0, Digital Transformation, Digitalization, SLR.
Abstract: In today's digital age, the fourth industrial revolution has given rise to Industry 4.0. This new paradigm has
brought new challenges for organizations, through a digital transformation. This digital transformation has
profoundly impacted the way businesses operate, leading to a fundamental shift in the Business Process
Management (BPM), affecting business models, processes, products, relationships and competencies. This
transformation is based on the use of cyber-physical systems and information and communication
technologies, in particular artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things. This paper aims to identify and
define the main challenges, limitations, and opportunities of BPM in the era of Industry 4.0. Furthermore, it
aims to identify potential future research directions. in addition to analyzing the impact of Industry 4.0
concepts and related technologies on the management of organizations and their business processes.
1 INTRODUCTION
The advent of contemporary technological advances
has led to the emergence of Industry 4.0, which can
be regarded as a consequence of the Fourth Industrial
Revolution (Xu, Xu, et Li 2018). This new paradigm
has brought changes in the functioning of the
organization through a digital transformation
affecting business models, processes, products and
skills (Flechsig et al. 2022). In the current business
environment, characterized by intense competition, a
fail-fast culture is imperative for organizations to
succeed (Szelągowski et Berniak-Woźny 2022).
Organizations are integrating digital technologies
into their core business processes to enhance
efficiency, improve customer experience, and drive
innovation (Vaska et al. 2021). In the era of Industry
4.0, organizations are confronted with complex
implementation issues surrounding the digital
transformation. These issues include the adoption of
new Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) and smart factory
technologies as the Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial
Intelligence (AI), and data analytics, as well as the
adaptation or replacement of core Enterprise
Architectures (EA), Communication Technologies
(ICT) infrastructures and processes (Xu, Xu, et Li
2018).
Unfortunately, many organizations lack the
necessary capabilities to effectively address these
issues (Di Ciccio, Marrella, et Russo 2015;
Szelągowski et Berniak-Woźny 2022).
Consequently, these organizations are carrying out
such transformation to adapt to the emerging
paradigm. This shift has led to the need for efficient
and effective BPM.
The transition from traditional industrial
ecosystems to Industry 4.0 will require not only the
development of new Information and ICT but also the
creation of new business models; The advent of
digitalization has profoundly impacted the way
businesses operate, leading to a fundamental shift in
the management of business processes (Colombo,
Schleuter, et Kircher 2015; Arnold, Kiel, et Voigt
2016). In this context, business process management
(BPM) plays a crucial role in supporting
organizations to achieve greater flexibility and
responsiveness (Grisold et al. 2021). It presents a
valuable and an advantageous tool through cost
reduction, process excellence, and continuous
process improvement, enabling organizations to
design, analyze, execute, monitor and optimize
important processes (Gartner 2018).
Khider, H., Meziane, A. and Hammoudi, S.
The Future of BPM in the Era of Industry 4.0: Exploring New Opportunities for Innovation.
DOI: 10.5220/0013477300003929
In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2025) - Volume 2, pages 915-924
ISBN: 978-989-758-749-8; ISSN: 2184-4992
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
915

According to Gartner in (Gartner 2018), BPM is
critical for the success of business transformation
initiatives. BPM can deliver this level of agility to
business operations in combination with other
disciplines, such as EA (Gartner 2016).
Furthermore, BPM plays a crucial role in helping
organizations identify and optimize their key business
processes. It enables organizations to quickly adapt to
changing business environments, including humans,
applications, and technology (Liu, Chen, et Chou
2011). Ultimately, this leads to improved operational
efficiency and increased competitiveness (Gartner
2018; Viriyasitavat et al. 2019; Baiyere, Salmela, et
Tapanainen 2020; Butt 2020; Szelągowski et
Berniak-Woźny 2022).
In alignment with the aforementioned concepts,
this paper discusses the BPM limitations,
opportunities, and challenges in the era of Industry
4.0 and provides insights into how organizations can
leverage BPM to improve their operational
efficiency, customer experience, innovation, and
competitiveness. Additionally, the paper aims to
identify potential future research directions and
analyze the impact of Industry 4.0 concepts and
related technologies on the management of
organizations and their business processes.
The remainder of this paper is organized as
follows: Section 2 provides a theoretical overview of
the fundamental concepts related to this study, basing
on an analysis of existing literature. Section 3
presents the challenges associated with Industry 4.0.
Section 4 offers a comprehensive overview of BPM.
Section 5 presents a systematic literature review
(SLR) on BPM in the era of Industry 4.0. Section 6
explores the opportunities that Industry 4.0 presents
for BPM. Finally, Section 7 concludes with an
analysis of the findings, and outlines potential future
research directions.
2 THEORETICAL
BACKGROUND
The fourth industrial revolution, commonly referred
to as Industry 4.0, represents a significant shift in the
way industries operate, driven by the convergence of
digitalization, digital transformation, and emerging
technologies (Gajšek and Vujica Herzog 2020). This
section aims to introduce these foundational concepts,
providing a comprehensive understanding of their
interrelationships and implications for modern
industry.
2.1 Digitalization
Digitization is the process of encoding analog
information into digital formats enabling computers
to store processes, and transmit such information
effectively. In contrast, digitalization describes how
to use digital technology to change existing business
processes” (Lee et al. 2021). According to Berlak et
al. in (Berlak, Hafner, et Kuppelwieser 2021),
digitalization involves optimizing existing business
processes through enhanced integration and
coordinated collaboration, in order to facilitate the
creation of new business opportunities.
2.2 Digital Transformation
Digital Transformation is the further stage after
digitalization, describing the successful upgrade and
change that leads to a new business model (Lee et al.
2021). It can be defined as the process of integrating
digital technologies and business processes within a
digital economy. This transformation focuses on
the
restructuring business operations to fully facilitating
the use of a company's core competencies through
digital technology to achieve a competitive advantage
(Liu, Chen, et Chou 2011). In the context of BPM,
digital transformation refers to the transformation of
business operations, services and models. This
comprehensive transformation covers all processes
within the enterprise, ultimately to building a digital
model of the enterprise, incorporating digitized
process attributes (Tupa et Steiner 2019).
2.3 Industry 4.0
The term “Industry 4.0” was first introduced in 2011
at the Hannover Fair in Germany (Adolph et al.
