A Comparison of Different Approaches of Model Editors for Automatic
Item Generation (AIG)
Florian Stahr
1 a
, Sebastian Kucharski
1 b
, Iris Braun
1 c
and Gregor Damnik
2 d
1
Chair of Distributed and Networked Systems, TUD Dresden University of Technology, Dresden, Germany
2
Chair of n, Germany
{florian.stahr, sebastian.kucharski, iris.braun, gregor.damnik}@tu-dresden.de
Keywords:
Automatic Item Generation, AIG, Assessment, Cognitive Model, Item Model.
Abstract:
The Automatic Item Generation (AIG) approach allows users to generate tasks or items based on user-defined
knowledge models created with associated editors. The challenge is that these editors typically require a cer-
tain level of technical expertise, which limits the users who can benefit from the AIG approach. To overcome
this, editors can be used with strict user guidance, following a purist approach to avoid feature overload. How-
ever, once users are familiar with AIG, the purist approach may hinder their productivity. This paper examines
the relationship between the users who can benefit from AIG, the AIG model editing approach used, and its
usability aspects. In addition, it tries to identify further perspectives for the development of AIG model editors
that make them accessible to both experienced and novice users. For this purpose, we conceptualized an editor
that allows more modeling freedom and compared it with a previously developed editor that enforces strict
user guidance. Our evaluation shows that the new editor can use more AIG features, but is harder to get used
to, and that an appropriate approach may be to dynamically adapt the guidance and features based on the user’s
goal and expertise.
1 INTRODUCTION
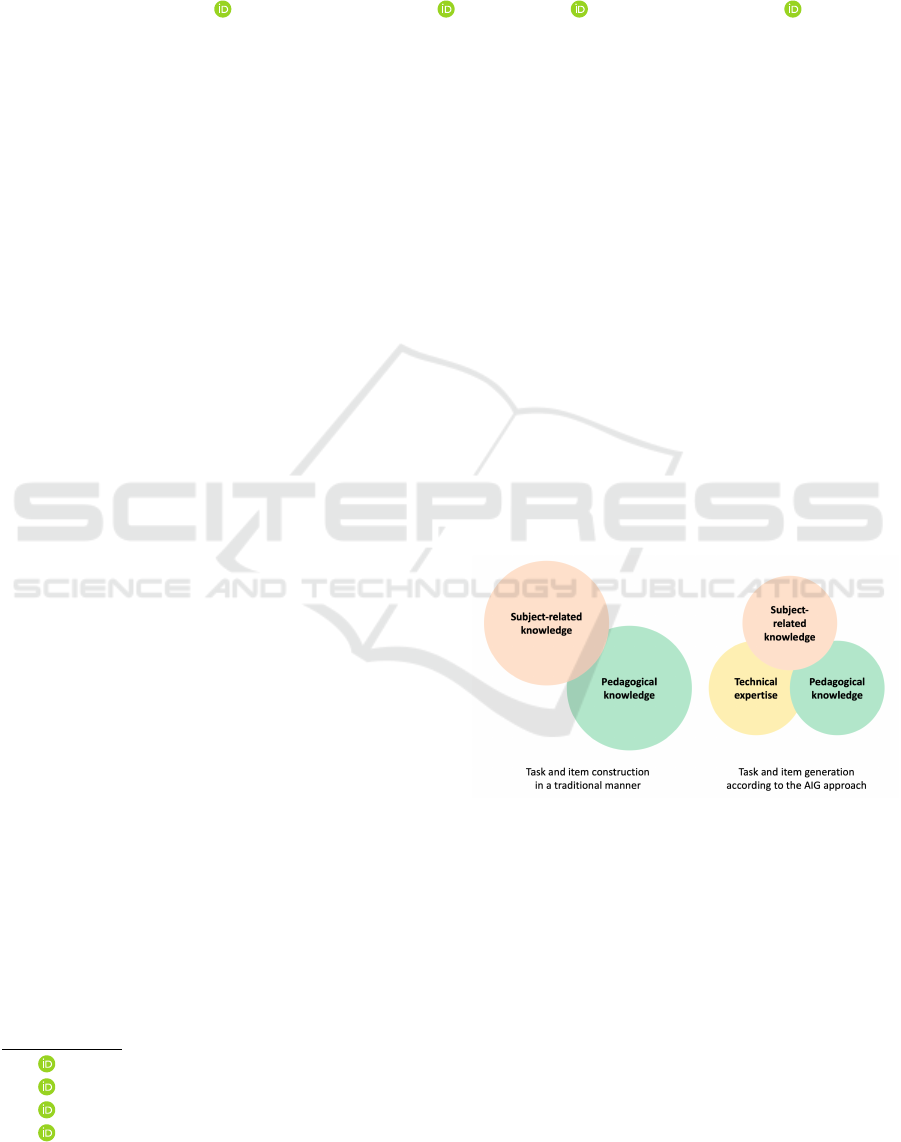
For the traditional construction of learning tasks and
(self-)test items, two types of knowledge are required
(Figure 1). First, subject-specific knowledge of do-
main experts is needed to specify the content of the
tasks and items (cf. e.g., (Krathwohl, 2002; Proske
et al., 2012)). For example, knowledge of the dif-
ferent characteristics of fish and mammals is required
to construct tasks or items related to the species of
vertebrates. Second, constructing tasks or items re-
quires pedagogical knowledge so that learners can un-
derstand and respond to them and achieve their learn-
ing goals. The goal is either to initiate a learning pro-
cess or to verify that a learning process has been suc-
cessfully completed (e.g., (Krathwohl, 2002; Proske
et al., 2012)). For this purpose, different types of tasks
or items, different operators and different interactive
components such as feedback or assistance have to be
considered (e.g., (Proske et al., 2012)). The fact that
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0001-2825-3507
b
https://orcid.org/0009-0003-4210-5281
c
https://orcid.org/0009-0000-0900-2158
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9829-6994
Figure 1: Knowledge domains required to construct learn-
ing tasks and test items in a traditional manner or according
to the AIG approach.
both types of knowledge are rarely found in the same
person makes the traditional task or item construction
process a complicated one, as a number of experts
must come together to construct a substantial task or
item pool for learning or testing purposes (Gierl et al.,
2012; Damnik et al., 2018).
Automatic Item Generation (AIG e.g., (Embret-
son and Yang, 2007; Gierl et al., 2012; Damnik et
al., 2018; Wancham et al., 2023; Kucharski et al.,
2023; Kucharski et al., 2024)) is an alternative ap-
proach to creating tasks or items that can reduce this
Stahr, F., Kucharski, S., Braun, I. and Damnik, G.
A Comparison of Different Approaches of Model Editors for Automatic Item Generation (AIG).
