
The Effectiveness of Simulation in Biomedical Engineering Education: A
Case Study
Ersilia Vallefuoco
a
, Maria Romano
b
and Alessandro Pepino
c
Department of Electrical Engineering and Information Technology,
University of Naples Federico II, via Claudio 21, Naples, Italy
Keywords:
Engineering Education, Simulation, Experiential Learning, Educational Innovation, Biomedical Engineering.
Abstract:
In the last decades, simulation has become an important tool in education, especially for the implementation
of specific pedagogical approaches. In this work, we illustrate how simulation is implemented in a biomedical
engineering course. Specifically, two simulation educational tools are currently used in the course to model
and analyze healthcare models and health networks. To evaluate the perception of simulation by students on
both student learning and subsequent professional careers, a survey was conducted. The survey, distributed
through social networks, targeted students in the past decade who are now employed in regular job positions.
78 alumni completed the questionnaire and indicated a high level of perceived effectiveness of simulation and
teaching course strategies, both in the study of course topics and in professional life.
1 INTRODUCTION
Biomedical engineering (BME) is dedicated to apply-
ing engineering principles to biomedical fields, fo-
cusing primarily on solving problems and improving
health, care processes, and overall quality of life for
patients (International Federation of Medical and Bi-
ological Engineers, 2024). In general, the BME de-
gree course is based on the fundamentals of human
anatomy and physiology and traditional engineering,
offering then specialization in several areas such as
medical instrumentation and imaging, biomechanics
and biomaterials, biosignal processing, rehabilitation
engineering, health informatics, and clinical engineer-
ing (Montesinos et al., 2023).
Problem solving is a key element of BME educa-
tion, and a variety of pedagogical strategies are used,
including problem-based (Long et al., 2022; Warnock
and Mohammadi-Aragh, 2016), project-based (Seti-
awan, 2019; Rezvanifar and Amini, 2019), and ex-
periential learning (Montesinos et al., 2023; Mon-
tesinos et al., 2022). To implement these methods,
innovative BME curricula have proposed the use of
simulation education tools (Singh et al., 2018; Singh
et al., 2019). Simulation facilitates exploration and
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3952-1500
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1133-1115
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6434-5145
analysis of real-world challenges and encourages stu-
dents to investigate and propose solutions, increasing
students’ motivation, collaboration, and participation
(Magana and de Jong, 2018). In addition, the possi-
bility of mixing synchronous and asynchronous learn-
ing, real-time feedback combined with the continu-
ous monitoring of students’ results, as well as the low
cost, have promoted the use of simulation and its tools
in the education of BME (Singh et al., 2018; Datta
et al., 2013).
The literature provides numerous examples of
simulation-based educational tools in BME. For in-
stance, in response to COVID-19 pandemic restric-
tions, (Allen and Barker, 2021) suggested the use
of an online virtual laboratory simulation to enhance
the learning experience. Similarly, simulation learn-
ing activities were integrated in a BME course at
the University of British Columbia (Harandi et al.,
2019). The blended learning course combined lec-
tures with practice activities using two specific sim-
ulation tools: ElectromagneticWorks for electric and
magnetic field modeling and simulation, and PartSim
for circuit analysis. Another recent study (Montesinos
et al., 2023) introduced an experiential learning ap-
proach to equip BME students with transdisciplinary
knowledge and skills aimed at improving hospital
and healthcare operations. The research employed
FlexSim Healthcare software to simulate and evaluate
patient-centered processes within a hospital environ-
854
Vallefuoco, E., Romano, M. and Pepino, A.
The Effectiveness of Simulation in Biomedical Engineering Education: A Case Study.
DOI: 10.5220/0013479800003932
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2025) - Volume 2, pages 854-859
ISBN: 978-989-758-746-7; ISSN: 2184-5026
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

ment. Additionally, (Cheng et al., 2023) investigated
the integration of artificial intelligence tools, such as
chatbots, to facilitate simulation activities in BME ed-
ucation.