2016). This concept, often referred to as the Fourth
Industrial Revolution, has emerged in the
manufacturing industry (Xu, Xu, et Li 2018).
Implementing Industry 4.0 involves a
number of
different technologies and techniques, including CPS,
IoT, cloud computing, blockchain, industrial
information integration and other related
technologies (Xu, Xu, et Li 2018). Industry 4.0 is
often described as
the Era of Intelligence, which
integrates information technology and operational
technology to achieve intelligence in a mass
customization paradigm, introducing technologies
such as the Internet of IoT, big data, AI, CPS, and
robotics into the factory environment (Guo et al.
2024).
ICEIS 2025 - 27th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
916

3 INDUSTRY 4.0 CHALLENGES
The rapid evolution of Industry 4.0 technologies has
transformed the landscape of modern industry,
creating exceptional opportunities
for innovation and
efficiency. However, organizations often face a
variety of challenges that can hinder the successful
implementation and integration of these advanced
technologies (Gažová, Papulová, et Smolka 2022).
Key challenges include usability (Zhang et al., 2020),
computational efficiency (Yang, Q. et al. 2019),
scalability (Bai et al., 2020), interoperability, and
storage capacity (Su et al. 2023). The implementation
of advanced technologies also introduces potential
risks that organizations must carefully manage,
including cyber security threats, data privacy
concerns, and the possibility of significant
disruptions during the transition phase (Almubarak et
al., 2020). The Industry 4.0 approach relies on the
deployment of intelligent, interconnected Cyber-
Physical Systems (CPS), which presents significant
security challenges. Many of these systems were not
originally designed with cyber security
considerations, making cyber security a critical
concern for organizations adopting the Industry 4.0
paradigm (Corallo, Lazoi, et Lezzi 2020). Another
significant challenge of Industry 4.0 is its insufficient
focus on human-centricity and system resilience
.(Guo
et al. 2024). Additionally, the integration of AI, IoT,
and Blockchain within BPM introduces several
challenges, including developing business process
collaboration, managing large data volumes,
implementing smart contracts, ensuring
interoperability with Blockchain technology,
achieving standardization, and addressing security
and privacy concerns
. (Viriyasitavat et al. 2018).
Currently, the management of Business processes in
industry 4.0 faces significant challenges, including
centralization, lack of verifiability, trust issues, and
insufficient automation (Stefanescu, D. et al., 2024).
This context highlights the importance of smart
contracts, which can address these shortcomings by
providing a more decentralized and automated
approach to BPM.
4 BUSINESS PROCESS
MANAGEMENT
Business Process Management (BPM) is the
combination of knowledge from business
administration and information technology, applied
to operational business processes (Weske 2019). In
practice, BPM is the application of methods,
techniques, and software to design, enact, control, and
analyze operational processes that involve humans,
organizations, applications, documents, and other
sources of information (van der Aalst, ter Hofstede, et
Weske 2003; Di Ciccio, Marrella, et Russo 2015).
The emergence of Industry 4.0 has brought new
challenges for organizations requiring them to
address the complexities of implementing the latest
Industry 4.0 technologies (Colombo, Schleuter, et
Kircher 2015; Arnold, Kiel, et Voigt 2016). In the
current digital era, it is imperative that established
BPM tools are adapted in order to align with the
evolving needs of enterprises (Viriyasitavat et al.,
2019). This involves not only the integration of novel
technologies but also the creation of new business
models and the adaptation or even replacement of
existing core EA, ICT infrastructures and business
processes (Xu, Xu, et Li 2018).
5 BPM IN THE AGE OF
INDUSTRY 4.0: A SYSTEMATIC
LITERATURE REVIEW
Many studies emphasize the critical role of BPM in
driving digital transformation and enhancing
operational efficiency in industry 4.0. While BPM
presents opportunities for industry 4.0, it also faces
significant limitations and challenges in this new era.
This section outlines a study focused on identifying
these challenges and exploring potential solutions. A
systematic literature review (SLR) of academic
research on Industry 4.0 and BPM was conducted to
analyze existing limitations and challenges, as well as
to identify potential opportunities for overcoming
them.
5.1 Methodology
This research employs a systematic literature review
approach, aligned with PRISIMA guidelines (Moher
et al. 2010), and comprises seven phases:
Phase 1: involved searching for articles in the
Science direct, IEEE, and ACM. using keywords,
("business process management" OR "BPM") AND
("challenges" OR "limitations" OR "opportunities")
AND (“Industry 4.0”) to focus on BPM related
challenges, limitations and opportunities.
Phase 2: excluded publications prior to 2015,
ensuring the inclusion of literature, by targeting
articles published between 2015 and 2025.
Phase 3: selected articles by subject area, including
manufacturing, Business, Management and
Accounting, Engineering, Computer Sciences,
Decision Sciences.