DOI: 10.5220/0013496000003932
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2025) - Volume 1 , pages 765-776
ISBN: 978-989-758-746-7; ISSN: 2184-5026
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
765
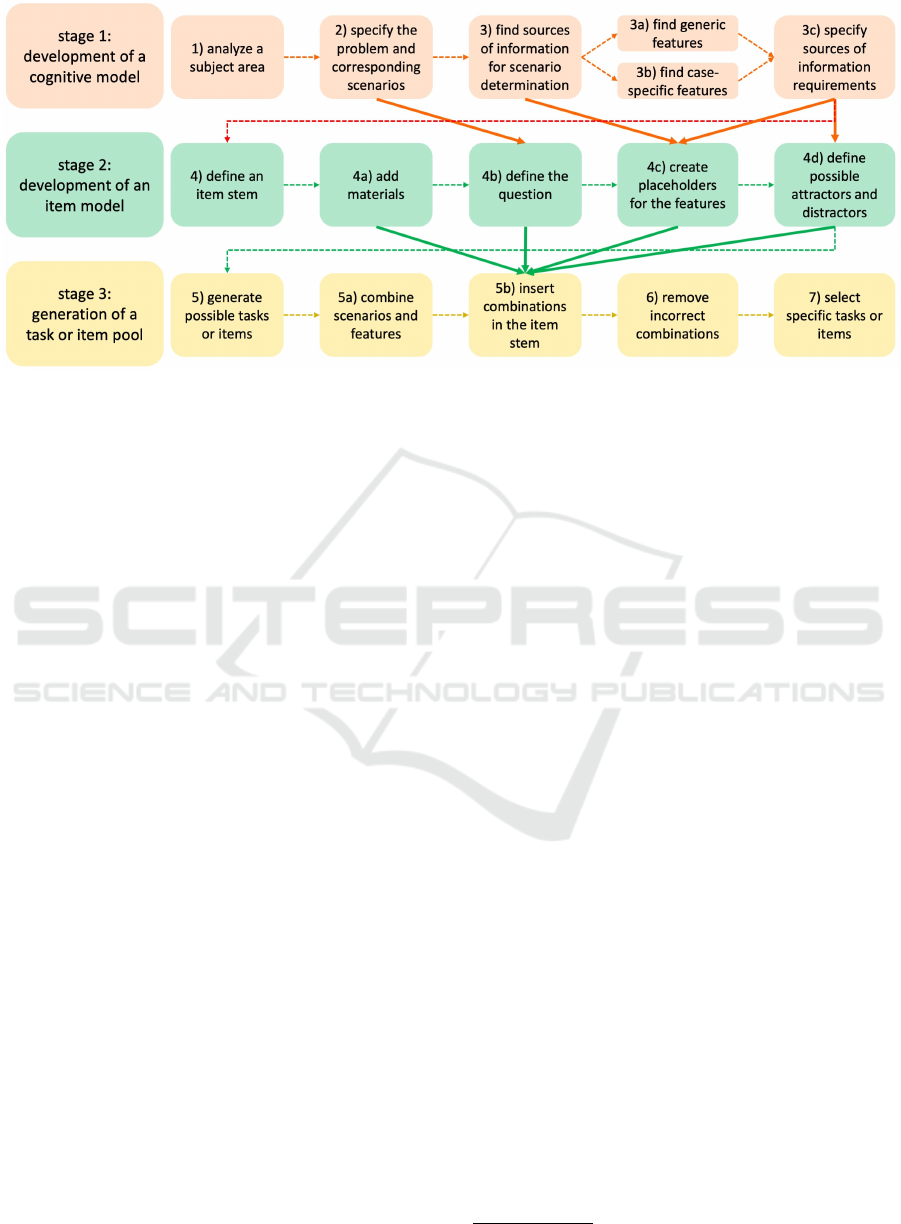
Figure 2: The stages of the traditional AIG process based on (Kosh et al., 2019) and (Gierl and Lai, 2016) that are connected
with the knowledge domains from Figure 1. Adapted from (Kucharski et al., 2024).
high effort per task or item (cf. e.g., (Kosh et al., 2019;
Kucharski et al., 2024)). With this approach, do-
main experts and pedagogical experts do not need to
come together to construct each task or item individu-
ally. Instead, domain experts first systematically rep-
resent their subject-specific knowledge using a cog-
nitive model. The pedagogical experts then use their
knowledge to specify an item model that defines what
the intended tasks or items should look like. Finally,
a software component uses both models to automati-
cally generate a set of tasks or items (cf. Figure 2 and
(Kucharski et al., 2024)).
One problem with AIG is that although it reduces
the amount of knowledge that needs to be speci-
fied per item by domain experts and pedagogical ex-
perts (cf. e.g., (Kosh et al., 2019; Kucharski et al.,
2024)), it requires a third type of knowledge (see Fig-
ure 1). This is the knowledge of technically experi-
enced users (i.e., computer scientists) that is needed to
translate the systematic representations of the domain
experts and the pedagogical experts into a machine-
readable format, to technically connect the represen-
tations of both experts, and to program the actual al-
gorithms that implement the generation of tasks and
items.
One possible solution to this problem could be a
tool that can be used to specify the required mod-
els, translate them internally into a machine-readable
format, and initiate the generation process. This
tool could reduce the required knowledge of techni-
cally experienced users by encapsulating this type of
knowledge. To do so, it would either have to be self-
explanatory and thus easy to use, or it would have to
include appropriate guidance features such as tutori-
als to make it easy to learn. The AIG Model Editor
(AME) has been developed with the goal to be such a
tool, according to the principle AIG for all (Kucharski
et al., 2023). This freely available editor
1
has al-
ready been used to generate item pools for various
domains such as biology, psychology, and computer
science that are comparable in quality to manually
constructed items (cf. (Kucharski et al., 2024)).
During several rounds of evaluation of this editor,
it was found that although good usability was exam-
ined for all evaluated user groups after a reasonable
learning process, the desired direction of further de-
velopment of our editor differed between the consid-
ered groups. On the one hand, there are users with a
low level of technical expertise who support the strict
guidance provided or want even more support. The
intention of the development of an editor that is fo-
cused on these users, is to ensure that everyone can
make use of the AIG approach, which is consistent
with our AIG for all principle. On the other hand,
there are users with a high level of technical exper-
tise who would prefer more freedom and less guid-
ance during the modeling process (cf. Section 3.2).
For this user group the goal is to speed up the pro-
cess of generating items using the AIG approach in
order to optimize the use that can be made out of this
approach. These two intentions are somewhat contra-
dictory, since more functionality usually means that a
tool is less easy to use, and thus more likely to be used
by fewer people, or only by certain people (i.e., peo-
ple with a high level of technical expertise). Other-
wise, an approach that allows more modeling freedom
can also be used to take advantage of aspects of the
AIG approach that were previously not applicable be-
1
https://ame.aig4all.org, November 3, 2024
AIG 2025 - Special Session on Automatic Item Generation
766

cause of the strict guidance provided.
The purpose of this paper is to analyze this rela-
tionship between the two AIG editing approaches, the
types of people who can use AIG, and the exploitable
aspects of the AIG approach. It is structured as fol-
lows. First, in Section 2 we present related work that
focuses on the study of AIG editors. Then, in Sec-
tion 3 we present the editor introduced earlier and de-
scribe the features implemented to make this editor
available to user groups with different levels of tech-
nical expertise and different level of prior knowledge.
In addition, in Section 3.2 we analyze the limitations
of this editor in terms of taking full advantage of the
AIG approach, which we have gathered over several
rounds of evaluation. In Section 4 we present a recon-
ceptualized AIG editor that provides more modeling
freedom and is designed to address the identified lim-
itations. We analyze this editor in terms of the ex-
tended capabilities of the AIG approach that it can
exploit, and in terms of the guidance functionalities
that have been elaborated to try to make this editor
still accessible to a wide range of users with different
levels of prior knowledge and technical expertise. In
Section 5 we present the evaluation results of both ed-
itors. In Section 6 we discuss the results of the evalu-
ation of both editors, highlighting what can be seen as
advantages or disadvantages depending on the type of
user. Section 7 concludes the paper and summarizes
insights for future research corresponding to model
editors for the AIG approach that can be derived from
our findings.
