
Training Telemedicine Robots: A Path Planning Optimization Method
for Educational and Medical Application
Artur Samojluk
a
and Aleksandra Szpakowska
b
Faculty of Mathematics and Computer Science, University of Warmia and Mazury in Olsztyn, Poland
Keywords:
Educational Technology, Path Planning, Mereological Potential Field Algorithm, Educational Telemedicine
Robot, Complex Labyrinth Map.
Abstract:
In this paper, we present a Path Planning Optimization Method (PPOM) designed for educational telemedicine
robots. Based on the mereological potential field algorithm, it integrates data preprocessing and optimization
tools to enhance efficiency. Our method addresses navigation challenges in complex, tightly spaced med-
ical environments while emphasizing its educational value. By incorporating data selection, cleaning, and
transformation, PPOM enables efficient path planning in maze-like layouts with long, narrow corridors, mim-
icking real-world hospital wards and patients’ homes. This equips telemedicine robots to navigate local traps
and tight spaces, providing a robust framework for training students and professionals in robot navigation
and decision-making. Simulation results confirm PPOM’s high performance in complex environments. The
algorithm ensures precise navigation and effective obstacle avoidance, making it ideal for telemedicine ap-
plications. Unlike classical methods that struggle with blocked nodes, PPOM selects sectors, minimizing
obstructions and improving computational efficiency. This enhances route passability, optimization, and reli-
ability in dynamic environments.
1 INTRODUCTION
With the changing world, the expectations and skills
of computer science students in using future technolo-
gies, such as telemedicine and robotics, are evolving.
To enhance student learning in the UWM lab, we built
obstacle models simulating hospital room conditions
and tested robot performance in these settings. Dur-
ing the experiments, we identified specific obstacle
configurations (beds, sanitation, medical devices) that
introduced a new challenge in path planning: posi-
tioning obstacles in a way that creates local traps for
the robot. Analyzing these critical cases using two
mathematical methods led to the development of a
path planning algorithm that effectively resolves this
issue. As part of an educational activity, students
implemented the algorithm model into a robot and
conducted successful physical simulations. The algo-
rithm is easily adaptable for new educational robots
and has broader applications in indoor path planning
for small robots. The successful implementation of
this algorithm has inspired students to engage more
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5822-2210
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2641-8846
deeply in scientific research, leading some to join the
robotics research club. The project’s execution marks
both a scientific and educational success.
It is worth mentioning that the use of team-
work and active learning methods in this project con-
tributed to the development of students’ competencies
in terms of cooperation and responsibility for joint ac-
tions. According to the results of the research (Planas-
Llad
´
o et al., 2021), self-assessment and peer assess-
ment in the context of teamwork in higher education
can significantly affect the development of students’
interpersonal and professional competencies, which
was also reflected in our project implementation. In
addition, the use of collaborative learning techniques,
such as group work and sharing knowledge and re-
sponsibility for the implementation of tasks, is in
line with the assumptions presented in the publication
(Taxirovna, 2024), (Falcione et al., 2019). Interac-
tive student engagement improves cognitive abilities
in the learning process and affects the overall educa-
tional development of young people. The study (Oth-
man and Zaın, 2015) assessed the effect of online col-
laboration on the cognitive abilities of programming
students, especially in the area of logical thinking and
problem-solving skills. The results showed that after
Samojluk, A. and Szpakowska, A.
Training Telemedicine Robots: A Path Planning Optimization Method for Educational and Medical Application.
DOI: 10.5220/0013481400003932
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2025) - Volume 1, pages 147-157
ISBN: 978-989-758-746-7; ISSN: 2184-5026
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
147
Figure 1: Graphic representation of system operation - path planning in a labyrinth.
the interactive session, the number of students with
a high level of logical thinking increased from 30%
to 51.7%, which is an improvement of 21.7%. Addi-
tionally, when analyzing the effectiveness of solving
programming tasks, it was shown that 53.3% (8 out of
15 groups) were able to solve more complex problems
requiring analysis. These results indicate that interac-
tive teaching methods based on online collaboration
can significantly support the development of students’
cognitive abilities in the area of programming. This
theory is also supported by the study (Nurdin and Se-
tiawan, 2016), in which interactive technologies in-
creased students’ cognitive abilities. These methods
not only increase student engagement but also pro-
mote the development of critical thinking and the abil-
ity to solve problems independently. Thanks to this
project, it was possible to achieve not only educa-
tional goals but also to awaken in students a passion
for further development in robotics and automation.
The main idea of this study on optimizing the path
planning process for telemedical robots came from
the key methodology developed by Polkowski and
Skowron (Polkowski and Skowron, 1996). The re-
sults of this work, which utilized mereological po-
tential fields, were applied in a subsequent pub-
lication (Polkowski and O
´
smiałowski, 2008), and
(O
´
smiałowski and Polkowski, 2010). The motivation
for researching using and improvement of path plan-
ning algorithms came from the implementation of an-
other telemedical project. The mentioned project fo-
cuses on creating a voice telemedical system that en-
ables remote and automated medical interviews with
patients, commissioned by the National Centre for
Research and Development in Poland. During the
project implementation, it was observed that the sys-
tem could more effectively fulfill it is assumptions in
a hospital context if it were possible for medical inter-
views could be conducted directly with patients. This
led to the idea of a robot that could monitor patients
in hospital wards and, if necessary, approach the bed
of a patient to conduct a conversation. Analysis re-
vealed that the layout of beds in the hospital, and it
is equipment, create a kind of labyrinth from the per-
spective of the robots, making it difficult to quickly
reach the destination. To the robot efficiently reach
the designated location without disrupting the staff of
the medical, taking into account the correct side of
the bed of the patient, it must be able to rapidly learn
the environment and dynamically plan paths to des-
ignated points. The research problem is associated
with the need to endow the robot with ’human spatial
intuition’ to enable planning the trip to the chosen lo-
cation (the problem of route passability). Thus, the
demand for quick and safe access to the telemedical
robot became the key motivation for conducting re-
search in this field.
This study aims to enhance the path planning pro-
posed by Szpakowska et al. in 2023 (Szpakowska
et al., 2023) which utilizes a mereological potential
field algorithm by applying an additional decision-
making system. The mentioned extension focuses on
reducing the number of generated potential fields by
analyzing and concerning defined sectors that repre-
sent the split part of a map. Additionally, there is an
effort to modify an existing path planning algorithm
by adding new functions like checking if two cho-
sen potential fields have not been connected by a line
crossing an obstacle field. Furthermore, this paper ap-
plies increased automation to the path-planning algo-
rithm. The process begins by generating the mereo-
logical potential field, and after that filtering the list
of potential fields by removing unnecessary data. The
action of reducing data starts from map analysis. A
decision-making system checks if between two close
sectors exists any vertical or horizontal connection, if
so the system treats sectors as passable. The num-
ber of potential sector combinations could be sub-
stantial; hence, one of the deciding factors is select-
ing the combination with the fewest sectors. The al-
gorithm analyzes sectors until it gets the list of con-
nected sectors from the determined start to the goal.