This study aims to explore the application of sim-
ulation in a BME course and to evaluate how effec-
tively the course and its methods translate to practical
use in the field of BME. Specifically, it focuses on the
Health Information Systems course offered in the first
year of the Master’s degree program in BME at the
University of Naples Federico II. The course covers
fundamentals of health systems and process analysis,
modeling and analysis of health databases, networked
health services, security, and privacy in health sys-
tems. It incorporates several simulation tools during
traditional lectures and asynchronous activities. To
investigate the longitudinal effectiveness of this learn-
ing approach, we developed a specific survey to mea-
sure the perception of students after they had entered
the workforce.
2 MATERIAL AND METHODS
2.1 Course Overview
The course “Health Information Systems”, offered in
the first year of the Master’s degree program in BME
at the University of Naples Federico II, aims to ex-
plore concepts related to health information systems
and their applications; a special emphasis is given to
the organizational analysis of healthcare systems as
an essential prerequisite for designing an information
system. The course consists of five sections:
• Discrete event simulation for the analysis of
healthcare organizational models.
• Network infrastructure services.
• Analysis and modeling of healthcare databases.
• Security and privacy.
• Web Accessibility.
At the end of the course, students can develop simple
prototypes of healthcare information systems in the
form of an organizational model and an IT network
infrastructure. They acquire also professional knowl-
edge for the analysis and design of business applica-
tions. Typically, the course is attended by an average
of 130 students per year.
Moodle is used as a learning management system
to structure the course. The Moodle course platform
creates a learning environment that allows students
to manage their study time efficiently, review lessons
through systematic recording of all class activities,
continuous interaction with the subject teacher, and
effectively manage all technical issues related to the
use of simulation tools (Magana and de Jong, 2018).
The platform is not an alternative to traditional teach-
ing but a support tool for implementing blended learn-
ing.
The course incorporates the use of simulation
tools to improve understanding of key topics, provide
practical examples, and then enhance the learning
processes and support a more objective assessment
of learning objectives, focusing more on the compe-
tencies acquired (Montesinos et al., 2023). The sim-
ulation educational tool and activities were applied
to the first two chapters, which account for approx-
imately 70% of the total course hours, while the re-
maining 30%, although with a particular emphasis on
operational aspects, is organized more traditionally,
through theoretical lectures, practical examples, and
exercises.
Course objectives include understanding compu-
tational modeling and simulation techniques in health
systems, examining how various parameters affect
these systems, and evaluating the accuracy and reli-
ability of simulation results.
2.2 Simulation Education Tools
In the first part of the course, students are introduced
to the most common organizational models in health-
care. An overview of the most common techniques
for static analysis of organizational systems is pro-
vided. These are essential for creating tools capable
of artificially reproducing (simulating) some of the
organizational models discussed in the introductory
part of the course. To enhance understanding, the in-
structor employs simulated interviews to illustrate the
functioning of traditional healthcare organizational
structures, including hospital management, ward op-
erations, and laboratory workflows. Subsequently, the
students learn how to describe the concepts concisely
expressed by stakeholders using typical Business Pro-
cess Management diagrams, such as use cases and ac-
tivity diagrams. They then progress to mastering the
techniques and tools required to model not only the
structural aspects but also the functionality of health-
care systems and their associated telecommunications
infrastructure. This process equips them with practi-
cal, real-world skills that are essential for identifying,
analyzing, and improving process-related challenges
in professional environments.
Students can install educational tools on their lap-
tops and collaborate in the classroom and remotely
using the tools available on the Moodle platform.
The Effectiveness of Simulation in Biomedical Engineering Education: A Case Study
855

2.2.1 Organizational Models Simulation
Simul8 (SIMUL8 Corporation, 2025), a discrete
event simulation software, is used as an educational
tool to model, analyze, and optimize complex pro-
cesses and systems. It is particularly effective in
healthcare settings, where it supports tasks such as op-
timizing patient flow, analyzing resource allocation,
and simulating hospital processes.