2 RELATED WORK
Various related work focuses on making AIG func-
tionality available to end users by providing appro-
priate editors or programming packages. Some rele-
vant approaches are presented below. There are also a
number of commercial solutions, presented in (Christ
et al., 2024), which are not discussed further. The
approaches presented typically focus only on provid-
ing the necessary capabilities to make the AIG ap-
proach available to a focused group of end users who
are occasional users with a low level of technical ex-
pertise. In contrast, this work focuses on investigating
the relationship between two diametrically opposed
AIG modeling approaches, the types of people who
can use AIG, and the exploitable aspects of the AIG
approach. Thus, it focuses on gathering insights on
how to build AIG editors with respect to user groups
and the aspects of AIG approaches that are intended
to be used by these user groups in general.
(Mortimer et al., 2012). presents the Item Genera-
tOR (IGOR) system. IGOR is a web-based tool, an
evolution of the previous monolithic desktop appli-
cation, that can be used by a community to work on
an item model as a basis for automatically generated
items. The item model contains all the information
needed to generate items, such as an item stem, re-
sponse options, auxiliary information and variables to
be adjusted during generation. Based on this model,
much research has been done to optimize and stan-
dardize the generation process, including the devel-
opment of a taxonomy of item model types. With the
advancement of the previous monolithic IGOR appli-
cation, research has moved towards the goal of mak-
ing the AIG process accessible not only to individ-
ual researchers developing AIG methods. However,
the comparison of different AIG modeling approaches
and the investigation of the relationship between the
modeling approach and the type of users who can
make use of the AIG approach, as well as the usable
AIG features, is not the focus of this research.
(Merker et al., 2023). introduced an approach
based on allowing the user to program the tasks or
items to be generated using the Python package Py-
Rope
2
according to the principle of coding, not click-
ing. PyRope provides pre-built functionality for pro-
viding context, feedback, and sample solutions for
generated tasks or items, as well as randomization
functionality during the generation process. The gen-
erated tasks or items can then be presented to the
learner in a variety of ways, such as a Jupyter note-
book. This approach imposes no restrictions on the
aspects of the AIG approach that can be used, but
it does require the user to have basic programming
skills, although the level of programming skills re-
quired is lowered by assembling the required func-
tionality from the provided package. This is a barrier
to usability for users with low technical expertise.
(Christ et al., 2024). presents the ALADIN tool.
The goal of ALADIN is to automatically generate
learning tasks whose difficulty can be configured ac-
cording to the learner’s prior knowledge, and to pro-
vide a tool that assists the learner in completing the
tasks by providing hints and solutions (Christ et al.,
2022). A user interface is provided for specifying the
generators to be used, based on a user-friendly drag-
and-drop assembly of defined generator elements in
a graph. Thus, although available to different user
groups, the aspects of the AIG approach that are avail-
2
https://github.com/PyRope-E-Assessment/pyrope,
November 10, 2024
A Comparison of Different Approaches of Model Editors for Automatic Item Generation (AIG)
767

able to all users are limited by the available generator
elements.
In the first step of the AIG process, the devel-
opment of a cognitive model, subject matter experts
should elicit their knowledge as a basis for item and
task development. While the described works present
tools that lead to the generation of items, they do not
provide mechanisms to help subject matter experts
perform the first step well and in the most support-
ive way. This first step can essentially be seen as
a form of knowledge structuring. There are several
forms available that could be used to accomplish such
a task in general, like concept maps, mind maps, and
knowledge graphs, to name a few. (Brade, 2015) has
developed requirements for a tool to assist in mak-
ing an expert’s implicit knowledge explicit, and in
the first iterations of structuring knowledge in gen-
eral. These include the ability to freely sketch and
edit, to freely place, rearrange, and categorize graphi-
cal objects, and to allow for temporary structures and
inconsistencies that can be resolved as the user de-
velops the correct structure. A good AIG tool should
meet these requirements in a way that best supports
subject matter experts in formalizing their knowledge
in the first step of the AIG process, upon which all
subsequent steps are built.
3 AIG FOR ALL
The AIG Model Editor (AME) was first introduced
and described in detail in (Kucharski et al., 2023). It is
a web application
1
that can be accessed by any inter-
ested user without any special system requirements,
such as the need to install specific software. The main
editing view of this editor is divided into two areas.
On the left side, the cognitive model (Gierl and Lai,
2013a) can be modeled. A cognitive model in the
AIG Model Editor is represented by multiple graphs
encapsulated in layers (Kucharski et al., 2023). The
sources of information in the cognitive model that de-
pend on each other are represented as nodes in these
graphs. The dependencies between them and their
features are represented by edges. Edges are speci-
fied by the modeler using drag-and-drop functional-
ity in the graphs. There are two types of layers, and
two types of graphs encapsulated within these lay-
ers. First, there is a base layer. The base layer en-
capsulates the cognitive model problem, which is the
central source of information (i.e., the central issue or
topic of the domain being modeled), and the sources
of information that are directly related to the cognitive
model problem. Second, there are several condition
layers. A condition layer encapsulates conditions be-
tween sources of information that are not the problem
in the form of logical implications.
On the right side of the editor, the item model can
be edited. The item model (Gierl and Lai, 2013a) con-
sists of several item templates that define the type and
appearance of the items to be generated, as well as
how the items should be generated (i.e., which sources
of information should be considered). Once defined,
the right side of the editor can also be used to trigger
the generation process, either for a selected set of item
templates or for all by inserting valid combinations of
features from the sources of information into the item
templates according to the constraints defined in the
cognitive model. The generation process is described
in detail in (Kucharski et al., 2023).
3.1 User Guidance
As described in Section 1, the AIG Model Editor was
developed with the idea of making the AIG approach
available to everyone. In order to do this, the editor
needs to address two issues that are included in the
notion of technical expertise (cf. Figure 1). First, the
editor must clarify what must be specified to make
the AIG approach work (i.e., which models and how
they interact). Second, the editor must explain how
to use itself, or be self-explanatory so that further ex-
planations are unnecessary. The goal was to imple-
ment both aspects in such a way that users who have
never heard of AIG, users with a lower level of tech-
nical expertise, users who are AIG experts, as well as
computer scientists could use the editor to generate
tasks or items using AIG. The four aspects of the AIG
Model Editor presented in this section have been de-
veloped and refined over several rounds of evaluation
to achieve this goal.
Linear Modeling Approach. The modeling ap-
proach of our editor is implemented through a linear
user interaction flow. In our editor’s implementation
of the AIG approach, we have reduced the number
of times that the user must choose one or more pro-
cessing paths that ultimately lead to the same goal as
proposed by (Baum et al., 2021), where the user has
a choice between a graphical modeling approach and
a textual modeling approach. This avoids the confu-
sion that can result from forcing the user to choose a
processing method in a process they do not yet fully
understand. So it simplifies the modeling process, and
the simpler the modeling process, the easier and faster
it can be understood by a non-technical user, and the
easier it is to create a tutorial to explain that process,
as described below.