The Future of BPM in the Era of Industry 4.0: Exploring New Opportunities for Innovation
917
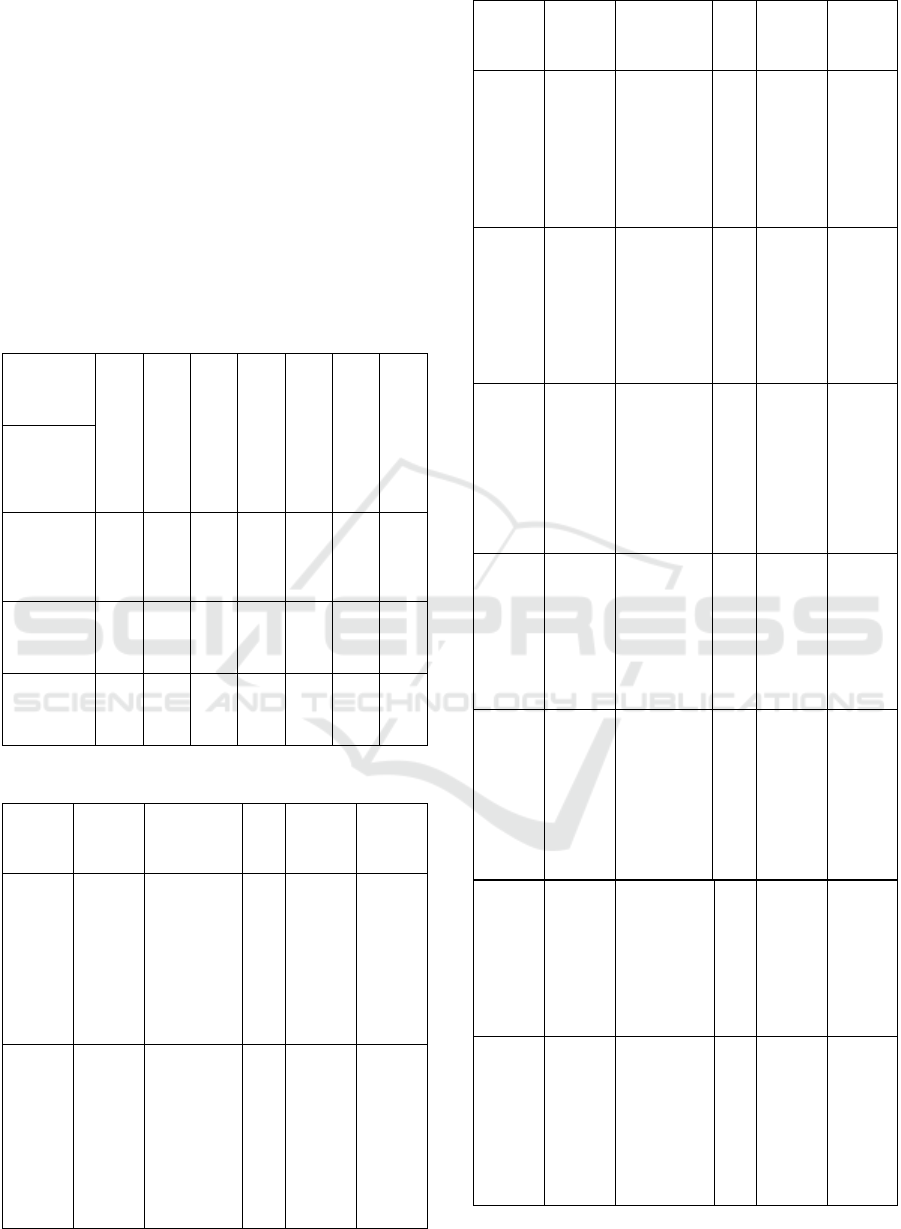
Phase 4: excluded no English publications.
Phase 5: exclusion of papers according to article type,
research and review papers only.
Phase 6: retained journals ranked in the top two
quartiles (Q1 and Q2) of the SCImago database
Phase 7: involves evaluation of the titles and
abstracts based on the paper's coverage of the
opportunities, challenges or limitations of BPM
and/or proposals for future BPM improvements.
This analysis resulted in 22 selected papers
summarized in Table 1 and selected papers are
detailed in Table 2.
Table 1: Number of works published in the Science direct,
IEEE and ACM in the period 2015-2025.
Phases
Phase 01
phase 02
Phase 03
Phase 04
Phase 05
Phase 06
Phase 07
Database
Science
Direct/
Elsevier
4268
2571
2130
2127
1853
1168
13
IEEE
2848
1212
1121
1118
129
76
6
ACM
3571
1389
988
988
122
88
3
Table 2: Selected paper according to the paper's coverage.
Science direct
(Czvetkó et al. 2022)
Data-driven business process
management-based
development of Industry 4.0
solutions
CIRP Journal of Manufacturing
Science and Technology
Q1
24
Science direct
Schulte et al. 2015)
Elastic Business Process
Management: State of the art
and open challenges for BPM in
the cloud
Future Generation Computer
Systems
Q1
96
Database
Authors
Title
Journal
Title
Journal
quality
assessment
score
Citation
Science direct
(Guo et al. 2024)
Industrial metaverse towards
Industry 5.0: Connotation,
architecture, enablers, and
challenges
Journal of Manufacturing
Systems
Q1
6
Science direct
(Su et al. 2023)
Technical challenges of Blockchain
technology for sustainable
manufacturing paradigm in
Industry 4.0 era using a fuzzy
decision support system
Technological Forecasting &
Social Change
Q1
58
Database
Authors
Title
Journal
Title
Journal
quality
assessment
score
Citation
Science direct
(Saraeian, Shirazi, et
Motameni 2018)
Towards an extended BPMS
prototype: Open challenges
of BPM to flexible and robust
orchestrate of uncertain
processes
Computer Standards &
Interfaces
Q1
19
Science direct
(Souifi et al. 2022)
Uncertainty of key
performance indicators for
Industry 4.0: A methodology
based on the theory of belief
functions
Computers in Industry
Q1
14
Science direct
(Kamble, S. S., Gunasekaran,
A., Ghadge, A., & Raut, R.