The returned sector list contains all potential fields
that fall within them. The truncated list of potential
fields in which any possible path certainly exists is
CSEDU 2025 - 17th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
148

passed to the path search algorithm, thanks to which
we have got the accurate path. The proposed solu-
tion solves the problem of complicated maps contain-
ing many obstacles. Examples of such an environ-
ment are hospital wards or homes of the patients. The
next sections will show the effectiveness of the pro-
posed algorithm. The mentioned research takes into
account labyrinthine cases and environments charac-
terized by long narrow corridors similar to different
types of medical environments. To get better results
we applied a path-planning algorithm, which gave us
a clear, unambiguous route. Such operations pro-
vided the optimal path for the telemedical robot. The
next part of the study will explore further developing
a decision-making system using principles of rough
sets.
1.1 Educational Applications
Interactive Learning Tools. The proposed algo-
rithm serves as a good platform for teaching robotics,
allowing students to gain practical understanding
of path-planning algorithms in realistic environments.
Development of Analytical Thinking. Students
learn to analyze problems and design solutions,
which strengthens their ability to think logically
and strategically in situations that require quick
decision-making.
Simulations in Education. The use of physical
simulations in laboratories enables students to gain
experience in environments resembling real-world
scenarios, enhancing their practical skills.
Interdisciplinary Integration. The project encour-
ages collaboration among students from different
fields, such as computer science, mechanics, and
medicine, promoting an interdisciplinary approach to
learning and problem-solving.
Supporting Innovation. The algorithm inspires stu-
dents to experiment with their own modifications and
develop new features, supporting creativity and inno-
vative thinking.
1.2 Research Applications
Algorithm Optimization. The PPOM method en-
ables further refinement of path-planning algorithms,
increasing their efficiency in complex environments.
Applications in Medicine. The algorithm is specif-
ically designed to meet the unique needs of medical
environments, such as narrow corridors and crowded
spaces in hospitals.
Solutions for Dynamic Environments. The algo-
rithm can be adapted to rapidly changing conditions,
making it an ideal tool for research in dynamic and
adaptive robotics.
Collaboration in Multi-Robot Systems. The
algorithm supports synchronization and coordination
among multiple robots, opening new opportunities
for research in multi-agent systems.
Foundation for Further Research. The research
findings can serve as a basis for developing new
methods in robotics, mereology theory, and decision-
making algorithms, supporting the advancement of
emerging technologies.
2 ROUGH SET THEORY AND
ROUGH MEREOLOGY
Rough set theory (Pawlak, 1992) employs lower and
upper approximations to facilitate the classification of
ambiguous data, providing a means to navigate uncer-
tainty without the need for additional external param-
eters. Rough sets have found extensive applications
in various fields, notably in data analysis, where they
aid in uncovering hidden patterns and relationships
within imprecise datasets (Komorowski et al., 1999).
Rough mereology (Polkowski and Skowron, 1996), a
subsequent development in this domain, extends the
foundational principles of rough sets to encompass
the concept of ’part to a degree’. Developed to ad-
dress the limitations in traditional mereology, rough
mereology allows for a more flexible understanding
of part-whole relationships in contexts where preci-
sion is unattainable. The reasoning based on rough
mereology introduces the concept of rough inclusion,
denoted as µ(x, y, r). This relation posits that x is a part
of y to a degree of at least r. Given our focus on spatial
objects, the rough inclusion is expressed as µ(X,Y, r)
if and only if
|X∩Y |
X
>= r, where X and Y represent n-
dimensional solids and |X| signifies the n-volume of
X. The synergy between these two theories provides
a comprehensive framework for the analysis of non-
binary, uncertain data structures. The ongoing evolu-
tion of rough set theory and rough mereology contin-
ues to contribute significantly to advancements in data
science, offering new perspectives and methodologies
for dealing with the complexities of modern data.
Training Telemedicine Robots: A Path Planning Optimization Method for Educational and Medical Application
149
3 BASIC POTENTIAL FIELDS
ALGORITHM AND SOME
UNIQUE ARRANGEMENT OF
OBSTACLES
We would like to begin by discussing the funda-
mental mechanisms of the potential fields algorithm
(Polkowski and Skowron, 1996), it is advantages,
as well as the critical situations that can arise when
using this algorithm. The concept of the potential
fields algorithm was introduced in works (Polkowski
and O
´
smiałowski, 2008) and (O
´
smiałowski and
Polkowski, 2010), (Osmialowski, 2011) in the last
paper special variant named the Square Fill Algo-
rithm. The mentioned method already was mod-
ified and later presented in Polkowski (Polkowski
et al., 2018), Zmudzinski and Artiemjew (Zmudzin-
ski and Artiemjew, 2017), Gnys (Gny
´
s, 2017) and
Szpakowska, Artiemjew and Cybowski (Szpakowska
et al., 2023) on which this paper based on.
3.1 Intersection Condition
The algorithm performs admirably in scenarios where
a limited number of obstacles are present. In cases
where the map offers ample open space for naviga-
tion, seamless operation is observed. However, chal-
lenges arise when applying the algorithm to maps re-
sembling mazes, characterized by a proliferation of
obstacles. In such instances, the algorithm occasion-
ally neglects crucial obstacle-avoidance rules, leading
to lapses in connecting the current field with the most
strategically advantageous option in the given step,
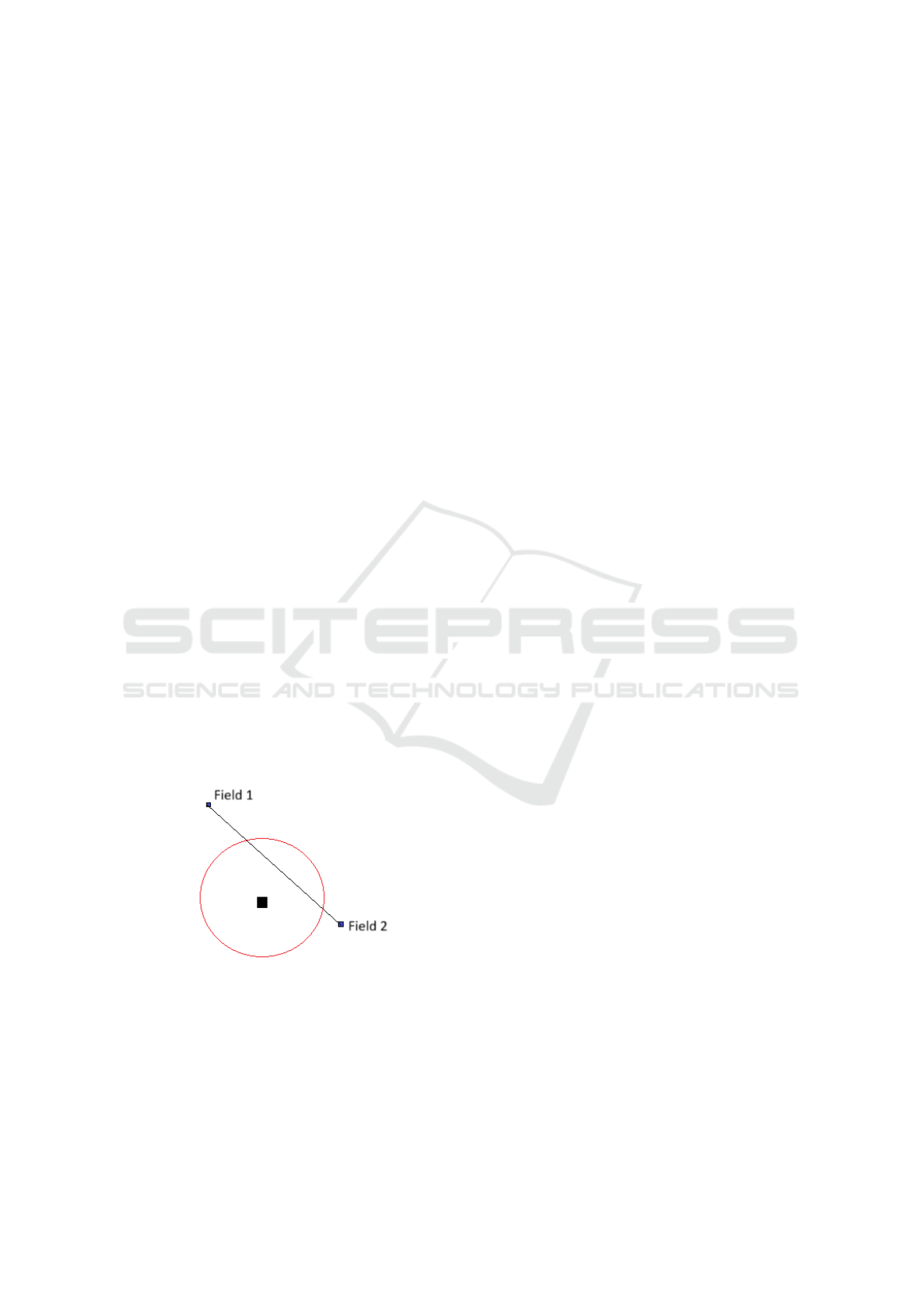
which is forbidden - see fig.2.