The modeling process follows the steps of the AIG
AIG 2025 - Special Session on Automatic Item Generation
768

approach, shown in Figure 2. The editor is designed
to natively guide the user through these steps, avoid-
ing the distractions of unnecessary features by striv-
ing for simplicity. To this end, a big plus as an en-
try point to the modeling process first guides the user
to specify the problem and automatically create the
appropriate source of information (cf. (Kucharski et
al., 2023)). Once the user understands where sources
of information need to be specified, the user can pro-
ceed to specify the additional sources of information
required. Connecting features is then done by drag-
and-drop, which is also supposed to be user friendly
(cf. Section 6). The user can proceed to the item
model on the right once the cognitive model on the
left is complete.
Divide and Conquer Principle. Instead of provid-
ing an overview of all elements in a domain (i.e., all
sources of information in a cognitive model), as pro-
posed by (Baum et al., 2021), we work with multiple
graphs showing only the connections between a re-
duced set of information sources that are related to
a specific subproblem of the overall cognitive model.
The advantage of a single graph is that it provides an
overview of all sources of information and their rela-
tionships at once. However, when there is more than
one central problem with connected sources of infor-
mation, but connections between multiple sources of
information, special mechanisms are needed to rep-
resent this information in a single graph as types of
edges, as suggested by (Baum et al., 2021). Read-
ing this information requires a higher level of techni-
cal expertise, while it has been found that the simpler
graphs resulting from splitting the graph can be read
by users with a lower technical expertise (Kucharski
et al., 2023).
In addition to the partitioning of the cognitive
model applied by AME, the cognitive model itself
is usually only a piece of the corresponding domain.
Typically, a domain consists of more than one prob-
lem, which are also interrelated as sources of infor-
mation. Although it is not technically required for the
generation process, we enforce the specification of a
problem for a cognitive model for the following rea-
son. Requiring a problem helps the user to structure
his or her knowledge by first defining a central point
and then gathering information about it, rather than
stumbling into an empty space of possibilities with-
out a clear idea of where to start. This is consistent
with the linear modeling approach described above.
Interactive Tutorial. To get started with AIG mod-
eling, we have built a tutorial into the editor. This
tutorial is automatically offered to new users and can
Figure 3: Welcome dialog of the AME interactive tutorial,
which explains the AIG process and the features of the edi-
tor.
be canceled and repeated at any time. It interactively
guides the user through the creation of an exemplary
model from the field of biology to ensure that it can be
understood by everyone. The tutorial explains how to
use the editor, the AIG approach itself, and what vari-
ous actions in the editor are used for in the context of
the AIG process, as shown in Figure 3.
It is therefore aimed at users who are new to the
AIG approach, as well as users with a lower under-
standing how to use the editor technically. Because of
the linear modeling approach described above, this tu-
torial can exhaustively cover the entire modeling pro-
cess, which is the same for each model to be created,
in a reasonable amount of time.
Sample Model. The same sample model created
during the tutorial can also be loaded as a starting
point for creating new custom models. Instead of
starting the modeling process from scratch, the user
can start from a working model or simply modify the
model to see how the generated items differ to learn
how the AIG process works with the editor. The sam-
ple model was designed to include a minimal set of
most of the available features, including a base layer,
some generic features, case-specific features, and a
condition layer (cf. (Kucharski et al., 2024)).
3.2 Limitations
During the use of the editor by lecturers with experi-
ence in AIG modeling for productive item generation,
some shortcomings of the editor became apparent.
A Comparison of Different Approaches of Model Editors for Automatic Item Generation (AIG)
769

While the editor focuses on modeling a well-
separated, usually bounded cognitive model, the lec-
turers expected to be able to model their entire do-
main. They then wanted to select the relevant parts of
the model by selecting the sources of information in
the item model. Although it is theoretically possible
to model entire domains with the editor, the imple-
mentation of the split representation of information
chosen for the divide and conquer principle is inap-
propriate for this use case. This is because the func-
tionality required for modeling large models quickly
and flexibly is not intended to be supported for rea-
sons of clarity. Specifically, only one layer can be
viewed at a time, sources of information cannot be
moved between layers, features cannot be moved be-
tween sources of information, and the source of in-
formation used as a problem in the base layer and the
source of information used as a condition in a condi-
tion layer cannot be changed. This makes it inconve-
nient to work with large models with different layers
and thus to represent complete knowledge domains.
However, the ability to work with cognitive models
that represent whole domains would allow the gen-
eration of more complex tasks and items, make AIG
more useful in practice, and improve the reusability
of the models created.
In addition, the editor makes heavy use of dialogs
that enforce a predefined modeling path and force the
modeler to focus on a particular part of the editor
at a time. This simplifies the modeling process for
new users by reducing the amount of information pre-
sented at a time and the number of actions that can
be performed. However, once the user has become
familiar with the editor, this lack of flexibility can be
a disadvantage. The need to open a dialog in order
to perform a certain action can cause the user’s train
of thought to be interrupted while using the editor.
In other words, carefully considered model additions
may be partially forgotten when a dialog is opened.
The reason for this is that only one model addition can
be realized at a time and opening a dialog seems to re-
position the focus by preparing the mind to perform
the action the dialog is for, while clearing thought-up
subsequent model additions. These must be mentally
rebuilt after the dialog is closed as the focus is reposi-
tioned, now back on the editor interface. These prob-
lems lead to the fact that the requirements developed
by (Brade, 2015) are not being fulfilled, in particu-
lar the ability to freely edit, place, and rearrange as
well as the possibility to resolve temporary inconsis-
tencies step by step. However, addressing these is-
sues would make the AIG process more attractive to
advanced users and more convenient for the rapid cre-
ation of large models.
Finally, the decision to minimize the configuration
options of the AIG process and instead force a con-
crete modeling path for the sake of clarity also limits
the exploitable features of the AIG process and pre-
vents the optimization of the path to the final items
based on the modeler’s experience. For example, con-
figuration options to adjust the grammar (e.g., arti-
cles) based on certain components of the items are
not supported by this editor.
4 OPTIMIZING THE USE OF AIG
WITH MORE MODELING
FREEDOM
To address the identified limitations, a new version of
the AIG Model Editor
3
was designed, implemented,
and evaluated. In planning this new release, it be-
came clear that providing greater modeling flexibil-
ity especially for advanced users requires more user
guidance during the creation of an AIG model for first
time users. Section 4.1 presents the new concept and
Section 4.2 new features to guide the user.
4.1 Concept of the Revised AIG Editor
With the requirement to be able to modify the parts of
a model more easily, the concept of everything being
a node was introduced. This means that each model
component is a node on a large canvas (Figure 4) that
can be easily moved and rearranged as needed during
the modeling process. It also generalizes all model
components through a common base data structure
and allows for easy expansion in the future. There are
10 kinds of nodes: features, sources of information
(SOIs), and layers for the cognitive model; item tem-
plates; item selections (cf. (Kucharski et al., 2024));
item generation runs; lists for item templates, item
selections, and item generation runs; and a list-based
model description.
Feature nodes only have a label and can be tagged
to represent false features. Links can be used to con-
nect features to model constraints. SOI nodes have
a label, are of a specific kind, and can have Feature
nodes attached to them. The available kinds of SOI
nodes are Source of Information, Problem, Condition
and Conclusion, which are based on what a source of
information node represented in the previous editor.