2020)
performance measurement
system for industry 4.0 enabled
smart manufacturing system in
SMMEs-A review and empirical
investigation
. International journal of
production economics
Q1
705
Science direct
(Bai, C. et al. ,2020)
Industry 4.0 technologies
assessment: A sustainability
perspective
International Journal of
Production Economics
Q1
847
Science direct
(Van Looy 2021)
a quantitative and qualitative
study of the link between
business process management
and digital innovation
Information & Management
Q1
77
ICEIS 2025 - 27th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
918
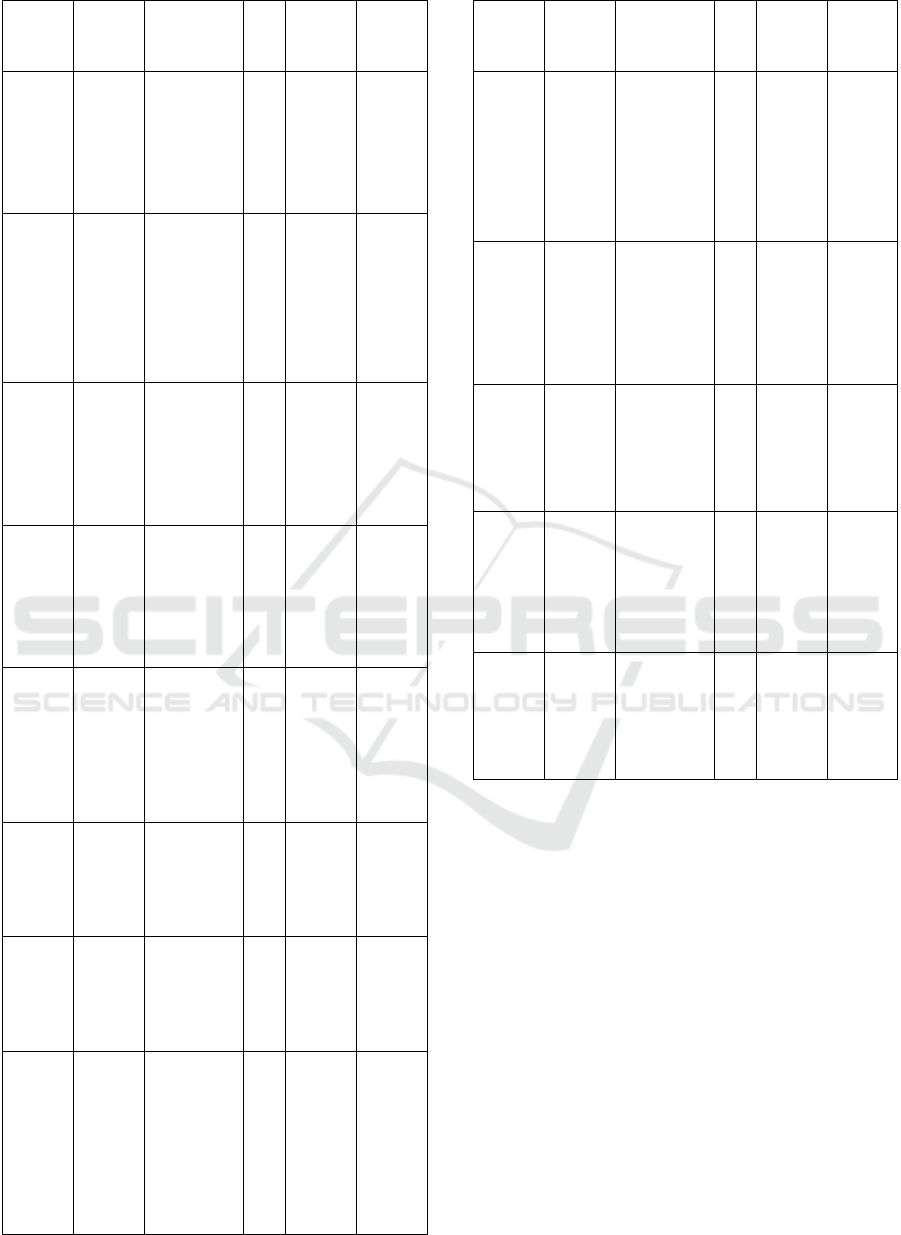
Database
Authors
Title
Journal
Title
Journal
quality
assessment
score
Citation
Science direct
(Pourmirza et al. 2017)
A systematic literature
review on the architecture
of business process
management systems
Information Systems
journal
Q1
44
Science direct
(Elghaish et al. 2021)
Blockchain and the ‘ Internet of
Things' for the construction
industry: research trends and
opportunities
Automation in Construction
Q1
127
IEEE
(Viriyasitavat et al. 2019)
Blockchain and Internet of
Things for Modern
Business Process in
Digital Economy
IEEE Transactions on
Computational Social
Q1
118
Science direct
(Arnold, Kiel, et Voigt
2016)
How Industry 4.0 changes
business models in
different manufacturing
industries
International Journal of
Innovation Management
Q2
252
Science direct
(Baiyere, Salmela, et
Tapanainen 2020)
Digital Transformation and
the New Logics of Business
Process Management
European Journal of
Information Systems
Q1
551
IEEE
(S. Moreira, et al,
2024)
Business Process
Automation in
SMEs: A Systematic
Literature Review
IEEE Access
Q1
3
Elsevier
(Nozari,
H.,&Ghahremani-
Nahr, l. .2024)
AI and machine
learning for real-
world problems.
In Advances In
Computers
Not assigned yet
67
IEEE
(Garcia-Garcia, etal .,2020)
Using Blockchain to Improve
Collaborative Business Process
Management: Systematic
Literature Review
IEEE Access
Q1
82
Database
Authors
Title
Journal
Title
Journal
quality
assessment
score
Citation
IEEE
(Bartlett, L., et al.,2023).
A review on business process
management system design: the
role of virtualization and work
design.
IEEE Access
Q1
5
IEEE
(Ahmed S. and Shahzad
K., 2022).
Augmenting Business
Process Model Elements
with End-User Feedback
IEEE Access
Q1
5
IEEE
(Cardoso P. B., et al.,
2024)
A Granular Risk
Analysis Approach for
IoT-Aware Business
Processes
IEEE Access
Q1
1
ACM
(Stefanescu, D. et
al.,2024)
Smart Contract Powered
Framework for the Next
Generation Industry 4.0
Business Model
Distributed Ledger
Technologies: Research
Note assigned yet
1
ACM
(Yang, Q. et al. 2019)
Federated machine
learning: Concept and
applications.
ACM Transactions on
Intelligent Systems and
Q1
7079
5.2 Findings
This section analyzes the findings on the
opportunities, challenges and limitations of current
BPM, along with recommended future directions.
The analysis is based on the analysis of 22 selected
documents listed in Table 2.
5.2.1 BPM Opportunities for Industry 4.0
In the Industry 4.0 era, improving business processes
provides new opportunities for organizational
transformation, including the redesign of business
models and value chains (Gancarczyk et Ujwary-Gil
2020), it establishes new alliances with IT,
reinforcing strategic goals, and improving optimizing
the efficiency and flexibility of the enterprise’s daily
operations (Xu, Xu, et Li 2018; Gancarczyk et
Ujwary-Gil 2020; Saraeian, Shirazi, et Motameni
The Future of BPM in the Era of Industry 4.0: Exploring New Opportunities for Innovation
919

2018; Castro et Teixeira 2021; Kernytska 2024). In
the context of Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing
systems, BPM plays a crucial role in ensuring that
processes are efficient, agile, and capable of adapting
to new technologies and market demands (Kamble, S.
S., Gunasekaran, A., Ghadge, A., & Raut, R. 2020).
The implementation of BPM significantly impacts
Industry 4.0. Companies adopting advanced BPM
strategy report benefits, such as increased production
efficiency, improved performance monitoring, cost
savings, and a higher rate of automation in production
(Gažová, Papulová, et Smolka 2022).