Figure 2: Unexpected intersection between current poten-
tial field and ’the most attractive field’, which should not
appear.
To solve this unexpected action the intersection
checking was applied. A few steps were added to the
existing patch search algorithm (Szpakowska et al.,
2023) to improve the performance of the program.
Initially, each iteration of the path planning func-
tion involves the creation of a linear function between
the current and next potential fields. Subsequently, an
obstacle field was established through the creation of
circular zones. The circle’s center coincided with the
obstacle’s center, and the radius was determined by a
parameter specified in the existing obstacle-checking
function.
The subsequent step focuses on verifying whether
the linear path intersects with any of the circular ob-
stacles. This was achieved by generating a series of
points along the path. The outcome, denoted as True
or False, determines the feasibility of establishing a
viable path between the two evaluated points, based
on the intersection or absence thereof with the obsta-
cle circles.
3.2 Unique Arrangement of Obstacles
The Mereological Potential Fields algorithm system-
atically extends from the goal towards the map bor-
ders, intelligently navigating to avoid obstacles. An
advantageous feature of this algorithm lies in it is
capacity to comprehensively explore the entire map.
The user can effortlessly discern a goal location based
solely on the spatial arrangement, leveraging the ac-
cumulation of potential fields.
Given this interdependence, it becomes evident
that the crucial factor is the strategic placement of
potential fields, influencing not only the goal posi-
tion but also delineating the locations of obstacles.
Despite the widespread presence of potential fields
throughout the whole map, their deployment may ap-
pear excessive in scenarios where a direct, optimal
path is sufficient.
Conversely, the abundance of potential fields
presents numerous opportunities. In intricate scenar-
ios characterized by a substantial number of obsta-
cles, the increased density of generated fields proves
invaluable for identifying alternative routes. Regret-
tably, challenges arise in cases where the fundamen-
tal path-planning algorithm struggles to cope, partic-
ularly in more intricate scenarios.
Figure 3 shows one of the examples of critical
cases when the path was not found. The algorithm
finishes work with the result of getting stuck in one
place, without any possibility to find the goal.
Map Legend:
• One-color painted square represents the start
point,
• Extreme markers determine map borders,
• Circles with squares describe obstacles and those
fields,
• Goal is represented by a marker
CSEDU 2025 - 17th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
150
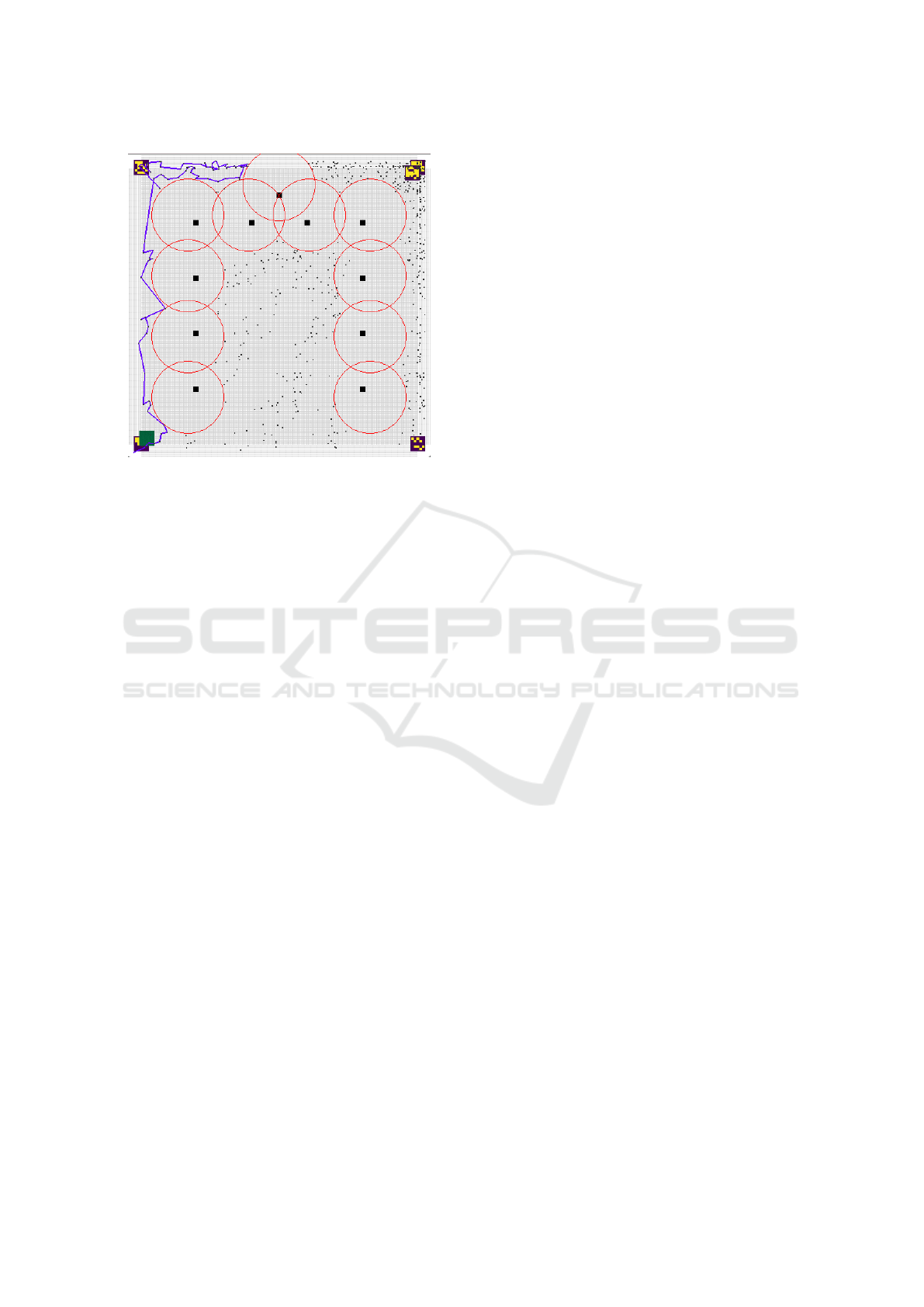
Figure 3: Critical case with determined goal position on
point (490,490) - down left corner, and start point in (10,10)
- top right corner.