Layer nodes are also of a certain kind (Base Layer or
Condition Layer), which also corresponds to their use
in the previous editor. What is different is that they
are essentially a rectangle that implies a group of SOI
3
https://ame-v2.aig4all.org, January 16, 2025
AIG 2025 - Special Session on Automatic Item Generation
770
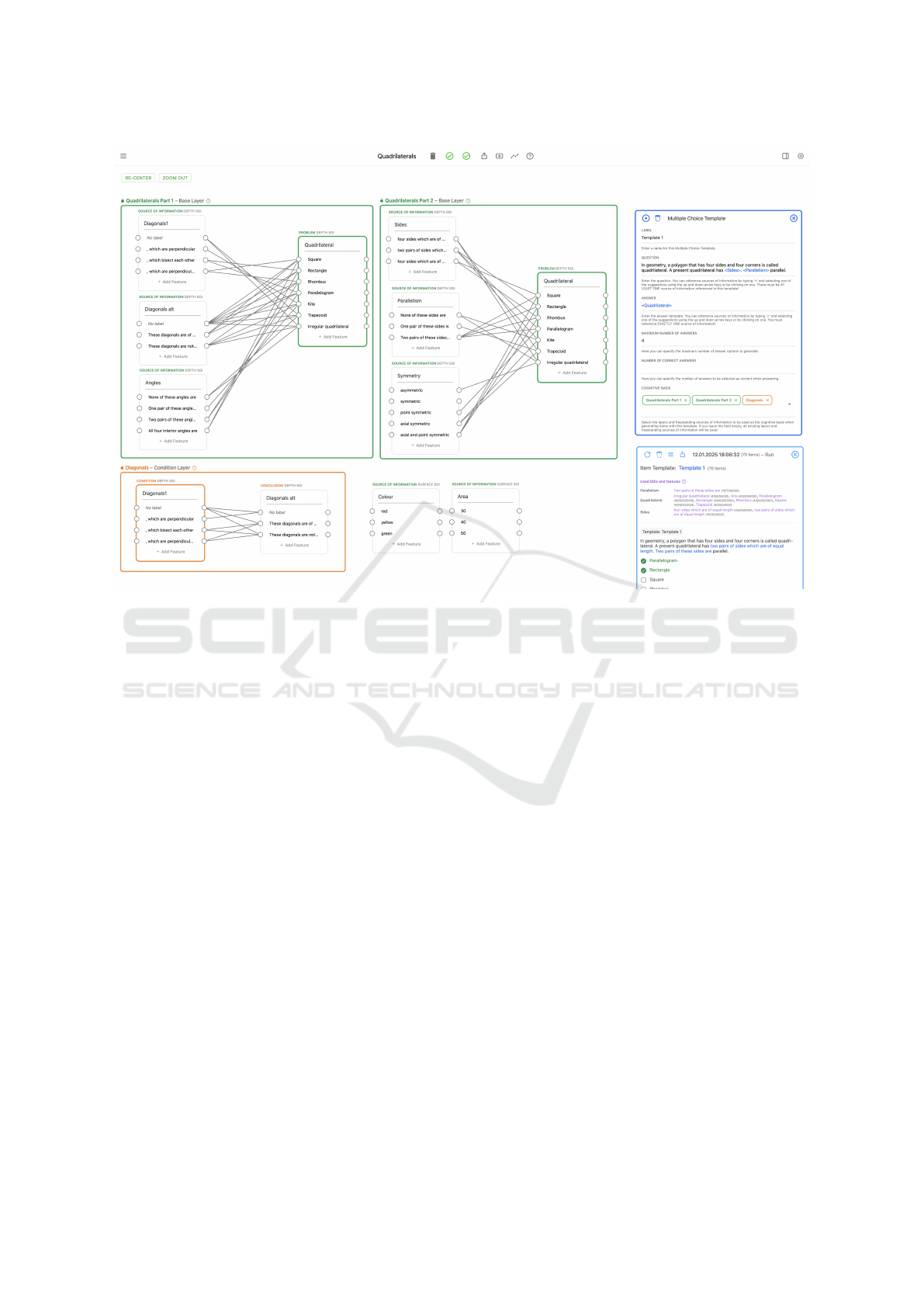
Figure 4: Screenshot of the second version of AME. It shows two base layers colored green, a condition layer colored orange,
two generic SOI nodes outside of the layers, a multiple choice item template in dark blue (top-right) and an item generation
run node in a lighter blue (bottom-right) listing generated items for the multiple choice item template. Within the editor,
“depth” is used as a synonym for “case-specific” and “surface” as a synonym for “generic” with regard to the function of
features and SOIs.
nodes when it encloses them. While each node can
be moved and arranged as needed during modeling,
a final model structure is expected for item genera-
tion. Therefore, base layers are expected to contain
one or more Source of Information SOI nodes and one
Problem SOI node. Condition layers are expected to
contain one or more Condition SOI nodes and one or
more Conclusion SOI nodes. Source of Information
SOI nodes may also be placed outside of any layer. In
this case, they are expected to have features without
any links as they represent generic features.
Item Template nodes and Item Selection nodes are
similar to the previous editor in terms of input fields.
The difference is that item templates have an addi-
tional field to specify their cognitive basis, i.e. a selec-
tion of layers and generic sources of information that
should be used exclusively for the generation of items
based on the given item template. In other words, a
model can have many layers and generic sources of
information, but only a subset of them can be used
during a generation for an item template as the user
chooses.
Item templates and item selections are now also
placed on the canvas. Each of them has a play button
to generate items. These are displayed after genera-
tion within the Item Generation Run nodes. Because
the canvas can get cluttered with many of these nodes,
each can be closed and reopened via a corresponding
list node for each node kind.
While the graphical representation of a model may
be easier to use in some situations, a more textual rep-
resentation may be more valuable in others. There-
fore, List Based Model Description nodes have been
added that allow to specify SOI nodes and their fea-
tures, as well as layers and their SOI nodes, in a more
textual list form. Once the model components have
been specified, the textual representation can be used
to generate graphical template nodes, so that a user
only needs to add links as needed, and can rearrange
and move nodes as the initial idea evolves.
4.2 User Guidance
Three new user guidance features have been intro-
duced. The first one is the User Guidance Center (Fig-
ure 5) with resources to educate the user. These are a
video giving an introduction to AIG in general and a
video providing a tutorial on how to create an AIG
A Comparison of Different Approaches of Model Editors for Automatic Item Generation (AIG)
771

Figure 5: Screenshot of the User Guidance Center dash-
board overlaid on the editor surface.
model with the editor. It also offers the possibility
to start from a sample model. By integrating these re-
sources directly into the editor, users can quickly refer
back to them when needed, as they are only a few, if
not one, click away.
The second user guidance feature is the User
Guidance Graph (Figure 6). It shows all the steps
involved in creating items from starting to create a
new model to using generated items. Its purpose is to
give users a quick overview about all the steps so they
can quickly evaluate what they have already done and
what is still to do until being able to finally use items.
The visibility of the User Guidance Graph can be tog-
gled so that the user can see it when needed, or not.
Each step can also be clicked. This will open the tuto-
rial video in the user guidance center and jump to the
timestamp of that step. This allows users to quickly
review how to perform the step if they have forgotten
how to do it.
The third new feature is near real-time feedback.