With Simul8, users visually build simulation mod-
els using components like queues, work centers, and
resources. The software also allows for the integra-
tion of real-world data from spreadsheets, databases,
and other sources, ensuring models are both accurate
and grounded in reality. Unlike traditional graphi-
cal process modeling tools, Simul8 enables users to
replicate the live behavior of organizational systems
in great detail. This means the software not only rep-
resents the structural aspects of a process but also sim-
ulates how its dynamics evolve over time. As a result,
students can perform both “As-Is” analyses to eval-
uate existing processes and “What-If” scenarios to
test potential improvements. This hands-on approach
gives them practical experience with the healthcare
challenges covered in the course and prepares them
to address organizational problems in real-world con-
texts.
To ensure sufficient practice, students have access
to a full version of the software for six months. This
extended timeframe allows them to develop the nec-
essary skills and achieve a high level of proficiency.
2.2.2 Network Systems Simulation
For the infrastructure part, students practice using
Cisco Packet Tracer (Cisco, 2025). This is a sim-
ulation tool for designing, configuring, and exam-
ining network operations in a virtual environment.
This interactive method can facilitate understanding
of telematic network operations and related problems.
Through a partnership between Cisco and the Uni-
versity of Naples Federico II, students benefit from
access to an educational version of Cisco Packet
Tracer.
2.3 Exam Procedure
The final exam for these two learning sections pro-
vides the design and development of a simulation
model and network infrastructure of a healthcare sys-
tem using the proposed simulation tools.
In the Moodle course platform, the instructor adds
an activity called ”assignment,” which allows the stu-
dent who intends to take the exam to submit a short
document explaining the context, process, and related
issues of the healthcare system that will be simulated.
Before the exam, the instructor evaluates and, if ap-
propriate, approves the document, authorizing the stu-
dent to independently develop the required simulation
model. The model will then be discussed during the
exam.
2.4 Longitudinal Qualitative Evaluation
The effectiveness and satisfaction of students with
this teaching approach are extensively demonstrated
through the teaching evaluation questionnaires that
students fill out every year before taking the exam.
However, these questionnaires do not provide any in-
formation regarding students’ perceptions of the skills
they have acquired once they enter the workforce and
have the opportunity to experience the actual impact
of the skills they have attained.
A questionnaire has been prepared to evaluate the
impact of the applied teaching methodology on the
professional life of the students. The questionnaire
was filled in exclusively by graduates of the BME
at the University of Naples Federico II, where the
course in Healthcare Information Systems is compul-
sory. The first part of the questionnaire asked for
general information, specifically the number of years
since graduation, the sector of employment, and the
number of months from graduation to the first job.
The second part of the questionnaire was designed to
investigate the perceived effectiveness of the course
content and simulation tools in the professional ca-
reer. Specifically, participants answer using a 5-point
Likert scale ranging from: absolutely no to absolutely
yes.
Collecting data from students after they leave uni-
versity can indeed be challenging. Once students
graduate and enter the workforce, they may become
geographically dispersed, making them difficult to
track and reach for follow-up studies. In addition,
they may become less engaged in university-related
activities and less likely to participate in surveys or
research studies. For this reason, the questionnaire
was administered through social channels, specifi-
cally Facebook and Linkedln, to facilitate the dissem-
ination of the survey and reach the largest number
of students. The survey was anonymized and partic-
ipants gave their consent before participating in the
survey.
3 RESULTS
A total of 78 answers were collected. Most of the
participants (44%) who completed the questionnaire
CSEDU 2025 - 17th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
856
graduated more than 5 years ago, while 42% gradu-
ated more than 10 years ago and 14% graduated one
year ago. 23% of the participants work in the health
informatics sector, 22% in clinical engineering, 24%
in consulting, 10% in services, 4% in sales, 3% in
manufacturing, and 14% in other sectors. 29% of the
participants found a job within two months of grad-
uation, 34% found a job after two months, and 37%
found a job before graduation.