Furthermore, BPM can drive process innovation
and digital transformation in organizations (Mendling
et al. 2020) by enhancing innovation, agility, and
sustainability through the integration of technologies
like AI, IoT, and Blockchain (Kernytska 2024).
Moreover, BPM enables organizations to adapt to
changing environments, enhancing their ability to
leverage emerging technologies and respond swiftly
to market fluctuations (Ortt, Stolwijk, et Punter
2020). BPM plays a crucial role in enabling
organizations to comply with industry standards,
mitigate risks, and enhance intellectual capital in the
digital era (Broccardo et al. 2024). By automating and
streamlining business processes, BPM significantly
improves operational efficiency and effectiveness
(Nosalska et al. 2019). Furthermore, it enhances
customer experience by enabling organizations to
deliver more personalized and responsive services
(Chauhan et Singh 2019).
In conclusion, BPM is a key tool to support the
digital transformation of organizations, enabling
them to become more competitive, innovative and
agile (Kernytska 2024).
5.2.2 BPM Challenges and Limitations in
the Era of Industry 4.0
While BPM has long been recognized as a key driver
of organizational efficiency, the digital age presents
new challenges (Imgrund and Janiesch 2019). These
challenges include the complexity of integrating
multiple systems and technologies, concerns about
data security and privacy, and the need to upskill the
workers. Resistance to up-skilling the workforce and
organizational changes can hinder BPM
implementation in Industry 4.0 (Szelągowski and
Berniak-Woźny 2022). Additionally, organizations
must enhance flexibility and adaptability to respond
to rapidly changing market conditions and
technological advancements (Chauhan and Singh
2019). Integrating BPM with emerging technologies
like AI, blockchain, and IoT make process
management more complex and subject to
uncertainty, posing significant challenges for
decision-making (Souifi et al. 2022). Current BPMSs
often manage only certain processes leading to
diverging expectations and outcomes (Saraeian,
Shirazi, and Motameni 2018; Pourmirza et al. 2017).
Moreover, the complexities of CPS, which integrate
computational and physical capabilities, require
effective uncertainty management to ensure
reliability (Souifi et al. 2022). The growth of data and
technology has led to significant changes in business
operations. Finally, the challenge of digital
innovation, particularly in creating value from data,
requires a transformation in BPM (Van Looy, 2021).
Security and openness, along with cost and flexibility,
represent a significant challenge in BPM, particularly
in BPM system components that include IoT devices.
BPM systems must seamlessly interact with these
technologies and to be able to leverage their
capabilities and improve business processes
(Elghaish et al. 2021).
BPM discipline has been subjected to significant
challenges in recent years, particularly in the context
of dynamic and complex business environments of
industry 4.0 (Grisold et al. 2021). Companies must
offer higher quality, customized products at
competitive prices and greater flexibility to improve
connectivity in their business processes (Fatorachian
and Kazemi, 2018). To achieve this, organizations
need properly coordinate their local and external
business units, thereby improving BPM flexibility
and optimazing the value chain of inter-
organizational business processes (Bazan and
Estevez 2022). The effectiveness of BPM systems in
Industry 4.0 can be compromised by data quality
issues. Ensuring high-quality data is essential for
accurate decision-making and optimal performance
within these systems (Yokogawa, 2020). The
verification of transactions, for instance, has emerged
as a significant challenge within the domain of
business processes (Viriyasitavat et al. 2019). In their
study, Kerpedzhiev et al. in (Kerpedzhiev et al. 2021)
introduced a new interpretation of the success factors
related to BPM from a digital Innovation perspective.
This perspective emphasizes the dynamic interplay
between technological advancements and
organizational processes, highlighting how digital
tools and methodologies can enhance BPM
effectiveness. However, additional research is
required to develop process innovation theories,
models, and applications that are context-specific and
applicable to various business environments (Van
Looy, 2021).
ICEIS 2025 - 27th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
920

5.2.3 BPM Future Directions
The challenges identified in BPM also present
significant opportunities for experts in business
informatics to develop innovative solutions and
frameworks. (Kerpedzhiev et al. 2021) outline key
challenges that BPM must address over the next
decade, emphasizing the importance of strategic
alignment between BPM and business objectives to
achieve meaningful results. A critical direction for
BPM is the integration of AI and machine learning,
which can facilitate more intelligent and autonomous
business processes (Chauhan & Singh, 2019).
Additionally, blockchain technology can enhance
transparency, security, and trust in business processes
(Ortt, Stolwijk, & Punter, 2020), while IoT will enable
real-time monitoring and optimization, improving
visibility and information sharing across supply chains
(Paksoy, Koçhan, & Ali, 2021). These technologies
can provide greater flexibility in production and
product design, reducing development time and
enabling the production of high-quality, customized
products (Chauhan & Singh, 2019; Fatorachian &
Kazemi, 2018). Exploring the intersection of IoT data
and BPM can lead to adaptive processes that respond
in real-time to changing conditions. Furthermore,
frameworks that integrate IoT technologies into
existing BPM systems are essential for maximizing
the benefits of digital transformation while ensuring
robust risk management (Cardoso et al., 2024). The
scalability and adaptability of BPM systems are
crucial for meeting the evolving demands of Industry
4.0 (Rosemann & vom Brocke, 2015). Current BPM
systems manage only certain processes, creating
opportunities for further research. Addressing
challenges related to security, cost, and flexibility
through blockchain technology (BCT) can facilitate
peer-to-peer transactions, reducing reliance on central
authorities (Garcia-Garcia et al., 2020). In this context,
BCT has to be integrated with BPM system
components that usually include IoT devices
(Elghaish F., et al, 2021). BPM should also focus on
balancing innovation and efficiency (Sliż, 2024) by
exploring digital options for process improvements,
complementing its traditional internal focus
(Eikebrokk, Olsen, & Garmann-Johnsen, 2024).