Inspired by how syntax errors are shown in program-
ming editors like VS Code for programming lan-
guages like TypeScript, the editor validates the cur-
rent model in the background every two seconds. If
errors are found, they are displayed at the location in
the model where they occurred. Such a location can
be a link or a specific node like a SOI node, or an
Item Template node, or, more specifically, a particu-
lar input field such as the one for the question of an
item template. While hovering an error indicator, the
error message is presented containing an explanation
of the error as well as a suggestion for a fix, which
can be applied by clicking a button if programmati-
cally possible. This functionality is intended to re-
duce the effort a user would have to figure out why an
item generation failed and how to fix the error. It is
also a tool to guide the user to arrive at the expected
final model structure, while allowing rapid restructur-
ing of individual parts of the model. In addition, it is
expected that seeing, understanding, and resolving er-
rors in this way should further the user’s understand-
ing of the expected final model structure, as well as
what each node represents and how it is intended to
be used. This is especially important for first time
users who haven’t yet internalized the knowledge of
AIG.
5 EVALUATIONS
Both editors were evaluated individually. The focus
lied on how easy they are to use by first time users
who are new to the editor and potentially new to AIG
too. As a quantitative measure, the System Usability
Scale (SUS) developed by (Brooke, 1996) was used in
both cases. It is a questionnaire containing 10 items
with a 5-point Likert scale, which are worded posi-
tively and negatively in alternating order, each consid-
ering a different aspect of usability. A score between
0 and 100 can be obtained by calculation. (Sauro,
2011) has determined that a score above 68 would in-
dicate a user-friendly system on average. In addition
to the SUS score, qualitative feedback was collected
through additional questions and observation of par-
ticipants during the tests.
5.1 Evaluation of First Editor Version
The test procedure and the quantitative results of the
evaluation of the first version of the editor have al-
ready been presented in (Kucharski et al., 2024). 12
people from different fields participated in the eval-
uation. They were first introduced to the editor both
orally and through the in-editor tutorial, then had to
create an AIG model on their own, generate items
with it, and finally give their feedback through a ques-
tionnaire. The editor achieved an average SUS score
of 81, which is above the threshold of 68 and indi-
cates usability between good and excellent (Bangor
et al., 2009). In terms of qualitative feedback, the par-
ticipants expressed that the interactive tutorial made
it easy for them to learn the features of the editors,
so that after the brief introduction to the AIG process,
they were able to quickly create their own models and
generate their own items, even though they were all
new to AIG. However, as they began to model more
complex scenarios, some of them complained about
a lack of flexibility in the item model, which made
it difficult for them to use the AIG approach effec-
tively. The reason was that in the example they chose
to model, the features of the sources of information
all required different articles (in German language).
Due to the principle of purism, to make the editor as
easy to learn as possible and thus accessible to every-
AIG 2025 - Special Session on Automatic Item Generation
772

Figure 6: Screenshot of the User Guidance Graph.
one, the editor does not support the configuration of
variations corresponding to tense, case, or other lin-
guistic properties. This made it difficult to use the
generation process effectively in the chosen use case
and still generate linguistically correct sentences.
5.2 Evaluation of Second Editor Version
The evaluation of the rebuild editor was slightly dif-
ferent. A total of nine people participated in the eval-
uation. They had different experiences with AIG in
the past, including none, research in the field, par-
ticipation in a previous evaluation of an AIG model
editor, or having used an AIG model editor in some
other way. The procedure was chosen to best re-
flect a real first user experience, where a new user
would both discover the editor and create an AIG
model completely on their own. Therefore, partic-
ipants were not given a verbal introduction, but in-
stead were instructed to watch the two introductory
videos in the User Guidance Center. They were then
given a schematic description of a cognitive model
and an item model similar to the visualization cho-
sen by (Gierl et al., 2012). They were instructed to
model them in the editor. After that, an item se-
lection should be created and employed to generate
items. This whole process was also shown in the tu-
torial video. Finally, the participants were asked to
extend the model on their own and to give their feed-
back via a questionnaire. The evaluation took place
via video conference, during which the participants
were observed both verbally and on their screen with
the editor open. Participants only received verbal help
if they got stuck and could not get out on their own.
The rebuild editor reached a SUS score of 66,
which is just below the threshold of 68 and indicates a
usability between ok and good (Bangor et al., 2009).
Regarding the editor concept, eight out of nine partic-
ipants agreed or strongly agreed that they liked the
concept of everything being a node in one canvas
(Figure 7). The User Guidance Center was also per-
ceived to be very helpful. Participants were less clear
about the helpfulness of the User Guidance Graph and
the near real-time feedback. One explanation for this
is that these features were not well integrated into the
editor or that their value was not clearly communi-
cated. On the other hand, it is plausible that they were
not needed during the evaluation because the focus
was on first time users and a predefined model had to
be realized. Their value may only become apparent
when an AIG model has to be created for a topic cho-
sen by the user alone, as it would be the case in the
real world.
In terms of user guidance and user education, all
participants agreed or strongly agreed that they un-
derstood the concept of AIG, but less agreed with
statements about the understanding of how individ-
ual model components or parts are realized within the
editor. This was especially true for the different sub-
models (i.e., cognitive models and item models) and
their relationship, the purpose of layers, why there is
not one graph but multiple, and the purpose of surface
SOIs.
As participants were observed during the test, this
problem was also present in the way the participants
solved the tasks. They have re-watched parts of the tu-
torial video while modeling, with some jumping back
and forth between re-watching and modeling. Also,
the videos were sped up twice by default. The inten-
tion was to make them more compact, as the AIG in-
troduction video was originally about 5 min 30 s long,
and the tutorial video about 27 min long. This turned
out to be a false intention, as all participants expressed
that they were too fast by default. Although there
were controls to slow them down, the audio quality
deteriorated in this case because the audio tracks were
not prepared for it.