The results of the survey questions about the effec-
tiveness of the course and the simulation are shown in
Fig. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7.
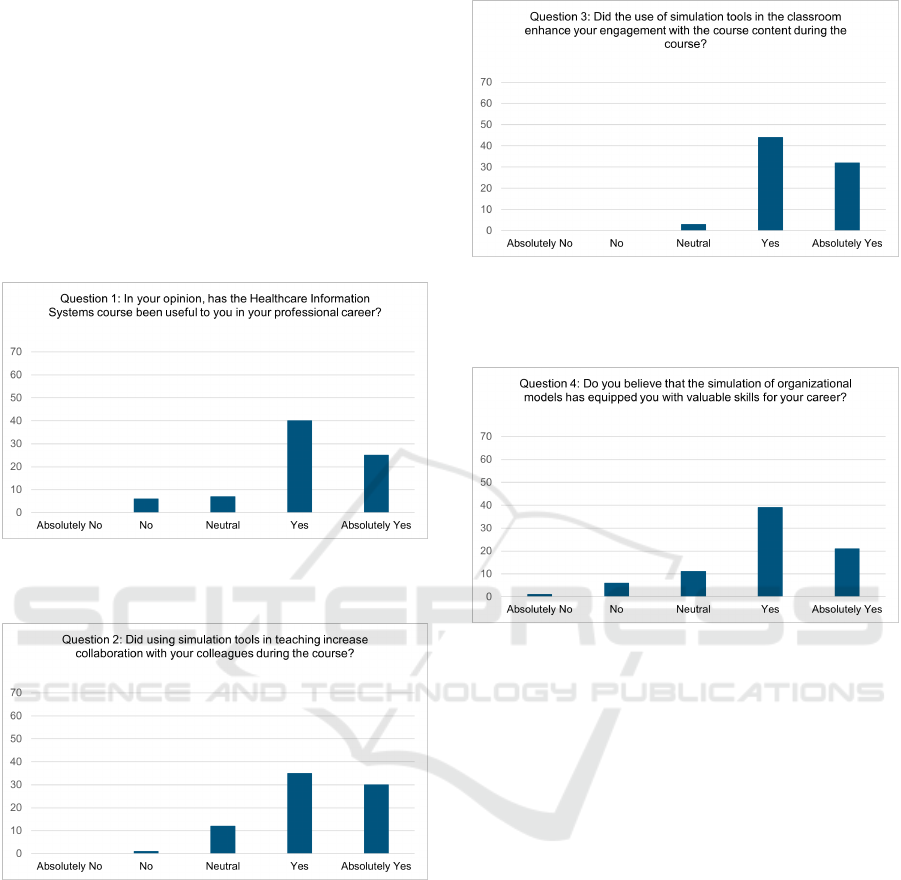
Figure 1: Results of Question 1. The figure illustrates the
responses to Q1 regarding participants’ perception of the
course’s overall usefulness.
Figure 2: Results of Question 2. The figure illustrates re-
sponses to Q2, which assessed whether the use of simula-
tion tools during teaching enhanced collaboration with col-
leagues throughout the course.
4 DISCUSSION AND
CONCLUSION
Simulation has become a critical component of BME
education, enabling the modeling, analysis, and opti-
mization of complex healthcare systems (Montesinos
et al., 2023). In this study, we propose a practical
example of simulation implementation in BME ed-
Figure 3: Results of Question 3. The figure shows re-
sponses to Q3, which evaluated whether the use of simu-
lation tools in the classroom enhanced student engagement
with the course content during the course.
Figure 4: Results of Question 4. The figure shows responses
to Q4, which examined whether the simulation of organiza-
tional models provided participants with valuable skills for
their careers.
ucation. Specifically, a learning experience was de-
signed for a Master’s course in BME using two ed-
ucational simulation tools: Simul8 and Cisco Packet
Tracer. These tools allow students to analyze and op-
timize healthcare systems. The educational activities
are organized and managed into the Moodle course.