6 BPM: CAPITALIZING ON
INDUSTRY 4.0
OPPORTUNITIES
The emergence of Industry 4.0 has transformed BPM
by enabling process automation, enhancing decision-
making capabilities, and increasing agility in
responding to market demands. A key opportunity
lies in improved process automation through the
integration of technologies such as IoT, AI, and
machine learning, which drive efficiency, cost
reduction, and quality enhancements (Nozari et al.,
2024; Bartlett et al., 2023). Digitalization of business
processes opens new avenues for innovative business
models and organizational structures (Broccardo et
al., 2024). The integration of information and
communication technology (ICT) with BPM not only
streamlines operations but also allows organizations
to swiftly adapt to changing market conditions
(Moreira et al., 2024). Furthermore, the convergence
of BPM with emerging technologies enhances
organizational efficiency and drives transformation
across various industries by facilitating information
transparency, data analysis, and rapid decision-
making (Elghaish et al., 2021). Industry 4.0 also
emphasizes customer-centric processes, aligning
business operations with customer needs to deliver
personalized and efficient experiences (Ahmed &
Shahzad, 2022). The advancement of IoT technology
enables organizations to implement IoT-aware
business processes, enhancing their ability to sense
and respond proactively to environmental changes
(Cardoso et al., 2024). Overall, Industry 4.0 offers
substantial cost savings in manufacturing through
improved process control, real-time monitoring, and
enhanced decision-making (Ghobakhloo, 2020;
Fatorachian & Kazemi, 2018).
7 SYNTHESIS AND
CONCLUSIONS
This systematic literature review has made several
significant contributions to the research domain at the
intersection of BPM and Industry 4.0:
A Comprehensive Overview: The SLR
provides a thorough examination of the current
state of research on BPM in the context of
Industry 4.0, highlighting key opportunities,
limitations, and future research directions. This
comprehensive overview serves as a
foundational resource for researchers and
practitioners seeking to understand the evolving
landscape of BPM in the digital age.
Identification of Key Challenges and
Opportunities: By synthesizing existing
literature, this review identifies critical
challenges that organizations face when
integrating BPM with Industry 4.0 technologies,
The Future of BPM in the Era of Industry 4.0: Exploring New Opportunities for Innovation
921

such as data security, process standardization,
and the need for agility. Additionally, it
highlights the opportunities presented by
advanced technologies like AI, IoT, and
blockchain, which can enhance process
automation and decision-making.
Framework for Future Research: The
findings of this review outline a framework for
future research that emphasizes the need for
studies focused on the integration of BPM with
emerging technologies. This framework
encourages researchers to explore innovative
practices that balance traditional BPM principles
with the demands of Industry 4.0, thereby
advancing theoretical and practical knowledge in
the field.
Insights into Risk Management: The
review underscores the role of BPM in
establishing robust risk management processes in
the face of increased cybersecurity threats and
data privacy concerns. This insight contributes to
the literature by emphasizing the importance of
integrating risk management into BPM
frameworks, particularly in the context of digital
transformation.
Focus on Customer-Centric Processes:
The synthesis highlights the shift towards
customer-centric processes facilitated by
Industry 4.0 technologies. This contribution
encourages further exploration of how BPM can
be adapted to enhance customer experiences and
align business processes with customer needs in
a rapidly changing environment.
Call for Interdisciplinary Research: By
addressing the convergence of BPM with various
advanced technologies, this review advocates for
interdisciplinary research that combines insights
from fields such as information systems,
operations management, and data analytics. This
call for collaboration can lead to more holistic
approaches to understanding and leveraging
BPM in the context of Industry 4.0.
In conclusion, the integration of BPM with
Industry 4.0 provides a foundation for organizations
to enhance their processes, drive innovation, and
improve overall performance. By leveraging the
strengths of both BPM and Industry 4.0 technologies,
organizations can position themselves for success in
the digital economy, ensuring they remain
competitive and responsive to the demands of the
future.
REFERENCES
Aalst, Wil M. P. van der, Arthur H. M. ter Hofstede, and
Mathias Weske. 2003. “Business Process Management:
A Survey.” In Lecture Notes in Computer Science
(Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial
Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics),
2678:1–12. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Adolph, Lars, Thomas Anlahr, Heinz Bedenbender,
Alexander Bentkus, Lennart Brumby, and Christian
Diedrich. 2016. “German Standardization Roadmap:
Industry 4.0.” Version 2. Berlin: DIN EV.
Ahmed S. and Shahzad K., "Augmenting Business Process
Model Elements with End-User Feedback," in IEEE
Access, vol. 10, pp. 115635-115651, 2022,
Alghamdi, Hassan. 2024. “Assessing the Impact of
Enterprise Architecture on Digital Transformation
Success: A Global Perspective.” Sustainability 16 (20):
8865.
Arnold, Christian, Daniel Kiel, and Kai-Ingo Voigt. 2016.
“How Industry 4.0 Changes Business Models in
Different Manufacturing Industries.” International
Journal of Innovation Management 20 (08): 1640015.
Baduge, S. K., Thilakarathna, S., Perera, J. S., Arashpour,
M., Sharafi, P., Teodosio, B., ... &Mendis, P. (2022).
Artificial intelligence and smart vision for building and
construction 4.0: Machine and deep learning methods
and applications. Automation in Construction, 141,
104440.
Bai, C., Dallasega, P., Orzes, G., & Sarkis, J. (2020).
Industry 4.0 technologies assessment: A sustainability
perspective. International journal of production
economics, 229, 107776.
Baiyere, Abayomi, HannuSalmela, and TommiTapanainen.
2020. “Digital Transformation and the New Logics of
Business Process Management” European Journal of
Information Systems 29 (3): 238–59.
Bartlett, L., Kabir, M. A., & Han, J. (2023). A review on
business process management system design: the role
of virtualization and work design. IEEE Access.
Bazan, Patricia, and Elsa Estevez. 2022. “Industry 4.0 and
Business Process Management: State of the Art and
New Challenges.” Business Process Management
Journal 28 (1): 62–80
Berlak, Joachim, Stefan Hafner, and Volker G.
Kuppelwieser. 2021. “Digitalization’s Impacts on
Productivity: A Model-Based Approach and Evaluation
in Germany’s Building Construction Industry.”
Production Planning & Control 32 (4): 335–45.
Bouwman, Harry, Shahrokh Nikou, Francisco J. Molina-
Castillo, and Mark de Reuver. 2018. “The Impact of
Digitalization on Business Models.” Digital Policy,
Regulation and Governance 20 (2): 105–24.
Broccardo, Laura, Paola Vola, Safiya Mukhtar Alshibani,
and Riccardo Tiscini. 2024. “Business Processes
Management as a Tool to Enhance Intellectual Capital
in the Digitalization Era: The New Challenges to Face.”