Another challenge was deciding what kind of
layer to add. The video mentioned when to use which
layer. However, it did not explain how to determine
this based on the graphical model description given to
the participants. This was also the case when condi-
A Comparison of Different Approaches of Model Editors for Automatic Item Generation (AIG)
773
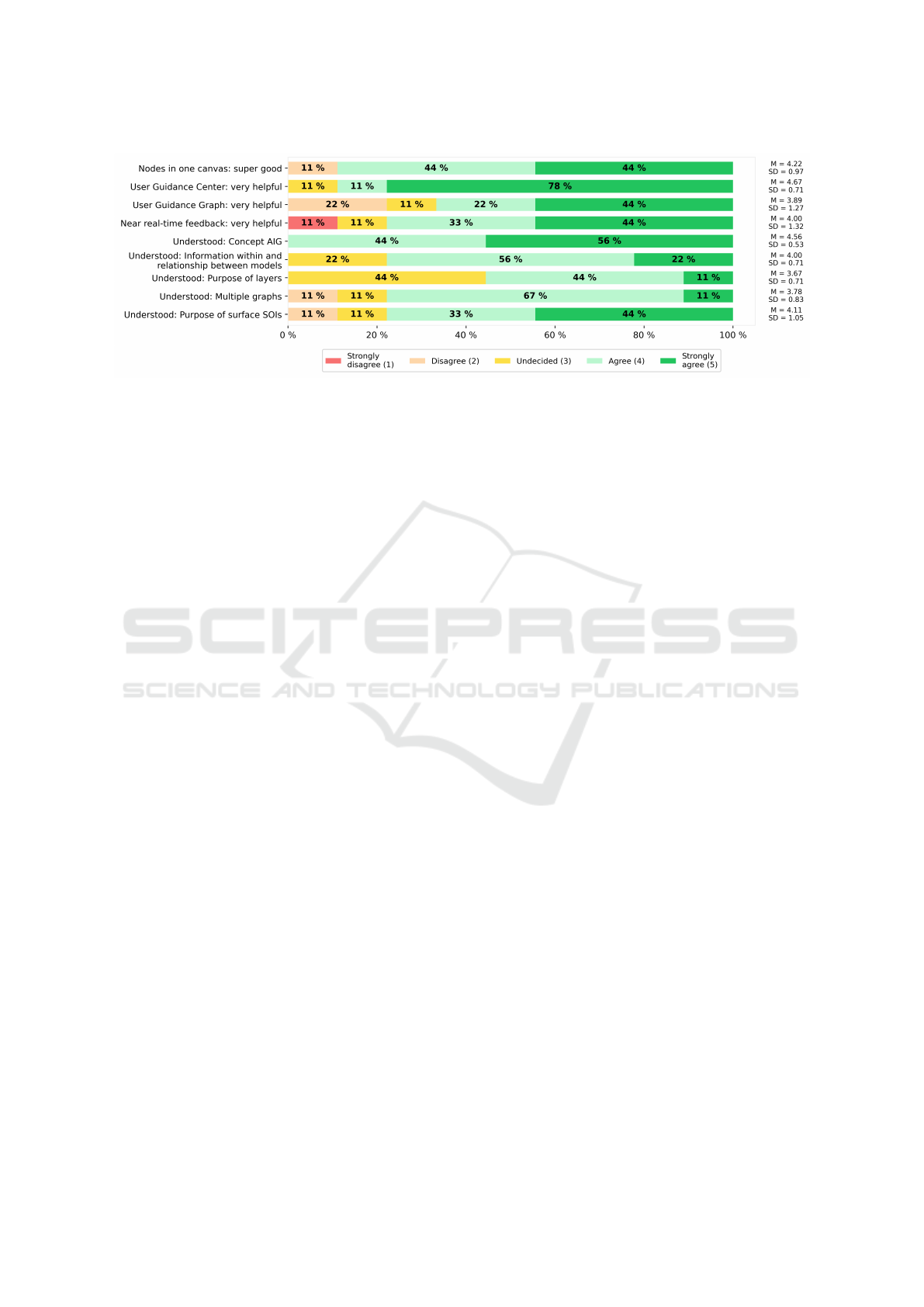
Figure 7: Results of the evaluation of the second editor version.
tions needed to be modeled. Besides, keeping track of
the impact of a new connection on all the conditions
already modeled in a condition layer was seen as an
additional difficulty.
Overall, a subset of participants felt well informed
and supported by both the tutorial video and the user
guidance graph about what steps to take and in what
order. Other participants felt overwhelmed from the
beginning or at times. They cited the amount of in-
formation contained in the videos, uncertainty about
what step they were in, and the need to know the AIG
approach as reasons for this perception. To mitigate
these reasons, recommendations were made such as
more clearly indicating the current step of the AIG
process, reducing the number of possible actions to
those required for the step, and better explaining when
to use which kind of SOI or layer.
6 DISCUSSION
The evaluations showed that there are big differences
between the two editor versions. The first version
achieved a SUS score of 81 and was therefore per-
ceived as good to excellent to use. It was expected
that it would be a challenge for the second version of
the editor to reach this score, especially since there
are fewer restrictions. The evaluation confirmed this
expectation, revealing a SUS score of only 66, just be-
low the threshold of 68. It showed that while the con-
cept of everything being a node was generally liked,
testers felt overwhelmed, e.g. by the amount of new
information they had to comprehend, or were some-
times not sure what action to take next. While it
should be noted that the process of both evaluations
was different, it is still possible to draw a number of
lessons from both evaluations.
For the first editor, it was decided to structure
the editor in a way that encourages users to follow
the predefined order of the steps of the AIG process.
This order is also communicated throughout the tu-
torial. This means that first time users can comfort-
ably work through a sequence of outlined steps and
get to know the AIG process as well as the editor. In
this way, the editor enforces that the model is always
in a valid state and ready to generate items. Conse-
quently, novice users of the editor or the AIG pro-
cess in general can rapidly initiate the process, as the
scope for errors is minimized, akin to the provision
of pre-built functional blocks by ALADIN (Christ et
al., 2022). Where such an approach works less effec-
tively is when users want to deviate from the prede-
fined functional blocks or sequence of steps, perform
steps only halfway, leaving the model in an invalid
state, and finish them non-linearly as ideas for extend-
ing the model emerge.
For the second editor, it was decided to general-
ize all model components in the form of nodes that
can be arranged and moved around as needed. This
allows for editor states that are invalid with respect to
the final expected model structure. It supports users
to more easily deviate from the linearity of the AIG
process and build a model more non-linearly, espe-
cially in the case of adding and moving features be-
tween sources of information, sources of information
between layers, and changing the kind of a SOI (i.e.
Problem, Source of Information, Condition, and Con-
clusion). This correlates with the freedom provided
by PyRope (Merker et al., 2023), which comes from
the ability to extend the generation functionality with
custom programming code. As a disadvantage of
more modeling freedom, the evaluation of the second
editor emphasized that without sufficient guidance,
especially first time users can become overwhelmed,
not knowing what to do next or what is left to do.
Another aspect by which the two editors can be
compared is the way in which they support cogni-
tive model content to be used for generation. The
AIG 2025 - Special Session on Automatic Item Generation
774

first editor version allows many different sources of
information to be used in many different layers. But
for the item generation, all available sources of in-
formation and layers make up the whole cognitive
model. It is not possible to exclude certain layers
or generic sources of information from the genera-
tion. To achieve this behavior, they would have to be
deleted. The second editor version has changed this
by allowing users to specify within the cognitive basis
of an item template which layers and generic sources
of information should be considered when generating
items based on it.
This enables two additional editor features, espe-
cially for advanced users. First, a broader knowledge
domain can be modeled within one model, but selec-
tively used for generation. Users can create multi-
ple different layers about different problems and if-
then relationships. But for a given item template, they
can choose on which layers and generic sources of in-
formation items generated by the template should be
based on, without having to delete all the others or to
create multiple models. Second, having everything in
one model should also facilitate the reuse, combina-
tion, and remix of existing model components, further
expanding the knowledge domain represented. What
this means is that while the first version of the edi-
tor encourages having multiple smaller task-specific
models, the second version of the editor allows espe-
cially advanced users to create larger domain-specific
models that essentially encompass multiple smaller
task-specific models.
7 CONCLUSION AND OUTLOOK
In this paper, we presented two versions of an AIG
model editor, both with different user personas in
mind. The first version focuses on providing a clear
path for first time users to create an AIG model. It
provides users with an interactive tutorial and a sam-
ple model to get them started quickly. The second
version re-conceptualizes the editor with the goal of
giving more capabilities especially to advanced users.
It introduces the concept of everything being a node
that can be freely moved and arranged on one large
canvas. It also adds user guidance features such as
near real-time feedback, the User Guidance Center,
and the User Guidance Graph to provide guardrails
for the additional freedom.