To solve the problem of complex cases we propose
the Route selection system (read Section 6)
4 ADDRESSING THE
CHALLENGE OF UNIQUE
ARRANGEMENT OF
OBSTACLES
The basic potential fields algorithm generated a se-
ries of exceptions that prevented finding a path to the
destination. After analyzing cases where such a situ-
ation occurred (see fig. 3), it was observed that they
were associated with directing the path into a closed
area (without passage), often characterized by a nar-
row entrance. Consequently, the algorithm in it is cur-
rent form was unable to find a return path. To avoid
this scenario, an improvement was introduced, con-
sisting of a probabilistic determination of whether the
designated path has a realistic chance of reaching the
destination. This approach involves a general exami-
nation of the map and identification of areas that could
be critical for planning a detailed route. Subsequently,
the basic algorithm is activated and steered towards
areas that have undergone preliminary examination
and, problematically, present a higher likelihood of
passage.
5 NEW CONCEPTION AND
DEVELOPMENT OF
MEREOLOGICAL POTENTIAL
FIELD ALGORITHM
In this section, the mechanics of the algorithm PPOM
are presented, along with a sequential description of
the actions that should be performed in a specified or-
der:
1. Obstacles are introduced onto the map, in this case
in the form of circles. Points overlapping with ob-
stacles are removed.
2. The points (potential fields) are generated on
a 2D map with coordinates (X,Y ) concerning
the rules of generating mereological potential
fields (Polkowski and O
´
smiałowski, 2008),(Os-
mialowski, 2011), using the square fill algo-
rithm (see references (Osmialowski, 2011), (Sz-
pakowska et al., 2023)).
3. The map is divided into sectors, with the mini-
mum division being 2x2 (4 sectors). The compu-
tational complexity increases with a higher divi-
sion of the map into sectors. A greater division
into sectors is recommended for maps with many
small, interconnected obstacles. Here, we use a
division into 3x3 (9 sectors), as per the following
scheme: We start numbering from the top left cor-
ner, numbering to the right.
An example of how the map is divided into sectors
is illustrated in Fig. 4.
4. For the sake of computation organization, sectors
are numbered starting from the top left corner, and
then from left to right (fig. 4).
5. Every sector is subjected to a separate drivability
analysis. The algorithm checks simplified paths
in each sector for four directions: vertical, hori-
zontal, diagonal left, and diagonal right (see fig.
4). Passable paths are marked in green, and im-
passable ones in red (fig. 4). In total, 12 paths are
checked for each sector, and the overall drivabil-
ity of a sector is calculated as the ratio of passable
paths to the number of paths tested.
6. Building potential paths in a sector perspective.
We determine all possible paths through sectors,
starting from the defined starting sector and end-
ing at the defined ending sector. The path can only
move forward, changing direction vertically, hori-
zontally, or diagonally, without repeating sectors.
7. Analyzing possible paths. Each potential path is
analyzed for drivability and components such as
the number of obstacles, points, and whether the
Training Telemedicine Robots: A Path Planning Optimization Method for Educational and Medical Application
151
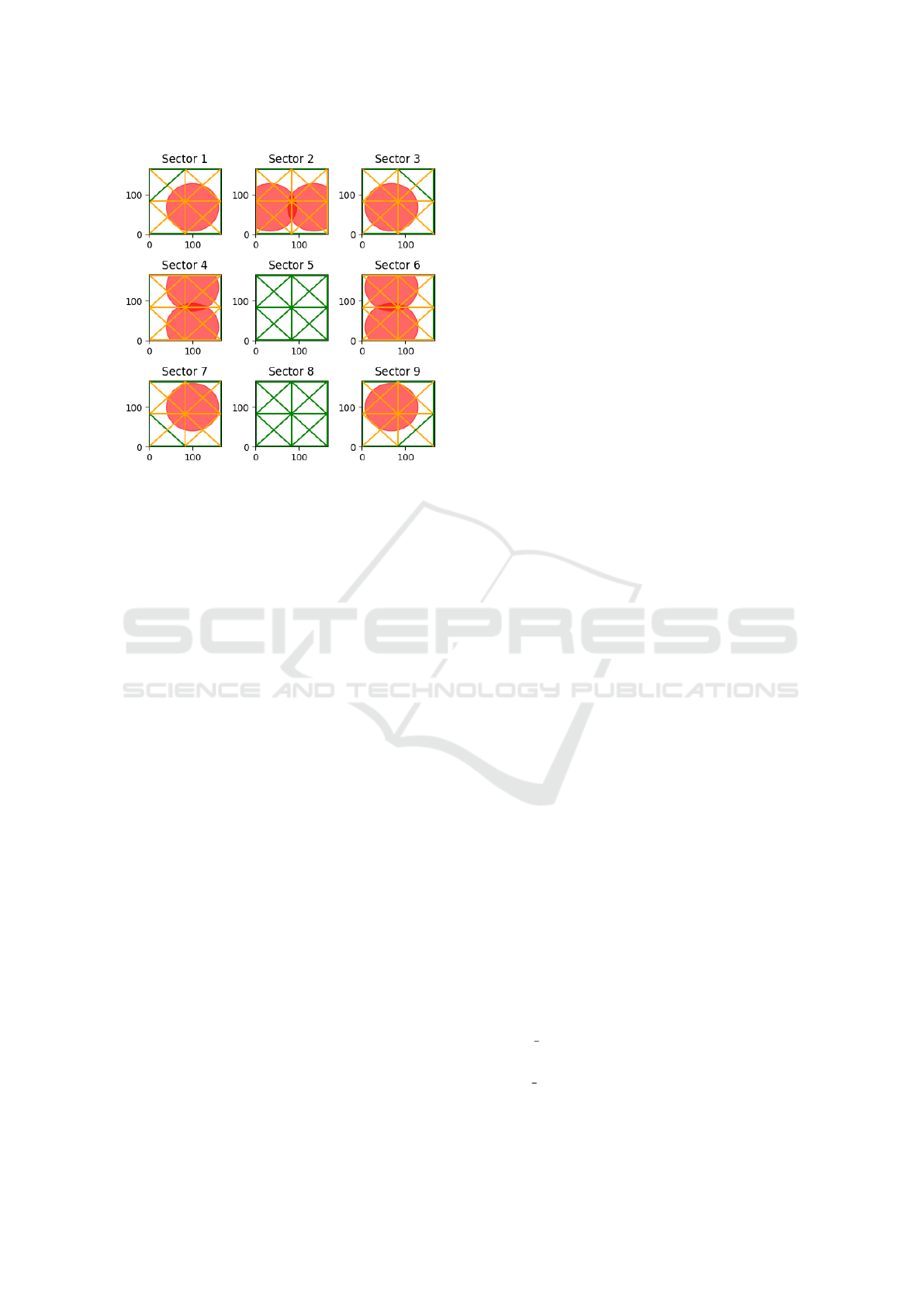
Figure 4: Testing sector passability.
path has at least one passable route in each sec-
tor. The probability of passage through the path is
calculated.