Journal of Intellectual Capital 25 (1): 60–91.
Butt, Javaid. 2020. “A Conceptual Framework to Support
Digital Transformation in Manufacturing Using an
ICEIS 2025 - 27th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
922

Integrated Business Process Management Approach.”
Designs 4 (3): 17.
Cardoso P. B., Respício A. and Domingos D., "A Granular
Risk Analysis Approach for IoT-Aware Business
Processes," in IEEE Access, vol. 12, pp. 142058-
142070, 2024.
Castro, S, and L Teixeira. 2021. “Industry 4.0 and Business
Process Management: An Exploratory Study on the
Bilateral Effects.” In Proceedings of the International
Conference on Industrial Engineering and Operations
Management, 4840–47.
Chauhan, Chetna, and Amol Singh. 2019. “A Review of
Industry 4.0 in Supply Chain Management Studies.”
Journal of Manufacturing Technology Management 31
(5): 863–86.
Chrusciak, Camilla Buttura, Anderson Luis Szejka, and
Osiris Canciglieri Junior. 2023. “An Exploratory
Literature Study into Digital Transformation to Support
Business Management Processes.” In International
Conference on Production Research, 513–21. Springer.
Di Ciccio, C., Marrella, A., & Russo, A. 2015.
“Knowledge-Intensive Processes: Characteristics,
Requirements and Analysis of Contemporary
Approaches”. Journal on Data Semantics, 4 (1): 29–57.
Colombo, Armando W., Dirk Schleuter, and Matthias
Kircher. 2015. “An Approach to Qualify Human
Resources Supporting the Migration of SMEs into an
Industrie4.0-Compliant Company Infrastructure.” In
IECON 2015 - 41st Annual Conference of the IEEE
Industrial Electronics Society, 003761–66. IEEE.
Corallo, Angelo, Mariangela Lazoi, and Marianna Lezzi.
2020. “Cybersecurity in the Context of Industry 4.0: A
Structured Classification of Critical Assets and
Business Impacts.” Computers in Industry 114
(January): 103165.
Czvetkó, Tímea, Alex Kummer, TamásRuppert, and
JánosAbonyi. 2022. “Data-Driven Business Process
Management-Based Development of Industry 4.0
Solutions.” CIRP Journal of Manufacturing Science
and Technology 36 (January): 117–32.
Dumitriu, Dan. 2018. “Research on the Trend and Potential
Impact of Adopting BPM Techniques over General
Performance of the Organization.” Procedia
Manufacturing 22: 575–82.
Eikebrokk, Tom R., Dag H. Olsen, and Niels F. Garmann-
Johnsen. 2024. “Conceptualizing Business Process
Management Capabilities in Digitalization Contexts.”
Procedia Computer Science 239 (2023): 330–37.
Elghaish, F., Hosseini, M. R., Matarneh, S., Talebi, S., Wu,
S., Martek, I., ... &Ghodrati, N. (2021). Blockchain and
the ‘Internet of Things' for the construction industry:
research trends and opportunities. Automation in
construction, 132, 103942.
Fatorachian, Hajar, and HadiKazemi. 2018. “A Critical
Investigation of Industry 4.0 in Manufacturing:
Theoretical Operationalisation Framework.”
Production Planning & Control 29 (8): 633–44.
Flechsig, Christian, Jacob Lohmer, Robert Voß, and Rainer
Lasch. 2022. “Business Process Maturity Model for
Digital Transformation: An Action Design Research
Study on The Integration of Information Technology.”
International Journal of Innovation Management 26
(03).
Gajšek, Brigita, and NatašaVujica Herzog. 2020. “Smart
Glasses in Sustainable Manual Order Picking Systems.”
Sustainable Logistics and Production in Industry 4.0:
New Opportunities and Challenges, 219–41.
Gancarczyk, Marta, and Anna Ujwary-Gil. 2020.
“Improving Business Processes and Process
Organization from the Industry 4.0 Perspective.” In
New Challenges in Economic Policy, Business, and
Management, 11–29.
Garcia-Garcia, Julian Alberto, et al. "Using blockchain to
improve collaborative business process management:
Systematic literature review." IEEE Access 8 (2020):
142312-142336.
Gartner. 2016. “BPM Is Critical to Business
Transformation Success.” Gartner. 2016.
https://www.gartner.com/smarterwithgartner/bpm-is-
critical-to-business-transformation-success.
Gartner. 2018. “Gartner Says BPM Is Critical for Business
Transformation Success.” 2018.
Gažová, Andrea, Zuzana Papulová, and DávidSmolka.
2022. “Effect of Business Process Management on
Level of Automation and Technologies Connected to
Industry 4.0.” Procedia Computer Science 200 (2019):
1498–1507.
Ghobakhloo, Morteza. 2020. “Industry 4.0, Digitization,
and Opportunities for Sustainability.” Journal of
Cleaner Production 252 (4): 119869.
Grisold, Thomas, Jan vomBrocke, Steven Gross, Jan
Mendling, Maximilian Röglinger, and Katharina Stelzl.
2021. “Digital Innovation and Business Process
Management: Opportunities and Challenges as
Perceived by Practitioners.” Communications of the
Association for Information Systems 49 (1): 556–71.
Guo, Junlang, JiewuLeng, J. Leon Zhao, Xueliang Zhou,
Yu Yuan, Yuqian Lu, Dimitris Mourtzis, et al. 2024.
“Industrial Metaverse towards Industry 5.0:
Connotation, Architecture, Enablers, and Challenges.”
Journal of Manufacturing Systems 76 (January): 25–42.
Horalek, Josef, Tereza Otcenaskova, Vladimir Sobeslav,
and Petr Tucnik. 2024. “A Business Process and Data
Modelling Approach to Enhance Cyber Security in
Smart Cities.” In Mobile Networks and Applications,
21:70–84.
Imgrund, Florian, and Christian Janiesch. 2019.
“Understanding the Need for New Perspectives on
BPM in the Digital Age: An Empirical Analysis.” In
Lecture Notes in Business Information Processing, 362
LNBIP:288–300.
Kamble, S. S., Gunasekaran, A., Ghadge, A., & Raut, R.
(2020). A performance measurement system for
industry 4.0 enabled smart manufacturing system in
SMMEs-A review and empirical investigation.