Both editors were evaluated individually using
slightly different methods. The first editor version
achieved a SUS score of 81 and the second version
a score of 66. While the scores are not directly com-
parable due to the different evaluation procedures, the
qualitative feedback collected reveals the themes of
the problems with each approach. Participants who
were new to AIG and evaluated the first editor ver-
sion, were able to quickly create an AIG model. The
restrictive nature of the editor only became apparent
as they moved beyond the initial learning phase and
attempted to model more complex scenarios.
Participants in the second evaluation were also
able to successfully create an AIG model and gener-
ate items, but there was a greater learning curve. This
was attributed to the amount of information contained
in the introductory videos, uncertainty about which
current AIG process step they were in, and the need
to know the AIG approach. As a mitigation, they sug-
gested that more guidance was needed.
All in all, the main questions that follow from this
work are: if there are different types of users with dif-
ferent types of needs and goals, sometimes in conflict,
should they all be accommodated within a single “su-
per” AIG model editor, and if so, how? Or should
there be a pool of multiple, more specialized editors
from which users can choose?
Our current view is that there is a case for both.
However, what seems to be an interesting step to in-
vestigate next is an editor for AIG model creation that
would combine both worlds of the presented editors.
This could look like this.
What the decisions made during the development
of both editors amount to is a set of restrictions for
each editor. From a technical point of view, it is ar-
gued that the second version is less restrictive than
the first, but could be limited to the first through sim-
ulation. For such a simulation, the current guidance
and modeling needs of the user need to be determined.
Based on this, a mechanism could dynamically adapt
the restrictions to be enforced by the editor when the
user needs either more guidance or more freedom in
modeling. The nature and feasibility of such a mech-
anism should be investigated by future work.
To accomplish this, the use of large language mod-
els as reasoning engines that could decide about the
user’s current guidance and modeling needs and sug-
gest and/or apply adjustments seems like a promising
possibility that should be explored.
REFERENCES
Bangor, A., Kortum, P., & Miller, J. (2009). De-
termining what individual SUS scores mean:
Adding an adjective rating scale. Journal of Us-
ability Studies, 4(3), 114–123.
Baum, H., Damnik, G., Gierl, M. & Braun, I. (2021).
A Shift in automatic Item Generation towards
A Comparison of Different Approaches of Model Editors for Automatic Item Generation (AIG)
775

more complex Tasks, INTED2021 Proceedings,
pp. 3235-3241.
Brade, M. (2015). Visualization methods for the inter-
active acquisition and structuring of information
in the context of free-form knowledge model-
ing [Visualisierungsmethoden f
¨
ur das interaktive
Erfassen und Strukturieren von Informationen
im Kontext der Freiform-Wissensmodellierung].
Doctoral Dissertation, TUD Dresden University
of Technology.
Brooke, J. B. (1996). SUS: A ’Quick and Dirty’ Us-
ability Scale.
Christ, P., Laue, R., & Munkelt, T. (2022). ALADIN
– Generator for Tasks and Solution (Hints) in
Computer Science and Related Fields [ALADIN
– Generator f
¨
ur Aufgaben und L
¨
osung(shilf)en
aus der Informatik und angrenzenden Diszi-
plinen].
Christ, P. L., Munkelt, T., & Haake, J. M.
(2024). An Authoring Tool for the Graph-
ical Configuration of Item Generators
[Ein Autorenwerkzeug zur grafischen
Konfiguration von Aufgabengeneratoren].
https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.33616.11528
Damnik, G., Gierl, M., Proske, A., K
¨
orndle, H., &
Narciss, S. (2018). Automatic Item Generation
as a Means to Increase Interactivity and Adap-
tivity in Digital Learning Resources [Automa-
tische Erzeugung von Aufgaben als Mittel zur
Erh
¨
ohung von Interaktivit
¨
at und Adaptivit
¨
at in
digitalen Lernressourcen]. In E-Learning Sym-
posium 2018 (pp. 5-16). Universit
¨
atsverlag Pots-
dam.
Embretson, S. E., & Yang, X. (2007). Automatic item
generation and cognitive psychology. In C. R.
Rao & S. Sinharay (Eds.), Handbook of statis-
tics: Psychometrics, Volume 26 (pp. 747–768).
Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Elsevier.
Gierl, M. J., Lai, H., & Turner, S. (2012). Using
automatic item generation to create multiple-
choice items for assessments in medical educa-
tion. Medical Education,46, 757–765.
Gierl, M. J., & Haladyna, T. M. (Eds.). (2013). Au-
tomatic item generation: Theory and practice.
Routledge.
Gierl, M. J., & Lai, H. (2013a). Evaluating the qual-
ity of medical multiple-choice items created with
automated processes. Medical education, 47(7),
726-733.
Gierl, M. J., & Lai, H. (2016). Automatic item gener-
ation. In S. Lane, M. R. Raymond, & T.M. Hala-
dyna (Eds.), Handbook of test development (2nd
ed., pp. 410–429). New York, NY: Routledge.
Kosh, A. E., Simpson, M. A., Bickel, L., Kellogg,
M., & Sanford-Moore, E. (2019). A cost–benefit
analysis of automatic item generation. Educa-
tional Measurement: Issues and Practice, 38(1),
48-53.
Krathwohl, D. R. (2002). A Revision Bloom’s Taxon-
omy: An Overview. Theory into Practice, 41(4),
212-218.
Kucharski, S., Damnik, G., Stahr, F., & Braun, I.
(2023). Revision of the AIG Software Toolkit:
A Contribute to More User Friendliness and
Algorithmic Efficiency. In J. Jovanovic, I.-A.
Chounta, J. Uhomoibhi, & B. McLaren: Pro-
ceedings of the 15th International Conference
on Computer Supported Education - Volume 2:
CSEDU. SciTePress, pages 410-417.
Kucharski, S., Stahr, F., Braun, I. & Damnik, G.
(2024). Overcoming Student Passivity with Au-
tomatic Item Generation. In O. Poquet, A.
Ortega-Arranz, O. Viberg, I.-A. Chounta, B.
McLaren and J. Jovanovic: Proceedings of the
16th International Conference on Computer Sup-
ported Education. SciTePress, pages 789 - 798.
Merker, J., Hain, H., Sch
¨
obel, K., & Brassel,
P. (2023). 6. E-Assessment in STEM Fields:
Coding Exercises with Python & Jupyter [E-
Assessment in MINT-F
¨
achern: Coden von
¨
Ubungsaufgaben mit Python & Jupyter]. Dig-
itale Lehre im Rahmen der Grundlagenausbil-
dung in MINT-F
¨
achern an Hochschulen, 96.
Mortimer, T., Stroulia, E., & Yazdchi, M. V. (2012).
IGOR: A Web-Based Automatic Item Genera-
tion Tool. In Automatic Item Generation (pp.
217-230). Routledge.
Proske, A., K
¨
orndle, H. & Narciss, S. (2012). Inter-
active learning tasks. In N. M. Seel (Ed.), Ency-
clopedia of the Sciences of Learning (pp. 1606-
1610). New York: Springer.
Sauro, J. (2011). Measuring usability with the Sys-
tem Usability Scale (SUS). Retrieved from
https://measuringu.com/sus/. Last accessed: Jan-
uary 13, 2025.
Wancham, K., Tangdhanakanond, K., & Kan-
janawasee, S. (2023). Development of the auto-
matic item generation system for the diagnosis
of misconceptions about force and laws of mo-
tion. Eurasia Journal of Mathematics, Science
and Technology Education, 19(6), em2282.
AIG 2025 - Special Session on Automatic Item Generation
776