8. Selection of passable routes. We eliminate all
paths from the list that contain at least one sector
deemed impassable.
9. Classification of routes, data discretization, and
selection of the best route using the designed clas-
sifier. We create a table of passable routes and
then apply discretization (according to a set of
rules) to select the best route according to the de-
cision matrix.
10. Extraction of route points. From the selected best
route, we record the points belonging to the route
sectors into a new array.
11. Implementation of the potential field algorithm.
We overlay the filtered map with a table of points
to maximize the chances of passage.
12. Generating the optimal route using the potential
field algorithm, maintaining flexibility within safe
sectors.
13. Apply the path smoothing algorithm by taking
into account 3 points in order.
In the next section, we will discuss the main at-
tributes that make up the path vector. The elements
discussed and the way they are classified is crucial for
the proper functioning of the algorithm.
6 PATH SELECTION SYSTEM
BASED
This section will discuss the decision-making mecha-
nisms used in the presented algorithm.
6.1 Choosing Proper Sectors for
Finding the Optimal Path
A decision-making system was employed to select
the optimal path among the vectors of paths contain-
ing various attributes. This approach allowed for the
development of an efficient decision-making mecha-
nism in situations where multiple paths meet the ba-
sic drivability condition. The primary condition for
path drivability is the presence of probabilistic con-
ditions allowing for passage between obstacles. If a
path in even one of the sectors on the planned route
contains a set of obstacles that prevent direct passage,
it is considered impassable (see fig. 4). When a path is
deemed passable, the probability of a successful pas-
sage is determined. The higher the probability, the
better the quality assessment of the path. The chance
of passability is one of the key attributes used in as-
sessing the quality of the path.
The decision-making mechanism used in the al-
gorithm employs Hamming distances (Waggener and
Waggener, 1995), (Hamming, 1950). Since the input
data metrics in vectors are numerical, there is a need
to discretize them. The data discretization process
was conducted according to specially defined formu-
las and rules for the algorithm, which establish thresh-
olds for determining binary values.
6.2 Data Preparation
In the current subsection, we will focus on the steps
responsible for data preparation and the rules applied
to prepare data for computation through discretiza-
tion.
Example data preparation (path vector discretiza-
tion):
[1, 0.5, 5, 438, 5] → [Yes, High, Low, High, Low].
The attribute names of the above vector (accord-
ing to the order of elements in the vector) are as fol-
lows:
• road pass → value from 0 to 1, discrete value:
No or Yes,
• pass probability → value from 0 to 1, where 1
is 100% pass probability, discrete value: Low or
High,
CSEDU 2025 - 17th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
152

• path length → counted in the number of sectors,
discrete value: Low or High,
• points on path → number of mereological points
on the path, discrete value: Low or High,
• obstacles on path → number of obstacles on the
path, discrete value: Low or High.
Next, we will discuss step by step how to dis-
cretize any vector.
6.2.1 Data Discretization
The data discretization process is a key element of the
presented algorithm and plays a crucial role in prepar-
ing data. Given the application of Hamming measures
in the decision-making model, it is essential to pro-
cess the data in such a way that numerical attributes
are converted into binary values. Special formulas
and rules have been developed for each attribute that
requires discretization. These rules define thresholds
that allow the transformation of numerical attributes
into binary decision values. Below, the applied for-
mulas are described in detail, and specific threshold
values are indicated, which are necessary for the algo-
rithm to perform calculations correctly. These formu-
las have been adapted to the specifics of the data and
the nature of the problem the algorithm is intended to
solve, thereby ensuring it is efficient and effective.
Discretization of the Number of Points on the
Path T
ρ
The following formula T
ρ
=
p
n
× l is used to calculate
the threshold indicator (average) expected number of
points that should be found on a path of a given length
l. Where T
ρ
is a Threshold Number Of Points, p rep-
resents the total number of points on the map, n is a
number of sectors calculated as rows × cols and l is
the length of the path.
For the attribute of the examined path to be clas-
sified as ’yes’, the actual number of potential field
points on the examined path must be greater than the
value T
ρ
. If the number of points is less than the value
T
ρ
, the attribute is marked as ’no’.
In the next step of the discretization process, we
will perform discretization of the path length.
Discretization of the Path Length T
λ
Determining whether a path is short (yes) or long (no)
is an essential attribute for making a good choice of
the optimal route. The optimal length of the path is
related to the number of sectors on the map. It is as-
sumed that paths no longer than the route along the
outer edges are considered quick to traverse (yes).
The threshold value of the path length is determined
by the following formula T
λ
= r + c. Where T
λ
is the
Threshold Path Length, r is the number of rows in the
grid, and c is the number of columns in the grid.
Remark. It should be noted that the exact thresh-
old value of the path length is r + c − 1; however, to
provide a larger buffer for routes and to avoid a situa-
tion where the path length is too dominant a factor, it
is better to use a threshold length equal to r + c.
Discretization of the Number of Obstacles on the
Path T
θ
The threshold indicator T
θ
=
o
n
× l, similar to the pre-
viously discussed threshold indicator of points T
ρ
,
is used to calculate the threshold (average) expected
number of obstacles that should be present on a path
of a given length l.
Where T
θ
is the Threshold Number Of Obstacles,
o is the total number of obstacles, n is computed as
rows × cols and l refers to the length of the path. For
the attribute of the examined route to be classified as
’yes’, the actual number of obstacles on the examined
path must be less than the value T
θ
. If the number of
obstacles is greater than the value T
θ
, the attribute is
marked as ’no’.
Next, we have to discuss the last, and one of the
most important indicators of the route, which defines
the probability of the passage of the route.
Discretization the Probability of Passage T
α
The discretization of the probability of passage at-
tribute T
α
was determined experimentally. The op-
timal threshold coefficient was set at T
α
= 0.35. This
value is related to the probability of passage and can
be interpreted as total freedom of movement on a
passable route. An actual value above 0.35 means that
more than 35% of all possible movements in sectors
(vertical, horizontal, and diagonal movements) of the
route are possible. The higher the indicator value, the
better the situation, hence if the attribute takes on a
value greater than 0.35, we consider it as ’yes’; val-
ues below this threshold are considered as ’no’.
6.3 Route Vector Similarity
Comparison
After performing the path discretization, we proceed
to check the degree of membership of the discretized
path vector concerning the learning matrix α (see tab.
1). For this purpose, we use the classifier, designed to
make decisions in the selection of the optimal path.
The classifier uses Hamming distances to calculate
the similarity between sets of attributes. Then, it
Training Telemedicine Robots: A Path Planning Optimization Method for Educational and Medical Application
153

performs upper and lower approximation calculations
and determines boundary values. Using the deter-
mined approximations and boundary values, a clas-
sification of the input attribute sets (path vectors) is
performed. Classification consists of finding the at-
tribute set in the α matrix that is most similar based
on Hamming distances. For new attribute sets entered
for classification, a decision from the α learning ma-
trix is assigned. The vector that shows the highest de-
gree of similarity to the ’yes’ decision is selected for
final use. When two vectors or more have the same
degree of similarity to the ’yes’ decision, the lowest
value of the degree of similarity to the ’no’ decision
decides the selection.