To investigate the usefulness of simulation use in
BME, a specific survey was created. The survey re-
vealed that almost all of the participants have been
working for more than 1 year and therefore have a
clear perception of their work needs. In addition,
it should be noted that the sectors of employment
are quite diversified, confirming that BME graduates
are very versatile professionals who find employment
in work environments far from the world of health.
(Sloane and Hosea, 2017). The majority of partici-
pants reported that the course content was useful in
their professional careers (Fig. 1). As shown in
Fig. 2 and 3, most participants acknowledged the role
of simulations in enhancing collaboration with col-
leagues and fostering greater engagement in course
activities. Similarly, participants indicated that the
The Effectiveness of Simulation in Biomedical Engineering Education: A Case Study
857
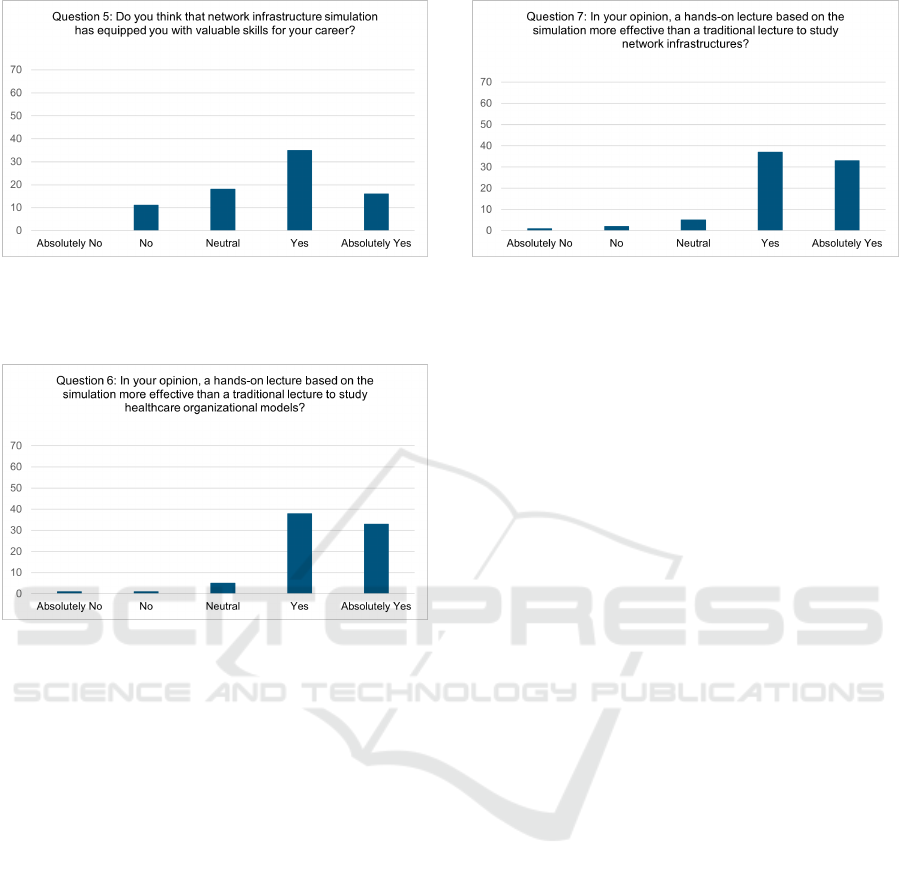
Figure 5: Results of Question 5. The figure illustrates re-
sponses to Q5, which evaluated whether the simulation of
network infrastructure provided participants with valuable
skills for their careers.
Figure 6: Results of Question 6. The figure shows responses
to Q6, which assessed whether a hands-on lecture based on
simulations is perceived as more effective than traditional
lectures for studying healthcare organizational models.
simulation had a significant impact on their career de-
velopment (Fig. 4 and 5). In addition, as illustrated
in Fig. 6 and 7, hands-on lectures incorporating simu-
lations were rated more favorably than traditional lec-
tures for studying course content. This preference was
emphasized in participant feedback, with several sug-
gestions to use simulation and its tools for multiple
courses in the curriculum.