International journal of production economics, 229,
107853.
Kernytska, Anna. 2024. “Beyond Optimization: The
Evolving Role of Business Process Management in
Industry Transformation.” 103 (4).
The Future of BPM in the Era of Industry 4.0: Exploring New Opportunities for Innovation
923

Kerpedzhiev, Georgi, Ulrich Matthias König, Maximilian
Röglinger, and Michael Rosemann. 2021. “An
Exploration into Future Business Process Management
Capabilities in View of Digitalization.” Business &
Information Systems Engineering 63 (2): 83–96.
Lee, Ching Hung, Chien Liang Liu, Amy J.C. Trappey,
John P.T. Mo, and Kevin C. Desouza. 2021.
“Understanding Digital Transformation in Advanced
Manufacturing and Engineering: A Bibliometric
Analysis, Topic Modeling and Research Trend
Discovery.” Advanced Engineering Informatics 50
(October): 101428.
Liu, Day‐Yang, Shou‐Wei Chen, and Tzu‐Chuan Chou.
2011. “Resource Fit in Digital Transformation”
Management Decision 49 (10): 1728–42.
Looy, Amy Van. 2021. “A Quantitative and Qualitative
Study of the Link between Business Process
Management and Digital Innovation” Information &
Management 58 (2): 103413.
Mendling, Jan, Brian T Pentland, Jan Recker, Jan
Mendling, and Brian T Pentland. 2020. “Building a
Complementary Agenda for Business Process
Management and Digital Innovation Digital
Innovation.” European Journal of Information Systems
29 (3): 208–19.
Moher, David, Alessandro Liberati, Jennifer Tetzlaff, and
Douglas G. Altman. 2010. “Preferred Reporting Items
for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The
PRISMA Statement.” International Journal of Surgery
8 (5): 336–41.
Nosalska, Katarzyna, Zbigniew MichałPiątek, Grzegorz
Mazurek, and Robert Rządca. 2019. “Industry 4.0:
Coherent Definition Framework with Technological
and Organizational Interdependencies.” Journal of
Manufacturing Technology Management 31 (5): 837–
62.
Nozari, H., Ghahremani-Nahr, J., &Szmelter-Jarosz, A.
(2024). AI and machine learning for real-world
problems. In Advances in Computers (Vol. 134, pp. 1-
12). Elsevier.
Ortt, Roland, Claire Stolwijk, and Matthijs Punter. 2020.
“Implementing Industry 4.0: Assessing the Current
State.” Journal of Manufacturing Technology
Management 31 (5): 825–36.
Paksoy, Turan, ÇiğdemKoçhan, and Sadia Samar Ali. 2021.
Logistics 4.0: Digital Transformation of Supply Chain
Management. CRC Press.
Pourmirza, Shaya, Sander Peters, Remco Dijkman, and
Paul Grefen. 2017. “A Systematic Literature Review on
the Architecture of Business Process Management
Systems.” Information Systems 66: 43–58.
Moreira, H. S. Mamede and A. Santos, "Business Process
Automation in SMEs: A Systematic Literature
Review," in IEEE Access, vol. 12, pp. 75832-75864,
2024,
Saraeian, Shideh, Babak Shirazi, and HomayunMotameni.
2018. “Towards an Extended BPMS Prototype: Open
Challenges of BPM to Flexible and Robust Orchestrate
of Uncertain Processes.” Computer Standards &
Interfaces 57: 1–19.
Sliż, Piotr. 2024. “Ambidextrous Business Process
Management: Unleashing the Dual Power of
Innovation and Efficiency BT.” In, edited by Jochen De
Weerdt and LuisePufahl, 552–64. Cham: Springer
Nature Switzerland.
Souifi, Amel, Zohra Cherfi Boulanger, Marc Zolghadri,
Maher Barkallah, and Mohamed Haddar. 2022.
“Uncertainty of Key Performance Indicators for
Industry 4.0: A Methodology Based on the Theory of
Belief Functions.” Computers in Industry 140: 103666.
Stefanescu, D., Montalvillo, L., Urbieta, A., Galán-García,
P., &UnzillaGalan, J. J. (2024). Smart Contract
Powered Framework for the Next Generation Industry
4.0 Business Model. Distributed Ledger Technologies:
Research and Practice, 3(4), 1-24.
Su, Dan, Lijun Zhang, Hua Peng, ParvanehSaeidi, and
ErfanBabaeeTirkolaee. 2023. “Technical Challenges of
Blockchain Technology for Sustainable Manufacturing
Paradigm in Industry 4.0 Era Using a Fuzzy Decision
Support System.” Technological Forecasting and
Social Change 188 (January): 122275.
Sierakowski. 2024. “BPM Challenges, Limitations and
Future Development Directions – a Systematic
Literature Review.” Business Process Management
Journal 30 (2): 505–57.
Tupa, Jiri, and Frantisek Steiner. 2019. “Industry 4.0 and
Business Process Management.” TehničkiGlasnik 13
(4): 349–55.
Vaska, Selma, Maurizio Massaro, Ernesto Marco
Bagarotto, and Francesca Dal Mas. 2021. “The Digital
Transformation of Business Model Innovation: A
Structured Literature Review.” Frontiers in Psychology
11 (January): 539363.
Viriyasitavat, Wattana, Li Da Xu, Zhuming Bi, and Vitara
Pungpapong. 2019. “Blockchain and Internet of Things
for Modern Business Process in Digital Economy—the
State of the Art.” IEEE Transactions on Computational
Social Systems 6 (6): 1420–32.
Weske, Mathias. 2019. “Business Process Management
Architectures.” In Business Process Management, 351–
84. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Xu, Li Da, Eric L. Xu, and Ling Li. 2018. “Industry 4.0:
State of the Art and Future Trends.” International
Journal of Production Research 56 (8): 2941–62.
Yang, Q., Liu, Y., Chen, T., & Tong, Y. (2019). Federated
machine learning: Concept and applications. ACM
Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology
(TIST), 10(2), 1-19.
Zhang, C., & Chen, Y. (2020). A review of research
relevant to the emerging industry trends: Industry 4.0,
IoT, blockchain, and business analytics. Journal of
Industrial Integration and Management, 5(01), 165-
180.
ICEIS 2025 - 27th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
924