6.4 Using Learning Matrix α
The decision-making system utilizes a defined deci-
sion matrix α. This matrix contains rules that deter-
mine the quality level of each path. The quality level
of a path is defined as the degree of membership of
the path vector to the most optimal solution (vector)
specified in the matrix α (see tab. 1). Decision vectors
marked as ’yes’ are considered the most desirable in
evaluating the path quality. The more a path attribute
vector resembles the optimal vector defined in matrix
α, the better it is considered in terms of quality com-
pared to other less similar vectors. Conversely, vec-
tors in matrix α marked as ’no’ are regarded as the
least desirable.
In the table below, the row with bold attributes
presents a sample decision for the path vector solved
using the PPOM method (see fig. 5):
[7, [7, 8, 9, 6, 3], 1, 0.4833333333333333, 5, 449, 5]
Next, the vector needs to be prepared for the
decision-making process. To do this, we omit the first
three attributes that are not required in the decision-
making process but are used to store information
about the path (Path ID, Path sectors, and Passabil-
ity). To make a decision, the Passability attribute
must be 1 (meaning that the path has a probabilistic
chance of being passable). The following attributes
remain pass probability, path length, points on path,
obstacles on path. For the presented example, we
create a shortened vector:
[0.4833333333333333, 5, 449, 5]
Now we discretize it according to the rules
described in the previous chapter and obtain the
vector:
[’High’, ’Low’, ’High’, ’Low’]
Next, we search the decision table α for the deci-
sion most similar to the analyzed vector.
Table 1: Learning Matrix α.
Pass probability Path length Points on path Obstacles on path Decision
High Low High Low yes
High Low Low Low yes
High Low Low High yes
High Low High High yes
High Low High High no
Low High Low Low no
Low High High High no
Low High Low High no
The learning matrix α was developed based on
experiments and achieved the best results in the
decision-making process of choosing the optimal
route.
In the next section, we will analyze several cases
of maps with obstacles that posed challenges for the
basic version of the algorithm. We will then compare
these cases with solutions generated by the improved
version of the potential fields algorithm.
7 ANALYSIS OF RESULTS
The results of the presented algorithm have been
demonstrated through the comparison of several re-
peatable critical scenarios, simulating situations that
telemedicine robots may encounter in real-world en-
vironments, such as hospitals or patients’ homes.
These scenarios are designed not only to evaluate the
algorithm’s efficiency but also to serve as educational
case studies for training purposes. The basic potential
field algorithm, known for its limitations in complex
environments, is contrasted with the improved ver-
sion, with the comparison structured as follows: the
basic algorithm is presented on the left side (critical
solution), and the improved algorithm – on the right
side.
As observed in the figures below (fig. 5), the crit-
ical scenarios involve situations such as navigating
through ’narrow passages’ or areas densely populated
with obstacles. These are particularly challenging due
to the limited number of potential field points in such
spaces. When the basic algorithm encounters an im-
passable obstacle, it often fails to recover by turning
back or finding an alternative path, leading to com-
plete route blockage.
In contrast, the improved algorithm employing
preprocesses the environment map to identify and
exclude areas with a high likelihood of obstruction.
This preprocessing step provides an opportunity for
learners to understand how predictive analysis and
preprocessing can significantly enhance the perfor-
mance of robotic systems. By directing the robot
CSEDU 2025 - 17th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
154
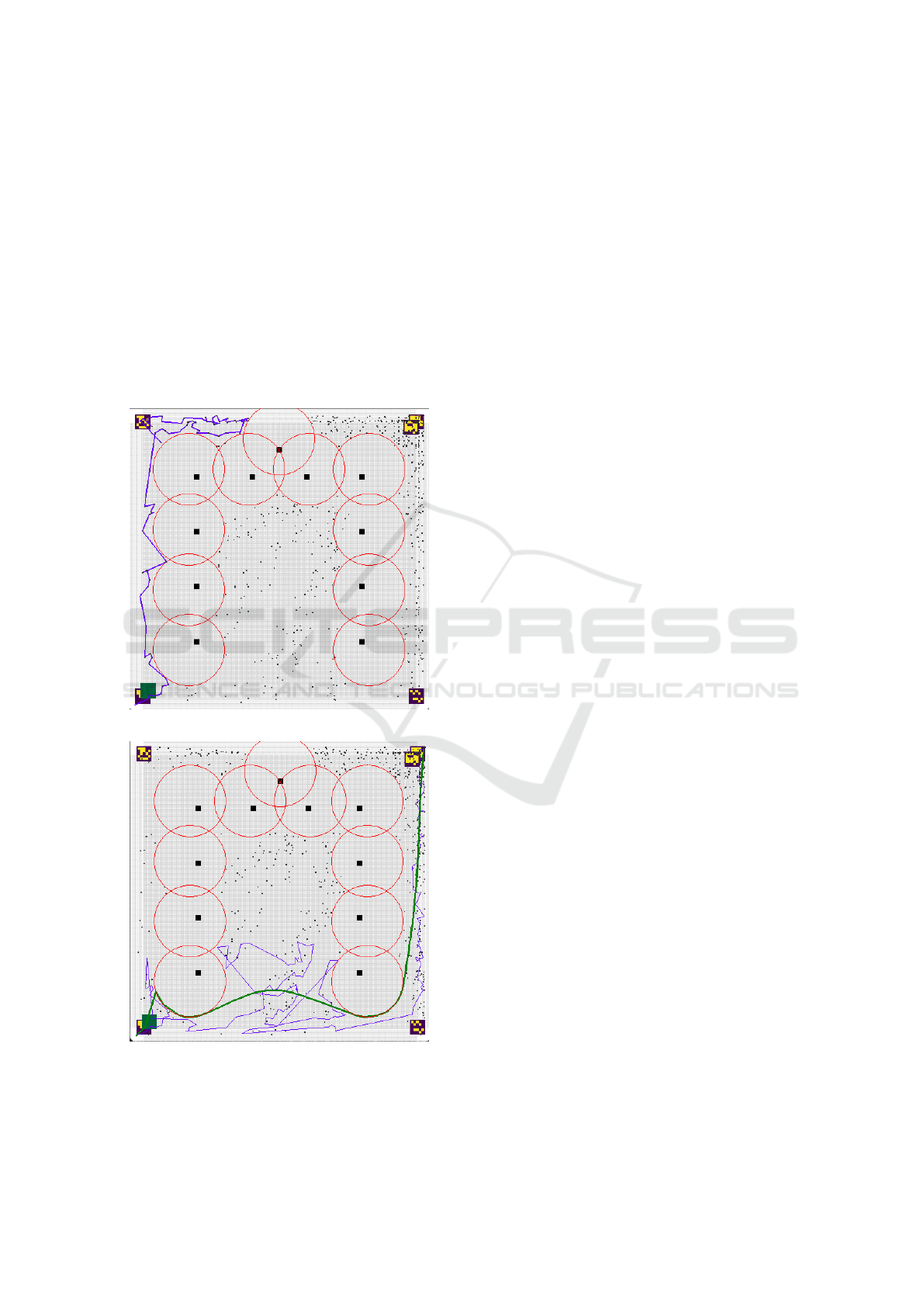
through passable sectors identified during preprocess-
ing, the improved algorithm ensures successful navi-
gation through previously impassable scenarios.