To our knowledge, this is the first study to assess
the perceived usefulness of simulation in biomedi-
cal engineers and to evaluate the impact of the BME
course and its strategies with a longitudinal perspec-
tive, not limited to the course feedback question-
naire typically administered at the end of a semester.
Consistent with the literature (Singh et al., 2018;
Mukherjee and Barker, 2021; Adam and Hashim,
2014; Lozano-Dur
´
an et al., 2023), our results indi-
cate a positive response to the use of simulation tools
both in learning and then in work settings. Further-
more, although the proposed simulation activities are
applied in a specific BME course, the current re-
sults confirm the usefulness of integrating active ped-
Figure 7: Results of Question 7. The figure illustrates re-
sponses to Q7, which evaluated whether a hands-on lecture
based on simulations is perceived as more effective than tra-
ditional lessons for studying network infrastructures.
agogical strategies and techniques in BME educa-
tion (Cyrus Rezvanifar and Amini, 2020; Rezvanifar
and Amini, 2019). This integration effectively sup-
ports the transfer of knowledge from lectures to prac-
tical applications in real-world settings (Singh et al.,
2018). Moreover, as the survey results show, simula-
tion can be an effective and versatile tool for improv-
ing the climate of collaboration and engagement in
the classroom, and thus the psychological well-being
of students (Singh et al., 2018; Singh et al., 2019; Ma-
gana and de Jong, 2018). The lessons can become an
opportunity not only to receive knowledge from the
instructor but also to discuss and work together on
concrete applications using these tools (Montesinos
et al., 2023).
It should be noted that implementing simulation-
based active learning modules poses several chal-
lenges for instructors, who need to review and re-
analyze course activities and documentation. How-
ever, as emphasized by (Mukherjee and Barker,
2021), a great deal of effort is required only in
the first edition of the course; subsequently, the
re-implementation of simulation activities becomes
more manageable. We have successfully managed
this process of re-implementation, largely due to the
Moodle platform.
The present study has several limitations. First,
although the sample of 78 participants provides valu-
able insights, the relatively small sample size and self-
selective nature of social media recruitment may not
be fully representative of the entire BME graduate
population. In addition, the use of purely qualita-
tive measures based on participants’ subjective per-
ceptions, while providing important findings, could
benefit from integration with more objective quanti-
tative measures to assess the actual impact on profes-
sional careers. Another limitation relates to the simu-
lation tools used. The use of a non-open access sim-
CSEDU 2025 - 17th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
858

ulation tool may reduce its replicability in other edu-
cational contexts. However, it is worth noting that the
simulation programs are free to students through the
educational version, resulting in minimal cost to the
university.
Further research should address these limitations
by expanding the sample size and assessing the longi-
tudinal efficacy of simulation-based learning in BME
education, particularly its impact on career outcomes.
This includes the evaluation of long-term career ef-
fects and the use of simulation capabilities in the
workplace.
REFERENCES
Adam, T. and Hashim, U. (2014). Comsol multiphysics
simulation in biomedical engineering. Advanced Ma-
terials Research, 832:511–516.
Allen, T. E. and Barker, S. D. (2021). Bme labs in the
era of covid-19: transitioning a hands-on integrative
lab experience to remote instruction using gamified
lab simulations. Biomedical Engineering Education,
1(1):99–104.
Cheng, K., Guo, Q., He, Y., Lu, Y., Gu, S., and Wu, H.
(2023). Exploring the potential of gpt-4 in biomed-
ical engineering: the dawn of a new era. Annals of
Biomedical Engineering, pages 1–9.
Cisco (2025). https://www.netacad.com/cisco-packet-
tracer, FAccessed Jan. 18, 2025.