These findings not only highlight the practical ad-
vantages of the enhanced method but also demon-
strate its pedagogical value in training students and
professionals. The ability to visualize and analyze
these critical cases fosters a deeper understanding
of robotic navigation challenges and equips learners
with the skills needed to address similar issues in di-
verse environments. By simulating such scenarios,
the framework provides a unique opportunity to com-
bine theoretical knowledge with hands-on problem-
solving experience.
(a) Case 1: critical solution
(b) Case 1: PPOM solution
Figure 5: Case 1: critical problem and PPOM solution.
In a further 9 case studies performed on maps with
a different configuration of obstacles and points, the
algorithm solved the passability problem and planned
the path correctly.
8 ALGORITHM COMPLEXITY
Path Planning Optimization Method (PPOM) is an ad-
vanced combination of two methodologies, integrat-
ing heuristic approaches for efficient path planning
in obstacle environments. This algorithm, through
its complex structure of operation, aims to overcome
the limitations of classical heuristic methods, which
in the case of an unfavorable obstacle configuration
can fall into the so-called ”local traps”, while requir-
ing a significant number of computations to find the
optimal path to the goal. In response to these chal-
lenges, PPOM implements a two-step approach: the
first module of the algorithm selects key sectors of
space that maximize the probability of finding the
optimal path, while the second module uses greedy
heuristic algorithms to choose the best local solution
in a previously defined space.
The first component of the algorithm acts as a
high-level selector, selecting the main sectors of space
based on the probability of minimizing interactions
with obstacles that could prevent further route search.
The number of possible paths in this part of the algo-
rithm is constant and equal to C = 235 (for dividing
the map into a 3x3 grid of sectors). This means that
the computational complexity of this phase is O(1),
which implies a constant computational complexity,
independent of the size of the input data.
The second component of the algorithm is respon-
sible for precise route determination using potential
fields that model the map space. The complexity of
this part of the algorithm is determined by the num-
ber of points in the potential field space. The number
of steps in this stage is proportional to the number of
points on the map, which leads to a linear complex-
ity of O(N), where N is the number of potential field
points.
Considering both stages of the algorithm’s opera-
tion, its overall computational complexity
is O(C * N), which indicates a linear dependence on
the number of points in the potential space.
It should be emphasized that the given complex-
ity refers to cases with the highest level of complex-
ity. In typical conditions, the computational complex-
ity of the algorithm is much more efficient, which is
beneficial in the context of a wide range of applica-
tions. Unlike classical path finding algorithms, which
do not take into account the aspect of route passability
Training Telemedicine Robots: A Path Planning Optimization Method for Educational and Medical Application
155
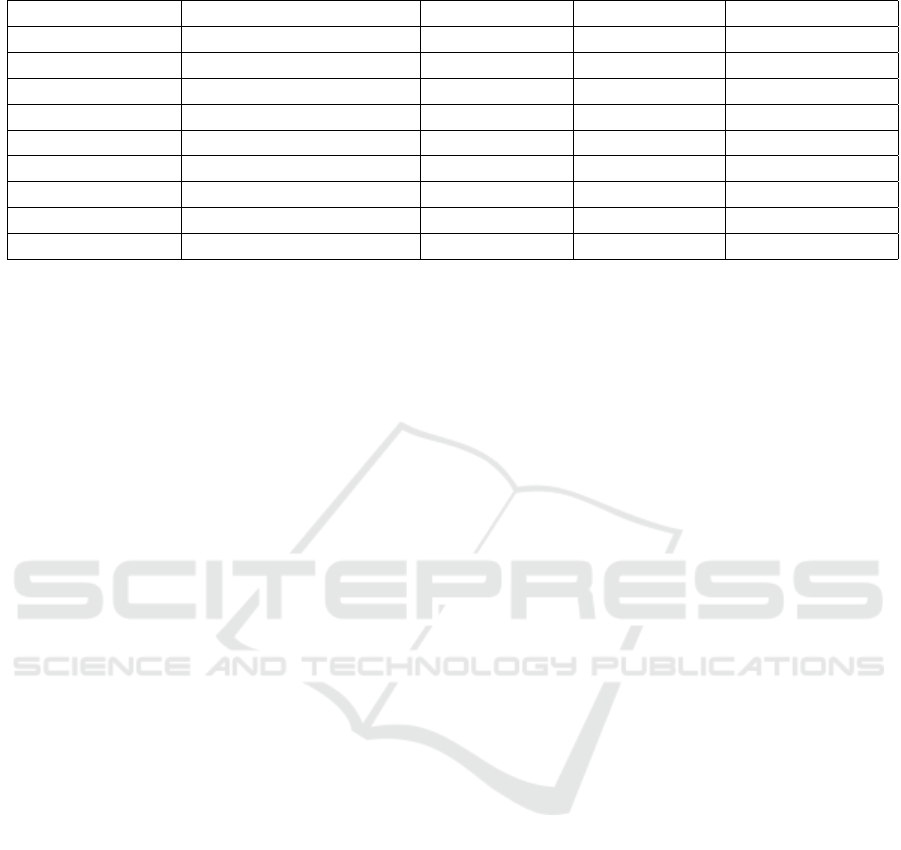
Table 2: Comparison of PPOM Algorithm with Other Pathfinding Algorithms.
Algorithm Computational Complexity Complexity Type Is PPOM faster? Paper Reference
PPOM O(C · N) Linear - -
A* O(b
d
) Exponential Yes (Hart et al., 1968)
Dijkstra O(E · logV + E +V · logV ) Polynomial Yes (Dijkstra, 1959)
BFS O(|V | + |E|) Linear No (Moore, 1959)
DFS O(|V | + |E|) Linear No (Tarjan, 1972)
Bellman-Ford O(|V | · |E|) Polynomial Yes (Bellman, 1958)
Johnson’s Algorithm O(|V |
2
log|V | + |V ||E|) Polynomial Yes (Johnson, 1977)
Floyd-Warshall O(|V |
3
) Polynomial Yes (Floyd, 1962)
IDA* O(b
d
) Exponential Yes (Korf, 1985)
in the face of obstacles, PPOM effectively copes with
this issue. In traditional algorithms, graphs contain-
ing obstacles generate decision nodes that can lead
to situations in which it is impossible to continue the
path search. PPOM eliminates this risk through intel-
ligent selection of sectors, minimizing the probability
of problematic decision nodes, which significantly in-
creases the efficiency and computational optimization
in environments with obstacles.
9 CONCLUSIONS
As a result of this research, a new algorithm has
been developed to enhance the performance of basic
path planning methods in environments with numer-
ous obstacles using potential fields. This improved
algorithm reduces the likelihood of paths leading into
’traps,’ which are typically closed areas with narrow
entrances. It incorporates a decision-making system
allowing for the selection of the most likely successful
path for a robot. Furthermore, it minimizes unneces-
sary wandering during path planning, which is partic-
ularly beneficial for large maps containing labyrinth-
like structures with dead ends.
The effectiveness of the improved algorithm was
assessed using 10 different critical scenarios, repre-
senting typical challenges of navigating ’narrow pas-
sages’ that lead to impassable routes. In 8 out of the
10 cases, the algorithm successfully identified a vi-
able path. The tests utilized a division of the map
into a 3x3 grid (3 columns and 3 rows), which proved
to be an optimal configuration relative to the obstacle
sizes used in the experiments. For environments with
significantly smaller obstacles, a larger grid division,
such as 4x4, is suggested. It is also recommended that
the division of the map be as symmetrical as possible,
with sector sizes close to square shapes to ensure uni-
form coverage.
However, increasing the map division size raises
the computational complexity, as the number of po-
tential paths grows significantly. It is therefore ad-
vised to determine the optimal grid size experimen-
tally, balancing computational efficiency with naviga-
tional precision.
This study achieved its objective by demonstrat-
ing the effectiveness of the proposed algorithms in
addressing complex navigational challenges. The re-
sults confirm that the algorithm excels in environ-
ments with intricate layouts, such as hospital wards
or patient residences resembling mazes. The gener-
ated paths ensure precise navigation while effectively
avoiding obstacles, making the system well-suited for
telemedicine applications.
Future applications of the PPOM algorithm in-
clude its integration into telemedical robots for prac-
tical use in real-world settings. These robots will
navigate hospital spaces while considering the phys-
ical layout of obstacles, such as medical equipment
in rooms. Furthermore, they will be equipped to ac-
tively and directly interact with patients, providing an
educational tool for training operators and students
in navigating complex environments with robotic sys-
tems.
Additionally, we plan to further improve the algo-
rithm and test it in the task of avoiding obstacles in
the form of rock mazes, simulating the movement of
a ground drone in desert conditions on Mars.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work has been supported by a grant from the
Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Re-
public of Poland under project number 23.610.007-
110 and a grant from the National Centre for Re-
search and Development in Poland, grant number:
POIR.01.01.01-00-0587/21 Development of telemed-
ical software for conducting automated subjective pa-
tient examination and enabling preliminary medical
diagnosis based on AI.
CSEDU 2025 - 17th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
156

REFERENCES
Bellman, R. (1958). On a routing problem. Quarterly of
Applied Mathematics, 16(1):87–90.
Dijkstra, E. W. (1959). A note on two problems in connex-
ion with graphs. Numerische Mathematik, 1:269–271.
Falcione, S., Campbell, E., McCollum, B., Chamberlain, J.,
Macias, M., Morsch, L., and Pinder, C. (2019). Emer-
gence of different perspectives of success in collabo-
rative learning. Canadian Journal for the Scholarship
of Teaching and Learning, 10(2):n2.
Floyd, R. W. (1962). Algorithm 97: Shortest path. Commu-
nications of the ACM, 5(6):345.
Gny
´
s, P. (2017). Mereogeometry based approach for be-
havioral robotics. In Rough Sets: International Joint
Conference, IJCRS 2017, Olsztyn, Poland, July 3–7,
2017, Proceedings, Part II, pages 70–80. Springer.
Hamming, R. W. (1950). Error detecting and error cor-
recting codes. The Bell system technical journal,
29(2):147–160.
Hart, P. E., Nilsson, N. J., and Raphael, B. (1968). A for-
mal basis for the heuristic determination of minimum
cost paths. IEEE Transactions on Systems Science and
Cybernetics, 4(2):100–107.
Johnson, D. B. (1977). Efficient algorithms for short-
est paths in sparse networks. Journal of the ACM,
24(1):1–13.
Komorowski, J., Pawlak, Z., Polkowski, L., and Skowron,
A. (1999). Rough sets: A tutorial. Rough fuzzy hy-
bridization: A new trend in decision-making, pages
3–98.
Korf, R. E. (1985). Depth-first iterative-deepening: An op-
timal admissible tree search. Artificial Intelligence,
27(1):97–109.
Moore, E. F. (1959). The shortest path through a maze. Pro-
ceedings of the International Symposium on the The-
ory of Switching, pages 285–292.
Nurdin, S. and Setiawan, W. (2016). Improving students’
cognitive abilities and creative thinking skills on tem-
perature and heat concepts through an exelearning-
assisted problem based learning. International Jour-
nal of Scientific & Technology Research, 5(12):59–63.
Osmialowski, P. (2011). Planning and navigation for mobile
autonomous robots spatial reasoning in player. Stage
System.
O
´
smiałowski, P. and Polkowski, L. (2010). Spatial reason-
ing based on rough mereology: a notion of a robot for-
mation and path planning problem for formations of
mobile autonomous robots. In Transactions on rough
sets XII, pages 143–169.
Othman, M. and Zaın, N. (2015). Online collaboration
for programming: Assessing students’ cognitive abil-
ities. Turkish Online Journal of Distance Education,
16(4):84–97.
Pawlak, Z. (1992). Rough sets: Theoretical aspects of rea-
soning about data.
Planas-Llad
´
o, A., Feliu, L., Arbat, G., Pujol, J., Su
˜
nol, J. J.,
Castro, F., and Mart
´
ı, C. (2021). An analysis of team-
work based on self and peer evaluation in higher edu-
cation. Assessment and Evaluation in Higher Educa-
tion, 46(2):191–207.
Polkowski, L. and O
´
smiałowski, P. (2008). A framework for
multiagent mobile robotics: Spatial reasoning based
on rough mereology in player/stage system. In Chan,
C.-C., Grzymala-Busse, J. W., and Ziarko, W. P., ed-
itors, Rough Sets and Current Trends in Computing,
pages 142–149, Berlin, Heidelberg. Springer Berlin
Heidelberg.
Polkowski, L. and O
´
smiałowski, P. (2008). A framework for
multiagent mobile robotics: Spatial reasoning based
on rough mereology in player/stage system. In Rough
Sets and Current Trends in Computing: 6th Inter-
national Conference, RSCTC 2008 Akron, OH, USA,
October 23-25, 2008 Proceedings 6, pages 142–149.
Springer.
Polkowski, L. and Skowron, A. (1996). Rough mereology:
A new paradigm for approximate reasoning. Interna-
tional Journal of Approximate Reasoning, 15(4):333–
365.
Polkowski, L., Zmudzinski, L., and Artiemjew, P. (2018).
Robot navigation and path planning by means of
rough mereology. In 2018 Second IEEE International
Conference on Robotic Computing (IRC), pages 363–
368. IEEE.
Szpakowska, A., Artiemjew, P., and Cybowski, W. (2023).
Navigational strategies for mobile robots using rough
mereological potential fields and weighted distance to
goal. In International Joint Conference on Rough Sets,
pages 549–564. Springer.
Tarjan, R. E. (1972). Depth-first search and linear graph
algorithms. SIAM Journal on Computing, 1(2):146–
160.
Taxirovna, A. S. (2024). Collaborative learning: Fo-
cusing on techniques that promote teamwork and
shared knowledge among students. SO ‘NGI ILMIY
TADQIQOTLAR NAZARIYASI, 7(1):118–123.
Waggener, B. and Waggener, W. N. (1995). Pulse code
modulation techniques. Springer Science & Business
Media.
Zmudzinski, L. and Artiemjew, P. (2017). Path planning
based on potential fields from rough mereology. In
Rough Sets: International Joint Conference, IJCRS
2017, Olsztyn, Poland, July 3–7, 2017, Proceedings,
Part II, pages 158–168. Springer.
Training Telemedicine Robots: A Path Planning Optimization Method for Educational and Medical Application
157