Cyrus Rezvanifar, S. and Amini, R. (2020). Self-efficacy
versus gender: Project-based active learning tech-
niques in biomedical engineering introductory com-
puter programming courses. Journal of Biomechani-
cal Engineering, 142(11):111004.
Datta, A. K., Rakesh, V., and Way, D. (2013). Simulation as
an integrator in an undergraduate biological engineer-
ing curriculum. Computer Applications in Engineer-
ing Education, 21(4):717–727.
Harandi, N. M., Jaeger, C. P., and Loewen, P. D. (2019).
Supporting active learning through team based prob-
lem solving and simulation in an integrated biomedi-
cal engineering course. Proceedings of the Canadian
Engineering Education Association (CEEA).
International Federation of Medical and Biological Engi-
neers (2024). IFMBE’s Strategic Plan. https://ifmbe.
org. Accessed Jan. 5, 2025.
Long, J., Dragich, E., and Saterbak, A. (2022). Problem-
based learning impacts students’ reported learning
and confidence in an undergraduate biomedical engi-
neering course. Biomedical Engineering Education,
2(2):209–232.
Lozano-Dur
´
an, A., Rudolphi-Solero, T., Nava-Baro, E.,
Ruiz-G
´
omez, M. J., and Sendra-Portero, F. (2023).
Training scientific communication skills on medical
imaging within the virtual world second life: Per-
ception of biomedical engineering students. Interna-
tional Journal of Environmental Research and Public
Health, 20(3):1697.
Magana, A. J. and de Jong, T. (2018). Modeling and simula-
tion practices in engineering education. Computer Ap-
plications in Engineering Education, 26(4):731–738.
Montesinos, L., Salinas-Navarro, D. E., and Santos-Diaz,
A. (2023). Transdisciplinary experiential learning
in biomedical engineering education for healthcare
systems improvement. BMC Medical Education,
23(1):207.
Montesinos, L., Santos-Diaz, A., Salinas-Navarro, D. E.,
and Cendejas-Zaragoza, L. (2022). Experiential learn-
ing in biomedical engineering education using wear-
able devices: a case study in a biomedical signals
and systems analysis course. Education Sciences,
12(9):598.
Mukherjee, D. and Barker, A. J. (2021). Using simulation-
based active learning strategies for teaching bioflu-
ids concepts. Journal of Biomechanical Engineering,
143(12):121011.
Rezvanifar, S. C. and Amini, R. (2019). Project-based ac-
tive learning techniques enhance computer program-
ming academic and career self-efficacy of undergrad-
uate biomedical engineering students. In 2019 ASEE
Annual Conference & Exposition.
Setiawan, A. W. (2019). Implementation of project-based
learning in biomedical engineering course in itb: op-
portunities and challenges. In World Congress on
Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering 2018:
June 3-8, 2018, Prague, Czech Republic (Vol. 1),
pages 847–850. Springer.
SIMUL8 Corporation (2025). https://www.simul8.com/.
Accessed Jan. 18, 2025.
Singh, A., Ferry, D., and Balasubramanian, S. (2019). Effi-
cacy of clinical simulation-based training in biomedi-
cal engineering education. Journal of biomechanical
engineering, 141(12):121011.
Singh, A., Ferry, D., and Mills, S. (2018). Improving
biomedical engineering education through continuity
in adaptive, experiential, and interdisciplinary learn-
ing environments. Journal of biomechanical engineer-
ing, 140(8):081009.
Sloane, E. and Hosea, F. (2017). Role of biomedical engi-
neers in the evolution of health-care systems. Human
resources for medical devices, the role of biomedical
engineers, pages 127–142.
Warnock, J. N. and Mohammadi-Aragh, M. J. (2016). Case
study: use of problem-based learning to develop stu-
dents’ technical and professional skills. European
Journal of Engineering Education, 41(2):142–153.
The Effectiveness of Simulation in Biomedical Engineering Education: A Case Study
859
